Compression Behavior of Rubber–Bentonite Mixture under Different Salinities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Test Soil Sample, Rubber, and Solution
1.2. Test Methods and Working Conditions
1.3. Test Instrument
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Compression Coefficient Change of MX80 Bentonite/Rubber Mixture
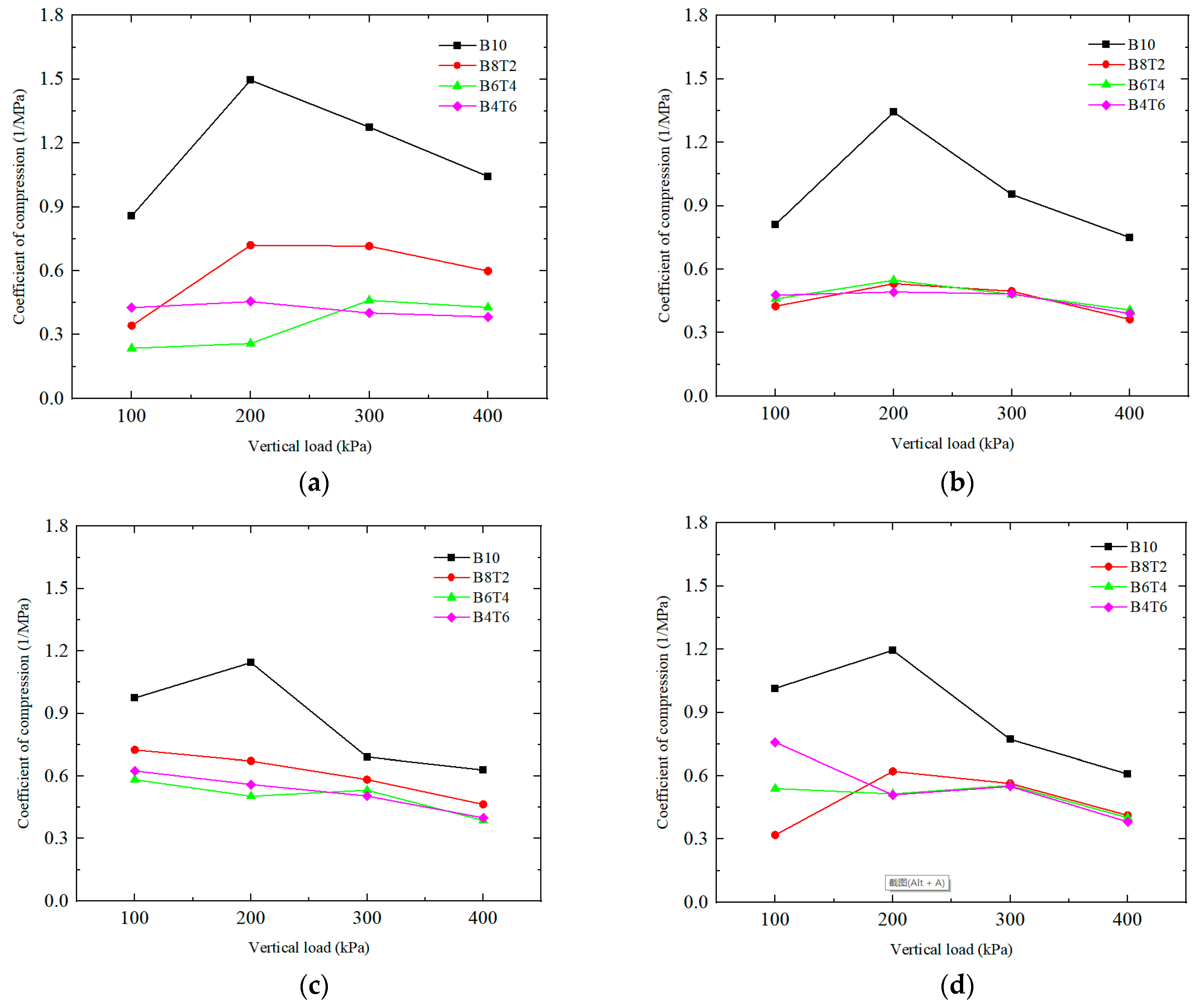
2.1.1. Influence of Different Mass Ratio on Compression Coefficient
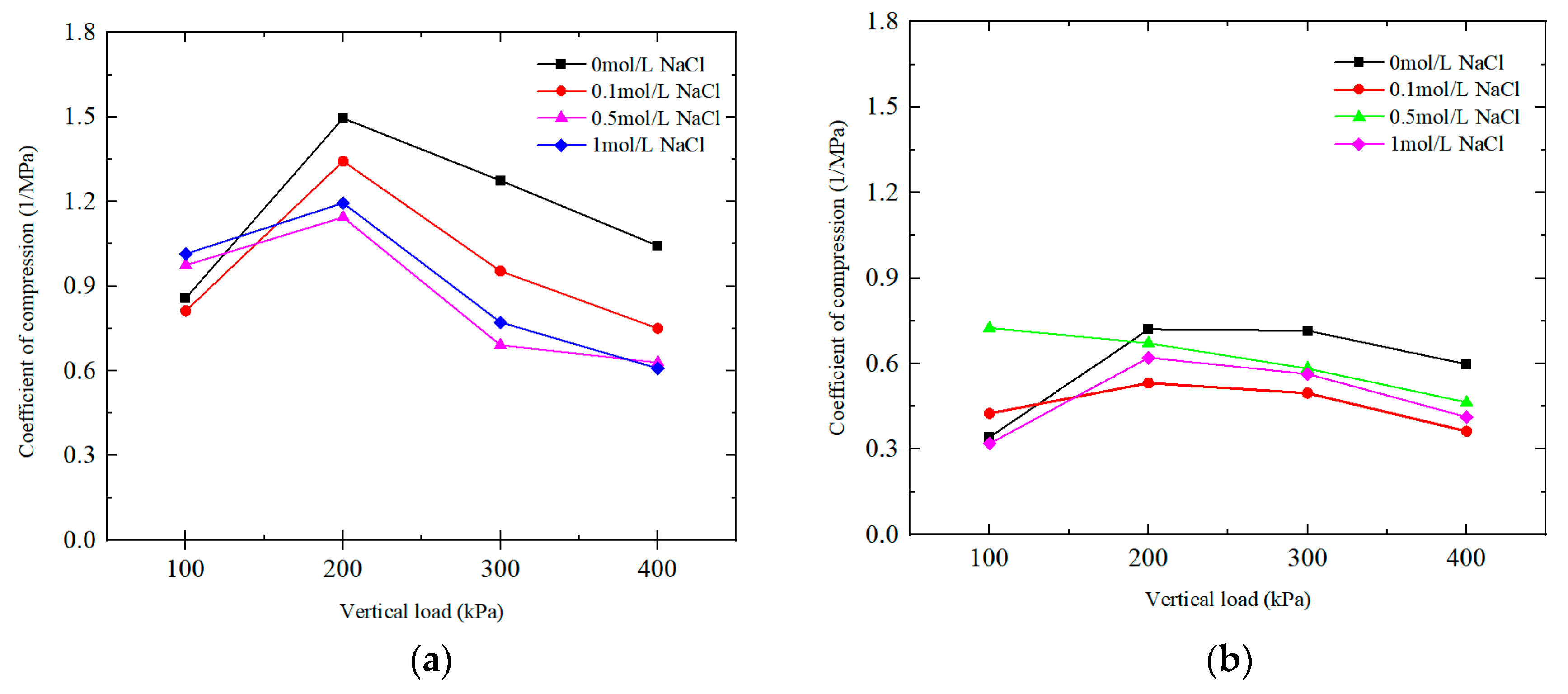
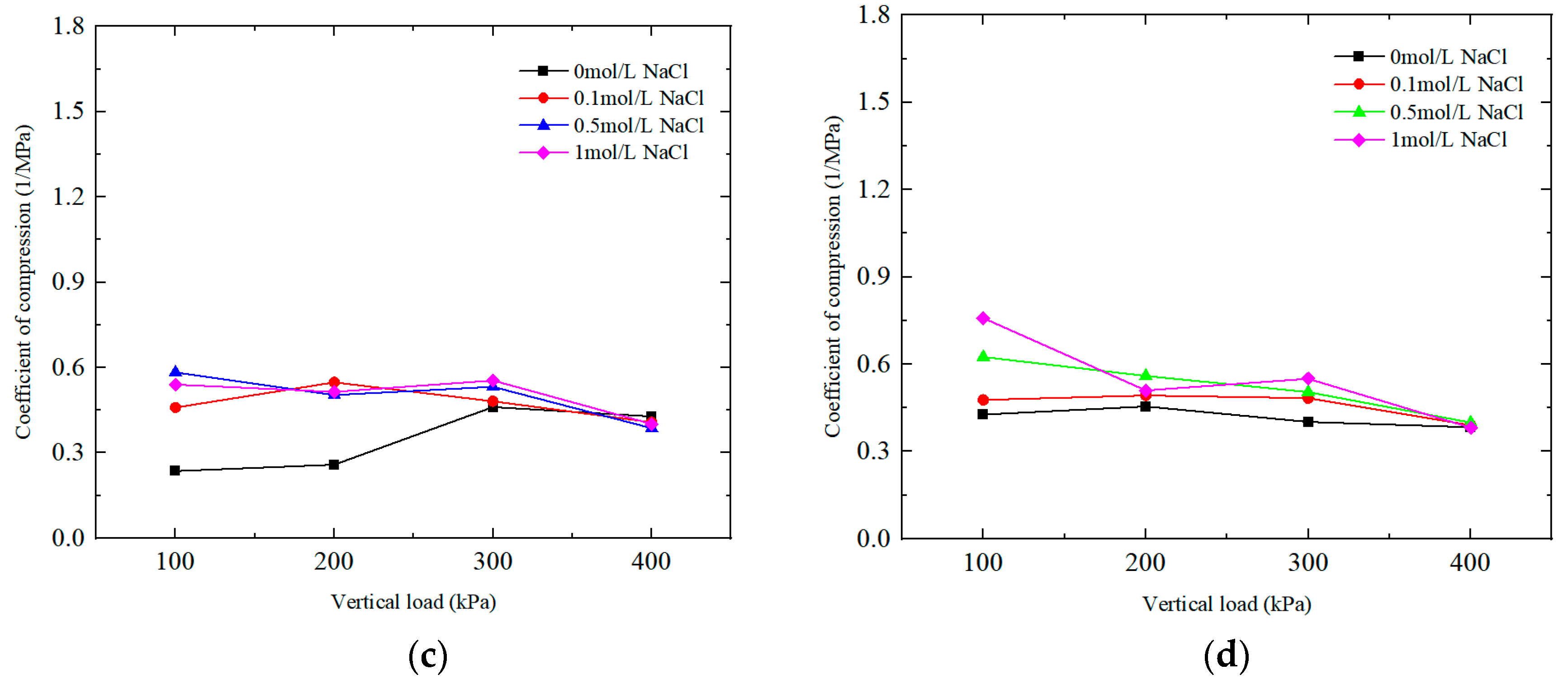
