Statistical Analysis on Random Matrices of Echo State Network in PEMFC System’s Lifetime Prediction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
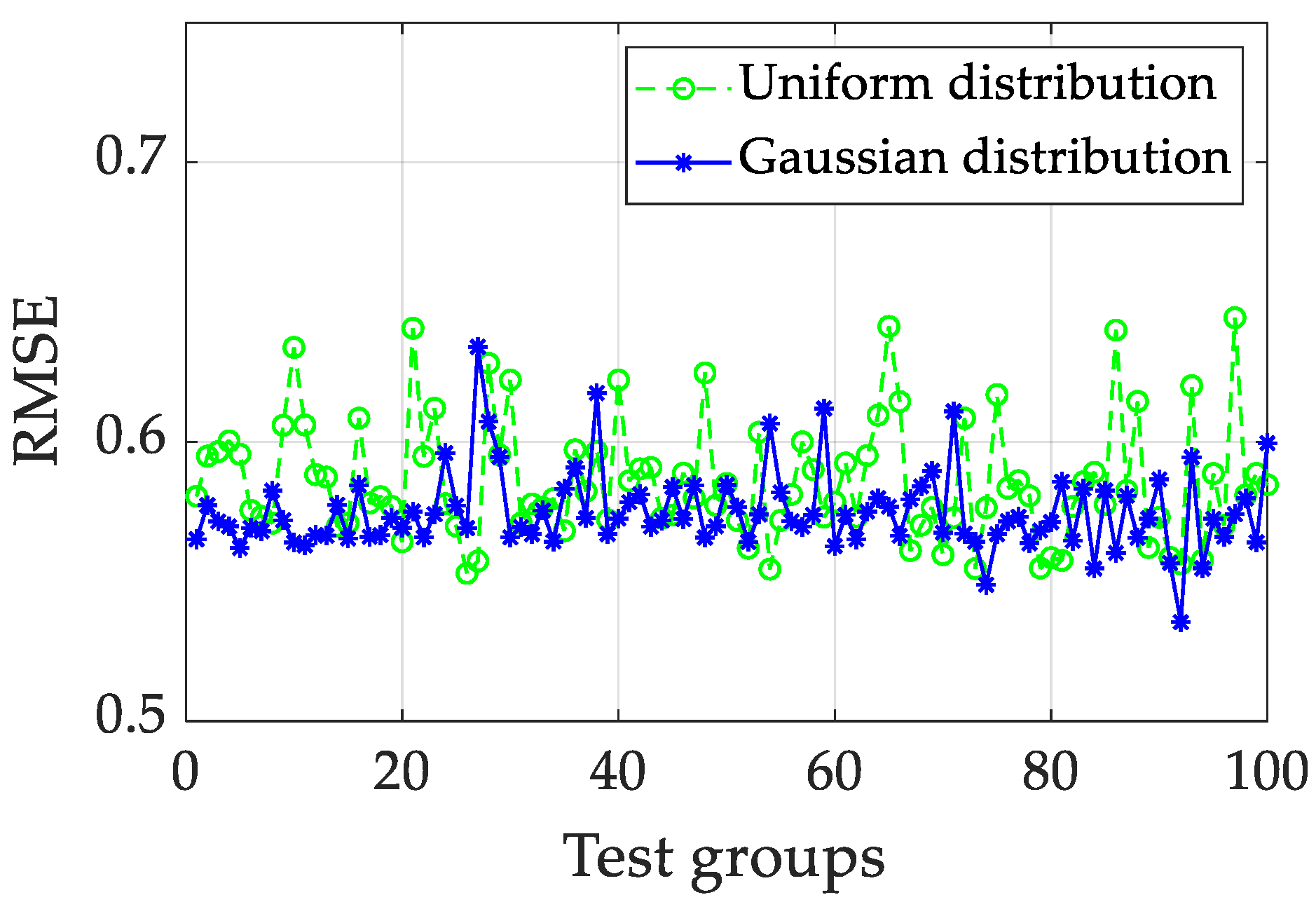
- The effects of two distribution shapes (uniform and Gaussian distribution) of Win and W on the prediction accuracy are explored;
- The metaheuristic technique of particle swarm optimization (PSO) is utilized to optimize the hyperparameters of the leaking rate, spectral radius, and regularization coefficient;
- The uncertainty of the ensemble ESN caused by the random matrices is statistically analyzed under three different operating conditions.
