A Review on Food Safety: The Case of Citrobacter sp., Fish and Fish Products
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Foodborne Diseases
3. Fish
| Hazard Type | Disease Causal Agent | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Biological | Bacteria | Vibrio spp., Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., Plesiomonas shigelloides, Edwardsiella tarda, Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Clostridium sp., Bacillus cereus, Campylobacter jejuni, Aeromonas spp., Citrobacter freundii, and Citrobacter braakii. |
| Parasites | Gnathostoma spp., Pseudoterranova spp., Anisakis spp., Phocanema spp., Angiostrongylus spp., Contracaecum spp., Diphyllobothrium spp., Phagicola spp., Clonorchis spp., Paragonimus spp., Heterophyes spp., and Cryptosporidium spp. | |
| Virus | Hepatitis A, hepatitis E, adenovirus, norovirus, astrovirus, rotavirus, and enterovirus. | |
| Fungi | Fusarium spp., Aspergillus spp., Penicillium spp. | |
| Chemical | Biotoxins | Tetrodotoxin, ciguatera (ciguatoxin, scaritoxin, maitotoxin, palytoxin, and okadaic acid), Gempilotoxin, and mycotoxins. |
| Heavy Metals | Lead, arsenic, cadmium, copper, mercury | |
| Organic Compounds | Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, polychlorinated biphenyls, polybrominated diphenyl ethers, dioxins, pesticides, microplastics, antibiotics, and hormones. | |
