Road Accident Hotspots on Jordan’s Highway Based on Geometric Designs Using Structural Equation Modeling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Road Accident Hotspots
2.2. Road Geometric and Road Safety
3. Methodology
3.1. Location
3.2. Data Preprocessing
3.3. Hot Spot Analysis: Getis-Ord Gi*
3.4. Structural Equation Modeling (SEM)
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Hotspots Analysis Results
4.2. SEM
4.2.1. Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA)
4.2.2. Measurement Model for Reflective Construct
4.2.3. Measurement Model for Formative Construct
4.2.4. Path Coefficient
4.3. Goodness of Fit of Model (GoF)
4.4. Normed Fit Index
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wijnen, W. Socio-economic costs of road crashes in middle-income countries: Applying a hybrid approach to Kazakhstan. IATSS Res. 2021, 45, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Status Report on Road Safety 2018. WHO. 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/violence_injury_prevention/road_safety_status/2018/en/ (accessed on 18 July 2022).
- Li, M.; Xie, H.; Shu, P. Study on the Impact of Traffic Accidents in Key Areas of Rural Roads. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tola, A.M.; Demissie, T.A.; Saathoff, F.; Gebissa, A. Severity, Spatial Pattern and Statistical Analysis of Road Traffic Crash Hot Spots in Ethiopia. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traffic Department. Yearly Statistical Report of Traffic Accidents. 2019. Available online: https://www.psd.gov.jo/images/docs/TrafficRep2019.pdf (accessed on 18 July 2022).
- Mitchell, A. The ESRI Guide to GIS Analysis Volume 3: Modeling Sustainability, Movement, and Interaction. ESRI Press, 2012; p. 419. Available online: https://books.google.jo/books?id=2VDogixBFA4C&q=The+Esri+Guide+to+GIS+Analysis,+Volume+3:+Modeling+Suitability,+Movement,+and+Interaction&dq=The+Esri+Guide+to+GIS+Analysis,+Volume+3:+Modeling+Suitability,+Movement,+and+Interaction&hl=ar&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjM (accessed on 18 July 2022).
- Mekonnen, A.A.; Beza, A.D.; Sipos, T. Estimating the Value of Statistical Life in a Road Safety Context Based on the Contingent Valuation Method. J. Adv. Transp. 2022, 2022, 3047794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadi, M.; Török, Á.; Tánczos, K. Study of the Economic Cost of Road Accidents in Jordan. Period. Polytech. Transp. Eng. 2018, 46, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Guo, Y.; Liu, P. Safety impacts of geometric design on freeway segments with closely spaced entrance and exit ramps. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2021, 163, 106461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlKheder, S.; Al Gharabally, H.; Al Mutairi, S.; Al Mansour, R. An Impact study of highway design on casualty and non-casualty traffic accidents. Injury 2022, 53, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galante, F.; Mauriello, F.; Pernetti, M.; Rella Riccardi, M.; Montella, A. Effects of Traffic Control Devices on Rural Curve Lateral Position. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2022, 2676, 162–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargoum, S.; Karsten, L.; El-Basyouny, K.; Chen, X. Enriching Roadside Safety Assessments Using LiDAR Technology: Disaggregate Collision-Level Data Fusion and Analysis. Infrastructures 2022, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedher, M.B.B.; Yun, D. Generalized Linear Models to Identify the Impact of Road Geometric Design Features on Crash Frequency in Rural Roads. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2022, 26, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, M.R.O.B.C.; Maia, M.L.A.; Kohlman Rabbani, E.R.; Lima Neto, O.C.C.; Andrade, M. Traffic accident prediction model for rural highways in Pernambuco. Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2022, 10, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-omari, B.; Ghuzlan, K.; Hasan, H. Traffic Accidents Trends and Characteristics in Jordan. 2013. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/db9e/73c8a37e2837b927eb24b2be79de5efe945f.pdf (accessed on 18 July 2022).
- Miqdady, T.; de Oña, J. Identifying the Factors That Increase the Probability of an Injury or Fatal Traffic Crash in an Urban Context in Jordan. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Gill, G.S.; Zhang, Y.; Vo, T.; Wen, F.; Li, Y. Exploring the modeling and site-ranking performance of Bayesian spatiotemporal crash frequency models with mixture components. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2020, 135, 105357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dereli, M.A.; Erdogan, S. A new model for determining the traffic accident black spots using GIS-aided spatial statistical methods. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2017, 103, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, B.; Gahr, B.; Dahlinger, A. An in-Vehicle Information System Providing Accident hotspot Warnings|Semantic Scholar. ECIS. 2016. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/An-in-Vehicle-Information-System-Providing-Accident-Ryder-Gahr/662134792653ae830a96c8da33a2b19c45a9d95b (accessed on 22 July 2021).
