Hull Form Optimization Study Based on Multiple Parametric Modification Curves and Free Surface Reynolds-Averaged Navier–Stokes (RANS) Solver
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Objective Ship
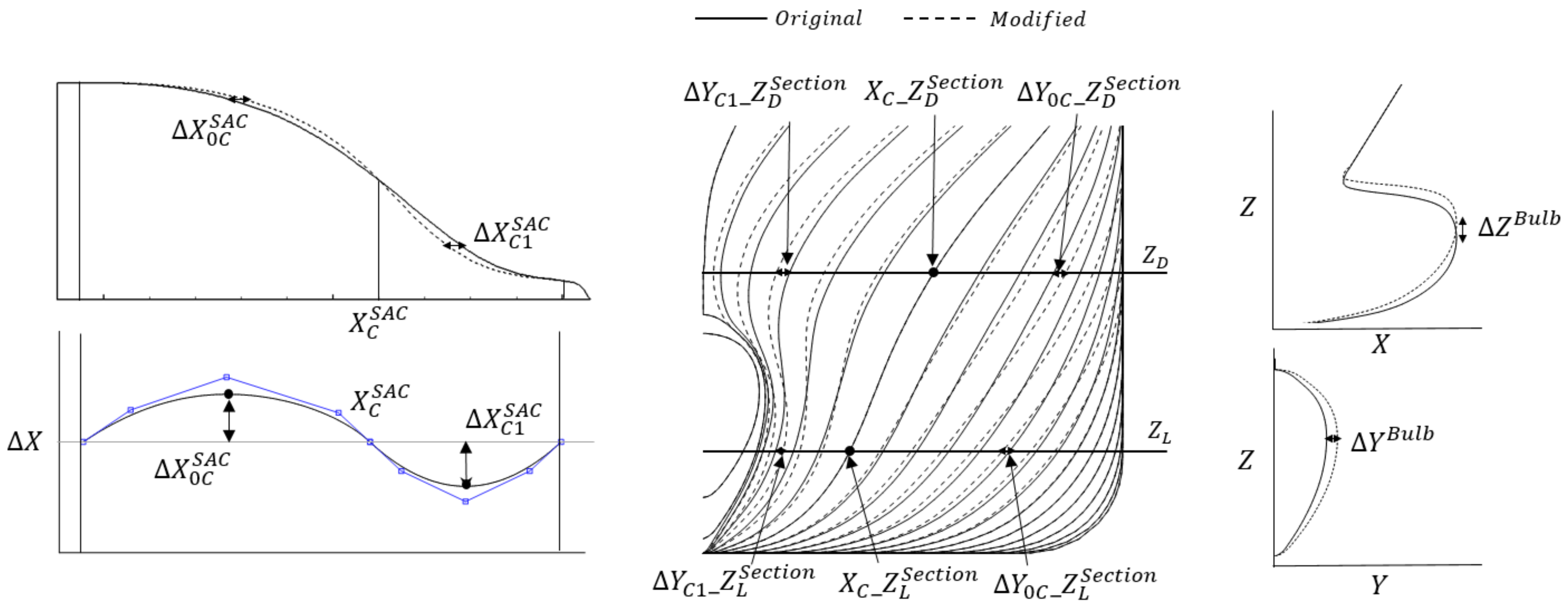
3. Hull Form Variation and Design Parameters
4. Free Surface RANS Solver and Validation
4.1. Governing Equations
4.2. Computational Domain and Boundary Conditions
4.3. Validation and Verification of CFD Results
4.4. CFD Validation with Respect to Running Attitude
5. Hull Form Optimization Process
5.1. SQP Algorithm
5.2. Practical Considerations for Optimization
6. Results
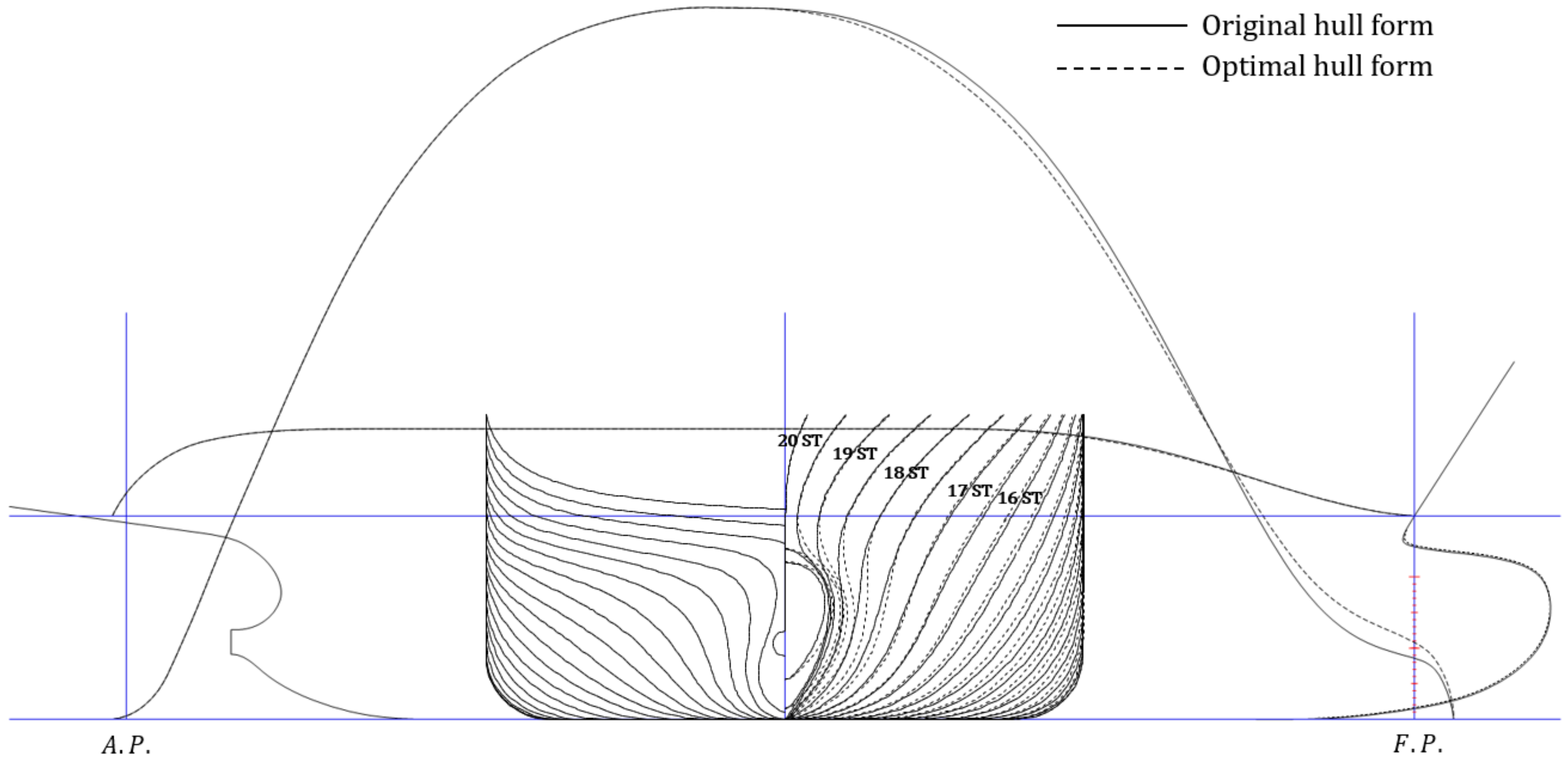
6.1. Hull Form Optimization Results
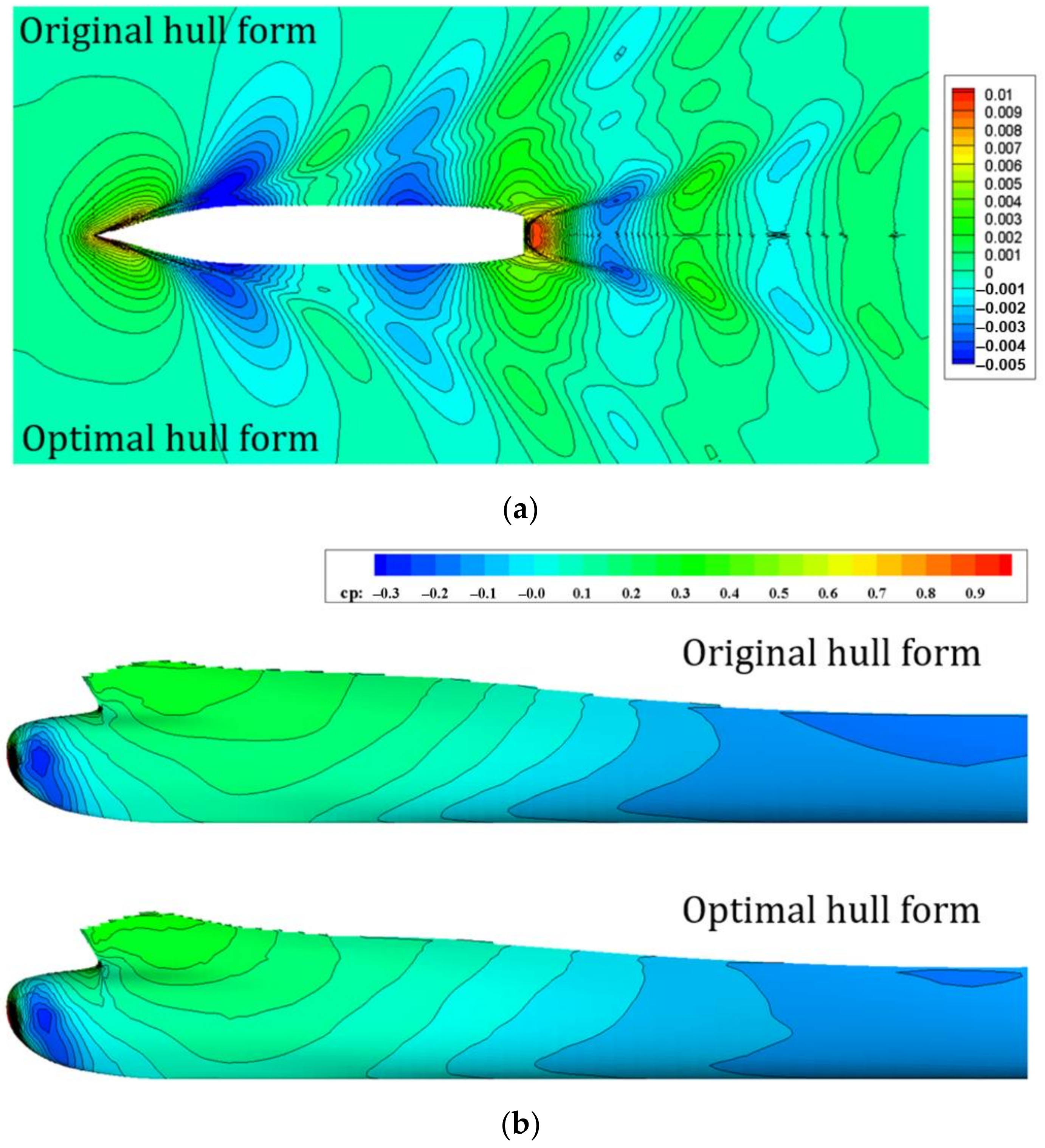
6.2. Optimal Hull
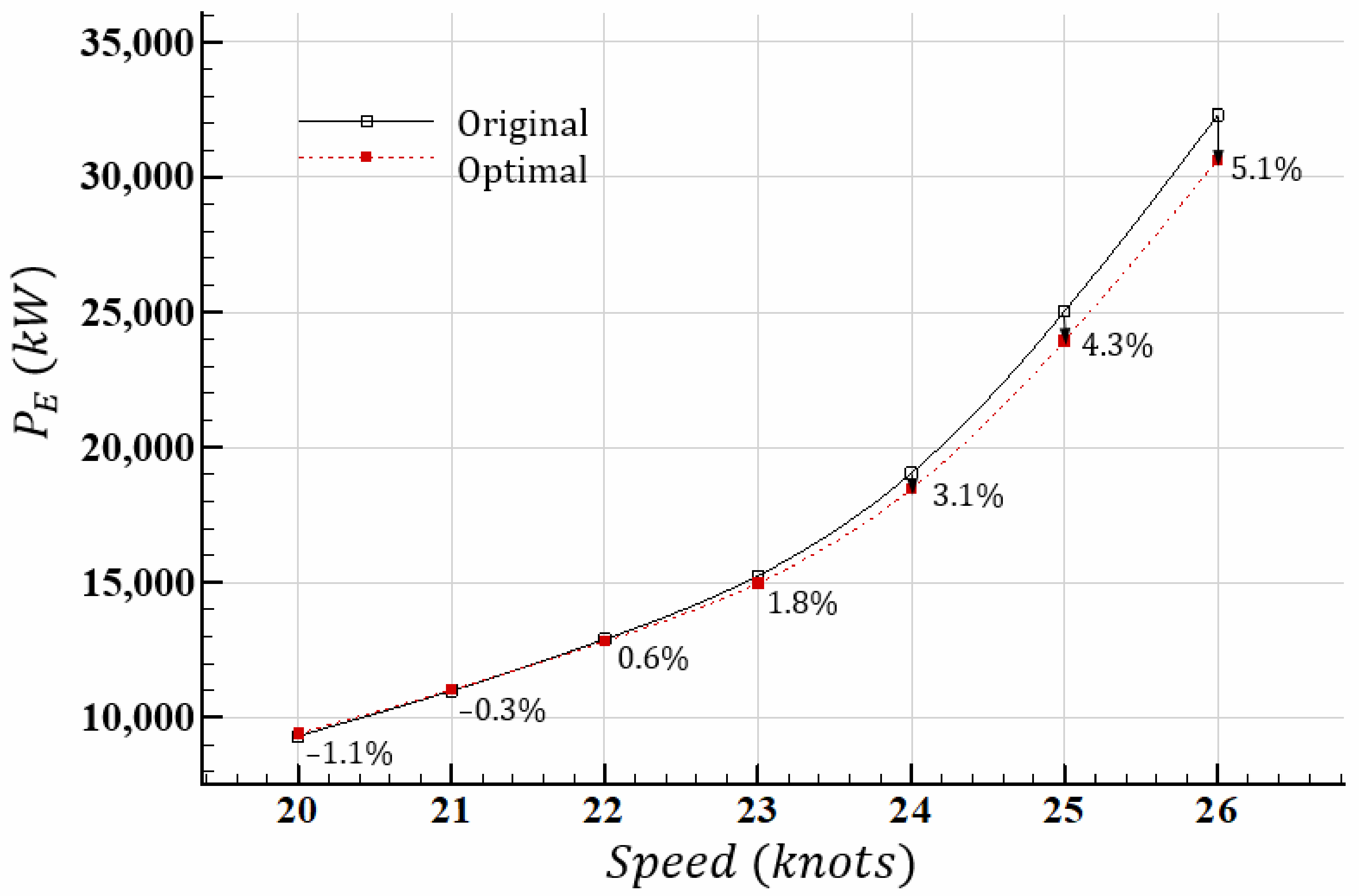
6.3. Extrapolation to Full Scale Performance
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peri, D.; Rossetti, M.; Campana, E.F. Design Optimization of Ship Hulls via CFD Techniques. J. Ship Res. 2001, 45, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejhalla, R.; Mrsa, Z.; Vukovic, S. A Genetic Algorithm approach to the problem of minimum ship wave resistance. Mar. Technol. SNAME News 2002, 39, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peri, D.; Campana, E. Multidisciplinary Design Optimization of a Naval Surface Combatant. J. Ship Res. 2003, 47, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, G.K.; Suzuki, K.; Kai, H. Hydrodynamic optimization of ship hull forms in shallow water. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2004, 9, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, Y.; Stern, F.; Himeno, Y. Computational Fluid Dynamics-Based Optimization of Surface Combatant. J. Ship Res. 2004, 28, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, G.K.; Suzuki, K.; Kai, H. Hydrodynamic optimization of a catamaran hull with large bow and stern bulbs installed on the center plane of the catamaran. