M-ary Amplitude Shift Keying Power and Information Synchronous Transmission Based on Phase-Shifted Full-Bridge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
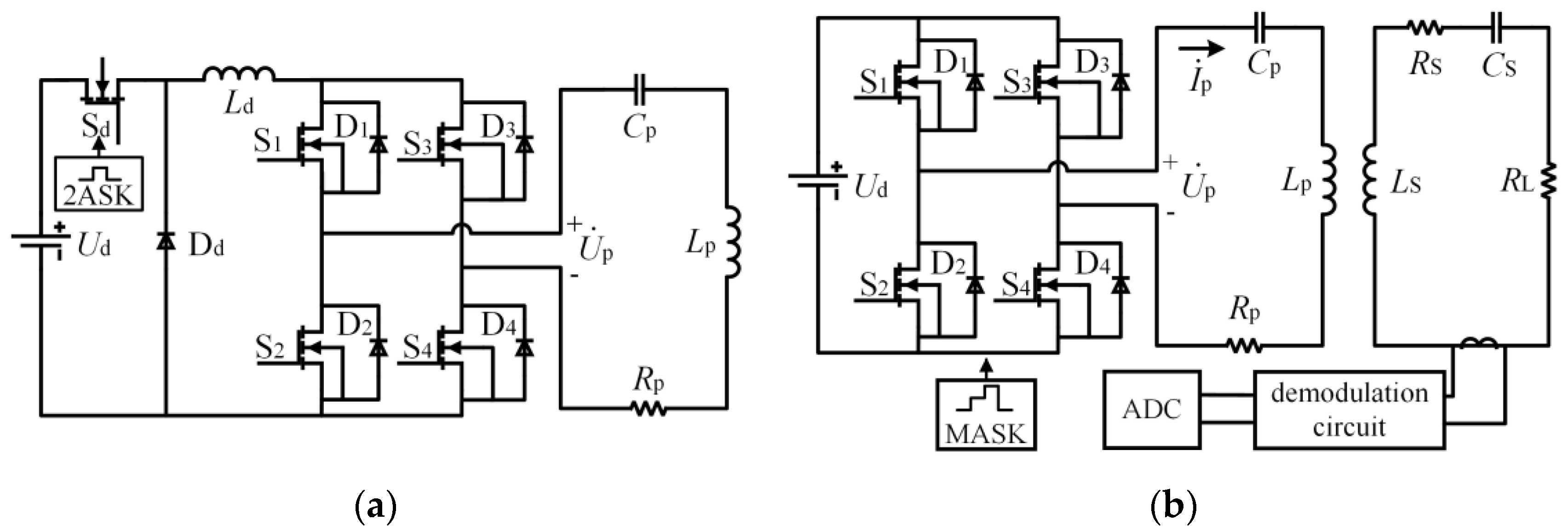
2. Structure and Modeling of the Proposed System
2.1. Structure of the Proposed System
2.2. Equivalent Model Analysis of the System
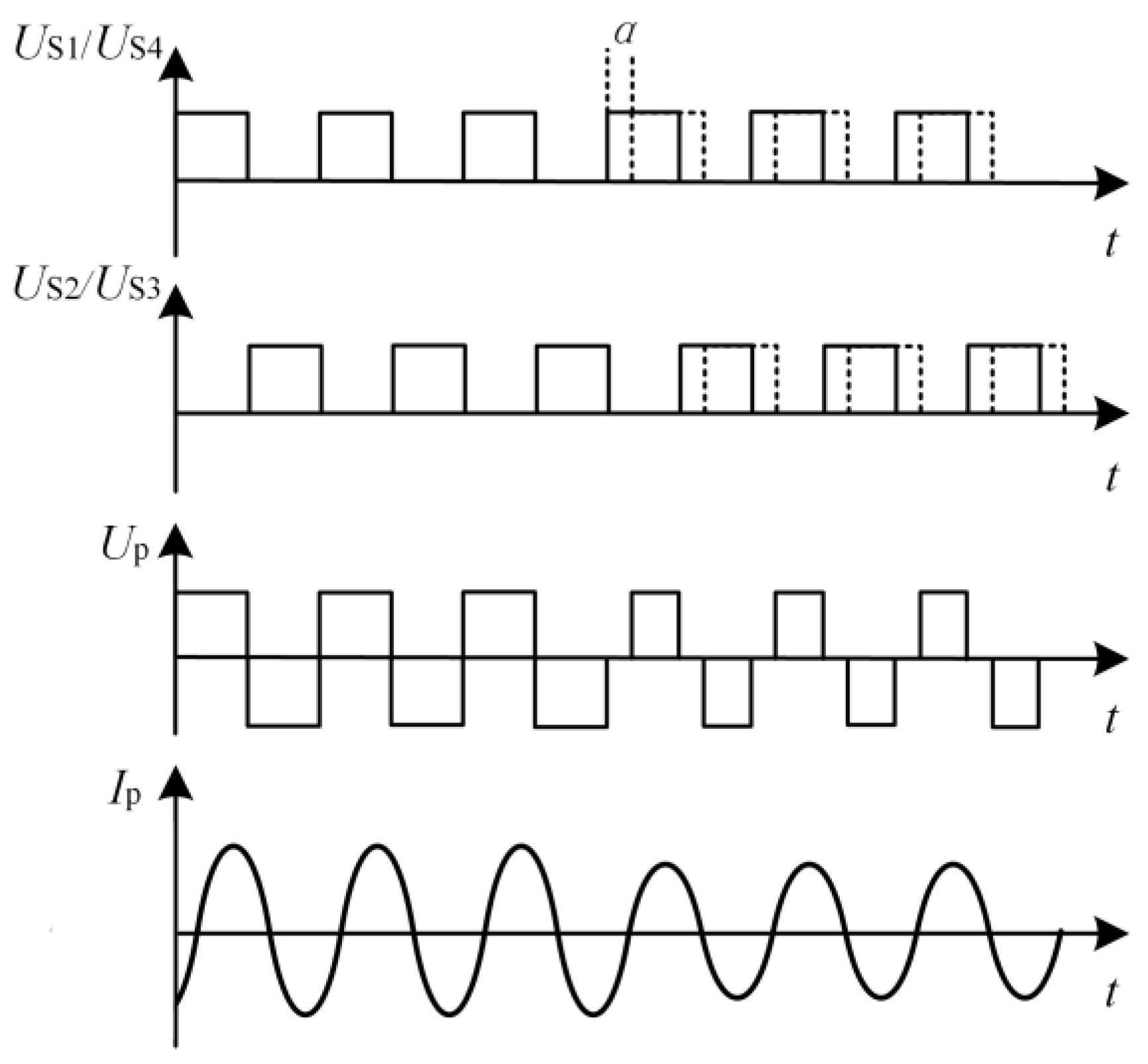
3. Synchronous Information Transmission Analysis
3.1. Information Modulation
3.2. Signal Demodulation
4. System Performance Analysis
4.1. Subsection
4.2. Analysis of Signal Transmission Rate
5. Experimental Verification
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, C.; Qiu, D.; Gu, W.; Zhang, B.; C’hen, Y.; Xiao, W. Multiload Wireless Power Transfer System With Constant Output Power and Efficiency. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 58, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, J. A simple and reconfigurable wireless power transfer system with constant voltage and constant current charging. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 37, 4921–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.B.; Kim, M.; Jang, I.G. Determination of the optimal resonant condition for multireceiver wireless power transfer systems considering the transfer efficiency and different rated powers with altered coupling effects. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 9, 2384–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Huang, J.; Feng, B.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Jian, J.; Wang, Z.; Tong, X. Undersea Wireless Power and Data Transfer System With Shared Channel Powered by Marine Renewable Energy System. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2022, 12, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.W.; Hwang, S.I.; Aziz, A.A.; Jang, H.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kang, D.S.; Kim, D.I. Simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (SWIPT) for Internet of Things: Novel receiver design and experimental validation. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 2996–3012. [Google Scholar]
- Sedehi, R.; Budgett, D.; Jiang, J.; Ziyi, X.; Dai, X.; Hu, A.P.; McCormick, D. A wireless power method for deeply implanted biomedical devices via capacitively coupled conductive power transfer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 36, 1870–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, J.; Kim, T.W.; Kawamura, A. Study on intelligent battery charging using inductive transmission of power and information. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2000, 15, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Clerckx, B.; Mitcheson, P.D. Signal and system design for wireless power transfer: Prototype, experiment and validation. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 7453–7469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besnoff, J.; Abbasi, M.; Ricketts, D.S. High data-rate communication in near-field RFID and wireless power using higher order modulation. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2016, 64, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besnoff, J.; Abbasi, M.; Ricketts, D.S. Ultrahigh-data-rate communication and efficient wireless power transfer at 13.56 MHz. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 2634–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieler, T.; Perrottet, M.; Nguyen, V.; Perriard, Y. Contactless power and information transmission. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2002, 38, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathge, C.; Kuschner, D. High efficient inductive energy and data transmission system with special coil geometry. In Proceedings of the 2009 13th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, Barcelona, Spain, 8–10 September 2009; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Van Boheemen, E.L.; Boys, J.T.; Covic, G.A. Dual-tuning IPT systems for low bandwidth communications. In Proceedings of the 2007 2nd IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Application, Harbin, China, 23–25 May 2007; pp. 586–591. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.C.; Lin, C.L.; Wu, Y.K. Simultaneous wireless power/data transfer for electric vehicle charging. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 64, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Jin, Y.; Yao, L. WiFi-ZigBee coexistence based on collision avoidance for wireless body area network. In Proceedings of the 2017 3rd International Conference on Big Data Computing and Communications (BIGCOM), Chengdu, China, 10–11 August 2017; pp. 245–250. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Liu, W.; Sivaprakasam, M.; Zhou, M.; Weiland, J.D.; Humayun, M.S. A dual band wireless power and data telemetry for retinal prosthesis. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, New York, NY, USA, 30 August–3 September 2006; pp. 4392–4395. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, C.; Lin, Z.; Du, J.; Hu, Y.; He, X. Wireless power and data transfer via a common inductive link using frequency division multiplexing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 7810–7820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Dai, X.; Zuo, Z.; You, A. Simultaneous wireless power transfer and full-duplex communication with a single coupling interface. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 36, 6313–6322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, S.; Fang, J.; Tang, Y. Synchronous rectification-based phase shift keying communication for wireless power transfer systems. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 4th Southern Power Electronics Conference (SPEC), Singapore, 10–13 December 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Sun, Y.; Su, Y.; Dai, Y.; Zhai, Y. Synchronous transmission of inductively coupled power and signal. J. Chongqing Inst. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 2009, 23, 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Wu, L.; Baoyun, W. High-efficiency coupling-insensitive wireless power and information transmission based on the phase-shifted control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 33, 7821–7831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Jia, R.; Wu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Zhou, Y. WPIT technology based on the fundamental-harmonic component for a single-channel and two-coil ICPT system. IET Power Electron. 2019, 12, 2608–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Tang, Y. Dual-side phase-shift control of wireless power transfer implemented on primary side based on driving windings. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 8999–9002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.; Agostinelli, M.; Vesti, S.; Oliver, J.A.; Cobos, J.A.; Huemer, M. A wireless charging system applying phase-shift and amplitude control to maximize efficiency and extractable power. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6338–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.; Park, J. A novel phase-control-based energy beamforming techniques in nonradiative wireless power transfer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 30, 6274–6287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, R.; Wu, J.; Li, W. Nature of power electronics and integration of power conversion with communication for talkative power. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Parameters | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Power supply | Ud | 24 V |
| Coil resistance | Rp, RS | 0.1 Ω |
| Transmitting coil self-inductance | Lp | 282.04 μH |
| Resonant capacitor | Cp, CS | 40 nF |
| Load | RL | 35 Ω |
| M-ary Signal | Voltage Amplitude | Phase Angle | Signal |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8-ary signal | 100% | 0° | 0 |
| 99.28% | 13.9° | 1 | |
| 98.57% | 19.4° | 2 | |
| 97.85% | 23.9° | 3 | |
| 97.14% | 27.6° | 4 | |
| 96.43% | 30.8° | 5 | |
| 95.71% | 33.8° | 6 | |
| 95% | 36.5° | 7 | |
| 16-ary signal | 100% | 0° | 0 |
| 99.67% | 9.5° | 1 | |
| 99.34% | 13.3° | 2 | |
| 99.01% | 16.2° | 3 | |
| 98.68% | 18.7° | 4 | |
| 98.35% | 21° | 5 | |
| 98.02% | 23° | 6 | |
| 97.69% | 24.8° | 7 | |
| 97.36% | 26.5° | 8 | |
| 97.03% | 28.1° | 9 | |
| 96.7% | 29.6° | A | |
| 96.37% | 31.1° | B | |
| 96.04% | 32.4° | C | |
| 95.71% | 33.8° | D | |
| 95.38% | 35.1° | E | |
| 95% | 36.5° | F |
| Parameters | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Resistances | R1, R12 | 2 kΩ |
| Resistances | R2, R3, R4, R13, R14 | 20 kΩ |
| Resistances | R5, R6, R11 | 500 Ω |
| Envelope capacitance | C1 | 10 μF |
| Smoothing capacitances | C2, C3 | 100 nF |
| Supply voltage | Uo | 16 V |
| Reference voltage | Uref | 8 V |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Pan, X.; Geng, Y.; Chu, Z.; Han, R.; Xue, M. M-ary Amplitude Shift Keying Power and Information Synchronous Transmission Based on Phase-Shifted Full-Bridge. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13010475
Zhang X, Pan X, Geng Y, Chu Z, Han R, Xue M. M-ary Amplitude Shift Keying Power and Information Synchronous Transmission Based on Phase-Shifted Full-Bridge. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(1):475. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13010475
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xin, Xuetong Pan, Yuehua Geng, Zhiqi Chu, Rongmei Han, and Ming Xue. 2023. "M-ary Amplitude Shift Keying Power and Information Synchronous Transmission Based on Phase-Shifted Full-Bridge" Applied Sciences 13, no. 1: 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13010475
APA StyleZhang, X., Pan, X., Geng, Y., Chu, Z., Han, R., & Xue, M. (2023). M-ary Amplitude Shift Keying Power and Information Synchronous Transmission Based on Phase-Shifted Full-Bridge. Applied Sciences, 13(1), 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13010475






