Artificial Intelligence Applications on Restaging [18F]FDG PET/CT in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Preliminary Report of Morpho-Functional Radiomics Classification for Prediction of Disease Outcome
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. [18F]FDG PET/CT Imaging
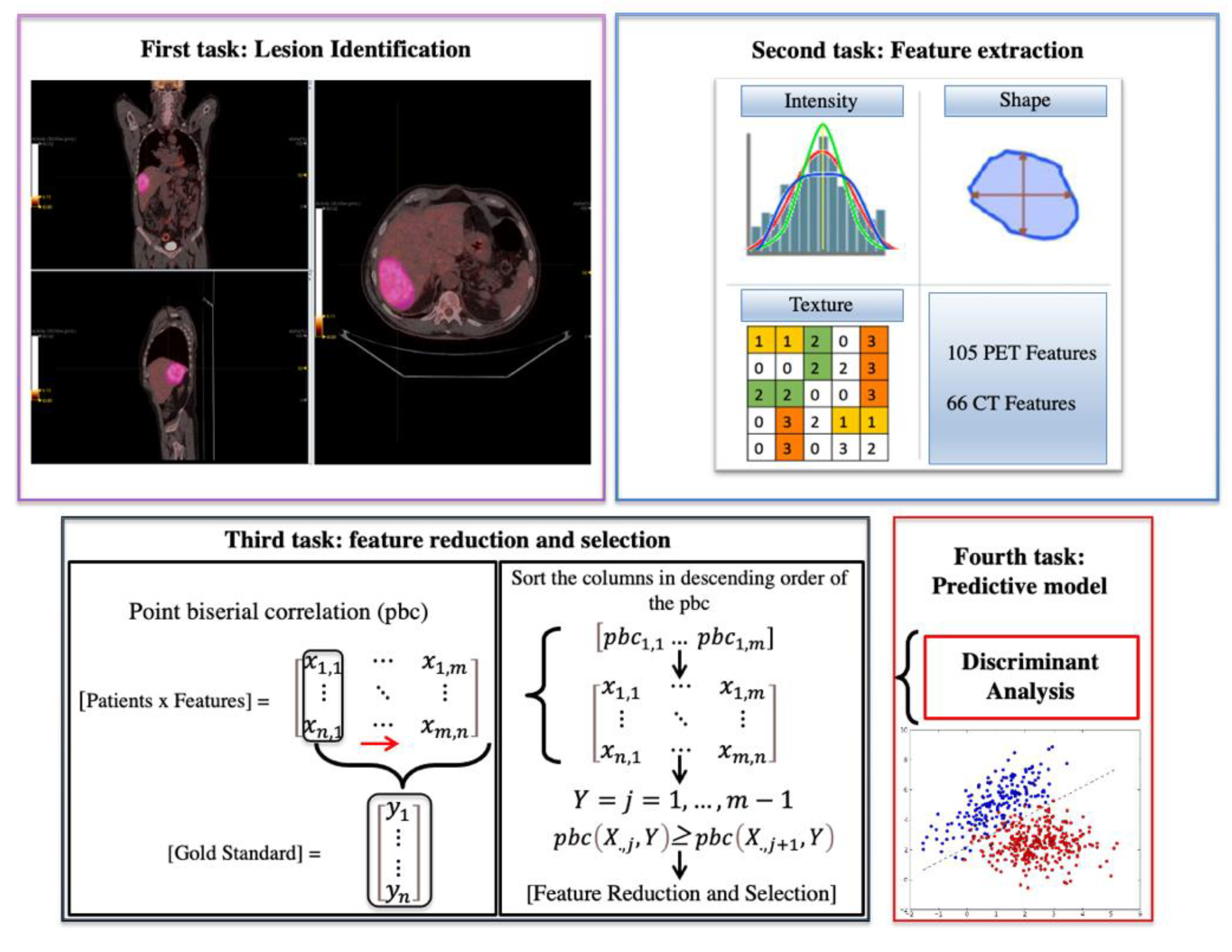
2.2. Radiomics Analysis
- Four predictive models per-lesion and -patient analysis: Performances of radiomics features extracted from PET and PET/CT, respectively, in assessing the treatment response for each lesion (without considering the patient treatment response) and in assessing the patient treatment response;
- Four models per-patient and -lesion analysis considering the only subset of liver lesions;
- Two models to evaluate the performances of PET and PET/CT radiomics features in discriminating liver metastasis from the rest of the other lesions.
