Featured Application
This work aims to further decrease the environmental footprint of alkali-activated materials by using an industrial wastewater to partially replace a commercial activator.
Abstract
Alkali-activated materials are generally considered a more sustainable alternative to Portland cement binders. This derives not only from the use of solid wastes as precursors, but also from the low temperatures required for their synthesis. However, to increase the environmental advantages of these materials, alternative activators should be explored, as the common route involves the use of commercial activators such as sodium silicate or sodium hydroxide solutions. In this work, the possibility of using an alkaline industrial wastewater, coming from a Portuguese paper and pulp industry, as a partial replacement of the commercial sodium hydroxide solution was studied. The results show that the use of the industrial wastewater decreased the workability of the pastes and their setting times, higher incorporations inducing a stronger reduction. Despite this, the results demonstrate the feasibility of replacing up to 25 vol.% of the sodium hydroxide solution with the industrial wastewater without compromising the mechanical performance of the binder. The compressive strength of this composition reached 22.7 MPa, this being slightly higher than the value seen in the reference (20.0 MPa). The use of a waste-containing activator, as reported here, might be a key driver to foster the wider use of this technology.
1. Introduction
Alkali-activated materials are alternative binders to the use of Portland cement in the construction sector [1,2,3] due to performance and environmental advantages. Performance advantages include faster strength gain, higher ultimate strength [4], and greater chemical resistance [5]. The environmental footprint of these materials can be much lower than that associated with Portland cement, provided that a suitable mixture composition is employed. A reduction of up to 80% in the CO2 emission when compared with clinker production has been reported [6], and in addition these eco-friendly binders can be produced using various industrial waste streams as solid precursors. This not only avoids the extraction and use of virgin raw materials, but also decreases their production costs and contributes to the circular economy, in line with the Waste Framework Directive [7]. Nevertheless, the industrial deployment of this technology is limited by several factors, including the use of expensive chemicals as activators, and the need to adjust the mixture composition according to the chemistry and mineralogy of the precursors (e.g., slags, fly ash, and metakaolin) [6,8]. Another challenging aspect of these binders lies in the control of the fresh-state properties. The workability of the mixtures is a key parameter during their synthesis; low workability can hinder the compaction of the slurries and lead to poor mechanical performance [9,10].
Alkali-activated materials are obtained by the alkali activation of alumina- and silica-containing precursors [11]. The use of waste-based solid precursors is a common approach. However, this is not the case for the activators, as most of the studies to date use commercial alkaline reagents, such as alkali hydroxides and/or alkali silicates where the alkali cation is usually potassium or sodium [1,12,13]. The use of commercial alkaline activators in the mixtures raises environmental and economic concerns [14,15]. For example, it has been reported that the production of 1 kg of sodium hydroxide generates between 0.3 [16] and 1.1 kg of CO2 [1]. In addition, the use of highly alkaline solutions also raises concerns regarding the safety of the operators during in situ applications, but this issue is less relevant in precasting [8].
Considering that the alkaline activators are the main contributors to the environmental footprint and cost of these materials, alternative activators must be explored as this would contribute to the large-scale adoption of this emergent technology. A promising strategy could be the use of alkaline industrial effluents, but this route has barely been considered [17] and this is demonstrated in recent reviews on the topic [1,16,18]. Most studies to date evaluated the use of silica-rich wastes as activators such as bottom ash, rice husk ash, and waste glass [18]. For example, rice husk ash, ground granulated blast furnace, and palm oil fuel ash have been studied [19]. The extraction of the reactive silica is performed by using fusion [20], hydrothermal, or thermochemical routes [21]. Despite being an interesting approach, these processes typically require high thermal treatments (e.g., 550 °C [20]; 150–330 °C [21]) and have associated costs. An alternative could be the use of industrial alkaline effluents that can be directly employed as activators, as proposed here, but this strategy is uncommon. One of the few exceptions is the use of a waste aluminium anodising etching solution in [22] and the use of an alkaline solution generated during the mould washing step in the aluminium casting industry [23]. Another rare example is the use of Bayer process liquor as a source of Na2O and Al2O3 in the synthesis of alkali-activated fly ash [24].
In the present work, and for the first time, the possibility of using an alkaline effluent generated by the pulp and paper industry is studied. It is used as a partial replacement of sodium hydroxide in the synthesis of alkali-activated materials derived from biomass fly ash. The industrial effluent contains a significant amount of sodium in its composition and a favourable pH endowing its use as activator. In fact, a recent study showed that this effluent can partially replace sodium hydroxide in the synthesis of activated carbons [25]. Another study showed that the effluent can replace the water used to prepare a sodium hydroxide solution, which was then used to produce alkali-activated materials [17]. Nevertheless, its use as an activator, rather than a simple water source, in the production of alkali-activated materials has never been evaluated to the best of our knowledge and will be investigated in the present study. Herein, the impact of the alkaline wastewater content in the fresh (workability, setting time) and hardened-state (compressive strength) properties of biomass fly-ash-derived alkali-activated materials was evaluated. In addition, dissolution tests were also performed to provide additional insights on the impact of the alkaline wastewater in the dissolution of silica, aluminium, and calcium from the solid precursors.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Biomass fly ash (FA) from a Portuguese pulp and paper factory (kraft process) and metakaolin (MK) from Univar, ArgicalTM M1200S, were used as precursors. FA has a much coarser particle-size distribution compared with the commercial precursor (MK), the mean particle size being 59 µm for FA and 5 µm for MK (see details in [26]). As commercial activators, sodium silicate D40 from Quimiamel (SiO2/Na2O = 3.1, H2O = 62.1 wt.%) and a solution of 10 M NaOH made from ERCROS reagent (99%) were used. An alkaline effluent (pH~11) from the same pulp and paper plant collected at the bleaching stage was used to partially replace the NaOH in the activator solution.
The biomass fly ash and the metakaolin were characterised by X-ray fluorescence (XRF) with a Philips X’Pert PRO MPD spectrometer. The effluent Na content was obtained by atomic emission (GBC 904 AA with pc control, GBC Avanta AAS Version 2.0). The chemical composition of the industrial wastewater was evaluated by inductively coupled plasma (ICP, Thermo Scientific iCAP 7000 Series, from Horiba Jobin Yvon, model Activa M from Longjumeau, France).
2.2. Alkali-Activated Material Preparation
Fly ash and metakaolin were mixed and homogenised in a bag in the 70/30 mass proportion. The activator was prepared by mixing sodium silicate and NaOH (75/25 mass proportion). The reference composition was selected following previous investigations by the authors [27,28]. Then, five additional formulations were prepared in which the NaOH solution was partially replaced by 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, or 25% (volume) of the alkaline wastewater. The highest amount of effluent (25 vol.%) was selected considering preliminary tests that showed a reduction in the paste’s workability as the amount of effluent increased (see discussion in Section 3.2). The NaOH or the NaOH/effluent solution was added to the sodium silicate and mixed for 10 min. Then, precursors and the activator were mixed during 5 min. Afterwards, the paste was transferred to metallic moulds of 2 cm × 2 cm × 4 cm, sealed with a plastic film and cured for 24 h at room temperature (23 ± 2 °C). Then, the specimens were demoulded and cured at ambient conditions (23 ± 2 °C) for an additional 27 days. To facilitate the reading, the following codes were used throughout the manuscript: reference (or 0_Ef), and then 5_Ef, 10_Ef, 15_Ef, 20_Ef, and 25_Ef for the compositions prepared with varying amounts of the alkaline effluent as NaOH replacement. Details of the compositions can be seen in Table 1. In the reference composition, the silica modulus (SiO2/Na2O) of the activating solution was 1.7.