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2005, 10, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Kai, H.; Kashiwabara, S. Studies on the optimization of stern hull form based on a potential flow solver. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2005, 10, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, E.F.; Peri, D.; Tahara, Y.; Stern, F. Shape optimization in ship hydrodynamics using computational fluid dynamics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2006, 196, 634–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, Y.; Peri, D.; Campana, E.F.; Stern, F. Computational fluid dynamics-based multiobjective optimization of a surface combatant using a global optimization method. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2008, 13, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biliotti, I.; Brizzolara, S.; Viviani, M.; Vernengo, G.; Danilo, R.; Galliussi, M.; Guadalupi, D.; Manfredini, A. Automatic Parametric Hull Form Optimization of Fast Naval Vessels. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Fast Sea Transportation FAST 2011, Honolulu, HI, USA, 26–29 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Choi, Y.B. Hydrodynamic hull form optimization using parametric models. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2012, 17, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.J. Research on optimization of hull lines for minimum resistance based on Rankine source method. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2012, 20, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.W.; Choi, H.J. Hydrodynamic Hull Form Design Using an Optimization Technique. Int. J. Ocean. Syst. Eng. 2013, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duy, T.N.; Hino, T.A. Study on the Stern Shape Optimization of a Container Ship using Navier–Stokes Analysis. J. Jpn. Soc. Nav. Archit. Ocean. Eng. 2015, 22, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, H.J. Hull-form optimization of a container ship based on bell-shaped modification function. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean. Eng. 2015, 7, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.H.; Choi, J.E.; Chun, H.H. Hull-form optimization of KSUEZMAX to enhance resistance performance. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean. Eng. 2015, 7, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.J.; Choi, J.E.; Chun, H.H. Hull-form optimization using parametric modification functions and particle swarm optimization. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2016, 21, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Yang, C. Hull form optimization of a cargo ship for reduced drag. J. Hydrodyn. B 2016, 28, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Changa, X.; Hua, A.K. A hydrodynamic optimization design methodology for a ship bulbous bow under multiple operating conditions. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2016, 10, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serani, A.; Fasano, G.; Liuzzid, G.; Lucidi, S.; Iemma, U.; Campana, E.F.; Stern, F.; Diez, M. Ship hydrodynamic optimization by local hybridization of deterministic derivative-free global algorithms. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2016, 59, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.W.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, I.; Choi, J.E. Bow hull-form optimization in waves of a 66,000 DWT bulk carrier. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean. Eng. 2017, 9, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sener, B.; Yildirim, M.E. Bulbous bow optimization of KCS in terms of partially parametric modeling. Int. J. Mech. Prod. Eng. 2018, 6, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Feng, B.; Liu, Z.; Chang, H. Hull surface modification for ship resistance performance optimization based on Delaunay triangulation. Ocean. Eng. 2018, 153, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Chang, X.; Yin, X.; Li, Z. Hydrodynamic Design Study on Ship Bow and Stern Hull Form Synchronous Optimization Covering Whole Speeds Range. Math. Probl. Eng. 2019, 2019, 2356369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Kim, D.J. Optimization Approach for a Catamaran Hull Using CAESES and STAR-CCM+. J. Ocean. Eng. Technol. 2020, 34, 272–276. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, A.; Zhao, M.; Wan, D. CFD-based multi-objective optimisation of S60 Catamaran considering Demihull shape and separation. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2020, 97, 102071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; El Moctar, O.; Schellin, T.E. Parametric Hull Form Optimization of Containerships for Minimum Resistance in Calm Water and in Waves. J. Mar. Sci. Appl. 2022, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Ouahsine, A.; Toan, K.T.; Sergent, P. Simulation of ship maneuvering in a confined waterway using a nonlinear model based on optimization techniques. Ocean Eng. 2017, 142, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Song, W.; Du, P.; Zhao, H. Multi-fidelity convolutional neural network surrogate model for aerodynamic optimization based on transfer learning. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33, 127121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, W.; Wan, D. Multi-fidelity Co-Kriging surrogate model for ship hull form optimization. Ocean Eng. 2022, 243, 110239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, W.; Wan, D. Resistance and wake distortion optimization of JBC considering ship-propeller interaction. Ocean Eng. 2022, 244, 110376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.W. On Ship’s Forms Derived by Formula. SNAME Trans. 1905, 47, 232–270. [Google Scholar]
- Creutz, G. Curve and Surface Design from Form Parameters by means of B-Splines. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 1977. (In German). [Google Scholar]
- Nowacki, H. Hull Form Variation and Evaluation. J. Kansai Soc. N.A. Jpn. 1993, 219, 173–184. [Google Scholar]
- Harries, S. Parametric Design and Hydrodynamic Optimization of Ship Hull Forms. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.C.; Nowacki, H. Parametric Design of Complex Hull Forms. J. Soc. Nav. Arch. Korea 2005, 9, 47–63. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.C.; Hwangbo, S.M. Surface Modeling of Forebody’s Hull Form Using Form Parameters and Fair-Skinning. J. Soc. Nav. Arch. Korea 2008, 9, 601–610. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.H.; Bang, N.S. A curve based hull form variation with geometric constraints of area and centroid. Ocean. Eng. 2017, 133, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackenby, H. On the systematic geometrical variation of ship forms. RINA Trans. 