| Biogenic Amines | Histamine, putrescine, and cadaverine. |
Microbiology of Fish
4. Citrobacter sp.
4.1. Citrobacter, Fish, and Animal Health
4.2. Citrobacter, Histamine, and Food Diseases by Fish Consumption
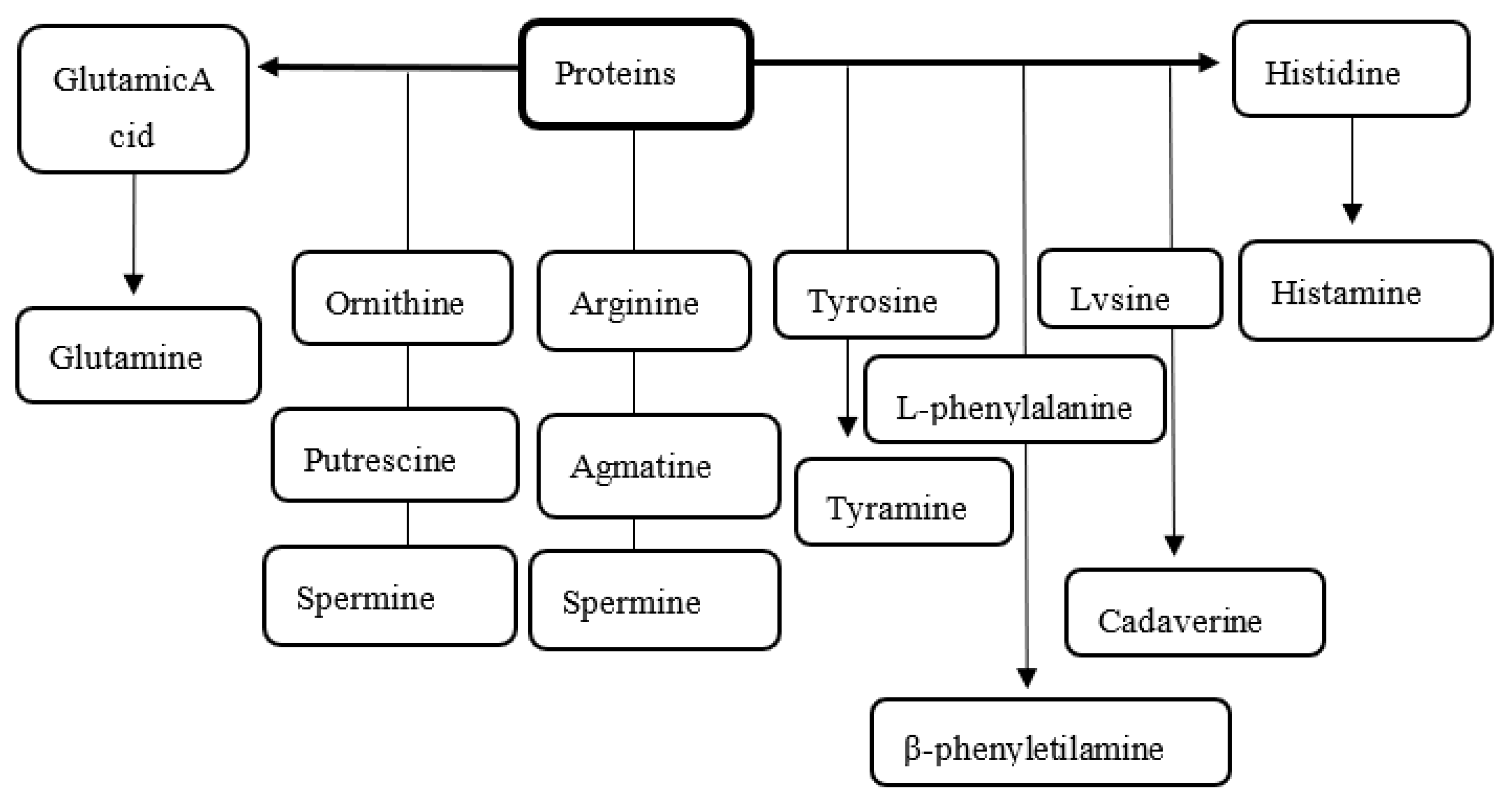
5. Isolation and Detection of Enterobacteria in Food Case: Citrobacter sp.
Determination of Biogenic Amines (Histamine) in Fish and Fish Products
6. Control and Prevention: Animal Health and Food Diseases by Consumption of Fish (Microbiology Contamination and Biogenic Amines)
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Paiva Soares, K.M.; Gonçalves, A.A. Qualidade e segurança do pescado. Rev. Inst. Adolfo Lutz. 2012, 71, 1–10. Available online: http://www.ial.sp.gov.br/resources/insituto-adolfo-lutz/publicacoes/rial/10/rial71_1_completa/1426.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2023).
- Huss, H.H. Aseguramiento de la Calidad de los Productos Pesqueros. FAO Documento Técnico de Pesca 334. Laboratorio Tecnológico. Ministerio de Pesca. Dinamarca. Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Agricultura y la Alimentación Roma. 1997. Available online: http://higiene.unex.es/Bibliogr/Libros/pescaFAO/indice.htm (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Huss, H.H. El Pescado Fresco: Su Calidad y Cambios de su Calidad. FAO Documento Técnico de Pesca 348. Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Agricultura y la Alimentación. Laboratorio Tecnológico. Ministerio de Pesca. Dinamarca. 1998. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/v7180s/v7180s00.htm (accessed on 3 March 2023).
- Herrera Arias, F.C.; Santos Buelga, J.A. Prevalencia de Salmonella spp. en pescado fresco expendido en Pamplona (Norte de Santander). Bistua Rev. Fac. Cienc. Básicas 2005, 3, 34–42. Available online: https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/903/90330205.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- Chong, A.; Peñuelas, M.; Guerrero, M.; Cabezas, C.; Díaz, O.; Martín, C.; Varela, C. Brotes de transmisión alimentaria. Red Nacional de Vigilancia Epidemiológica. 2012–2020. Bol. Epidemiológico Semin. 2021, 29, 53–63. Available online: https://revista.isciii.es/index.php/bes/article/view/1157 (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- Friesema, I.H.M.; Slegers-Fitz-James, I.A.; Wit, B.; Franz, E. Surveillance and characteristics of food-borne outbreaks in the Netherlands, 2006 to 2019. Euro Surveill. 2022, 27, 2100071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alerte, V.; Cortés, S.; Díaz, J.; Vollaire, J.; Espinoza, M.E.; Solari, V.; Torres, M. Brotes de enfermedades transmitidas por alimentos y agua en la Región Metropolitana, Chile (2005–2010). Rev. Chilena Infectol. 2012, 29, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Espinosa, L.; Varela, C.; Martínez, E.V.; Cano, R. Brotes de enfermedades transmitidas por alimentos. España, 2008-2011 (excluye brotes hídricos). Bol. Epidemiológico Semin. 2014, 22, 130–145. Available online: https://repisalud.isciii.es/bitstream/handle/20.500.12105/14377/BES_22_11_1.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Cortés Sánchez, A.D.J.; Espinosa Chaurand, L.D.; Díaz Ramírez, M.; Torres Ochoa, E. Plesiomonas: A review on food safety, fish-borne diseases, and tilapia. Sci. World J. 2021, 2021, 3119958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales Ramírez, L.C.; Alvarado Ospina, M.A.; Castillo Fonseca, L.A.; Camacho Beltran, Y.C. Estudio bacteriológico de la calidad del pescado fresco, Bagre (Pseudoplatystoma sp.) y Mojarra Roja (Oreochromis sp.) comercializado en el municipio de El Colegio, Cundinamarca (Colombia). Nova 2011, 9, 149–157. Available online: https://hemeroteca.unad.edu.co/index.php/nova/article/download/497/1070 (accessed on 10 January 2023). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuertes Vicente, H.G.; Paredes López, F.; Saavedra Gálvez, D.I. Buenas prácticas de manufactura y preservación a bordo: Pescado inocuo. Big Bang Faustiniano. 2018, 3, 41–45. Available online: http://datos.unjfsc.edu.pe/index.php/BIGBANG/article/view/234 (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- Eltholth, M.; Fornace, K.; Grace, D.; Rushton, J.; Häsler, B. Assessing the chemical and microbiological quality of farmed tilapia in Egyptian fresh fish markets. Glob. Food Sec. 2018, 17, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Fuente Salcido, N.M.; Corona, J.E.B. Inocuidad y bioconservación de alimentos. Acta Univ. 2010, 20, 43–52. Available online: https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/416/41613084005.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, C.A.