Table 1.
Mixture composition of the studied formulations. The amount of effluent used to replace sodium hydroxide is provided in mL, and the corresponding vol.% is given.
2.3. Alkali-Activated Material Characterisation
2.3.1. Fresh Paste Characterisation
- 1.
- Consistency and setting time
Consistency and the setting time of the fresh paste were evaluated at room temperature. The flow table test (to determine consistency) was performed in accordance with the EN 1015-3 (2007). A fixed amount of fresh paste was placed on the mould and then after removing the mould and rotating the handle 15 times, the spread of the paste was measured.
The initial and final setting times were determined in accordance with EN 196-3, using a Vicat needle. The fresh paste was placed on a semi-conical mould and the needle was placed above the paste. It was released and the needle penetration in the paste was measured at regular intervals of time (5 or 10 min). To measure the final setting time with accuracy, a needle with a ring attached was used and the final time corresponded to the time when no visible ring mark was observed. The setting time was evaluated for the reference, and for the compositions coded as 15_Ef and 25_Ef.
- 2.
- Dissolution assays
Dissolution tests were performed to measure the dissolution of Ca, Si, and Al from the precursors. In these tests, 0.2 g of the solid precursors (metakaolin and fly ash) was added to 50 mL of the activating solution (10 M NaOH mimicking the reference composition, or NaOH/effluent at a 75:25 volume ratio).
The solids and the activating solution were magnetically stirred for various contact times, ranging from 5 min to 60 min. After this, the samples were centrifuged, and liquid aliquots were extracted and neutralised prior to the evaluation using inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES, Horiba JobinYvon, Activa M, Kyoto, Japan). The detection limits for Al, Ca, and Si were 20 µg/L, 50 µg/L, and 100 µg/L, respectively.
- 3.
- Calorimetric characterisation
To further characterise the impact of the alkaline effluent on the fresh-state properties of the alkali-activated materials, the heat evolution of the pastes upon curing was monitored during 24 h by using a quasi-adiabatic calorimeter [29]. Two compositions were evaluated, the reference (prepared without the effluent) and the composition containing the highest amount of the alkaline effluent (coded as 25_Ef). The tests were performed using a climatic chamber (Fitoclima 300 EP10, Aralab) at 23 °C and 65% RH. A thermocouple was placed inside the cells and the data acquired with an acquisition device (Data Logger Switch Unit 34970A from Agilent). Four samples per composition were measured. It should be noted that the mixture of the pastes was performed outside the cell, and therefore the initial heat evolution could not be measured.
2.3.2. Hardened State Characterisation
The compressive strength of the samples was determined after 1 and 28 days curing. A Universal Testing Machine Shimadzu, AG-25 TA was used at 0.5 mm/min, in accordance with the standard EN 1015-11:1999. For each formulation, 4 samples were analysed.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterisation of the Solid Precursors and the Industrial Wastewater
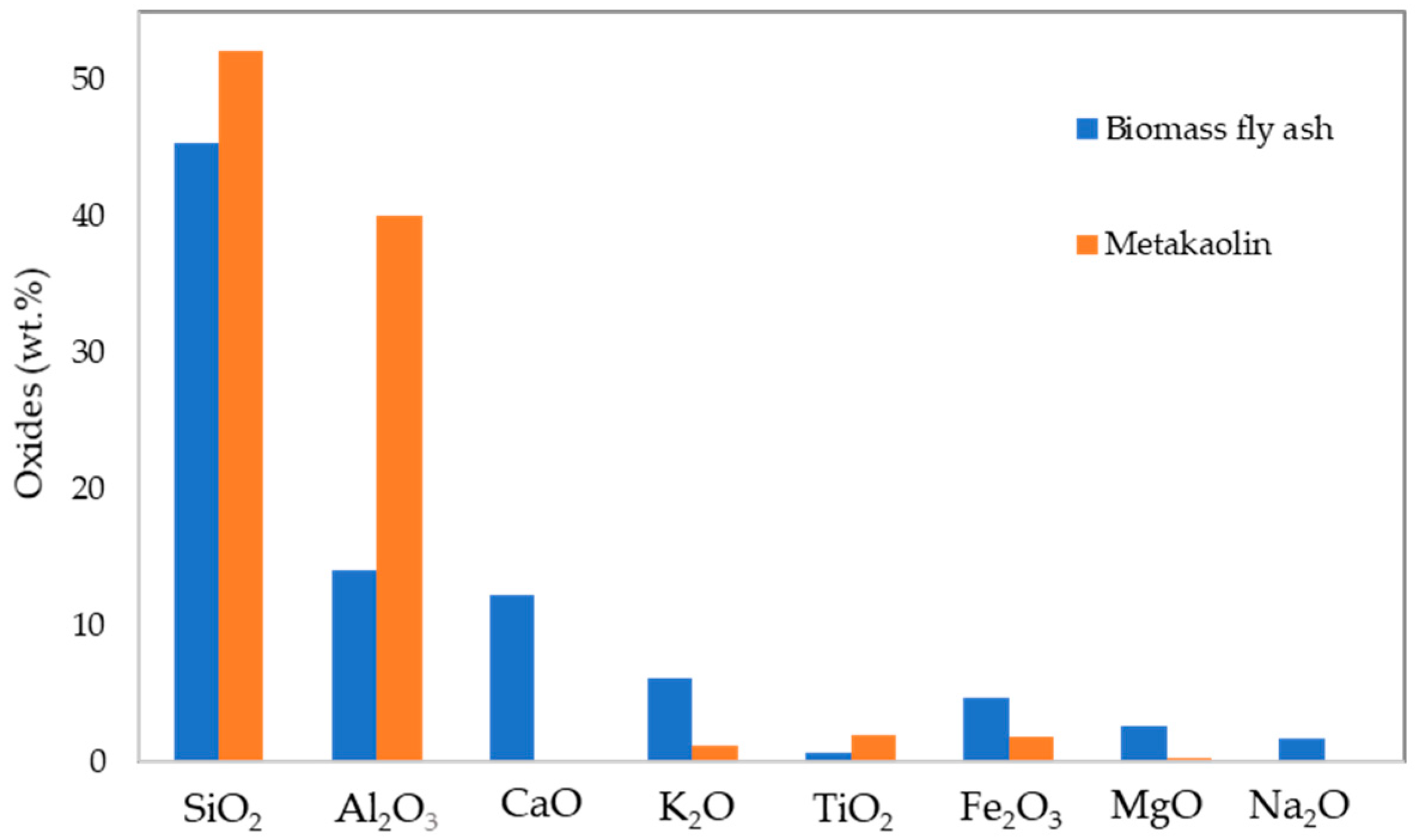
In Figure 1, the chemical composition of metakaolin and biomass fly ash measured as oxides (by XRF) is presented. Metakaolin is mainly composed of SiO2 (52.1 wt.%) and Al2O3 (40.1 wt.%). Other relevant oxides include TiO2 (2.0 wt.%), Fe2O3 (1.9 wt.%), and K2O (1.1 wt.%).