1950, 92, 289–309. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Chun, H.H.; Jung, K.H. Hull-form Optimization by Modification Function of Bell-shaped Distribution. J. Soc. Nav. Arch. Korea 2006, 43, 550–559. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.Y.; Yang, C.; Francis, N. Hull Form Optimization for Reduced Resistance and Improved Seakeeping via Practical Designed-Oriented CFD Tools. In Proceedings of the Grand Challenges in Modeling & Simulation, Ottawa, ONT, Canada, 11–14 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.J. Parametric Modification Function based Multiobjective Optimization for Ship Design. Ph.D. Thesis, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea, 2008. (In Korean). [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.W.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, I. Study on hull form variation of fore body based on multiple parametric modification curves. J. Soc. Nav. Arch. Korea 2022. in press (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Park, I.R.; Kim, K.S.; Van, S.H.; Kim, Y.C. Development of a Numerical Method for the Evaluation of Ship Resistance and Self-Propulsion Performances. J. Soc. Nav. Arch. Korea 2011, 48, 147–157. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, I.R.; Kim, K.S.; Van, S.H. Feasibility Study on Numerical Towing Tank Application to Predictions of Resistance and Self-Propulsion Performances for a Ship. In Proceedings of the Gothenburg 2010 A Workshop on CFD in Ship Hydrodynamics, Gothenburg, Sweden, 8–10 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tokyo 2015 A Workshop on CFD in Ship Hydrodynamics. Available online: https://t2015.nmri.go.jp/ (accessed on 1 August 2016).







