Cutting Flute and Thread Design on Self-Tapping Pedicle Screws Influence the Insertion Torque and Pullout Strength
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
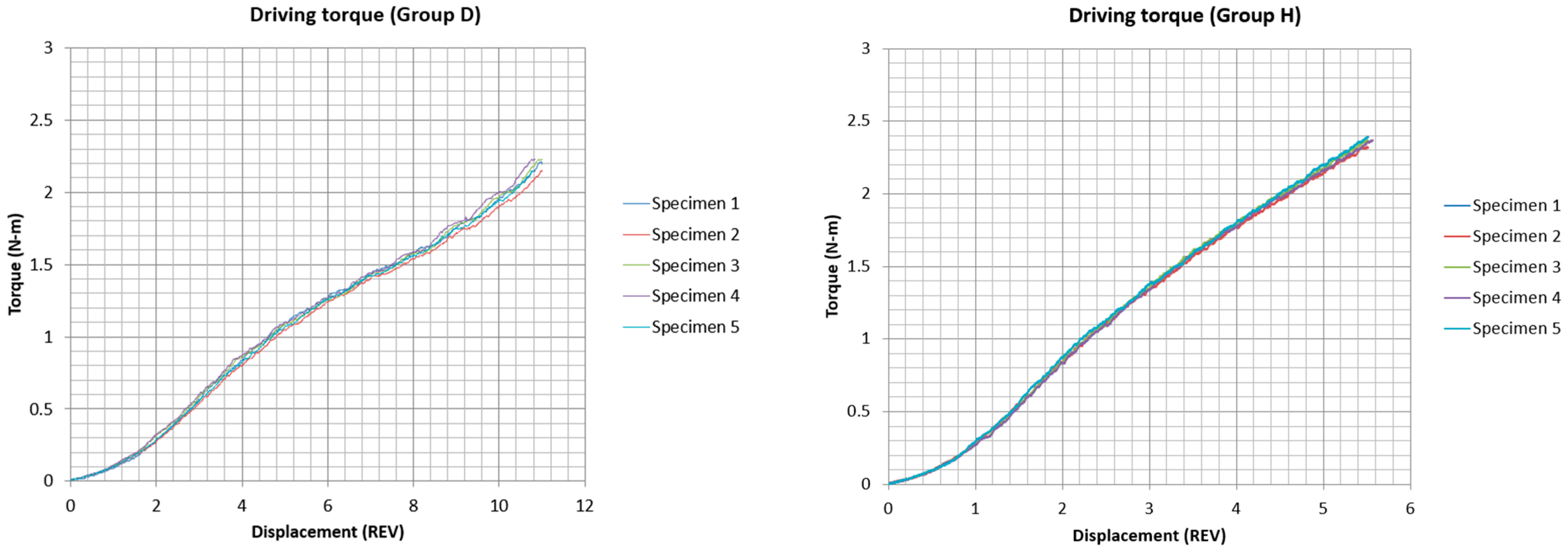
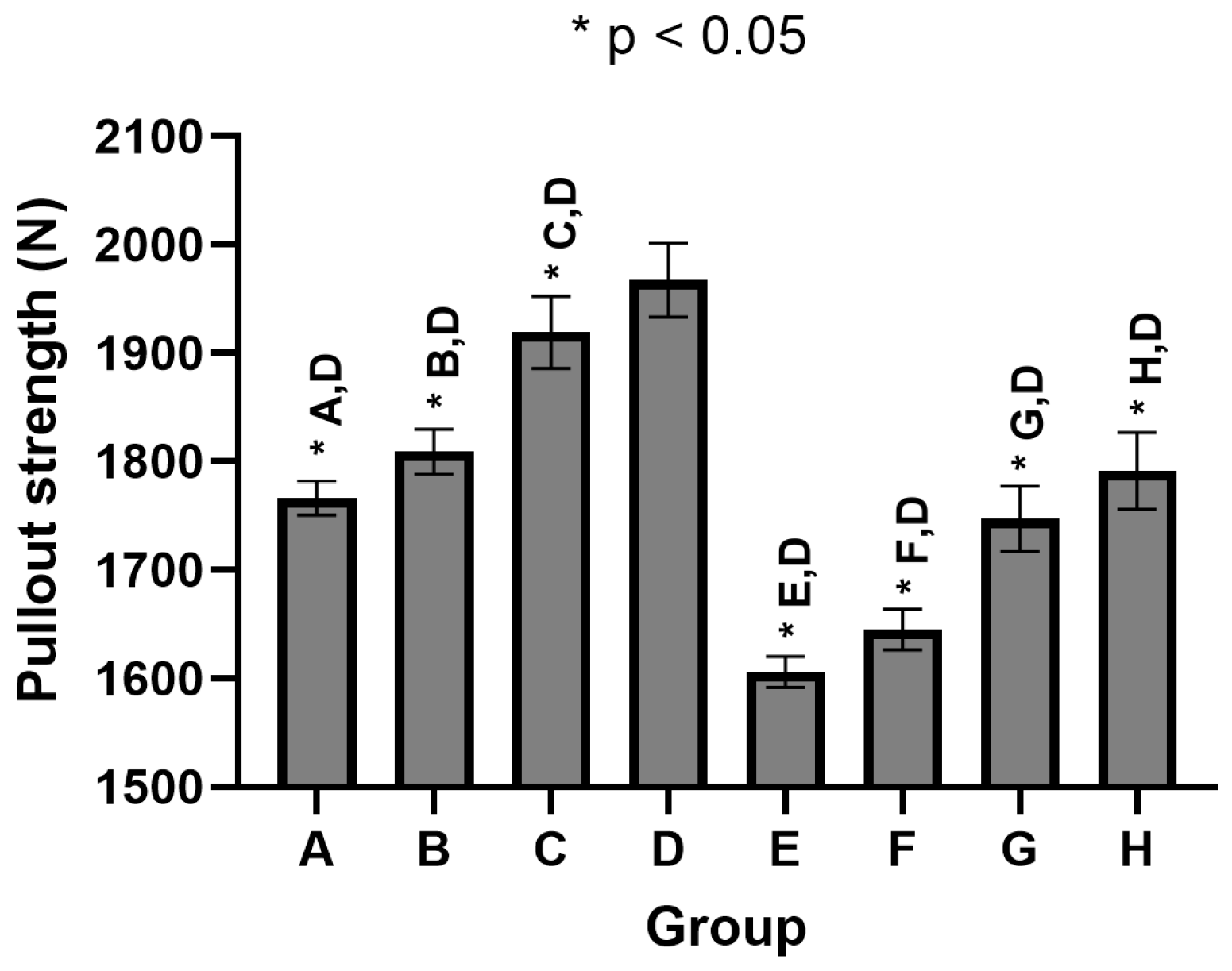
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bickley, B.T.; Hanel, D.P. Self-Tapping versus Standard Tapped Titanium Screw Fixation in the Upper Extremity. J. Hand Surg. 1998, 23, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.A.R.; Abed, R.A.K.; Issa, S.A.A.; Jamil, N. The Efficacy of Self-Tapping and Self-Drilling Inter-Maxillary Fixation Screw in Maxillofacial Surgery. Ann. Trop. Med. Public Health 2020, 23, 231–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Specification and Test Methods for Metallic Medical Bone Screws. Available online: https://www.astm.org/f0543-13.html (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- Ansell, R.H.; Scales, J.T. A Study of Some Factors Which Affect the Strength of Screws and Their Insertion and Holding Power in Bone. J. Biomech. 1968, 1, 279–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, F.M.; Abernathie, D.L. A Comparison of Pullout Strength for Pedicle Screws of Different Designs: A Study Using Tapped and Untapped Pilot Holes. Spine 2006, 31, E867–E870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronderos, J.F.; Jacobowitz, R.; Sonntag, V.K.H.; Crawford, N.R.; Dickman, C.A. Comparative Pull-out Strength of Tapped and Untapped Pilot Holes for Bicortical Anterior Cervical Screws. Spine 1997, 22, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Nassar, S.A.; Yang, X. Pullout Performance of Self-Tapping Medical Screws. J. Biomech. Eng. 2011, 133, 111002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battula, S.; Schoenfeld, A.J.; Sahai, V.; Vrabec, G.A.; Tank, J.; Njus, G.O. The Effect of Pilot Hole Size on the Insertion Torque and Pullout Strength of Self-Tapping Cortical Bone Screws in Osteoporotic Bone. J. Trauma—Inj. Infect. Crit. Care 2008, 64, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- You, Z.H.; Bell, W.H.; Schneiderman, E.D.; Ashman, R.B. Biomechanical Properties of Small Bone Screws. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1994, 52, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerby, S.; Scott, C.C.; Evans, N.J.; Messing, K.L.; Carter, D.R. Effect of Cutting Flute Design on Cortical Bone Screw Insertion Torque and Pullout Strength. J. Orthop. Trauma 2001, 15, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzistergos, P.E.; Sapkas, G.; Kourkoulis, S.K. The Influence of the Insertion Technique on the Pullout Force of Pedicle Screws: An Experimental Study. Spine 2010, 35, E332–E337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.; Cho, S.K.; Wu, C. The biomechanics of pedicle screw-based instrumentation. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 2010, 92, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacob, A.T.; Ingalhalikar, A.V.; Morgan, J.H.; Channon, S.; Lim, T.H.; Torner, J.C.; Hitchon, P.W. Biomechanical Comparison of Single- and Dual-Lead Pedicle Screws in Cadaveric Spine. Journal of neurosurgery. Spine 2008, 8, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohn, E.A.; Chu, B.; Martin, A.; Yu, E.; Telles, C.; Leasure, J.; Lynch, T.L.; Kondrashov, D. The Pedicles Are Not the Densest Regions of the Lumbar Vertebrae: Implications for Bone Quality Assessment and Surgical Treatment Strategy. Glob. Spine J. 2017, 7, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.-H.; Park, J.W.; Shin, Y.H. The Insertional Torque of a Pedicle Screw Has a Positive Correlation with Bone Mineral Density in Posterior Lumbar Pedicle Screw Fixation. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 2012, 94, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Shiota, M.; Fujii, M.; Shimogishi, M.; Munakata, M. Effects of Implant Thread Design on Primary Stability—a Comparison between Single- and Double-Threaded Implants in an Artificial Bone Model. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2020, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addevico, F.; Morandi, M.; Scaglione, M.; Solitro, G.F. Screw Insertion Torque as Parameter to Judge the Fixation. Assessment of Torque and Pull-out Strength in Different Bone Densities and Screw-Pitches. Clin. Biomech. 2020, 72, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, P.; Xiong, W.; Tan, B.; Geng, W.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Li, D. Influence of Thread Pitch, Helix Angle, and Compactness on Micromotion of Immediately Loaded Implants in Three Types of Bone Quality: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 983103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinley, C.L.; Behrents, R.; Kim, K.B.; Sridhar, C.; Kyung, H.M.; Buschang, P.H. Pitch and Longitudinal Fluting Effects on the Primary Stability of Miniscrew Implants. Angle Orthod. 2009, 79, 1156–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsai, W.C.; Chen, P.Q.; Lu, T.W.; Wu, S.S.; Shih, K.S.; Lin, S.C. Comparison and Prediction of Pullout Strength of Conical and Cylindrical Pedicle Screws within Synthetic Bone. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2009, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fleury, R.B.C.; Shimano, A.C.; Matos, T.D.; Teixeira, K.D.O.; Romero, V.; Defino, H.L.A. The Role of Pedicle Screw Surface on Insertion Torque and Pullout Strength. Rev. Bras. Ortop. 2020, 55, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



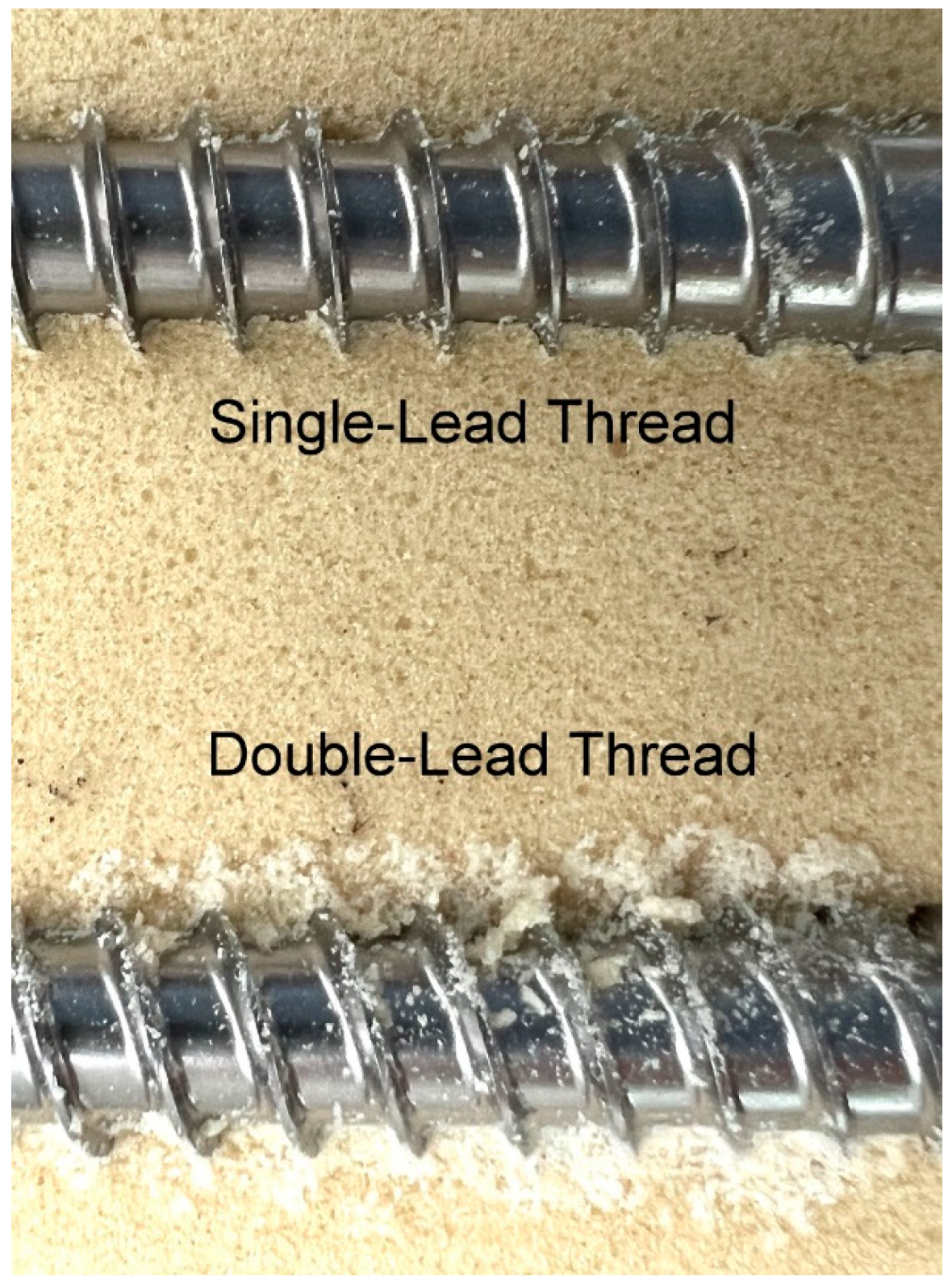
| Screw Group | Lead of Thread | Number of Cutting Flutes | Length of Flutes (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | single-lead | 2 | 2.9 |
| B | 3 | ||
| C | 2 | 9.5 | |
| D | 3 | ||
| E | double-lead | 2 | 2.9 |
| F | 3 | ||
| G | 2 | 9.5 | |
| H | 3 |