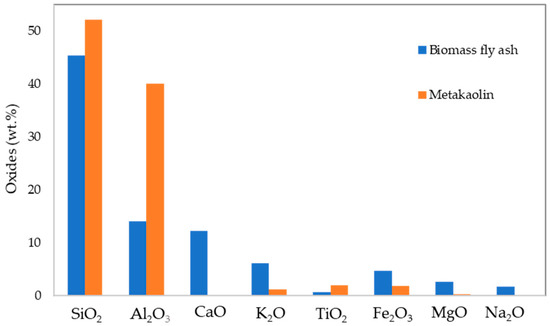
Figure 1.
Chemical composition of MK and FA.
The biomass fly ash is a silica-rich precursor, SiO2 accounting for 45.4 wt.%. The waste also contains significant amounts of Al2O3 (14.0 wt.%), CaO (12.2 wt.%), K2O (6.1 wt.%), and Fe2O3 (4.6 wt.%). Other oxides include MgO (2.6 wt.%) and Na2O (1.6 wt.%). The differences in the chemical composition of the precursors will affect their alkali activation, metakaolin being more prone to alkali activation compared with the biomass fly ash (additional details in [30]). For this reason, in the present study a mixture of biomass fly ash (70 wt.%) and metakaolin (30 wt.%) was used.
The sodium content in the alkaline effluent was measured by atomic emission. The results show that it contained 1116.7 ± 138.5 ppm of sodium. The molar concentration of Na+ in the effluent was 0.05 mol/dm3. The sodium content coupled with the effluent pH suggests the possibility to act as an activator. Nevertheless, the sodium content in the effluent is much lower than the amount present in the sodium hydroxide solution, and for this reason the silica modulus (SiO2/Na2O) in the activator will increase as the effluent content in the activating solution increases. The silica modulus of the activating solution is known to affect the properties of the alkali-activated materials [31]. It has been reported that optimum modulus ranges are comprehended between one and two, depending on the nature of the precursors [32].
The chemical composition of the industrial wastewater was evaluated by ICP, and results are presented in Table 2. The results show that sodium is the major element present in the effluent, while lower amounts of chloride and trace amounts of potassium were also detected. The sodium content measured by this technique is rather similar to the value determined by atomic emission, and this provides additional evidence of the wastewater alkalinity.

Table 2.
Chemical composition measured by ICP of the industrial effluent.
3.2. Fresh Paste Characterisation
3.2.1. Consistency and Setting Time
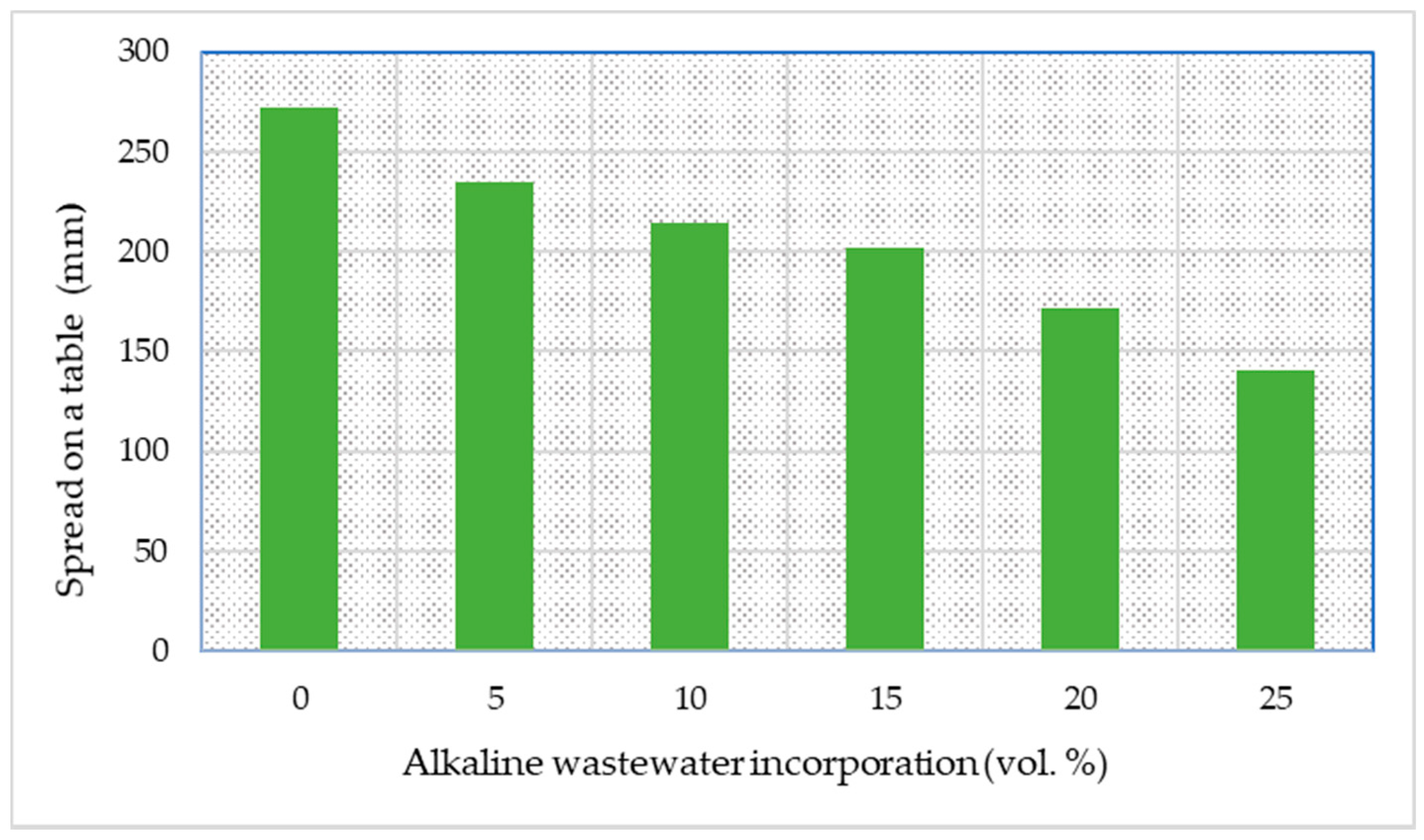
Figure 2 presents the flow table values measured for the various compositions. The results show that the workability of the pastes decreases with the increase in the effluent amount. The spread values ranged from 272.5 mm (reference) to 140.5 mm (25_Ef). Considering the decrease in the pastes’ workability, higher amounts of effluent were not considered, as the objective of the present study was to keep the mixture composition unchanged. Nevertheless, the lowest spread values here reported is superior to that seen in [33] when the slag amount in the alkali-activated pastes was ≥70 wt.% (~100 mm), being lower than the minimum value reported in [34] (178.8 mm) for alkali-activated pastes produced using a mixture of high-calcium fly ash and slag as solid precursors. Previous works in the literature suggest that for alkali-activated mortars, a spread between 180 and 220 mm typically ensures good workability, compaction, and homogeneity for construction applications [35]. In fact, 160 mm was still considered an acceptable value, while 110 mm was related to a state of unworkability [35]. It should be noted that the value seen for the composition containing 25 vol.% of effluent (140.5 mm) is slightly below the acceptable limit; however, the workability of the pastes can be tuned by modifying the recipe or by adding a suitable superplasticiser. Moreover, the values here reported are similar to those reported for fly-ash-granulated ground blast-furnace slag (GGBS)-based geopolymer mortar (87–189 mm) [36] and for dreg-containing alkali-activated materials (150–280 mm) [27].
