Low Carbon Optimization of Deep Foundation Pit Support in Undulating Strata
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Engineering Situation
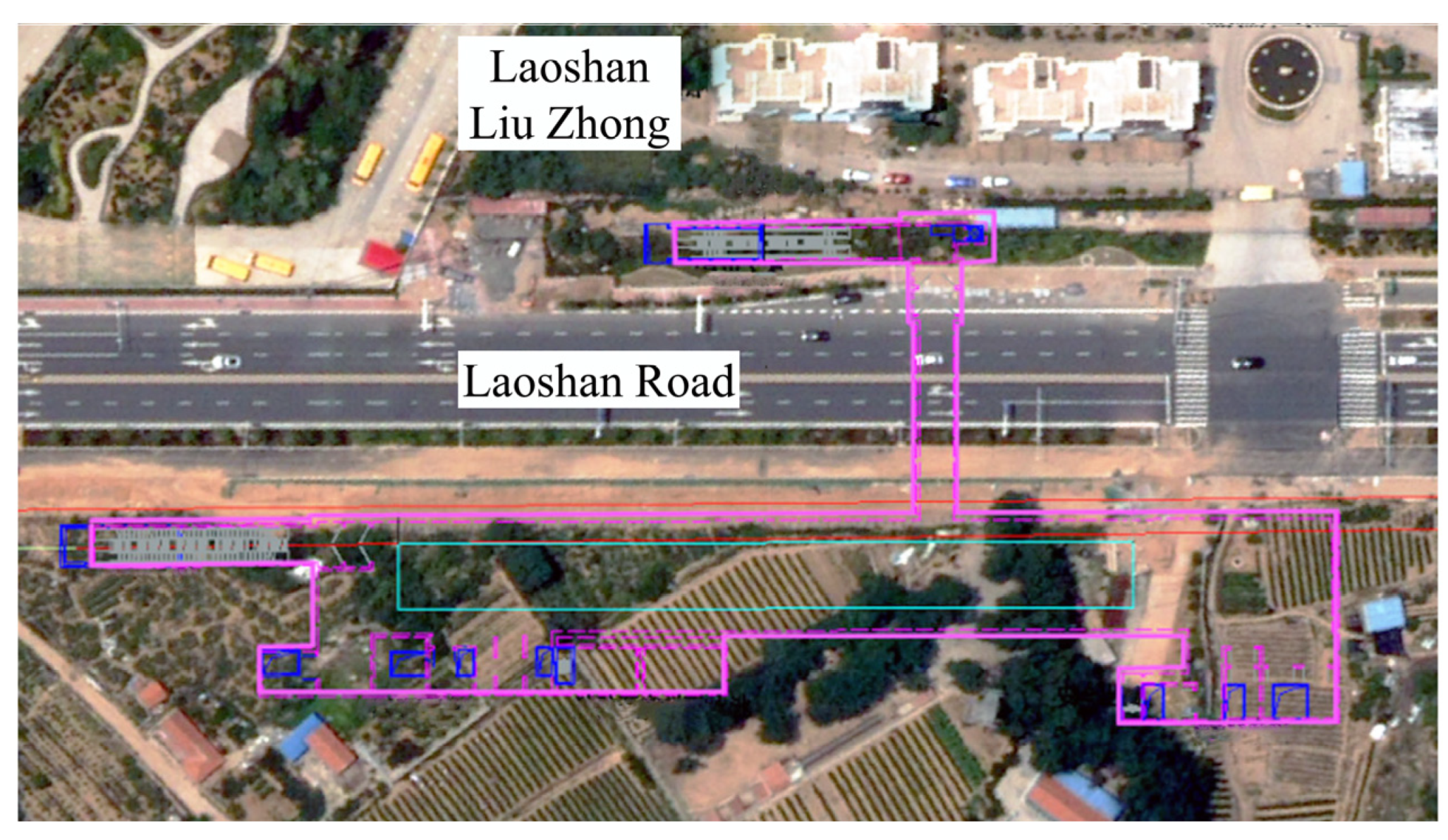
2.1. Site Condition
2.2. Support Design Scheme
3. Foundation Pit Support Scheme Design
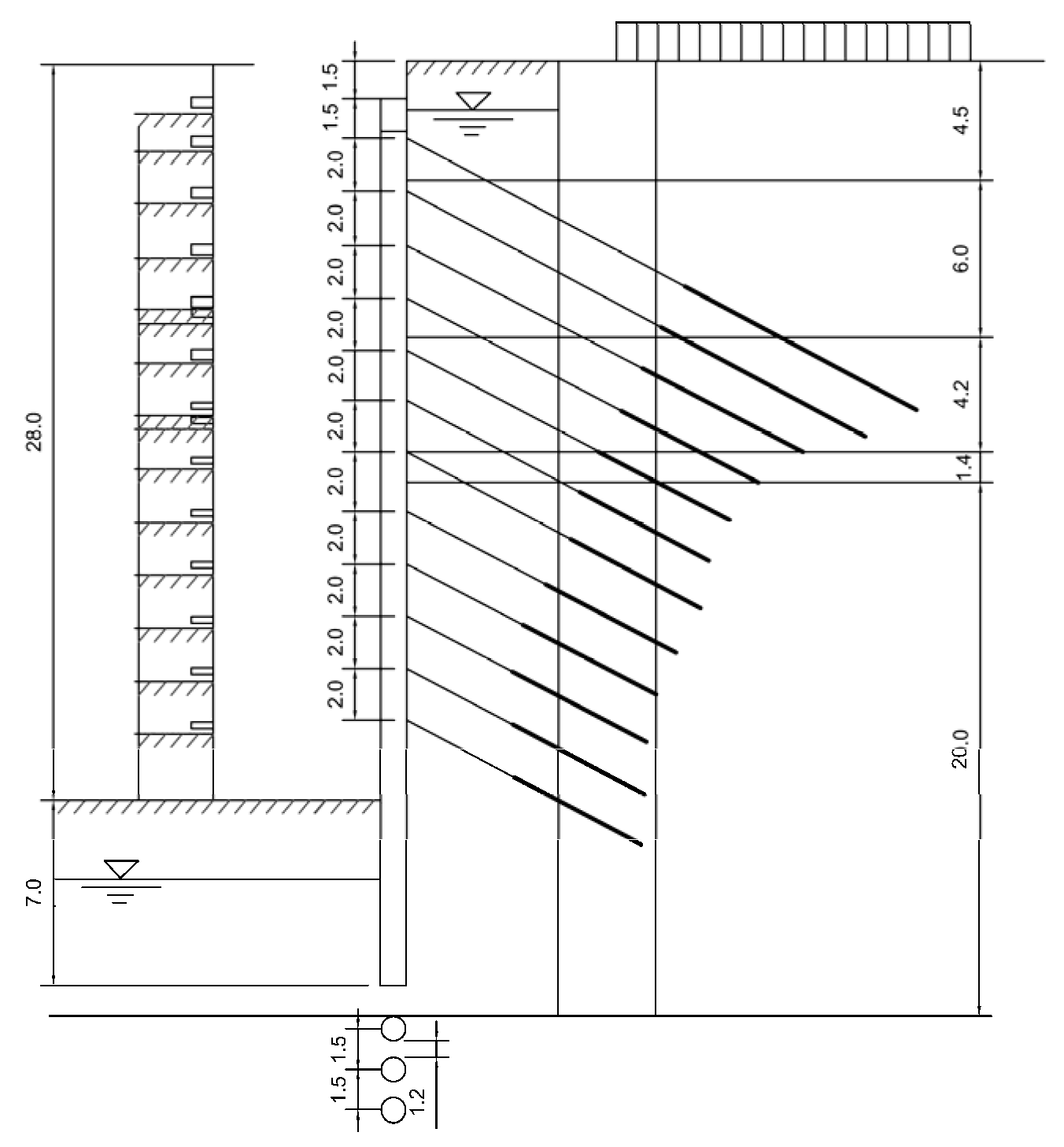
3.1. Theoretical Calculation Design
3.1.1. Calculation Model
3.1.2. Calculation Working Conditions
3.2. Numerical Simulation Optimization
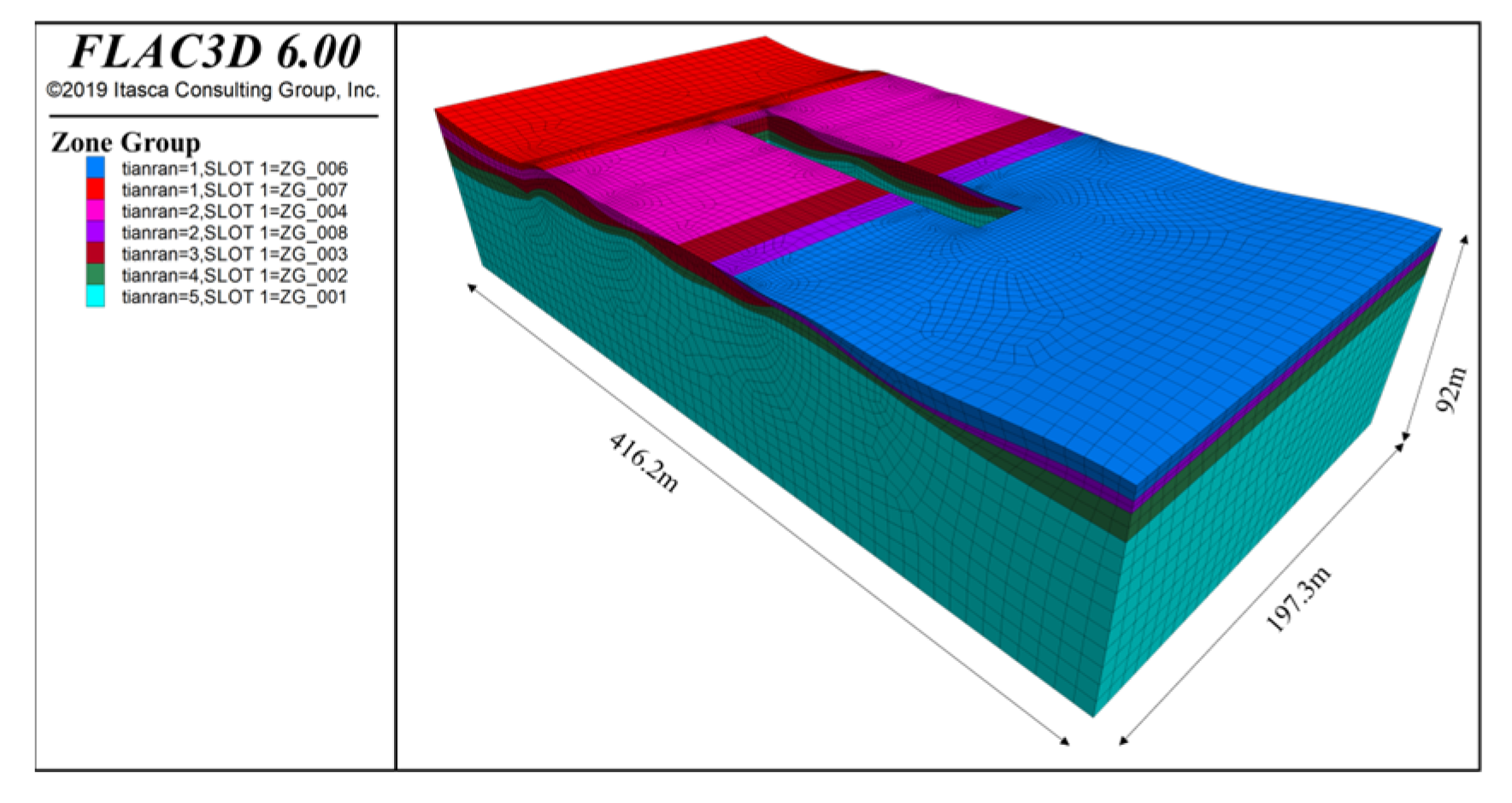
3.2.1. Numerical Simulation Optimization Scheme
3.2.2. Foundation Pit Numerical Model
- (1)
- Soil layer model and parameters
- (2)
- Structural unit parameters
4. Calculation Results Comparison Analysis
4.1. Theoretical Design Calculation Results Analysis
4.1.1. Foundation Pit Deformation Analysis
4.1.2. Internal Force Analysis of Deep Foundation Pit Support
4.1.3. Overall Stability Analysis of Deep Foundation Pit
4.2. Analysis of Numerical Simulation Optimization
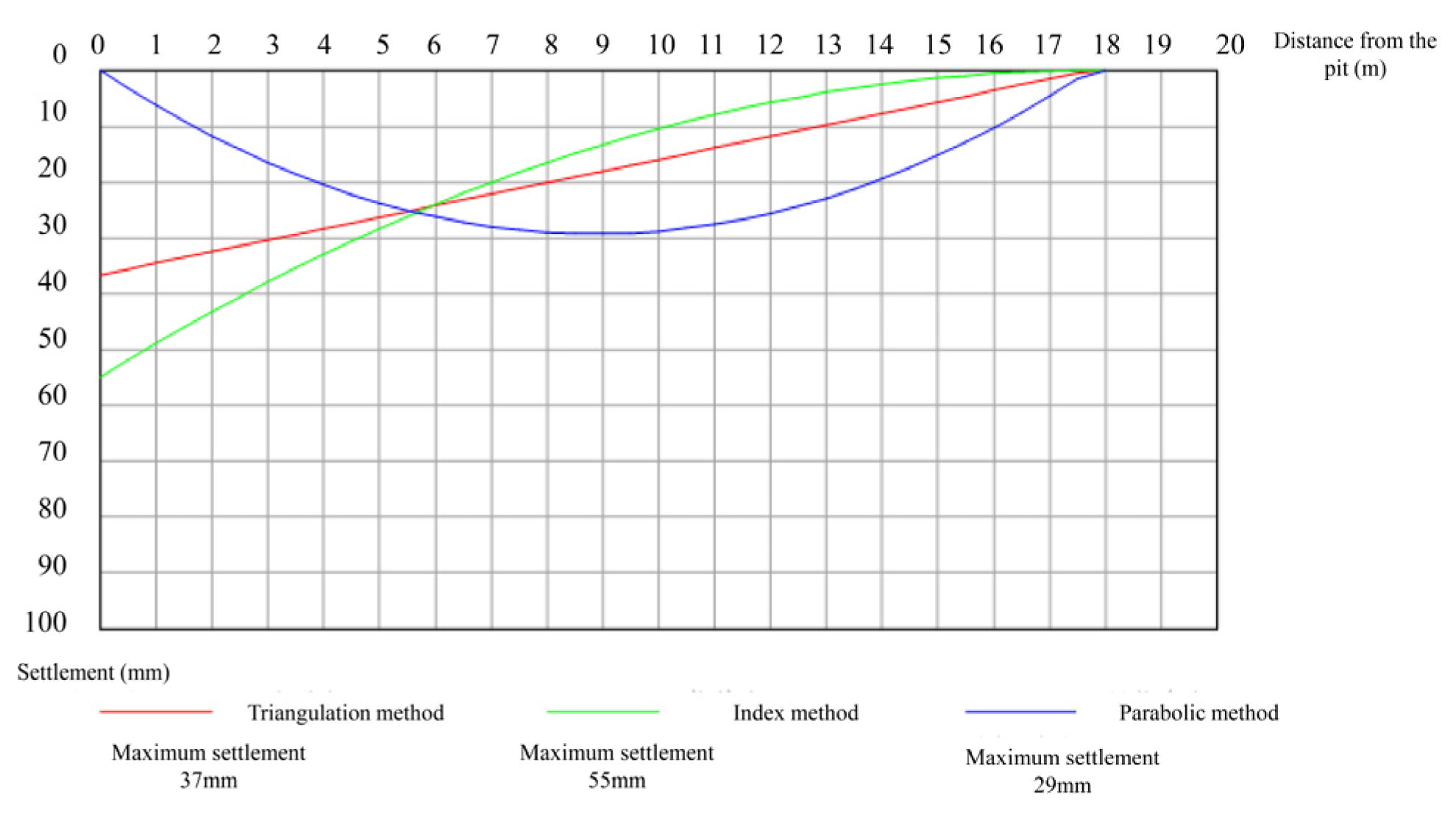
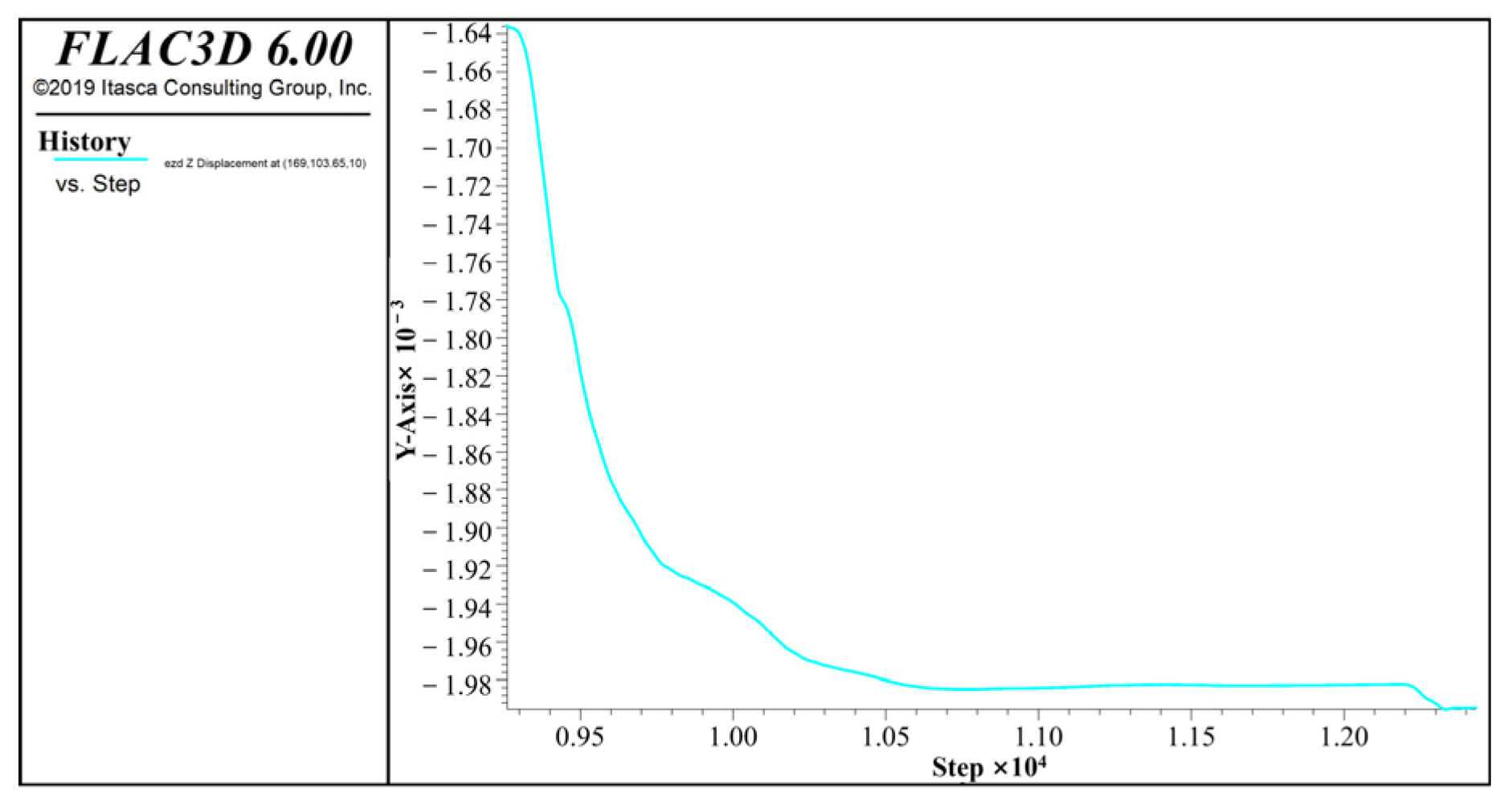
4.2.1. Results of Foundation Pit Settlement
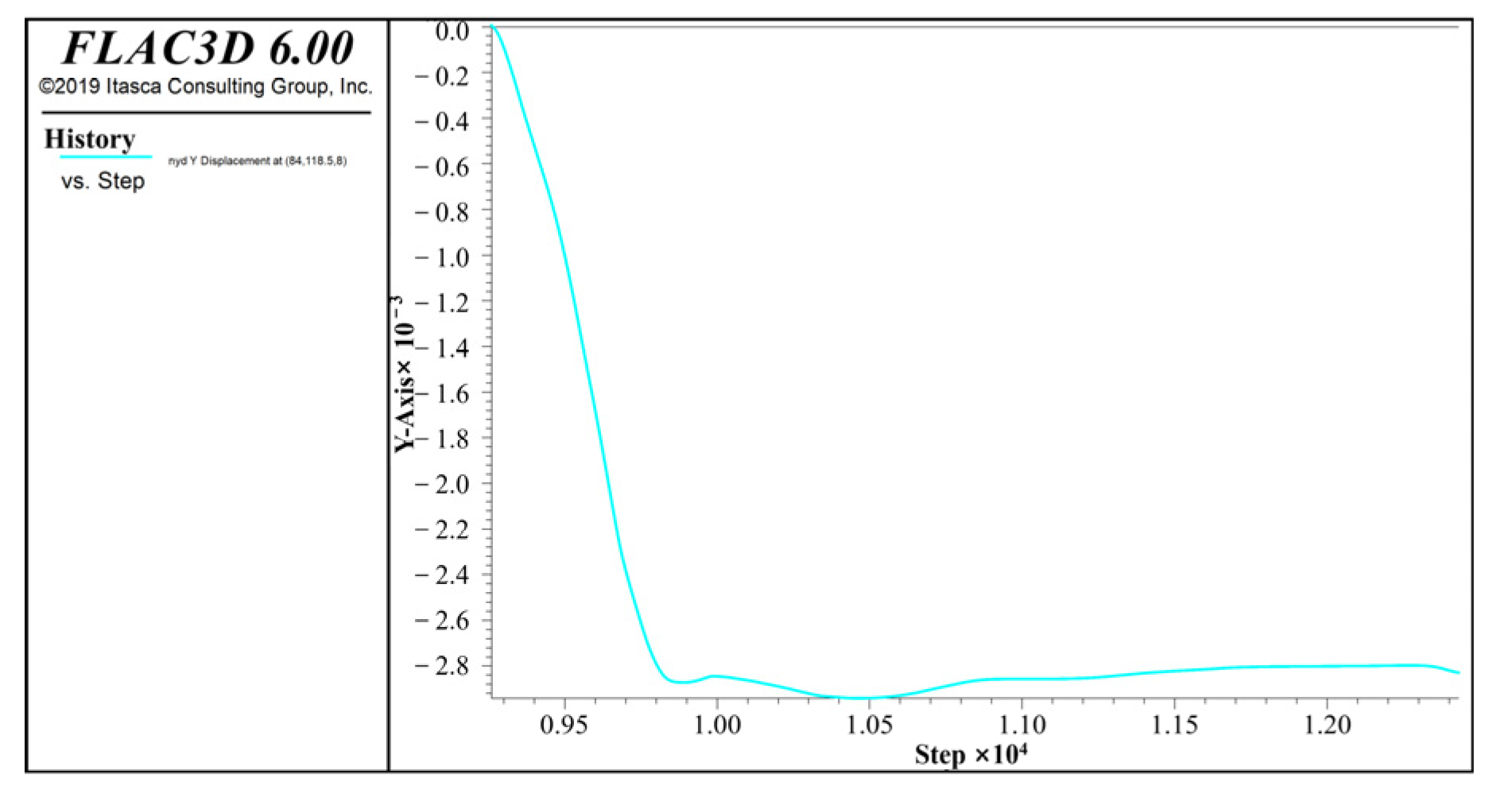
4.2.2. Horizontal Displacement of Foundation Pit Sidewalls by Numerical Calculation
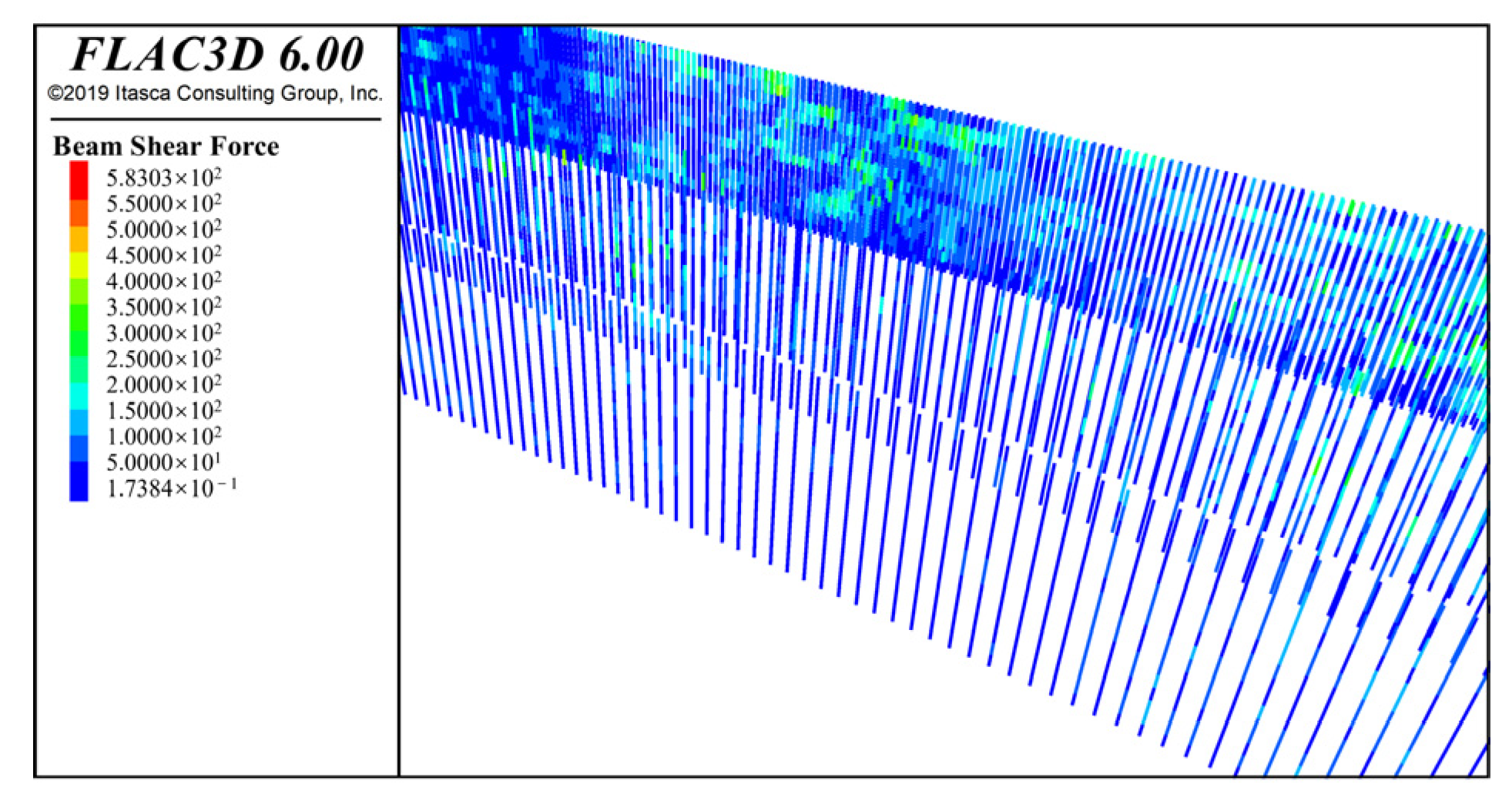
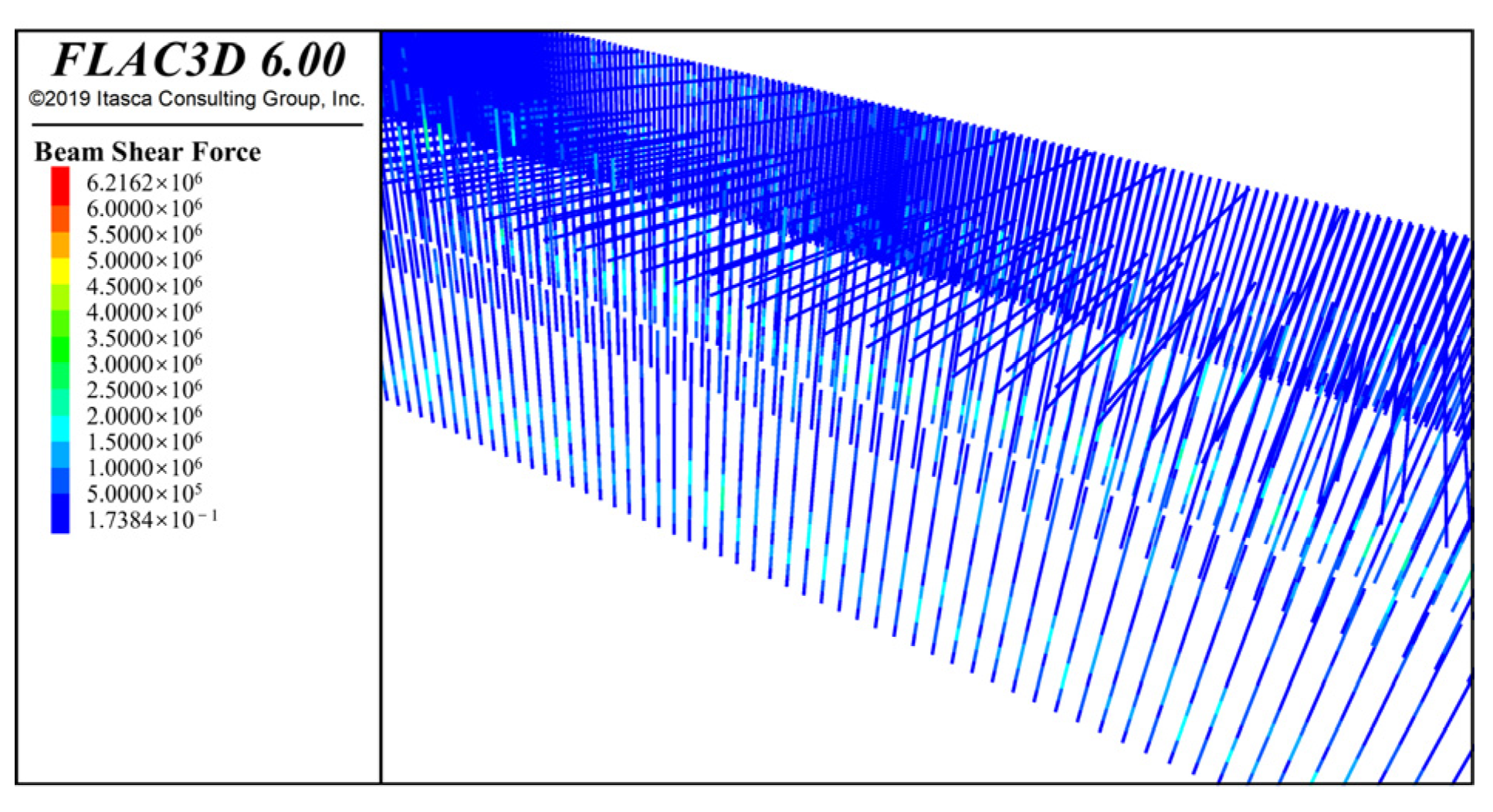
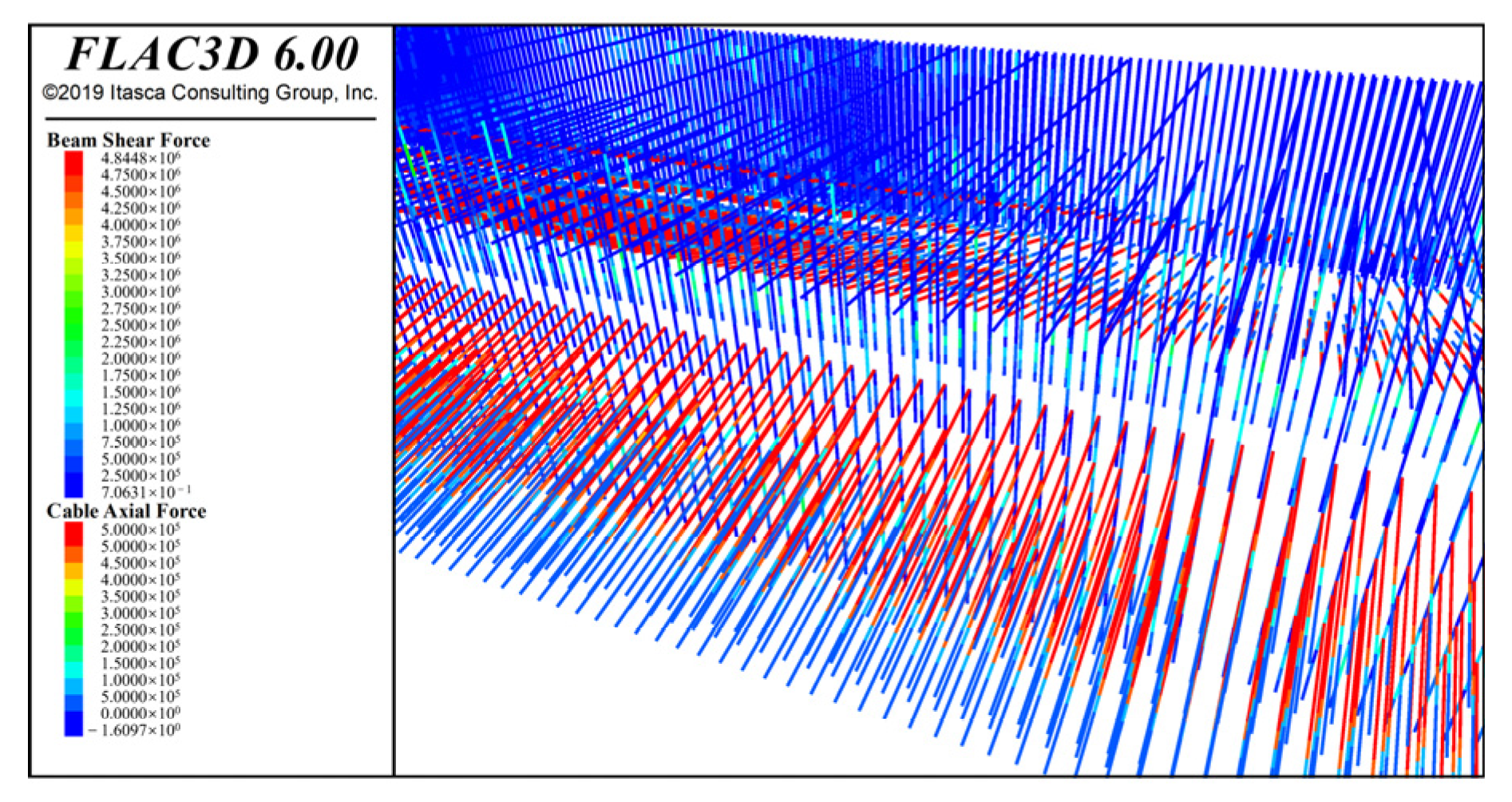
4.2.3. Results of the Internal Force of Structural Element Simulation
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Computer-aided software is used to design the supporting structure of the deep foundation pit. The maximum settlement of the foundation pit is 55 mm, which is less than 0.2% of the depth of the foundation pit (56 mm). The maximum horizontal displacement of the foundation pit is 33.94 mm, which is less than 0.3% of the depth of the foundation pit (84 mm). The maximum shear force of the supporting pile is 1341.8 kN, and the maximum internal force of the anchor rod is 1295.88 kN;
