Featured Application
This study presents a comprehensive and stepwise strategy for utilizing coffee by-products as a sustainable source to develop bioactive food ingredients and nutraceuticals. Coffee by-products can be transformed into versatile functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals by implementing green extraction techniques and employing a biorefinery approach. These products offer a wide range of benefits, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-obesity effects, as well as the potential to regulate energy metabolism and blood sugar levels and serve as adjunct therapies for conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders. This research not only contributes to the creation of functional food products and supplements but also promotes sustainability and addresses the prevention and management of chronic diseases.
Abstract
Coffee production generates significant amounts of by-products, posing challenges for waste management in the industry. Recent research has revealed that coffee by-products are rich in bioactive compounds suitable to produce functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals. In this review, we explore biorefinery strategies for extracting and utilizing bioactive compounds from coffee by-products, including the production of bio-based chemicals and materials, as well as the extraction of phenolic compounds, antioxidants, and dietary fiber for food applications. We propose a stepwise approach for the development of functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals from coffee by-products, covering the identification of needs, comprehensive characterization, in vitro and in vivo research, unraveling the mechanism of action, food and nutraceutical formulation, sensory analysis, shelf-life stability, scale-up, randomized control trials, and biostatistics and bioinformatic integration. Additionally, we discuss the market potential, regulatory issues, and technological innovation surrounding the commercialization of coffee by-product-based products. Emphasizing the importance of regulatory compliance and sustainability in the coffee industry, this review highlights the potential of coffee by-products to be transformed from waste into valuable functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals, offering a promising avenue for waste reduction and promoting sustainability in the coffee industry.
1. Introduction
Coffee is one of the world’s main commodities representing the second most consumed beverage after water, with annual rates of 42.6 L per capita and a global intake of 3 billion 0.2 L cups of coffee per day [1]. The personal global consumption ranking is led by Scandinavian countries, headed by Finnish people with a yearly consumption of around 9.4 kg of roasted coffee per capita (equivalent to 6–8 cups per day). This superior demand turns coffee beans into one of the globe’s top-traded agro-industrial products. According to the International Coffee Organization, about 171.3 million 60 kg bags of coffee beans are estimated to be produced in 2022/2023, following a robust increasing biannual trend in forthcoming years due to the endless rising of consumer demand. Surprisingly, the mentioned production results insufficiently cover the predicted consumption estimations for a second consecutive year, i.e., around 178.5 million bags [2], which could explain the 1.9% volume growth expected for the coffee market in 2024 [2]. This agro-industrial and socioeconomic paradigm rationalizes the worldwide concern relative to the environmental impact of coffee cultivation and manufacturing, owing to the notable amount of by-products delivered by this food sector.
Waste management is one of the most challenging problems we currently handle worldwide. Presently, food systems are highly inefficient since around one-third of the food produced is wasted and not consumed [3]. Food is lost or wasted at every stage of the food supply chain, from farming to consumption. Therefore, to ensure sustainable management of food waste, food by-products should be utilized before they become waste, thus increasing the food system’s sustainability which constitutes a milestone of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The SDGs seek to restructure the agriculture and food systems to decrease hunger, achieve food security, and improve nutrition while reducing food waste and losses along supply chains [4]. A sustainable food system delivers food security and nutrition without endangering the economic, social, and environmental foundations for producing safe and nutritious foods for future generations. Consequently, the food system generates economic value-added benefits (economic sustainability), has widespread social benefits including nutritional and health benefits, and is equitable in distributing the economic value-added (social sustainability) plus a favorable or neutral environmental effect (environmental sustainability) [5]. Undoubtedly, the coffee agroindustry must also face this challenge focused on waste management. Indeed, coffee by-products from wet and dry processing—coffee husk, parchment, pulp, mucilage, and silverskin—represent nearly 50% of the coffee cherry on a dry weight basis [2]. Global coffee production delivers over 23 million tons of waste annually, estimating 0.2 and 0.5 tons of coffee pulp and coffee husk by 1 ton of coffee produced by wet and dry processes, respectively, and 8 kg of silverskin by 1 ton of roasted beans [6,7]. Even though the abovementioned coffee by-products have been traditionally used for low-value applications such as animal feed or composting for soil fertilization, coffee waste is liable to end up in landfills where it usually is spontaneously decomposed, producing unpleasant smells and acidic leaches able to damage the neighboring soil by lixiviation. It also releases greenhouse gases with a direct impact on climate change, alongside harming soil and water sources when these by-products are dumped into streams because of their cytotoxic and ecotoxic effects [8]. Moreover, they are known for their remarkable resistance to natural degradation, involving long residence periods, resulting in a severe environmental and even energetic impact. Such circumstances raise awareness and inspire the scientific community to research valorization strategies, which minimize the coffee agroindustry’s environmental and energetic impacts and could produce added-value products following circular economy principles [9]. Thereby, novel application outcomes could result in economically gainful opportunities for coffee agro-industry stakeholders through the direct marketing of added-value products. Furthermore, the valorization of coffee waste can contribute to the diversification of income streams for coffee farmers, reducing their dependence on volatile commodity prices [10]. This can help to enhance the stability and resilience of coffee-producing regions, particularly in developing countries where coffee production is a significant source of income. The economic potential of coffee waste is further supported by the growing demand for sustainable and healthy products in the global market [11].
Biorefinery strategies for coffee waste are gaining importance as a means to reduce this environmental impact while generating economic value [12]. Using coffee waste to produce functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals offers a sustainable solution to the waste problem while creating a value-added product with potential health benefits [13]. Over the last few years, scientific research has demonstrated that coffee waste still contains valuable compounds, including carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and bioactive compounds such as dietary fiber, phenolic compounds, and caffeine. Following the scientometric analysis published by Durán-Aranguren et al. [6], the annual scientific production has experienced a notable rise since 2010, with the highest rate of publications for coffee husk and coffee pulp by-products in recent years. The most renowned biorefinery valorization strategies approached to date are directed at the coffee by-products’ microbial transformation; their environmental applications as sources of biosorbents, biopesticides, or fertilizers; their transformation into biofuels from thermochemical processing such as syngas or biodiesel; their contribution to producing sustainable materials such as ceramic aggregates or food packaging substitutes; or their bioactive compounds exploitation [6]. Within the latest news, their use as bioactive ingredients for food and nutraceuticals formulation from both raw materials and their extracts seems one of the most comprehensive applications with greater growth prospects, with a doubtless sustainable benefit for human health because of their evidenced useful properties. In addition, the production of such food-like products from coffee waste offers a unique selling proposition for companies seeking to meet the worldwide demand for sustainable and healthy products. Validation of the new products derived from coffee by-products is essential to ensure their safety, efficacy, and market acceptance [14]. A systematic approach is required to establish a strong scientific foundation for functional food claims and to validate the bioactive compounds and their potential health benefits [15]. This validation process ensures confidence in the economic potential of coffee waste utilization and supports the development of sustainable and healthy products for the market [16].
This comprehensive review aims to provide an in-depth overview of the biorefinery strategies and multistep approaches to producing bioactive food ingredients and nutraceuticals from coffee by-products. We begin by summarizing the relevant aspects of coffee by-products and their potential as food ingredients with health benefits. We explore three key biorefinery strategies: the production of bio-based chemicals and materials, green aqueous extraction of bioactive compounds for food applications, and utilization of coffee by-products in food processing. We cover a wide range of topics, including the characterization of coffee by-products, in vitro and in vivo research studies on the bioactivity and health benefits of coffee by-product-derived compounds, randomized control trials evaluating the efficacy and safety of coffee by-product-derived nutraceuticals in human subjects, and sensory analysis of food products containing coffee by-product-derived ingredients. Furthermore, we address the regulatory considerations and challenges associated with the commercialization of coffee by-product-derived products, along with the technological innovations and optimization strategies for their production. We also explore the economic potential of coffee by-products and their implications for sustainable agriculture and food systems and highlight future directions for research and innovation in this field.
2. Composition, Availability, and Technological and Safety Constraints of Coffee By-Products
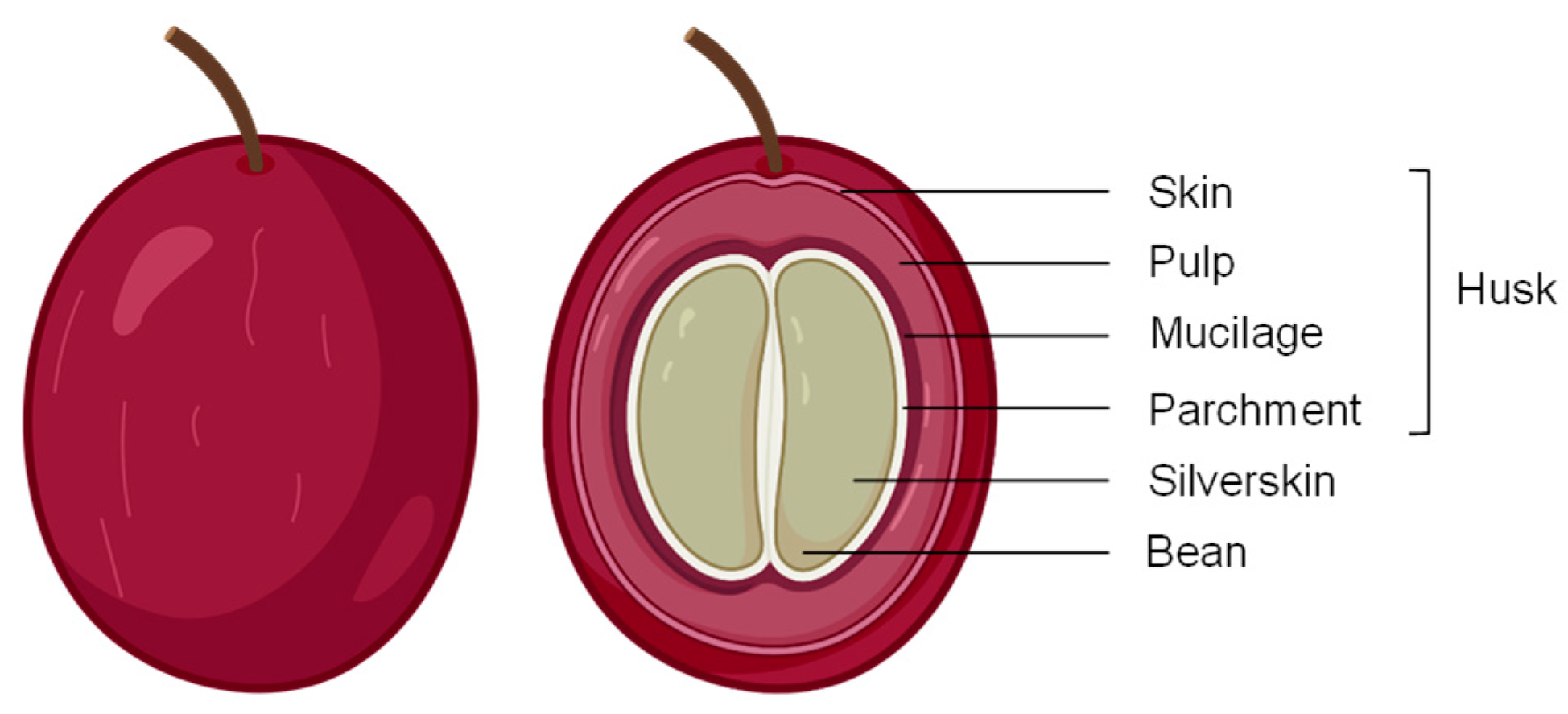
Coffea arabica L. (Arabica coffee) and Coffea canephora (Robusta coffee), both members of the Rubiaceae family, are the most important plant species in the international coffee trade [17]. During coffee beverage preparation, approximately 90% of the coffee cherry’s edible sections are discarded as agricultural waste or by-products. Coffee by-products have aroused considerable interest because of their abundance and excellent chemical composition [18]. The coffee cherry (Figure 1) comprises an outer skin or pericarp, which is green in unripe and red in ripe fruits, covering a soft and sweet pulp or outer mesocarp. Subsequently, a viscous and highly hydrated mucilage layer (pectin layer) and a thin yellowish endocarp (the parchment) are found. Ultimately, the silverskin covers two or three green coffee beans (endosperm) [19].
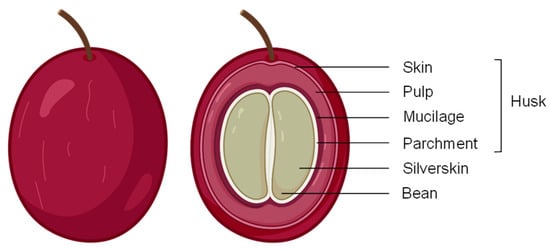
Figure 1.
Coffee cherry anatomy from the outside to the inside (skin, pulp, mucilage, parchment—comprising the coffee husk, silverskin, and coffee bean).
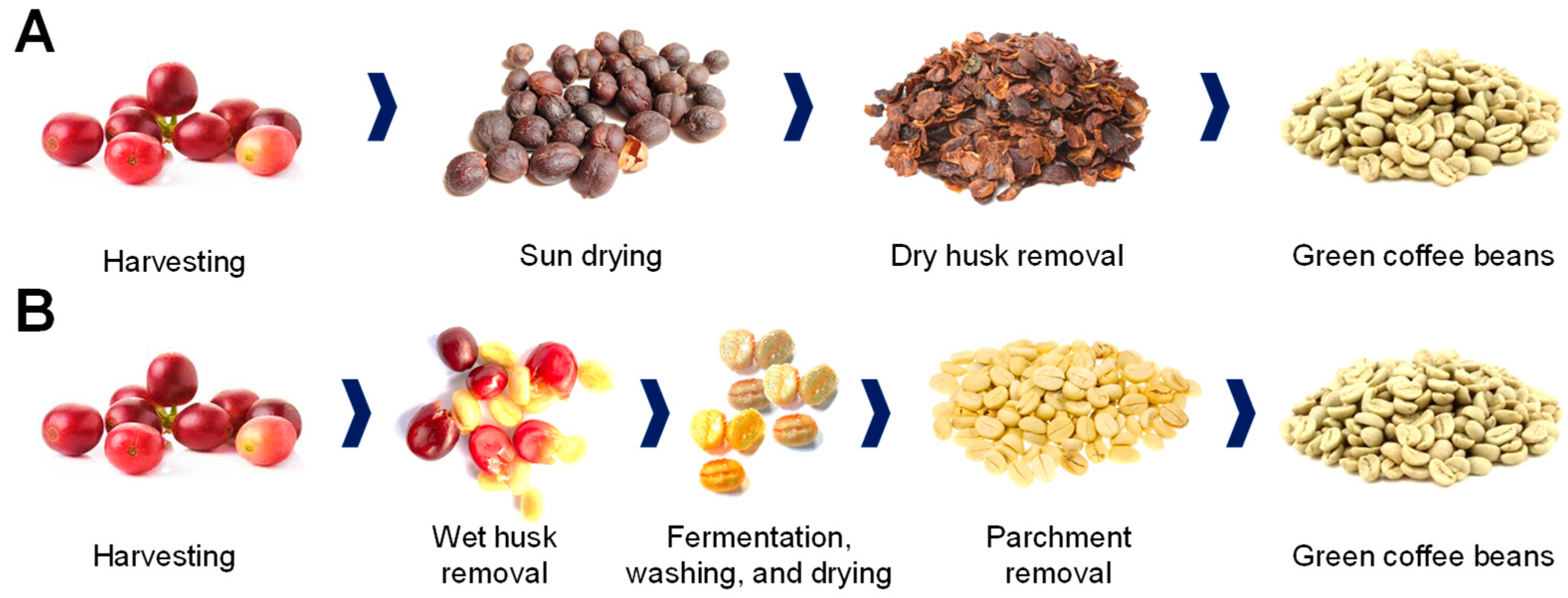
The coffee cherries are converted into green coffee beans by removing the cherry outer layers using either a wet or dry method (Figure 2) [20]. The dry method (Figure 2A), widely used in Robusta-producing countries, is more technologically simple. To achieve optimal drying, the freshly picked cherries are either uniformly distributed and sun-dried for 2–4 weeks in yards (natural drying) or mechanically dried until the moisture content is reduced to less than 12%. Subsequently, the coffee cherries are mechanically de-husked, and the skin, pulp, mucilage, and parchment are separated from the beans [17,21]. The wet processing (Figure 2B), commonly used for Arabica coffees, is more commercially valued, and needs various tools to extract the green bean. A de-pulper is first utilized to remove the skin and pulp that covers the bean [21]. Once de-pulped, the mucilage still covers the coffee bean; thus, it is removed through a 24–72 h fermentation [17]. Then, the bean covered by the parchment is washed, drained, and dried until the moisture content is about 10% [21]. Finally, a hulling machine is used to remove the parchment [18].