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, V.C.; Calderón-Rangel, A. Contaminantes microbiológicos en un mercado del sur de Montería: Un riesgo para la salud pública. Cienc. Agric. 2017, 14, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soto Varela, Z.; Pérez Lavalle, L.; Estrada Alvarado, D. Bacterias causantes de enfermedades transmitidas por alimentos: Una mirada en Colombia. Rev. Salud Uninorte 2016, 32, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olea, A.; Díaz, J.; Fuentes, R.; Vaquero, A.; García, M. Vigilancia de brotes de enfermedades transmitidas por alimentos en Chile. Rev. Chilena Infectol. 2012, 29, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torrens, H.R.; Argilagos, G.B.; Cabrera, M.S.; Valdés, J.B.; Sáez, S.M.; Viera, G.G. Las enfermedades transmitidas por alimentos, un problema sanitario que hereda e incrementa el nuevo milenio. Rev. Electrónica De Vet. 2015, 16, 1–27. Available online: https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/636/63641401002.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Mendez, M.M.; Rodríguez, J.; Arístides, R.; Minier Pouyou, L.; Zayas Tamayo, E.; Soler Santana, R. Caracterización de agentes bacterianos aislados en brotes de enfermedades transmitidas por alimentos. MEDISAN 2020, 24, 235–251. Available online: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1029-30192020000200235&lng=es&tlng=pt (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- López Aday, D.; Rivero Álvarez, E.; Martínez Torres, A.; Alegret Rodríguez, M. Enfermedades transmitidas por alimentos en Villa Clara. Rev. Cubana Hig. Epidemiol. 2013, 51, 203–213. Available online: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1561-30032013000200009&lng=es&tlng=es (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Aminharati, F.; Ehrampoush, M.H.; Dallal, M.M.S.; Yaseri, M.; Tafti, A.A.D.; Rajabi, Z. Citrobacter freundii foodborne disease outbreaks related to environmental conditions in Yazd Province, Iran. Iran. J. Public Health 2019, 48, 1099. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6635343/pdf/IJPH-48-1099.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2023). [CrossRef]
- Hashim, M.H.; Al Khafaji, M.H. Isolation and identification of Citrobacter freundii from chicken meat samples using cultural and molecular techniques. Iraqi J. Sci. 2018, 59, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA and ECDC (European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control). The European Union One Health 2020 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2021, 19, 1–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba Quintero, G.; Ramírez De León, J.A.; Cortés Ruiz, J.A.; Sánchez Humaran, I.L.; Ruelas Inzunza, J.R.; Moreno Hernández, J.M. Contenido de histamina y calidad microbiológica de pescado comercializado en Mazatlán, Sinaloa. BIOtecnia 2012, 14, 3–12. Available online: https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/6729/672971151001.pdf (accessed on 18 February 2023). [CrossRef]
- FAO. El Estado Mundial de la Pesca y la Acuicultura 2020. La Sostenibilidad en Acción; The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Roma, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, D.T. Bacterial zoonoses of fishes: A review and appraisal of evidence for linkages between fish and human infections. Vet. J. 2015, 203, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novotny, L.; Dvorska, L.; Lorencova, A.; Beran, V.; Pavlik, I. Fish: A potential source of bacterial pathogens for human beings. Vet. Med. Czech. 2004, 49, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mhango, M.; Mpuchane, S.F.; Mpuchane, B.A. Incidence of indicator organisms, opportunistic and pathogenic bacteria in fish. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 2010, 10, 4202–4218. Available online: https://www.ajol.info/index.php/ajfand/article/view/62898/50798 (accessed on 18 February 2023). [CrossRef]
- Bosch, A.C.; O’Neill, B.; Sigge, G.O.; Kerwath, S.E.; Hoffman, L.C. Heavy metals in marine fish meat and consumer health: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buras, N.; Duek, L.; Niv, S.; Hepher, B.; Sandbank, E. Microbiological aspects of fish grown in treated wastewater. Water Res. 1987, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, M.; Valladares, J.; Grass, G.; Pico, Y. Microbiota de interés para la salud pública de Oreochromis spp. (tilapia roja) cultivada en jaulas flotantes en agua dulce. Rev. Cub. Investig. Pesq. 2011, 28, 74–80. Available online: https://aquadocs.org/bitstream/handle/1834/4662/Mayel%C3%ADn.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 6 January 2023).