2. Mathematical Backgrounds
2.1. Echo State Network
2.2. Particle Swarm Optimization
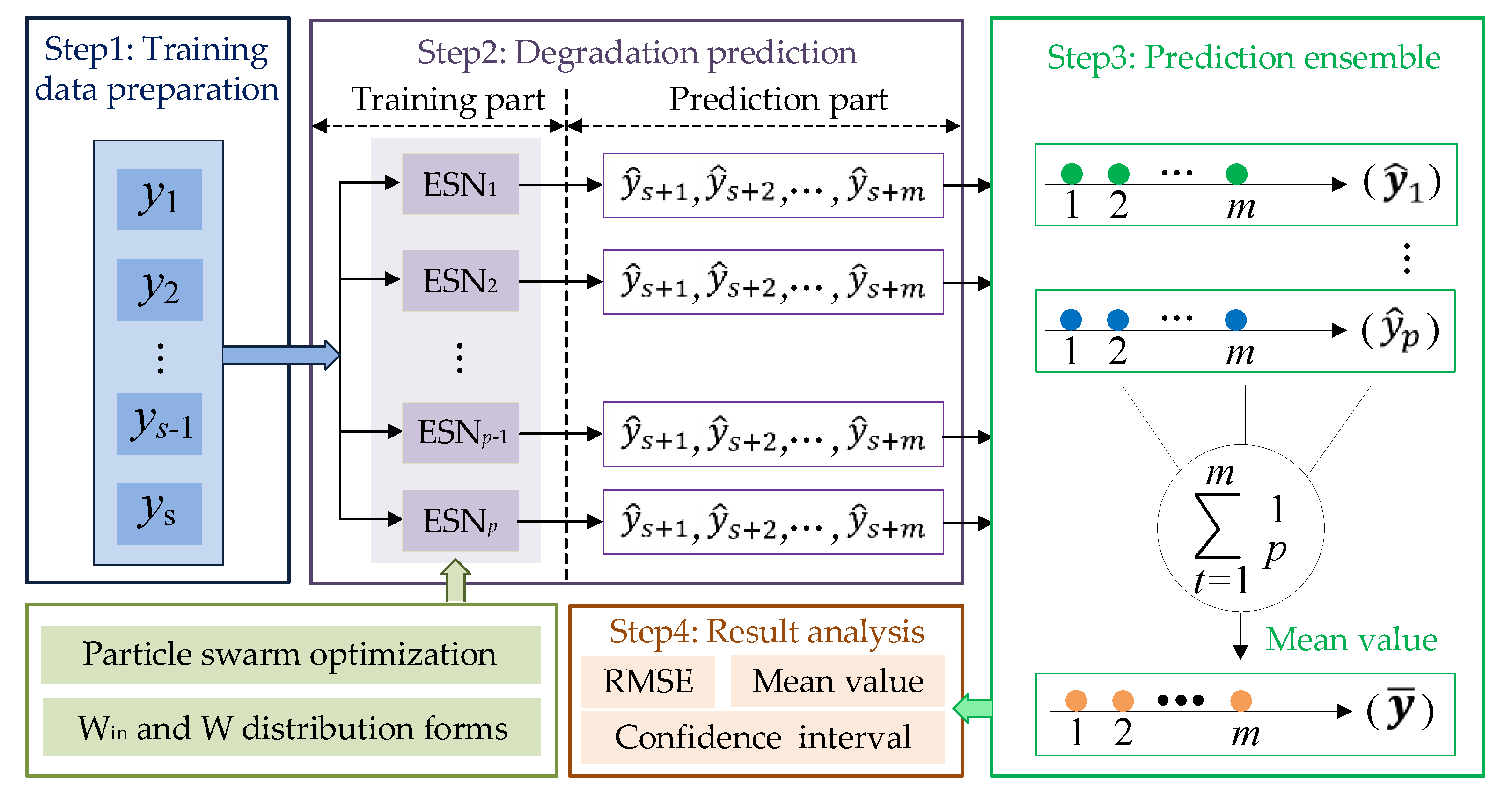