- W/Yohannes, A.Y.; Minale, A.S. Identifying the Hot Spot Areas of Road Traffic Accidents. Jordan J. Civ. Eng. 2015, 9, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakali, L.; Kwon, T.J.; Fu, L. Identification of crash hotspots using kernel density estimation and kriging methods: A comparison. J. Mod. Transp. 2015, 23, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, M.; Wang, X.; Lee, J.; Abdel-Aty, M.; Mao, S. Transferability of safety performance functions and hotspot identification for freeways of the United States and China. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2020, 139, 105493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemulapalli, S.S.; Ulak, M.B.; Ozguven, E.E.; Sando, T.; Horner, M.W.; Abdelrazig, Y.; Moses, R. GIS-based Spatial and Temporal Analysis of Aging-Involved Accidents: A Case Study of Three Counties in Florida. Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 2017, 10, 537–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Alluri, P.; Gan, A.; Wu, W. Spatial analysis of macro-level bicycle crashes using the class of conditional autoregressive models. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2018, 118, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikanth, L.; Srikanth, I.; Arockiasamy, M. Identification of Traffic Accident Hotspots using Geographical Information System (GIS). Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2019, 9, 4429–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashtarkhani, S.; Kiani, B.; Bergquist, R.; Bagheri, N.; VafaeiNejad, R.; Tara, M. An age-integrated approach to improve measurement of potential spatial accessibility to emergency medical services for urban areas. Int. J. Health Plan. Manag. 2020, 35, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazneen, S.; Rezapour, M.; Ksaibati, K. Application of Geographical Information System Techniques to Determine High Crash-Prone Areas in the Fort Peck Indian Reservation. Open Transp. J. 2020, 14, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhadour, W.; Zraqou, J.; Al-Helali, A.; Al-Ghananeem, S. Traffic Accidents Detection using Geographic Information Systems (GIS). Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2021, 12, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazaymeh, K.; Almagbile, A.; Alomari, A.H. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Traffic Accidents Hotspots Based on Geospatial Techniques. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajed, Y.; Shafabakhsh, G.; Bagheri, M. Hotspot location identification using accident data, traffic and geometric characteristics. Eng. J. 2019, 23, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikanth, L.; Srikanth, I. A Case Study on Kernel Density Estimation and Hotspot Analysis Methods in Traffic Safety Management. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on COMmunication Systems and NETworkS, COMSNETS 2020, Bengaluru, India, 7–11 January 2020; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Trondheim, Norway, 2020; pp. 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, K.G.; Liu, P.; Lin, L.-T. Determining the road traffic accident hotspots using GIS-based temporal-spatial statistical analytic techniques in Hanoi, Vietnam. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, 23, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manap, N.; Borhan, M.N.; Yazid, M.R.M.; Hambali, M.K.A.; Rohan, A. Identification of Hotspot Segments with a Risk of Heavy-Vehicle Accidents Based on Spatial Analysis at Controlled-Access Highway. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooch, J.P.; Gayah, V.V.; Donnell, E.T. Safety performance functions for horizontal curves and tangents on two lane, two way rural roads. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2018, 120, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qu, X.; Jin, S. Hotspot identification considering daily variability of traffic flow and crash record: A case study. J. Transp. Saf. Secur. 2020, 12, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaidat, M.; Ramadan, T. Traffic Accidents at Hazardous Locations of Urban Roads. Jordan J. Civ. Eng. 2012, 6, 436–447. [Google Scholar]
