The Modelling of Rock Fragmentation Mechanisms by Carbide Buttons Using the 3D Discrete Element Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Numerical Simulation Model
2.1. GPU-Based Discrete Element Method
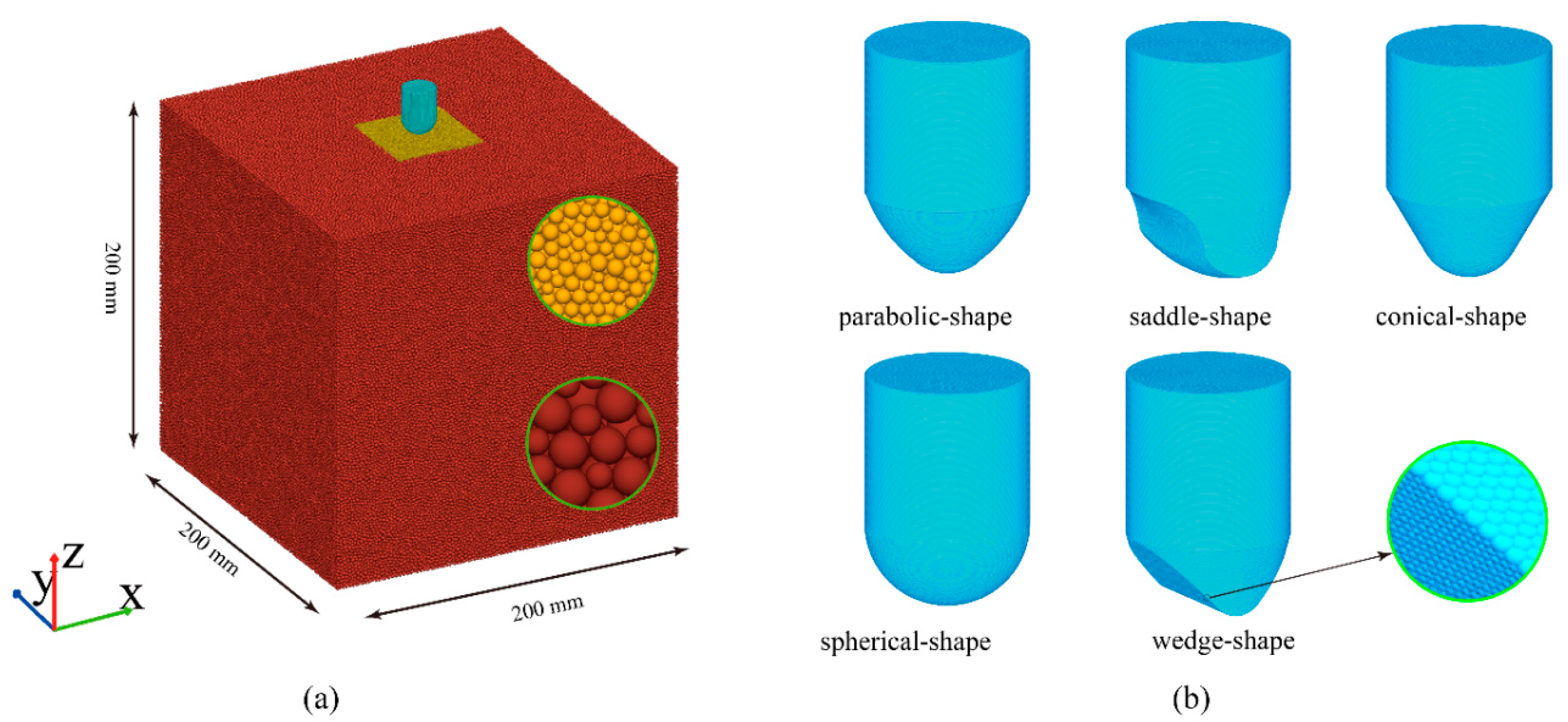
2.2. Model Setup
2.2.1. Numerical Model
2.2.2. Calibration
2.3. Numerical Monitoring
2.3.1. Crack Events
2.3.2. Damage Value
3. Model Validation
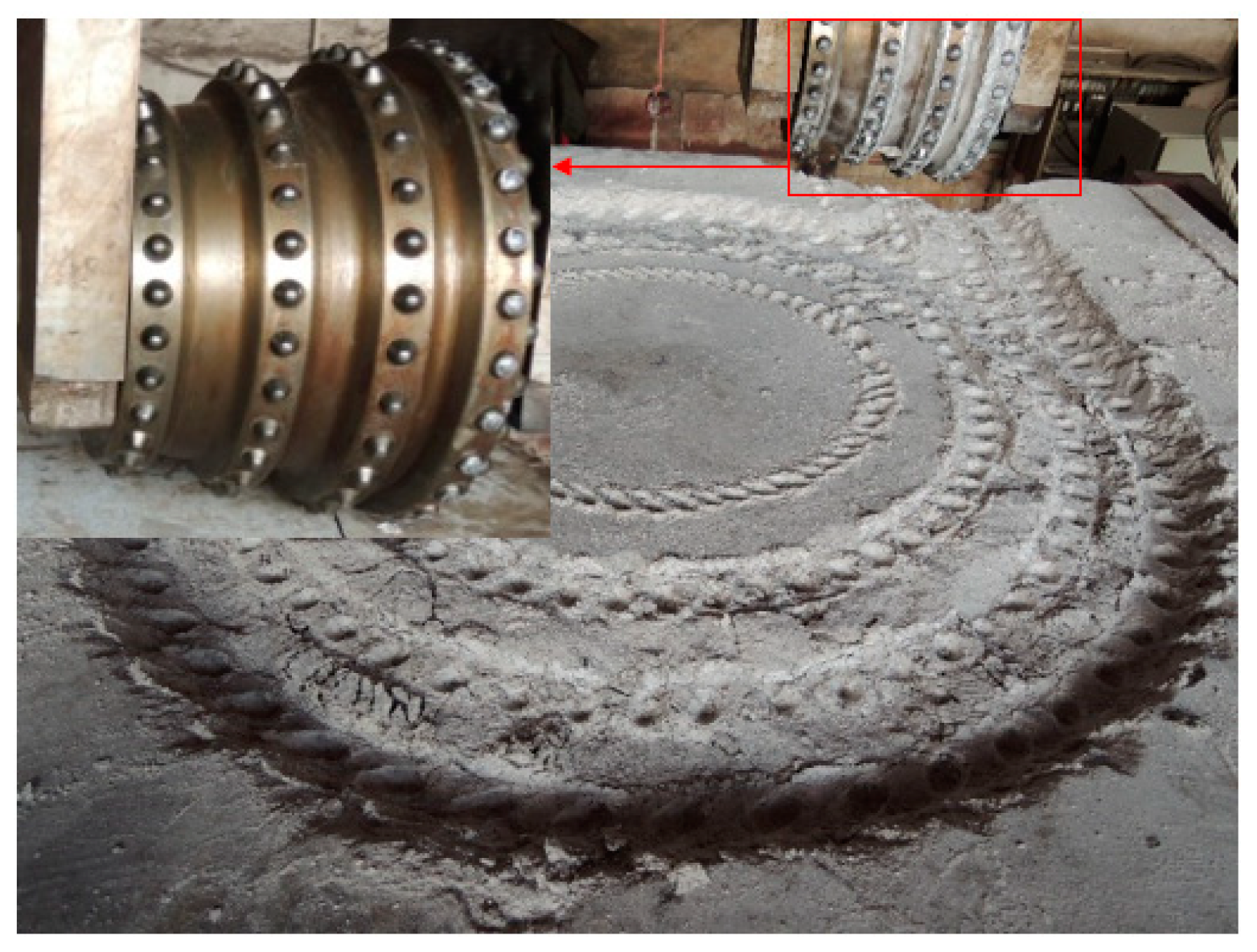
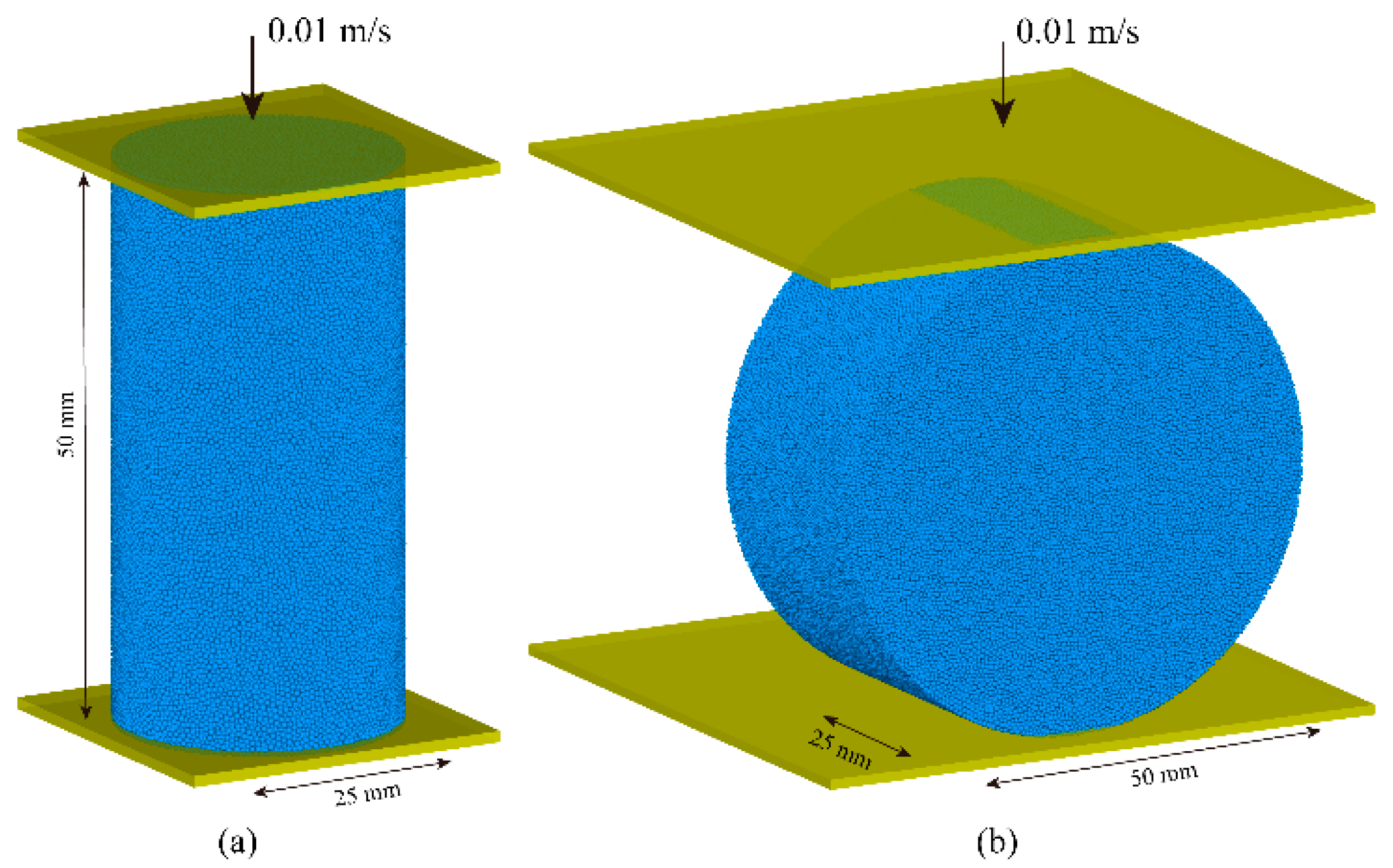
3.1. Experimental Design
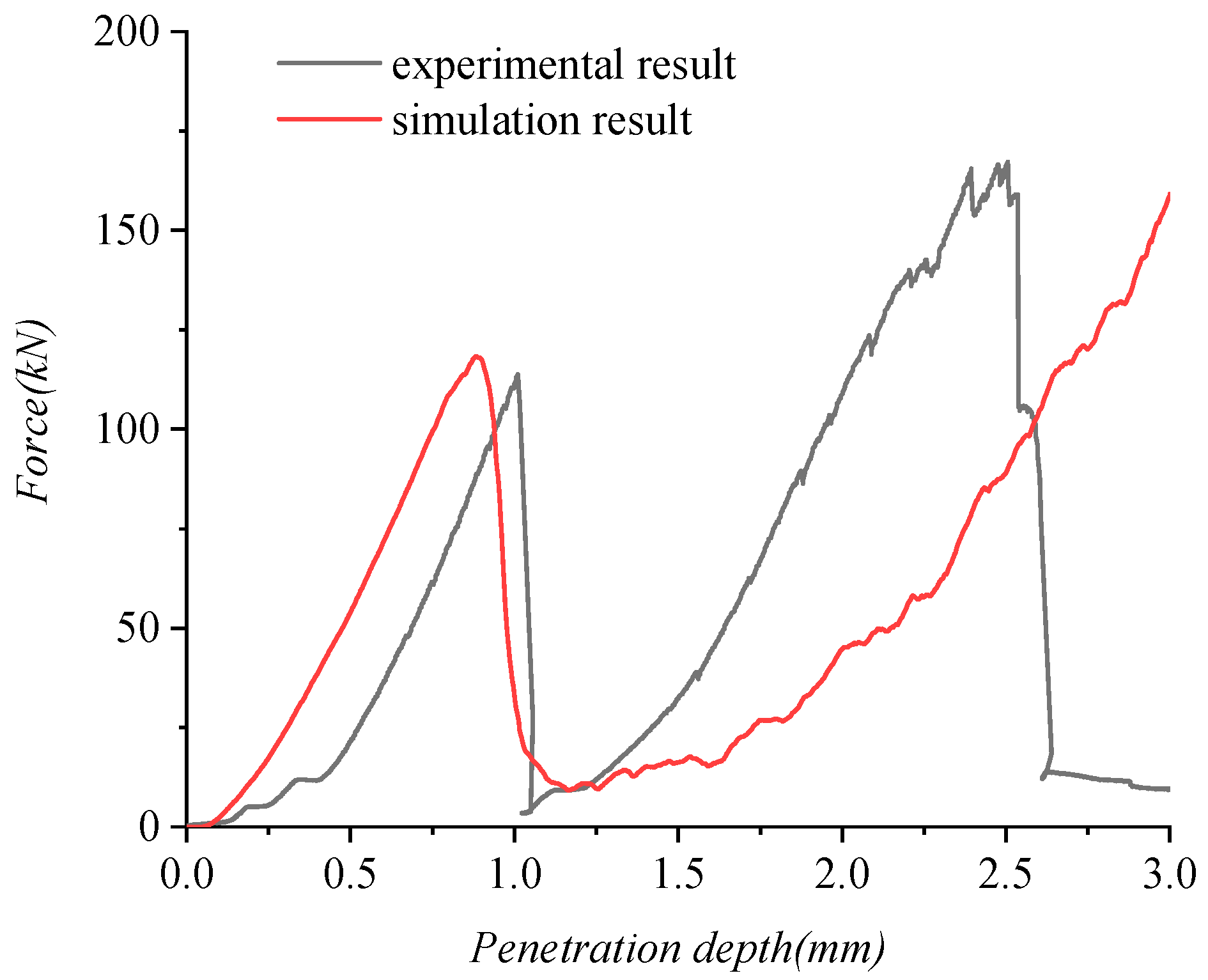
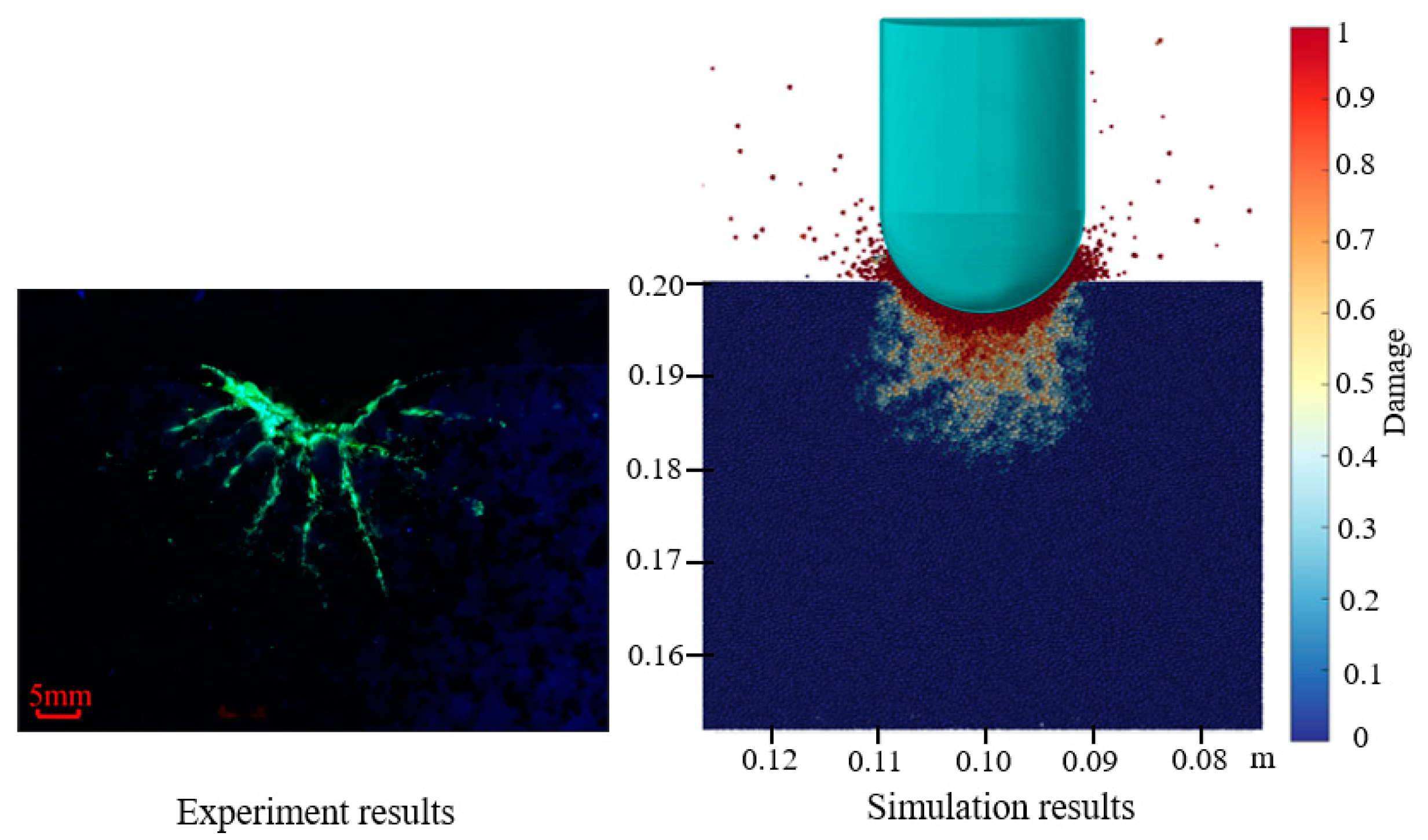
3.2. Validation
4. Analysis of the Rock Breaking Process
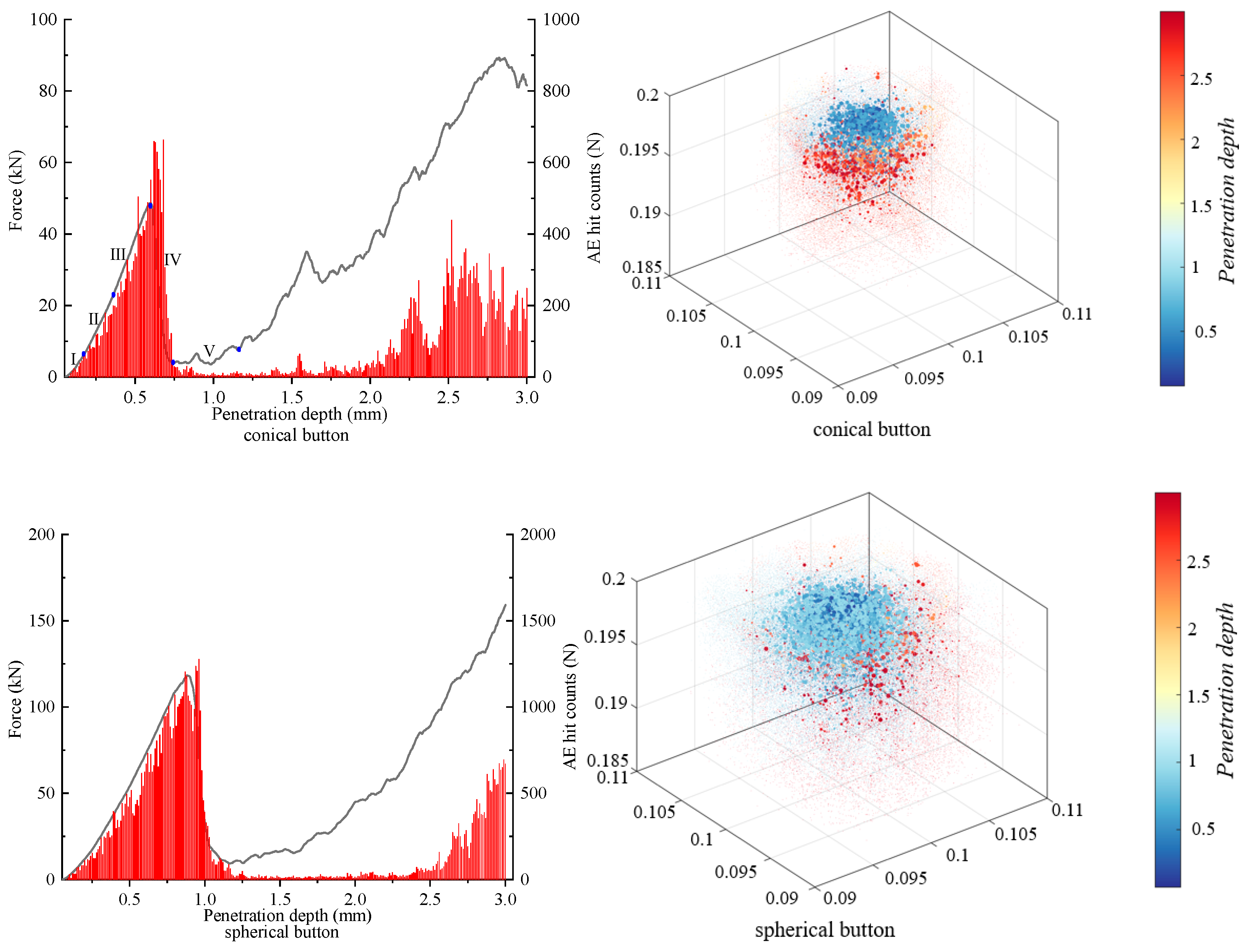
4.1. Force–Penetration Depth Curve and AE Events
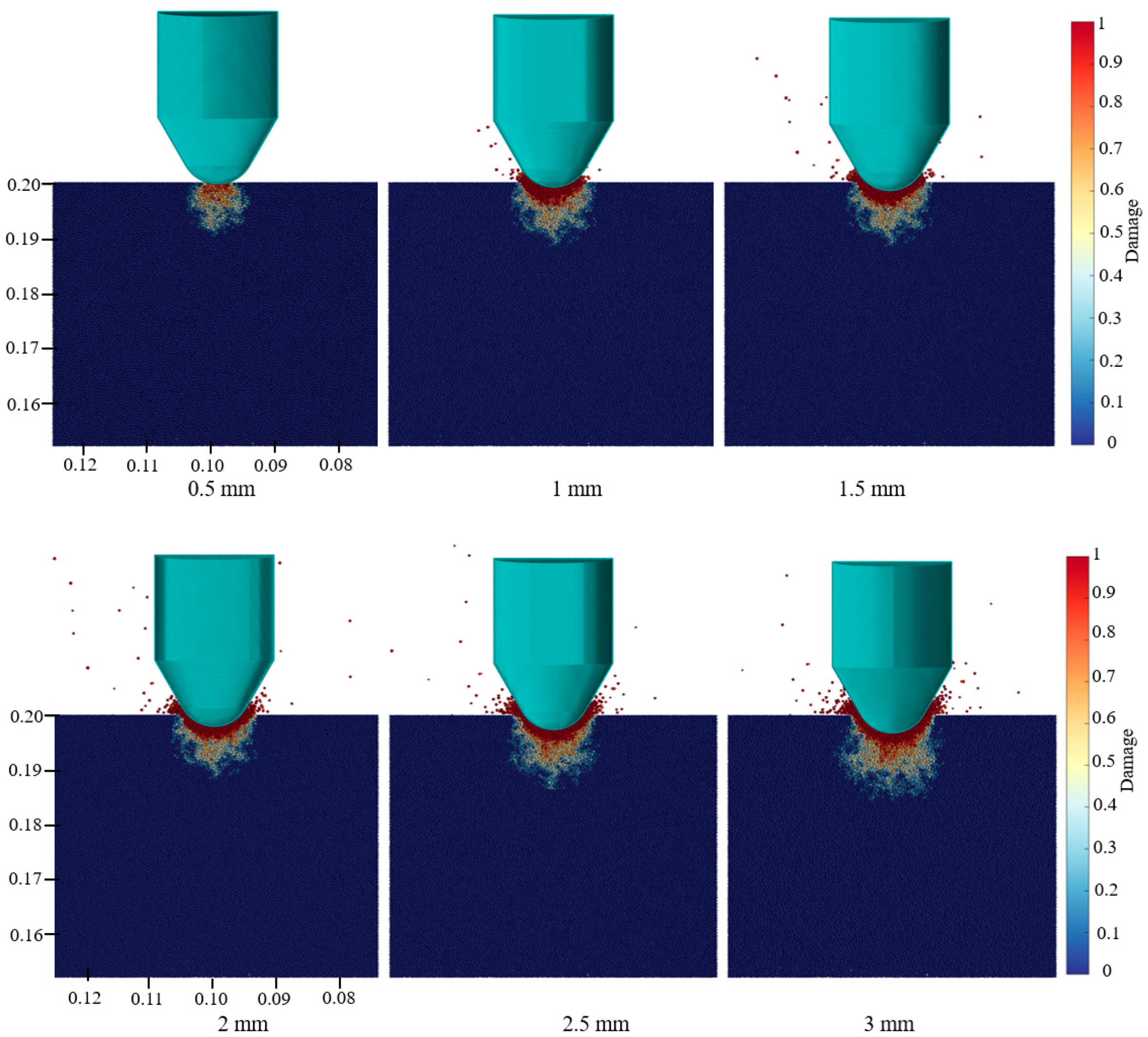
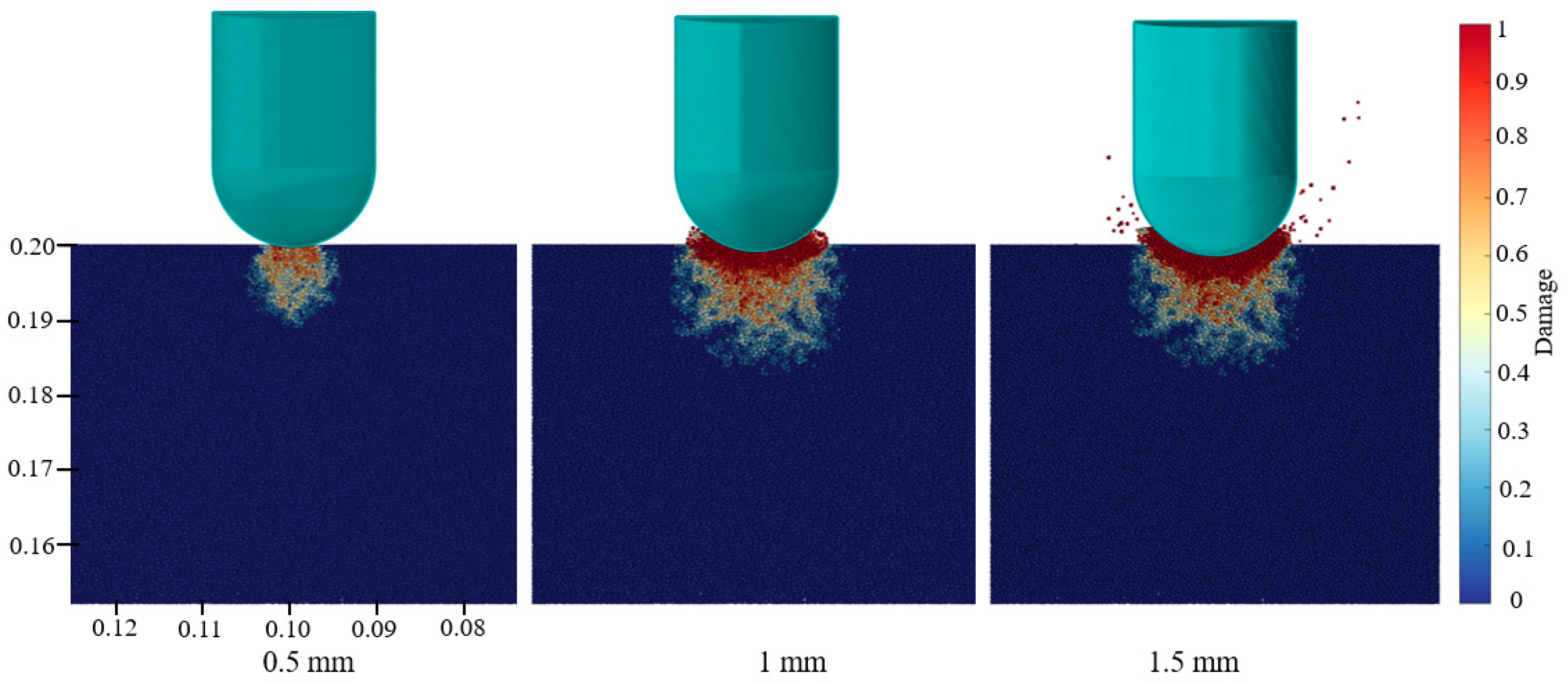
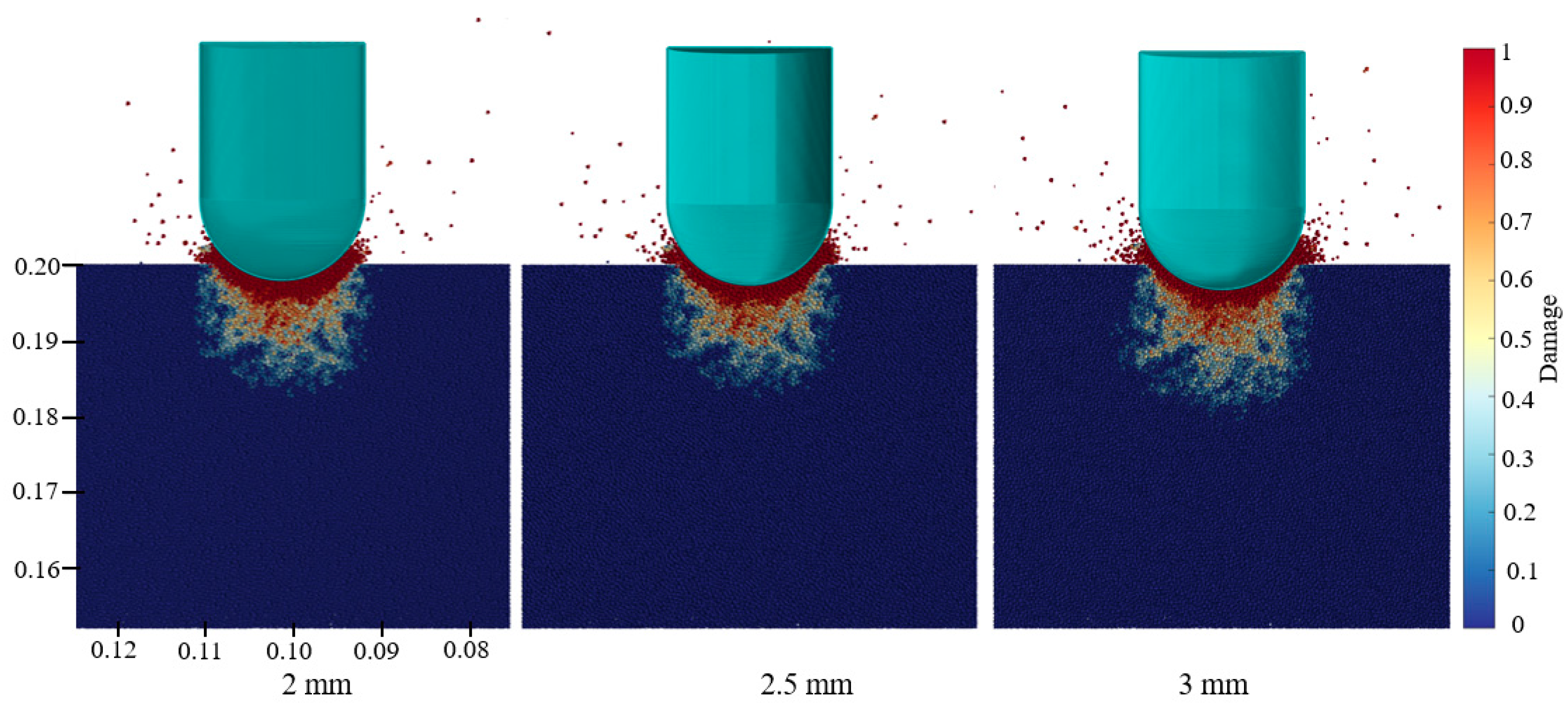
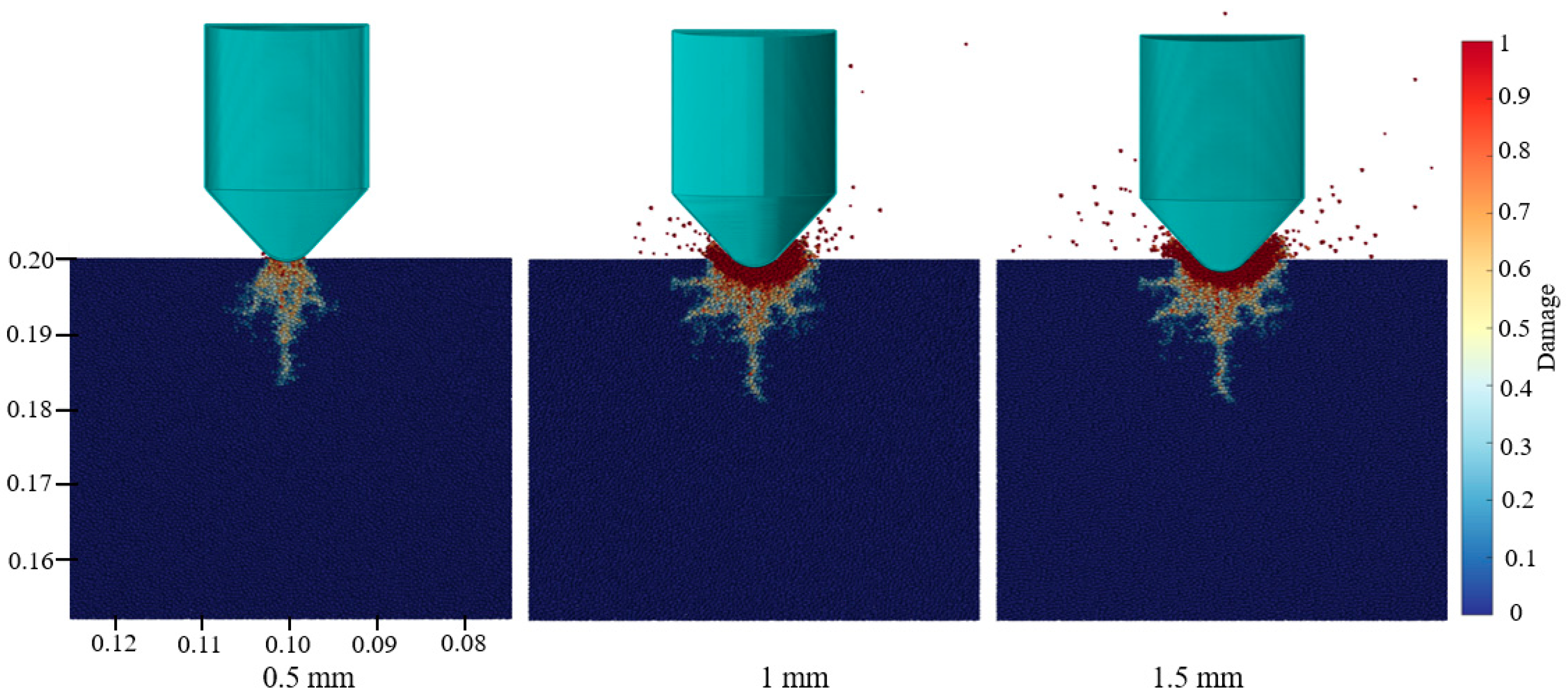
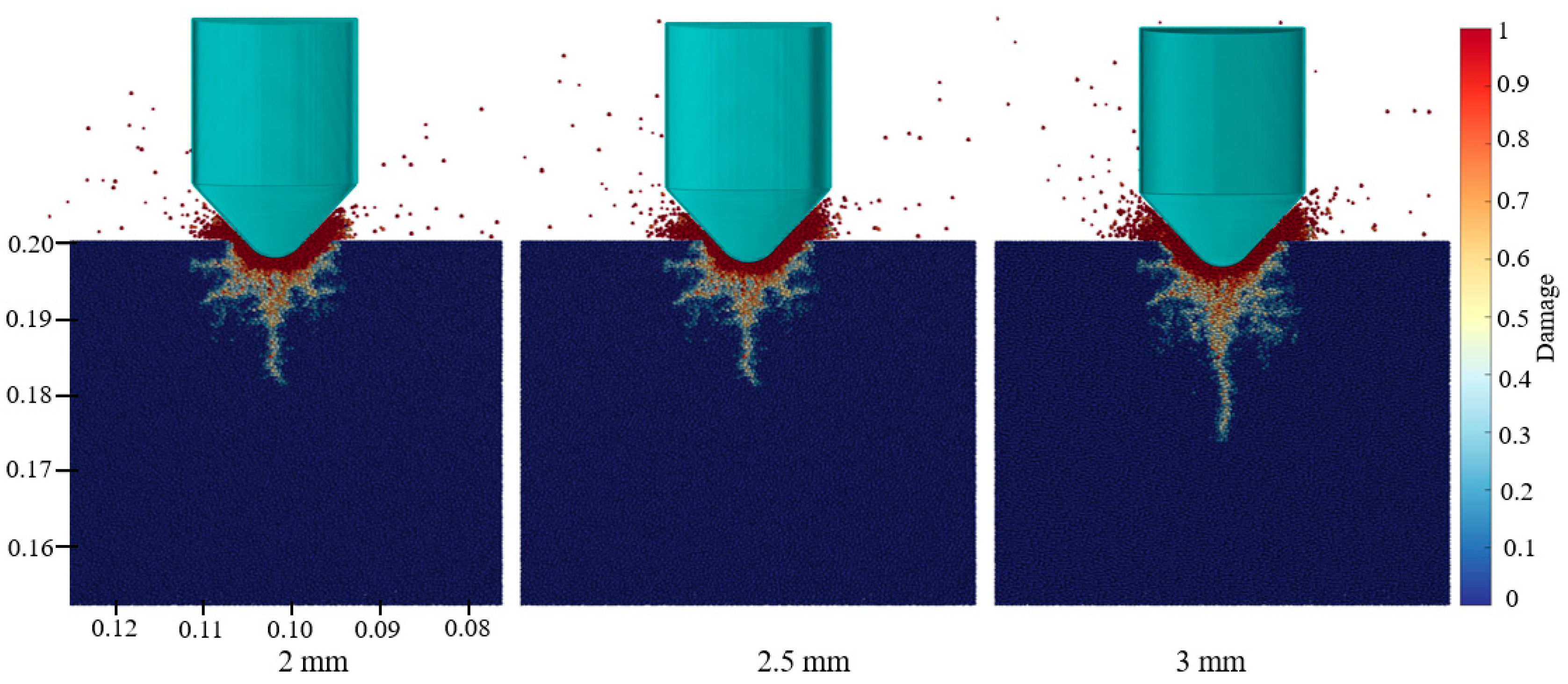
4.2. Crack Propagation Pattern
4.3. Stress Distribution
5. Cutting Performance Evaluation
5.1. Penetration Index
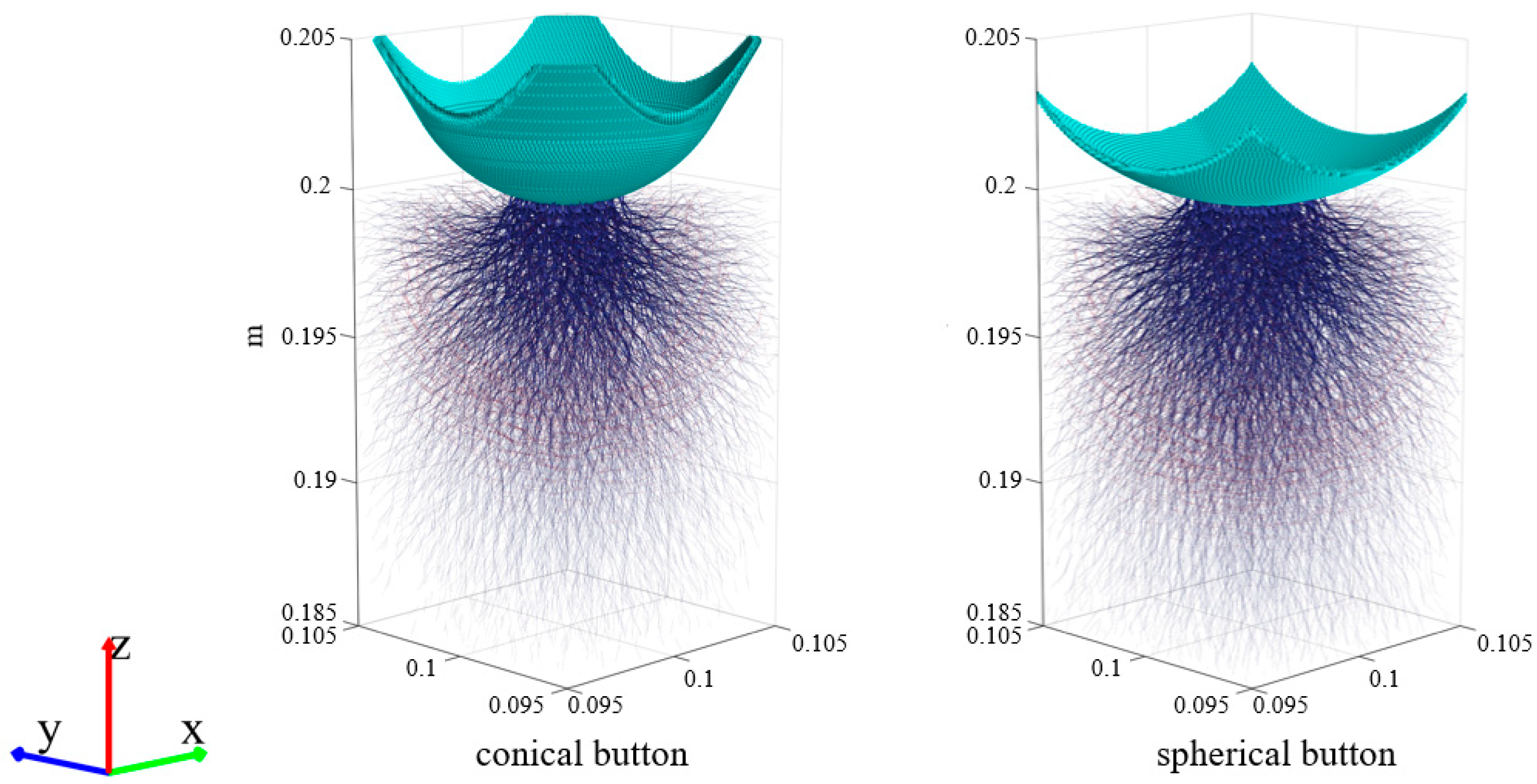
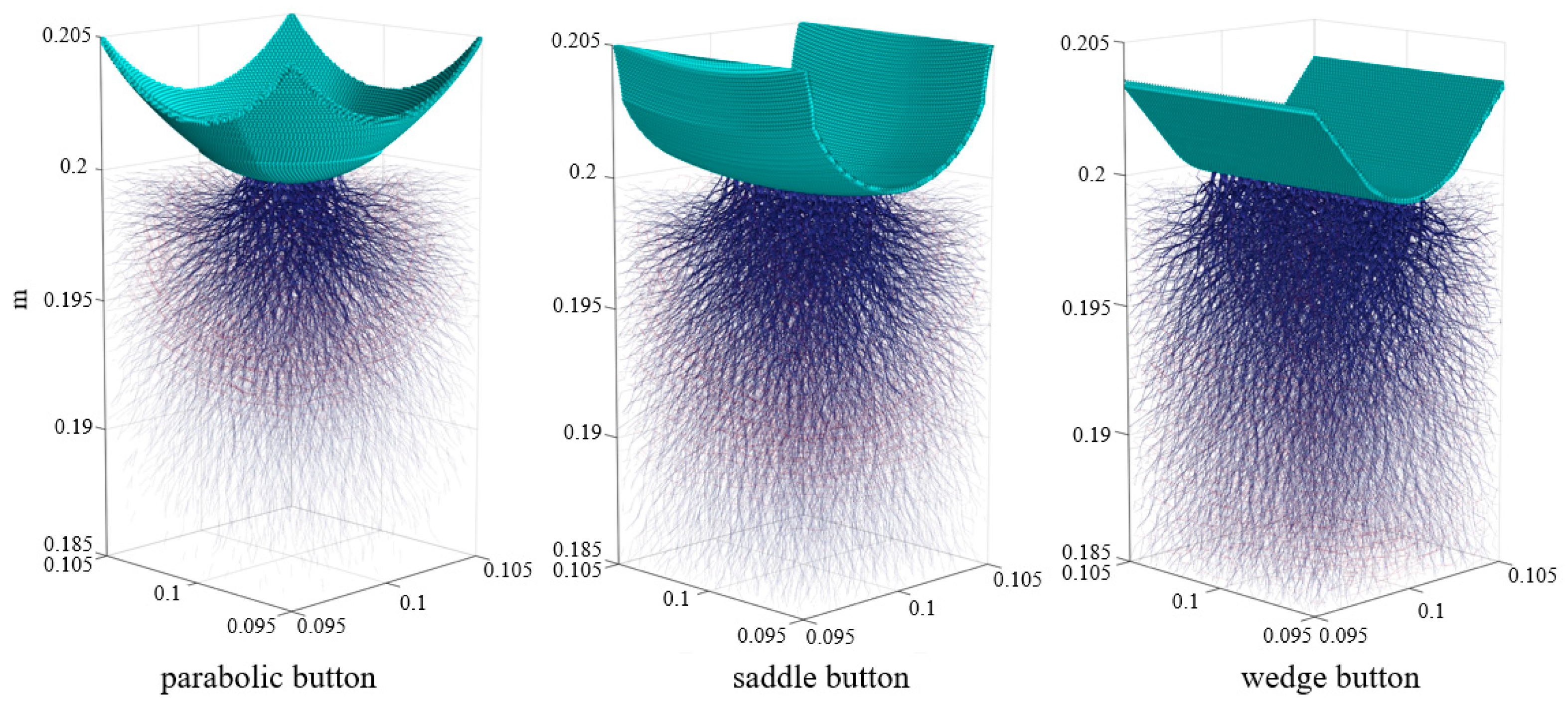
5.2. Crack Pattern
5.3. Specific Energy
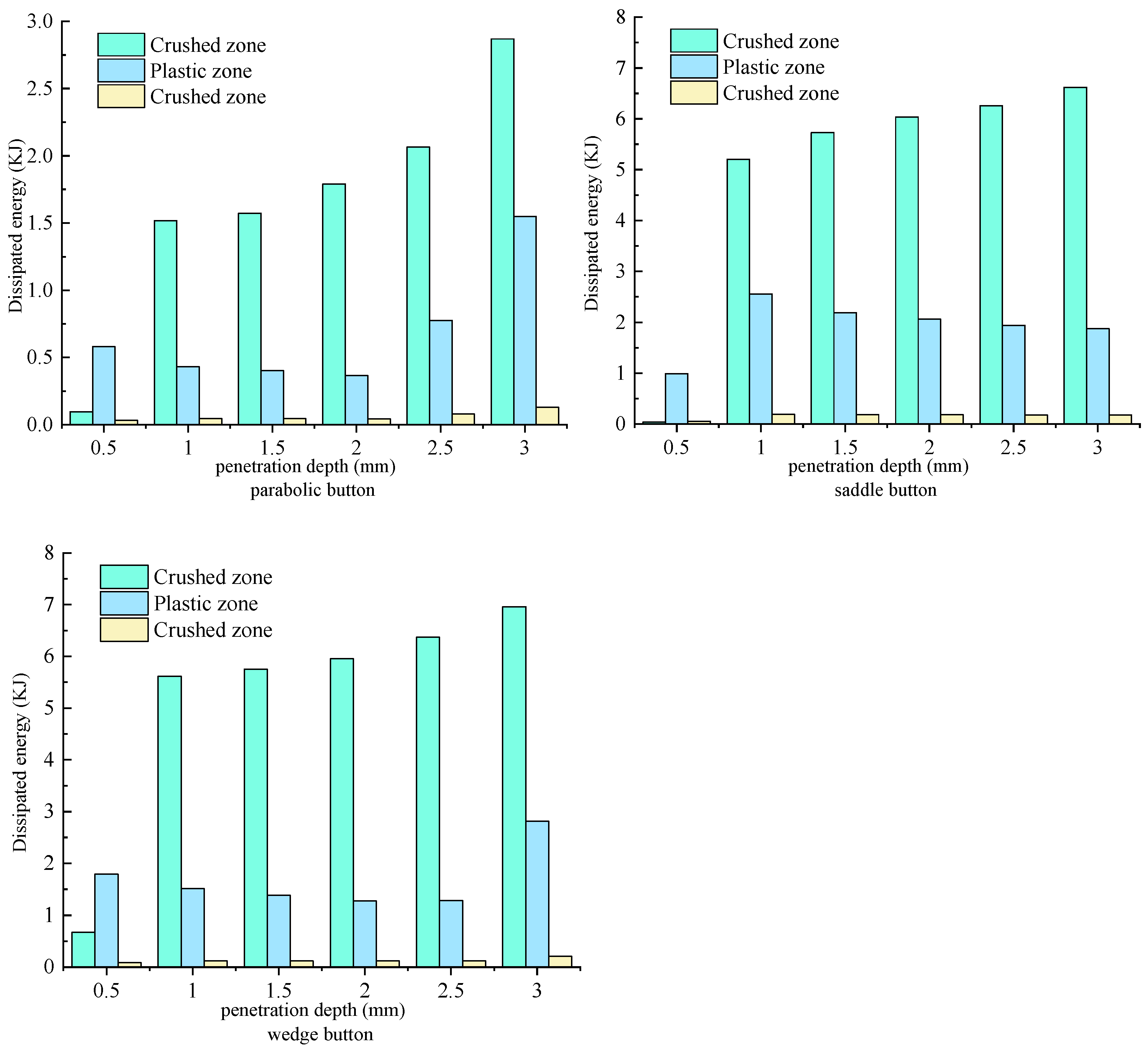
5.4. Energy Dissipation Distribution
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kujundžić, T.; Korman, T.; Macenić, M. State of the art of drilling large diameter boreholes for deposition of high level waste and spent nuclear fuel. Rud.-Geološko-Naft. Zb. 2012, 24, 49–59. [Google Scholar]
- Autio, J.; Kirkkomäki, T. Boring of Full Scale Deposition Holes Using a Novel Dry Blind Boring Method; Report POSIVA-96-07; Posiva Oy: Eurajoki, Finland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, C.; Johansson, Å. Boring of Full Scale Deposition Holes at the Äspö Hard Rock Laboratory. Operational Experiences Including Boring Performance and a Work Time Analysis; Svensk Kärnbränslehantering AB SWECO: Solna, Sweden, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Yin, L.; Zhang, H.; Gong, Q. Rock Fragmentation Mechanism and Efficiency Under Inserted-tooth Roller Cutter by Rotary Cutting Test. China J. Highw. Transp. 