2.3. Implementation of Ensemble ESN
3. Experimental Results
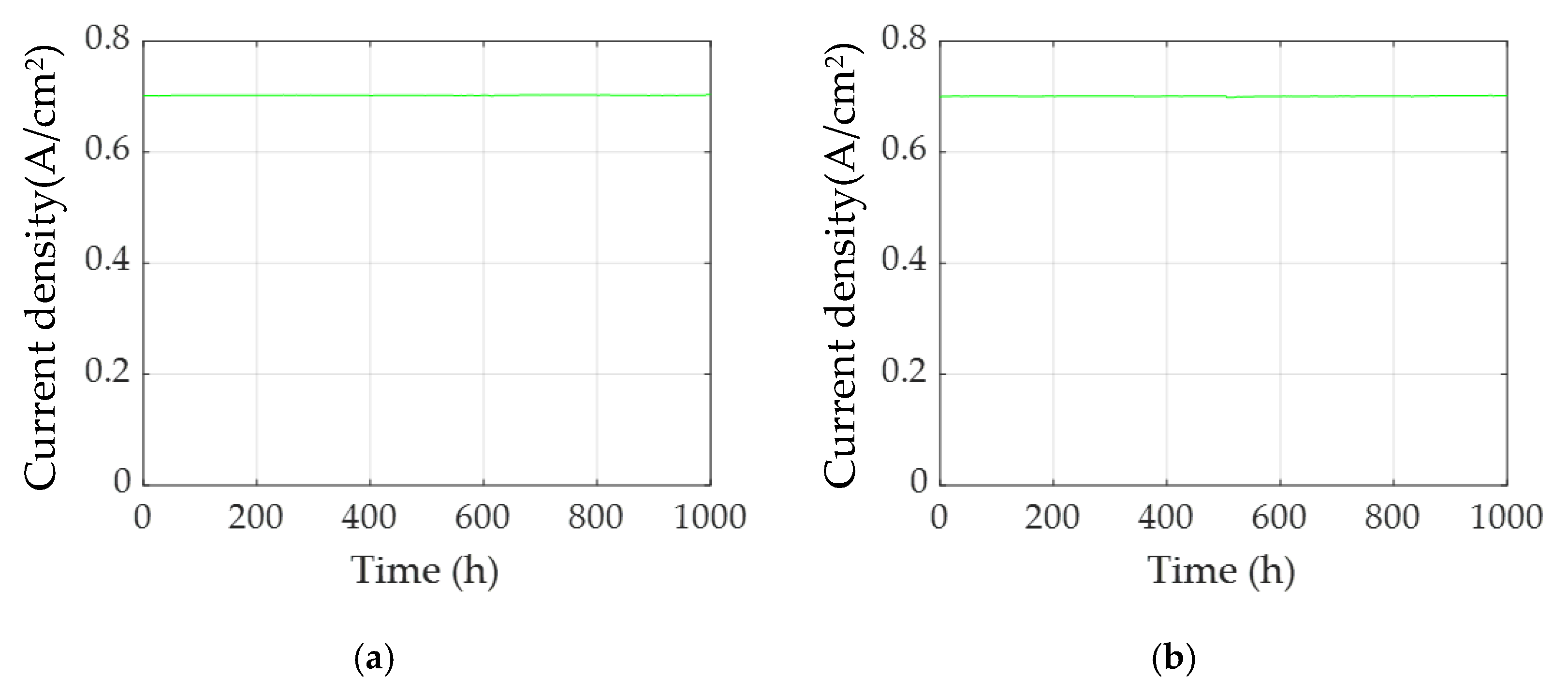
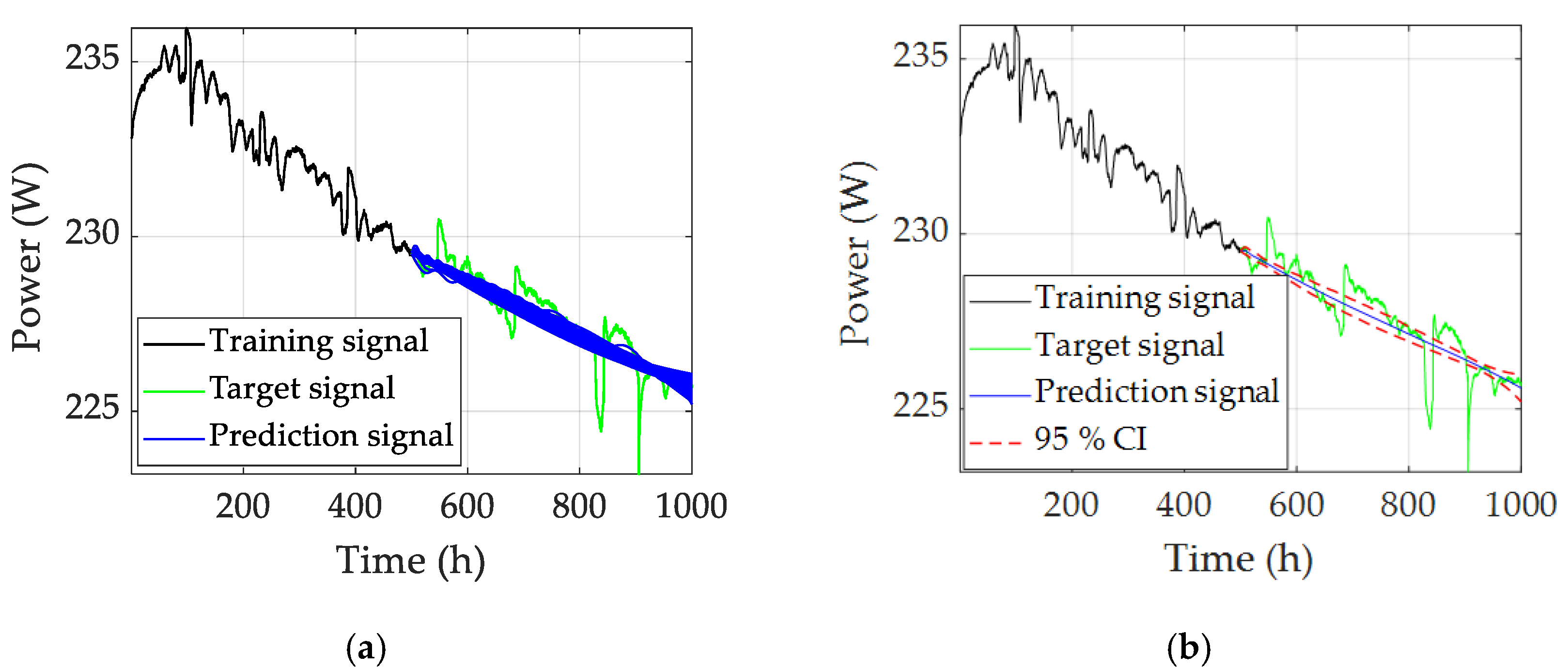
