The Role of Auditory and Visual Components in Reading Training: No Additional Effect of Synchronized Visual Cue in a Rhythm-Based Intervention for Dyslexia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Interventions
2.4. Measures
2.4.1. Primary Outcomes
2.4.2. Secondary Outcomes
2.5. Analytic Plan
3. Results
3.1. Participants’ Characteristics
3.2. RRT Immediate Effects
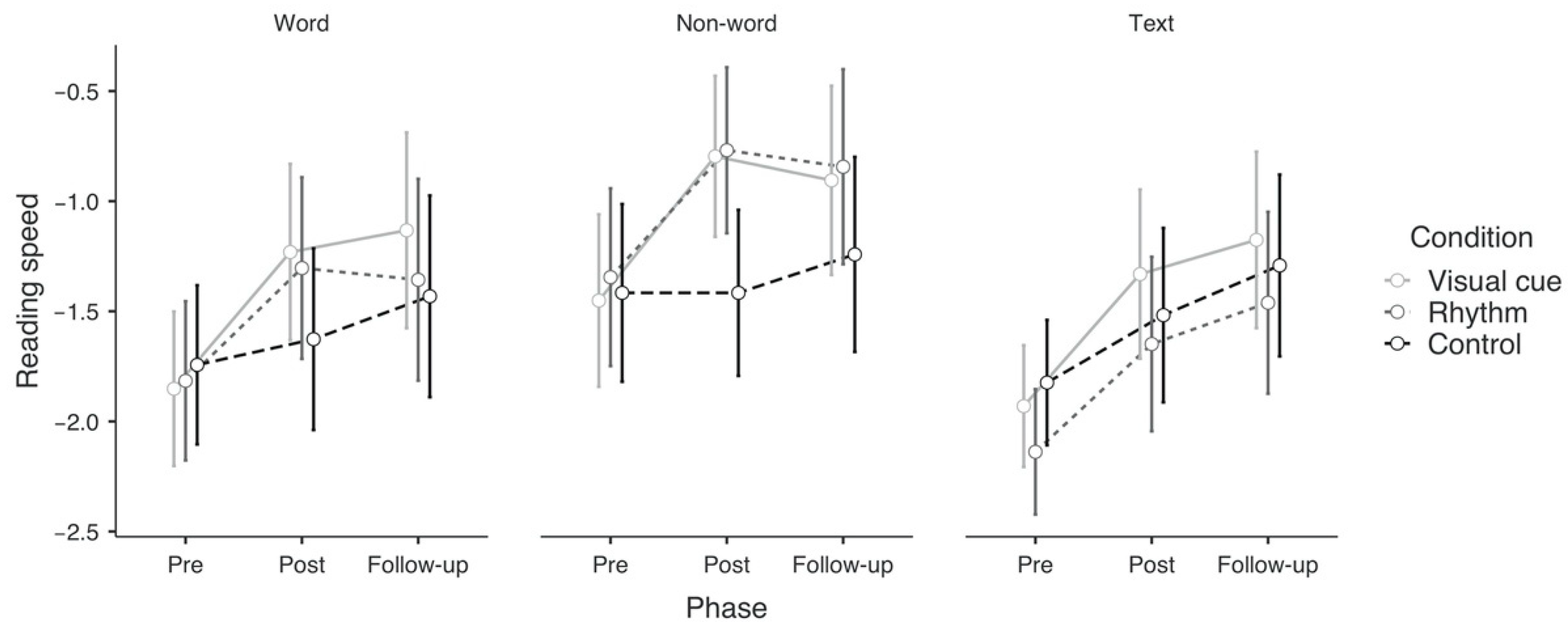
3.2.1. Pre-Post Effects on Primary Outcomes
3.2.2. Pre-Post Effects on Secondary Outcomes
3.3. RRT Medium-Term Effects
3.3.1. Pre-Follow-Up Effects on Primary Outcomes
3.3.2. Pre-Follow-Up Effects on Secondary Outcomes
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cancer, A.; Antonietti, A. Music-Based and Auditory-Based Interventions for Reading Difficulties: A Literature Review. Heliyon Psychol. under revision.