2.1.2. Influence of Salt Solution Concentration on Compression Coefficient
2.1.3. Effect of Salt Solution Concentration on Compression Modulus under Different Vertical Loads
2.2. Modulus of Compression Change of MX80 Bentonite/Rubber Mixture
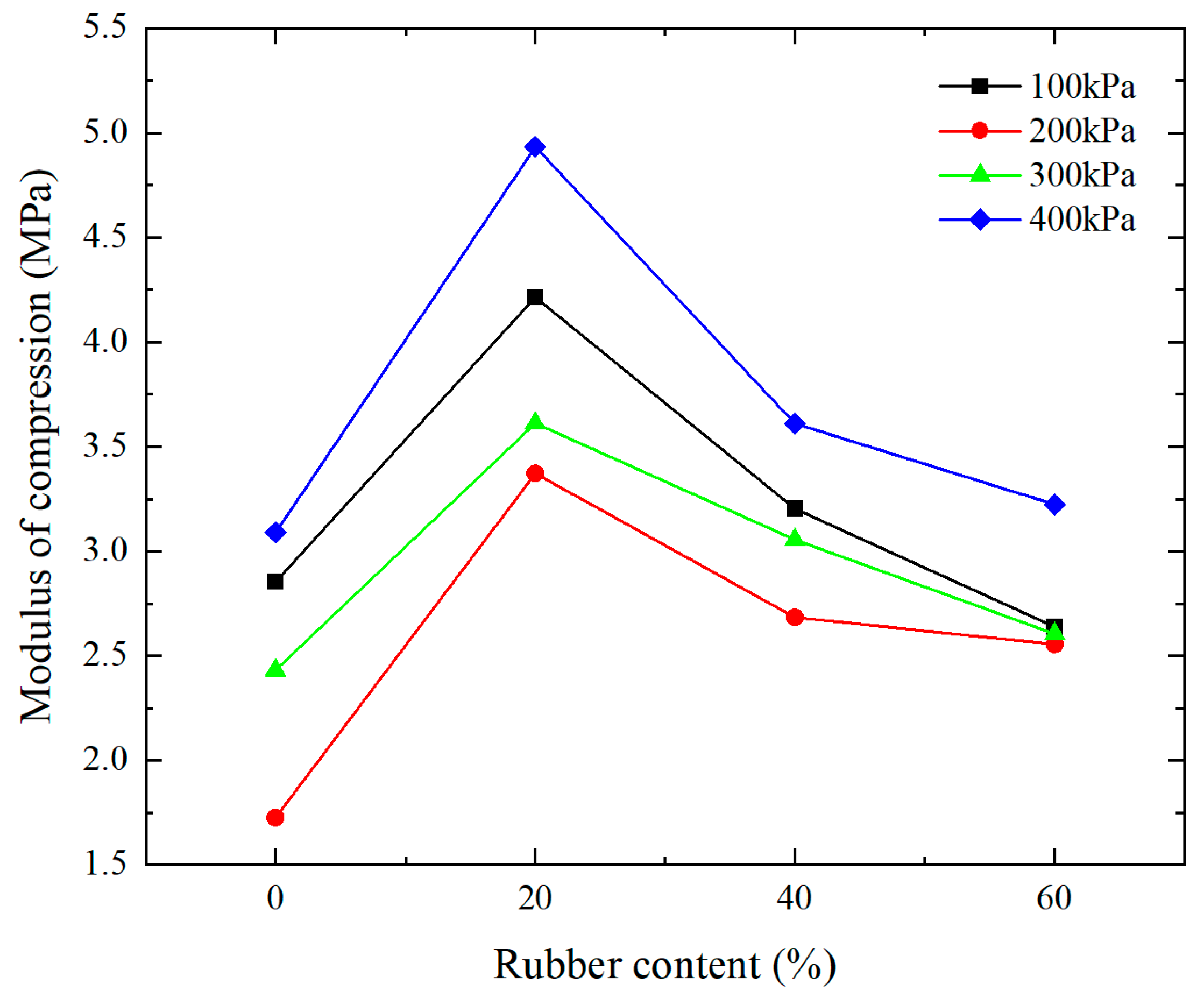
