Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis Using Machine Learning: A Survey
Abstract
:1. Introduction
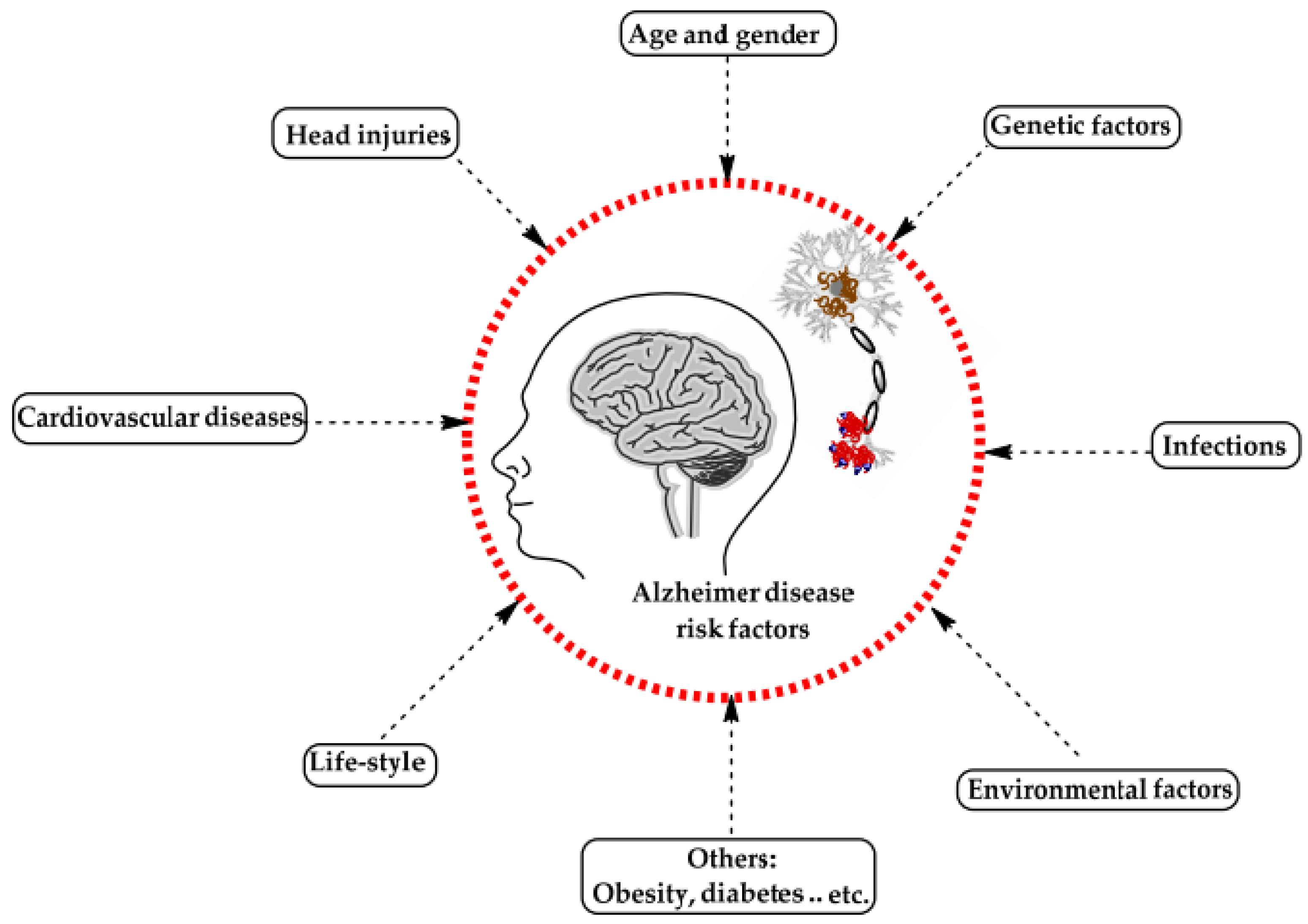
2. Alzheimer’s Disease
3. Review Methodology
4. Literature Review
- Convolutional network feature extraction can be error-prone, and some features may be overlooked during learning;
- The feature selection phase either did not exist or was not carried out correctly in these experiments;
- A unique technique, such as an artificial neural network or a support vector machine, is utilized for classification.
4.1. Machine Learning Algorithms
4.2. Support Vector Machine
4.3. Image Processing Techniques
4.4. Other Methods
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures. Alzheimer’s & Dementia; Alzheimer’s Association’s Publication & Wiley: Chicago, IL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Rajput, A. Does essential tremor increase the risk of dementia? No. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2022, 163, 233–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, J.; Langerman, H. Alzheimer’s Disease-Why We Need Early Diagnosis. Degener. Neurol. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2019, 9, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- 15th Conference Clinical Trials Alzheimer’s Disease, November 29–December 2, 2022, San Francisco, CA, USA: Posters (Clinical Trial Alzheimer’s Disease). J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 9 (Suppl. S1), 51–248.