- Goswami, U. A Temporal Sampling Framework for Developmental Dyslexia. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2011, 15, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, U.; Power, A.J.; Lallier, M.; Facoetti, A. Oscillatory “Temporal Sampling” and Developmental Dyslexia: Toward an over-Arching Theoretical Framework. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giraud, A.-L.; Ramus, F. Neurogenetics and Auditory Processing in Developmental Dyslexia. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cason, N.; Schön, D. Rhythmic Priming Enhances the Phonological Processing of Speech. Neuropsychologia 2012, 50, 2652–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torppa, R.; Faulkner, A.; Huotilainen, M.; Järvikivi, J.; Lipsanen, J.; Laasonen, M.; Vainio, M. The Perception of Prosody and Associated Auditory Cues in Early-Implanted Children: The Role of Auditory Working Memory and Musical Activities. Int. J. Audiol. 2014, 53, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castles, A.; Friedmann, N. Developmental Dyslexia and the Phonological Deficit Hypothesis. Mind Lang. 2014, 29, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellutino, F.R.; Fletcher, J.M.; Snowling, M.J.; Scanlon, D.M. Specific Reading Disability (Dyslexia): What Have We Learned in the Past Four Decades? J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2004, 45, 2–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowling, M.J.; Melby-Lervåg, M. Oral Language Deficits in Familial Dyslexia: A Meta-Analysis and Review. Psychol. Bull. 2016, 142, 498–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, S.; Gori, S.; Ruffino, M.; Pedrolli, K.; Facoetti, A. A Causal Link between Visual Spatial Attention and Reading Acquisition. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stein, J. The Magnocellular Theory of Developmental Dyslexia. Dyslexia Chichester Engl. 2001, 7, 12–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramus, F.; Marshall, C.R.; Rosen, S.; Van der Lely, H.K.J. Phonological Deficits in Specific Language Impairment and Developmental Dyslexia: Towards a Multidimensional Model. Brain 2013, 136, 630–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menghini, D.; Finzi, A.; Benassi, M.; Bolzani, R.; Facoetti, A.; Giovagnoli, S.; Ruffino, M.; Vicari, S. Different Underlying Neurocognitive Deficits in Developmental Dyslexia: A Comparative Study. Neuropsychologia 2010, 48, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, D.; Coull, J.T.; Schön, D. Metrical Rhythm Implicitly Orients Attention in Time as Indexed by Improved Target Detection and Left Inferior Parietal Activation. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2014, 26, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, E.G. Thalamic Circuitry and Thalamocortical Synchrony. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2002, 357, 1659–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quené, H.; Port, R.F. Effects of Timing Regularity and Metrical Expectancy on Spoken-Word Perception. Phonetica 2005, 62, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, S.; Dalla Bella, S. It Is Better When Expected: Aligning Speech and Motor Rhythms Enhances Verbal Processing. Lang. Cogn. Neurosci. 2016, 31, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncaglia-Denissen, M.P.; Schmidt-Kassow, M.; Kotz, S.A. Speech Rhythm Facilitates Syntactic Ambiguity Resolution: ERP Evidence. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaugnacco, E.; Lopez, L.; Terribili, C.; Zoia, S.; Buda, S.; Tilli, S.; Monasta, L.; Montico, M.; Sila, A.; Ronfani, L.; et al. Rhythm Perception and Production Predict Reading Abilities in Developmental Dyslexia. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagliarini, E.; Scocchia, L.; Granocchio, E.; Sarti, D.; Stucchi, N.; Guasti, M.T. Timing Anticipation in Adults and Children with Developmental Dyslexia: Evidence of an Inefficient Mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taub, G.E.; Lazarus, P.J. The Effects of Training in Timing and Rhythm on Reading Achievement. Contemp. Issues Educ. Res. 2012, 5, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer, A.; Bonacina, S.; Lorusso, M.L.; Lanzi, P.L.; Antonietti, A. Rhythmic Reading Training (RRT): A Computer-Assisted Intervention Program for Dyslexia. In Pervasive Computing Paradigms for Mental Health; Serino, S., Matic, A., Giakoumis, D., Lopez, G., Cipresso, P., Eds.; Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 249–258. ISBN 978-3-319-32269-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bonacina, S.; Cancer, A.; Lanzi, P.L.; Lorusso, M.L.; Antonietti, A. Improving Reading Skills in Students with Dyslexia: The Efficacy of a Sublexical Training with Rhythmic Background. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cancer, A.; Stievano, G.; Pace, G.; Colombo, A.; Brembati, F.; Donini, R.; Antonietti, A. Remedial Interventions for Italian Children with Developmental Dyslexia: Comparing the Rhythmic Reading Training to the ‘Abilmente’ Approach. Psychol. Music. under revision.