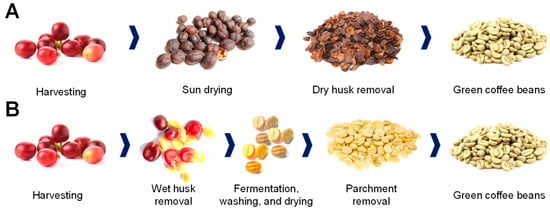
Figure 2.
Dry (A) and wet (B) processing of freshly harvested coffee beans to produce green coffee beans.
2.1. Husk
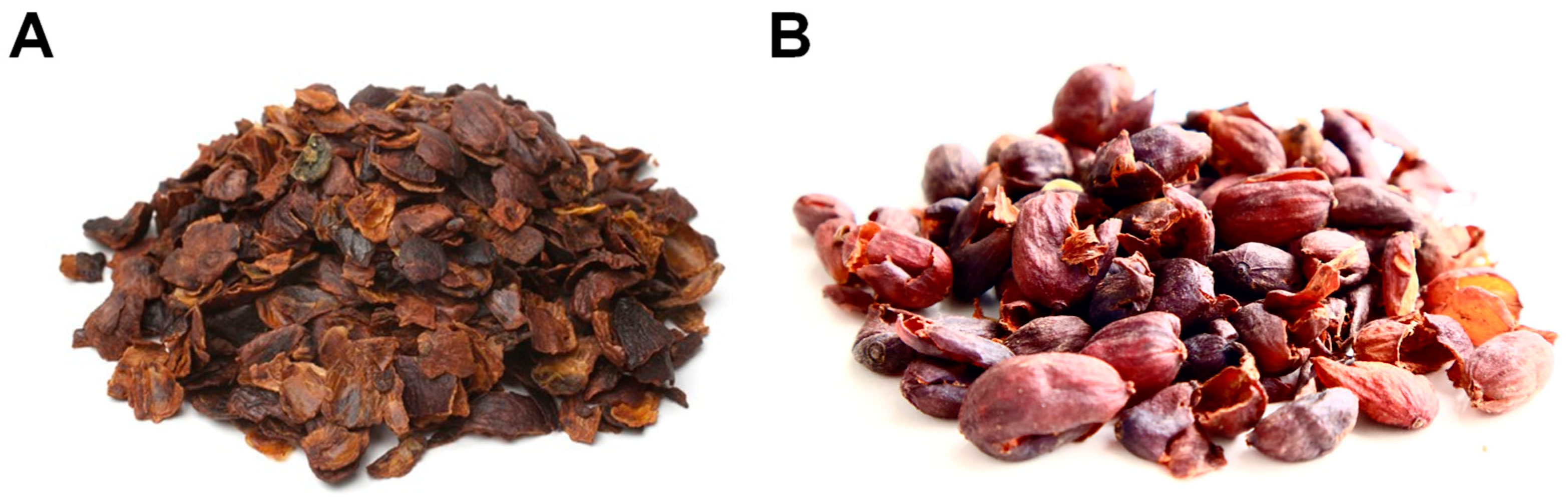
The coffee husk is the first by-product produced during coffee processing. This by-product is generated in coffee-producing countries at 40 kg per 100 kg of green coffee beans [22]. The definition and composition of the coffee husk depend on the processing method employed. Dry coffee husks obtained through the dry processing method (Figure 3A), consist of skin, pulp, mucilage, and parchment and are rich in insoluble dietary fiber. They contain approximately 30% hemicelluloses, 25% cellulose, and 24% lignin (Table 1) [23,24,25,26]. Coffee husks are also sources of phytochemicals, including phenolic compounds, which account for approximately 1.2% and mainly include anthocyanins and proanthocyanidins [27].

Figure 3.
Coffee husks obtained by the dry (A) and wet (B) processing methods.

Table 1.
Chemical composition of coffee by-products obtained through coffee processing. Values expressed in dry matter.
Coffee husks generated through the wet method (known as wet husk or pulp) (Figure 3B) are composed of skin and pulp and contain significant levels of phenolic compounds (1.5%) and caffeine (1.3%) [28]. The wet husk contains four major groups of phenolic compounds: hydroxycinnamic acids, flavanols, flavonols, and anthocyanidins [28]. The primary phenolic compounds in coffee husks are chlorogenic and protocatechuic acids, which account for more than 80% of the overall phenolic compounds [29]. Other phenolic compounds identified in coffee husks are epicatechin, catechin, rutin, ferulic acid, and cyanidin-3-glucoside and 3-rutinoside [18]. In addition, the coffee pulp presents lower lipid (0.5–2%) and mineral (8–9.5%) content, and higher protein (8–17%), moisture (78%), and carbohydrates content (~58–85%) than the coffee parchment (Table 1). These differences in composition between the dry and the wet husk provide unique opportunities for their utilization in various applications, from dietary fiber enrichment to the extraction of bioactive compounds [42]. Exploring these distinctions and utilizing the specific properties of dry and wet husk can lead to the development of innovative products and contribute to the sustainable utilization of coffee by-products.
The coffee husk is a substantial by-product generated during coffee processing, with a production rate of approximately 40 kg per 100 kg of green coffee beans in coffee-producing countries [22]. Coffee husks obtained from the dry processing method account for nearly 45% of the coffee cherry [19], while coffee husks obtained from the wet processing method represent around 29% of the dry weight of the entire cherry [21]. This indicates a significant quantity of coffee husk being generated annually (around 4 million tons), considering the global coffee production of 171.3 million 60 kg bags [43]. With this global coffee production resulting in millions of tons of coffee husk annually, exploring effective strategies for managing this by-product and maximizing its utilization potential is necessary.
In terms of technological and safety constraints, coffee husk handling and disposal entrain a severe environmental problem due to its high moisture and low bulk density [44]. These characteristics make handling, processing, and utilization of coffee husk more complex. Its fibrous composition and low compactability can hinder efficient extraction and incorporation into value-added products [45]. Additionally, the high moisture content of the coffee husk can contribute to difficulties in storage and transportation, as well as potential mold growth [46]. To overcome the technological constraints and optimize the utilization of the coffee husk, further research and development efforts are necessary. These efforts should focus on developing innovative technologies and processing methods that enable efficient extraction of valuable components, such as dietary fiber, phenolic compounds, and caffeine, while ensuring safety and scalability [47]. Although research seeks value-added applications for the coffee husk, such as in bioprocessing [48], further exploration of alternative uses and applications can contribute to its value as a sustainable resource.
Recently, the European Commission approved the dried coffee husk from Coffee arabica L. as a novel food to be used as an ingredient for infusions and non-alcoholic drinks, with its maximum use levels from 2–6 g of husk/100 mL [49]. Considering the history of the use of the coffee husk as food and the proposed uses and use levels, no toxicological studies were required by the European Commission. The precautions and use restrictions are related to caffeine intake, which should not exceed 150 mg/L in the products containing this novel food. No safety concerns are noted regarding the concentration of contaminants (e.g., heavy metals, pesticide residues, organic contaminants) which depends mainly on the production process (cultivation) that has been sufficiently described. Notwithstanding, quality control measures should be implemented throughout the processing of coffee husk to ensure safety and minimize potential contaminants [50]. Regular testing for pesticide residues, heavy metals, mycotoxins, and other contaminants should be conducted to comply with food safety regulations and guarantee the quality and purity of coffee husk-derived ingredients [14]. Addressing the technological and safety constraints associated with the coffee husk will not only contribute to the efficient utilization of this by-product but also promote sustainability and reduce waste within the coffee industry [21]. By implementing appropriate processing techniques and ensuring strict quality control measures, the coffee husk can be transformed into valuable ingredients and contribute to the circular economy.
2.2. Mucilage
The coffee mucilage is a pectin layer found between the pulp and the parchment (Figure 4). After de-pulping, the mucilage remains attached to the coffee bean, and being highly hydrated, is an impediment to further drying the beans. As a result, before the beans can be dried and processed, the mucilage must be degraded by wet fermentation, which is solubilized by yeast, bacteria, and fungi. The mucilage is an extremely hydrated sticky tissue, comprised of 1% pectins with a high degree of esterification with uronic acid being the major constituent, followed by arabinose, galactose, xylose, rhamnose, and glucose as neutral non-cellulosic monosaccharides. In terms of composition, this coffee by-product is mainly constituted of water (84%), protein (7%), soluble sugars (4%), total dietary fiber (1.5%), caffeine (1%), and ash (1%) [18]. The micronutrients found in the coffee mucilage include Ca, Fe, Mg, K, P, and Na [32]. Phenolic compounds, including flavonoids and tannins, have also been reported in the coffee mucilage [25].

Figure 4.
Coffee pulp (wet coffee husk) and de-pulped coffee cherry showing the mucilage covering the coffee bean and partially removed.
This by-product is generated in countries that produce coffee using the wet method [12]. The mucilage is produced at 20 kg per 100 kg of fresh coffee cherries [51]. Given its high moisture content, mucilage poses challenges for drying and processing, requiring wet fermentation to facilitate subsequent processing steps [52]. Technological constraints associated with mucilage include the need for specialized equipment and controlled fermentation conditions to ensure the appropriate degradation and removal of the mucilage layer [53]. The sticky nature of the coffee mucilage can complicate handling and processing, requiring specific techniques like washing (a method to rinse off the fermented mucilage) and mechanical de-mucilaging (where a machine is used to physically strip away the mucilage without damaging the coffee bean) for its removal [54]. However, advances in processing technology and optimization of fermentation parameters have been explored to overcome these constraints and enhance the utilization of the coffee mucilage in value-added applications [52].
Nonetheless, it is important to consider potential contaminations in the coffee mucilage due to the fermentation process. Improper fermentation conditions or inadequate hygiene practices during wet fermentation may lead to microbial contamination, including the growth of undesirable microorganisms such as molds, bacteria, or yeasts [53]. These contaminants can affect the quality and safety of the coffee mucilage and its derived products. Proper hygiene practices, strict quality control measures, and adherence to food safety regulations are crucial during wet fermentation and subsequent processing steps to mitigate potential contaminations. Regular monitoring and testing for microbial contaminants should be implemented to ensure the safety of coffee mucilage-derived ingredients and products [52]. By implementing appropriate quality assurance protocols, the risk of contamination can be minimized, allowing for the safe utilization of the coffee mucilage in value-added applications.
2.3. Parchment
The coffee parchment is the yellowish fibrous endocarp covering and dividing the two hemispheres of the coffee seed. The coffee parchment is produced at 39 kg per 100 kg of fresh coffee cherries [51]. In the wet processing, the coffee parchment is separated from other by-products after the beans have been dried and dehulled (Figure 5). This process allows for the collection of the parchment and its use separately from other by-products. In contrast, in the dry process, the coffee parchment is removed from the green bean, along with the skin, pulp, and mucilage, and is part of the coffee husk.

Figure 5.
Coffee parchment flakes as obtained by the wet method.
In terms of composition, the coffee parchment primarily consists of a high proportion of carbohydrates (~56%), predominantly in the form of dietary fiber. The main components of the parchment’s dietary fiber are cellulose (40–49%), hemicellulose (25–32%), and lignin (33–35%) [26,34,55,56,57]. It also contains low levels of fat (~0.3%), proteins (~3%), minerals (0.5–1%), and a variable moisture content (~8–10%). Caffeine and total phenolic compounds may account for approximately 1% and 2%, respectively [36,58].
As it represents 6% of the cherries’ dry weight, it is produced at a rate of approximately 39 kg per 100 kg of fresh coffee cherries [51]. Therefore, it is an abundant by-product of coffee processing. Technological constraints associated with the coffee parchment include its fibrous nature, which can make it challenging to process and incorporate into various applications [59,60]. Further research and development efforts are needed to explore efficient and cost-effective methods for the extraction, purification, and utilization of the valuable components present in the coffee parchment [61]. This will help maximize its potential as a sustainable resource and enhance its value as a functional food ingredient [35].
The coffee parchment is generally considered safe for consumption, with studies confirming the absence of pesticides and mycotoxins, except for a minimal content of ochratoxin A (OTA) below the European Commission limit [14,62]. A toxicity analysis was performed to complete the safety assessment, showing no adverse effects or mortality following the administration of 2 g/kg body weight of parchment to rats [14]. However, it is important to note that the coffee parchment, like other coffee by-products, should undergo rigorous quality control measures to ensure safety and minimize potential contaminants. Regular testing for pesticide residues, mycotoxins, and other contaminants should be conducted to ensure compliance with food safety regulations [63]. This is especially important as the coffee parchment is often used as a raw material to produce functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals, where the safety and purity of the starting material are crucial for the final product quality.
2.4. Silverskin
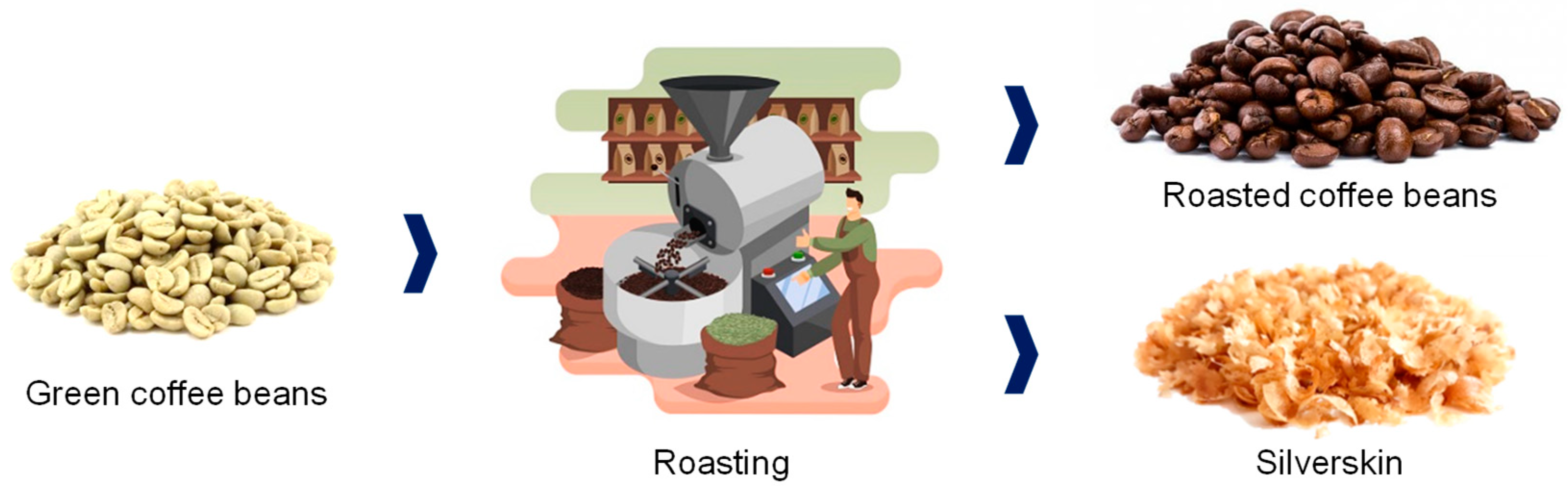
Green coffee beans are shipped to coffee-consuming countries, where their quality is evaluated based on odor and taste tests, as well as by size, form, color, hardness, and existence of defects [20]. Once received, beans are checked to confirm their quality and stored until being roasted. The roasting process consists of three steps: drying, roasting, and cooling. During the drying process, water and volatile compounds are slowly released, and the color of the coffee beans changes from green to yellow. Roasting reactions alter both the beans’ physical and chemical properties, resulting in a complex mixture of Maillard reaction products [21].
The silverskin, the thin tegument covering the bean, is detached at this point (Figure 6). The coffee silverskin is the only by-product of the coffee roasting process [17,64]. This by-product contains low moisture (4–7%), lipids (1.2–3%), and mineral content (5–9%). Proteins (8–20%) and carbohydrates (62–67%), mainly forming dietary fiber (52–70%), are the main component of the coffee silverskin [14,38,39,65]. The dietary fiber fraction comprises celluloses (~18–24%), hemicelluloses (~13–17%), and lignin (~29%) [39]. Caffeine is the main phytochemical in the coffee silverskin, followed by the chlorogenic acids (caffeoylquinic acids, dicaffeoylquinic acids, lactones of caffeoylquinic acids, coumaroylquinic acids, feruloylquinic acids, lactones of feruloylquinic acids, and feruloyl-caffeoylquinic acids) [38,40]. Other phenolic compounds found in coffee silverskin include caffeic, protocatechuic, and vanillic acids [41].
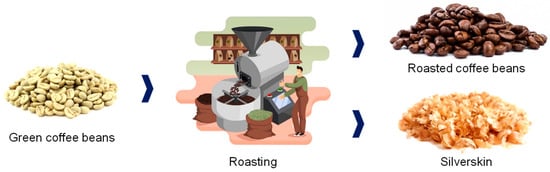
Figure 6.