- Dinius Cassandra, J.; Pocknell, C.E.; Caffrey, M.P.; Roche, R.A.P. Cognitive interventions for memory and psychological well-being in aging and dementias. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1070012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonci, A.; Fiori, S.; Higashi, H.; Tanaka, T.; Verdini, F. An Introductory Tutorial on Brain–Computer Interfaces and Their Applications. Electronics 2021, 10, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loued-Khenissi, L.; Döll, O.; Preuschoff, K. An Overview of Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Techniques for Organizational Research. Organ. Res. Methods 2018, 22, 17–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, J. A spectral sampling algorithm in dynamic causal modelling for resting-state fMRI. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2023, 44, 2981–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankovic, J.; Mazziotta, J.; Pomeroy, S. (Eds.) Alzheimer disease and other dementias. In Bradley and Daroff’s Neurology in Clinical Practice, 8th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, J.; Zhang, Q.-H.; Yang, X.; Wang, P.; Sun, X.-C.; Yan, S.-Y.; Li, A.; Zhao, W.-W.; Cao, D.-N.; Wang, Y.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of white matter in Alzheimer’s disease: A global bibliometric analysis from 1990 to 2022. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1163809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.A.; Fox, N.C.; Sperling, R.A.; Klunk, W.E. Brain imaging in Alzheimer’s disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes and Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderghal, K. Classification of Multimodal MRI Images Using Deep Learning: Application to the Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Image Processing [eess.IV]; Université Ibn Zohr: Agadir, Morocco; Université de Bordeaux: Bordeaux, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ban, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lao, H. Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease using structure highlighting key slice stacking and transfer learning. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 5855–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coraggio, L.; Coretto, P. Selecting the number of clusters, clustering models, and algorithms. A unifying approach based on the quadratic discriminant score. J. Multivar. Anal. 2023, 196, 105181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinola, O.O.; Ezugwu, A.E.; Agushaka, J.O.; Abu Zitar, R.; Abualigah, L. Multiclass feature selection with metaheuristic optimization algorithms: A review. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 19751–19790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taye, M.M. Understanding of Machine Learning with Deep Learning: Architectures, Workflow, Applications and Future Directions. Computers 2023, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Song, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. A Review of Deep-Learning-Based Medical Image Segmentation Methods. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, C. The State of the Art of Dementia Research: New Frontiers; Alzheimers Disease International: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Prince, M.; Wimo, A.; Guerchet, M.; Ali, G.C.; Wu, Y.-T.; Prina, M. The global impact of dementia: An analysis of prevalence, incidence, cost, and trends. World Alzheimer Rep. 2015, 2015, 84. [Google Scholar]
- Bomasang-Layno, E.; Bronsther, R. Diagnosis and Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: An Update. Del. J. Public Health 2021, 7, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounden, V.; Bhatt, H.; Jialal, I. Renal Function Tests; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507821/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Scahill, R.I.; Schott, J.M.; Stevens, J.M.; Rossor, M.N.; Fox, N.C. Mapping the evolution of regional atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease: Unbiased analysis of fluid-registered serial MRI. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 4703–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keles, M.K.; Kilic, U. Classification of Brain Volumetric Data to Determine Alzheimer’s Disease Using Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm as Feature Selector. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 82989–83001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanakkanavar, N.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, B. MRI Segmentation and Classification of Human Brain Using Deep Learning for Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Survey. Sensors 2020, 20, 3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, J.C. Principles and practice of functional MRI of the human brain. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masood, M.; Nazir, T.; Nawaz, M.; Mehmood, A.; Rashid, J.; Kwon, H.-Y.; Mahmood, T.; Hussain, A. A Novel Deep Learning Method for Recognition and Classification of Brain Tumors from MRI Images. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapica-Topczewska, K.; Collin, F.; Tarasiuk, J.; Czarnowska, A.; Chorąży, M.; Mirończuk, A.; Kochanowicz, J.; Kułakowska, A. Assessment of Disability Progression Independent of Relapse and Brain MRI Activity in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis in Poland. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khuzaie, F.E.K.; Bayat, O.; Duru, A.D. Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease using 2D MRI slices by the convolutional neural network. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2021, 2021, 6690539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.; Chung, Y.-C.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, W.-S.; Oh, I.-S. Classification and Visualization of Alzheimer’s Disease using Volumetric Convolutional Neural Network and Transfer Learning. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gray, K.R. Machine Learning for Image-Based Classification of Alzheimer’s Disease; Imperial College London: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi-Ghahnavieh, A.; Luo, S.; Chiong, R. Transfer learning for Alzheimer’s disease detection on MRI images. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Industry 4.0, Artificial Intelligence, and Communications Technology (IAICT), Bali, Indonesia, 1–3 July 2019; pp. 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazal, T.M.; Abbas, S.; Munir, S.; Ahmad, M.; Issa, G.F.; Zahra, S.B.; Khan, M.A.; Hasan, M.K. Alzheimer Disease Detection Empowered with Transfer Learning. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 70, 5005–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestor, P.J.; Scheltens, P.; Hodges, J.R. Advances in the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S34–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazem, A.; Mansoori, G. Nanotechnology for Alzheimer’s disease detection and treatment. Insci. J. 2011, 1, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Li, M.; Luo, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Bi, Y. Alzheimer’s disease detection using depthwise separable convolutional neural networks. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 203, 106032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petti, U.; Baker, S.; Korhonen, A. A systematic literature review of automatic Alzheimer’s disease detection from speech and language. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2020, 27, 1784–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, J.; Zhang, Y. An ensemble of deep convolutional neural networks for Alzheimer’s disease detection and classification. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.01675. [Google Scholar]
- Balagopalan, A.; Eyre, B.; Rudzicz, F.; Novikova, J. To BERT or not to BERT: Comparing Speech and Language-Based Approaches for Alzheimer’s Disease Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.01551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folego, G.; Weiler, M.; Casseb, R.F.; Pires, R.; Rocha, A. Alzheimer’s Disease Detection Through Whole-Brain 3D-CNN MRI. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 534592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balagopalan, A.; Novikova, J.; Rudzicz, F.; Ghassemi, M. The effect of heterogeneous data for Alzheimer’s disease detection from speech. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.12254. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Si, X.; Chen, Y.; Chao, Y.; Lin, C.-P.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Ming, D.; Li, Q. Hippocampus- and thalamus-related fiber-specific white matter reductions in mild cognitive impairment. Cereb. Cortex 2021, 32, 3159–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasso, E.; Agosta, F.; Piramide, N.; Filippi, M. Progression of grey and white matter brain damage in Parkinson’s disease: A critical review of structural MRI literature. J. Neurol. 2020, 268, 3144–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Thibeau-Sutre, E.; Diaz-Melo, M.; Samper-González, J.; Routier, A.; Bottani, S.; Dormont, D.; Durrleman, S.; Burgos, N.; Colliot, O. Convolutional neural networks for classification of Alzheimer’s disease: Overview and reproducible evaluation. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 63, 101694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, J.; Zhang, Y. Brain MRI analysis for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis using an ensemble system of deep convolutional neural networks. Brain Inform. 2018, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neugroschl, J.; Wang, S. Alzheimer’s Disease: Diagnosis and Treatment Across the Spectrum of Disease Severity. Mt. Sinai J. Med. A J. Transl. Pers. Med. 2011, 78, 596–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheltens, P. Imaging in Alzheimer’s disease. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 11, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.C.P.; Mintun, M.; Buckner, R.L.; Morris, J.C. Imaging of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroimaging 2003, 13, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khachaturian, Z.S. Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Arch. Neurol. 1985, 42, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, R.; Ramírez, J.; Górriz, J.M.; Puntonet, C.G.; Initiative, A.D.N. Association rule-based feature selection method for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 11766–11774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.M.; Holtzman, D.M. Alzheimer Disease: An Update on Pathobiology and Treatment Strategies. Cell 2019, 179, 312–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.; Spinola, M.; Camara, J.; Badia, S.B.; Cavaco, S. Feasibility of Pitch and Rhythm Musical Distortions as Cueing Method for People with Dementia in AR Cognitive Stimulation Tasks. In Proceedings of the IEEE 9th International Conference on Serious Games and Applications for Health (SeGAH), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 4–6 August 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, R.T.; Goswami, S.P. Assessment of Cognitive-Communicative Functions in Persons with Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia of Alzheimer’s Type. In Handbook of Research on Psychosocial Perspectives of Human Communication Disorders; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Asl, E.; Keynton, R.; El-Baz, A. Alzheimer’s disease diagnostics by adaptation of 3D convolutional network. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martyn, C.N.; Barker, D.J.; Osmond, C.; Harris, E.C.; Edwardson, J.A.; Lacey, R.F. Geographical relation between Alzheimer’s disease and aluminum in drinking water. Lancet 1989, 333, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, K.; Czarnecka, K.; Mikiciuk-Olasik, E.; Szymanski, P. New Perspectives of Alzheimer Disease Diagnosis—The Most Popular and Future Methods. Med. Chem. 2018, 14, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberdi, A.; Aztiria, A.; Basarab, A. On the early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease from multimodal signals: A survey. Artif. Intell. Med. 2016, 71, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhushan, I.; Kour, M.; Kour, G.; Gupta, S.; Sharma, S.; Yadav, A. Alzheimer’s disease: Causes & treatment–A review. Ann. Biotechnol. 2018, 1, 1002. [Google Scholar]