2.3. Diagnostic Performance Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. [18F]FDG PET/CT Findings
3.2. Follow-Up
3.3. Radiomics Features Analysis
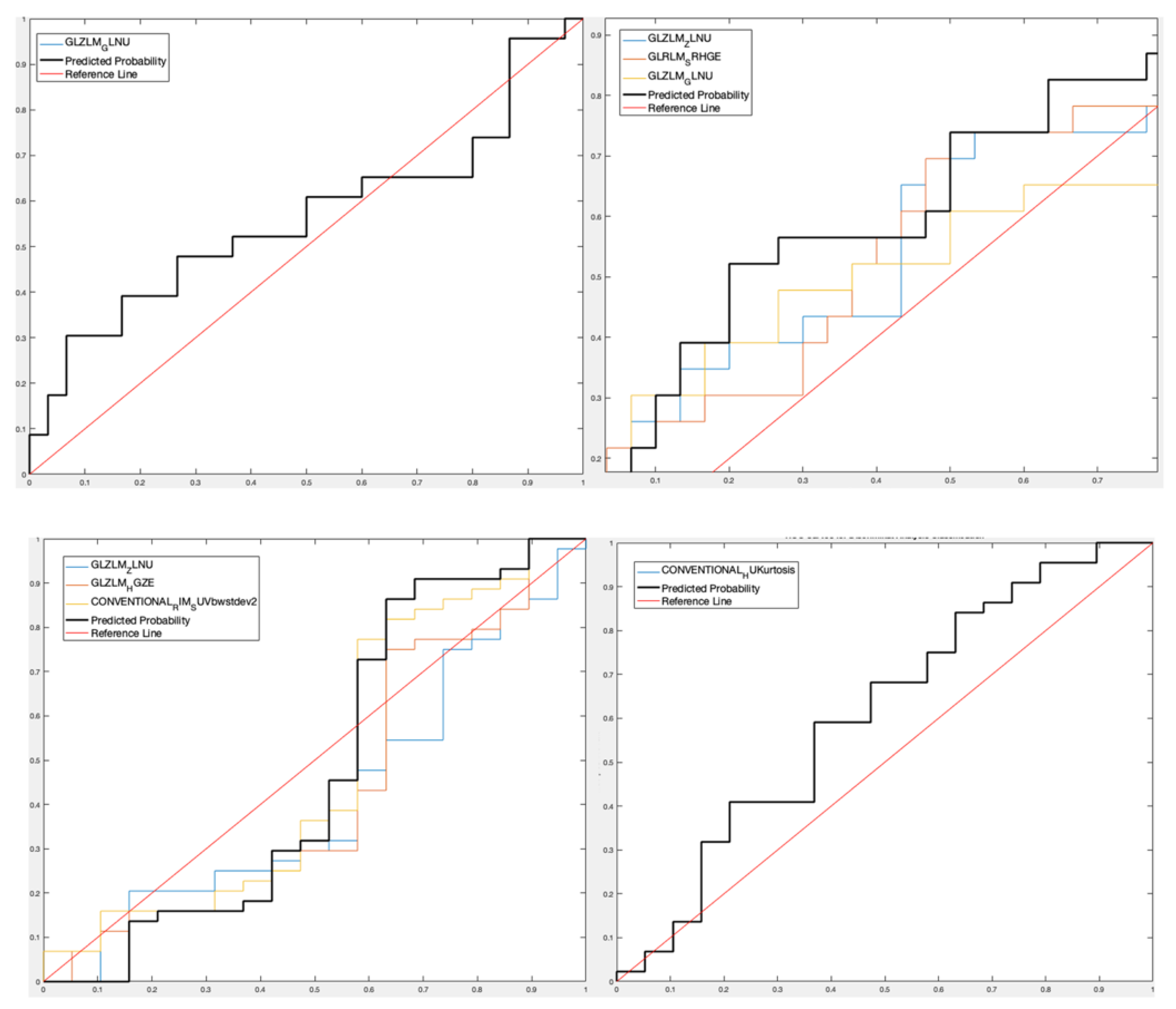
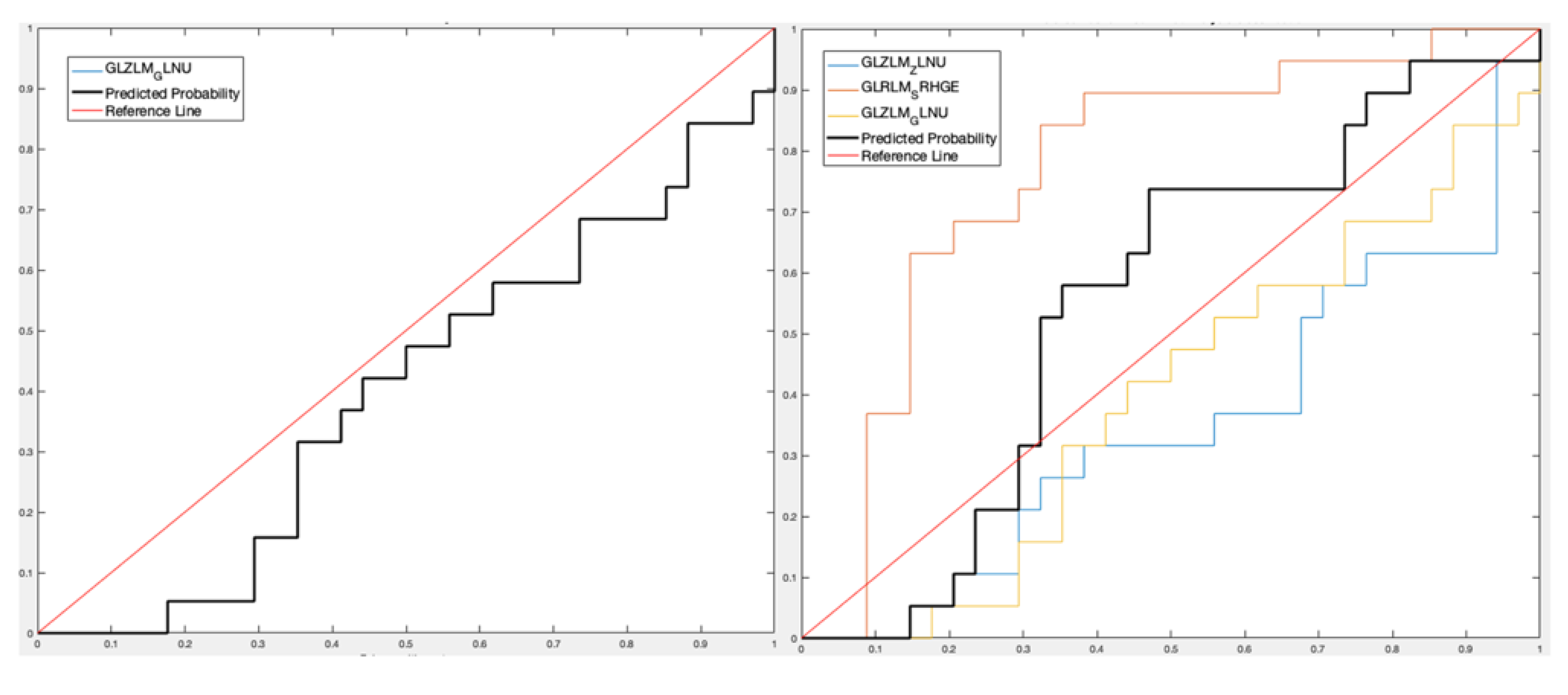
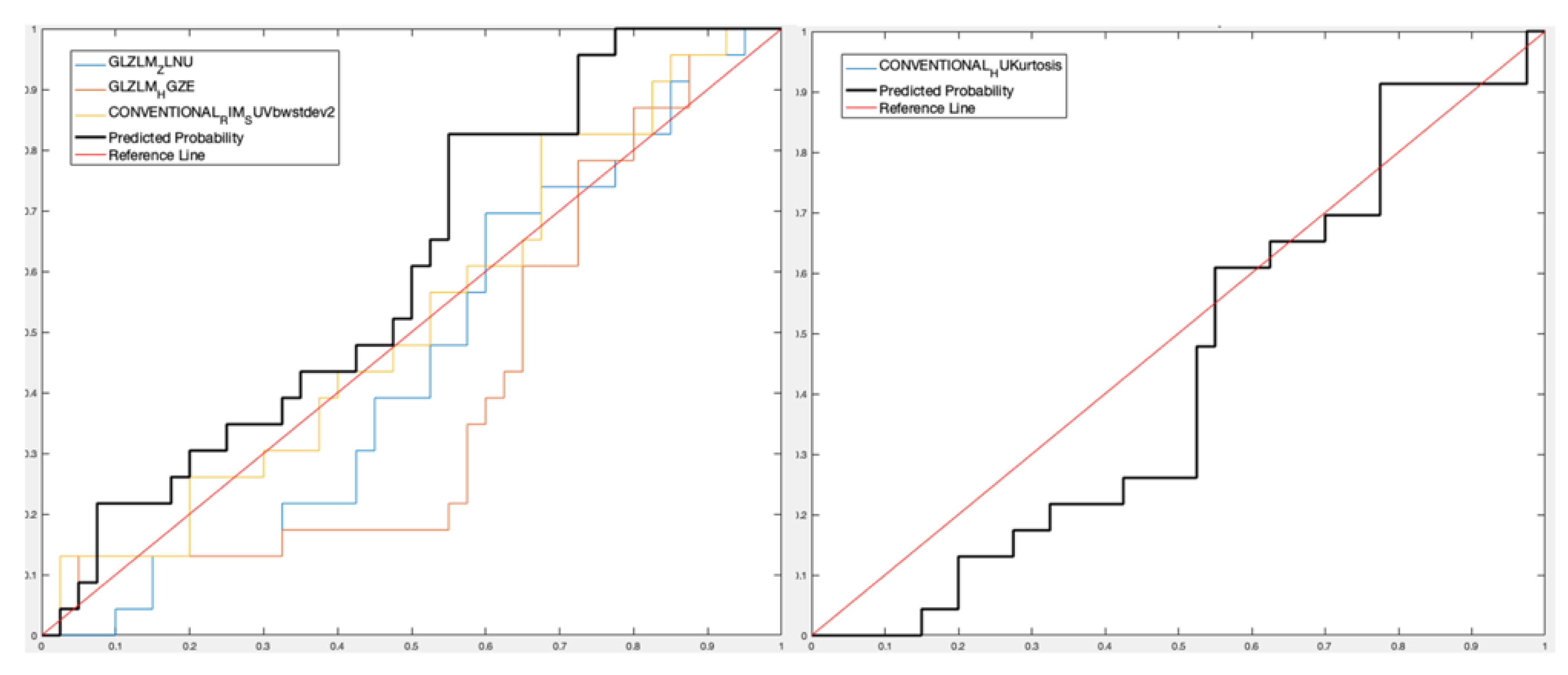
- For lesion analysis, GLRLM-based feature gray-level non-uniformity (GLZLM_GLNU) was selected [15,16] considering the only PET data set obtaining a Sensitivity 90.11%, Specificity 36.78%, Accuracy 66.72%, and AUROC 56.52% for the predictive DA classifier, while three features (GLZLM_ Zone Length Non-Uniformity—GLZLM_ ZLNU, and GLRLM_Short Run High Gray-Level Emphasis—GLRLM_SRHGE—between the CT features