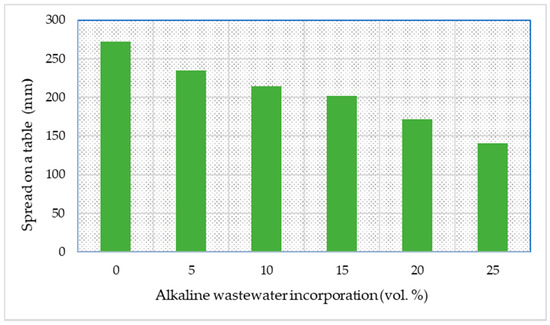
Figure 2.
Influence of the alkaline wastewater content on the workability of the pastes (consistency determined by the flow on a table method).
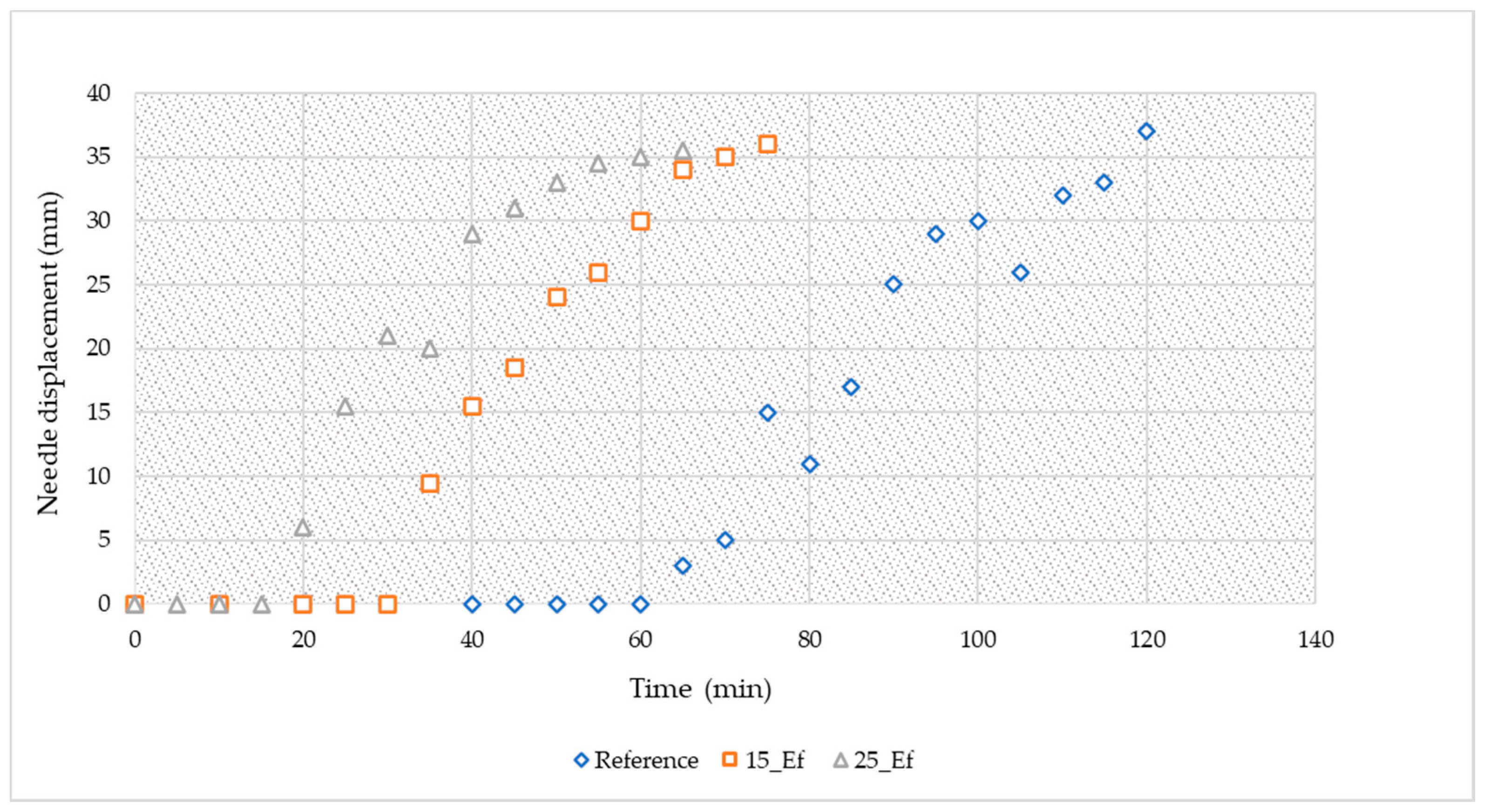
Figure 3 presents the Vicat needle penetration upon curing for the three studied compositions (reference, 15_Ef and 25_Ef). In line with the spread results, increasing the amount of effluent in the compositions decreases the initial and final setting times of the pastes. The initial setting of the reference was 67.5 min, while in the effluent-containing pastes the initial setting was much faster (32.5 min—15_Ef, and 17.5 min—25_Ef paste). The final setting follows the same trend: the setting being 160 min for the reference composition, while for the effluent-containing compositions the setting occurs earlier (105 min and 75 min for the 15_Ef and 25_Ef, respectively).
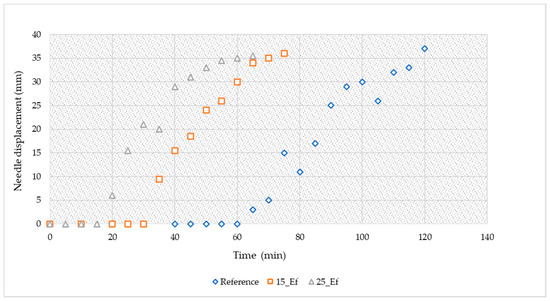
Figure 3.
Needle displacement measured with the Vicat method for the studied compositions.
The setting time of the alkali-activated materials is usually related to the calcium amount. Studies show that there is an exponential decrease in the setting time with an increase in calcium content [37]. It is also known that the calcium enhances the rate and extent of metakaolin dissolution, causing faster setting [27]. The biomass fly ash used here had ~12.2 wt.% of CaO, which can play a major role in the pastes’ setting behaviour. The decrease in the setting time for the effluent-containing compositions suggests differences in the calcium dissolution compared with that seen in the reference, possibly due to the lower pH of the effluent compared with the sodium hydroxide solution. This feature will be further discussed in the following section (dissolution tests). Future work should be carried out to understand the impact of the effluent on the nature (sodium- or calcium-rich gel) and quantity of the produced gel.