- (2)
- The numerical simulation method is used to establish a three-dimensional deep foundation pit model, and the support scheme is optimized. The final settlement of the surface, the maximum horizontal displacement, and the force of the support structure are less than the design value of the theoretical calculation;
- (3)
- This paper combines computer-aided design software and numerical simulation software and plays to their respective advantages. Computer-aided design software has great advantages in the selection of supporting forms, and numerical simulation can intuitively reveal the stress and displacement changes of the foundation pit structure. The combination of the two can not only improve efficiency but also reduce the waste of resources. While improving the design economy, it greatly saves resources and achieves low-carbon design.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, G.; Zhang, T.; Cheng, X.S. Effect of foundation piles on excavation stability and its calculation. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2017, 39, 5–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Li, J.; Tang, Y. Basal-heave stability of excavations considering groundwater level and pore water pressure fluctuations by upper bound method. Rock Soil Mech. 2011, 32, 3653. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, N.; Hui, M.L. The research of the single row piles designing in deep foundation pit. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Advanced Engineering Materials and Technology, Guangzhou, China, 22–23 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.X.; Yang, Q.; Feng, Z.J. Deep foundation pit supporting structure considering pile-soil interaction Elastic foundation beam method. Highw. Traffic Technol. (Appl. Technol. Ed.) 2020, 16, 140–142. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.Q.; Xu, J.B.; Yang, X.H.; Yan, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Tan, L.; Fei, D.; Li, J.; Luo, Y. Elastic Foundation Beam Solution of Tensile Flexible Retaining Wall. Int. J. Steel Struct. 2022, 22, 622–631. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Li, B.; Liu, D.; Han, X. Study on the Influence of Large Irregular Deep Foundation Pit Excavation on Adjacent Buildings in the Soft Soil. Area J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2023, 1, 140–145. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Niu, J.; Li, Z.; Feng, C.; Wang, B.; Chen, K. Combined support system and calculation model for deep foundation pits in fill soil areas. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhou, T.; Zhong, Y.; Ji, X.; Sun, S.; Lin, J.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.; Guo, C.; Lin, H. Influence Law of Foundation Pit Excavation on Stress of Surrounding Tunnel Bolt. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.S.; Li, Z.M. Analysis of Deep Foundation Pit Pile-Anchor Supporting System Based on FLAC3D. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 1699292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.S.; Liu, Z.D. Optimization Design of Bracing Project of Deep Foundation Pit at the First Yangtza River’s. Build. Struct. 2000, 11, 51–54. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.; Xin, Y.H. Optimum Design for The Bracing Structure with Double-row Piles of Deep Foundation Pit. Optim. Cap. Constr. 