and GLZLM_GLNU between the PET features) were selected considering the PET/CT data set with Sensitivity 78.22%, Specificity 51.75%, Accuracy 66.63%, and AUROC 65.22%;
- For patient analysis, three features (GLZLM_ZLNU, GLZLM_High Gray-level Zone -GLZLM_HGZ-, Conventional Radial Intensity Mean Standardized Uptake Value body weight standard deviation squared -CONVENTIONAL_RIM_SUVbwstdev2-) were selected considering the PET-only data set with Sensitivity 32.07%, Specificity 92.11%, Accuracy 73.95% and AUROC 47.97%, and one feature (Conventional Hounsfield Unit Kurtosis -CONVENTIONAL_HUKurtosis-) was selected considering the PET/CT data set with Sensitivity 33.81%, Specificity 83.76%, Accuracy 68.70%, and AUROC 61%.
- For lesion analysis, one PET feature (GLZLM_GLNU) with Sensitivity 70.15%, Specificity 23.48%, Accuracy 54.21%, and AUROC 39.94%, and three PET/CT features (GLZLM_ZLNU, and GLRLM_SRHGE between the CT features and GLZLM_GLNU between the PET features) with Sensitivity 64.39%, Specificity 76.71%, Accuracy 68.69%, and AUROC 55.26%;
- For patient analysis, three PET features (GLZLM_ZLNU, GLZLM_HGZ, CONVENTIONAL_RIM_SUVbwstdev2) with Sensitivity 44.42%, Specificity 84.37%, Accuracy 59.03%, and AUROC 60.11%, and one PET/CT feature (CONVENTIONAL_HUKurtosis) with Sensitivity 33.12%, Specificity 73.74%, Accuracy 47.88%, and AUROC 43.48%.