- Submitted, A.T.; Partial, I.N.; Of, F.; Requirements, T.H.E.; The, F.O.R.; Of, D.; Science, M.O.F. Simultaneous Optimization of Vertical and Horizontal Road Alignments. Ph.D. Thesis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kobryń, A. Optimization of Vertical Alignment using General Transition Curves. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2017, 22, 2549–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bíl, M.; Andrášik, R.; Sedoník, J. A detailed spatiotemporal analysis of traffic crash hotspots. Appl. Geogr. 2019, 107, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhafedh, A. A Novel Hybrid Method for Measuring the Spatial Autocorrelation of Vehicular Crashes: Combining Moran’s Index and Getis-Ord Gi* Statistic. Open J. Civ. Eng. 2017, 7, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soltani, A.; Askari, S. Exploring spatial autocorrelation of traffic crashes based on severity. Injury 2017, 48, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhafedh, A. Identifying Vehicular Crash High Risk Locations along Highways via Spatial Autocorrelation Indices and Kernel Density Estimation. World J. Eng. Technol. 2017, 5, 198–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Achu, A.L.; Aju, C.D.; Suresh, V.; Manoharan, T.P.; Reghunath, R. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Road Accident Incidents and Delineation of Hotspots Using Geospatial Tools in Thrissur District, Kerala, India. KN—J. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. 2019, 69, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassan, S. Modeling and evaluating the relationship between the radius superelevation and comfort speed in horizontal curves. Adv. Transp. Stud. 2013, 30, 23–42. Available online: https://web.b.ebscohost.com/abstract?direct=true&profile=ehost&scope=site&authtype=crawler&jrnl=18245463&AN=89642255&h=g4rXcks6vGkS%2FekxvhGTCgafF88k1fkCM0b5BjjedxgiTI6GtZ0Muyfvmf388E%2FLdD9A0DJPKZ3F25O%2B8PwCnw%3D%3D&crl=c&resultNs=AdminWebAuth&resultLoc (accessed on 23 April 2022).
- Colak, H.E.; Memisoglu, T.; Erbas, Y.S.; Bediroglu, S. Hot spot analysis based on network spatial weights to determine spatial statistics of traffic accidents in Rize, Turkey. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, C.; Akçit, N. Traffic accident analysis using GIS: A case study of Kyrenia City. In Third International Conference on Remote Sensing and Geoinformation of the Environment (RSCy2015); SPIE: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015; Volume 9535, p. 953514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavousi, A.; Moradi, A.; Rahmani, K.; Zeini, S.; Ameri, P. Geographical distribution of at fault drivers involved in fatal traffic collisions in Tehran, Iran. Epidemiol. Health 2020, 42, e2020002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moradi, A.; Soori, H.; Kavousi, A.; Eshghabadi, F.; Jamshidi, E.; Zeini, S. Spatial Analysis to Identify High Risk Areas for Traffic Crashes Resulting in Death of Pedestrians in Tehran. Med. J. Islam. Repub. Iran 2016, 30, 450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.K.; Crawford, T.; Schmidlin, T.W. Spatio-temporal analysis of road traffic accident fatality in Bangladesh integrating newspaper accounts and gridded population data. GeoJournal 2018, 83, 645–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satria, R.; Castro, M. GIS Tools for Analyzing Accidents and Road Design: A Review. In Transportation Research Procedia; Elsevier B.V: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2016; Volume 18, pp. 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, K.; Shakeel, K.; Rashidi, T.H.; Kim, I. Measuring users’ satisfaction of the road network using structural equation modeling. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2021, 16, 792–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortum, A.; Atalay, A. Spatial analysis of road mortality rates in Turkey. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Transp. 2015, 168, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harirforoush, H.; Bellalite, L. A new integrated GIS-based analysis to detect hotspots: A case study of the city of Sherbrooke. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2019, 130, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, S.; Yoshiki, S.; Saeki, R.; Mimura, Y.; Ando, R.; Nanba, S. Development and application of traffic accident density estimation models using kernel density estimation. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2016, 3, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mestri, R.A.; Rathod, R.R.; Garg, R.D. Identification and Removal of Accident-Prone Locations Using Spatial Data Mining. In Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 33, pp. 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleerux, N. Geographic information system-based analysis to identify the spatiotemporal patterns of road accidents in sri racha, chon buri, Thailand. Curr. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2020, 20, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manap, N.; Brhan, M.; Yazid, M.; Hambali, M.; Rohan, A. Determining Spatial Patterns of Road Accidents at Expressway by Applying Getis-Ord Gi* Spatial Statistic. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2019, 8, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, J.; Ohri, A.; Kumar, B. Spatial and Statistical Analysis of Road Accidents Hot Spots Using GIS. 2015. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/291973317_Spatial_and_statistical_analysis_of_road_accidents_hot_spots_using_GIS (accessed on 11 December 2020).