2001, 6, 32–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.Q. Spoke Method of Soil-Nail Bracing Structure and Its Optimization. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi’an, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.M.; Wang, P.P.; Wang, L.J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.C. Deformation evolution law and optimization design of huge deep foundation pit excavation. J. Chang. Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 2022, 19, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.; Chen, L. Optimum selection of supporting scheme for deep foundation pit based on fuzzy mathematics theory. J. Jilin Jianzhu Univ. 2019, 36, 23–31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deng, R.; Zhou, L. Optimising the supporting structure of a bridge’s foundation pit based on hybrid neural network. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. 2022, 18, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Su, W.J.; Ding, L.Y.; Luo, H.; Love, P.E.D. Predicting Safety Risks in Deep Foundation Pits in Subway Infrastructure Projects: Support Vector Machine Approach. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2017, 31, 04017052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.B. Construction Risk Assessment of Deep Foundation Pit Projects Based on the Projection Pursuit Method and Improved Set Pair Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.C.; Bai, T.H. Construction Control System of Mechanical State of Metro Deep Foundation Pit in Soft Soil. Tunn. Constr. 2019, 39, 44–52. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Du, J.; Yang, J. Multi-Objective Optimization of Supporting Plan for Deep Foundation Using Entropy-Based Um-Dea; Czech Technical University in Prague-Central Library: Prague, Czech Republic, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, G.; Gong, X.N. Analysis of Lateral Displacement Law of Deep Foundation Pit Support in Soft Soil Based on Improved MSD Method. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5550214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.D.; Guan, C.S.; Zhou, J. Environmental Impact and Hazard Control Method on Deep Foundation Pit Supporting Engineering. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 2195, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Effect of genetic algorithm in optimizing deep foundation pit supporting structure. Arabian J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

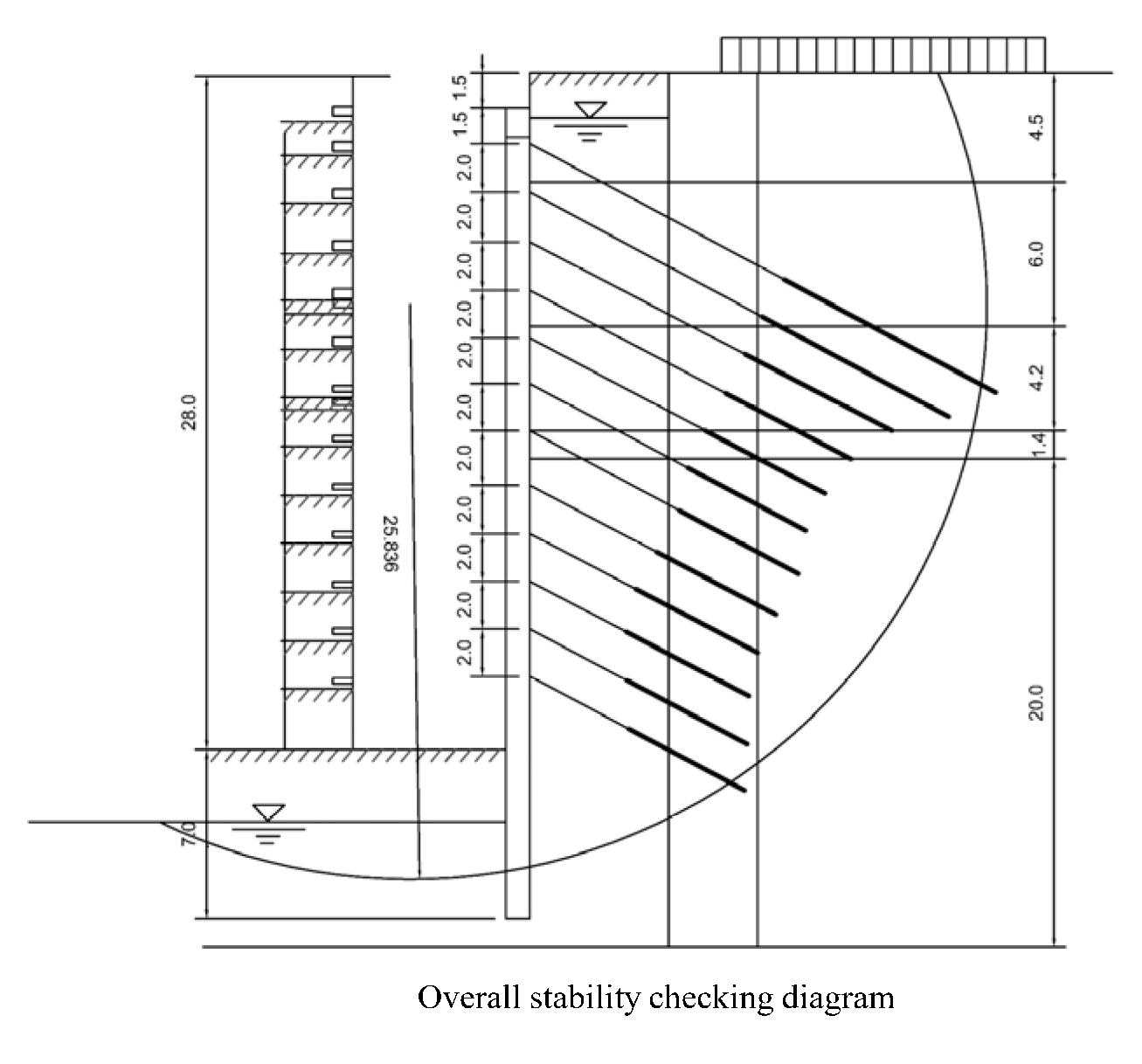

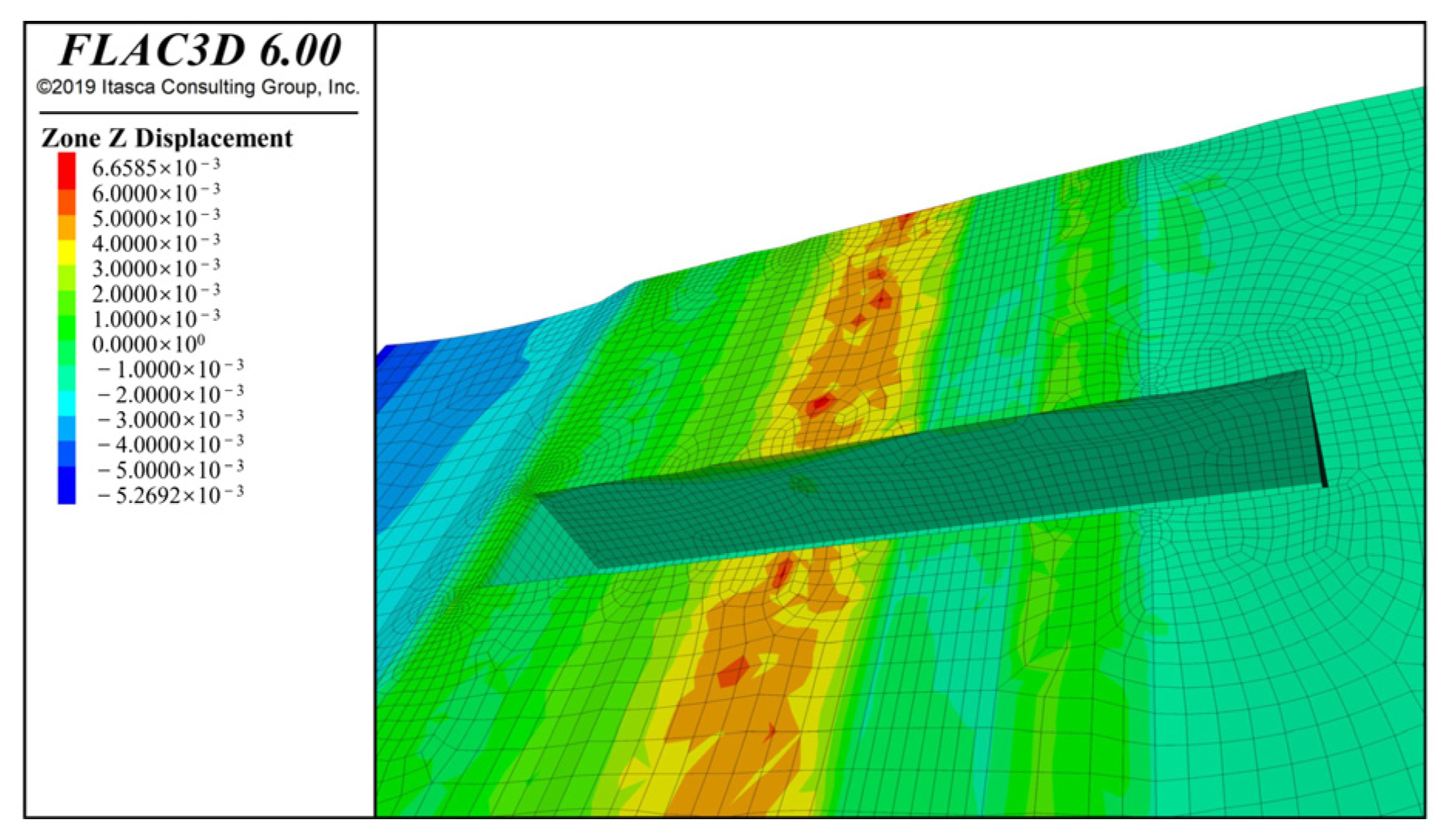
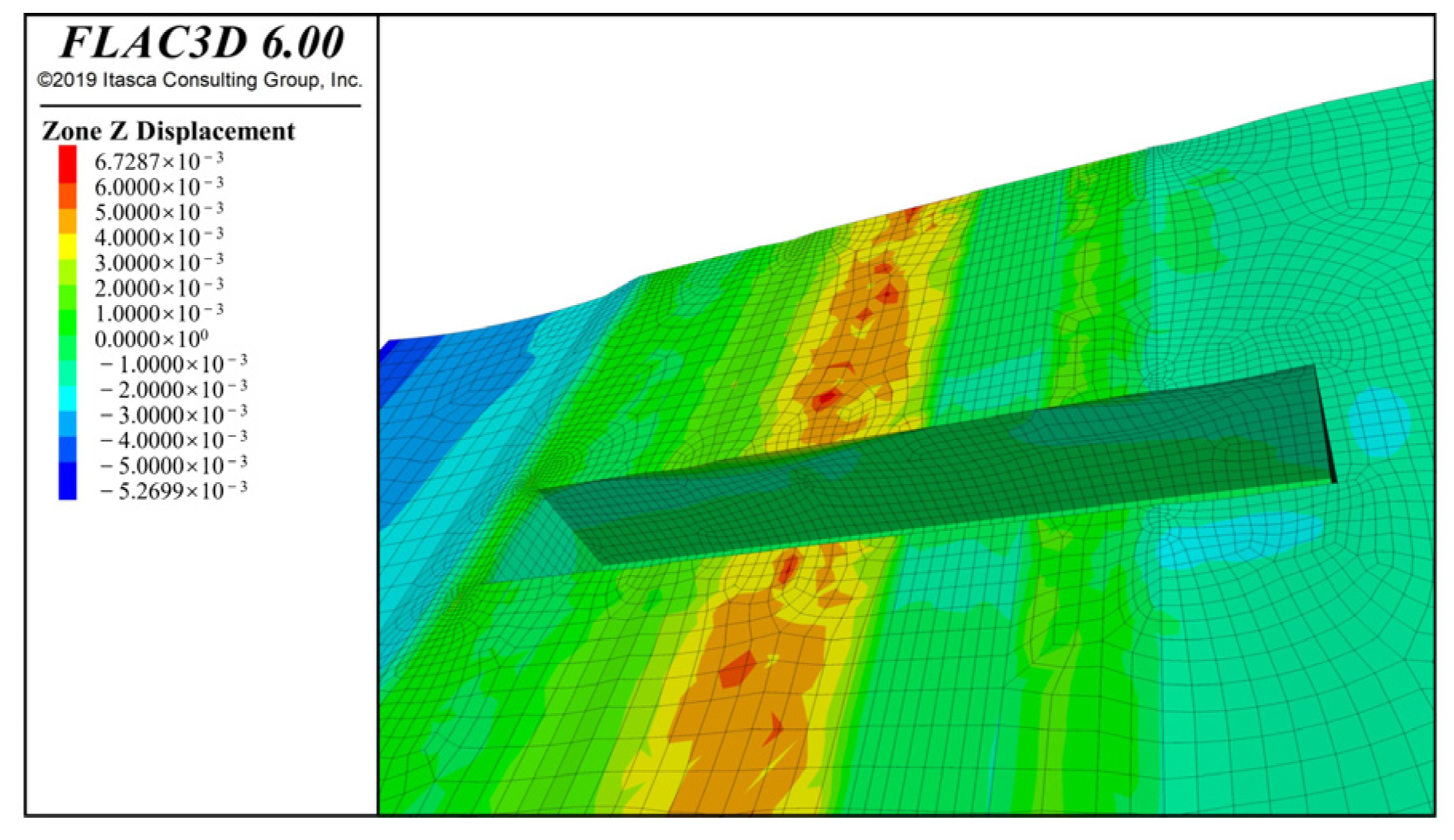
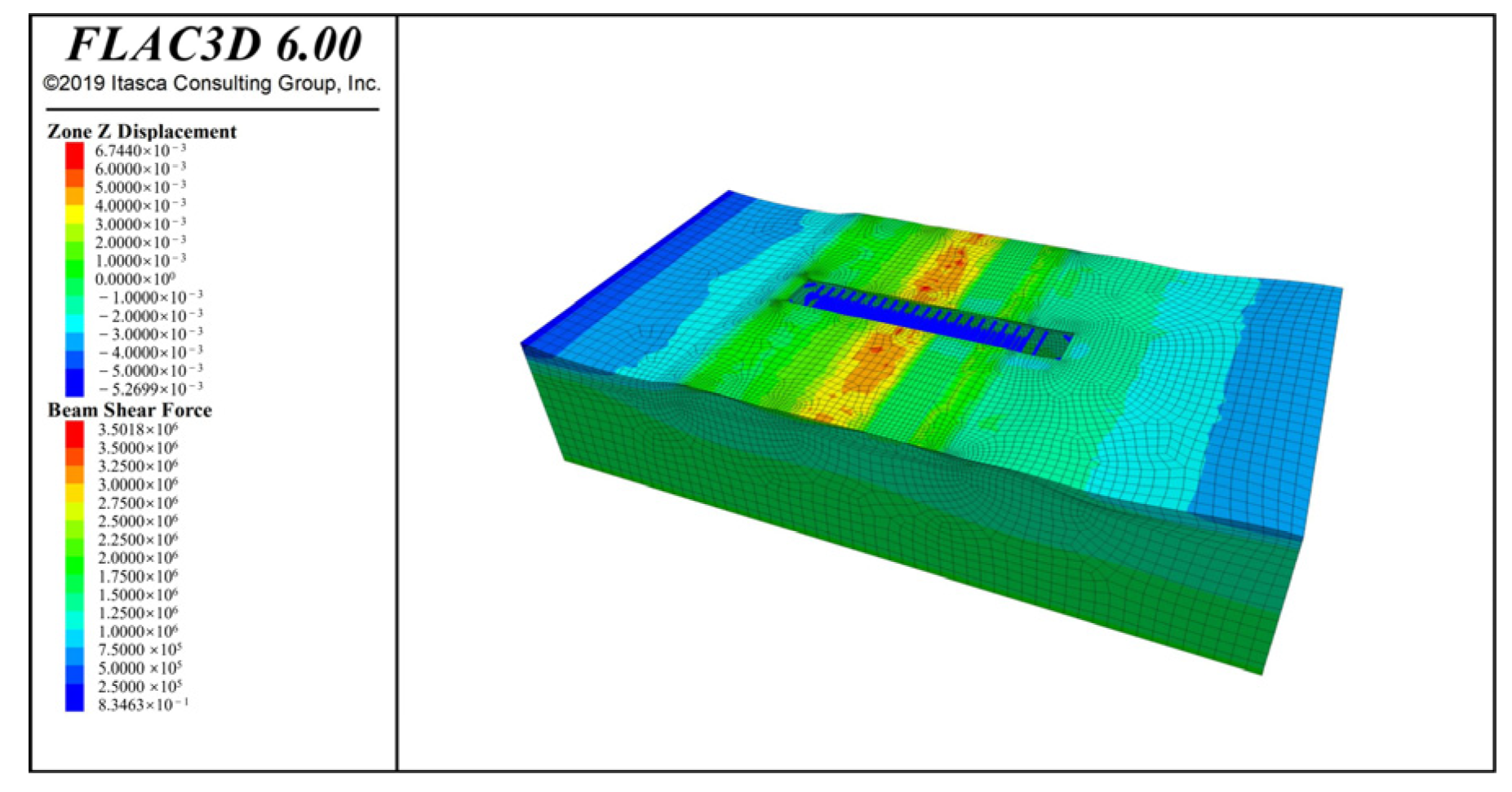
| No. | Hydrogeology | Depth/m | γ/(kN·m−3) | c/kPa | φ/° | qsik/kPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Plain fill | 4.5 | 18 | 16 | 20 | 20 |
| 2 | Coarse-grained sand with clayey soil | 4.2 | 20.5 | 9 | 38 | 120 |
| 3 | Strongly weathered granite | 1.4 | 23 | 7.5 | 43 | 180 |
| 4 | Moderately weathered granite | 2.75 | 26 | 16 | 55 | 400 |
| 5 | Slightly weathered granite | 15 | 26.5 | 22 | 65 | 800 |
| Foundation Pit Depth H/m | Embedment Depth/m | Concrete Strength | Pile Diameter/m | Pile Spacing/m | Crown Beam Width/m | Crown Beam Height/m | Overload/kPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28 | 7 | C45 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1 | 1.2 | 20 |