Obtention of coffee silverskin during the roasting of green coffee beans.
The coffee silverskin represents about 4% of the green coffee beans [17,64]. The roasting of 4 tons of coffee yields approximately 30 kg of coffee silverskin [66]. Considering the world coffee annual production (171.3 million 60 kg bags of coffee beans) [43], 76 thousand tons of the coffee silverskin are produced each year worldwide in coffee-transforming countries. Its fibrous and thin nature poses unique technological constraints for its processing and utilization in various applications [67]. Challenges arise due to its low density and high inflammability, requiring careful handling and storage to ensure safety and prevent potential fire hazards [68]. Moreover, the physical characteristics of the coffee silverskin, including low compactability and poor flowability, may require specialized equipment and processing techniques to achieve effective extraction, purification, and incorporation into value-added products [69]. To overcome these challenges and maximize the commercial viability of the coffee silverskin as a sustainable resource, further research and development efforts are needed to explore innovative solutions and optimize processing methods [70]. This includes the development of efficient and cost-effective technologies that enable the extraction and recovery of valuable components from the coffee silverskin while ensuring safety and scalability [71]. Exploring alternative uses and applications that potentiate the unique properties of the coffee silverskin, such as its antioxidant and antimicrobial potential, can further enhance its value as a functional food ingredient and nutraceutical resource [72].
The occurrence of chemical, biological, and processing contaminants has also been examined to guarantee the nutritional quality and safety of the ingredients derived from the coffee silverskin [14]. The absence of pesticides and mycotoxins was confirmed in the coffee silverskin, although it was close to the limit set by the European Commission for roasted coffee (400 μg/kg) but less than the amount established for instant coffee (900 μg/kg) [73]. Nevertheless, no genotoxicity and cytotoxicity were observed in human liver cells treated with various concentrations of coffee silverskin [74]. Acute and sub-acute oral administration studies in animals have also demonstrated the safety of the coffee silverskin extract at the tested doses [55]. Nevertheless, it remains essential to maintain strict quality control measures during processing and conduct regular testing for contaminants to ensure the safety of coffee silverskin-derived ingredients [75]. Addressing the technological and safety constraints associated with the coffee silverskin not only maximizes its utilization potential but also contributes to the circular economy by reducing waste and creating value from this by-product of the coffee roasting process [76].
3. Biorefinery Strategies for Upcycling Coffee By-Products
3.1. Biorefinery as a Sustainable Approach for Circular Bioeconomy
Biorefinery is a sustainable approach that generates a variety of products from multiple biomass materials, utilizing relevant conversion technologies to carry out this transformation [77]. The biorefinery concept emerges as a possible solution to the present waste disposal challenges facilitating high value-added compounds production [78]. This approach complements conventional waste use practices (animal feed, composting, incineration, and landfill). Biorefinery has been identified as the second generation of waste valorization and reuse strategies for higher-value marketable production products [79]. Furthermore, this innovative valorization strategy has also been regarded as one of the most promising approaches to achieving a resource-efficient circular bioeconomy because it reduces human-induced environmental risks, creates new business possibilities, and uses energy more efficiently [80].
Likewise, the circular bioeconomy seeks to increase human well-being and social justice while substantially reducing environmental risks and resource scarcity [81]. The bioeconomy concept has long been associated with converting biological resources into goods and materials. The circular bioeconomy is a bioeconomy in which products and materials are recycled and reduced to a high degree [82]. Recycling and other circular waste management strategies are critical components of the circular bioeconomy model, as shown by the sustainable, resource-efficient valorizing of biomass using biorefineries and repurposing residues and wastes [83].
This biorefinery approach could result in active biomolecules for medicinal, cosmetic, food, and non-food applications. Proteins, polysaccharides, fibers, and flavor compounds are examples of high-value materials that can be processed and reused as food ingredients [84,85]. They are commonly used as texturizing, preserving, or coloring ingredients in the food industry, as well as active compounds in cosmetic or pharmaceutical products. These components must be obtained using extraction methods to isolate the targeted components from the matrix. In this regard, plenty of green chemical and biochemical procedures are pursuing that goal through process optimization to obtain higher extraction efficiency while reducing extraction time, energy use, the amount of solvent consumed in the process, environmental impact, economic costs, and waste generation [86,87]. Within them, the solute to solvent dissolution and its further diffusion abroad the matrix (solid-liquid extraction’s phenomenon) could be considered the most widely used strategy for compound recovery, using both organic solvents and water (or their combinations). On this matter, the usefulness of water as a solvent for bioactive compound extraction has been deeply explored since one of the associated advantages is compliance with the safety requirements for food-like applications. Indeed, water is the most eco-friendly traditional solvent to consider for green processes. At room temperature, ionic and polar compounds dissolve easily in water, while less polar compounds dissolve more easily at higher temperatures. Moreover, water is non-toxic, non-flammable, inexpensive, and readily available [88]. This conventional extraction method is well-established and relatively easy to operate [89]. Water-based extraction techniques play a crucial role within the biorefinery framework. They are extensively used to extract and recover active biomolecules from the biomass matrix, such as phenolic compounds from coffee by-products. However, for some purposes, water-based extractions could result in nonselective procedures involving high economic, energy, and resource expenses [2]. Thus, advanced chemical and physicochemical techniques based on mass transfer enhancement through the water’s solvation power tuning and/or cell wall weakening (i.e., high pressurized hot water, microwave-assisted or ultrasound-assisted extraction), are gaining interest within the scientific community because of their improved efficiency and selectivity rates, while being more environmentally sustainable compared to other alternatives [90,91].
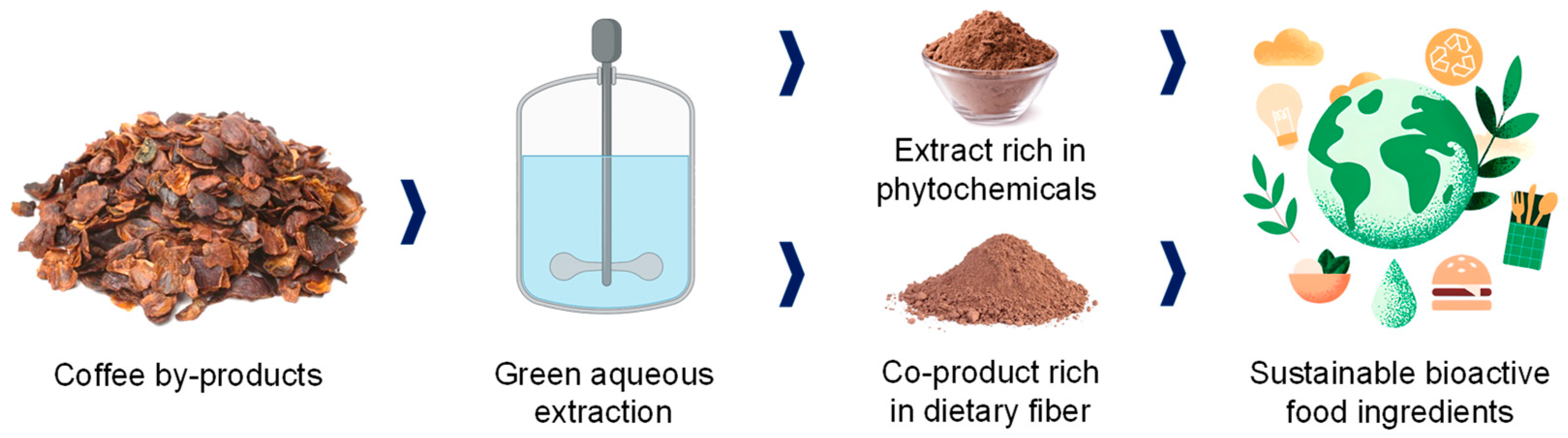
Therefore, water-based green extractions from coffee agroindustry by-products following a biorefinery approach (Figure 7) involve obtaining the targeted compounds (i.e., phenolic compounds) from the food matrices and valorizing the possible co-products generated (i.e., enriched dietary fiber material) to safely create value-added products that are free of toxic compounds.
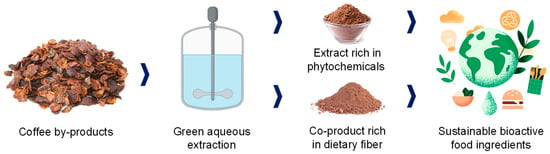
Figure 7.
Biorefinery approach in the revalorization of coffee by-products through green extraction.
3.2. Biorefinery and Coffee By-Products for Bioactive Food Ingredients Production
3.2.1. Husk
The conventional use of the coffee husk is to prepare the “Cascara Beverage” traditionally consumed in Yemen and Ethiopia [29], and for composting in coffee-producing countries [92,93]. Current uses for the coffee husk include mushroom cultivation [94], lignin extraction [95], recovery of biomolecules from the lignin alkali hydrolysate [96], bioethanol production [45,97], biosorbents preparation [98,99], and animal feed [46]. Other biotechnological applications proposed for this by-product are the production of enzymes: amylase [100], xylanase [101], endoglucanase [102], protease [103], peptidase [104], and tannase [105], among others [106]; and biomolecules such as carotenoids [107], gallic [108], citric [109], succinic [110], lactic [111], and gibberellic acids [112], and fruity flavor compounds [113].
However, recent studies have provided new evidence to support the use of the coffee husk as a food ingredient for human consumption [114,115,116]. Simple, low-cost, and eco-friendly aqueous extraction methods were used to produce extracts enriched in bioactive compounds with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anti-adipogenic properties [117,118,119,120], demonstrating the feasibility of using water as the only extractant of the coffee husk’s phenolic compounds. Aqueous extracts yielded around 7–29%, being composed of caffeine (1%), chlorogenic acids (0.3%), and protocatechuic acid (0.1%), among other phenolic compounds [115,117,118]. Soluble sugars (glucose, fructose, and sucrose) were also present (~12%), as well as soluble proteins (5–7%). Most aqueous extracts are composed of soluble dietary fiber (~68%), which is solubilized together with phenolic compounds and other non-identified phytochemicals [114,115,117].
Therefore, the existing evidence concerning coffee husk aqueous extracts supports the potential use of these extracts to modulate metabolic syndrome biomarkers and, consequently, prevent cardiometabolic diseases. Likewise, the valorization of the whole coffee husk flour and the water-insoluble residue obtained after the aqueous extractions, which are rich in antioxidant dietary fiber [114,115], provide a more sustainable approach for the complete revalorization of coffee husks. All ingredients from the coffee husk revealed health-promoting properties associated with the prevention of metabolic syndrome. In conclusion, the coffee husk has shown a high concentration of dietary fiber and phenolic compounds. Considering its chemical composition and its biological activities demonstrated in multiple investigations, the coffee husk could be converted into two ingredients: an aqueous extract that could be used as a health-promoting food ingredient and another fraction that could be implemented as a source of antioxidant dietary fiber. This mixed high-fiber and phenolic compound content makes the coffee husk very appealing as a nutraceutical and ingredient in functional foods since combined antioxidant and fiber contents are likely to positively impact health, from the gastrointestinal tract to peripheral tissues.
3.2.2. Mucilage
The coffee mucilage, a by-product of coffee processing, holds promise for various applications in the food industry. It contains valuable nutrients, including protein, carbohydrates, fiber, fat, and potassium, which can be utilized in flour, baking mixes, nutritional supplements, and nutraceuticals [121]. The fermentation of the coffee mucilage involves microorganisms such as yeasts and lactic acid bacteria, which contribute to the breakdown of mucilage and the creation of flavor-active components. These components find use in food additives, flavorings, and extracts [53]. Additionally, the extraction of simple sugars from the coffee mucilage can serve as a substrate for anaerobic digestion, enabling the production of methane and bioethanol [122,123]. Fermentation of coffee mucilage can also yield ethanol, which finds application as a biofuel or in beverage production [123,124]. The microbial community involved in coffee mucilage fermentation significantly influences the process and impacts the final product quality [125]. The introduction of yeasts in the fermentation process has been found to enhance coffee quality [54]. Furthermore, coffee mucilage fermentation involves microorganisms that play a crucial role in mucilage degradation and the generation of flavor-active components [52]. Research has investigated the fate of mucilage cell wall polysaccharides during coffee fermentation, revealing high levels of uronic acids in crude pectic substances [126]. The microbial utilization of the mucilage as a growth substrate results in the production of secondary metabolites, including organic acids, alcohols, esters, ketones, and aldehydes, which can affect the fermentation’s impact on the final product quality [31]. Moreover, the coffee mucilage exhibits functional and technological properties suitable for producing bioplastics in the food industry [127]. However, it is important to note that the substantial waste generated by the coffee industry can pose environmental risks [123].
In addition to its potential environmental impact, the coffee mucilage presents an opportunity for extracting bioactive compounds for use in food applications. The mucilage extract and flour derived from coffee fruits contain phenolic compounds, antioxidants, caffeine, lipidic compounds, dietary fiber, proteins, and peptides, as well as aromatic and volatile compounds [24]. By utilizing waste products like the coffee mucilage, bioactive molecules can be produced for pharmaceutical, cosmetic, food, and non-food applications [24]. Furthermore, coffee mucilage exhibits industrial potential, with studies highlighting its value as a source of raw pectins, antioxidants, and flavonoids [24]. Recent findings have demonstrated the inhibitory effect of coffee mucilage extracts on certain Gram-positive bacteria, although the specific compounds responsible for this activity remain unknown. The chemical composition of the mucilage and its potential as a prebiotic that impacts gut microbiota are areas that require further exploration [25]. Additionally, the potential of the total mucilage, including cellulose, as a thickener or in other applications warrants further investigation [128].
3.2.3. Parchment
Studies exploring coffee parchment’s use as a food ingredient are recent. However, the product’s significant health-promoting and technologically appealing features are opening its potential use as an ingredient in the food industry. The optimal conditions yielded high phytochemicals as reported by Iriondo-deHond et al. [14], who found a 2.3% yield and an extract containing high caffeine levels (1.3 mg/g) and a lower concentration of chlorogenic acid (0.14 mg/g). The main phenolic compounds in the coffee parchment are hydroxybenzoic and hydroxycinnamic acids (chlorogenic, vanillic, protocatechuic, and p-coumaric acids) [58]. These compounds are associated with the coffee parchment’s in vitro antioxidant and antifungal properties [36,58].
In addition, the coffee parchment is also a potential source of dietary fiber. The coffee parchment is rich in insoluble dietary fiber (89%), mostly lignin (~30%), xylans (~28%), and cellulose (~10%). In previous studies, the presence of xylans [129], cellulose, and lignin [14] was similarly confirmed. The antioxidant capacity of the dietary fiber compared to the antioxidant potential associated with phenolic compounds was also studied, showing higher dietary fiber antioxidant potential than that of associated phenolic compounds, indicating that cell wall components (mainly lignin and xylans) may also be contributing to the antioxidant properties [19].
The coffee parchment’s technological features (water holding capacity, water absorption, swelling capacities, oil holding capacity, and gelation capacities) open the potential for food applications both as physiological and technological ingredients. The main factors influencing hydration properties are the polysaccharide composition and their organization within the cell walls. In general, coffee parchment showed good hydration properties, suggesting that this by-product could be used as a functional ingredient to reduce calories or modify the viscosity and texture of formulated foods. Moreover, hydration properties are also related to some physiological effects such as hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic, exhibiting a potential for glucose adsorption, retarded diffusion, and inhibited α-amylase, which led to lower starch digestibility. Similarly, the coffee parchment exhibited in vitro hypolipidemic properties, including pancreatic lipase inhibition and cholesterol and bile salts binding [34].
Recent investigations also explored the synthesis of xylo-oligosaccharides from coffee parchment [129]. Xylo-oligosaccharides could be a valuable product since they possess prebiotic features as functional food ingredients with tremendous potential [130]. The aqueous extracts could also be produced if the extracted phytochemicals are economically profitable (nutraceutical or pharmaceutical purposes). Following a biorefinery approach, the water-insoluble residue could also be revalorized as a dietary fiber source exhibiting properties similar to the non-extracted coffee parchment [34].
The main use of the parchment is addressed as a source of antioxidant dietary fiber. Coffee parchment has been added to gluten-free bread (2–4%) [35]. The addition led to increases in dietary fiber, phenolic compounds, and antioxidant capacity without modifying the appearance of the bread and its texture properties. Consumer acceptance studies found that a 4% replacement gave the final product a distinct bitter taste due to the presence of caffeine [35]. The work suggested that a debittering step should be considered to increase the coffee parchment quantity in gluten-free bread in order to enhance its sensory and nutritional properties [35]. Therefore, using the water-insoluble residue from the coffee parchment would allow for producing bread with higher dietary fiber content and maintain its health-promoting properties. Similarly, cookies with 1–5% coffee parchment flour were developed by Cubero-Castillo et al. as a strategy to increase the dietary fiber content and enhance cookies’ antioxidant capacity [56]. In this research, adding the coffee parchment flour to the cookie dough did not generate consumer rejection.