- Yadav, D.K.; Ghodmare, S.D.; Naveen Kumar, N. Mitigation of Blackspots on Highways by the Application of Safe System Approach. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 52, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rousan, T.M.; Umar, A.A.; Al-Omari, A.A.; Goniewicz, K.; Czerski, R.; Kustra, M. Characteristics of Crashes Caused by Distracted Driving on Rural and Suburban Roadways in Jordan. Infrastructures 2021, 6, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghafli, A.; Mohamad, E.; Ahmed, A.Z. The effect of geometric road conditions on safety performance of abu dhabi road intersections. Safety 2021, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.H.; Teik Hua, L.; Hamid, H.; Azarkerdar, A. Relationship of Accident Rates and Road Geometric Design. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 357, 012040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, S.; Wang, K.; Oh, C.; Chang, J. Development of Highway Safety Policies by Discriminating Freeway Curve Alignment Features. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 22, 1418–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnaik, M.M. Effects of Highway Geometric Elements on Accident Modelling. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Civil Engineering National Institute of Technology Rourkela, Odisha, India, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, D.J.; Yang, J.R.; Liu, H.H.; Chiang, H.-S.; Wang, L.Y. Analysis of Environmental Factors on Intersection Accidents. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retallack, A.E.; Ostendorf, B. Relationship Between Traffic Volume and Accident Frequency at Intersections. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kronprasert, N.; Boontan, K.; Kanha, P. Crash prediction models for horizontal curve segments on two-lane rural roads in Thailand. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, M.F.; Hassan, S.A.; Mashros, N. The impact of roadway conditions towards accident severity on federal roads in Malaysia. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yao, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cai, J. Identification of the Impact of Radius Ratio of Horizontal to Vertical Curves on Highway Safety. In Proceedings of the CICTP 2020, Xi’an, China, 14–16 August 2020; pp. 4762–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Qiang, T. Spatial distribution of traffic accident density at urban road intersection considering severity. Jiangsu Daxue Xuebao (Ziran Kexue Ban)/J. Jiangsu Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 44, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuaddous, M.; Al-Hares, A.; Faten Albtoush, A.M.; Aldiabat Al-Btoosh, J.A. Identification and Ranking of Accident Black Spots in Jordan. Civ. Eng. Archit. 2022, 10, 1661–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FHWA (Federal Highway Administration). Roadway Departure Safety—Safety|Federal Highway Administration. 2011. Available online: https://safety.fhwa.dot.gov/local_rural/training/fhwasa1109/app_c.cfm (accessed on 22 July 2020).
- Mitchell, A. The ESRI Guide to GIS Analysis, Volume 2|Spatial Measurements and Statistics (Volume 1). 2005. Available online: https://esripress.esri.com/display/index.cfm?fuseaction=display&websiteID=86&moduleID=0 (accessed on 22 July 2022).