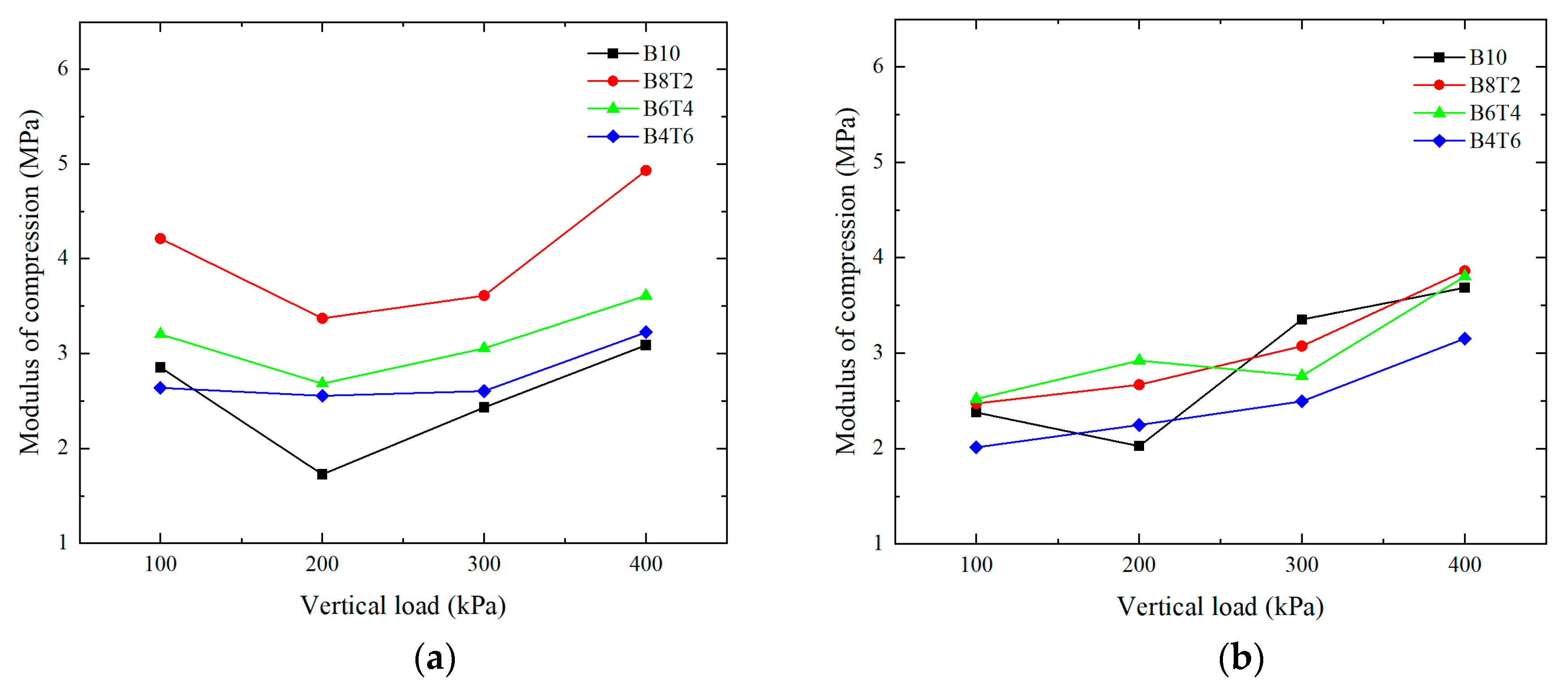
2.2.1. Effect of Rubber Content on Compression Modulus under Different Vertical Loads
2.2.2. Influence of Different Mass Ratios on Compression Modulus
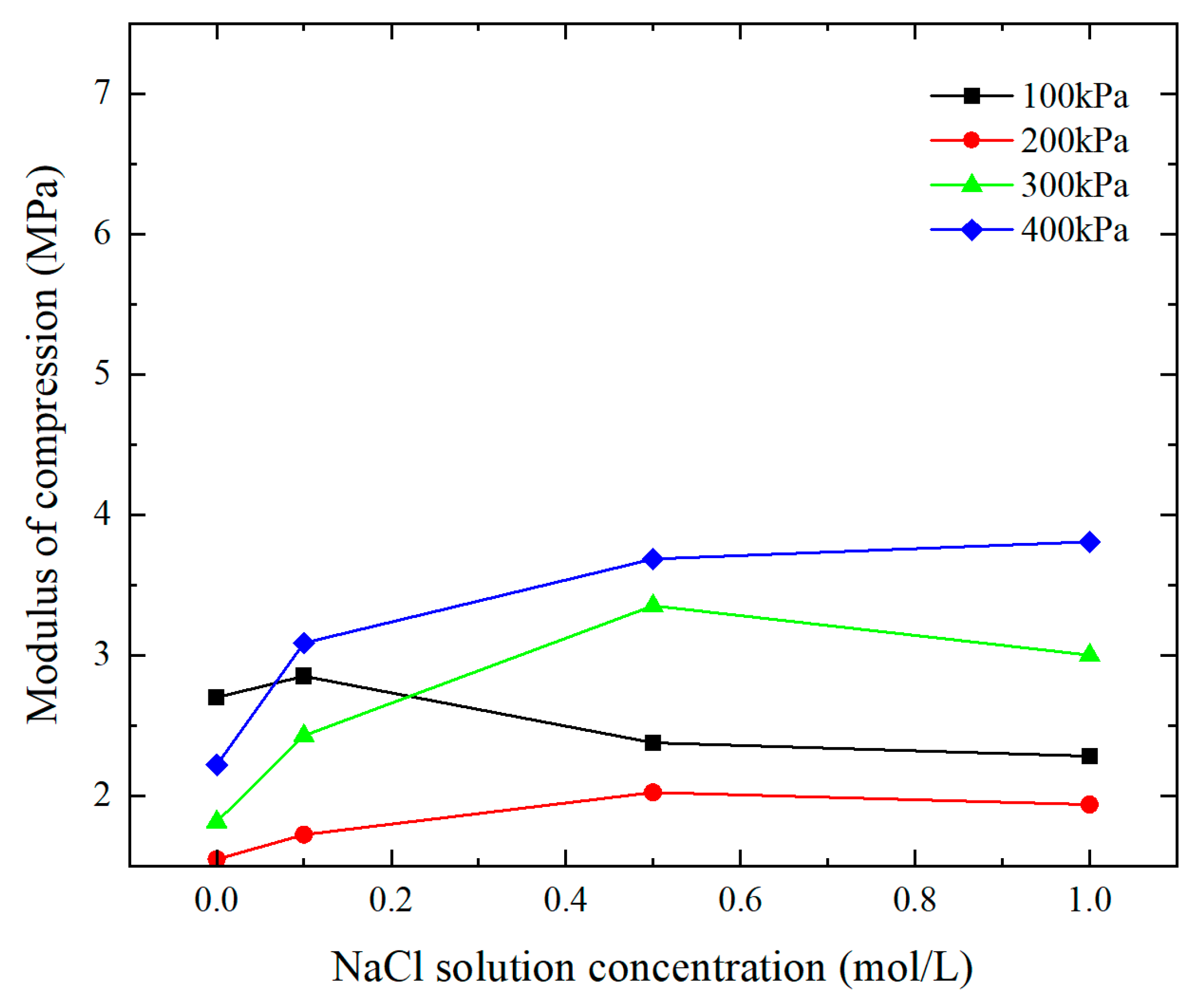
2.2.3. Effect of Salt Solution Concentration on Compression Modulus under Different Vertical Loads
3. Conclusions
- The effects of temperature and duration on the microstructural evolution mechanism of external cushion particles should be explored to address the release of decay heat from radioactive waste stored in a storage tank.