3.2.2. Dissolution Tests
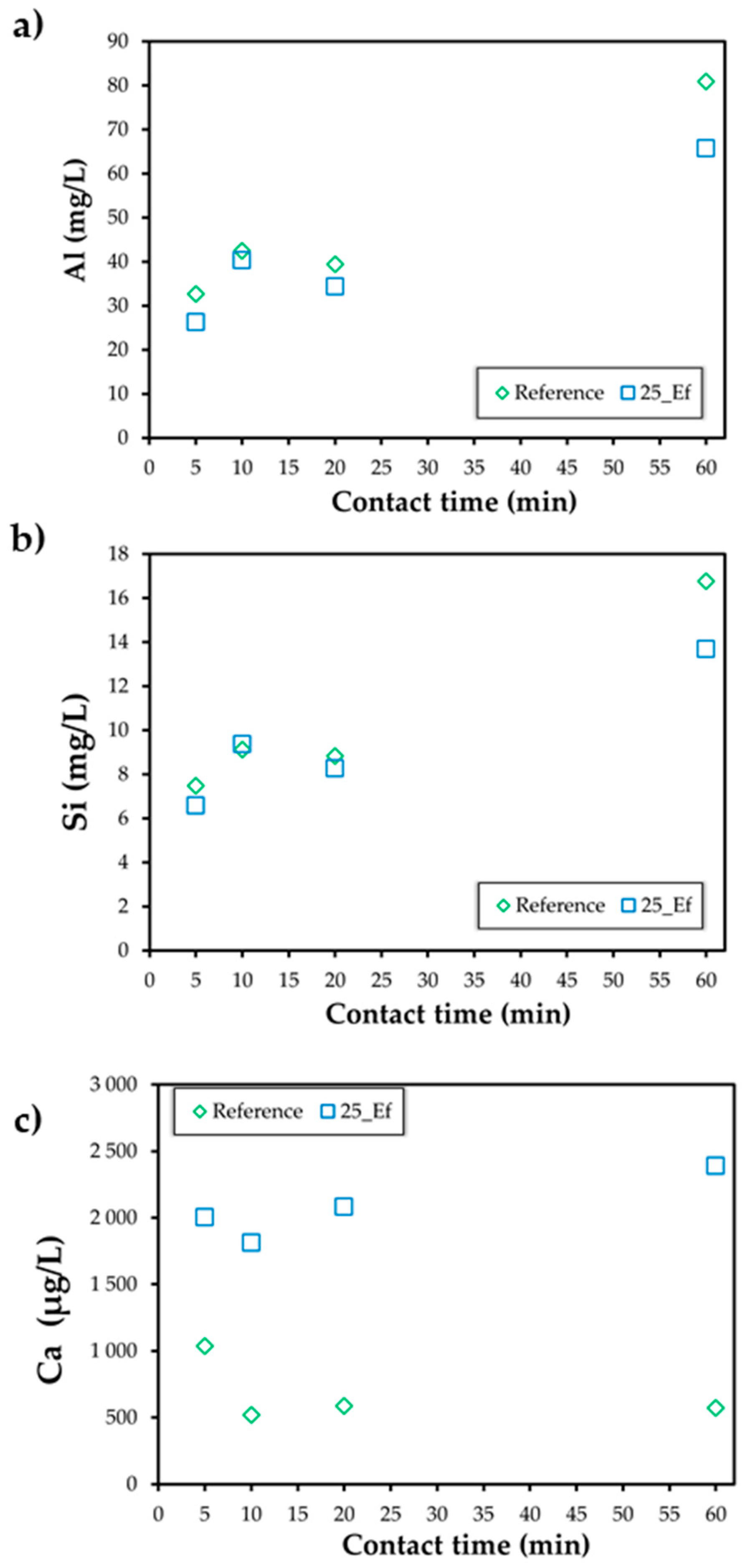
Figure 4 presents the Al, Si, and Ca leaching from the precursors for the two studied compositions (reference and 25_Ef). The results show a much higher dissolution of aluminium and silicon from the precursors compared with calcium, and this regardless of the incorporation of the effluent. In the reference, and after 5 min, the Al dissolution concentration reached 33 mg/L, this being 4.4 times higher than the Si (7 mg/L) and 33 times higher than the Ca (1 mg/L). Longer contact time further enhanced the dissolution of Al and Si, these elements reaching 81 mg/L and 17 mg/L after 60 min. Interestingly, the incorporation of the alkaline effluent affected the Al and the Ca dissolution, while the Si concentration in solution was mostly unaffected in the first 20 min. A twofold increase was observed in the Ca dissolution after the first 5 min in the effluent-containing assay compared with the reference batch. The differences in the Ca dissolution concentration were further extended with the use of longer contact times. On the contrary, after 60 min lower dissolution of Al and Si was seen in the effluent-containing assay, the values were roughly 22% lower than those seen when using the NaOH activator (reference composition). These differences in the Al, Si, and Ca dissolution are attributed to the lower pH of the effluent (pH~11) compared with the 10 M NaOH (pH~14.5). When 25 vol.% of the NaOH is replaced by the effluent, a decrease in the pH is to be forecasted and this hinders the dissolution of Al and Si. In fact, previous studies have demonstrated that a decrease in the activator pH decreases the solubility of Al and Si [38]. Our results also show that the calcium concentration in solution increases substantially when the effluent is employed as activator, and this explains the faster setting and lower spread values seen in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
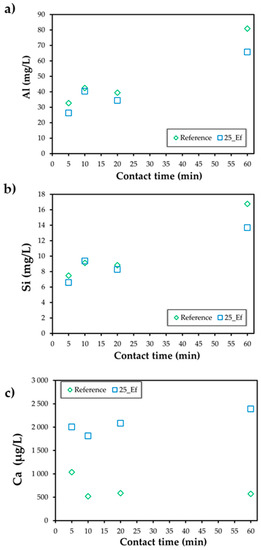
Figure 4.
Dissolution of Al (a), Si (b), and Ca (c) for the studied compositions.