- Fan, Y.; Chen, J.; Shirkey, G.; John, R.; Wu, S.R.; Park, H.; Shao, C. Applications of structural equation modeling (SEM) in ecological studies: An updated review. Ecol. Process. 2016, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hair, J.F.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M.; Danks, N.P.; Ray, S. An Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling; SAGE Publications: London, UK, 2021; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarka, P. An overview of structural equation modeling: Its beginnings, historical development, usefulness and controversies in the social sciences. Qual. Quant. 2017, 52, 313–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, H.; Ahn, J.W. Model Setting and Interpretation of Results in Research Using Structural Equation Modeling: A Checklist with Guiding Questions for Reporting. Asian Nurs. Res. 2021, 15, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, I.; Abdelgawad, H.; Said, D. Studying driving behavior and risk perception: A road safety perspective in Egypt. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2022, 69, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.A.R.; Ahmad, N.; Shen, Y.; Pirdavani, A.; Basheer, M.A.; Brijs, T. Road safety risk assessment: An analysis of transport policy and management for low-, middle-, and high-income Asian countries. Sustainability 2018, 10, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Hair, J.F.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Hair, J.F. Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling. In Handbook of Market Research; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K. Corrected goodness-of-fit test in covariance structure analysis. Psychol. Methods 2019, 24, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liang, C. The Analysis of Spatial Pattern and Hotspots of Aviation Accident and Ranking the Potential Risk Airports Based on GIS Platform. J. Adv. Transp. 2018, 2018, 4027498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briz-Redón, Á.; Martínez-Ruiz, F.; Montes, F. Spatial analysis of traffic accidents near and between road intersections in a directed linear network. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2019, 132, 105252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Zhang, S.R. Identification and ranking of accident black spots using advanced empirical Bayes method. Chang’an Daxue Xuebao (Ziran Kexue Ban)/J. Chang’an Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 39, 115–126. [Google Scholar]
- Billah, K.; Adegbite, Q.; Sharif, H.O.; Dessouky, S.; Simcic, L. Analysis of Intersection Traffic Safety in the City of San Antonio, 2013–2017. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




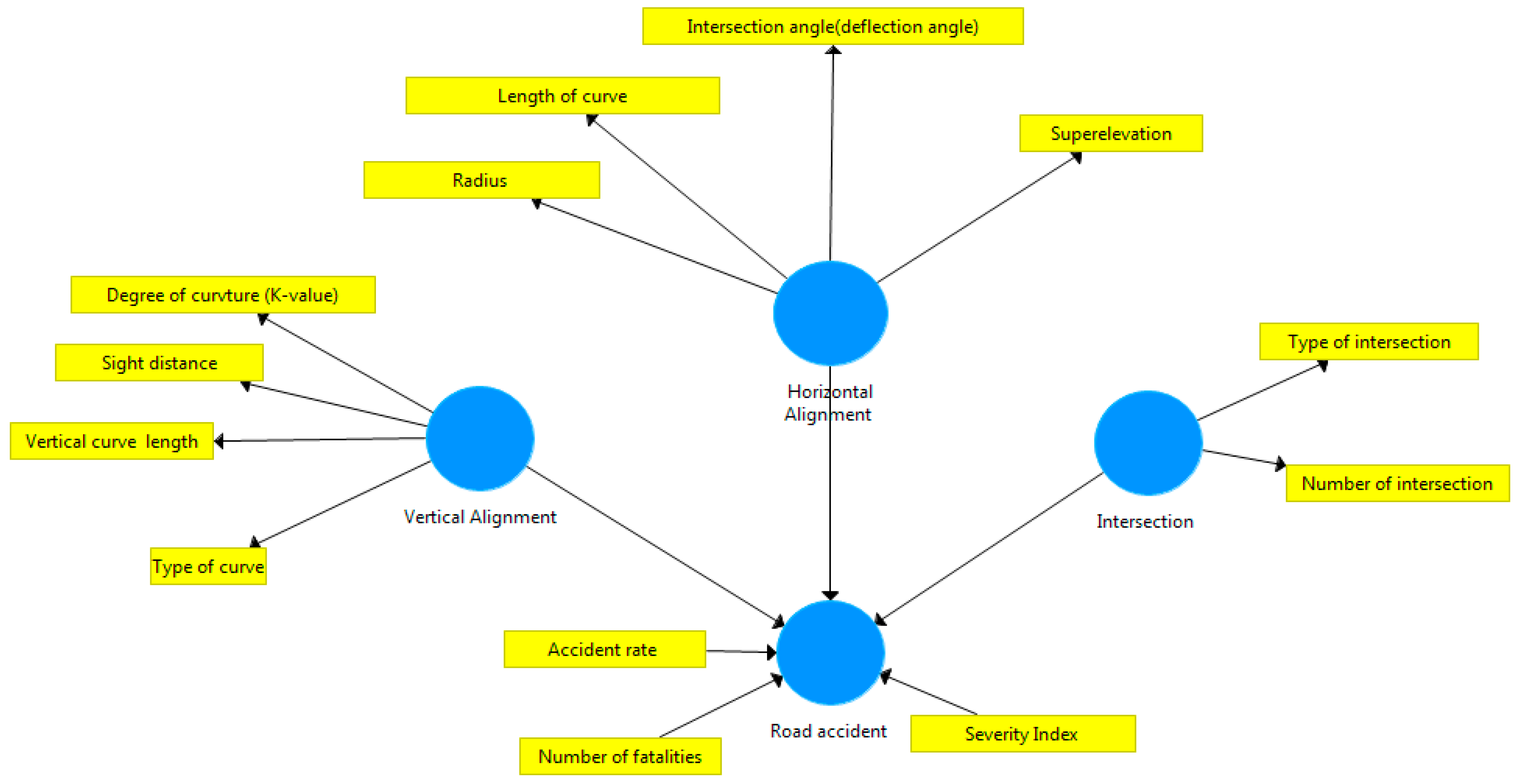


| The Variables | Definition | Indicator | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal Alignment | It is described as consisting of a series of straight lines, and circular curves | Radius of curve (R) | The radius of the circle determines the curve’s “sharpness” or “flatness” |
| Length of curve (L) | The distance between the point of curve (PC) and the point of tangent | ||
| Intersection angle (I) | The tangents’ direction change, equivalent to the central angle of the curve | ||
| Superelevation (e) | In this method of infrastructure construction for roadway curves, the outer pavement edge is elevated above the inner edge | ||