- Sabbagh, M.N.; Lue, L.-F.; Fayard, D.; Shi, J. Increasing Precision of Clinical Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease Using a Combined Algorithm Incorporating Clinical and Novel Biomarker Data. Neurol. Ther. 2017, 6, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, A.; Yang, S.; Feng, Z.; Wang, M.; Ahmad, A.S.; Khan, R.; Maqsood, M.; Yaqub, M. A Transfer Learning Approach for Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease on MRI Images. Neuroscience 2021, 460, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association, A. 2018 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 367–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Li, S.; Xiao, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Ma, X. Computer aided Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis by an unsupervised deep learning technology. Neurocomputing 2019, 392, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, S.; Singh, P.; Jain, D.K.; Bharill, N.; Gupta, A.; Prasad, M. Data-Driven Approach based on Feature Selection Technique for Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Glasgow, UK, 19–24 July 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, E.; Hasan, M.; Hassan, S.Z.; Azmi, T.H.; Rahman, A.; Parvez, M.Z. Deep Learning Based Binary Classification for Alzheimer’s Disease Detection using Brain MRI Images. In Proceedings of the 15th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Kristiansand, Norway, 9–13 November 2020; pp. 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuttler, J.M.; Moore, E.R.; Hosfeld, V.D.; Nadolski, D.L. Treatment of Alzheimer disease with CT scans: A case report. Dose-response 2016, 14, 1559325816640073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohan, G.; Subashini, M.M. MRI based medical image analysis: Survey on brain tumor grade classification. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2018, 39, 139–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachinger, C.; Reuter, M. Domain adaptation for Alzheimer’s disease diagnostics. Neuroimage 2016, 139, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rathore, S.; Habes, M.; Iftikhar, M.A.; Shacklett, A.; Davatzikos, C. A review on neuroimaging-based classification studies and associated feature extraction methods for Alzheimer’s disease and its prodromal stages. Neuroimage 2017, 155, 530–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamińska, D.; Smółka, K.; Zwoliński, G. Detection of Mental Stress through EEG Signal in Virtual Reality Environment. Electronics 2021, 10, 2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobed, A.; Hasanzadeh, M. Biosensing: The best alternative for conventional methods in detection of Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ang, C.K.E.; Acharya, U.R.; Cheong, K.H. Application of Artificial Intelligence techniques for the detection of Alzheimer’s disease using structural MRI images. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 41, 456–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamerlan, A.; An, S.S.A.; Hulme, J. Advances in amyloid beta oligomer detection applications in Alzheimer’s disease. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 129, 115919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajeri, M.; Behnam, B.; Barreto, G.E.; Sahebkar, A. Carbon nanomaterials and amyloid-beta interactions: Potentials for the detection and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease? Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 143, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Vergallo, A.; Caraci, F.; Cuello, A.C.; Lemercier, P.; Vellas, B.; Giudici, K.V.; Baldacci, F.; Hänisch, B.; Haberkamp, M.; et al. Future avenues for Alzheimer’s disease detection and therapy: Liquid biopsy, intracellular signaling modulation, systems pharmacology drug discovery. Neuropharmacology 2021, 185, 108081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koric, L.; Guedj, E.; Habert, M.; Semah, F.; Branger, P.; Payoux, P.; Le Jeune, F. Molecular imaging in the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 172, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, I.R.; Boyle, A.J.; Vasdev, N. Improving PET Imaging Acquisition and Analysis with Machine Learning: A Narrative Review with Focus on Alzheimer’s Disease and Oncology. Mol. Imaging 2019, 18, 1536012119869070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, A.; Bhagat, N. Insight into the molecular imaging of Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2016, 2016, 7462014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Yang, Z.L.; Lu, G.M.; Yang, G.F.; Zhang, L.J. PET/MR Imaging: New Frontier in Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Dementias. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosla, A.; Khandnor, P.; Chand, T. A comparative analysis of signal processing and classification methods for different applications based on EEG signals. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 40, 649–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuyvers, E.; Sleegers, K. Genetic variations underlying Alzheimer’s disease: Evidence from genome-wide association studies and beyond. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodily, P.M.; Initiative, T.A.D.N.; Fujimoto, M.S.; Page, J.T.; Clement, M.J.; Ebbert, M.T.W.; Ridge, P.G. A novel approach for multi-SNP GWAS and its application in Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tosto, G.; Reitz, C. Genome-wide Association Studies in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2013, 13, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambert, J.