Furthermore, coffee parchment could be transformed into other renewable products. It may be a source of cellulose to produce cellulose-based goods [131]. Lignocellulosic fibers and lignin are two of the world’s most valuable natural resources and have great potential to increase bioplastics biodegradability by replacing synthetic fibers. Lignin has proven to function as a bioplastic plasticizer, stabilizer, or bio-compatibilizer, making coffee parchment an outstanding candidate for sustainable packaging [132]. Coffee parchment can also be a source of caffeine and phenolic compounds for edible film production with antifungal properties [36]. Additionally, coffee parchment has also been utilized for various purposes, including the production of non-food-related products such as particleboard [26,133], composite reinforcement [134], and, ultimately, as a source of renewable energy via combustion [135].
Until now, coffee parchment applications as a food ingredient remain largely unexplored. Notwithstanding the favorable chemical composition of the coffee parchment aqueous extract and in vitro antioxidant capacity, this coffee by-product should preferably be used as a source of antioxidant dietary fiber since extraction yields are relatively low. Nonetheless, research pinpoints the need to fractionate the coffee parchment, generating a soluble extract and an insoluble residue. Both fractions can be revalorized into differentiated products through a biorefinery approach, avoiding more waste production. New coffee parchment applications in the food industry as a natural source of antioxidant dietary fiber should be strongly considered to revalue this by-product.
3.2.4. Silverskin
Studies have explored the aqueous extraction of the coffee silverskin to develop food ingredients with healthy properties. Sustainable aqueous extraction of phytochemicals from coffee silverskin has been proposed according to del Castillo et al. (patent number WO 2013/004873) [136]. This extract is a sustainable source of bioactive compounds such as chlorogenic acid (2.8 mg/g) and caffeine (19.2 mg/g), but the major component in coffee silverskin extract is soluble dietary fiber (22%) [137].
Based on its chemical composition and observed biological activity, the green aqueous extract could be used as a healthy food ingredient. Coffee silverskin extract could be consumed as a nutraceutical or added to the most appropriate food matrix based on sensory customer acceptance. The food applications of coffee silverskin extract in beverages [137], biscuits [138], and bread [114] have been described. Coffee silverskin extracts can also be applied to produce functional yogurts [67]. Other sustainable potential uses for this extract include cosmeceuticals production since compounds from coffee silverskin protect skin cells from UV damage and prevent skin aging. Moreover, the extract presents adequate properties to be included in a cosmetic formulation [139,140].
The coffee silverskin flour and water-insoluble residue (from the phytochemicals green extraction) can also be used as a fiber-rich food ingredient, with the ultimate goal of recycling the whole by-product. The coffee silverskin water-insoluble residue contains 70% dietary fiber, with the majority being insoluble. This fraction also comprises 10–20% proteins and about 3% fat, depending on the species. This fraction also reported in vitro antioxidant and prebiotic properties [65]. Likewise, dietary fiber fermentation releases short-chain fatty acids, which modulate anti-inflammatory gene and protein expression [141]. OTA was detected in the coffee silverskin water-insoluble residue at lower levels (2.9 μg/kg) than those permitted by the European Commission. However, no other mycotoxins or pesticides were found [62]. Furthermore, coffee silverskin dietary fiber has been used to enhance the nutritional quality of biscuits by improving the moisture, texture, thickness, and color of the novel biscuits [138]. The coffee silverskin has been used as a dietary fiber ingredient to formulate bread, reducing its caloric density. Moreover, cakes with up to 30% coffee silverskin water-insoluble residue as a flour substitute have been developed, improving moisture content, textural, and sensory attributes [142,143]. Cakes with coffee silverskin water-insoluble residue exhibited physical and sensory properties similar to the control cake [142].
Alternative sustainable uses of coffee silverskin are polylactic acid production as a replacement for synthetic polymers [144], cellulose isolation and purification for the development of sustainable packaging [145] and biofilms [146], the production of butanol [147], succinic acid [148], bio-oil [149], composites [69], and adsorbent [150], as well as an energy source through pyrolysis [151]. Antioxidants and value-added bioactive compounds are produced from the coffee silverskin via pyrolysis [152]. More research is being conducted demonstrating the presence of a plethora of bioactive compounds and coffee bean roasting-derived phytochemicals that provide health benefits in biological systems [153].
According to circular economy strategies, the coffee should be fully revalorized either as flour or fractionated into two different ingredients (extract and water-insoluble residue), generating zero residues. Research has corroborated the coffee silverskin components’ nutritional properties and biological activity. Thus, the different applications of coffee silverskin as a food ingredient and its safety validation have confirmed its viability as a sustainable food ingredient or nutraceutical for human consumption.
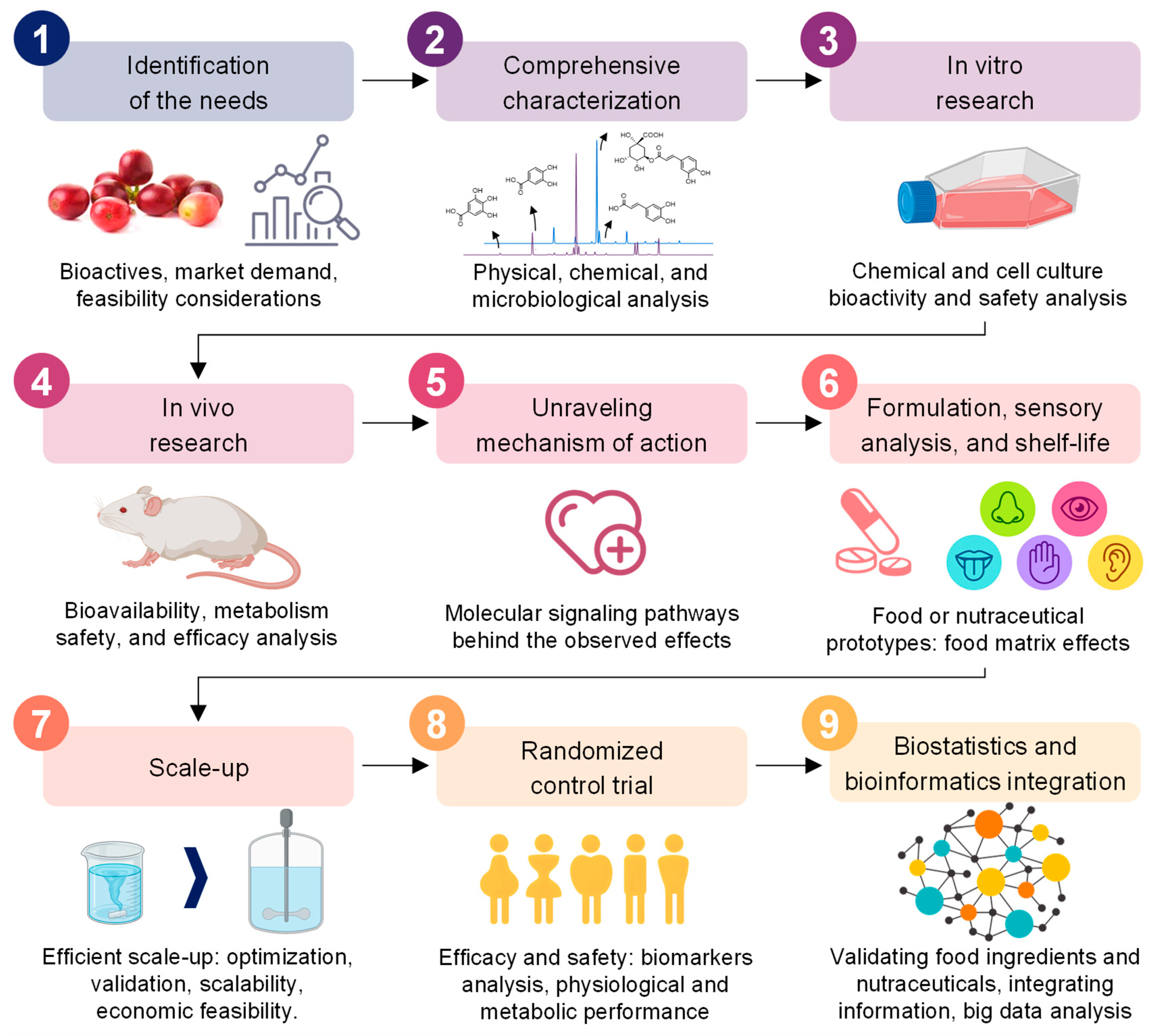
4. Stepwise Strategy for Valorizing and Validating Coffee By-Products as Bioactive Food Ingredients and Nutraceuticals
Based on the knowledge generated around the chemical composition of coffee by-products and the growing interest in their valorization as healthy food ingredients, specific research strategies need to be gradually addressed to gather all the information required to use coffee by-products as bioactive food ingredients and nutraceuticals for the prevention of chronic diseases [154]. A stepwise approach is essential to ensure the revalorization of coffee by-products and enhance the food system’s sustainability (Figure 8). Harmoniously, the green production of healthy food ingredients from these by-products can result in a strategy to prevent chronic diseases [155].
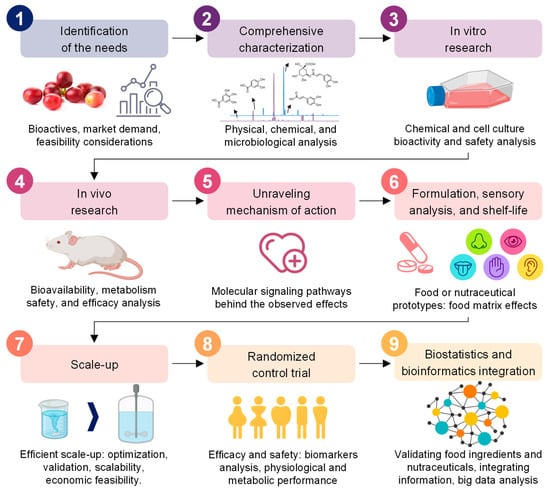
Figure 8.
The different steps followed to valorize and validate coffee by-products into bioactive food ingredients or nutraceuticals.
4.1. Identification of the Needs
The first step is to identify the specific needs that the products should meet. This involves considering the desired bioactive compounds and functional properties, as well as the market demand and feasibility of the food products [156]. Through this process, a clear set of goals and priorities is established, effectively guiding the development of these products.
One important issue in identifying the needs is the bioactivity of the compounds present in coffee by-products. They are known to contain various bioactive compounds, such as phenolic compounds and caffeine, which have been linked to various health benefits [89]. Therefore, it is essential to determine which compounds are of interest and how they can be extracted and utilized in the development of functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals [157]. Another consideration is the functional properties of the products. For example, if the goal is to develop a nutritional supplement, the product should have a high concentration of the desired bioactive compounds and be formulated to ensure maximum absorption and bioavailability in the body [158]. Similarly, if the target is to develop a food ingredient, the product should have desirable functional properties such as flavor, texture, and stability [159].
In addition to considering the technical aspects of the products, it is important to contemplate market demand and feasibility. This involves assessing consumer preferences and trends, as well as the availability and cost of raw materials and the processing methods [160]. By taking these factors into account, the development of functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals from coffee by-products can be guided by market demand and feasibility, leading to more successful and sustainable products [161].
4.2. Comprehensive Characterization
After identifying the needs, the next step is to characterize the coffee by-products-derived food ingredients or nutraceuticals comprehensively. This involves analyzing the composition and properties of the product to ensure it meets the identified needs and is safe for consumption, including a range of analyses such as chemical, physical, and microbiological analyses. These analyses provide information on the product’s nutritional content, functional properties, and safety [162]. For example, proximate analysis can be used to determine the product’s moisture, protein, fat, and carbohydrate content, while rheological testing can be used to evaluate the texture and viscosity [163]. The microbiological examination is also important to ensure that the product is free from harmful microorganisms [164].
In addition to the traditional analyses, newer techniques such as metabolomics and proteomics can provide a more detailed understanding of the product’s composition [165]. Metabolomics can be used to identify and quantify small molecule metabolites in the product, while proteomics can be used to analyze the protein content and identify potential bioactive peptides [166]. Comprehensive characterization is essential to ensure that the food ingredient or nutraceutical meets the identified needs and is safe for consumption [167]. By analyzing the product’s composition, properties, and safety aspects, any potential issues can be identified and addressed, leading to a more successful and safer product. These techniques allow for the characterization of extracts obtained using the biorefinery strategy and ingredients rich in bioactive compounds [168]. It is essential to employ a range of analytical tools to gain a comprehensive understanding of the constituents from coffee and its by-products. Spectrophotometric analysis methods such as UV-VIS and fluorimetry are complemented by the use of advanced techniques like LC-MS/MS, GC-MS/MS, and NMR to characterize the diverse array of bioactive compounds present [169].
4.3. In Vitro Research
In vitro studies play a crucial role in the initial evaluation of the bioactivity and safety of coffee by-product-derived ingredients, as they provide a controlled laboratory environment to examine their effects on biological systems [170]. Given the abundance of bioactive compounds found in coffee by-products and their diverse biological effects, employing multiple experimental approaches is necessary to gain a comprehensive understanding of their activity [171]. These in vitro studies allow for the assessment of various properties, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial activities of coffee by-product-derived compounds. Of particular interest is evaluating the antioxidant activity, as coffee by-products are known to contain phenolic compounds which exhibit potent antioxidant properties [15]. Phenolic compounds from coffee by-products have been recognized as bioactive components with antioxidant properties [58,115,172]. In vitro studies have also been conducted to compare the phytochemicals from coffee by-products and their potential to reduce markers of inflammation, oxidative stress, adipogenesis, and insulin resistance [41,119,173]. Coffee silverskin melanoidins, formed via the Maillard reaction, have been assessed for their bioactivity [174]. The coffee husk has been evaluated as an innovative antioxidant dietary fiber ingredient [42]. Additionally, in vitro assays can determine the potential of coffee by-product-derived ingredients to inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria [175]. Moreover, in vitro studies serve as a valuable tool to optimize the processing conditions and formulation of food ingredients or nutraceuticals [176]. For example, researchers can investigate the effects of different processing parameters, such as temperature and pH, on the bioactivity and stability of the final product. In vitro studies also aid in determining the optimal concentration of coffee by-product-derived compounds to maximize their bioactivity in the formulation [89].
Furthermore, it is essential to conduct in vitro bioaccessibility, bioavailability, and toxicological studies to evaluate bioactive compounds’ release, absorption, and safety [177]. Bioaccessibility studies have been conducted to evaluate the release and absorption of bioactive compounds from coffee by-products and the changes in antioxidant activity during in vitro gastrointestinal digestion [33,120,153]. Safety studies allow for a comprehensive assessment of potential allergenicity, genotoxicity, and other safety aspects associated with coffee by-product-derived ingredients [37]. While in vitro research provides valuable insights into the bioactivity and safety of coffee by-product-derived compounds, it is important to acknowledge its limitations in predicting their effects in vivo [178]. Hence, conducting subsequent in vivo studies using animal and human models is necessary to confirm the bioactivity and safety of these ingredients.
4.4. In Vivo Research
Animal studies provide valuable information on the bioactivity, safety, and efficacy of coffee by-product-derived compounds [179]. In vivo animal models can be used to evaluate the effect of the coffee by-product-derived ingredients on specific health conditions, such as obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, or neurodegenerative diseases [180]. In a study by Benyelles et al., an aqueous extract from the coffee parchment was investigated for its anti-obesity effects in a rat model of fructose-induced obesity. The study found that the coffee parchment extract reduced adipose fat accumulation and improved glucose metabolism. It also alleviated metabolic disorders associated with obesity, such as hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, hyperlipidemia, and oxidative stress [181]. Similarly, Bhandarkar et al. conducted a study on the effects of dietary supplementation with freeze-dried coffee pulp in rats with metabolic syndrome induced by a high-carbohydrate, high-fat diet. The results demonstrated that the coffee pulp supplementation improved various metabolic parameters, including body weight, abdominal fat, blood pressure, lipid profiles, glucose tolerance, and gut microbiota composition [182]. Animal studies can also provide valuable information on the bioavailability and metabolism of the compounds [183]. For example, animal models can be used to evaluate the absorption and distribution of the compounds in the body, as well as their metabolism and excretion [183]. Fernandez-Gomez et al. investigated the bioaccessibility, bioavailability, and bioactivity of a coffee silverskin extract, demonstrating that chlorogenic acids and caffeine were metabolized in the gastrointestinal tract and their metabolites exhibited chemo-protective effects on pancreatic cells under diabetic conditions [184]. Animal models can also be employed to assess the potential for adverse effects associated with coffee by-product-derived compounds. Conducting thorough safety evaluations and toxicological studies in animal models is essential to ensure the absence of harmful contaminants or adverse effects associated with the coffee by-product-derived bioactive ingredients [185]. Assessing potential allergenicity, genotoxicity, and long-term safety profiles is crucial [186]. Iriondo-DeHond et al. conducted a study on a coffee silverskin extract to assess its nutritional value, safety, and effects on key biological functions, evidencing no adverse effects on hormone secretion, antioxidant, or anti-inflammatory biomarkers. The results indicate that coffee silverskin is a safe and beneficial food ingredient with potential health benefits that might improve gut health by leading to the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) [55]. Regulating gut health is of utmost importance as it reinforces the intestinal function as the primary defense against various disorders, including those affecting cardiometabolic health [187].