- Cancer, A.; Bonacina, S.; Antonietti, A.; Salandi, A.; Molteni, M.; Lorusso, M.L. The Effectiveness of Interventions for Developmental Dyslexia: Rhythmic Reading Training Compared with Hemisphere-Specific Stimulation and Action Video Games. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer, A.; Stievano, G.; Pace, G.; Colombo, A.; Antonietti, A. Cognitive Processes Underlying Reading Improvement during a Rhythm-Based Intervention. A Small-Scale Investigation of Italian Children with Dyslexia. Children 2019, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cancer, A.; Sarti, D.; de Salvatore, M.; Granocchio, E.; Chieffo, D.P.R.; Antonietti, A. Dyslexia Telerehabilitation during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Results of a Rhythm-Based Intervention for Reading. Children 2021, 8, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A. Independent Effects of Bottom-up Temporal Expectancy and Top-down Spatial Attention. An Audiovisual Study Using Rhythmic Cueing. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2015, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doherty, J.R. Synergistic Effect of Combined Temporal and Spatial Expectations on Visual Attention. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 8259–8266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cestnick, L.; Coltheart, M. The Relationship between Language-Processing and Visual-Processing Deficits in Developmental Dyslexia. Cognition 1999, 71, 231–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facoetti, A.; Zorzi, M.; Cestnick, L.; Lorusso, M.L.; Molteni, M.; Paganoni, P.; Umiltà, C.; Mascetti, G.G. The Relationship between Visuo-Spatial Attention and Nonword Reading in Developmental Dyslexia. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 2006, 23, 841–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrick, L.E.; McNew, M.E.; Pruden, S.M.; Castellanos, I. Intersensory Redundancy Promotes Infant Detection of Prosody in Infant-Directed Speech. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2019, 183, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrick, L.E.; Lickliter, R. Intersensory Redundancy Guides Early Perceptual and Cognitive Development. In Advances in Child Development and Behavior; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; Volume 30, pp. 153–187. ISBN 978-0-12-009730-2. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. The ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders: Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Guidelines; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992; ISBN 978-92-4-154422-1. [Google Scholar]
- Weschler, D. Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-Fourth Edition (WISC-IV) Administration and Scoring Manual; Psychological Association: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- ISS Consensus Conference “Disturbi Specifici Dell’apprendimento”. Available online: https://www.aiditalia.org (accessed on 4 August 2021).
- Sartori, G.; Job, R. DDE-2: Batteria per la Valutazione della Dislessia e della Disortografia Evolutiva-2 [Assessment Battery for Developmental Reading and Spelling Disorders]; Giunti O.S.: Florence, Italy, 2007; ISBN 978-88-09-40301-7. [Google Scholar]
- Cornoldi, C.; Carretti, B. Prove MT-3 Clinica: La Valutazione delle Abilità di Lettura e Comprensione per la Scuola Primaria e Secondaria di I Grado; Giunti Edu: Florence, Italy, 2016; ISBN 978-88-09-84159-8. [Google Scholar]
- Zoccolotti, P.; de Luca, M.; Di Filippo, G.; Judica, A.; Spinelli, D. Prova di Lettura di Parole e Non Parole. [Word and Pseudo-Word Reading Test—WPRT]; IRCCS Fondazione Santa Lucia: Rome, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- De Luca, M.; Di Filippo, G.; Judica, A.; Spinelli, D.; Zoccolotti, P. Test di Denominazione Rapida e Ricerca Visiva di Colori, Figure e Numeri. [Rapid Naming Test and Visual Search of Colours, Figures, and Numbers]; IRCCS Fondazione Santa Lucia: Rome, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Marinelli, C.V.; Zoccolotti, P.; Romani, C. The Ability to Learn New Written Words Is Modulated by Language Orthographic Consistency. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkman, M.; Kirk, U.; Kemp, S. NEPSY-II; Pearson: London, UK, 2007; ISBN 978-0-15-823427-4. [Google Scholar]