- The impact of groundwater on the external cushion, particularly the microstructural evolution of free boundaries, during wetting–drying cycles should be considered. The effects of these cycles on the engineering mechanics properties of the cushion should be investigated to gain a comprehensive understanding of its horizontal and vertical stability.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chai, M. Deep Processing and Application of Bentonite. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Z.J. Selection and basic properties of buffer materials for deep geological disposal of high-level radioactive wastes in China. J. Petromineral. 2005, 6, 583–586. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Chen, X. Dynamic response of bridge abutment to sand-rubber mixtures backfill under seismic loading conditions. J. Vibroeng. 2017, 19, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Sun, H.; Jing, L.; Dong, R. Geotechnical Seismic Isolation System Based on Rubber-Sand Mixtures for Rural Residence Buildings: Shaking Table Test. Materials 2022, 15, 7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, A.; Serino, G.; Strano, S.; Terzo, M. Experimental investigation of a low-cost elastomeric anti-seismic device using recycled rubber. Meccanica 2015, 50, 2201–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, A.; Guidi, L.G. Base isolation issues in Italy: Integrated architectural and structural designs. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 130, 105912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Li, G.; Gou, X.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Y. Seismic Performance and Engineering Application Investigation of a New Alternative Retainer. Polymers 2022, 14, 3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FE-Analysis of an Isolation Element Made of High Damping Rubber Undergoing Extreme Large Strains and Stresses. Available online: https://www.webofscience.com/wos/alldb/full-record/WOS:000251796000064 (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- Cheng, X.; Xu, X.; Jing, L.; Liang, H.; Cui, J. Seismic Behavior of Shear Keys Enhanced with Novel Energy Absorption Devices in Immersion Joints Based on Pseudo-Static Tests. Materials 2022, 15, 4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habieb, A.B.; Milani, G.; Quaglini, V.; Milani, F. Experimentation and numerical modelling of recycled rubber pads for seismic isolation under accelerated ageing. In Proceedings of the Central European Symposium on Thermophysics 2019 (CEST), Banska Bystrica, Slovakia, 16–18 October 2019; p. 420006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Li, H.J.; Wu, J.F. Base-Isolated Multi-Storey Reinforced Concrete Frame Structure Modal Analysis. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 204–208, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polukoshko, S.; Martinovs, A.; Gonca, V. Specifics of behavior and calculation of elastomeric shock absorber under impact loading. In Proceedings of the 17th International Scientific Conference Engineering for Rural Development, Jelgava, Latvia, 23–25 May 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Shen, S.; Shen, Z.; Gong, R. Experimental investigation on the effectiveness of laminated rubber bearings to isolate metro generated vibration. Measurement 2018, 122, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Oua, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, S. Full-scale tests and analytical model of the Teflon-based lead rubber isolation bearings. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2013, 48, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Kim, J.H. Prediction of long-term creep deflection of seismic isolation bearings. J. Vibroeng. 2017, 19, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kashif, N.; Albijanic, B.; Xu, J.J.; Syahida, S.; McGrath, T.; Tadesse, B.; Nazir, M.K. Grinding of highly viscous bentonite containing slurries. Appl. Clay Sci. 2023, 232, 106794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Cui, Y.