- Romero-Jarero, J.M.; Negrete-Redondo, M.D.P. Presencia de bacterias Gram positivas en músculo de pescado con importancia comercial en la zona del Caribe mexicano. Rev. Mex. Biodivers. 2011, 82, 599–606. Available online: https://www.scielo.org.mx/pdf/rmbiodiv/v82n2/v82n2a19.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, I.; Rosmini Marcelo, A.; Armenta, R. Tecnología de Productos de Origen Acuático; Editorial Limusa: Mexico City, México, 2009; p. 532. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.R.; Ran, C.; Ringø, E.; Zhou, Z.G. Progress in fish gastrointestinal microbiota research. Rev Aquac. 2018, 10, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flores, B.; González, N.; Bravo, A.; Mora-Sánchez, B.; Torres, D.; Jirón, W.; Balcázar, J.L. Identificación de bacterias patógenas en peces capturados en el Pacífico frente a Nicaragua. Cienc. Mar. 2021, 47, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guentzel, M.N. Escherichia, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Serratia, Citrobacter, and Proteus. In Medical Microbiology, 4th ed.; Baron, S., Ed.; University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996; Chapter 26. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK8035/ (accessed on 2 March 2023).
- Romero Cabello, R. Microbiología y Parasitología Humana: Bases Etiológicas de las Enfermedades Infecciosas y Parasitarias, 3rd ed.; Médica Panamericana: Mexico City, Mexico, 2007; p. 999. [Google Scholar]
- Daza-Hernández, A.L.; Arroyo-Escalante, S.; Bravo-Escobar, G.A. Identificación de Citrobacter koseri comonuevo patógeno en pacientes con rinitis crónica. An. Orl. Mex. 2014, 59, 1–10. Available online: https://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/anaotomex/aom-2014/aom141a.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2023).
- Anderson, P.M.; Del, R.; Calderón, P.V. Microbiología alimentaria. In Metodología Analítica para Alimentos y Bebidas, 2nd ed.; Editorial Diaz de Santos S.A.: Madrid, Spain, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- De Pádua, S.B.; Peixoto, M.D.; Sebastião, F.A.; Pilarski, F.; Martins, M.; Ishikawa, M.M. Isolation, characterization and pathology of Citrobacter freundii infection in native Brazilian catfish Pseudoplatystoma. Braz. J. Vet. Pathol. 2014, 7, 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Kolínská, R.; Španělová, P.; Dřevínek, M.; Hrabák, J.; Žemličková, H. Species identification of strains belonging to genus Citrobacter using the biochemical method and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Folia Microbiol. 2015, 60, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffer, M.I.; Lucero, C.; Pichel, M. Capítulo II.c.1.4. Salmonella, Edwardsiella, Citrobacter. En Manual de Microbiología Clínica de la Asociación Argentina de Microbiología. Volumen I Bacterias de Importancia Clínica. Editores Horacio a. Lopardo. Silvia C. Predari, Carlos Vay. 2016. Available online: https://www.aam.org.ar/descarga-archivos/Parte21Enterobacterias.pdf (accessed on 28 March 2023).
- Duman, M.; Saticioglu, I.B.; Buyukekiz, A.G.; Balta, F.; Altun, S. Molecular characterization and antimicrobial resistance profile of atypical Citrobacter gillenii and Citrobacter sp. isolated from diseased rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2017, 10, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayatullah, A.R.; Effendi, M.H.; Plumeriastuti, H.; Wibisono, F.M.; Hartadi, E.B.; Sofiana, E.D. A Review of the opportunistic pathogen Citrobacter freundii in piglets post weaning: Public Health Importance. Sys. Rev. Pharm. 2020, 11, 767–773. Available online: https://www.sysrevpharm.org/articles/a-review-of-the-opportunistic-pathogen-citrobacter-freundii-in-piglets-post-weaning--public-health-importance.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Sánchez Códez, M.I.; Alonso Ojembarrena, A.; Arca Suárez, J. Gramnegativos infrecuentes como agentes etiológicos de infecciones nosocomiales en una Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos Neonatales. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. 2018, 31, 288. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6166260/pdf/revespquimioter-31-288.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- Collado García, O.; Barreto Rodríguez, H.; Rodríguez Torrens, H.; Barreto Argilagos, G.; Abreu Guirado, O. Especies bacterianas asociadas a infecciones del tracto urinario. Rev. Arch. Médico Camagüey 2017, 21, 479–486. Available online: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1025-02552017000400006&lng=es&tlng=es (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Meseguer Ruiz, V.; Carmona Martín, M.M.; Polo Romero, F.J.; Fernández Rodríguez, A.; Barba Romero, M.A.; Sáez Mendez, L. Bacteriemia por Citrobacter freundii: Presentación de dos casos. An. Med. Interna 2002, 19, 54. Available online: http://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0212-71992002000200011&lng=es&tlng=es (accessed on 26 January 2023). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altun, S.; Duman, M.; Buyukekiz, A.G.; Ozyigit, M.O.; Karatas, S.; Turgay, E. Isolation of Citrobacter braakii from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Isr. J. Aquacult. Bamidgeh 2013, 65, 915–922. [Google Scholar]
- Jeremić, S.; Jakić-Dimić, D.; Veljović, L.J. Citrobacter freundii as a cause of disease in fish. Acta Vet. 2003, 53, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puello-Caballero, L.P.; Montoya-Campuzano, O.I.; Castañeda-Monsalve, V.A.; Moreno-Murillo, L.M. Caracterización de la microbiota presente en el intestino de Piaractus brachypomus (Cachamablanca). Rev. Salud Anim. 2018, 40, 1–12. Available online: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0253-570X2018000200002&lng=es&nrm=iso> (accessed on 25 February 2023).