| Vertical alignment | It is described as consisting of grades (or tangents) linked by vertical curves | Length of vertical curve | The distance between beginning of vertical curve (BVC) to end of vertical curve (EVC) |
| K-value | The vertical curve’s length in terms of A’s percentage change | ||
| Type of curve (crest or sag) | Curves connecting inclined sections of road to form a crest | ||
| Sight distance | The smallest distance exposed to a driver’s view on a two-way road that enables him to safely pass another vehicle ahead while avoiding traffic coming from the opposite direction is known as overtaking or passing sight distance | ||
| Intersections | A road segment that is shared by two or more roads | Type of intersection | T-grade intersections, interchanges |
| Number of intersections | The number of intersections on the road section | ||
| Road accidents | A situation where one or more vehicles are involved in an accident that causes property damage, injuries, or fatalities | Number of fatalities | The number of injuries that usually result in death, either directly or as a result of complications, within one month of the injury’s occurrence (secondary data) |
| Accidents rate | It is calculated by taking exposure data such as traffic volume and road length into account | ||
| Severity index | A non-dimensional value indicating the danger of a road location (calculated using Jordan’s guidelines) |
| Point Number | Severity Index | Level Ranges | Z-Score | p-Value | Gi-Bin | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 76 | High | 5.550 | 0.000 | 3 | 36°3′16.162″ E 31°16′40.41″ N |
| 2 | 50 | Medium | 8.455 | 0.000 | 3 | 35°59′41.6″ E 30°57′43.408″ N |
| 3 | 50 | Medium | 8.455 | 0.000 | 3 | 35°59′41.74″ E 30°57′43.337″ N |
| 4 | 49 | Medium | 4.180 | 0.000 | 3 | 36°3′55.985″ E 31°18′44.856″ N |
| 5 | 37 | Medium | 3.513 | 0.000 | 3 | 36°3′8.531″ E 31°31′23.773″ N |
| 6 | 33 | Medium | 2.260 | 0.040 | 2 | 36°4′49.439″ E 31°23′2.023″ N |
| 7 | 29 | Low | 4.145 | 0.000 | 3 | 35°14′49.909″ E 29°40′42.223″ N |
| 8 | 24 | Low | 3.579 | 0.000 | 3 | 36°1′24.42″ E 31°12′38.527″ N |
| 9 | 24 | Low | 3.741 | 0.000 | 3 | 35°39′38.514″ E 30°10′15.596″ N |
| 10 | 21 | Low | 3.789 | 0.000 | 3 | 35°39′45.711″ E 30°10′19.184″ N |
| 11 | 20 | Low | 1.821 | 0.082 | 1 | 35°47′24.093″ E 30°28′1.652″ N |
| 12 | 15 | Low | 3.405 | 0.001 | 3 | 36°1′41.137″ E 31°13′0.107″ N |
| 13 | 15 | Low | 1.687 | 0.061 | 1 | 35°12′59.686″ E 29°39′28.277″ N |
| 14 | 15 | Low | 1.686 | 0.061 | 1 | 35°45′50.167″ E 30°22′53.996″ N |
| 15 | 13 | Low | 3.789 | 0.000 | 3 | 35°39′43.013″ E 30°10′17.518″ N |
| 16 | 13 | Low | 3.579 | 0.000 | 3 | 36°1′22.79″ E 31°12′36.712″ N |
| 17 | 12 | Low | 3.579 | 0.000 | 3 | 36°1′23.057″ E 31°12′37.972″ N |
| 18 | 12 | Low | 5.364 | 0.000 | 3 | 36°3′12.595″ E 31°16′32.867″ N |
| 19 | 12 | Low | 3.741 | 0.000 | 3 | 35°39′38.894″ E 30°10′15.816″ N |
| 20 | 12 | Low | 5.364 | 0.000 | 3 | 36°3′12.593″ E 31°16′32.867″ N |
| 21 | 12 | Low | 3.176 | 0.001 | 3 | 36°3′9.684″ E 31°31′18.455″ N |
| 22 | 10 | Low | 2.051 | 0.018 | 2 | 36°3′9.187″ E 31°31′24.147″ N |
| Latent Variable | KMO |
|---|---|
| Horizontal Alignment | 0.767 |
| Vertical Alignment | 0.610 |
| Intersection | 0.828 |
| Road Accident | 0.782 |