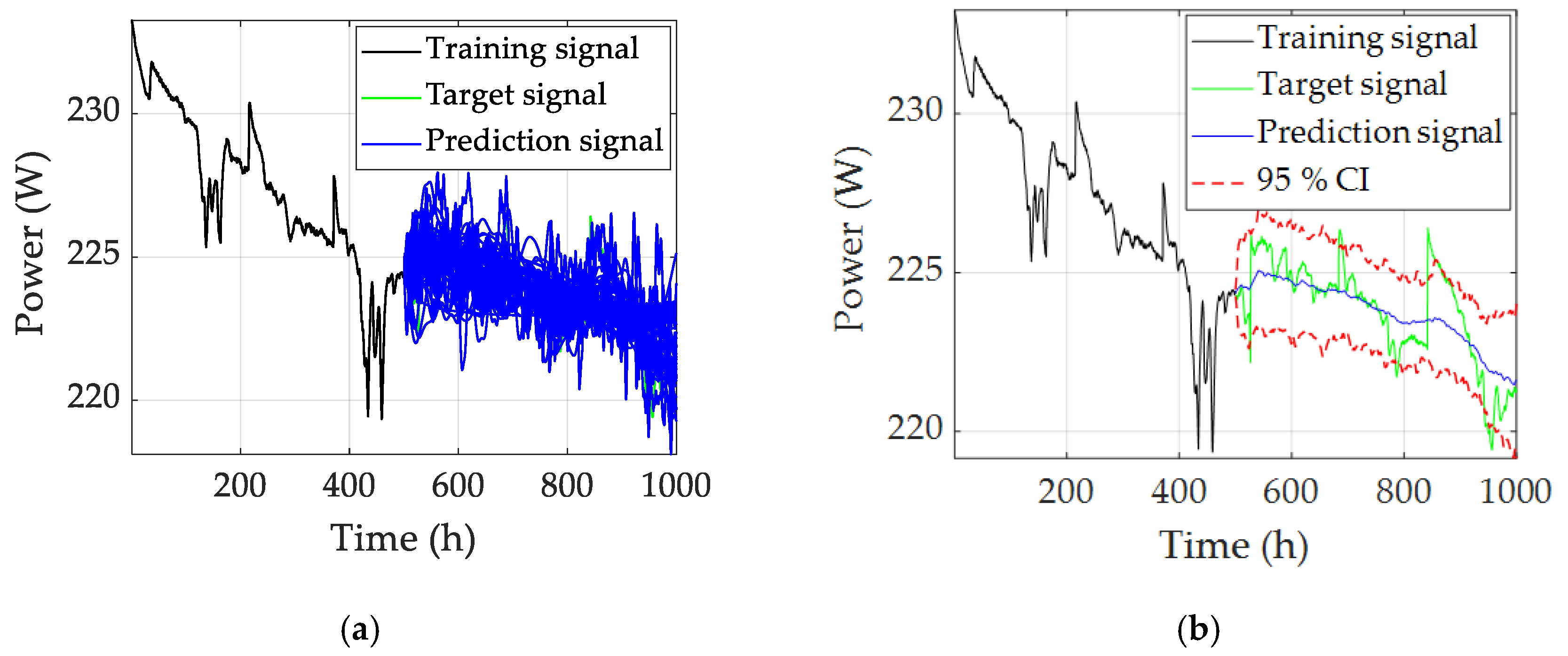
3.1. Steady-State Operating Condition
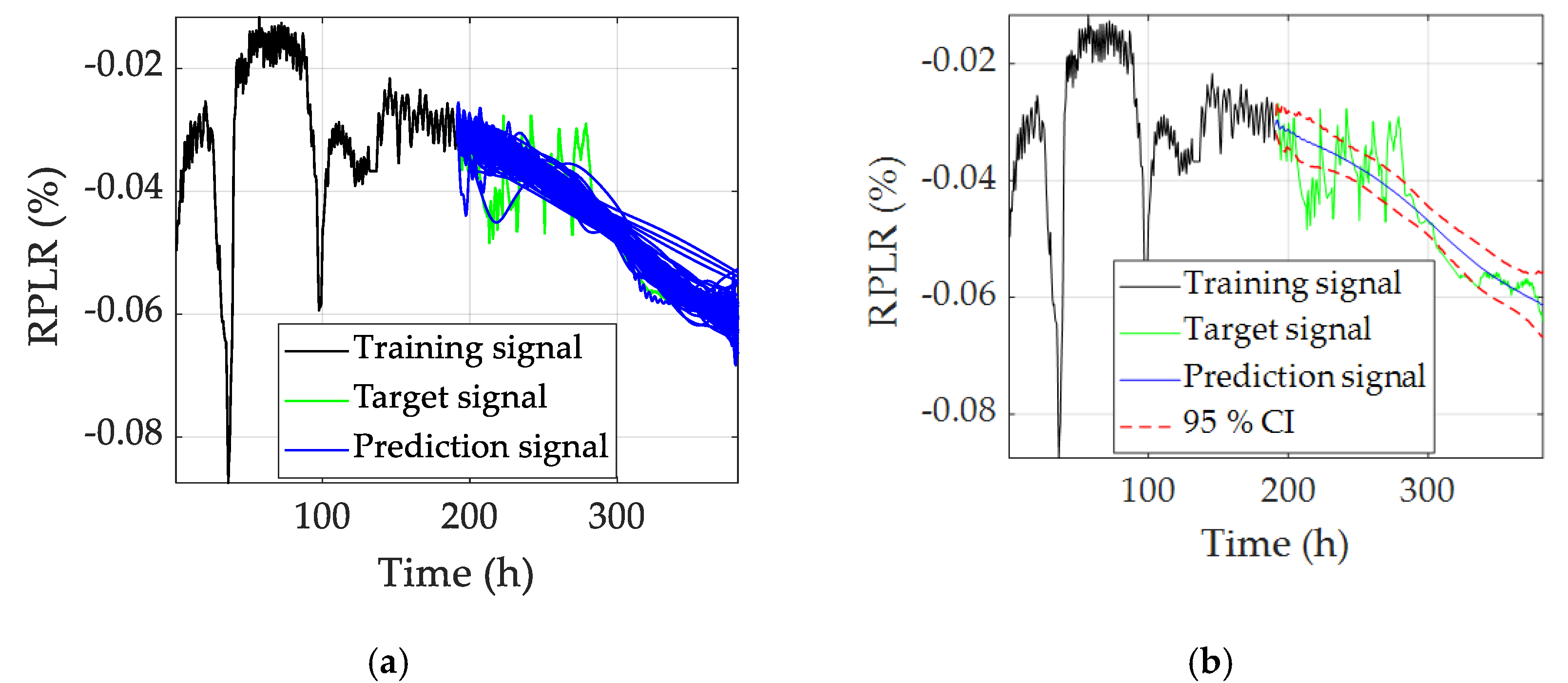
3.2. Quasi-Dynamic Operating Condition