- Lü, A.; Hu, X.; Zheng, L.; Zhu, A.; Cao, C.; Jiang, J. Isolation and characterization of Citrobacter spp. from the intestine of grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idellus. Aquaculture 2011, 313, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B.; Austin, D.A.; Munn, C.B. Bacterial Fish Pathogens: Disease of Farmed and Wild Fish; Springer: Chichester, UK, 2007; Volume 26, p. 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandeira, G., Jr.; Dos Santos, A.C.; de Freitas Souza, C.; Baldissera, M.D.; dos Santos Moreira, K.L.; da Veiga, M.L.; Baldisserotto, B. Citrobacter freundii infection in silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen): Hematological and histological alterations. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 125, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillén-Velasco, S.; Ponce-Alquicira, E.; Farrés-González, S.A.; Guerrero-Legarreta, I. Histamine production by two Enterobacteriaceae strains isolated from tuna (Thunnus thynnus) and jack mackerel (Trachurus murphyii). Int J. Food Prop. 2004, 7, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Capillas, P.C.; Jiménez-Colmenero, F. Aminas biógenas: Importancia toxicológica. Electron. J Biomed. 2010, 3, 58–60. Available online: https://www.biomed.uninet.edu/2010/n3/ruiz-capillas.html (accessed on 26 February 2023).
- Galleguillos, A.M. 21. Aminas Biogénicas—Nuevos Indicadores Químicos Utilizados Como Criterios de Calidad en Harina de Pescado. In Control de Calidad de Insumos y Dietas Acuícolas. I Curso Regional de Capacitación (Santiago de Chile, 20/9-8/10/1993) Organizado por el Proyecto AQUILA II y Ejecutado por Fundación Chile; Programa Cooperativo Gubernamental. gcp/rla/102/it. Proyecto Aquila II. Editor Emilio Castro Campos; Documento de Campo No 16; FAO-ITALIA: Rome, Italy, 1994; Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/ab482s/AB482S00.htm#TOC (accessed on 20 February 2023)documento de campo No 16. 1994.
- Izquierdo, P.; Sandrea, L.; Allara, M.; González, P.; García, A.; Valecillos, Y. Evaluación bacteriológica y contenido de histamina en pescado desmenuzado precocido en Venezuela. Rev. Científica 2004, 14, 467–473. Available online: https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/959/95914513.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Niven, C.F., Jr.; Jeffrey, M.B.; Corlett, D.A., Jr. Differential plating medium for quantitative detection of histamine-producing bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1981, 41, 321–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graü, C.; Sánchez, D.; Zerpa, A.; Ballenilla, O.; Berti, O. Estudio de la microflora asociada a la formación de histamina en sardina (Sardinella aurita). Rev. Científica Fac. Cienc. Vet. 2003, 13, 199–205. Available online: https://produccioncientificaluz.org/index.php/cientifica/article/download/14979/14956/#:~:text=El%20objetivo%20de%20este%20trabajo,%2D0%2C5%C2%B0C (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Torres, G.; Izquierdo, P.; Aliara, M.; García, A. Efecto de la temperatura y tiempo de almacenamiento sobre el crecimiento de bacterias productoras de histamina en dos especies de pescado: Lisa (Mugil curema) y róbalo (Centropomus undecimalis). Rev. Científica Fac. Cienc. Vet. 2003, 13, 263–269. Available online: https://produccioncientificaluz.org/index.php/cientifica/article/view/14986 (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Restrepo, M.; Torres, G.; Medina, Z.; García, A.; Piñero, M.; Allara, M. Efecto del pH sobre la Producción de Histamina por Enterobacterias Presentes en Músculo de Cachama Negra (Colossoma Macropomum). Rev. Científica 2015, 25, 11–18. Available online: https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/959/95934122002.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Moreira, J.D.O.V. Segurança Microbiológica e Bactérias Produtoras de Histamina em Cavala (Scomberomorus Cavalla Cuvier, 1829) e Dourado (Salminus Brasiliensis Cuvier, 1816) Comercializados em MACEIÓ-AL. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal de Alagoas-UFAL, Macejo, Brazil, 2018. Available online: https://www.repositorio.ufal.br/jspui/bitstream/riufal/3821/1/Seguran%C3%A7a%20microbiol%C3%B3gica%20e%20bact%C3%A9rias%20produtoras%20de%20histamina%20em%20cavala%20%28Scomberomorus%20cavalla%20Cuvier%2C%201829%29%20e%20dourado%20%28Salminus%20brasiliensis%20Cuvier%2C%201816%29%20comercializados%20em%20MACEI%C3%93-AL.pdf (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- Surya, T.; Sivaraman, B.; Alamelu, V.; Priyatharshini, A.; Arisekar, U.; Sundhar, S. Rapid methods for histamine detection in fishery products. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2019, 8, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, K.S.; Galeno, L.S.; Mendonça, C.J.S.; Carvalho, I.A.; Costa, F.N. Occurrence of pathogenic and spoilage bacteria in salmon sashimi: Histamine and antimicrobial susceptibility evaluation. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2020, 23, e2019085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gram, L. Microbiological spoilage of fish and seafood products. In Compendium of the Microbiological Spoilage of Foods and Beverages; Sperber, W.H., Doyle, M.P., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA; Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; London, UK, 2009; pp. 87–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guergué-Díaz de Cerio, O.; Barrutia-Borque, A.; Gardeazabal-García, J. Escombroidosis: Abordaje práctico. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2016, 107, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, D.; Jiménez-Díaz, M.; Arias-Echandi, L. Estudio de la estabilidad microbiológica de la barracuda a través del tiempo de almacenaje en Costa Rica. Arch. Latinoam. Nutr. 2011, 61, 183–188. Available online: http://ve.scielo.org/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0004-06222011000200010&lng=es&tlng=es (accessed on 22 February 2023).
- Elika. Histamina. Elika Fundación Vasca para la Seguridad Agroalimentaria. 2021. Available online: https://seguridadalimentaria.elika.eus/fichas-de-peligros/histamina/#limites (accessed on 25 February 2023).
- FDA—Food and Drug Administration. Bad Bug Book, Foodborne Pathogenic Microorganisms and Natural Toxins, 2nd ed.; Benner, R.A., Jr., Ed.; Scombrotoxin; 2012; pp. 208–209. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/83271/download (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- Bou, G.; Fernández-Olmos, A.; García, C.; Sáez-Nieto, J.A.; Valdezate, S. Métodos de identificación bacteriana en el laboratorio de microbiología. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2011, 29, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, C.A.E.; Silva, G.J.A. Patrón de Bandas Genéticas en Pseudomonas Aeruginosa y Citrobacter Diversus Aislados en Productos Agrícolas y Aguas de Riego. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad Nacional de Chimborazo, Riobamba, Chimborazo, 2021. Available online: http://dspace.unach.edu.ec/bitstream/51000/8093/3/6.-TESIS%20Evelyn%20Alexandra%20D%C3%ADaz%20Cadena%20%20Y%20Jhonny%20Alfredo%20Silva.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Madigan, M.T.; Martinko, J.M.; Parker, J.B. Biología de los Microorganismos, 10th ed.; Pearson Educación S.A.: Madrid, Spain, 2004; p. 1096. [Google Scholar]
- Gary, W.; Procop, D.L.; Church, G.S.; Hall, W.M.; Janda, E.W.; Koneman, P.C.; Schreckenberger, G.L. Woods. In Koneman’s Color Atlas and Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology, 7th ed.; Editorial Jones & Bartlett Learning: Burlington, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pławinska-Czarnak, J.; Wódz, K.; Kizerwetter-Swida, M.; Nowak, T.; Bogdan, J.; Kwiecinski, P.; Kwiecinski, A.; Anusz, K. Citrobacter braakii Yield False-Positive Identification as Salmonella, a Note of Caution. Foods 2021, 10, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, F.; Garro, L.; Rodríguez, E.; Zeledón, Z. Evaluación de la presencia de bacterias en alimentos y en el ambiente de una sección de oncología de un hospital nacional, San José, Costa Rica. Arch. Latinoam. Nutr. 2004, 54, 303–307. Available online: http://ve.scielo.org/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0004-06222004000300008&lng=es&tlng=es (accessed on 8 February 2023).