3.2.3. Calorimetric Characterisation
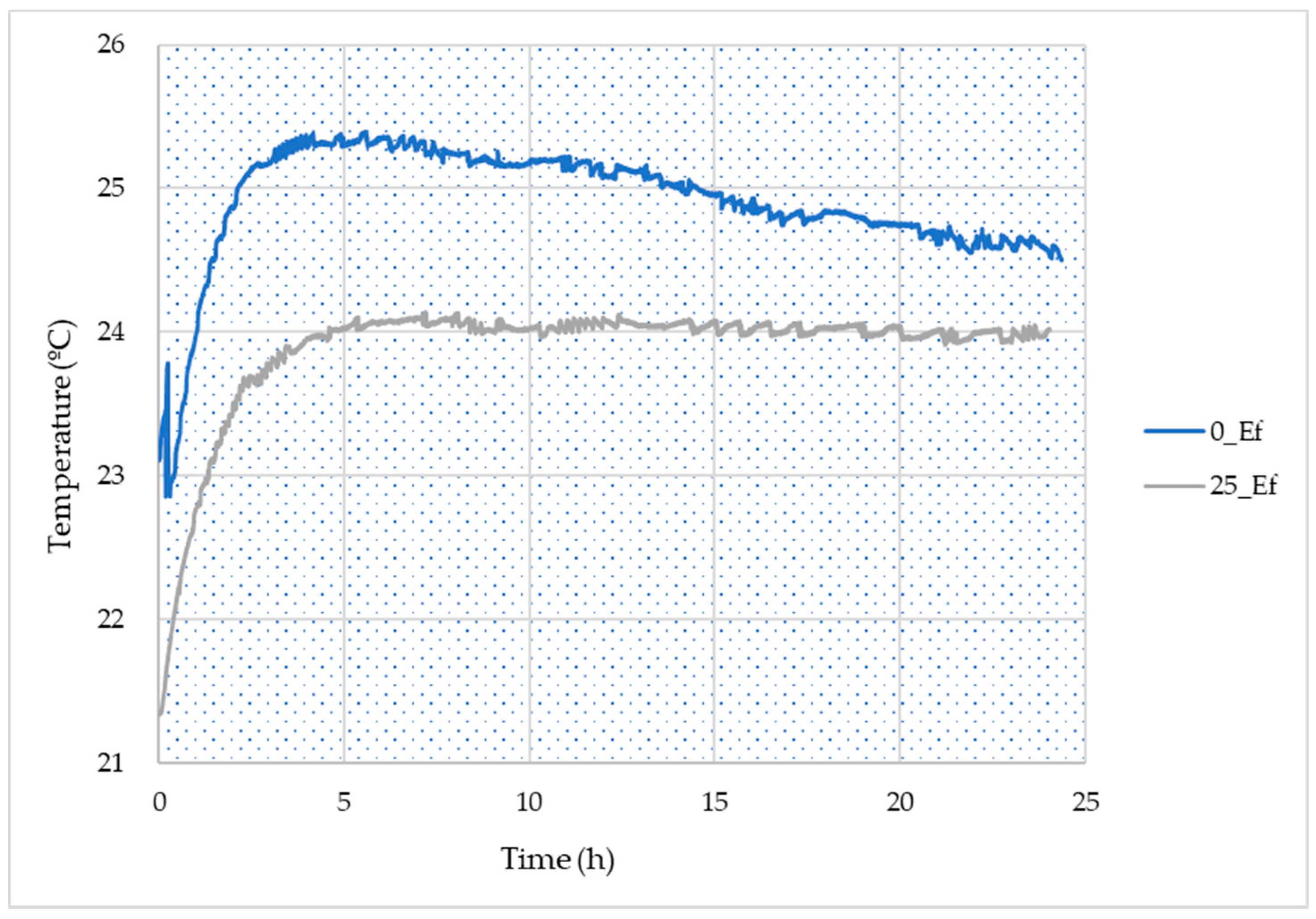
Figure 5 shows the temperature evolution within the studied pastes (ref and 25_Ef) upon curing. The results show that the reference composition reached a higher maximum temperature compared with the paste containing the effluent, and this suggests a slower or lower reaction when the industrial wastewater is employed. These results are aligned with the lower Al and Si dissolution seen in Figure 4. The decrease in heat evolution seen when using the effluent might be due to the lower amount of Al in the solution, as this can influence the exothermic reaction [39].
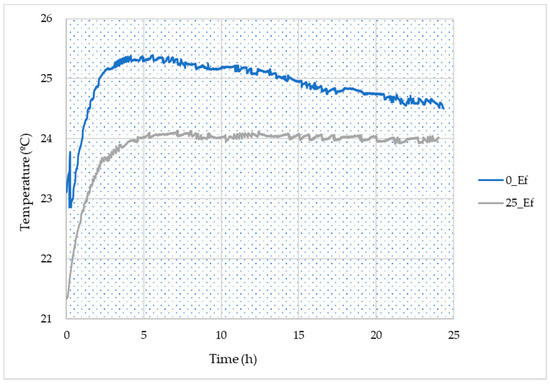
Figure 5.
Temperature evolution upon curing measured for the reference and the 25_Ef formulations.
3.3. Hardened State Characterisation: Compressive Strength
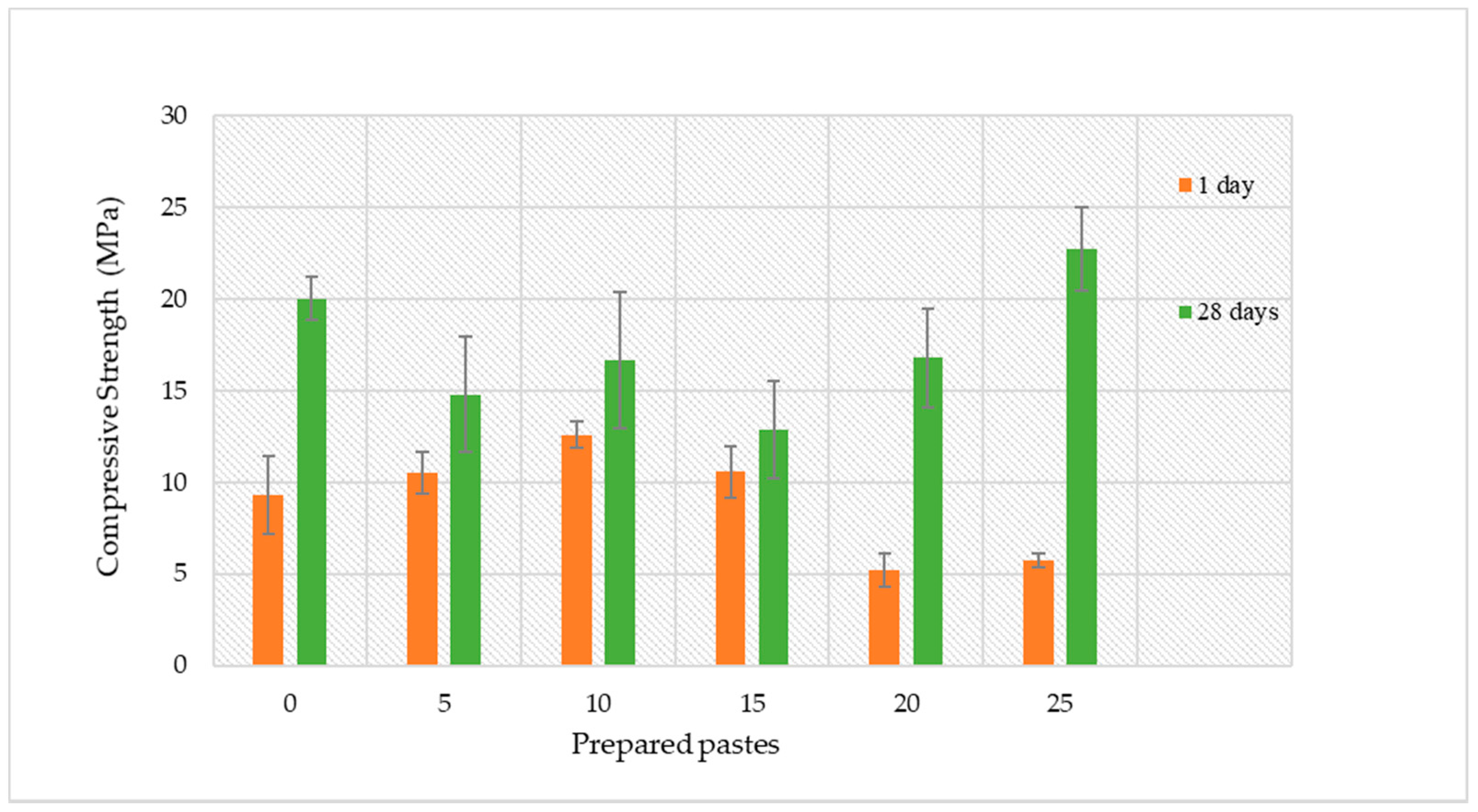
The compressive strength values of the various compositions measured at the 1st and 28th days is shown in Figure 6. The results show that at the 1st day and for incorporation contents up to 15 vol.%, the impact of the effluent on the specimens’ compressive strength is minor, while higher amounts induce a decrease. This might be related to the lower dissolution of Al and Si observed in the dissolution assays (see Figure 4), which cause a delay in the geopolymerisation reactions. The lower strength seen at the 1st day can also be correlated with the lower maximum temperature seen in the calorimetric assays (see Figure 5) for the effluent-containing composition compared with the reference (prepared without adding the effluent). The decrease in the maximum temperature of the pastes can be attributed to the lower alkalinity of the effluent compared with the NaOH, hindering the dissolution of the reactive fraction of the precursors [40]. In fact, previous studies have observed a decrease in the heat evolution (measured by calorimetry) as the ratio of SiO2-to-Na2O of the activating solution rises [41] in line with our results. The higher earlier strength seen for the reference composition is connected with the superior dissolution of Si and Al from the precursors contributing towards the higher strength of these specimens.