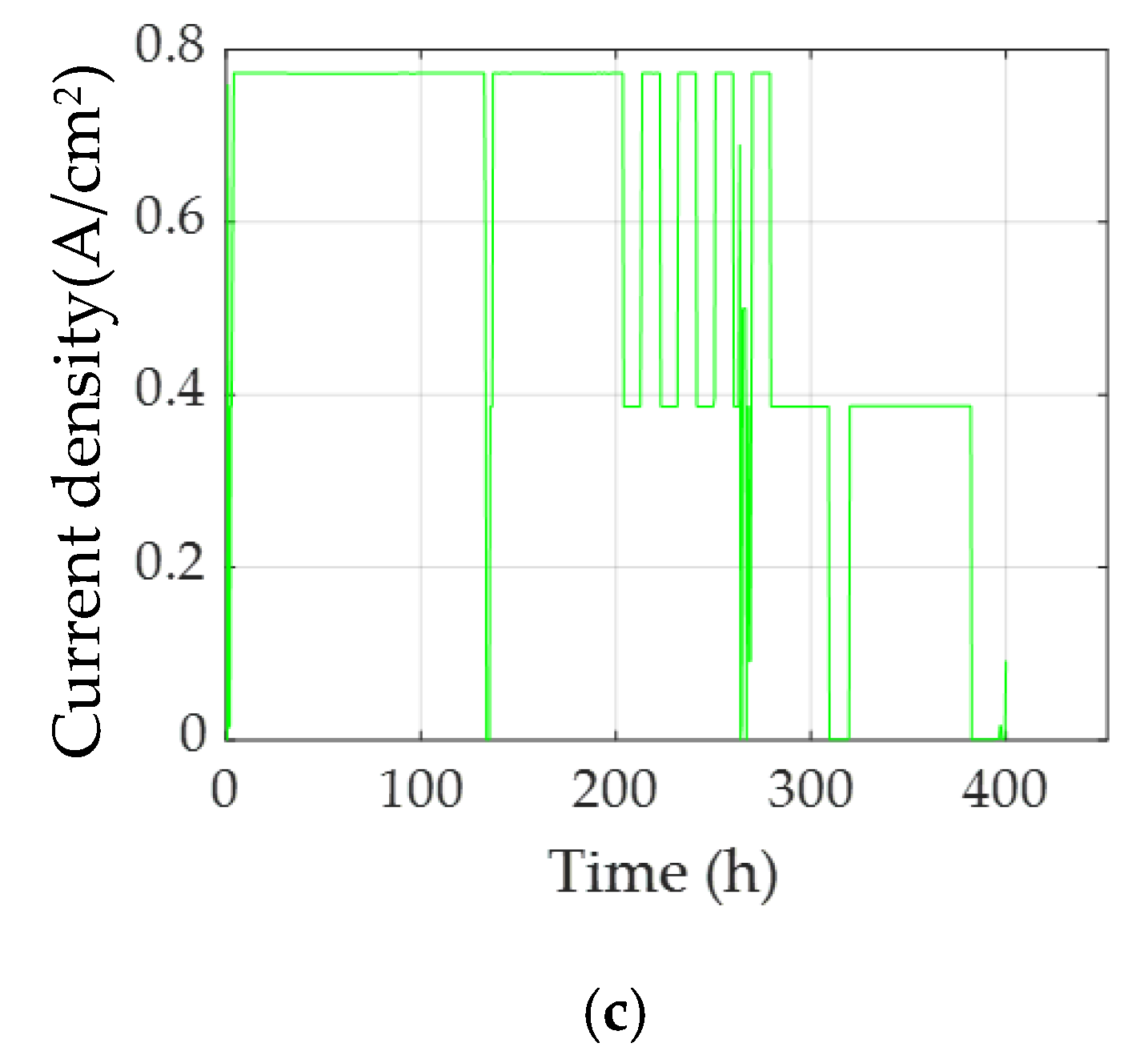
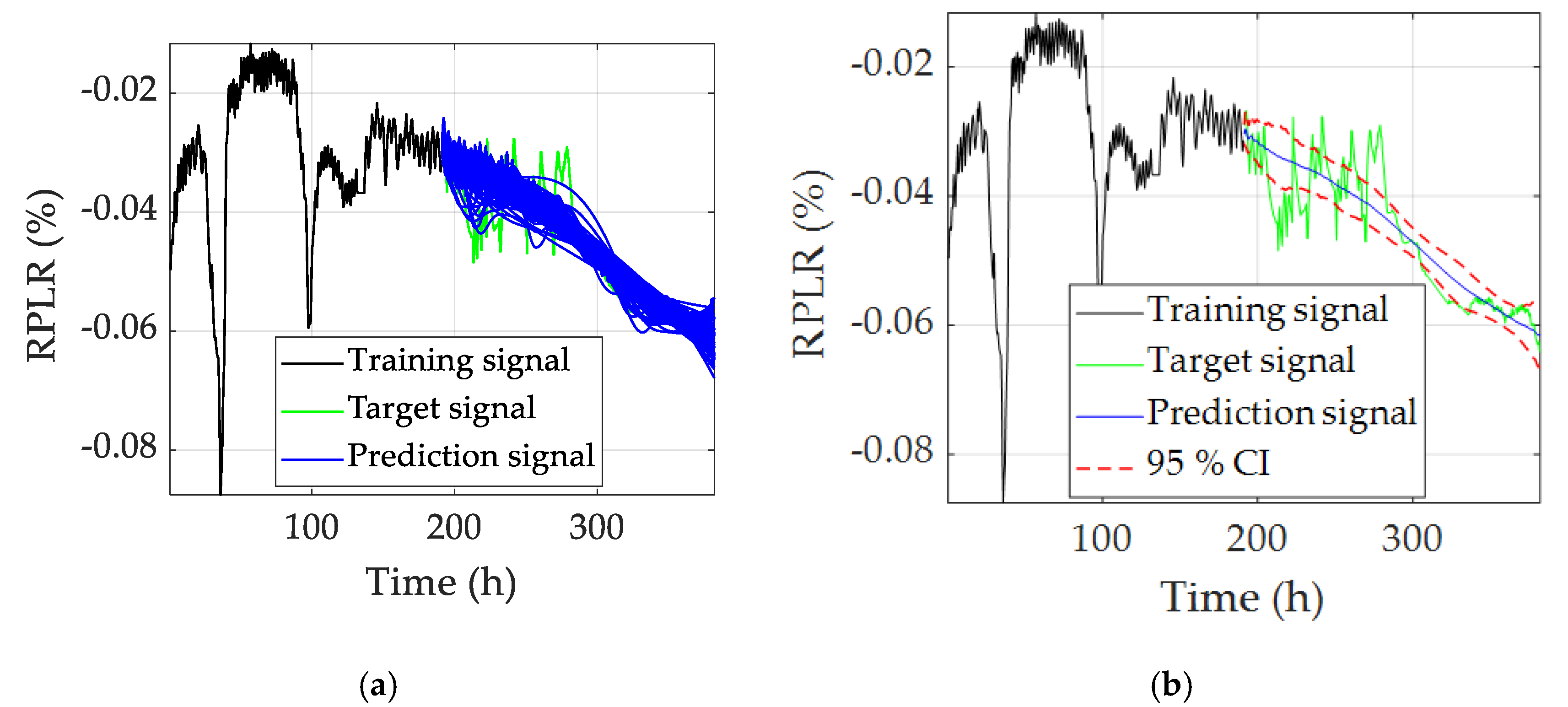
3.3. Dynamic Operating Condition
4. Conclusions
- 1.