4.5. Unraveling Mechanism of Action
Unraveling the mechanism of action of coffee by-products and understanding how these compounds exert their beneficial effects is crucial for optimizing the final bioactive ingredients or nutraceuticals and exploring new applications [180]. Mechanistic studies typically employ in vitro and in vivo models to identify the cellular and molecular pathways targeted by coffee by-product-derived compounds. In vitro studies allow for the evaluation of the compounds’ effects on specific enzymes or signaling pathways, while in vivo studies may provide insights into the compounds’ impact on biomarkers of oxidative stress, inflammation, and other relevant biological processes [188].
Numerous mechanisms of action have been proposed for the beneficial effects of bioactive compounds found in coffee by-products. These mechanisms include antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities, as well as the regulation of signal transduction and gene expression [189]. Phytochemicals present in coffee by-products can exhibit biological activity through various mechanisms, such as direct free radical scavenging, down-regulation of radical production, inhibition of enzymes involved in the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and up-regulation of antioxidant enzymes [190]. Extract from the coffee husk (dry and wet) and the coffee silverskin have proven to stimulate the activity of catalase and superoxide dismutase upon a pro-oxidant elicitation [191,192]. These protective effects of coffee by-product-derived compounds may be attributed to their ability to modulate the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/antioxidant response element (ARE) signaling pathway [191,193]. Additionally, coffee by-product-derived bioactive compounds may contribute to the regulation of energy metabolism, making them potential candidates for combating obesity and metabolic disorders. These compounds can affect lipid metabolism (AMPK and CPT-1), adipogenesis (FASN and SREBP-1c), and thermogenesis (PGC1-α and UCP-1) pathways, thereby influencing body weight and energy balance [119]. Coffee by-product-derived compounds have been found to exhibit the ability to inhibit SREBP-2 and HMGCR, thus modulating cholesterol homeostasis [194,195]. Furthermore, some coffee by-product-derived compounds, such as chlorogenic acids, have been associated with antidiabetic effects through their ability to enhance insulin sensitivity and regulate glucose metabolism. Coffee by-products can modulate INSR, AKT-PI3K, and IRS-1 related pathways and can modulate the expression of glucose transporters (GLUT-2 and GLUT-4) [192]. Therefore, a molecular nutrition approach is needed to assess the effect of coffee by-products’ bioactive compounds on whole-body physiology and health status at the molecular and cellular levels. The precise identification of the molecular pathways underlying human metabolism is essential for promoting health and preventing disease [196]. Mechanistic studies also provide valuable insights into the potential adverse effects associated with coffee by-product-derived compounds. Evaluating their interactions with specific receptors or signaling pathways can help identify possible side effects and guide the development of safe and effective products [37].
4.6. Food and Nutraceutical Formulation, Sensory Analysis, and Shelf-Life Stability
After identifying bioactive compounds and evaluating their efficacy and safety through in vitro and in vivo studies, the next step for upcycling coffee by-products into bioactive food ingredients and nutraceuticals is food production and sensory analysis [156]. Food production involves the formulation and development of food prototypes that incorporate coffee by-product-derived ingredients. This process requires careful consideration of various factors, such as the selection of suitable extraction, concentration, and purification methods to optimize the bioactive compound content and functionality [197]. When formulating nutraceuticals, specific considerations need to be addressed. These include ensuring that appropriate dosages of the bioactive compounds are incorporated, maximizing their bioavailability and bioactivity in the body, and complying with regulatory guidelines for health claims and safety [198]. Nutraceutical formulations may require additional processing steps, such as encapsulation or microencapsulation, to protect the bioactive compounds and enhance their stability and delivery [199]. One crucial aspect to consider during food and nutraceutical formulation is the effect of the food matrix on the bioactivity and bioavailability of the incorporated bioactive compounds [200]. The interaction between the bioactive compounds and other components in the food matrix can influence their release, absorption, and subsequent physiological effects in the body. Understanding these interactions is crucial for optimizing the formulation to maximize the desired health benefits [201].
Sensory analysis plays a critical role in food production, as it assesses the acceptability and palatability of the final product. This evaluation encompasses various sensory attributes, including appearance, aroma, taste, texture, and overall acceptability [202]. By conducting sensory analysis, either through trained sensory panelists or consumer panels, valuable insights can be gained into the product’s sensory characteristics and potential areas for improvement [202].
Furthermore, thoroughly studying the final product’s stability and shelf-life is crucial. Assessing the potential degradation or loss of bioactivity in coffee by-product-derived ingredients during storage and transportation is of great importance. Stability testing is typically performed under various storage conditions to monitor changes in bioactivity, sensory attributes, and microbiological quality, ensuring that the product maintains its efficacy and safety throughout its intended shelf-life [203].
4.7. Scale-Up
Scale-up involves transitioning from laboratory-scale production to larger-scale production to meet the demands of commercial production. The production process is optimized during the scale-up process to ensure efficiency and accommodate increased volume. This may involve adjusting the production equipment, modifying the processing methods, and sourcing raw materials in larger quantities [204]. Validation studies play a crucial role in the scale-up process, as they are conducted to ensure that the final product meets rigorous safety and quality standards. These studies verify the consistency and reliability of the product, addressing factors such as composition, stability, and microbiological safety [32]. Additionally, it is essential to assess the scalability of the production process, considering factors such as the scalability of the extraction methods, the availability of raw materials at a larger scale, and the environmental impact of the scale-up process [205]. Furthermore, during scale-up, it is essential to evaluate the economic feasibility of the production process. This involves assessing the cost-effectiveness of larger-scale production, including considerations such as raw material costs, equipment investments, labor requirements, and market demand [206]. Economic feasibility studies help determine the viability of scaling up the production of bioactive food ingredients and nutraceuticals derived from coffee by-products, ensuring that the final product can be produced and marketed sustainably and economically.
4.8. Randomized Control Trial
Conducting randomized control trials (RCTs) is essential to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the final product in human subjects [207]. RCTs employ a study design and methodology that includes randomization, blinding, and control groups to minimize bias and confounding variables. The study population should be carefully selected to ensure they meet the inclusion and exclusion criteria, and the sample size should be large enough to provide sufficient statistical power [208]. In addition to assessing the efficacy of coffee by-product-derived nutraceuticals, it is important to consider their nutrikinetics, which involves studying their absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion in the human body [209]. Furthermore, the gut microbiota plays a crucial role in the metabolism and bioactivity of bioactive compounds. Therefore, evaluating the impact of coffee by-product-derived nutraceuticals on gut microbiota composition and function is essential [210]. Advancements in personalized and precision nutrition have highlighted the importance of considering individual variations in response to dietary interventions. Integrating personalized and precision nutrition approaches into RCTs can enhance the understanding of how coffee by-product-derived nutraceuticals interact with individual characteristics, leading to more effective and personalized nutritional interventions [211]. Evaluation of safety is also a critical component of RCTs. Adverse events and side effects should be carefully monitored and reported [208].
4.9. Biostatistics and Bioinformatics Integration
Building a solid and reliable scientific foundation for functional food claims requires demonstrating the bio-efficacy of functional food components in vivo, extending beyond in vitro experiments [212]. Therefore, comprehensive evaluations are necessary to validate the functionality of coffee by-product-derived food ingredients, utilizing a range of experimental models, including in vitro models, cell culture models, animal studies, and, ultimately, human preclinical and clinical trials [207]. These diverse approaches allow for a thorough understanding of the effects of coffee by-product-derived compounds on human health. Biostatistical and bioinformatic techniques play an indispensable role in effectively integrating and interpreting the wealth of information generated throughout the various steps, from extraction to characterization, in vitro and in vivo analyses, and human clinical trials [213,214]. These techniques enable the synthesis and analysis of large and complex datasets, facilitating a more comprehensive understanding of the effects of coffee by-product-derived compounds on human health. Moreover, the advent of big data science and analysis has further enriched the capabilities of researchers. Through the application of advanced data analytics, researchers can extract valuable insights from vast amounts of information, uncovering patterns and associations that were previously inaccessible [215]. Recent advancements in artificial intelligence have drawn attention to its capacity to learn and model both linear and non-linear relationships between variables, unveiling hidden and valuable information for decision-making [216]. Artificial intelligence algorithms, such as machine learning and deep learning, can significantly enhance the analysis and interpretation of complex datasets related to coffee by-products. These approaches provide deeper insights into coffee by-product-derived compounds’ chemical composition, biological activity, and toxicity, supporting informed decision-making in developing functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals [217]. Integrating biostatistical and bioinformatic tools, coupled with emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and big data analysis, empowers researchers to unlock the full potential of coffee by-products and contribute to developing innovative and evidence-based functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals [218]. Consequently, after following a holistic approach for gathering the information needed to valorize coffee by-products as food ingredients, all the new knowledge generated about their chemistry, biological activity, and toxicity could be adequately managed, integrated, and interpreted.
5. Commercialization, Regulation, and Technological Innovation
5.1. Market Potential and Commercialization
The development of functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals from coffee by-products presents an opportunity for the coffee industry to expand its product portfolio and enter new markets [197,219]. The market potential for these products is significant, with increasing consumer demand for sustainable and health-promoting food options [220]. In addition, using coffee by-products in these products can contribute to a circular economy and promote waste reduction, further enhancing the appeal of these products to environmentally conscious consumers [221]. To fully realize the market potential of these products, however, it is important to consider the commercialization process. This includes identifying target markets, developing effective marketing strategies, and establishing distribution channels [222]. Collaboration between coffee producers, processors, and food companies may be necessary to ensure the success of these products in the market [223].
In this context, coffee’s primary by-products are traditionally consumed in several coffee-producing countries, although few commercial products are currently available in the market. In countries such as Yemen (where it is called Qishr), Ethiopia (where it is referred to as Hashara), and Bolivia (known as Sultana), coffee husk drinks are quite common, with each having a unique method of consumption [224]. These coffee by-products are typically prepared as infusions with hot water and various spices and can be enjoyed either hot or cold. Baba Seed, a leading coffee company, is recognized for creating Qishr Sparkling Iced Tea, a beverage that is helping to alleviate the environmental impact of coffee production [225]. This beverage is prepared by brewing husks with spices (cinnamon and ginger) and is characterized by high phenolic compounds and a low caffeine content (a quarter of the caffeine of a cup of black coffee). In contrast, Nestlé has developed a product called Nescafé Nativ Cascara, which is made from upcycled coffee berry husks after farmers separate and sun-dry the coffee berry [226]. The result is a refreshing, lightly sparkling, caffeinated beverage with floral and fruity notes. An American multinational chain of coffeehouses, like Starbucks Coffee Company, launched the Cascara Latte in 2017 [227]. In this case, cascara is not consumed as tea but as a syrup, made by boiling coffee cherry skin with sugar and water. It is important to note that the primary coffee by-products are being marketed globally as tea bags. This innovative approach maximizes resources and encourages the production of more sustainable products. For instance, Tabifruit from the Spanish roaster Supracafé Ltd. commercialized coffee husk tea bags with different aromas (such as orange, passion fruit, and berries) to enhance the sweet and fruity flavors of the coffee husk [228]. Overall, the commercialization of coffee by-product-derived products requires a multifaceted approach that considers market potential, regulatory considerations, and technological innovation. Collaboration and continuous research and development will be essential to ensure the success of these products in the market.
5.2. Regulatory Issues and Standards
Regulatory considerations are an important aspect to consider in the development and commercialization of functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals derived from coffee by-products [229]. The regulatory landscape for these products varies by region, and it is vital to comply with the relevant regulations in order to ensure market success and consumer safety [230,231]. In Europe, functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals are regulated under the European Union‘s novel food regulation. This regulation requires a safety assessment and authorization for any novel food or food ingredient that has not been consumed significantly in the EU prior to 1997. The authorization process can be lengthy and expensive, but it is necessary to ensure the safety and efficacy of these products [232]. In Asia, regulations for functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals vary by country. In Japan, for example, functional food ingredients are regulated under the Foods for Specified Health Uses (FOSHU) system, which requires a scientific review of the health claims made by these products [233]. In China, they are regulated under the Food Safety Law, which requires safety assessments and labeling requirements [234]. In Canada, functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals are classified as either foods or natural health products (NHPs) based on their intended use and claims. Functional food ingredients that make health claims are categorized as NHPs and require authorization from Health Canada before they can be legally marketed. The authorization process for NHPs involves a comprehensive review of safety, efficacy, and quality evidence submitted by manufacturers [235]. In the United States, these ingredients are regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and are subject to safety and efficacy requirements. The FDA requires that these products be safe, effective, and labeled appropriately [236].
Including coffee by-products in the European food sector and ensuring human health protection is essential to know if these are considered novel foods. The European specific legislation about novel food is contained in regulation (EU) No. 2015/2283 and (EU) No. 2017/2468 and No. 2017/2469 [232,237,238]. Dried coffee berries (husk or cascara) are considered novel. The term novel food included in this regulation is referred as “a food is considered to be novel if it has not been regularly consumed by humans in the EU before 15 May 1997, when the first novel food Regulation came into force” [239]. Moreover, there is another pathway for the approval of novel foods: a notification for a traditional food from a third country. The implementation of the dried cherry pulp and its infusion, specified in the regulation from the European Commission as traditional foods, has been recently published [240]. For the silverskin, a consultation request is currently determining its novel food status. The food products must be evaluated for safety and toxicological aspects during the approval procedure. Limitations on the utilization of coffee by-products are associated with their caffeine and acrylamide content (obtained after the roasting process). The caffeine content in foods formulated with coffee by-products should be below the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) safety level for daily caffeine consumption of 400 mg for the general population and 200 mg for lactating women. The acrylamide limit established by the EFSA for coffee and instant coffee is 450 and 900 µg/kg, respectively [241]. The absence of pesticides and mycotoxins is a required determination that must also be carried out.
In conclusion, navigating the regulatory landscape for functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals derived from coffee by-products can be complex, but it is essential to ensure compliance and safety. Companies need to work closely with regulatory agencies in their respective regions to ensure compliance and to stay up to date with evolving regulations.
5.3. Technological Innovation
Technological innovation is a crucial factor for successfully developing and commercializing functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals derived from coffee by-products. Patents play a pivotal role in protecting the intellectual property of these innovations and providing a competitive advantage in the market. Numerous patents have been developed to enhance the utilization value of coffee processing by-products for various applications (Table 2). Coffee by-products have been explored for waste utilization in the industrial sector. For instance, coffee by-products can be mixed with steel-making slag as an organic adsorbent to recover or remove phosphorus [242]. Additionally, they can be used in conjunction with acid mine drainage sludge to remove formaldehyde from the air [243]. Coffee husk, through composting processes, can also serve as a fertilizer [244].

Table 2.
Summary of the main patents developed from different coffee by-products.
Extraction efficacy and selectivity of bioactive compounds from coffee wastes have been the focus of many studies, which heavily rely on the extraction method and conditions employed. Cold extraction methods have been used to produce high-aroma instant coffee powder [245], while lactic fermentation of coffee pulp and skin can yield β-damascenone, a potent fruity floral flavor compound [246]. Freeze concentration, a low-temperature processing technology, has been utilized to obtain an extract with a high coffee fresh fruit fragrance from coffee pulp [247]. Conversely, hot water extraction of coffee residues has been explored as an economical cryoprotectant for lactic acid bacteria due to the presence of chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, and caffeine as active ingredients [248]. Conventional solvent extraction methods involving centrifugation, separation, and distillation steps have also been developed to obtain a phenolic compound-rich powder with beneficial effects [249]. Nowadays, eco-friendly physical methods based on mechanical extraction, filtering, and concentration of fresh pulp under pressure and temperature conditions are used to achieve active extracts from coffee pulp [250].
In the food industry, coffee by-products have found applications in the bakery sector, where enriched dietary fiber products with high antioxidant capacity and rich flavor have been developed. For instance, crisp biscuits have been prepared by mixing coffee pericarp powder (outer skin) with other ingredients, resulting in a product that combines bioactive properties with desirable sensory characteristics [251]. Grinding coffee by-products, mixed with rice husk, have been utilized to create pellets with bioactive properties [252]. Coffee pulp as a pigment powder has been employed in ice cream formulations, conveying health-enhancing properties due to its anthocyanin content [253]. Moreover, coffee by-products have recently gained interest as bioactive ingredients for preventing cancer metastasis or alleviating and treating cancer [259,260].