- Kwak, H.L.; Han, S.K.; Park, S.; Park, S.H.; Shim, J.Y.; Oh, M.; Kim, H.Y. Development of a Rapid and Accurate Identification Method for Citrobacter Species Isolated from Pork Products Using a Matrix-Assisted Laser-Desorption Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDITOF MS). J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 1537–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Książczyk, M.; Kuczkowski, M.; Dudek, B.; Korzekwa, K.; Tobiasz, A.; Korzeniowska-Kowal, A.; Bugla-Płoskońska, G. Application of routine diagnostic procedure, VITEK 2 compact, MALDI-TOF MS, and PCR assays in identification procedure of bacterial strain with ambiguous phenotype. Curr. Microbiol. 2016, 72, 570–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, N.; Puk, K.; Guz, L. Bacterial flora associated with diseased freshwater ornamental fish. J. Vet. Res. 2017, 61, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, B.S.; Wang, J.T.; Choong, Y.M. A rapid gas chromatographic method for the determination of histamine in fish and fish products. Food Chem. 2003, 82, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOM-242-SSA1-2009. Productos y Servicios. Productos de la Pesca Frescos, Refrigerados, Congelados Y Procesados. Especificaciones Sanitarias y Métodos de Prueba. Norma Oficial Mexicana. Gobierno de México. Available online: https://www.dof.gob.mx/normasOficiales/4295/salud2a/salud2a.htm#:~:text=Productos%20y%20servicios-,%20NOR-MA%20Oficial%20Mexicana%20NOM%2D242%2DSSA1%2D2009%2C%20Productos,que%20dice%3A%20Estados%20Unidos%20Mexicanos (accessed on 10 February 2023).
- Altieri, I.; Semeraro, A.; Scalise, F.; Calderari, I.; Stacchini, P. European official control of food: Determination of histamine in fish products by a HPLC–UV-DAD method. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Zhuang, D.; Hu, X.; Zhang, S.; He, Z.; Zeng, M.; Chen, X. Rapid determination of histamine in fish by thin-layer chromatography-image analysis method using diazotized visualization reagent prepared with p-nitroaniline. Anal. Methods. 2018, 10, 3386–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manterola, J.; Bó, M.; Sanzano, P. Determinación de Histamina en Conservas de Pescado Mediante la Técnica de Cromatografía en Capa Delgada. Bachelor’s Thesis, Facultad de Ciencias Veterinarias-UNCPBA, Tandil, Argentina, 2017. Available online: https://ridaa.unicen.edu.ar:8443/server/api/core/bitstreams/b5d42125-705b-4115-b88e-8653c7219f8b/content (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Arciniega, G. Determinación de Histamina por el Método de ELISA en Pescado Fresco Comercializado en el Mercado Municipal “El Arenal” de la Ciudad de Cuenca. In Conference Proceedings UTMACH, 2017 . Volume 1, pp. 1160–1170. Available online: https://investigacion.utmachala.edu.ec/proceedings/index.php/utmach/article/view/199 (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- Ma, H.; Shieh, K.J. ELISA technique. Nat Sci. 2006, 4, 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- Munir, M.A.; Mackeen, M.M.M.; Heng, L.Y.; Badri, K.H. Study of histamine detection using liquid chromatography and gas chromatography. ASM Sci. J. 2021, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscarella, M.; Magro, S.L.; Campaniello, M.; Armentano, A.; Stacchini, P. Survey of histamine levels in fresh fish and fish products collected in Puglia (Italy) by ELISA and HPLC with fluorimetric detection. Food Control. 2013, 31, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.A.; Badri, K.H. The importance of derivatizing reagent in chromatography applications for biogenic amine detection in food and beverages. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2020, 2020, 5814389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbuena Rivarola, E.D. Manual Básico de Sanidad Piscícola; Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Alimentación y la Agricultura (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2011; Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/as830s/as830s.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- OMS. Cinco Claves para Una Mayor Inocuidad de los Productos de Acuicultura con Objeto de Proteger la Salud Pública; 2016; Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS): Geneva, Switzerland; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/1067738/retrieve#:~:text=Mantener%20una%20buena%20higiene%20personal%202.,salud%20de%20los%20peces%205 (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- CA. Código Internacional Recomendado de Prácticas—Principios Generales de Higiene de los Alimentos. Codex Alimentarius—Higiene de los Alimentos—Textos Básicos, 2nd ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1997. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/y1579s/y1579s00.htm#Contents (accessed on 25 February 2023).
- OMS. Manual Sobre las CINCO claves Para la Inocuidad de los Alimentos; Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS): Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; Available online: https://www.who.int/es/publications/i/item/9789241594639 (accessed on 3 March 2023).
- OMS. Código de Prácticas para el Pescado y los Productos Pesqueros, 2nd ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2012. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/i2382s/i2382s.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2023).
- OIRSA. Manual de Buenas Prácticas de Manufactura para Productos Acuícolas y Pesqueros; Dirección Regional de Inocuidad de Alimentos, Organismo Internacional Regional de Sanidad Agropecuaria (OIRSA): San Salvador, El Salvador, 2017; Available online: https://www.oirsa.org/contenido/biblioteca/-Manual%20de%20buenas%20pr%C3%A1cticas%20de%20manufactura%20en%20productos%20acu%C3%ADcolas%20y%20pesqueros%20-%20OIRSA.pdf (accessed on 23 February 2023).