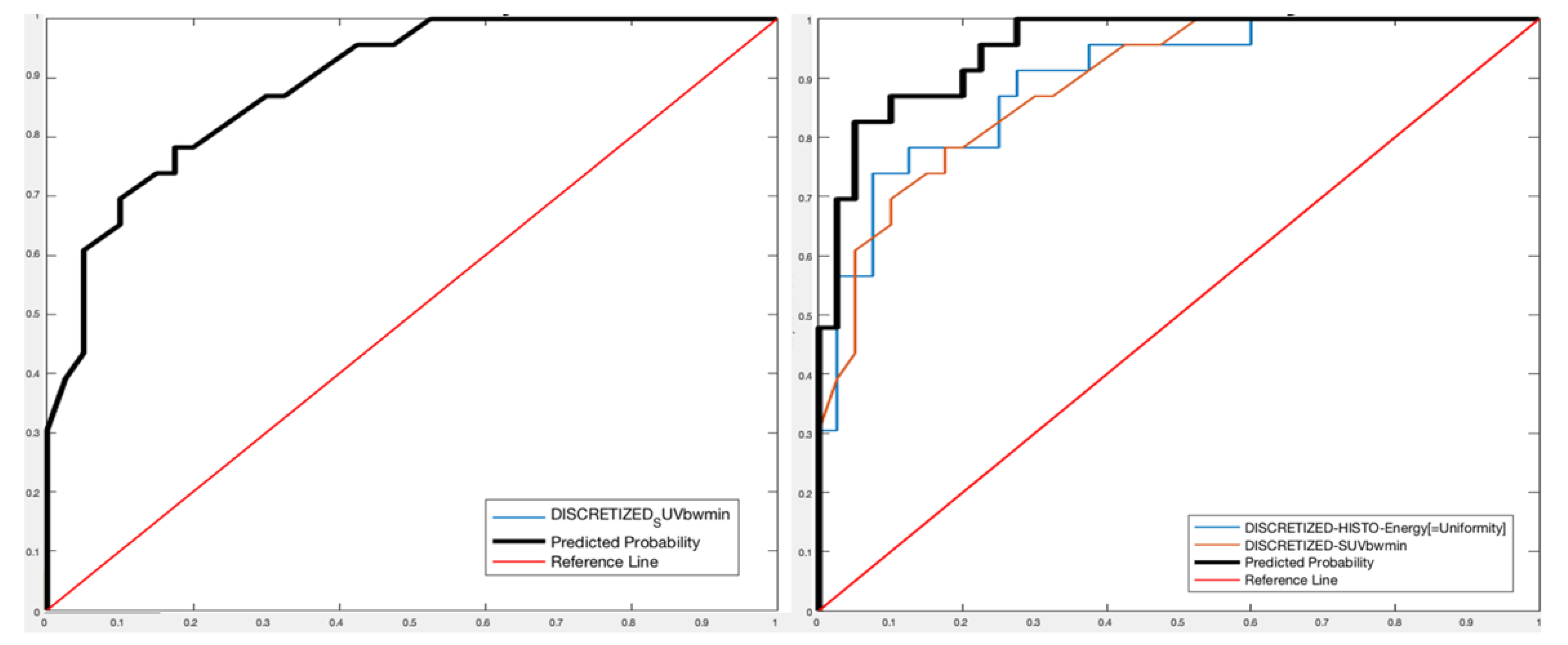
- For PET images, one feature (Discretized SUVbw minimum—DISCRETIZED_SUVbwmin-) was extracted with Sensitivity 73.78%, Specificity 83.02%, Accuracy 76.91%, and AUROC 88.91%;
- For PET/CT images, two features (Discretized histogram energy—DISCRETIZED_HISTO_Energy—between the CT features and DISCRETIZED_SUVbwmin between the PET features) were extracted with Sensitivity 89.46%, Specificity 93.63%, Accuracy 91.02%, and AUROC 95.33%.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Eresen, A.; Lu, Y.; Yang, J.; Shangguan, J.; Velichko, Y.; Yaghmai, V.; Zhang, Z. Radiomics signature for the preoperative assessment of stage in advanced colon cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laudicella, R.; Comelli, A.; Stefano, A.; Szostek, M.; Crocè, L.; Vento, A.; Spataro, A.; Comis, A.D.; La Torre, F.; Gaeta, M.; et al. Artificial Neural Networks in Cardiovascular Diseases and its Potential for Clinical Application in Molecular Imaging. Curr. Radiopharm. 2020, 14, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, G.J.; Azad, G.; Owczarczyk, K.; Siddique, M.; Goh, V. Challenges and Promises of PET Radiomics. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liberini, V.; Laudicella, R.; Capozza, M.; Huellner, M.; Burger, I.; Baldari, S.; Terreno, E.; Deandreis, D. The Future of Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Surveillance: A Systemic Review on Immunotherapy and Immuno-PET Radiotracers. Molecules 2021, 26, 2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerhoefer, M.E.; Materka, A.; Langs, G.; Häggström, I.; Szczypiński, P.; Gibbs, P.; Cook, G. Introduction to Radiomics. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, P.; Laudicella, R.; Gentile, R.; Scalisi, S.; Stefano, A.; Russo, G.; Emanuele, G.; Domenico, A.; Giancarlo, P.; Sinagra, E.; et al. Potential clinical value of quantitative fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose-PET/computed tomography using a graph-based method analysis in evaluation of incidental lesions of gastrointestinal tract: Correlation with endoscopic and histopathological findings. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2019, 40, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, A.; Harimoto, N.; Yokobori, T.; Araki, K.; Kubo, N.; Igarashi, T.; Tsukagoshi, M.; Ishii, N.; Yamanaka, T.; Handa, T.; et al. FDG-PET reflects tumor viability on SUV in colorectal cancer liver metastasis. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 25, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.; Ganeshan, B.; Irshad, S.; Lawler, K.; Eisenblätter, M.; Milewicz, H.; Rodriguez-Justo, M.; Miles, K.; Ellis, P.; Ng, T.; et al. The use of molecular imaging combined with genomic techniques to understand the heterogeneity in cancer metastasis. Br. J. Radiol. 2014, 87, 20140065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.-W.; Shen, W.-C.; Chen, W.T.-L.; Hsieh, T.-C.; Yen, K.-Y.; Chang, J.-G.; Kao, C.-H. Metabolic Imaging Phenotype Using Radiomics of [18F]FDG PET/CT Associated with Genetic Alterations of Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2019, 21, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Xin, B.; Hao, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, S.; Xu, J.; Wang, X. Quantitative Prediction of Microsatellite Instability in Colorectal Cancer with Preoperative PET/CT-Based Radiomics. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 702055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boellaard, R.; Delgado-Bolton, R.; Oyen, W.J.G.; Giammarile, F.; Tatsch, K.; Eschner, W.; Verzijlbergen, F.J.; Barrington, S.F.; Pike, L.C.; Weber, W.A.; et al. FDG PET/CT: EANM procedure guidelines for tumour imaging: Version 2. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 42, 328–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nioche, C.; Orlhac, F.; Boughdad, S.; Reuzé, S.; Goya-Outi, J.; Robert, C.; Pellot-Barakat, C.; Soussan, M.; Frouin, F.; Buvat, I. LIFEx: A Freeware for Radiomic Feature Calculation in Multimodality Imaging to Ac-celerate Advances in the Characterization of Tumor Heterogeneity. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4786–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stefano, A.; Leal, A.; Richiusa, S.; Trang, P.; Comelli, A.; Benfante, V.; Cosentino, S.; Sabini, M.G.; Tuttolomondo, A.; Altieri, R.; et al. Robustness of PET Radiomics Features: Impact of Co-Registration with MRI. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comelli, A.; Stefano, A.; Coronnello, C.; Russo, G.; Vernuccio, F.; Cannella, R.; Salvaggio, G.; Lagalla, R.; Barone, S. Radiomics: A New Biomedical Workflow to Create a Predictive Model. In Annual Conference on Medical Image Understanding and Analysis; Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 280–293. Volume 1248 CCIS, ISBN 9783030527907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, S.; Cannella, R.; Comelli, A.; Pellegrino, A.; Salvaggio, G.; Stefano, A.; Vernuccio, F. Hybrid descriptive-inferential method for key feature selection in prostate cancer radiomics. Appl. Stoch. Model. Bus. Ind. 2021, 37, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefano, A.; Comelli, A.; Bravatà, V.; Barone, S.; Daskalovski, I.; Savoca, G.; Sabini, M.G.; Ippolito, M.; Russo, G. A preliminary PET ra-diomics study of brain metastases using a fully automatic segmentation method. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.; Stefano, A.; Alongi, P.; Comelli, A.; Catalfamo, B.; Mantarro, C.; Longo, C.; Altieri, R.; Certo, F.; Cosentino, S.; et al. Feasibility on the Use of Radiomics Features of 11[C]-MET PET/CT in Central Nervous System Tumours: Preliminary Results on Potential Grading Discrimination Using a Machine Learning Model. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 5318–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comelli, A.; Stefano, A.; Bignardi, S.; Coronnello, C.; Russo, G.; Sabini, M.G.; Ippolito, M.; Yezzi, A. Tissue Classification to Support Local Active Delineation of Brain Tumors. In Annual Conference on Medical Image UnderStanding and Analysis; Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 3–14. Volume 1065 CCIS, ISBN 9783030393427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuocolo, R.; Comelli, A.; Stefano, A.; Benfante, V.; Dahiya, N.; Stanzione, A.; Castaldo, A.; De Lucia, D.R.; Yezzi, A.; Imbriaco, M. Deep Learning Whole-Gland and Zonal Prostate Segmentation on a Public MRI Dataset. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 54, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comelli, A.; Coronnello, C.; Dahiya, N.; Benfante, V.; Palmucci, S.; Basile, A.; Vancheri, C.; Russo, G.; Yezzi, A.; Stefano, A. Lung Segmentation on High-Resolution Computerized Tomography Images Using Deep Learning: A Preliminary Step for Radiomics Studies. J. Imaging 2020, 6, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefano, A.; Comelli, A. Customized Efficient Neural Network for COVID-19 Infected Region Identification in CT Images. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staal, F.C.; van der Reijd, D.J.; Taghavi, M.; Lambregts, D.M.; Beets-Tan, R.G.; Maas, M. Radiomics for the Prediction of Treatment Outcome and Survival in Patients with Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review. Clin. Color. Cancer 2020, 20, 52–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Cho, E.S.; Park, E.J.; Baik, S.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Park, C.; Yeu, Y.; Clemenceau, J.R.; et al. Radiomics Features of 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron-Emission Tomography as a Novel Prog-nostic Signature in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.-C.; Chen, S.-W.; Wu, K.-C.; Lee, P.-Y.; Feng, C.-L.; Hsieh, T.-C.; Yen, K.-Y.; Kao, C.-H. Predicting pathological complete response in rectal cancer after chemoradiotherapy with a random forest using 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and computed tomography radiomics. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovinfosse, P.; Polus, M.; Van Daele, D.; Martinive, P.; Daenen, F.; Hatt, M.; Visvikis, D.; Koopmansch, B.; Lambert, F.; Coimbra, C.; et al. FDG PET/CT radiomics for predicting the outcome of locally advanced rectal cancer. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2018, 45, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, V.; Mazzetti, S.; Bertotto, I.; Chiarenza, C.; Cauda, S.; Delmastro, E.; Bracco, C.; Di Dia, A.; Leone, F.; Medico, E.; et al. Predicting locally advanced rectal cancer response to neoadjuvant therapy with 18F-FDG PET and MRI radiomics features. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2019, 46, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Helden, E.J.; Vacher, Y.J.L.; van Wieringen, W.N.; van Velden, F.H.P.; Verheul, H.M.W.; Hoekstra, O.S.; Boellaard, R.; Menke-van der Houven van Oordt, C.W. Radiomics analysis of pre-treatment [18F]FDG PET/CT for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer undergoing palliative systemic treatment. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2018, 45, 2307–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bundschuh, R.A.; Dinges, J.; Neumann, L.; Seyfried, M.; Zsótér, N.; Papp, L.; Rosenberg, R.; Becker, K.; Astner, S.T.; Essler, M.; et al. Textural Parameters of Tumor Heterogeneity in ¹⁸F-FDG PET/CT for Therapy Response Assessment and Prognosis in Patients with Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bang, J.-I.; Ha, S.; Kang, S.-B.; Lee, K.-W.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, J.-S.; Oh, H.-K.; Lee, H.-Y.; Kim, S.E. Prediction of neoadjuvant radiation chemotherapy response and survival using pretreatment [18F]FDG PET/CT scans in locally advanced rectal cancer. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2015, 43, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, P.; Laudicella, R.; Stefano, A.; Caobelli, F.; Comelli, A.; Vento, A.; Sardina, D.; Ganduscio, G.; Toia, P.; Ceci, F.; et al. Choline PET/CT features to predict survival outcome in high risk prostate cancer restaging: A preliminary machine-learning radiomics study. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alongi, P.; Stefano, A.; Comelli, A.; Laudicella, R.; Scalisi, S.; Arnone, G.; Barone, S.; Spada, M.; Purpura, P.; Bartolotta, T.V.; et al. Radiomics analysis of 18F-Choline PET/CT in the prediction of disease outcome in high-risk prostate cancer: An explorative study on machine learning feature classification in 94 patients. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 4595–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmim, A.; Bak-Fredslund, K.P.; Ashrafinia, S.; Lu, L.; Schmidtlein, C.; Subramaniam, R.M.; Morsing, A.; Keiding, S.; Horsager, J.; Munk, O.L. Prognostic modeling for patients with colorectal liver metastases incorporating FDG PET radiomic features. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 113, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, A.K.; Mithun, S.; Jaiswar, V.; Sherkhane, U.B.; Purandare, N.C.; Prabhash, K.; Rangarajan, V.; Dekker, A.; Wee, L.; Traverso, A. Repeatability and reproducibility study of radiomic features on a phantom and human cohort. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creasy, J.M.; Cunanan, K.M.; Chakraborty, J.; McAuliffe, J.C.; Chou, J.; Gonen, M.; Ba, V.S.K.; Weiser, M.R.; Balachandran, V.P.; Drebin, J.A.; et al. Differences in Liver Parenchyma are Measurable with CT Radiomics at Initial Colon Resection in Patients that Develop Hepatic Metastases from Stage II/III Colon Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 28, 1982–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| All Patients (n = 52) | |
|---|---|
| Age (Mean ± SD) | 62.28 ± 11.23 y |
| Sex | |
| Male | 41 (77.35%) |
| Female | 11 (22.65%) |
| Grading | |
| G1 | 2 (3.85%) |