| Name | Symbol | Full Scale | Model Scale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scale ratio | λ | 31.6 | |
| Length between perpendiculars [m] | 230.0 | 7.2786 | |
| Breadth [m] | 32.2 | 1.0190 | |
| Draft [m] | 10.8 | 0.3418 | |
| Block coefficient | 0.6505 | ||
| Wetted surface area [m2] | 9530 | 9.5541 | |
| Design speed (m/s) | 12.3466 (24 knots) | 2.197 | |
| Froude number | 0.26 | ||
| Reynolds number | 2.58 × 109 | 1.40 × 107 | |
| Modification Function | Design Variable | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAC Shape | Fixed X position | ||
| X movement at shoulder part * | |||
| X movement at entrance part | |||
| Section Shape | ) | ||
| ) | |||
| ) | |||
| ) | |||
| ) * | |||
| ) | |||
| Bulb Shape | Z movement of bulb height | ||
| Y movement of bulb breadth |
| Grid | Hull Surface Mesh | No of Grid Points | Sinkage | Trim (°) | Computational Time (h) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp. | - | - | - | - | 3.711 | −0.0019 | −0.169 | - |
| Coarse | 114 × 51 | 1.62 M | 0.744 | 2.852 | 3.596 (96.9%) | −0.0022 | −0.180 | 3 |
| Medium | 162 × 71 | 2.70 M | 0.779 | 2.850 | 3.629 (97.8%) | −0.0021 | −0.173 | 5 |
| Fine | 230 × 101 | 4.61 M | 0.774 | 2.853 | 3.627 (97.7%) | −0.0022 | −0.206 | 10 |
| Running Attitudes | Sinkage | Trim (°) | Computational Time (h) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free | 0.779 | 2.850 | 3.629 | −0.0021 | −0.173 | 5 |
| Fixed | 0.774 | 2.774 | 3.512 (96.8%) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2 |
| Fixed with static sinkage & trim | 0.790 | 2.846 | 3.636 (100.2%) | −0.0021 | −0.173 | 2 |
| Running Attitudes | Sinkage | Trim (°) | Computational Time (h) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free | 0.7280 | 2.8360 | 3.5640 | −0.0020 | −0.174 | 5 |
| Fixed with static sinkage & trim | 0.7352 | 2.8350 | 3.5702 (100.2%) | −0.0021 | −0.173 | 2 |
| Modification Function | Design Variable | Initial Value | Range | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAC Shape | 16.297 ST | −2.0 ST, +2.0 ST | 0.05 ST | ||
| 0.0 ST | −1.0 ST, +1.0 ST | 0.02 ST | |||
| Section Shape | 17.215 ST | −2.0 ST, +2.0 ST | 0.05 ST | ||
| 0.0 B | −0.03 B, +0.03 B | 3.11 × 10−4 B | |||
| 0.0 B | −0.03 B, +0.03 B | 3.11 × 10−4 B | |||
| 15.852 ST | −2.0 ST, +2.0 ST | 0.05 ST | |||
| 0.0 B | −0.03 B, +0.03 B | 3.11 × 10−4 B | |||
| Bulb Shape | 0.0 T | −0.09 T, +0.09 T | 1.85 × 10−3 T | ||
| 0.0 B | −0.03 B, +0.03 B | 6.21 × 10−4 B |
| Running Attitudes | Computational Time for Each Simulation (h) | Parallel Computing | Number of CPU Cores | Number of Simulations | Total Computational Time (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free | 5 | No | 24 | 190 | 5 × 190 = 950 |
| Fixed with static sinkage & trim | 2 | No | 24 | 190 | 2 × 190 = 380 |