-J.; Talandier, J. Compaction and sealing properties of bentonite/claystone mixture: Impacts of bentonite fraction, water content and dry density. Eng. Geol. 2021, 287, 106122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-M.; Xu, G.-Q.; Liu, S.-F.; Chen, Z.-R. Study on Compaction Expansion Characteristics of buffer/Backfill Materials in Chinese high-level waste disposal Repository. Uranium Geol. 2001, 1, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.-R.; Xu, S.-X. Study on compaction characteristics of lime and fly ash stabilized expansive soil subgrade. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. 2002, 9, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Shi, M.-L. Study on bimodal characteristics of compaction curve of Lime-modified expansive soil. Rock Soil Mech. 2011, 32, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Meng, Y.; Wei, S.; Weimin, Y.; Chen, Y. Cracking and sealing behavior of the compacted bentonite upon technological voids filling. Eng. Geol. 2021, 292, 106244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-G.; Tang, C.-S.; Zhu, C.; Shi, B.; Liu, Y.-M. Compression, swelling and rebound behavior of GMZ bentonite/additive mixture under coupled hydro-mechanical condition. Eng. Geol. 2017, 221, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cui, Y. Investigation on compression behaviour of highly compacted GMZ01 bentonite with suction and temperature control. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2012, 252, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H. Compaction properties of granular bentonites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2006, 31, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.-M.; Qian, L.-X.; Chen, B.; Yu, C. Microstructure of Gaomiaozi bentonite under high pressure. J. Tongji Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2009, 37, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, P.-J.; Ye, W.-M.; Chen, Y.-G.; Chen, B.; Cui, Y.-J. Influence of strain-rate on hydromechanical behavior of highly compacted GMZ01 bentonite. Eng. Geol. 2015, 195, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cokca, E.; Yilmaz, Z. Use of rubber and bentonite added fly ash as a liner material. Waste Manag. 2004, 24, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, N.M.; Mishra, A.K. Effect of salt permeants on the consolidation and hydraulic behaviour of fibre treated black cotton soil for landfill application. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 369, 133339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effect of Inorganic Salt Solutions on Some Geotechnical Properties of Soil-Bentonite Mixtures as Barriers. Available online: https://www.webofscience.com/wos/alldb/full-record/WOS:000292123400004 (accessed on 4 June 2023).
- Mishra, A.K.; Ohtsubo, M.; Li, L.; Higashi, T. Controlling factors of the swelling of various bentonites and their correlations with the hydraulic conductivity of soil-bentonite mixtures. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 52, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard for Geotechnical Test Methods. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=kxaUMs6x7-5KB1kF296ShrYo_9ZoYIWW4VfT4bfQP25xUu13oQ_hU6dQu3ie_tjMWuo5koMwfcWzLFYwXn6UEg%3d%3d&uniplatform=NZKPT (accessed on 4 June 2023).
- Bekhiti, M.; Trouzine, H.; Rabehi, M. Influence of waste tire rubber fibers on swelling behavior, unconfined compressive strength and ductility of cement stabilized bentonite clay soil. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 208, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Influencing Factor | Working Condition |
|---|---|
| Salt solution concentration | 0 mol, 0.1 mol, 0.5 mol, 1 mol |
| Rubber content (mass ratio) | 0%, 20%, 40%, 60% |
| Consolidation pressure | 100 kPa, 200 kPa, 300 kPa, 400 kPa |