| Number | Support Anchor Type | Horizontal Spacing (m) | Vertical Spacing (m) | Angle of Incidence (°) | Overall Length (m) | Length of Anchorage Section (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | internal bracing | 9.000 | 1.500 | --- | --- | --- |
| 2 | Anchor Rod | 1.500 | 1.500 | 25.00 | 24.00 | 9.50 |
| 3 | Anchor Rod | 1.500 | 2.000 | 25.00 | 23.50 | 10.00 |
| 4 | Anchor Rod | 1.500 | 2.000 | 25.00 | 20.00 | 7.50 |
| 5 | Anchor Rod | 1.500 | 2.000 | 25.00 | 19.00 | 7.50 |
| 6 | internal bracing | 3.000 | 0.500 | --- | --- | --- |
| 7 | Anchor Rod | 1.500 | 1.500 | 25.00 | 16.50 | 6.00 |
| 8 | Anchor Rod | 1.500 | 2.000 | 25.00 | 15.50 | 6.00 |
| 9 | internal bracing | 3.000 | 0.500 | --- | --- | --- |
| 10 | Anchor Rod | 1.500 | 1.500 | 25.00 | 15.00 | 6.00 |
| 11 | Anchor Rod | 1.500 | 2.000 | 25.00 | 14.00 | 6.00 |
| 12 | Anchor Rod | 1.500 | 2.000 | 25.00 | 13.00 | 6.00 |
| 13 | Anchor Rod | 1.500 | 2.000 | 25.00 | 12.50 | 6.00 |
| 14 | Anchor Rod | 1.500 | 2.000 | 25.00 | 12.50 | 6.00 |
| 15 | Anchor Rod | 1.500 | 2.000 | 25.00 | 12.50 | 6.00 |
| Number | Support Type | Horizontal Spacing (m) | Vertical Spacing (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Reinforced concrete internal support | 9 | 1.5 |
| 2 | Steel pipe supports | 3 | 7 |
| 3 | Steel pipe supports | 3 | 4 |
| Number | Anchor Type | Horizontal Spacing/m | Vertical Spacing/m | Angle of Incidence/° | Overall Length/m | Length of Anchorage Section/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Anchor Rod | 1.500 | 2.000 | 15.00 | 13.00 | 7.00 |
| 2 | Anchor Rod | 1.500 | 2.000 | 15.00 | 13.00 | 7.00 |
| 3 | Anchor Rod | 1.500 | 2.000 | 15.00 | 13.00 | 6.00 |
| 4 | Anchor Rod | 1.500 | 2.000 | 15.00 | 12.00 | 6.00 |
| 5 | Anchor Rod | 1.500 | 2.000 | 15.00 | 12.00 | 6.00 |