| Latent Variable | Indicator | Horizontal Alignment (Factor 1) | Vertical Alignment (Factor 2) | Road Intersection (Factor 3) | Road Accident (Factor 4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal alignment | Radius of curve | 0.601 | 0.014 | −0.256 | 0.094 |
| Superelevation | 0.856 | 0.005 | −0.413 | −0.094 | |
| Length of curve | 0.350 | −0.102 | −0.020 | −0.102 | |
| Intersection angle | 0.603 | 0.318 | −0.117 | −0.114 | |
| Vertical alignment | K-value | 0.303 | 0.600 | 0.082 | −0.120 |
| Vertical length | 0.212 | 0.602 | 0.075 | −0.059 | |
| Sight distance | −0.067 | 0.684 | −0.065 | −0.145 | |
| Type of curve | 0.331 | −0.373 | 0.030 | 0.11 | |
| Intersection | Type of intersection | −0.331 | −0.114 | 0.867 | 0.555 |
| Number of intersections | 0.230 | 0.051 | −0.801 | −0.351 | |
| Road accident | Accident rate | −0.223 | −0.209 | 0.681 | 0.790 |
| Severity index | −0.086 | −0.115 | 0.280 | 0.797 | |
| Number of fatalities | −0.416 | −0.310 | 0.340 | 0.728 |
| Variables | Indicator | Factor Loading | AVE | CRA | Cronbach’s Alpha |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal alignment | Radius | 0.794 | 0.600 | 0.747 | 0.502 |
| Superelevation | 0.732 | ||||
| Intersection angle of curve | 0.577 | ||||
| Vertical alignment | Degree of curvature (k-value) | 0.904 | 0.501 | 0.703 | 0.501 |
| Sight distance | 0.564 | ||||
| Vertical curve length | 0.575 | ||||
| Intersection | Type of intersection | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Variables | Indicator | Standardized Estimates | T-Value | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Road accident | Accident rate | 0.617 | 5.052 | 1.175 |
| Severity index | 0.435 | 4.324 | 2.167 | |
| Number of fatalities | 0.699 | 8.402 | 1.937 |
| Relationship | Beta | Std Error | T-Value | p-Value | Decision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal alignment Road accident | −0.316 | 0.104 | 2.922 | 0.004 | Supported ** |
| Vertical alignment Road accident | −0.118 | 0.090 | 1.311 | 0.190 | Not Supported |
| Intersection Road accident | 0.597 | 0.057 | 10.570 | 0.000 | Supported ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aldala’in, S.A.; Abdul Sukor, N.S.; Obaidat, M.T.; Abd Manan, T.S.B. Road Accident Hotspots on Jordan’s Highway Based on Geometric Designs Using Structural Equation Modeling. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8095. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148095
Aldala’in SA, Abdul Sukor NS, Obaidat MT, Abd Manan TSB. Road Accident Hotspots on Jordan’s Highway Based on Geometric Designs Using Structural Equation Modeling. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(14):8095. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148095
Chicago/Turabian StyleAldala’in, Shatha Aser, Nur Sabahiah Abdul Sukor, Mohammed Taleb Obaidat, and Teh Sabariah Binti Abd Manan. 2023. "Road Accident Hotspots on Jordan’s Highway Based on Geometric Designs Using Structural Equation Modeling" Applied Sciences 13, no. 14: 8095. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148095
APA StyleAldala’in, S. A., Abdul Sukor, N. S., Obaidat, M. T., & Abd Manan, T. S. B. (2023). Road Accident Hotspots on Jordan’s Highway Based on Geometric Designs Using Structural Equation Modeling. Applied Sciences, 13(14), 8095. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148095