- The random characteristics of Win and W affect the lifetime prediction results. The prediction results are presented in the statistical form by the ensemble computing technique, and this helps the user to analyze the uncertainties of the randomness. After the data analysis, a 95% confidence interval (CI) is given, which better qualifies the reliability of the result.
- 2.
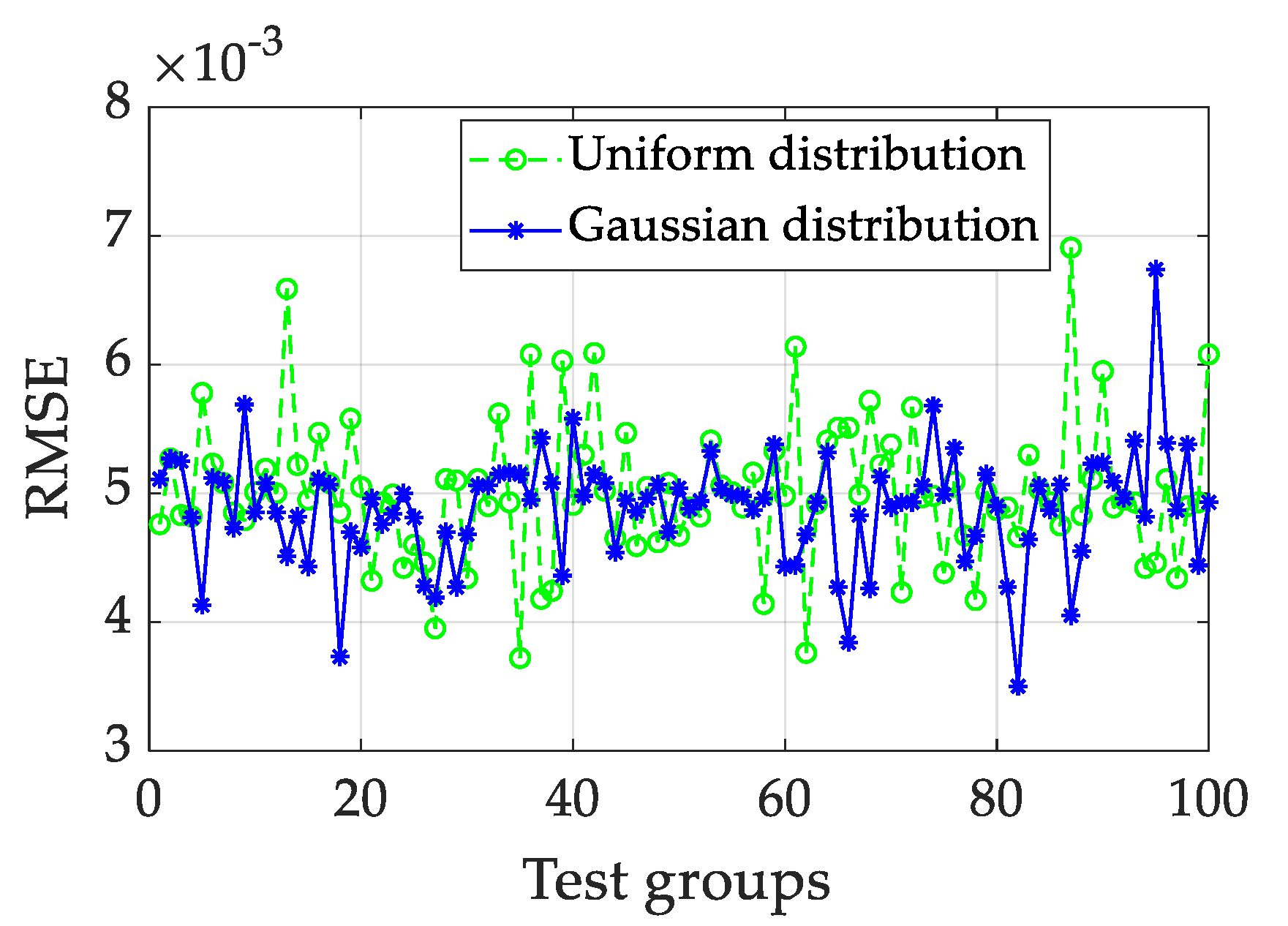
- Based on the uniform and Gaussian distribution shapes of Win and W, the prediction performances are fully compared. To analyze the effects of random matrices, the PSO method is used to optimize the hyperparameters of the ESN. Based on the comparison results, the Gaussian distribution of Win and W can decrease the prediction error slightly when compared to the uniform distribution. However, the effects of two different distribution shapes on the prediction results are rather insignificant.
- 3.