| 6 | Anchor Rod | 15.000 | 2.000 | 15.00 | 12.00 | 6.00 |
| Number | Name | γ/(kN·m−3) | c/kPa | φ/° | Young’s Modulus/Mpa | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Plain fill | 1800 | 16 | 10 | 23 | 0.3 |
| 2 | Coarse-grained sand with clayey soil | 2050 | 9 | 27 | 32 | 0.25 |
| 3 | Strongly weathered granite | 2300 | 7.5 | 30 | 9000 | 0.23 |
| 4 | Moderately weathered granite | 2600 | 16 | 40 | 15,000 | 0.17 |
| 5 | Strongly weathered granite | 2650 | 22 | 48 | 22,000 | 0.14 |
| Number | Name | Distance from the Ground/m | Young’s Modulus/(×105 Mpa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Cross-Sectional Area/m2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bored Pile | 1.5 | 3.2 | 0.28 | 23 |
| 2 | Steel pipe piles | 14 | 3.5 | 0.3 | 7 |
| Young’s Modulus/(×105 Mpa) | Compressive Strength/kN | Tensile Strength/kN | Cross-Sectional Area/(×10−4 m2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1 | 300 | 3000 | 3.14 |
| Number | Name | Distance from the Ground/m | Young’s Modulus/(×105 Mpa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Cross-Sectional Area/m2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Reinforced concrete beams | 1.5 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 1.08 |
| 2 | Steel pipe beam | 8.5 | 3.55 | 0.27 | 0.502 |
| 3 | Steel pipe beam | 11.5 | 3.55 | 0.27 | 0.502 |
| Internal Force Type | Calculated Value by Elastic Method | Classical Method of Calculating Values | Internal Force Design Value | Practical Value of Internal Force |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum bending moment inside foundation pit (kN·m) | 2504.24 | 2146.62 | 2926.83 | 2926.83 |
| Maximum bending moment outside foundation pit (kN·m) | 2358.81 | 2207.47 | 2756.86 | 2756.86 |