2018, 31, 150–159. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.; Huang, X.; Gao, M.; Pang, J. Numerical Discrete Element Analyses for Rock-Breaking Effects of Inserted-Tooth Hob and Cooperative Mechanism Between the Inserted Tooth. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2023, 41, 1325–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.Q. Some Basic Problems in Rock Breakage by Blasting and by Indentation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Luleå, Luleå, Sweden, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Lindqvist, P.A. Rock Fragmentation by Indentation and Disc Cutting. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Luleå, Luleå, Sweden, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, S.S.; Goldsmith, W. Investigation of Crack Formation During Loading of Brittle Rock. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 1990, 23, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.S. Investigations of Pneumatic Percussive Processes Involving Rocks. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, N.G.W.; Hood, M.; Tsai, F. Obervations of crack growth in hard rock loaded by an indenter. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1984, 21, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, B.; Xia, Y.; Lin, L.; Zhang, X.; He, Y.; Liu, Y. Experimental study on the adaptability of cutters with different blade widths under hard rock and extremely hard rock conditions. Acta Geotech. 2020, 15, 3283–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Yang, W.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Gao, M. Experimental investigation on hard rock fragmentation of inserted tooth cutter using a newly designed indentation testing apparatus. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. Numerical Modelling of the Rock Fragmentation Process by Mechanical Tools. Ph.D. Thesis, Luleå University of Technology, Luleå, Sweden, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.H.; Labuz, J.F. Indentation of rock by wedge-shaped tools. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2006, 43, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, G.; Song, H.; Kang, Y. Experimental investigation of deformation and failure mechanisms in rock under indentation by digital image correlation. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2012, 96, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zhang, H.; Fu, D.; Kang, Y.; Huang, G.; Qu, C.; Cai, Z. Experimental study on damage evolution of rock under uniform and concentrated loading conditions using digital image correlation. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2013, 36, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Yao, W.; Xia, K.; Li, Z. Investigation of the rate dependence of fracture propagation in rocks using digital image correlation (DIC) method. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2015, 138, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.J.; Gong, Q.M.; Ma, H.S.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, X. Use of indentation tests to study the influence of confining stress on rock fragmentation by a TBM cutter. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2014, 72, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Zheng, J.; Ren, J. Effect of loading rate on failure characteristics of asphalt mixtures using acoustic emission technique. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 364, 129835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.B.; Yao, X.H.; Gong, Q.M.; Ma, H.; Li, X. Comparison study on rock crack pattern under a single normal and inclined disc cutter by linear cutting experiments. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2015, 50, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, K.; Zhang, C.; Lv, X. 3D numerical simulation study of rock breaking of the wavy PDC cutter and field verification. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 203, 108578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Wang, W.; Fan, L.; Zha, C.; Li, J.; Liu, G. Experimental and numerical investigations on rock-breaking mechanism of rotary percussion drilling with a single PDC cutter. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazerani, T.; Zhao, J. Micromechanical parameters in bonded particle method for modelling of brittle material failure. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2010, 34, 1877–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wong, L.N.Y.; Teh, C.I.; Li, Z. Modeling Micro-cracking Behavior of Bukit Timah Granite Using Grain-Based Model. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2017, 51, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.N.Y.; Peng, J. Numerical investigation of micro-cracking behavior of brittle rock containing a pore-like flaw under uniaxial compression. Int. J. Damage Mech. 2020, 29, 1543–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, J.H.; Yang, X.R.; Zhang, A.; Yu, M. Monte Carlo simulations of deformation behaviour of unbound granular materials based on a real aggregate library. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2023, 24, 2165650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Qian, G.P.; Yu, H.A.; Yao, D.; Shi, C.; Zhang, C. Evaluation of coarse aggregate movement and contact unbalanced force during asphalt mixture compaction process based on discrete element method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 328, 127004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.M.; Zhao, J.; Hefny, A.M. Numerical simulation of rock fragmentation process induced by two TBM cutters and cutter spacing optimization. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2006, 21, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Wong, L.N.Y. Cracking Processes in Rock-Like Material Containing a Single Flaw Under Uniaxial Compression: A Numerical Study Based on Parallel Bonded-Particle Model Approach. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2011, 45, 711–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Wong, L.N.Y. Crack Initiation, Propagation and Coalescence in Rock-Like Material Containing Two Flaws: A Numerical Study Based on Bonded-Particle Model Approach. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2012, 46, 1001–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.M.; Zhao, J.; Jiao, Y.Y. Numerical modeling of the effects of joint orientation on rock fragmentation by TBM cutters. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2005, 20, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.M.; Jiao, Y.Y.; Zhao, J. Numerical modelling of the effects of joint spacing on rock fragmentation by TBM cutters. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2006, 21, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, T.; Oh, J. A Study of Optimal Rock-Cutting Conditions for Hard Rock TBM Using the Discrete Element Method. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2012, 45, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.P.; Zhai, S.F.; Bi, J. Two-Dimensional Numerical Simulation of Rock Fragmentation by TBM Cutting Tools in Mixed-Face Ground. Int. J. Geomech. 