Another area of interest is the development of new materials with a high degree of biodegradability for packaging purposes. For example, roasted coffee by-products have been used as composite materials for containers or mixed with other agri-food by-products, such as coconut and grains, to enhance packaging and manufacturing processes [254]. Bioplastics incorporating coffee residual products have emerged as an alternative to sustainable packaging solutions [255]. Composite materials comprising components made from coffee silverskin or parchment have been utilized for the production of dispensing capsules [256,257]. Recent innovations include the utilization of coffee beans as solid fuels; however, challenges related to incomplete combustion and the generation of harmful gases, such as carbon monoxide, have been observed. To address this, a patent was developed to produce pellets containing coffee by-products that burn more efficiently and can be smoothly used as a solid fuel [258].
Overall, technological innovation, as demonstrated by patents, is a critical driver for the development and commercialization of functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals derived from coffee by-products. Continued investment in research and development in these areas is essential for companies and researchers to stay competitive and meet the evolving needs and demands of the market.
6. Challenges, Opportunities, and Directions for Research in Coffee By-Products Valorization
The stepwise strategy and biorefinery approach have shown promising results in upcycling coffee by-products into functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals. However, several technical challenges need to be addressed in the production of functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals from coffee by-products. These include optimizing extraction and processing methods, stabilizing bioactive compounds, and obtaining and maintaining safe coffee by-products. The extraction and processing methods used to obtain coffee by-products greatly affect the yield and quality of the final product. Current methods, such as solvent extraction and enzymatic hydrolysis, have limitations in terms of efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness [261]. Novel methods such as microwave-assisted extraction, supercritical fluid extraction, and pulsed electric field extraction show potential for improving the production of bioactive compounds from coffee by-products [262,263,264]. Other potential research areas include the use of enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation to produce novel functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals [265,266]. Optimization of these methods can help maximize the recovery of bioactive compounds such as phenolic compounds and caffeine to allow their use in industry [89]. The stabilization processes of these compounds are crucial for maintaining the functional properties of the final product. Therefore, the development of appropriate methods is necessary to ensure the stability and bioactivity of coffee by-product-derived ingredients and nutraceuticals [36,267]. To further enhance our understanding of coffee by-products and their potential as a source of bioactive compounds, future research should not only investigate innovative extraction and processing techniques but also emphasize the identification and isolation of novel bioactive compounds. Advanced foodomic and multi-omic strategies coupled with big data analysis can be employed to unravel the intricate mechanisms of action underlying the bioactivity of these compounds [165]. While in vitro and in vivo studies have yielded valuable insights into the bioactivity of coffee by-product-derived compounds, expanding our knowledge regarding their safety and toxicity profiles is crucial, especially concerning higher doses or long-term exposure. Further research is warranted to comprehensively assess the potential risks associated with these compounds and ensure their safe utilization.
Additionally, coffee by-product-derived products face several economic challenges that must be addressed to ensure their successful integration into the market. One of the main challenges is the cost-effectiveness of producing and marketing coffee by-product-derived products [268]. The production costs associated with these products’ extraction, processing, and formulation can be high, making them less competitive in the market. The functional food ingredients market can be complex and competitive, requiring effective marketing strategies to ensure successful commercialization. In this regard, regulations related to food additives, dietary supplements, and functional foods are constantly evolving and can be subjected to interpretation by regulatory agencies [269,270]. Another challenge associated with commercializing coffee by-product-derived functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals is compliance with labeling and health claim regulations [271].
On the other hand, coffee production can negatively impact the environment and social welfare, including deforestation, soil degradation, and labor issues. Nevertheless, coffee by-products present opportunities for promoting a circular economy and reducing waste generation [272]. Biorefinery strategies can be implemented to extract valuable components from these by-products and generate new products. The production of functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals from coffee by-products can present an opportunity for a circular economy, offer consumers health benefits, and further contribute to social sustainability [273]. Integrating biorefinery strategies into coffee production can then help mitigate these impacts by reducing waste generation, promoting sustainable agricultural practices, and creating economic opportunities for small-scale farmers [274]. In fact, developing integrated biorefinery systems that use coffee by-products and other agro-industrial residues can maximize the value and impact of these materials, potentially transforming the industry into a more sustainable and circular model [275]. By embracing a holistic approach that considers the entire value chain of coffee production, we can create a more sustainable and resilient coffee industry for the future.
Overall, future research and innovation in coffee by-product valorization should aim to increase the efficiency, sustainability, and diversity of functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals that can be produced. This approach will further reduce food waste, improve public health, and promote sustainable agriculture. Further research and innovation in this field can lead to the development of new products with enhanced bioactivity, safety, and sustainability, ultimately benefiting both consumers and the environment. While the valorization of coffee by-products presents both challenges and opportunities in pursuing sustainable and innovative solutions, there are promising research directions and opportunities for improvement. With continued research, innovation, and collaboration, we can pave the way for a more efficient, sustainable, and resilient coffee industry that delivers health benefits to consumers while protecting the environment. The journey towards maximizing the value of coffee by-products is ongoing, and by building on existing knowledge and exploring new frontiers, we can create a brighter future for coffee by-product valorization.
7. Conclusions
In conclusion, this review underscores the significant potential of coffee by-products as bioactive food ingredients and nutraceuticals. The comprehensive characterization, utilization of a stepwise strategy, and biorefinery approaches have demonstrated their effectiveness in valorizing coffee by-products. The major conclusions of this study are as follows: (i) coffee by-products possess substantial potential as a source of bioactive compounds with diverse health benefits; (ii) the stepwise strategy and biorefinery approach offer efficient and sustainable pathways for transforming coffee by-products into value-added food ingredients and nutraceuticals; (iii) commercialization of coffee by-product-derived products will require overcoming technological and regulatory barriers. However, several gaps and limitations in the current knowledge have been identified to advance our understanding. These include the need for in-depth investigations to elucidate the precise mechanisms of action and identify specific bioactive compounds responsible for the observed effects of coffee by-products. Additionally, comprehensive studies are necessary to evaluate the long-term safety and potential adverse effects of consuming coffee by-product-derived products. Future research directions have been proposed to address these gaps and drive innovation in this field. Conducting comprehensive studies to identify and characterize the bioactive compounds present in coffee by-products and unravel their mechanisms of action will provide valuable insights. Investigating the safety profiles and potential interactions of coffee by-product-derived products for long-term consumption is crucial for ensuring their suitability as functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals. Exploring innovative extraction techniques and biorefinery processes will optimize the production efficiency, yield, and quality of bioactive compounds from coffee by-products. Furthermore, assessing food products’ sensory and functional properties incorporating coffee by-product-derived ingredients will enhance their acceptability, market potential, and consumer satisfaction. Addressing these gaps and pursuing these research directions will foster the development of bioactive, safe, and sustainable new food products. This will benefit consumers by offering functional and nutritious options and contribute to the coffee industry’s environmental and economic sustainability. Overall, this review has provided comprehensive insights into the potential of coffee by-products, identified key research gaps, and outlined future research directions, thus advancing our understanding of their applications in functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.R.-H., Y.A. and M.A.M.-C.; Formal analysis, S.C. and M.R.-H.; Funding acquisition, M.A.M.-C.; Investigation, M.R.-H., Y.A., V.B., A.G.-R., S.C., C.B. and M.A.M.-C.; Project administration, M.A.M.-C.; Resources, M.A.M.-C.; Supervision, M.A.M.-C.; Visualization, Y.A. and M.R.-H.; Writing—original draft, M.R-H, Y.A., V.B., A.G.-R. and M.A.M.-C.; Writing—review and editing, M.R.-H., V.B., A.G.-R., Y.A. and M.A.M.-C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the COCARDIOLAC (RTI 2018-097504-B-I00) and ECOPULP (TED2021-129262A-I00) projects from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation and the Excellence Line for University Teaching Staff within the Multiannual Agreement between the Community of Madrid and the UAM (2019–2023). M. Rebollo-Hernanz received funding from the FPU program of the Ministry of Universities for his predoctoral fellowship (FPU15/04238) and a grant for the requalification of the Spanish university system (CA1/RSUE/2021-00656).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- United Nations. International Coffee Association Development Report; United Nations: New York, NY, USA; Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1–84. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Gil-Ramírez, A.; Martín-Trueba, M.; Benítez, V.; Aguilera, Y.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A. Valorization of coffee pulp as bioactive food ingredient by sustainable extraction methodologies. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigdeloo, M.; Teymourian, T.; Kowsari, E.; Ramakrishna, S.; Ehsani, A. Sustainability and Circular Economy of Food Wastes: Waste Reduction Strategies, Higher Recycling Methods, and Improved Valorization. Mater. Circ. Econ. 2021, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bilali, H.; Callenius, C.; Strassner, C.; Probst, L. Food and nutrition security and sustainability transitions in food systems. Food Energy Secur. 2019, 8, e0015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béné, C.; Oosterveer, P.; Lamotte, L.; Brouwer, I.D.; de Haan, S.; Prager, S.D.; Talsma, E.F.; Khoury, C.K. When food systems meet sustainability—Current narratives and implications for actions. World Dev. 2019, 113, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Aranguren, D.D.; Robledo, S.; Gomez-Restrepo, E.; Valencia, J.W.A.A.; Tarazona, N.A.; Duran-Aranguren, D.D.; Robledo, S.; Gomez-Restrepo, E.; Valencia, J.W.A.A.; Tarazona, N.A. Scientometric overview of coffee by-products and their applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 7605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejna, A. Potential applications of by-products from the coffee industry in polymer technology—Current state and perspectives. Waste Manag. 2021, 121, 296–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.S.; Mello, F.V.C.; Filho, S.T.; Carpes, R.M.; Honório, J.G.; Marques, M.R.C. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety Impacts of discarded co ff ee waste on human and environmental health. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 141, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebreeyessus, G.D. Towards the sustainable and circular bioeconomy: Insights on spent coffee grounds valorization. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stufano, P.; Perrotta, A.; Labarile, R.; Trotta, M. The second life of coffee can be even more energizing: Circularity of materials for bio-based electrochemical energy storage devices. MRS Energy Sustain. 2022, 9, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.G.; Cho, E.J.; Maskey, S.; Nguyen, D.T.; Bae, H.J. Value-Added Products from Coffee Waste: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisti, L.; Celli, A.; Totaro, G.; Cinelli, P.; Signori, F.; Lazzeri, A.; Bikaki, M.; Corvini, P.; Ferri, M.; Tassoni, A.; et al. Monomers, materials and energy from coffee by-products: A review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Castillo, M.D.; Iriondo-DeHond, A.; Martinez-Saez, N.; Fernandez-Gomez, B.; Iriondo-DeHond, M.; Zhou, J.R. Applications of recovered compounds in food products. In Handbook of Coffee Processing By-Products: Sustainable Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 171–194. ISBN 9780128112915. [Google Scholar]
- Iriondo-DeHond, A.; Aparicio García, N.; Fernandez-Gomez, B.; Guisantes-Batan, E.; Velázquez Escobar, F.; Blanch, G.P.; San Andres, M.I.; Sanchez-Fortun, S.; del Castillo, M.D. Validation of coffee by-products as novel food ingredients. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 51, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasballah, K.; Lestari, W.; Listiawan, M.Y.; Sofia, S. Coffee by-products as the source of antioxidants: A systematic review. F1000Research 2022, 11, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Saez, N.; Castillob, M.D. Development of Sustainable Novel Foods and Beverages Based on Coffee By-Products for Chronic Diseases. Encycl. Food Secur. Sustain. 2018, 1, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.C.; Rodrigues, F.; Nunes, M.A.A.; Vinha, A.F.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. State of the art in coffee processing by-products. In Handbook of Coffee Processing By-Products: Sustainable Applications; Galanakis, C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 1–26. ISBN 978-0-12-811290-8. [Google Scholar]
- Esquivel, P.; Jiménez, V.M. Functional properties of coffee and coffee by-products. Food Res. Int. 2012, 46, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Castillo, M.D.; Fernandez-Gomez, B.; Martinez-Saez, N.; Iriondo-DeHond, A.; Mesa, M.D. Coffee By-Products. In Coffee: Production, Quality and Chemistry; Farah, A., Ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Oxfordshire, UK, 2019; ISBN 9781782620044. [Google Scholar]
- Mussatto, S.I.; Machado, E.M.S.; Martins, S.; Teixeira, J.A. Production, Composition, and Application of Coffee and Its Industrial Residues. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2011, 4, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, P.S.; Madhava Naidu, M. Sustainable management of coffee industry by-products and value addition—A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 66, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICO. Total Production by All Exporting Countries 2016; ICO: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Prata, E.R.B.A.; Oliveira, L.S. Fresh coffee husks as potential sources of anthocyanins. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 1555–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekalo, S.A.; Reinhardt, H.W. Fibers of coffee husk and hulls for the production of particleboard. Mater. Struct. 2010, 43, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Sanchez, F.; Lajarim, R.; De, I.; Carvalho, O.; Ribeiro, A.; Martins, C.; Jelley, R.E.; Fedrizzi, B.; Soleo, C. Metabolite characterization of fifteen by-products of the coffee production chain: From farm to factory. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriondo-Dehond, A.; Iriondo-Dehond, M.; Del Castillo, M.D. Applications of compounds from coffee processing by-products. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, M.; Ferreira, H.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Alves, R.C.; Machado, M.; Ferreira, H.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Alves, R.C. Coffee by-products : An underexplored source of prebiotic ingredients. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Coronel, M.A.; Marnet, N.; Kolli, V.S.K.; Roussos, S.; Guyot, S.; Augur, C. Characterization and estimation of proanthocyanidins and other phenolics in coffee pulp (Coffea arabica) by thiolysis-high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 1344–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeger, A.; Kosińska-Cagnazzo, A.; Cantergiani, E.; Andlauer, W. Bioactives of coffee cherry pulp and its utilisation for production of Cascara beverage. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.; Pimpley, V.; Warudkar, K.; Murthy, P.S. Valorisation of Coffee Pulp for Development of Innovative Probiotic Beverage Using Kefir : Physicochemical, Antioxidant, Sensory Analysis and Shelf Life Studies. Waste Biomass Valorization 2022, 13, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhalis, H.; Cox, J.; Zhao, J. Coffee fermentation: Expedition from traditional to controlled process and perspectives for industrialization. Appl. Food Res. 2023, 3, 100253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrego, D.; Zapata-Zapata, A.D.; Kim, D. Optimization and scale-up of coffee mucilage fermentation for ethanol production. Energies 2018, 11, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez, V.; Rebollo-Hernanz, M.; Aguilera, Y.; Bejerano, S.; Cañas, S.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A. Extruded coffee parchment shows enhanced antioxidant, hypoglycaemic, and hypolipidemic properties by releasing phenolic compounds from the fibre matrix. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 1097–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, V.; Rebollo-Hernanz, M.; Hernanz, S.; Chantres, S.; Aguilera, Y.; Martin-Cabrejas, M.A. Coffee parchment as a new dietary fiber ingredient: Functional and physiological characterization. Food Res. Int. 2019, 122, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littardi, P.; Rinaldi, M.; Grimaldi, M.; Cavazza, A.; Chiavaro, E. Effect of Addition of Green Coffee Parchment on Structural, Qualitative and Chemical Properties of Gluten-Free Bread. Foods 2020, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirón-Mérida, V.A.; Yáñez-Fernández, J.; Montañez-Barragán, B.; Barragán Huerta, B.E. Valorization of coffee parchment waste (Coffea arabica) as a source of caffeine and phenolic compounds in antifungal gellan gum films. LWT 2019, 101, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorbeer, L.; Schwarz, S.; Franke, H.