| Free | 5 | Yes | 432 | 20 | 5 × 20 = 100 |
| Fixed with static sinkage & trim | 2 | Yes | 432 | 20 | 2 × 20 = 40 |
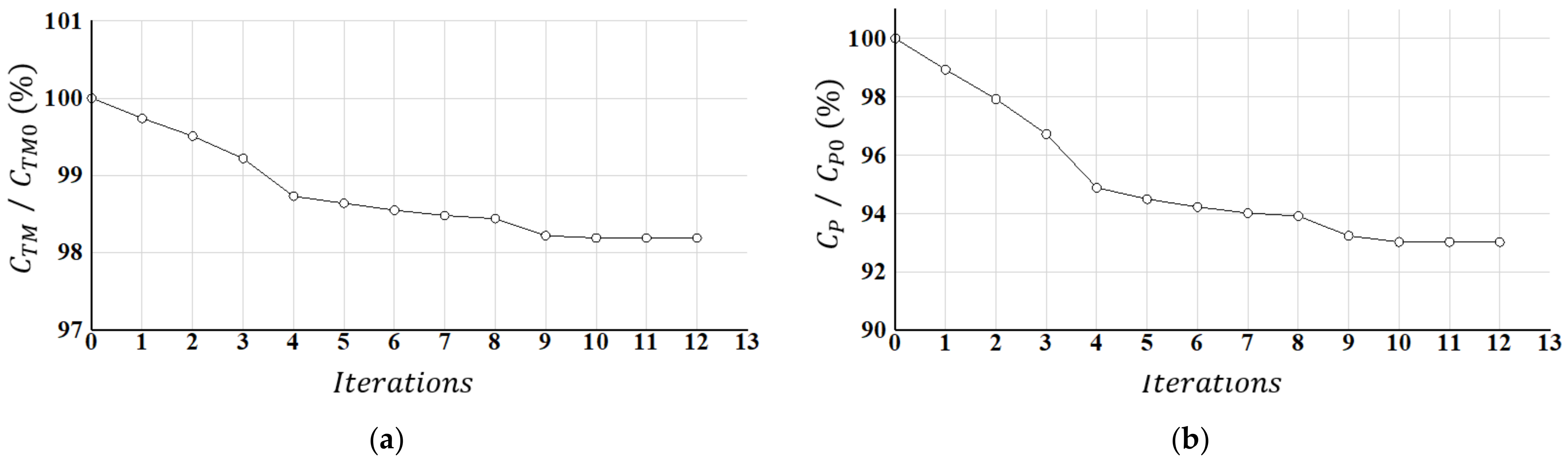
| Iteration | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (original) | 0.7904 | 100.00 | 2.8456 | 3.6361 | 100.00 |
| 1 | 0.7819 | 98.93 | 2.8448 | 3.6267 | 99.74 |
| 2 | 0.7739 | 97.92 | 2.8444 | 3.6183 | 99.51 |
| 3 | 0.7645 | 96.72 | 2.8431 | 3.6076 | 99.22 |
| 4 | 0.7499 | 94.88 | 2.8401 | 3.5900 | 98.73 |
| 5 | 0.7469 | 94.49 | 2.8399 | 3.5867 | 98.67 |
| 6 | 0.7447 | 94.22 | 2.8386 | 3.5833 | 98.55 |
| 7 | 0.7430 | 94.01 | 2.8379 | 3.5810 | 98.48 |
| 8 | 0.7423 | 93.91 | 2.8373 | 3.5795 | 98.44 |
| 9 | 0.7369 | 93.23 | 2.8345 | 3.5714 | 98.22 |
| 10 (optimal) | 0.7352 | 93.02 | 2.8350 | 3.5702 | 98.19 |
| 11 | 0.7352 | 93.02 | 2.8350 | 3.5702 | 98.19 |
| Displacement (m3) | Wetted Surface Area (m3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | 52,030 | 0.6505 | 9495 | −1.47 |
| Optimal | 52,036 | 0.6506 | 9497 | −1.34 |
| Hull Form | Sinkage | Trim (°) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | 0.779 | 2.850 | 3.629 | −0.0021 | −0.173 |
| Optimal | 0.728 (93.5%) | 2.836 (99.5%) | 3.564 (98.2%) | −0.0020 | −0.174 |
| Hull Form | Wetted Surface Area (m3) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | 9495 | 3.629 | 2.831 | 0.798 | 1.378 | 2.078 | 1542.7 | 19,047 |
| Optimal | 9497 | 3.564 (98.2%) | 2.831 | 0.733 (91.9%) | 1.378 | 2.012 (96.8%) | 1494.5 | 18,452 (96.9%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.-W.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-I.; Lee, I. Hull Form Optimization Study Based on Multiple Parametric Modification Curves and Free Surface Reynolds-Averaged Navier–Stokes (RANS) Solver. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052428
Park S-W, Kim S-H, Kim Y-I, Lee I. Hull Form Optimization Study Based on Multiple Parametric Modification Curves and Free Surface Reynolds-Averaged Navier–Stokes (RANS) Solver. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(5):2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052428
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Sung-Woo, Seung-Hyeon Kim, Yang-Ik Kim, and Inwon Lee. 2022. "Hull Form Optimization Study Based on Multiple Parametric Modification Curves and Free Surface Reynolds-Averaged Navier–Stokes (RANS) Solver" Applied Sciences 12, no. 5: 2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052428
APA StylePark, S.-W., Kim, S.-H., Kim, Y.-I., & Lee, I. (2022). Hull Form Optimization Study Based on Multiple Parametric Modification Curves and Free Surface Reynolds-Averaged Navier–Stokes (RANS) Solver. Applied Sciences, 12(5), 2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052428