| G2 | 23 (44.23%) |
| G2–G3 | 2 (3.85%) |
| G3 | 10 (19.23%) |
| Unknown | 15 (28.84%) |
| First Adjuvant Therapy | |
| Radiotherapy | 1 (1.92%) |
| Chemotherapy | 49 (94.2%) |
| Cht+RT | 2 (3.85%) |
| PET Lesions | |
| Liver | 23 (36.51%) |
| Lymph nodes | 13 (19.05%) |
| Lungs | 8 (12.7%) |
| Presacral | 7 (11.11%) |
| Peritoneum | 4 (6.35%) |
| Rectum | 3 (4.76%) |
| Spleen | 2 (3.17%) |
| Bones | 2 (3.17%) |
| Thorax | 1 (1.59%) |
| Stages At Diagnosis | |
| Stage I | 4 (7.69%) |
| Stage II | 9 (17.30%) |
| Stage III | 13 (25%) |
| Stage IV | 10 (19.23%) |
| Unknown | 16 (30.76%) |
| Sensitivity | Specificity | Accuracy | AUROC | Features Selected | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET per-lesion | 90.11% | 36.78% | 66.72% | 56.52% | GLZLM_GLNU | ||
| PET/CT per-lesion | 78.22% | 51.75% | 66.63% | 65.22% | GLZLM_ZLNU (CT) | GLRLM_SRHGE (CT) | GLZLM_GLNU (PET) |
| PET per-patient | 32.07% | 92.11% | 73.95% | 47.97% | GLZLM_ZLNU | GLZLM_HGZ | CONVENTIONAL_RIM_SUVbwstdev2 |
| PET/CT per-patient | 33.81% | 83.76% | 68.70% | 61.00% | CONVENTIONAL_HUKurtosis | ||
| Sensitivity | Specificity | Accuracy | AUROC | Features Selected | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET per-lesion | 70.15% | 23.48% | 54.21% | 39.94% | GLZLM_GLNU | ||
| PET/CT per-lesion | 64.39% | 76.71% | 68.69% | 55.26% | GLZLM_ZLNU (CT) | GLRLM_SRHGE (CT) | GLZLM_GLNU (PET) |
| PET per-patient | 44.42% | 84.37% | 59.03% | 60.11% | GLZLM_ZLNU | GLZLM_HGZ | CONVENTIONAL_RIM_SUVbwstdev2 |
| PET/CT per-patient | 33.12% | 73.74% | 47.88% | 43.48% | CONVENTIONAL_HUKurtosis | ||
| Sensitivity | Specificity | Accuracy | AUROC | Features Selected | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET liver | 73.38% | 83.02% | 76.91% | 88.91% | DISCRETIZED_SUVbwmin | |
| PET/CT liver | 89.46% | 93.63% | 91.02% | 95.33% | DISCRETIZED_HISTO_Energy (CT) | DISCRETIZED_SUVbwmin (PET) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alongi, P.; Stefano, A.; Comelli, A.; Spataro, A.; Formica, G.; Laudicella, R.; Lanzafame, H.; Panasiti, F.; Longo, C.; Midiri, F.; et al. Artificial Intelligence Applications on Restaging [18F]FDG PET/CT in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Preliminary Report of Morpho-Functional Radiomics Classification for Prediction of Disease Outcome. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12062941
Alongi P, Stefano A, Comelli A, Spataro A, Formica G, Laudicella R, Lanzafame H, Panasiti F, Longo C, Midiri F, et al. Artificial Intelligence Applications on Restaging [18F]FDG PET/CT in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Preliminary Report of Morpho-Functional Radiomics Classification for Prediction of Disease Outcome. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(6):2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12062941
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlongi, Pierpaolo, Alessandro Stefano, Albert Comelli, Alessandro Spataro, Giuseppe Formica, Riccardo Laudicella, Helena Lanzafame, Francesco Panasiti, Costanza Longo, Federico Midiri, and et al. 2022. "Artificial Intelligence Applications on Restaging [18F]FDG PET/CT in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Preliminary Report of Morpho-Functional Radiomics Classification for Prediction of Disease Outcome" Applied Sciences 12, no. 6: 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12062941
APA StyleAlongi, P., Stefano, A., Comelli, A., Spataro, A., Formica, G., Laudicella, R., Lanzafame, H., Panasiti, F., Longo, C., Midiri, F., Benfante, V., La Grutta, L., Burger, I. A., Bartolotta, T. V., Baldari, S., Lagalla, R., Midiri, M., & Russo, G. (2022). Artificial Intelligence Applications on Restaging [18F]FDG PET/CT in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Preliminary Report of Morpho-Functional Radiomics Classification for Prediction of Disease Outcome. Applied Sciences, 12(6), 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12062941