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Toxicological Assessment of Roasted Coffee Silver Skin (Testa of Coffea sp.) as Novel Food Ingredient. Molecules 2022, 27, 6839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Zamora, A.; Pastoriza, S.; Rufián-Henares, J.A. Revalorization of coffee by-products. Prebiotic, antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. LWT -Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 61, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, L.F.; Teixeira, J.A.; Mussatto, S.I. Chemical, Functional, and Structural Properties of Spent Coffee Grounds and Coffee Silverskin. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 3493–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresciani, L.; Calani, L.; Bruni, R.; Brighenti, F.; Del Rio, D. Phenolic composition, caffeine content and antioxidant capacity of coffee silverskin. Food Res. Int. 2014, 61, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebollo-Hernanz, M.; Zhang, Q.; Aguilera, Y.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A.; Gonzalez de Mejia, E. Relationship of the phytochemicals from coffee and cocoa by-products with their potential to modulate biomarkers of metabolic syndrome in vitro. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Muñoz, P.; Rebollo-Hernanz, M.; Braojos, C.; Cañas, S.; Gil-Ramirez, A.; Aguilera, Y.; Martin-Cabrejas, M.A.; Benitez, V. Comparative Investigation on Coffee Cascara from Dry and Wet Methods: Chemical and Functional Properties. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2021, 6, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ico, T.; Indicator, C.; Milds, T.C.M.; York, N.; Futures, L.; York, T.N.; Milds, O.; Naturals, B.; Milds, C.; America, S.; et al. Colombian Milds-Other Milds Differential Tightens, I-CIP Averages; International Coffee Organization: London, UK, 2023; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Pandey, A.; Mohan, R.; Soccol, C.R. Use of various coffee industry residues for the cultivation of Pleurotus ostreatus in solid state fermentation. Acta Biotechnol. 2000, 20, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouvea, B.M.; Torres, C.; Franca, A.S.; Oliveira, L.S.; Oliveira, E.S. Feasibility of ethanol production from coffee husks. Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 31, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzafera, P. Degradation of caffeine by microorganisms and potential use of decaffeinated coffee husk and pulp in animal feeding. Sci. Agric. 2002, 59, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cangussu, L.B.; Melo, J.C.; Franca, A.S.; Oliveira, L.S. Chemical Characterization of Coffee Husks, a By-Product of Coffea arabica Production. Foods 2021, 10, 3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, L.R.P.; Biasetto, C.R.; Araujo, A.R.; del Bianchi, V.L. Enhanced extraction of phenolic compounds from coffee industry’s residues through solid state fermentation by Penicillium purpurogenum. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 35, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turck, D.; Bohn, T.; Castenmiller, J.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-ernst, K.I.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; Mcardle, H.J.; Naska, A.; Pelaez, C.; et al. Safety of dried coffee husk (cascara) from Coffea arabica L. as a Novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucheli, P.; Kanchanomai, C.; Meyer, I.; Pittet, A. Development of ochratoxin A during Robusta (Coffea canephora) coffee cherry drying. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrão, J.E.M. Café, A Bebida Negra Dos Sonhos Claros; Chaves Ferreira-Publicações: Lisboa, Portugal, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Haile, M.; Kang, W.H. The Role of Microbes in Coffee Fermentation and Their Impact on Coffee Quality. J. Food Qual. 2019, 2019, 4836709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinícius de Melo Pereira, G.; Soccol, V.T.; Brar, S.K.; Neto, E.; Soccol, C.R. Microbial ecology and starter culture technology in coffee processing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2775–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariyam, S.; Kistanti, A.; Karyadi, J.N.W.; Widiyastuti, R.J. Improving coffee quality through yeast addition in the fermentation process to support sustainable coffee production. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1005, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriondo-Dehond, A.; Rios, M.B.; Herrera, T.; Rodriguez-Bertos, A.; Nuñez, F.; Andres, M.I.S.; Sanchez-Fortun, S.; Del Castillo, M.D. Coffee silverskin extract: Nutritional value, safety and effect on key biological functions. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubero-Castillo, E.; Bonilla-Leiva, A.R.; García-Velasques, E. Coffee Berry Processing By-Product Valorization : Coffee Parchment as a Potential Fiber Source to Enrich Bakery Goods. J. Food Nutr. Popul. Health 2017, 1, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza Martinez, C.L.; Alves Rocha, E.P.; Oliveira Carneiro, A.d.C.; Borges Gomes, F.J.; Ribas Batalha, L.A.; Vakkilainen, E.; Cardoso, M. Characterization of residual biomasses from the coffee production chain and assessment the potential for energy purposes. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 120, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, Y.; Rebollo-Hernanz, M.; Cañas, S.; Taladrid, D.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A. Response surface methodology to optimise the heat-assisted aqueous extraction of phenolic compounds from coffee parchment and their comprehensive analysis. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 4739–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernand, K.; Soulaïmana, A.; Lezin, B.E.; Lazare, N.K.; Yao, A.R.E.; Severin, A. Potential use of Coffee Bean Parchment as Substrate for Soilless Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Cultivation in Gabon. Int. J. Sci. 2019, 8, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa Campos, G.A.; Perez, J.P.H.; Block, I.; Sagu, S.T.; Saravia Celis, P.; Taubert, A.; Rawel, H.M. Preparation of Activated Carbons from Spent Coffee Grounds and Coffee Parchment and Assessment of Their Adsorbent Efficiency. Processes 2021, 9, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phitakwinai, S.; Thepa, S.; Nilnont, W. Thin-layer drying of parchment Arabica coffee by controlling temperature and relative humidity. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2921–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Commission of the European Communities. Commission Regulation (EC) No 123/2005 of 26 January 2005 amending Regulation (EC) No 466/2001 as regards ochratoxin A. Off. J. Eur. Union 2005, 2005, L 25/3–L 25/5. [Google Scholar]
- Klingel, T.; Kremer, J.I.; Gottstein, V.; Rajcic de Rezende, T.; Schwarz, S.; Lachenmeier, D.W. A Review of Coffee By-Products Including Leaf, Flower, Cherry, Husk, Silver Skin, and Spent Grounds as Novel Foods within the European Union. Foods 2020, 9, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, Y.; Inouye, K. Review on utilization and composition of coffee silverskin. Food Res. Int. 2014, 61, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, R.C.; Esposito, F.; Napolitano, A.; Ritieni, A.; Fogliano, V. Characterization of a new potential functional ingredient: Coffee silverskin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 1338–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.S.G.; Alves, R.C.; Vinha, A.F.; Barreira, S.V.P.; Nunes, M.A.; Cunha, L.M.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Optimization of antioxidants extraction from coffee silverskin, a roasting by-product, having in view a sustainable process. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 53, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolino, M.; Barbosa-Pereira, L.; Ghirardello, D.; Botta, C.; Rolle, L.; Guglielmetti, A.; Borotto Dalla Vecchia, S.; Zeppa, G. Coffee silverskin as nutraceutical ingredient in yogurt: Its effect on functional properties and its bioaccessibility. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 4267–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.S.G.; Alves, R.C.; Vinha, A.F.; Costa, E.; Costa, C.S.G.; Nunes, M.A.; Almeida, A.A.; Santos-Silva, A.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Nutritional, chemical and antioxidant/pro-oxidant profiles of silverskin, a coffee roasting by-product. Food Chem. 2018, 267, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejna, A.; Barczewski, M.; Kosmela, P.; Mysiukiewicz, O.; Kuzmin, A. Coffee Silverskin as a Multifunctional Waste Filler for High-Density Polyethylene Green Composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amran, M.A.; Palaniveloo, K.; Fauzi, R.; Satar, N.M.; Mohidin, T.B.; Mohan, G.; Razak, S.A.; Arunasalam, M.; Nagappan, T.; Sathiya Seelan, J.S. Value-Added Metabolites from Agricultural Waste and Application of Green Extraction Techniques. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, J.A.B.; Andrade, N.; Machado, S.; Costa, A.S.G.; Puga, H.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Martel, F.; Alves, R.C. Valorizing Coffee Silverskin Based on Its Phytochemicals and Antidiabetic Potential: From Lab to a Pilot Scale. Foods 2022, 11, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martuscelli, M.; Esposito, L.; Di Mattia, C.D.; Ricci, A.; Mastrocola, D. Characterization of Coffee Silver Skin as Potential Food-Safe Ingredient. Foods 2021, 10, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/2158 of 20 November 2017 establishing mitigation measures and benchmark levels for the reduction of the presence of acrylamide in food. Off. J. Eur. Union 2017, 204, 24–44. [Google Scholar]
- Iriondo-DeHond, A.; Haza, A.I.; Ávalos, A.; del Castillo, M.D.; Morales, P. Validation of coffee silverskin extract as a food ingredient by the analysis of cytotoxicity and genotoxicity. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toschi, T.G.; Cardenia, V.; Bonaga, G.; Mandrioli, M.; Rodriguez-estrada, M.T. Coffee Silverskin : Characterization, Possible Uses, and Safety Aspects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 10836–10844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezińska, R.; Wirkowska-Wojdyła, M.; Piasecka, I.; Górska, A. Application of Response Surface Methodology to Optimize the Extraction Process of Bioactive Compounds Obtained from Coffee Silverskin. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubando, A.T.; Felix, C.B.; Chen, W.H. Biorefineries in circular bioeconomy: A comprehensive review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A. Green chemistry, catalysis and valorization of waste biomass. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2016, 422, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.S.K.; Pfaltzgraff, L.A.; Herrero-Davila, L.; Mubofu, E.B.; Abderrahim, S.; Clark, J.H.; Koutinas, A.A.; Kopsahelis, N.; Stamatelatou, K.; Dickson, F.; et al. Food waste as a valuable resource for the production of chemicals, materials and fuels. Current situation and global perspective. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 426–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizami, A.S.; Rehan, M.; Waqas, M.; Naqvi, M.; Ouda, O.K.M.; Shahzad, K.; Miandad, R.; Khan, M.Z.; Syamsiro, M.; Ismail, I.M.I.; et al. Waste biorefineries: Enabling circular economies in developing countries. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 1101–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amato, D.; Droste, N.; Allen, B.; Kettunen, M.; Lähtinen, K.; Korhonen, J.; Leskinen, P.; Matthies, B.D.; Toppinen, A. Green, circular, bio economy: A comparative analysis of sustainability avenues. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 716–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carus, M.; Dammer, L. The Circular Bioeconomy—Concepts, Opportunities, and Limitations. Ind. Biotechnol. 2018, 14, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, A.S.; Gonçalves, A.; Santos, J.M.R.C.A. Circular bioeconomy strategies: From scientific research to commercially viable products. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, M.S. Natural Antioxidants: Sources, Compounds, Mechanisms of Action, and Potential Applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2011, 10, 221–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiano, A. Recovery of biomolecules from food wastes—A review. Molecules 2014, 19, 14821–14842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perino, S.; Chemat, F. Green process intensification techniques for bio-refinery. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 25, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Abert Vian, M.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Nutrizio, M.; Režek Jambrak, A.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Barba, F.J.; Binello, A.; Cravotto, G. A review of sustainable and intensified techniques for extraction of food and natural products. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 2325–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartonen, K.; Riekkola, M.L. Water as the First Choice Green Solvent. In The Application of Green Solvents in Separation Processes; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 19–55. ISBN 9780128054437. [Google Scholar]
- Bondam, A.F.; Diolinda da Silveira, D.; Pozzada dos Santos, J.; Hoffmann, J.F. Phenolic compounds from coffee by-products: Extraction and application in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 123, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastas, P.; Eghbali, N. Green Chemistry: Principles and Practice. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemat, F.; Vian, M.A.; Cravotto, G. Green extraction of natural products: Concept and principles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 8615–8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shemekite, F.; Gómez-Brandón, M.; Franke-Whittle, I.H.; Praehauser, B.; Insam, H.; Assefa, F. Coffee husk composting: An investigation of the process using molecular and non-molecular tools. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadi, D.; Daba, G.; Beyene, A.; Luis, P.; Van der Bruggen, B. Composting and co-composting of coffee husk and pulp with source-separated municipal solid waste: A breakthrough in valorization of coffee waste. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2019, 8, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, M.C.S.; Naozuka, J.; Da Luz, J.M.R.; De Assunão, L.S.; Oliveira, P.V.; Vanetti, M.C.D.; Bazzolli, D.M.S.; Kasuya, M.C.M. Enrichment of Pleurotus ostreatus mushrooms with selenium in coffee husks. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho Oliveira, F.; Srinivas, K.; Helms, G.L.; Isern, N.G.; Cort, J.R.; Gonçalves, A.R.; Ahring, B.K. Characterization of coffee (Coffea arabica) husk lignin and degradation products obtained after oxygen and alkali addition. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 257, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrouh, B.; de Souza, R.O.A.; da Silva Florindo, R.H.; Lofrano, R.C.Z.; de Oliveira, A.M. Extraction and Identification of Biomolecules from Lignin Alkaline Hydrolysate from Coffee Husk. Waste and Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Martínez, J.L.; Aguilar-Uscanga, M.G.; Bolaños-Reynoso, E.; López-Zamora, L. Optimization of Chemical Pretreatments Using Response Surface Methodology for Second-Generation Ethanol Production from Coffee Husk Waste. Bioenergy Res. 2020, 14, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhogbi, B.G. Potential of coffee husk biomass waste for the adsorption of Pb(II) ion from aqueous solutions. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2017, 6, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, W.E.; Franca, A.S.; Oliveira, L.S.; Rocha, S.D. Untreated coffee husks as biosorbents for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, P.S.; Madhava Naidu, M.; Srinivas, P. Production of α-amylase under solid-state fermentation utilizing coffee waste. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 1246–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, P.S.; Naidu, M.M. Production and Application of Xylanase from Penicillium sp. Utilizing Coffee By-products. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 5, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navya, P.N.; Pushpa, S.M. Production, statistical optimization and application of endoglucanase from Rhizopus stolonifer utilizing coffee husk. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 36, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, S.; Muthusamy, G.; Balakrishnan, S.; Duraisamy, S.; Thangasamy, S.; Seralathan, K.K.; Chinnappan, S. Optimization of protease production from surface-modified coffee pulp waste and corncobs using Bacillus sp. by SSF. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antier, P.; Minjares, A.; Roussos, S.; Viniegragonzález, G. New approach for selecting pectinase producing mutants of Aspergillus niger well adapted to solid state fermentation. Biotechnol. Adv. 1993, 11, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhoite, R.N.; Murthy, P.S. Biodegradation of coffee pulp tannin by Penicillium verrucosum for production of tannase, statistical optimization and its application. Food Bioprod. Process. 2015, 94, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usha Rani, M.; Anu Appaiah, K.A. Gluconacetobacter hansenii UAC09-mediated transformation of polyphenols and pectin of coffee cherry husk extract. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.D.; Melo, M.M.; Coimbra, J.M.; Reis, K.C.d.; Schwan, R.F.; Silva, C.F. Solid coffee waste as alternative to produce carotenoids with antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. Waste Manag. 2018, 82, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhoite, R.N.; Navya, P.N.; Murthy, P.S. Statistical optimization of bioprocess parameters for enhanced gallic acid production from coffee pulp tannins by penicillium verrucosum. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 43, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankaranand, V.S.; Lonsane, B.K. Coffee husk: An inexpensive substrate for production of citric acid by Aspergillus niger in a solid-state fermentation system. World, J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1994, 10, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessie, W.; Zhu, J.; Xin, F.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, M. Bio-succinic acid production from coffee husk treated with thermochemical and fungal hydrolysis. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 41, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleissner, D.; Neu, A.K.; Mehlmann, K.; Schneider, R.; Puerta-Quintero, G.I.; Venus, J. Fermentative lactic acid production from coffee pulp hydrolysate using Bacillus coagulans at laboratory and pilot scales. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, C.M.M.; Oliveira, B.H.; Pandey, A.; Soccol, C.R. Coffee Husk as Substrate for the Production of Gibberellic Acid by Fermentationy. In Coffee Biotechnology and Quality; Sera, T., Soccol, C.R., Pandey, A., Roussos, S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 401–408. ISBN 978-90-481-5565-1. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, M.; Christen, P.; Pandey, A.; Soccol, C.R. Fruity flavour production by Ceratocystis fimbriata grown on coffee husk in solid-state fermentation. Process Biochem. 2000, 35, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmetti, A.; Fernandez-Gomez, B.; Zeppa, G.; Del Castillo, M.D. Nutritional quality, potential health promoting properties and sensory perception of an improved gluten-free bread formulation containing inulin, rice protein and bioactive compounds extracted from coffee byproducts. Polish J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2019, 69, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebollo-Hernanz, M.; Cañas, S.; Taladrid, D.; Benítez, V.; Bartolomé, B.; Aguilera, Y.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A.; Rebollo-Hernanz, M.; Cañas, S.; Taladrid, D.; et al. Revalorization of coffee husk: Modeling and optimizing the green sustainable extraction of phenolic compounds. Foods 2021, 10, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañas, S.; Rebollo-Hernanz, M.; Cano-Muñoz, P.; Aguilera, Y.; Benítez, V.; Braojos, C.; Gila-Díaz, A.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, P.; Cobeta, I.M.; de Pablo, Á.L.L.; et al. Critical Evaluation of Coffee Pulp as an Innovative Antioxidant Dietary Fiber Ingredient: Nutritional Value, Functional Properties, and Acute and Sub-Chronic Toxicity. Proceedings 2021, 70, 65. [Google Scholar]