| Group | Average Insertion Torque (Nm) during Initial Screw Revolutions | Average Max. Insertion Torque (Nm) | STD | Average Pullout Strength (N) | STD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Rev. | 2nd Rev. | 3rd Rev. | 4th Rev. | |||||
| A | 0.100 | 0.294 | 0.586 | 0.902 | 2.365 | 0.093 | 1766 | 15.8 |
| B | 0.110 | 0.323 | 0.610 | 0.923 | 2.415 | 0.103 | 1809 | 20.7 |
| C | 0.100 | 0.294 | 0.561 | 0.833 | 2.2 | 0.034 | 1919 | 33.2 |
| D | 0.103 | 0.317 | 0.589 | 0.858 | 2.17 | 0.042 | 1967 | 34.0 |
| E | 0.299 | 0.928 | 1.605 | 2.143 | 2.974 | 0.115 | 1606 | 14.3 |
| F | 0.300 | 0.895 | 1.566 | 2.101 | 2.929 | 0.037 | 1645 | 18.8 |
| G | 0.259 | 0.847 | 1.415 | 1.906 | 2.568 | 0.091 | 1747 | 30.4 |
| H | 0.282 | 0.849 | 1.360 | 1.790 | 2.36 | 0.028 | 1791 | 35.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, L.-C.; Hsieh, Y.-Y.; Tsuang, F.-Y.; Kuo, Y.-J.; Chiang, C.-J. Cutting Flute and Thread Design on Self-Tapping Pedicle Screws Influence the Insertion Torque and Pullout Strength. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12041956
Wu L-C, Hsieh Y-Y, Tsuang F-Y, Kuo Y-J, Chiang C-J. Cutting Flute and Thread Design on Self-Tapping Pedicle Screws Influence the Insertion Torque and Pullout Strength. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(4):1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12041956
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Lien-Chen, Yueh-Ying Hsieh, Fon-Yih Tsuang, Yi-Jie Kuo, and Chang-Jung Chiang. 2022. "Cutting Flute and Thread Design on Self-Tapping Pedicle Screws Influence the Insertion Torque and Pullout Strength" Applied Sciences 12, no. 4: 1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12041956
APA StyleWu, L.-C., Hsieh, Y.-Y., Tsuang, F.-Y., Kuo, Y.-J., & Chiang, C.-J. (2022). Cutting Flute and Thread Design on Self-Tapping Pedicle Screws Influence the Insertion Torque and Pullout Strength. Applied Sciences, 12(4), 1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12041956