| Total number of samples | 64 groups |
| Rubber Content | Solution Concentration/Vertical Load | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | Mean Value | Standard Deviation | Variance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0.857724 | 1.495222 | 1.274996 | 1.043178 | 1.168 | 0.277 | 0.077 |
| 0.1 | 0.812494 | 1.342873 | 0.953552 | 0.750429 | 0.965 | 0.266 | 0.071 | |
| 0.5 | 0.974466 | 1.144429 | 0.691191 | 0.628869 | 0.860 | 0.242 | 0.059 | |
| 1 | 1.014464 | 1.194814 | 0.772119 | 0.608679 | 0.898 | 0.259 | 0.067 | |
| 20% | 0 | 0.342022 | 0.720047 | 0.715547 | 0.598539 | 0.594 | 0.177 | 0.031 |
| 0.1 | 0.4254 | 0.5317 | 0.4963 | 0.3634 | 0.454 | 0.075 | 0.006 | |
| 0.5 | 0.7246 | 0.6716 | 0.5832 | 0.4639 | 0.611 | 0.114 | 0.013 | |
| 1 | 0.3194 | 0.6212 | 0.5636 | 0.4126 | 0.479 | 0.138 | 0.019 | |
| 40% | 0 | 0.236 | 0.2581 | 0.4609 | 0.4277 | 0.346 | 0.115 | 0.013 |
| 0.1 | 0.4592 | 0.5481 | 0.4815 | 0.4074 | 0.474 | 0.058 | 0.003 | |
| 0.5 | 0.5834 | 0.5033 | 0.5324 | 0.3865 | 0.501 | 0.083 | 0.007 | |
| 1 | 0.5398 | 0.5143 | 0.5545 | 0.4012 | 0.502 | 0.070 | 0.005 | |
| 60% | 0 | 0.4268 | 0.4546 | 0.402 | 0.3835 | 0.417 | 0.031 | 0.001 |
| 0.1 | 0.477 | 0.4927 | 0.4833 | 0.3904 | 0.461 | 0.047 | 0.002 | |
| 0.5 | 0.625 | 0.56 | 0.5044 | 0.3991 | 0.522 | 0.096 | 0.009 | |
| 1 | 0.7582 | 0.5096 | 0.55 | 0.3821 | 0.550 | 0.156 | 0.024 |
| Rubber Content | Solution Concentration/Vertical Load | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | Mean Value | Standard Deviation | Variance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 2.702703 | 1.550388 | 1.818182 | 2.222222 | 2.073 | 0.502 | 0.252 |
| 0.1 | 2.853158 | 1.72628 | 2.431094 | 3.089132 | 2.525 | 0.598 | 0.358 | |
| 0.5 | 2.378917 | 2.025616 | 3.353884 | 3.686259 | 2.861 | 0.786 | 0.618 | |
| 1 | 2.285122 | 1.940197 | 3.002353 | 3.808533 | 2.759 | 0.828 | 0.685 | |
| 20% | 0 | 5.241418 | 2.489674 | 2.505332 | 2.995096 | 3.308 | 1.310 | 1.717 |
| 0.1 | 4.214109 | 3.371604 | 3.612093 | 4.933081 | 4.033 | 0.697 | 0.486 | |
| 0.5 | 2.47403 | 2.66927 | 3.073871 | 3.864371 | 3.020 | 0.616 | 0.379 | |
| 1 | 5.612654 | 2.885837 | 3.18077 | 4.344842 | 4.006 | 1.243 | 1.544 | |
| 40% | 0 | 6.234088 | 5.700289 | 3.192113 | 3.439899 | 4.642 | 1.549 | 2.401 |
| 0.1 | 3.20393 | 2.684263 | 3.055545 | 3.611303 | 3.139 | 0.383 | 0.147 | |
| 0.5 | 2.521846 | 2.923196 | 2.76342 | 3.806584 | 3.004 | 0.560 | 0.314 | |
| 1 | 2.725537 | 2.860674 | 2.653282 | 3.66711 | 2.977 | 0.468 | 0.219 | |
| 60% | 0 | 2.949031 | 2.76869 | 3.130961 | 3.281998 | 3.033 | 0.222 | 0.050 |
| 0.1 | 2.638672 | 2.55459 | 2.604276 | 3.223992 | 2.755 | 0.314 | 0.099 | |
| 0.5 | 2.013834 | 2.247583 | 2.495334 | 3.153712 | 2.478 | 0.492 | 0.242 | |
| 1 | 1.660045 | 2.469871 | 2.288448 | 3.294024 | 2.428 | 0.674 | 0.454 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, T.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Xie, Z.; Lin, S.; Nong, X. Compression Behavior of Rubber–Bentonite Mixture under Different Salinities. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8134. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148134
Wan T, Lu Y, Zeng Z, Xie Z, Lin S, Nong X. Compression Behavior of Rubber–Bentonite Mixture under Different Salinities. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(14):8134. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148134
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Tong, Yi Lu, Zhenming Zeng, Zeli Xie, Shan Lin, and Xingzhong Nong. 2023. "Compression Behavior of Rubber–Bentonite Mixture under Different Salinities" Applied Sciences 13, no. 14: 8134. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148134
APA StyleWan, T., Lu, Y., Zeng, Z., Xie, Z., Lin, S., & Nong, X. (2023). Compression Behavior of Rubber–Bentonite Mixture under Different Salinities. Applied Sciences, 13(14), 8134. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148134