- Stambak, M. Le Problème du Rythme Dans le Développement de l’enfant et Dans les Dyslexies d’évolution. Enfance 1951, 4, 480–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ireland, K.; Parker, A.; Foster, N.; Penhune, V. Rhythm and Melody Tasks for School-Aged Children with and without Musical Training: Age-Equivalent Scores and Reliability. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goswami, U.; Thomson, J.; Richardson, U.; Stainthorp, R.; Hughes, D.; Rosen, S.; Scott, S.K. Amplitude Envelope Onsets and Developmental Dyslexia: A New Hypothesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10911–10916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huss, M.; Verney, J.P.; Fosker, T.; Mead, N.; Goswami, U. Music, Rhythm, Rise Time Perception and Developmental Dyslexia: Perception of Musical Meter Predicts Reading and Phonology. Cortex 2011, 47, 674–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richardson, U.; Thomson, J.M.; Scott, S.K.; Goswami, U. Auditory Processing Skills and Phonological Representation in Dyslexic Children. Dyslexia 2004, 10, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasinski, A.C.; McAuley, J.D.; Snyder, J.S. How Modality Specific Is Processing of Auditory and Visual Rhythms?: Rhythm Processing. Psychophysiology 2016, 53, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facoetti, A.; Trussardi, A.N.; Ruffino, M.; Lorusso, M.L.; Cattaneo, C.; Galli, R.; Molteni, M.; Zorzi, M. Multisensory Spatial Attention Deficits Are Predictive of Phonological Decoding Skills in Developmental Dyslexia. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2010, 22, 1011–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, N.; Foxe, J.J.; Molholm, S. Impairments of Multisensory Integration and Cross-Sensory Learning as Pathways to Dyslexia. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 47, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, Z.; Rüsseler, J.; Gerth, I.; Münte, T.F. Audiovisual Speech Integration in the Superior Temporal Region Is Dysfunctional in Dyslexia. Neuroscience 2017, 356, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, S.; Gori, S.; Ruffino, M.; Viola, S.; Molteni, M.; Facoetti, A. Action Video Games Make Dyslexic Children Read Better. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franceschini, S.; Bertoni, S.; Ronconi, L.; Molteni, M.; Gori, S.; Facoetti, A. “Shall We Play a Game?”: Improving Reading through Action Video Games in Developmental Dyslexia. Curr. Dev. Disord. Rep. 2015, 2, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franceschini, S.; Trevisan, P.; Ronconi, L.; Bertoni, S.; Colmar, S.; Double, K.; Facoetti, A.; Gori, S. Action Video Games Improve Reading Abilities and Visual-to-Auditory Attentional Shifting in English-Speaking Children with Dyslexia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Visual Cue | Rhythm | No Intervention | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 10.7 (1.71) | 10.6 (1.41) | 11.0 (1.89) |
| Sex 1 | |||
| Male | 12 (57.1) | 12 (57.1) | 8 (50.0) |
| Female | 9 (42.9) | 9 (42.9) | 8 (50.0) |
| Total IQ 2 | 104 (13.3) | 104 (10.3) | 101 (10.4) |
| Pre-test reading | |||
| Speed (z-scores) | −1.81 (0.71) | −1.73 (0.69) | −1.66 (0.57) |
| Accuracy (z-scores) | −2.62 (2.17) | −2.11 (1.49) | −3.25 (2.72) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cancer, A.; De Salvatore, M.; Granocchio, E.; Andreoli, L.; Antonietti, A.; Sarti, D. The Role of Auditory and Visual Components in Reading Training: No Additional Effect of Synchronized Visual Cue in a Rhythm-Based Intervention for Dyslexia. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12073360
Cancer A, De Salvatore M, Granocchio E, Andreoli L, Antonietti A, Sarti D. The Role of Auditory and Visual Components in Reading Training: No Additional Effect of Synchronized Visual Cue in a Rhythm-Based Intervention for Dyslexia. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(7):3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12073360
Chicago/Turabian StyleCancer, Alice, Marinella De Salvatore, Elisa Granocchio, Luca Andreoli, Alessandro Antonietti, and Daniela Sarti. 2022. "The Role of Auditory and Visual Components in Reading Training: No Additional Effect of Synchronized Visual Cue in a Rhythm-Based Intervention for Dyslexia" Applied Sciences 12, no. 7: 3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12073360
APA StyleCancer, A., De Salvatore, M., Granocchio, E., Andreoli, L., Antonietti, A., & Sarti, D. (2022). The Role of Auditory and Visual Components in Reading Training: No Additional Effect of Synchronized Visual Cue in a Rhythm-Based Intervention for Dyslexia. Applied Sciences, 12(7), 3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12073360