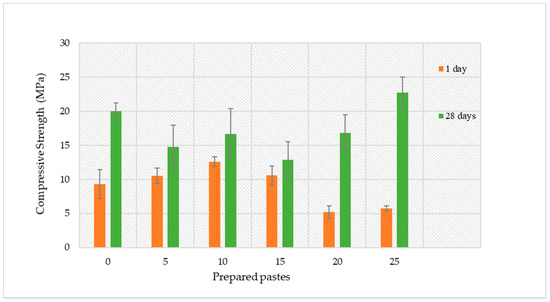
Figure 6.
Compressive strength for the various compositions measured at the 1st and 28th day.
After 28 days the composition containing the highest amount of effluent (25 vol.%) shows a compressive strength higher than the reference, and this suggests that the system was able to recover from the delay in the early strength. At this stage, the compressive strength of this composition reaches 22.7 ± 2.3 MPa, while the reference reaches 20.0 ± 1.2 MPa. The distinct strength evolution for these compositions suggests that the use of high alkalinity (reference), while favouring the earlier strength gain, might be detrimental to the subsequent geopolymerisation, resulting in lower strength development [29,42].
In any case, these results demonstrate the feasibility of using an alkaline wastewater to partially replace the commercial activator (e.g., NaOH). It should be noted that this compressive strength is much higher than the minimum values required for masonry applications, belonging at least to the class M10 [43]. Nevertheless, it should be noted that the mechanical strength of the specimens is only one of the requirements for masonry applications. Indeed, future work should be carried out to optimise the pastes’ setting times. Moreover, the industrial wastewater variability and the possible impact on the properties of the synthesised materials should be studied.
4. Conclusions
This work shows the possibility of using an alkaline industrial wastewater, from a Portuguese paper and pulp industry, as a partial replacement of the commercial sodium hydroxide in the synthesis of biomass fly ash alkali-activated materials. The use of the wastewater was found to decrease the workability of the pastes as well as the initial and final setting times, and this feature limited the maximum incorporation content to 25 vol.% (compared with the NaOH). The lower workability and faster setting were associated with the higher Ca dissolution coupled with the lower Al and Si dissolution observed when using the effluent, as demonstrated by the dissolution assays. The results show that the use of the industrial wastewater (content ≥ 20 vol.%) induced a lower earlier strength compared with the reference due to the lower alkalinity of the effluent, which hinders the dissolution of the reactive fraction in the precursors. Despite the lower early strength, the composition containing the highest amount of effluent (25 vol.%) reached a compressive strength on the 28th day slightly superior (22.7 MPa) to the value observed for the reference (20.0 MPa); this demonstrates the possibility of using an industrial alkaline waste as a partial replacement of commercial activators without compromising the compressive strength of the specimens. Future work should be carried out to maximise the wastewater incorporation volumes using superplasticisers or by tuning the mixture composition.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, R.M.N. and J.A.L.; methodology, C.C.N., L.S. and R.M.N.; validation, C.C.N., L.S. and R.M.N.; formal analysis, C.C.N., L.S. and R.M.N.; investigation, C.C.N. and L.S.; resources, M.P.S., R.M.N. and J.A.L.; writing—original draft preparation, C.C.N., R.M.N. and J.A.L.; writing—review and editing, C.C.N., L.S., M.P.S., R.M.N. and J.A.L.; supervision, R.M.N. and J.A.L.; funding acquisition, R.M.N. and J.A.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge the project ERA-MIN/0001/2019 (SMART-G—Smart Geopolymers). R.M. Novais also acknowledges the FCT support under the grant (2020.01135.CEECIND). This work was developed within the scope of the project CICECO-Aveiro Institute of Materials, UIDB/50011/2020, UIDP/50011/2020 and LA/P/0006/2020, financed by national funds through the FCT/MEC (PIDDAC).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This work was presented at the workshop “Engineering and circular economy: the road to sustainability” funded as a part of the ECO-MET-AL Project (PID2019-109520RB-I00), “Can industrial and mining metalliferous wastes produce green lightweight aggregates? Applying the Circular Economy” funded by the Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities and ERDF funds, framed in the “Grants for “R&D&I Projects” in the framework of the State Programmes for the Generation of Knowledge and Scientific and Technological Strengthening of the R&D&I System and R&D&I oriented to the Challenges of Society, Call 2019. The authors would like to acknowledge Tânia Gameiro for performing the atomic emission tests.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Adesanya, E.; Perumal, P.; Luukkonen, T.; Yliniemi, J.; Ohenoja, K.; Kinnunen, P.; Illikainen, M. Opportunities to improve sustainability of alkali-activated materials: A review of side-stream based activators. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 125558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesgari, S.; Akbarnezhad, A.; Xiao, J.Z. Recycled geopolymer aggregates as coarse aggregates for Portland cement concrete and geopolymer concrete: Effects on mechanical properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 236, 117571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imtiaz, L.; Ur Rehman, S.K.; Memon, S.A.; Khan, M.K.; Javed, M.F. A review of recent developments and advances in eco-friendly geopolymer concrete. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tailby, J.; MacKenzie, K.J.D. Structure and mechanical properties of aluminosilicate geopolymer composites with Portland cement and its constituent minerals. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obonyo, E.; Kamseu, E.; Melo, U.C.; Leonelli, C. Advancing the use of secondary inputs in geopolymer binders for sustainable cementitious composites: A review. Sustainability 2011, 3, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Provis, J.L.; Reid, A.; Wang, H. Geopolymer foam concrete: An emerging material for sustainable construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 56, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizza, M.; Natali, M.; Garbin, E.; Tamburini, S.; Secco, M. Assessment of geopolymers with Construction and Demolition Waste (CDW) aggregates as a building material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 181, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.L. Alkali-activated materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 114, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, Y.M.; Heah, C.Y.; Mohd Mustafa, A.B.; Kamarudin, H. Structure and properties of clay-based geopolymer cements: A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 83, 595–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, J. A review on properties of fresh and hardened geopolymer mortar. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 152, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulugöl, H.; Kul, A.; Yıldırım, G.; Şahmaran, M.; Aldemir, A.; Figueira, D.; Ashour, A. Mechanical and microstructural characterization of geopolymers from assorted construction and demolition waste-based masonry and glass. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakharev, T. Resistance of geopolymer materials to acid attack. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaze, C.R.; Lecomte-Nana, G.L.; Adesina, A.; Nemaleu, J.G.D.; Kamseu, E.; Chinje Melo, U. Influence of mineralogy and activator type on the rheology behaviour and setting time of laterite based geopolymer paste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 126, 104345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Cui, M.; Wang, J.; Lyu, X. Preparation of eco-friendly one-part geopolymers from gold mine tailings by alkaline hydrothermal activation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, B.C.; Williams, R.P.; Lay, J.; Van Riessen, A.; Corder, G.D. Costs and carbon emissions for geopolymer pastes in comparison to ordinary portland cement. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 1080–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendes, B.C.; Pedroti, L.G.; Vieira, C.M.F.; Marvila, M.; Azevedo, A.R.G.; Franco de Carvalho, J.M.; Ribeiro, J.C.L. Application of eco-friendly alternative activators in alkali-activated materials: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 35, 102010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeli, M.; Tobaldi, D.M.; Seabra, M.P.; Labrincha, J.A. Mix design and mechanical performance of geopolymeric binders and mortars using biomass fly ash and alkaline effluent from paper-pulp industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnahhal, M.F.; Kim, T.; Hajimohammadi, A. Waste-derived activators for alkali-activated materials: A review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 118, 103980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emdadi, Z.; Asim, N.; Amin, M.H.; Yarmo, M.A.; Maleki, A.; Azizi, M.; Sopian, K. Development of green geopolymer using agricultural and industrial waste materials with high water absorbency. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Naggar, M.R.; El-Dessouky, M.I. Re-use of waste glass in improving properties of metakaolin-based geopolymers: Mechanical and microstructure examinations. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 132, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinai, R.; Soutsos, M. Production of sodium silicate powder from waste glass cullet for alkali activation of alternative binders. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 116, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogundiran, M.B.; Nugteren, H.W.; Witkamp, G.J. Geopolymerisation of fly ashes with waste aluminium anodising etching solutions. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Cristelo, N.; Miranda, T.; Palomo, Á. Sustainable alkali activated materials: Precursor and activator derived from industrial wastes. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 1200–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Riessen, A.; Jamieson, E.; Kealley, C.S.; Hart, R.D.; Williams, R.P. Bayer-geopolymers: An exploration of synergy between the alumina and geopolymer industries. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 41, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Caetano, A.P.F.; Seabra, M.P.; Labrincha, J.A.; Pullar, R.C. Extremely fast and efficient methylene blue adsorption using eco-friendly cork and paper waste-based activated carbon adsorbents. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Carvalheiras, J.; Senff, L.; Labrincha, J.A. Upcycling unexplored dregs and biomass fly ash from the paper and pulp industry in the production of eco-friendly geopolymer mortars: A preliminary assessment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 184, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Carvalheiras, J.; Senff, L.; Seabra, M.P.; Pullar, R.C.; Labrincha, J.A. In-depth investigation of the long-term strength and leaching behaviour of inorganic polymer mortars containing green liquor dregs. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Senff, L.; Carvalheiras, J.; Labrincha, J.A. Bi-layered porous/cork-containing waste-based inorganic polymer composites: Innovative material towards green buildings. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Ascensão, G.; Buruberri, L.H.; Senff, L.; Labrincha, J.A. Influence of blowing agent on the fresh- and hardened-state properties of lightweight geopolymers. Mater. Des. 2016, 108, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buruberri, L.H.; Tobaldi, D.M.; Caetano, A.; Seabra, M.P.; Labrincha, J.A. Evaluation of reactive Si and Al amounts in various geopolymer precursors by a simple method. J. Build. Eng. 2019, 22, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firdous, R.; Stephan, D. Effect of silica modulus on the geopolymerization activity of natural pozzolans. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 219, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Hua, S. Effects of mix design parameters on heat of geopolymerization, set time, and compressive strength of high calcium fly ash geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 228, 116763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedeljković, M.; Li, Z.; Ye, G. Setting, strength, and autogenous shrinkage of alkali-activated fly ash and slag pastes: Effect of slag content. Materials 2018, 11, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teo, W.; Shirai, K.; Lim, J.H.; Jack, L.B.; Nikbakht, E. Experimental Investigation on Ambient-Cured One-Part Alkali-Activated Binders Using Combined High-Calcium Fly Ash (HCFA) and Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag (GGBS). Materials 2022, 15, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeli, M.; Senff, L.; Tobaldi, D.M.; Carvalheiras, J.; Seabra, M.P.; Labrincha, J.A. Unexplored alternative use of calcareous sludge from the paper-pulp industry in green geopolymer construction materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 246, 118457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Dai, J.G.; Zhao, T.J.; Guo, S.Y.; Zhang, P.; Mu, B. Alternation of traditional cement mortars using fly ash-based geopolymer mortars modified by slag. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 203, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiatchon, P.R.J.; Dollente, I.J.R.; Abulencia, A.B.; De Guzman Libre, R.G.; Villoria, M.B.D.; Guades, E.J.; Promentilla, M.A.B.; Ongpeng, J.M.C. Investigation on the compressive strength and time of setting of low-calcium fly ash geopolymer paste using response surface methodology. Polymers 2021, 13, 3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phair, J.W.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. Effect of silicate activator pH on the leaching and material characteristics of waste-based inorganic polymers. Miner. Eng. 2001, 14, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, O.; Ukrainczyk, N.; Ballschmiede, C.; Koenders, E. Reactivity and microstructure of metakaolin based geopolymers: Effect of fly Ash and liquid/solid contents. Materials 2019, 12, 3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Y. Geopolymerization process of alkali-metakaolinite characterized by isothermal calorimetry. Thermochim. Acta 2009, 493, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, D.; Neithalath, N. Reaction kinetics in sodium silicate powder and liquid activated slag binders evaluated using isothermal calorimetry. Thermochim. Acta 2012, 546, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somna, K.; Jaturapitakkul, C.; Kajitvichyanukul, P.; Chindaprasirt, P. NaOH-activated ground fly ash geopolymer cured at ambient temperature. Fuel 2011, 90, 2118–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeli, M.; Senff, L.; Tobaldi, D.M.; La Scalia, G.; Seabra, M.P.; Labrincha, J.A. Innovative recycling of lime slaker grits from paper-pulp industry reused as aggregate in ambient cured biomass fly ash-based geopolymers for sustainable construction material. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).