-C.; Ibrahim-Verbaas, C.A.; Harold, D.; Naj, A.C.; Sims, R.; Bellenguez, C.; Jun, G.; DeStefano, A.L.; Bis, J.C.; Beecham, G.W.; et al. Meta-analysis of 74,046 individuals identifies 11 new susceptibility loci for Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desikan, R.S.; Fan, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Schork, A.J.; Cabral, H.J.; Cupples, L.A.; Thompson, W.K.; Besser, L.; Kukull, W.A.; Holland, D.; et al. Genetic assessment of age-associated Alzheimer disease risk: Development and validation of a polygenic hazard score. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Escott-Price, V.; Bellenguez, C.; Wang, L.-S.; Choi, S.-H.; Harold, D.; Jones, L.; Holmans, P.; Gerrish, A.; Vedernikov, A.; Richards, A.; et al. Gene-wide analysis detects two new susceptibility genes for Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moussa, M.N.; Steen, M.R.; Laurienti, P.J.; Hayasaka, S. Consistency of Network Modules in Resting-State fMRI Connectome Data. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolz, R.; Julkunen, V.; Koikkalainen, J.; Niskanen, E.; Zhang, D.P.; Rueckert, D.; Soininen, H.; Lötjönen, J.; Initiative, T.A.D.N. Multi-Method Analysis of MRI Images in Early Diagnostics of Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patil, K.; Kale, G. Study on Dignosis of Alzheimer’s by Using Neural Networks. Int. J. 2016, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Naami, B.; Gharaibeh, N.; Kheshman, A.A. Automated detection of Alzheimer disease using region growing technique and artificial neural network. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. Int. J. Biomed. Biol. Eng. 2013, 7, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Lahmiri, S.; Boukadoum, M. Alzheimer’s Disease Detection in Brain Magnetic Resonance Images Using Multiscale Fractal Analysis. ISRN Radiol. 2013, 2013, 627303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eskildsen, S.F.; Coupé, P.; Fonov, V.; Collins, D.L. Detecting Alzheimer’s disease by morphological MRI using hippocampal grading and cortical thickness. In Proc MICCAI Workshop Challenge on Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Dementia Based on Structural MRI Data; ResearchGate: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 38–47. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, A.; Kumar, P.S.J. Improved Digital Image Processing based Detection for Alzheimer’s disease using MATLAB. Int. J. Adv. Arts Sci. Eng. 2015, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ogiela, L.; Ogiela, M.R. Advances in Cognitive Information Systems; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defigueiredo, R.J.; Shankle, W.R.; Maccato, A.; Dick, M.B.; Mundkur, P.; Mena, I.; Cotman, C.W. Neural-network-based classification of cognitively normal, demented, Alzheimer disease and vascular dementia from single photon emission with computed tomography image data from brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 5530–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.D. Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease: An fMRI marker for people at risk? Nat. Neurosci. 2000, 3, 973–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javaid, M.; Haleem, A.; Singh, R.P.; Suman, R.; Rab, S. Significance of machine learning in healthcare: Features, pillars and applications. Int. J. Intell. Netw. 2022, 3, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, E.; Pepe, A.; Gaser, C.; Huttunen, H.; Tohka, J. Machine learning framework for early MRI-based Alzheimer’s conversion prediction in MCI subjects. Neuroimage 2014, 104, 398–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Shen, D.; Initiative, A.D.N. Predicting Future Clinical Changes of MCI Patients Using Longitudinal and Multimodal Biomarkers. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davatzikos, C.; Bhatt, P.; Shaw, L.M.; Batmanghelich, K.N.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Prediction of MCI to AD conversion, via MRI, CSF biomarkers, and pattern classification. Neurobiol. Aging 2011, 32, 2322-e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Vos, F.; Schouten, T.M.; Hafkemeijer, A.; Dopper, E.G.P.; van Swieten, J.C.; de Rooij, M.; van der Grond, J.; Rombouts, S.A.R.B. Combining multiple anatomical MRI measures improves Alzheimer’s disease classification. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 1920–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Heuvel, M.P.; Pol, H.E.H. Exploring the brain network: A review on resting-state fMRI functional connectivity. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010, 20, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaee, A.; Ebrahimzadeh, A.; Babajani-Feremi, A. Application of advanced machine learning methods on resting-state fMRI network for identification of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Imaging Behav. 2015, 10, 799–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaee, A.; Ebrahimzadeh, A.; Babajani-Feremi, A. Identifying patients with Alzheimer’s disease using resting-state fMRI and graph theory. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 2132–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, L.; Yan, H.; Dai, R.; Zhong, C.; Wang, H.; Wei, W.; Xue, T.; Feng, Y.; et al. Investigation of the effective connectivity of resting state networks in Alzheimer’s disease: A functional MRI study combining independent components analysis and multivariate Granger causality analysis. NMR Biomed. 