- Combining the ESN with other methods to improve the prediction accuracy and exploring the prognostic methods to realize the online lifetime prediction will be the focuses of our future work.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, Y.; Li, Q.; Huang, L.; Sun, C.; Wang, T.; Chen, W. Adaptive uncertainty sets-based two-stage robust optimization for economic dispatch of microgrid with demand response. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2020, 14, 3608–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zou, X.; Li, R.; Li, L.; Chen, W.; Liu, H. Optimal sizing for an integrated energy system considering degradation and seasonal hydrogen storage. Appl. Energy 2021, 302, 117542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, T.; Li, S.; Chen, W.; Liu, H.; Breaz, E.; Gao, F. Online extremum seeking-based optimized energy management strategy for hybrid electric tram considering fuel cell degradation. Appl. Energy 2021, 285, 116505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yin, L.; Yang, H.; Wang, T.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, W. Multiobjective optimization and data-driven constraint adaptive predictive control for efficient and stable operation of PEMFC system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 12418–12429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Outbib, R.; Dou, M.; Zhao, D. A novel long short-term memory networks-based data-driven prognostic strategy for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 10395–10408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Pahon, E.; Péra, M.C.; Gao, F. A review on lifetime prediction of proton exchange membrane fuel cells system. J. Power Sources 2022, 529, 231256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Lv, H.; Zhou, D.; Xue, Q.; Jin, L.; Zhou, W.; Yang, D.; Zhang, C. Deep learning based prognostic framework towards proton exchange membrane fuel cell for automotive application. Appl. Energy 2021, 281, 115937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.; Li, Z.; Roche, R.; Jemei, S.; Zerhouni, N. Degradation identification and prognostics of proton exchange membrane fuel cell under dynamic load. Control Eng. Pract. 2022, 118, 104959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadaeghi, F.; Jaeger, H. Computing optimal discrete readout weights in reservoir computing is NP-hard. Neurocomputing 2019, 338, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thiede, L.A.; Parlitz, U. Gradient based hyperparameter optimization in echo state networks. Neural Netw. 2019, 115, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morando, S.; Jemei, S.; Gouriveau, R.; Zerhouni, N.; Hissel, D. Fuel cells prognostics using echo state network. In Proceedings of the 39th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON), Vienna, Austria, 10–13 November 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morando, S.; Jemei, S.; Hissel, D.; Gouriveau, R.; Zerhouni, N. Predicting the remaining useful lifetime of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell using an echo state network. In Proceedings of the International Discussion on Hydrogen Energy and Applications (IDHEA), Nantes, France, 12–14 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Chen, Y.; Wenchao, Z.; Xie, C.; Wu, F. Remaining useful life prediction of PEMFC based on cycle reservoir with jump model. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 40001–40013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morando, S.; Jemei, S.; Hissel, D.; Gouriveau, R.; Zerhouni, N. Proton exchange membrane fuel cell ageing forecasting algorithm based on echo state network. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 1472–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Pahon, E.; Péra, M.C.; Gao, F. Multi-timescale lifespan prediction for PEMFC systems under dynamic operating conditions. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 8, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Pahon, E.; Péra, M.C.; Gao, F. Lifespan prediction for proton exchange membrane fuel cells based on wavelet transform and echo state network. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 8, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morando, S.; Jemei, S.; Hissel, D.; Gouriveau, R.; Zerhouni, N. ANOVA method applied to proton exchange membrane fuel cell ageing forecasting using an echo state network. Math. Comput. Simul. 2017, 131, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Pahon, E.; Péra, M.-C.; Gao, F. Remaining useful life prediction of PEMFC systems under dynamic operating conditions. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 231, 113825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzi, R.; Morando, S.; Steiner, N.Y.; Péra, M.C.; Hissel, D.; Larger, L. Multi-reservoir echo state network for proton exchange membrane fuel cell remaining useful life prediction. In Proceedings of the 44th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON), Washington, DC, USA, 21–23 October 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzi, R.; Yousfi-Steiner, N.; Péra, M.C.; Hissel, D.; Larger, L. An echo state network for fuel cell lifetime prediction under a dynamic micro-cogeneration load profile. Appl. Energy 2021, 283, 116297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Outbib, R. Adaptive prognostic of fuel cells by implementing ensemble echo state networks in time varying model space. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hua, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Péra, M.-C.; Gao, F. Remaining useful life prediction of PEMFC systems based on the multi-input echo state network. Appl. Energy 2020, 265, 114791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichard, L.; Harel, F.; Ravey, A.; Venet, P.; Hissel, D. Degradation prediction of PEM fuel cell based on artificial intelligence. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 14953–14963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Mao, L.; Yu, J.; Huang, W.; He, Q.; Jackson, L. Long-term performance prediction of PEMFC based on LASSO-ESN. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoli, G.; Ferraro, M.; Sergi, F.; Brunaccini, G.; Antonucci, V. Data driven models for a PEM fuel cell stack performance prediction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 11628–11638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Baraldi, P.; Cadet, C.; Yousfi-Steiner, N.; Bérenguer, C.; Zio, E. An ensemble of models for integrating dependent sources of information for the prognosis of the remaining useful life of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 124, 479–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Javed, K.; Gouriveau, R.; Zerhouni, N.; Hissel, D. Prognostics of proton exchange membrane fuel cells stack using an ensemble of constraints based connectionist networks. J. Power Sources 2016, 324, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukoševičius, M. A practical guide to applying echo state networks. In Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 659–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Kudithipudi, D. An ensemble learning approach to the predictive stability of echo state networks. J. Inform. Math. Sci. 2018, 10, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouikhi, N.; Fdhila, R.; Ammar, B.; Rokbani, N.; Alimi, A.M. Single- and multi-objective particle swarm optimization of reservoir structure in echo state network. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Xie, X.; Lin, L.; Wang, F. Genetic algorithm optimized double-reservoir echo state network for multi-regime time series prediction. Neurocomputing 2017, 238, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yan, X. Optimizing the echo state network with a binary particle swarm optimization algorithm. Knowl. Based Syst. 2015, 86, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Test Group | ESN1 | ESN2 | ESN3 | ESN4 | ESN5 | ESN6 | ESN7 | ESN8 | ESN9 | ESN10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hyper-para. | α | 0.80000 | 0.24477 | 0.80000 | 0.80000 | 0.10000 | 0.61598 | 0.55070 | 0.28000 | 0.10000 | 0.10000 |
| 0.38125 | 0.69227 | 0.79748 | 0.93218 | 0.20756 | 0.57188 | 0.56348 | 0.72581 | 0.18374 | 0.17359 | ||
| 0.00100 | 0.00900 | 0.00900 | 0.00900 | 0.00164 | 0.00363 | 0.00100 | 0.00900 | 0.00136 | 0.00340 | ||
| RMSE | 0.58050 | 0.59487 | 0.59647 | 0.60032 | 0.59554 | 0.57550 | 0.57331 | 0.57092 | 0.60588 | 0.63377 | |
| Test Group | ESN1 | ESN2 | ESN3 | ESN4 | ESN5 | ESN6 | ESN7 | ESN8 | ESN9 | ESN10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hyper-para. | α | 0.90000 | 0.90000 | 0.90000 | 0.85000 | 0.39040 | 0.90000 | 0.90000 | 0.71572 | 0.90000 | 0.90000 |
| 0.19560 | 0.33440 | 0.44590 | 0.10000 | 0.86250 | 0.10000 | 0.31760 | 0.10000 | 1.41060 | 0.10000 | ||
| 0.00100 | 0.00320 | 0.00650 | 0.00660 | 0.00350 | 0.00110 | 0.00100 | 0.00100 | 0.00100 | 0.00120 | ||
| RMSE | 0.56508 | 0.57730 | 0.57151 | 0.56970 | 0.56199 | 0.56915 | 0.56801 | 0.58255 | 0.57192 | 0.56398 | |
| Test Group | ESN1 | ESN2 | ESN3 | ESN4 | ESN5 | ESN6 | ESN7 | ESN8 | ESN9 | ESN10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hyper-para. | α | 0.29901 | 0.10970 | 0.10820 | 0.13740 | 0.10000 | 0.34770 | 0.10000 | 0.41590 | 0.10800 | 0.12280 |
| 1.90000 | 1.80230 | 1.74110 | 1.90000 | 1.62237 | 1.55670 | 1.90000 | 1.42740 | 1.42460 | 1.61780 | ||
| 0.00299 | 0.00710 | 0.00860 | 0.00150 | 0.00900 | 0.00110 | 0.00900 | 0.00890 | 0.00900 | 0.00100 | ||
| RMSE | 1.07394 | 1.01290 | 1.02710 | 1.10380 | 1.41801 | 1.03080 | 1.88830 | 1.28040 | 1.09540 | 1.49140 | |
| Test Group | ESN1 | ESN2 | ESN3 | ESN4 | ESN5 | ESN6 | ESN7 | ESN8 | ESN9 | ESN10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hyper-para. | α | 0.87000 | 0.35830 | 0.38420 | 0.10110 | 0.87420 | 0.54400 | 0.84620 | 0.82820 | 0.10000 | 0.10900 |
| 1.36500 | 1.80570 | 1.58110 | 1.51860 | 1.47940 | 1.90000 | 1.83080 | 1.43060 | 1.76060 | 1.86000 | ||
| 0.00790 | 0.00830 | 0.00900 | 0.00900 | 0.00330 | 0.00900 | 0.00880 | 0.00100 | 0.00100 | 0.00580 | ||
| RMSE | 1.03890 | 0.93920 | 1.28170 | 0.89560 | 0.96380 | 1.37308 | 1.05020 | 0.97690 | 1.13970 | 0.90080 | |
| Test Group | ESN1 | ESN2 | ESN3 | ESN4 | ESN5 | ESN6 | ESN7 | ESN8 | ESN9 | ESN10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hyper-para. | α | 0.12483 | 0.25671 | 0.15844 | 0.11213 | 0.34245 | 0.23291 | 0.23923 | 0.14834 | 0.26963 | 0.36064 |
| 1.43205 | 1.74959 | 1.35257 | 1.53465 | 1.18192 | 1.33707 | 1.90000 | 1.23153 | 1.37328 | 1.25512 | ||
| 0.00218 | 0.00524 | 0.00900 | 0.00900 | 0.00129 | 0.00405 | 0.00100 | 0.00900 | 0.00165 | 0.00253 | ||
| RMSE | 0.00476 | 0.00527 | 0.00483 | 0.00482 | 0.00578 | 0.00523 | 0.00508 | 0.00485 | 0.00479 | 0.00501 | |
| Test Group | ESN1 | ESN2 | ESN3 | ESN4 | ESN5 | ESN6 | ESN7 | ESN8 | ESN9 | ESN10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hyper-para. | α | 0.30376 | 0.47659 | 0.54372 | 0.50078 | 0.13709 | 0.57584 | 0.32100 | 0.28035 | 0.11564 | 0.39271 |
| 1.64620 | 1.29902 | 1.55139 | 1.71862 | 1.38232 | 1.44123 | 1.43160 | 1.59497 | 1.50729 | 1.90000 | ||
| 0.00634 | 0.00900 | 0.00586 | 0.00900 | 0.00900 | 0.00638 | 0.00157 | 0.00625 | 0.00900 | 0.00900 | ||
| RMSE | 0.00511 | 0.00527 | 0.00525 | 0.00481 | 0.00413 | 0.00512 | 0.00509 | 0.00473 | 0.00569 | 0.00485 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Péra, M.-C.; Gao, F. Statistical Analysis on Random Matrices of Echo State Network in PEMFC System’s Lifetime Prediction. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3421. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12073421
Hua Z, Zheng Z, Péra M-C, Gao F. Statistical Analysis on Random Matrices of Echo State Network in PEMFC System’s Lifetime Prediction. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(7):3421. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12073421
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Zhiguang, Zhixue Zheng, Marie-Cécile Péra, and Fei Gao. 2022. "Statistical Analysis on Random Matrices of Echo State Network in PEMFC System’s Lifetime Prediction" Applied Sciences 12, no. 7: 3421. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12073421
APA StyleHua, Z., Zheng, Z., Péra, M.-C., & Gao, F. (2022). Statistical Analysis on Random Matrices of Echo State Network in PEMFC System’s Lifetime Prediction. Applied Sciences, 12(7), 3421. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12073421