- Izquierdo, P.; Aliara, M.; Torres, G.; Fernández, A.; Paulinkevicius, M.; Fuenmayor, J. Bacterias productoras de histamina en tres especies de pescado. Rev. Científica Fac. Cienc. Vet. 2001, 11, 431–436. Available online: https://produccioncientificaluz.org/index.php/cientifica/article/view/14799 (accessed on 16 January 2023).
- Avdalov, N. Manual de Control de Calidad de los Productos de la Acuicultura. Perú; Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Alimentación y la Agricultura (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2012; Available online: https://www.infopesca.org/sites/default/files/complemento/publilibreacceso/320/manual-de-control-de-calidad-de-los-productos-de-la-acuicultura.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Lloret, J.; Ferrer, D.; Font, T.; Pedro-Botet, J.M.N.M.; Bartra, J.; Demestre, M. Salud y Pescado Beneficios y Riesgos. Histamina; Universitat de Girona: Girona, Spain; Gobierno de España: Madrid, Spain, 2015. Available online: http://salutipeix.udg.edu/es/histamina-indicador-fiable.html (accessed on 13 February 2023).
- ANVISA. Ministério da Saúde—MS Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária–Resolução de Diretoria Colegiada—RDC Nº 12, de 2 de Janeiro de 2001. Governo Brasileiro: Brasilia, Brazil. Available online: https://www.gov.br/agricultura/pt-br/assuntos/inspecao/produtos-vegetal/legislacao-1/biblioteca-de-normas-vinhos-e-bebidas/resolucao-rdc-no-12-de-2-de-janeiro-de-2001.pdf/@@download/file/resolucao-rdc-no-12-de-2-de-janeiro-de-2001.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- RM. Resolución Ministerial N.° 591-2008-MINSA. “Norma Sanitaria que Establece los Criterios Microbiológicos de Calidad Sanitaria e Inocuidad para los Alimentos y Bebidas de Consumo Humano”; Gobierno de Perú: Lima, Peru, 2008. Available online: https://www.gob.pe/institucion/minsa/normas-legales/247682-591-2008-minsa (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- RTCA. Reglamento Técnico Centroamericano. Alimentos. Criterios Microbiológicos para la Inocuidad de Alimentos. RTCA 67.04.50:08 Anexo de Resolución No. 243-2009. 2009. Available online: https://www.oirsa.org/contenido/2017/El_Salvador_INOCUIDAD/26.%20RTCA%2067%2004%2050%2008%20CRITERIOS%20MICROBIOLOGICOS%20PARA%20LA%20INOCUIDAD%20DE%20ALIMENTOS.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2023).

| Test | Citrobacter spp. | Escherichia spp. | Salmonella spp. | Edwardsiella spp. | Klebsiella spp. | Serratia sp. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mobility | + | + | + | + | − | + |
| Gram stain | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Urease | − | − | − | − | + | − |
| β-galactosidase | + | + | − | − | + | + |
| Citrate | + | − | + | − | + | + |
| Methyl red | + | + | + | + | − | −/+ |
| Voges–Proskauer | − | − | − | − | − | + |
| Indole | − | + | − | + | − | − |
| Alanine deaminase | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Gas from glucose | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Arginine | +/− | −/+ | +/− | − | − | − |
| Ornithine | −/+a | +/− | + | + | − | + |
| Test | S. enterica subsp. enterica | P. mirabilis | C. freundii | C. koseri |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2S | +a | + | + | − |
| Phenylalanine deaminase | − | + | − | − |
| Lysine decarboxylase | + | − | − | − |
| β-galactosidase | − | − | + | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cortés-Sánchez, A.D.J.; Salgado-Cruz, M.d.l.P.; Diaz-Ramírez, M.; Torres-Ochoa, E.; Espinosa-Chaurand, L.D. A Review on Food Safety: The Case of Citrobacter sp., Fish and Fish Products. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6907. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13126907
Cortés-Sánchez ADJ, Salgado-Cruz MdlP, Diaz-Ramírez M, Torres-Ochoa E, Espinosa-Chaurand LD. A Review on Food Safety: The Case of Citrobacter sp., Fish and Fish Products. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(12):6907. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13126907
Chicago/Turabian StyleCortés-Sánchez, Alejandro De Jesús, María de la Paz Salgado-Cruz, Mayra Diaz-Ramírez, Erika Torres-Ochoa, and Luis Daniel Espinosa-Chaurand. 2023. "A Review on Food Safety: The Case of Citrobacter sp., Fish and Fish Products" Applied Sciences 13, no. 12: 6907. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13126907
APA StyleCortés-Sánchez, A. D. J., Salgado-Cruz, M. d. l. P., Diaz-Ramírez, M., Torres-Ochoa, E., & Espinosa-Chaurand, L. D. (2023). A Review on Food Safety: The Case of Citrobacter sp., Fish and Fish Products. Applied Sciences, 13(12), 6907. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13126907