2012, 25, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greicius, M.D.; Krasnow, B.; Reiss, A.L.; Menon, V. Functional connectivity in the resting brain: A network analysis of the default mode hypothesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 100, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supekar, K.; Menon, V.; Rubin, D.; Musen, M.; Greicius, M.D. Network Analysis of Intrinsic Functional Brain Connectivity in Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2008, 4, e1000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Armstrong, C.C.; Moody, T.D.; Feusner, J.D.; McCracken, J.T.; Chang, S.; Levitt, J.G.; Piacentini, J.C.; O’neill, J. Graph-theoretical analysis of resting-state fMRI in pediatric obsessive–compulsive disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 193, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohn-Hokke, P.E.; Elting, M.W.; Pijnenburg, Y.A.; van Swieten, J.C. Genetics of dementia: Update and guidelines for the clinician. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2012, 159, 628–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, B.L.; Ocal, D.; Peters, A.; Bancroft, M.J.; Cash, D.; Kaski, D.; Crutch, S.J.; Yong, K.X.X. Altered visual and haptic verticality perception in posterior cortical atrophy and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Physiol. 2021, 600, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, A.W.; Baglat, P.; Gupta, G. Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis using Deep Learning Techniques. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2020, 9, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, G.; Souroujon, D.; Shaul, R.; Bloch, A.; Leventhal, A.; Lockett, J.; Shalev, V. A patient like me—An algorithm-based program to inform patients on the likely conditions people with symptoms like theirs have. Medicine 2019, 98, e17596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talwar, P.; Silla, Y.; Grover, S.; Gupta, M.; Agarwal, R.; Kushwaha, S.; Kukreti, R. Genomic convergence and network analysis approach to identify candidate genes in Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, V.S.; Srinivas, K.; Kumar, G.S.; Sujin, G. Protein interaction network for Alzheimer’s disease using computational approach. Bioinformation 2013, 9, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, M.R.; Islam, T.; Turanli, B.; Zaman, T.; Faruquee, H.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Mollah, M.N.H.; Nanda, R.K.; Arga, K.Y.; Gov, E.; et al. Network-based approach to identify molecular signatures and therapeutic agents in Alzheimer’s disease. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2019, 78, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Initiative, F.T.A.D.N.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, F.; Bian, C.; Yao, X.; Yan, J.; Xu, Z.; Risacher, S.L.; et al. Multivariate genome wide association and network analysis of subcortical imaging phenotypes in Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beheshti, I.; Demirel, H.; Farokhian, F.; Yang, C.; Matsuda, H.; The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Structural MRI-based detection of Alzheimer’s disease using feature ranking and classification error. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 137, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beheshti, I.; Demirel, H.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Feature-ranking-based Alzheimer’s disease classification from structural MRI. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 34, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beheshti, I.; Demirel, H.; Matsuda, H.; The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Classification of Alzheimer’s disease and prediction of mild cognitive impairment-to-Alzheimer’s conversion from structural magnetic resource imaging using feature ranking and a genetic algorithm. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 83, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yuan, H.; Shen, D.; The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Multimodal classification of Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. NeuroImage 2011, 55, 856–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Liu, S.; Cai, W.; Che, H.; Pujol, S.; Kikinis, R.; Feng, D.; Fulham, M.J.; ADNI. Multimodal neuroimaging feature learning for multiclass diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 62, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, P.; Kumari, C.U.; Kumar, M.; Pavani, T. Detection and analysis of Alzheimer’s disease using various machine learning algorithms. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 45, 1502–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schouten, T.M.; Koini, M.; de Vos, F.; Seiler, S.; de Rooij, M.; Lechner, A.; Schmidt, R.; Heuvel, M.V.D.; van der Grond, J.; Rombouts, S.A. Individual classification of Alzheimer’s disease with diffusion magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage 2017, 152, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimitriadis, S.; Liparas, D.; Tsolaki, M.N. Random forest feature selection, fusion and ensemble strategy: Combining multiple morphological MRI measures to discriminate among healhy elderly, MCI, cMCI and alzheimer’s disease patients: From the alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative (ADNI) database. J. Neurosci. Methods 2018, 302, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donnelly-Kehoe, P.A.; Pascariello, G.O.; Gómez, J.C.; Initiative, A.D.N. Looking for Alzheimer’s Disease morphometric signatures using machine learning techniques. J. Neurosci. Methods 2018, 302, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben Ammar, R.; Ben Ayed, Y. Language-related features for early detection of Alzheimer Disease. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 176, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrolahzadeh, M.; Rahnamayan, S.; Haddadnia, J. Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis using genetic programming based on higher order spectra features. Mach. Learn. Appl. 2021, 7, 100225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Teng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, X. Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease based on regional attention with sMRI gray matter slices. J. Neurosci. Methods 2021, 365, 109376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balne, S.; Elumalai, A. Machine learning and deep learning algorithms used to diagnosis of Alzheimer’s. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 5151–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, H.-I.; Lee, S.-W.; Shen, D. Hierarchical feature representation and multimodal fusion with deep learning for AD/MCI diagnosis. Neuroimage 2014, 101, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, D.G.; McLaughlin, P.M.; Woo, E.; Hwang, K.; Hurtz, S.; Ramirez, L.; Eastman, J.; Dukes, R.; Kapur, P.; DeRamus, T.P.; et al. Novel verbal fluency scores and structural brain imaging for prediction of cognitive outcome in mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimer’s Dement. Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2016, 2, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, H.; Pan, X.; Xu, M.; Lan, R.; Luo, X. Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease via an attention-based multi-scale convolutional neural network. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 238, 107942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salami, F.; Bozorgi-Amiri, A.; Hassan, G.M.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.; Datta, A. Designing a clinical decision support system for Alzheimer’s diagnosis on OASIS-3 data set. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 74, 103527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habuza, T.; Zaki, N.; Mohamed, E.A.; Statsenko, Y. Deviation from Model of Normal Aging in Alzheimer’s Disease: Application of Deep Learning to Structural MRI Data and Cognitive Tests. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 53234–53249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Yu, H.; Zhu, L.; Liu, J.; Wu, L. Feature Extraction and Identification of Alzheimer’s Disease based on Latent Factor of Multi-Channel EEG. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 1557–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendl, J.; Hauberg, M.E.; Girdhar, K.; Im, E.; Vicari, J.M.; Rahman, S.; Fernando, M.B.; Townsley, K.G.; Dong, P.; Misir, R.; et al. The three-dimensional landscape of cortical chromatin accessibility in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 1366–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batool, A.; Hussain, M.; Abidi, S.M.R. A Brief Review of Big Data used in Healthcare Organization-Survey study. J. NCBAE 2022, 1, 8–18. [Google Scholar]
- Kabir, M.T.; Uddin, S.; Begum, M.; Thangapandiyan, S.; Rahman, S.; Aleya, L.; Mathew, B.; Ahmed, M.; Barreto, G.E.; Ashraf, G. Cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease: Multitargeting strategy based on anti-Alzheimer’s drugs repositioning. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 3519–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minocha, T.; Birla, H.; Obaid, A.A.; Rai, V.; Sushma, P.; Shivamallu, C.; Moustafa, M.; Al-Shehri, M.; Al-Emam, A.; Tikhonova, M.A.; et al. Flavonoids as Promising Neuroprotectants and Their Therapeutic Potential against Alzheimer’s Disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 6038996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, M.; Cui, X.; Li, C. Protective Effects of Flavonoids against Alzheimer’s Disease: Pathological Hypothesis, Potential Targets, and Structure–Activity Relationship. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Sood, A.; Lang, D.K.; Bhatia, S.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Aleya, L.; Behl, T. Potential of flavonoids as anti-Alzheimer’s agents: Bench to bedside. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 26063–26077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, H.; Wei, S.; Liu, F.; Chen, Y. Alzheimer’s Disease Prediction Algorithm Based on Group Convolution and a Joint Loss Function. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 1854718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sappagh, S.; Saleh, H.; Ali, F.; Amer, E.; Abuhmed, T. Two-stage deep learning model for Alzheimer’s disease detection and prediction of the mild cognitive impairment time. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 14487–14509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, M.; Alberts, I.; Sun, X.; Li, T.; Rominger, A.; Zuo, C.; Han, Y.; Shi, K.; Initiative, F.T.A.D.N. Using radiomics-based modelling to predict individual progression from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 49, 2163–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.J.; Seo, Y.; Choe, Y.S.; Jang, H.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.P.; Initiative, F.T.A.D.N. Predicting conversion of brain β-amyloid positivity in amyloid-negative individuals. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2022, 14, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, J.V.; Duraisamy, B.; Simon, B.C.; Bhaskaran, P. Alzheimer’s disease classification using pre-trained deep networks. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 71, 103217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandrini, M.; Biagetti, G.; Crippa, P.; Falaschetti, L.; Luzzi, S.; Turchetti, C. EEG-Based Alzheimer’s Disease Recognition Using Robust-PCA and LSTM Recurrent Neural Network. Sensors 2022, 22, 3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahendran, N.; PM, D.R.V. A deep learning framework with an embedded-based feature selection approach for the early detection of the Alzheimer’s disease. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 141, 105056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Liu, Z.; He, W.; Cai, J.; Hu, L. Application of 3D Whole-Brain Texture Analysis and the Feature Selection Method Based on within-Class Scatter in the Classification and Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Ther. Innov. Regul. Sci. 2022, 56, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eroglu, Y.; Yildirim, M.; Cinar, A. mRMR -based hybrid convolutional neural network model for classification of Alzheimer’s disease on brain magnetic resonance images. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2021, 32, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanjewar, M.G.; Parab, J.S.; Shaikh, A.Y. Development of framework by combining CNN with KNN to detect Alzheimer’s disease using MRI images. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 82, 12699–12717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Jung, H.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.; Ahn, M. Diagnostic Classification and Biomarker Identification of Alzheimer’s Disease with Random Forest Algorithm. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Xiao, R.; Liu, X.; Qiao, H.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Du, J. Adaptive LASSO logistic regression based on particle swarm optimization for Alzheimer’s disease early diagnosis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2021, 215, 104316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdulAzeem, Y.; Bahgat, W.M.; Badawy, M. A CNN based framework for classification of Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 10415–10428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolova, L.G. Alzheimer disease. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2016, 22, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, X.; Fei, G.; Lu, J.; Jin, L.; Pan, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, C.; Sang, S.; Liu, H.; Hu, W.; et al. Measurement of Blood Thiamine Metabolites for Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis. Ebiomedicine 2016, 3, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jain, R.; Jain, N.; Aggarwal, A.; Hemanth, D.J. Convolutional neural network based Alzheimer’s disease classification from magnetic resonance brain images. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2019, 57, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Test Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Physical and neurological exam | Physical | A medical professional will conduct a physical examination. The neurological examination may encompass the evaluation of reflexes as an assessment component. The current topic of discussion pertains to the physiological aspects of muscle tone and strength. The capacity to rise from a seated position and ambulate to a different location within a given space. The faculties of vision and audition, coordination, and balance. |
| Lab test | Blood | The utilization of blood tests can aid in excluding alternative etiologies of cognitive impairment and amnesia, such as hypothyroidism or inadequate vitamin concentrations. Beta-amyloid protein and tau protein levels can also be quantified through blood tests. However, the accessibility of these tests is limited, and coverage may be restricted. |
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) | Brain Imaging | Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) employs a combination of radio waves and a potent magnetic field to generate comprehensive visual representations of the brain. However, exhibiting atrophy in specific brain regions linked to Alzheimer’s, MRI scans also eliminate alternative ailments. In the assessment of dementia, an MRI is typically favored over a CT scan. |
| Computerized tomography (CT) | Brain Imaging | The computed tomography (CT) scan, a specialized form of X-ray imaging, can generate cross-sectional visual representations of the human brain. Typically, it excludes the presence of neoplasms, cerebrovascular accidents, and cranial traumas. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) employs radiofrequency waves and a potent magnetic field to generate intricate visual representations of the human brain. However, exhibiting atrophy in specific brain regions linked to Alzheimer’s, MRI scans also eliminate alternative ailments. In the assessment of dementia, an MRI is typically favored over a CT scan. |
| Positron emission tomography (PET) | Brain Imaging | Positron emission tomography (PET) can acquire visual representations of the pathological progression. In the process of conducting a PET scan, a radiopharmaceutical tracer of low intensity is administered intravenously to enable the identification of a specific cerebral characteristic. |
| Genetic test | Genetic | The utilization of genetic testing is not advised for the majority of individuals undergoing evaluation for Alzheimer’s disease. Individuals with a familial background of early-onset Alzheimer’s disease may contemplate the matter. |
| Reference | Methodology | Performance (%) |
|---|---|---|
| [116] | SVM | 92.48 |
| [117] | Fisher | 96.32 |
| [118] | SVM with genetic algorithm | 96.80 |
| [118] | SVM with image processing | 93.30 |
| [119] | Multi-modal neuroimaging | 91.40 |
| [120] | Image processing and weight extraction operations | 95 |
| [123] | Stochastic random forest | 93 |
| [124] | PCA with SVM | 95 |
| [129,131,132] | CNN with various architectures (average) | 98.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dara, O.A.; Lopez-Guede, J.M.; Raheem, H.I.; Rahebi, J.; Zulueta, E.; Fernandez-Gamiz, U. Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis Using Machine Learning: A Survey. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148298
Dara OA, Lopez-Guede JM, Raheem HI, Rahebi J, Zulueta E, Fernandez-Gamiz U. Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis Using Machine Learning: A Survey. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(14):8298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148298
Chicago/Turabian StyleDara, Omer Asghar, Jose Manuel Lopez-Guede, Hasan Issa Raheem, Javad Rahebi, Ekaitz Zulueta, and Unai Fernandez-Gamiz. 2023. "Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis Using Machine Learning: A Survey" Applied Sciences 13, no. 14: 8298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148298
APA StyleDara, O. A., Lopez-Guede, J. M., Raheem, H. I., Rahebi, J., Zulueta, E., & Fernandez-Gamiz, U. (2023). Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis Using Machine Learning: A Survey. Applied Sciences, 13(14), 8298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148298