| Maximum shear force (kN) | 1325.29 | 1040.69 | 1822.27 | 1822.27 |
| Anchor Road Number | Maximum Internal Force Elasticity Method (kN) | Maximum Internal Force Classical Method (kN) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.00 | 385.71 |
| 2 | 300.00 | 8.00 |
| 3 | 450.00 | 10.00 |
| 4 | 400.00 | 12.00 |
| 5 | 550.00 | 128.33 |
| 6 | 300.00 | 128.33 |
| 7 | 450.00 | 10.00 |
| 8 | 450.00 | 12.00 |
| 9 | 550.00 | 128.33 |
| 10 | 800.00 | 10.00 |
| 11 | 800.00 | 10.00 |
| 12 | 800.00 | 10.00 |
| 13 | 800.00 | 15.00 |
| 14 | 750.00 | 15.00 |
| 15 | 550.00 | 15.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Lai, J.; Wang, W.; Wu, X.; Xu, J.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Z. Low Carbon Optimization of Deep Foundation Pit Support in Undulating Strata. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6562. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116562
Liu Y, Lai J, Wang W, Wu X, Xu J, Xie H, Zhang Z. Low Carbon Optimization of Deep Foundation Pit Support in Undulating Strata. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(11):6562. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116562
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yun, Jie Lai, Wei Wang, Xiong Wu, Jiangbo Xu, Haodong Xie, and Zixuan Zhang. 2023. "Low Carbon Optimization of Deep Foundation Pit Support in Undulating Strata" Applied Sciences 13, no. 11: 6562. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116562
APA StyleLiu, Y., Lai, J., Wang, W., Wu, X., Xu, J., Xie, H., & Zhang, Z. (2023). Low Carbon Optimization of Deep Foundation Pit Support in Undulating Strata. Applied Sciences, 13(11), 6562. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116562