2018, 18, 06018004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Li, H.B.; Liu, Y.Q.; Zhou, Q.; Xia, X. Numerical simulation of rock fragmentation mechanisms subject to wedge penetration for TBMs. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 53, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, W.; He, X. The investigation of rock indentation simulation based on discrete element method. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 21, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Hu, D.; He, M.; Xia, Y. Comparative Study on Rock Breaking Performances by Arc and Wedge TBM Hob with Two Blades. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2021, 39, 4581–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Zhao, G.F.; Gong, Q.; Zhao, X.-B. Three-dimensional coupled numerical modelling of lab-level full-scale TBM disc cutting tests. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 114, 103997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Meng, D. 3D numerical modelling of rock fracture with a hybrid finite and cohesive element method. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2018, 199, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojek, J.; Oñate, E.; Labra, C.; Kargl, H. Discrete element simulation of rock cutting. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2011, 48, 996–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, O.; Akcin, N.A. Numerical simulation of rock cutting using the discrete element method. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2011, 48, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Zhou, X.P.; Gong, Q.M. The modelling of rock breakage process by TBM rolling cutters using 3D FEM-SPH coupled method. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2017, 61, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, H. A Fine Simulation Analysis of Rock Fragmentation Mechanism of TBM Disc Cutter with DEM. Comput. Exp. Simul. Eng. 2020, 75, 1189–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucgul, M.; Saunders, C.; Fielke, J.M. Comparison of the discrete element and finite element methods to model the interaction of soil and tool cutting edge. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 169, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Gong, Q.; Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Yin, L. Rock Chip Properties of TBM Penetration in Jointed Rock Masses Based on an Improved DICE2D Simulation. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2022, 55, 7547–7568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cundall, P.A.; Strack, O.D. A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies. Geotechnique 1979, 29, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potyondy, D.O.; Cundall, P.A. A bonded-particle model for rock. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2004, 41, 1329–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, C.; Shadabfar, M.; Zhang, J. Rock fragmentation induced by a TBM disc-cutter considering the effects of joints: A numerical simulation by DEM. Comput. Geotech. 2021, 136, 104230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Xu, W.J.; Liu, G.Y. A contact detection algorithm for triangle boundary in GPU-based DEM and its application in a large-scale landslide. Comput. Geotech. 2021, 138, 104371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Y.; Xu, W.J.; Sun, Q.C.; Govender, N. Study on the particle breakage of ballast based on a GPU accelerated discrete element method. Geosci. Front. 2020, 11, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labra, C.; Rojek, J.; Onate, E. Discrete/Finite Element Modelling of Rock Cutting with a TBM Disc Cutter. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2017, 50, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.M.; Cheatham, J.B. Analysis of the indentation of a compacting material by a perfectly rough wedge. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1972, 9, 475–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Micro Parameters | Macro Parameters from Experiments | Macro Parameters Predicted by Simulation |
|---|---|---|
| Cement effective modulus = 5.7 GPa | E = 23 GPa | E = 23 GPa |
| Ratio of cement normal to shear stiffness = 0.2 | ν = 0.19 | ν = 0.19 |
| Tensile strength = 28 MPa | UCS = 108 MPa | UCS = 106 MPa |
| Cohesion strength c = 50 MPa | BTS = 6.5 MPa | BTS = 6.5 MPa |
| Friction angle = 15° | ||
| Moment contribution coefficient = 0.5 | ||
| Bond−radius multiplier = 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Gong, Q.; Zhou, X.; Yin, L.; Ma, H. The Modelling of Rock Fragmentation Mechanisms by Carbide Buttons Using the 3D Discrete Element Method. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6090. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106090
Ma Y, Gong Q, Zhou X, Yin L, Ma H. The Modelling of Rock Fragmentation Mechanisms by Carbide Buttons Using the 3D Discrete Element Method. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(10):6090. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106090
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yanan, Qiuming Gong, Xiaoxiong Zhou, Lijun Yin, and Hongsu Ma. 2023. "The Modelling of Rock Fragmentation Mechanisms by Carbide Buttons Using the 3D Discrete Element Method" Applied Sciences 13, no. 10: 6090. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106090
APA StyleMa, Y., Gong, Q., Zhou, X., Yin, L., & Ma, H. (2023). The Modelling of Rock Fragmentation Mechanisms by Carbide Buttons Using the 3D Discrete Element Method. Applied Sciences, 13(10), 6090. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106090