- Duangjai, A.; Suphrom, N.; Wungrath, J.; Ontawong, A.; Nuengchamnong, N.; Yosboonruang, A. Comparison of antioxidant, antimicrobial activities and chemical profiles of three coffee (Coffea arabica L.) pulp aqueous extracts. Integr. Med. Res. 2016, 5, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoni, C.; Bruni, I.; Guzzetti, L.; Dell’Agli, M.; Sangiovanni, E.; Piazza, S.; Regonesi, M.E.; Maldini, M.; Spezzano, R.; Caruso, D.; et al. Valorizing coffee pulp by-products as anti-inflammatory ingredient of food supplements acting on IL-8 release. Food Res. Int. 2018, 112, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebollo-Hernanz, M.; Zhang, Q.; Aguilera, Y.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A.; Gonzalez de Mejia, E. Phenolic compounds from coffee by-products modulate adipogenesis-related inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and insulin resistance in adipocytes, via insulin/PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 132, 110672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañas, S.; Rebollo-Hernanz, M.; Braojos, C.; Benítez, V.; Ferreras-Charro, R.; Dueñas, M.; Aguilera, Y.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A. Understanding the Gastrointestinal Behavior of the Coffee Pulp Phenolic Compounds under Simulated Conditions. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, S.F.; Silva, J.D.S.E.; Moreli, A.P.; Donzeles, S.M.L.; Ribeiro, M.D.F.; Victor, D.G.; dos Santos, V.S. Nutrient Contents in the Mucilaginal Extract and in the Flour From the Skin of Coffee Fruits. J. Agric. Sci. Res. 2022, 3, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sariñana, B.Y.; Díaz-González, A.; De León-Rodriguez, A.; Saldaña-Trinidad, S.; Pérez-Luna, Y.D.C.; Guerrero-Fajardo, C.A.; Sebastian, P.J. Methane production from coffee crop residues. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 24, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadira, P.-S.B.; Sergio, S.-T.; Fernando, S.; Sebastian, P.; Eapen, D. Bioethanol Production from Coffee Mucilage. Energy Procedia 2014, 57, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirwa, O.; Nyagahungu, I.; Bitwayiki, C. Ethanol prodution from mucilage and pulp of processed coffee. Ukr. Food J. 2016, 5, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuela-Martínez, A.E.; Romero-Tabarez, M.; Zapata-Zapata, A.D. Functional diversity of microbial communities associated with fermentation processes in coffee (Coffea arabica L.). Coffee Sci. 2021, 16, e161825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avallone, S.; Guiraud, J.-P.; Guyot, B.; Olguin, E.; Brillouet, J.-M. Fate of Mucilage Cell Wall Polysaccharides during Coffee Fermentation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 5556–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, G.; Passos, C.P.; Ferreira, P.; Coimbra, M.A.; Gonçalves, I. Coffee by-products and their suitability for developing active food packaging materials. Foods 2021, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avallone, S.; Guiraud, J.-P.J.-P.; Guyot, B.; Olguin, E.; Brillouet, J.-M.J.-M. Polysaccharide Constituents of Coffee-Bean Mucilage. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 1308–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Fernandez, R.; Poerio, T.; Nabarlatz, D.; Giorno, L.; Mazzei, R. Enzymatic hydrolysis of xylan from coffee parchment in membrane bioreactors. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 7346–7354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, M.E.; García-Martin, A.; Comendador Morales, P.; Wojtusik, M.; Santos, V.E.; Kovensky, J.; Ladero, M. Production of Oligosaccharides from Agrofood Wastes. Fermentation 2020, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apuzzo, J. Cellulosic Composition Containing Coffee Parchment Cellulose and Uses Thereof. Patent WO 2018/136763 Al, 3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Ching, Y.; Chuah, C. Applications of Lignocellulosic Fibers and Lignin in Bioplastics: A Review. Polymers 2019, 11, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scatolino, M.V.; Costa, A.D.O.; Júnior, J.B.G.; Protásio, T.D.P.; Mendes, R.F. Eucalyptus wood and coffee parchment for particleboard production: Physical and mechanical properties. Cienc. Agrotecnologia 2017, 41, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, R.S.; Tienne, L.G.; Souza, D.D.H.; Marques, M.D.F.V.; Monteiro, S.N. Characterization of coffee parchment and innovative steam explosion treatment to obtain microfibrillated cellulose as potential composite reinforcement. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 9412–9421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saenger, M.; Hartge, E.U.; Werther, J.; Ogada, T.; Siagi, Z. Combustion of coffee husks. Renew. Energy 2001, 23, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Castillo, M.D.; Ibañez, E.; Amigo-Benavent, M.; Herrero, M.; Plaza del Moral, M.; Ullate, M. Application of Products of Coffee Silverskin in Anti-Ageing Cosmetics and Functional Food. Patent WO2013/004873, 10 January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Saez, N.; Ullate, M.; Martin-Cabrejas, M.A.; Martorell, P.; Genovés, S.; Ramon, D.; Del Castillo, M.D. A novel antioxidant beverage for body weight control based on coffee silverskin. Food Chem. 2014, 150, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Serna, E.; Martinez-Saez, N.; Mesias, M.; Morales, F.J.; Castillo, M.D. Del Use of Coffee Silverskin and Stevia to Improve the Formulation of Biscuits. Polish J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 64, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.; Gaspar, C.; Palmeira-De-Oliveira, A.; Sarmento, B.; Amaral, M.H.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Application of Coffee Silverskin in cosmetic formulations: Physical/antioxidant stability studies and cytotoxicity effects. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessada, S.M.F.; Alves, R.C.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Coffee silverskin: A review on potential cosmetic applications. Cosmetics 2018, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, K.; De Vos, P.; Priebe, M.G. Butyrate and other short-chain fatty acids as modulators of immunity: What relevance for health? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2010, 13, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateş, G.; Elmacı, Y. Physical, chemical and sensory characteristics of fiber-enriched cakes prepared with coffee silverskin as wheat flour substitution. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 13, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateş, G.; Elmacı, Y. Coffee silverskin as fat replacer in cake formulations and its effect on physical, chemical and sensory attributes of cakes. LWT 2018, 90, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, I.S.; Chbib, H.; Mahmoud, H.M. The synthesis, production & economic feasibility of manufacturing PLA from agricultural waste. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2019, 12, 100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghooneh, A.; Mohammad Amini, A.; Behrouzian, F.; Razavi, S.M.A. Characterisation of cellulose from coffee silverskin. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 2830–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, G.; Gonçalves, I.; Barra, A.; Nunes, C.; Ferreira, P.; Coimbra, M.A. Coffee silverskin and starch-rich potato washing slurries as raw materials for elastic, antioxidant, and UV-protective biobased films. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijosa-Valsero, M.; Garita-Cambronero, J.; Paniagua-García, A.I.; Díez-Antolínez, R. Biobutanol production from coffee silverskin. Microb. Cell Fact. 2018, 17, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niglio, S.; Procentese, A.; Russo, M.E.; Sannia, G.; Marzocchella, A. Investigation of Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Coffee Silverskin Aimed at the Production of Butanol and Succinic Acid by Fermentative Processes. Bioenergy Res. 2019, 12, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polidoro, A.D.S.; Scapin, E.; Lazzari, E.; Silva, A.N.; dos Santos, A.L.; Caramão, E.B.; Jacques, R.A. Valorization of coffee silverskin industrial waste by pyrolysis: From optimization of bio-oil production to chemical characterization by GC × GC/qMS. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 129, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Pozo, C.; Rego, F.; Yang, Y.; Puy, N.; Bartrolí, J.; Fàbregas, E.; Bridgwater, A.V. Converting coffee silverskin to value-added products by a slow pyrolysis-based biorefinery process. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 214, 106708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzi, S.; Buratti, C.; Bartocci, P.; Marseglia, G.; Fantozzi, F.; Barbanera, M. A simplified method for kinetic modeling of coffee silver skin pyrolysis by coupling pseudo-components peaks deconvolution analysis and model free-isoconversional methods. Fuel 2020, 278, 118260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Pozo, C.; Bartrolí, J.; Alier, S.; Puy, N.; Fàbregas, E. Production of antioxidants and other value-added compounds from coffee silverskin via pyrolysis under a biorefinery approach. Waste Manag. 2020, 109, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaldo, L.; Narváez, A.; Izzo, L.; Graziani, G.; Ritieni, A. In Vitro Bioaccessibility and Antioxidant Activity of Coffee Silverskin Polyphenolic Extract and Characterization of Bioactive Compounds Using UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS. Molecules 2020, 25, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sut, S.; Baldan, V.; Faggian, M.; Peron, G.; Acqua, S.D. Nutraceuticals, A New Challenge for Medicinal Chemistry. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 3198–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teigiserova, D.A.; Hamelin, L.; Thomsen, M. Towards transparent valorization of food surplus, waste and loss: Clarifying definitions, food waste hierarchy, and role in the circular economy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 136033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alongi, M.; Anese, M. Re-thinking functional food development through a holistic approach. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 81, 104466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Chávez, G.J.; Villa, J.A.; Ayala-Zavala, J.F.; Heredia, J.B.; Sepulveda, D.; Yahia, E.M.; González-Aguilar, G.A.; Joana Gil-Chávez, G.; Villa, J.A.; Fernando Ayala-Zavala, J.; et al. Technologies for Extraction and Production of Bioactive Compounds to be Used as Nutraceuticals and Food Ingredients: An Overview. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2013, 12, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Gómez, V.; González-Barrio, R.; Periago, M.J. Interaction between Dietary Fibre and Bioactive Compounds in Plant By-Products: Impact on Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, C.M. Functionality of food components and emerging technologies. Foods 2021, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandri, M.; Kachrimanidou, V.; Papapostolou, H.; Papadaki, A.; Kopsahelis, N. Sustainable Food Systems: The Case of Functional Compounds towards the Development of Clean Label Food Products. Foods 2022, 11, 2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayle, P.G.; Lin, Y. Market effects of new product introduction: Evidence from the brew-at-home coffee market. J. Econ. Manag. Strateg. 2022, 31, 525–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, P.; Lin, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, H. Recent advances in the application of metabolomics for food safety control and food quality analyses. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 1448–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Saez, N.; García, A.T.; Pérez, I.D.; Rebollo-Hernanz, M.; Mesías, M.; Morales, F.J.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A.; del Castillo, M.D. Use of spent coffee grounds as food ingredient in bakery products. Food Chem. 2017, 216, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, D.; Barba, F.J.; Bursać Kovačević, D.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Cruz, A.G.; Putnik, P. Functional Foods: Product Development, Technological Trends, Efficacy Testing, and Safety. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 11, 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés, A.; Álvarez-Rivera, G.; Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Herrero, M.; Ibáñez, E.; Cifuentes, A. Foodomics: Analytical Opportunities and Challenges. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 366–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzaal, M.; Saeed, F.; Hussain, M.; Shahid, F.; Siddeeg, A.; Al-Farga, A. Proteomics as a promising biomarker in food authentication, quality and safety: A review. Food Sci. Amp. Nutr. 2022, 10, 2333–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkir, P.; Kemahlioglu, K.; Yucel, U. Foodomics: A new approach in food quality and safety. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 108, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira da Silva, B.; Barreira, J.C.M.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Natural phytochemicals and probiotics as bioactive ingredients for functional foods: Extraction, biochemistry and protected-delivery technologies. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasov, A.G.; Zotchev, S.B.; Dirsch, V.M.; Orhan, I.E.; Banach, M.; Rollinger, J.M.; Barreca, D.; Weckwerth, W.; Bauer, R.; Bayer, E.A.; et al. Natural products in drug discovery: Advances and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo Pereira, G.V.G.V.; de Carvalho Neto, D.P.D.P.; Magalhães Júnior, A.I.A.I.; do Prado, F.G.F.G.; Pagnoncelli, M.G.B.M.G.B.; Karp, S.G.S.G.; Soccol, C.R. Chemical Composition and Health Properties of Coffee and Coffee By-Products; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 91, pp. 65–96. [Google Scholar]
- Zengin, G.; Sinan, K.I.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Angeloni, S.; Mustafa, A.M.; Vittori, S.; Maggi, F.; Caprioli, G. Chemical composition, antioxidant and enzyme inhibitory properties of different extracts obtained from spent coffee ground and coffee silverskin. Foods 2020, 9, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebollo-Hernanz, M.; Fernández-Gómez, B.; Herrero, M.; Aguilera, Y.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A.; Uribarri, J.; Del Castillo, M.D. Inhibition of the Maillard reaction by phytochemicals composing an aqueous coffee silverskin extract via a mixed mechanism of action. Foods 2019, 8, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Gomez, B.; Ramos, S.; Goya, L.; Mesa, M.D.; del Castillo, M.D.; Martín, M.Á. Coffee silverskin extract improves glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and protects against streptozotocin-induced damage in pancreatic INS-1E beta cells. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Cruz, S.T.; Iriondo-DeHond, A.; Herrera, T.; Lopez-Tofiño, Y.; Galvez-Robleño, C.; Prodanov, M.; Velazquez-Escobar, F.; Abalo, R.; Del Castillo, M.D. An Assessment of the Bioactivity of Coffee Silverskin Melanoidins. Foods 2019, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.A.P.; Farah, A.; Silva, D.A.M.; Nunan, E.A.; Glória, M.B.A. Antibacterial Activity of Coffee Extracts and Selected Coffee Chemical Compounds against Enterobacteria. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8738–8743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granato, D.; Shahidi, F.; Wrolstad, R.; Kilmartin, P.; Melton, L.D.; Hidalgo, F.J.; Miyashita, K.; van Camp, J.; Alasalvar, C.; Ismail, A.B.; et al. Antioxidant activity, total phenolics and flavonoids contents: Should we ban in vitro screening methods? Food Chem. 2018, 264, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dima, C.; Assadpour, E.; Dima, S.; Jafari, S.M. Bioavailability and bioaccessibility of food bioactive compounds; overview and assessment by in vitro methods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2862–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek, M.; Benaida-Debbache, N.; Garofulić, I.E.; Galić, K.; Avallone, S.; Voilley, A.; Waché, Y. Antioxidants and Bioactive Compounds in Food: Critical Review of Issues and Prospects†. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erskine, E.; Gültekin Subaşl, B.; Vahapoglu, B.; Capanoglu, E. Coffee Phenolics and Their Interaction with Other Food Phenolics: Antagonistic and Synergistic Effects. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 1595–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stromsnes, K.; Lagzdina, R.; Olaso-gonzalez, G.; Gimeno-mallench, L.; Gambini, J. Pharmacological properties of polyphenols: Bioavailability, mechanisms of action and biological effects in in vitro studies, animal models and humans. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benyelles, M.; Merzouk, H.; Merzouk, A.Z.; Imessaoudene, A.; Medjdoub, A.; Mebarki, A. Valorization of Encapsulated Coffee Parchment Extracts as Metabolic Control for High Fructose Diet-Induced Obesity, Using Wistar Rat as Animal Model. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandarkar, N.S.; Mouatt, P.; Majzoub, M.E.; Thomas, T.; Brown, L.; Panchal, S.K. Coffee pulp, a by-product of coffee production, modulates gut microbiota and improves metabolic syndrome in high-carbohydrate, high-fat diet-fed rats. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ochoa, Á.; de la Luz Cádiz-Gurrea, M.; Fernández-Moreno, P.; Rojas-García, A.; Arráez-Román, D.; Segura-Carretero, A. Recent Analytical Approaches for the Study of Bioavailability and Metabolism of Bioactive Phenolic Compounds. Molecules 2022, 27, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Gomez, B.; Lezama, A.; Amigo-Benavent, M.; Ullate, M.; Herrero, M.; Martín, M.Á.; Mesa, M.D.; del Castillo, M.D. Insights on the health benefits of the bioactive compounds of coffee silverskin extract. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 25, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolasco, A.; Squillante, J.; Esposito, F.; Velotto, S.; Romano, R.; Aponte, M.; Giarra, A.; Toscanesi, M.; Montella, E.; Cirillo, T. Coffee Silverskin: Chemical and Biological Risk Assessment and Health Profile for Its Potential Use in Functional Foods. Foods 2022, 11, 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidis, N.; Franke, H.; Schwarz, S.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Risk Assessment of Trigonelline in Coffee and Coffee By-Products. Molecules 2023, 28, 3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taladrid, D.; Rebollo-Hernanz, M.; Martin-Cabrejas, M.A.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V.; Bartolomé, B. Grape Pomace as a Cardiometabolic Health-Promoting Ingredient: Activity in the Intestinal Environment. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunyadi, A. The mechanism(s) of action of antioxidants: From scavenging reactive oxygen/nitrogen species to redox signaling and the generation of bioactive secondary metabolites. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 2505–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, T.; Tan, B.; Yin, Y.; Blachier, F.; Tossou, M.C.B.B.; Rahu, N. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: What Polyphenols Can Do for Us? Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 7432797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurutas, E.B. The importance of antioxidants which play the role in cellular response against oxidative/nitrosative stress: Current state. Nutr. J. 2015, 15, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañas, S.; Rebollo-Hernanz, M.; Martín-Trueba, M.; Braojos, C.; Gil-Ramírez, A.; Benítez, V.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A.; Aguilera, Y. Exploring the potential of phenolic compounds from the coffee pulp in preventing cellular oxidative stress after in vitro digestion. Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebollo-Hernanz, M.; Aguilera, Y.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A.; Gonzalez de Mejia, E. Activating Effects of the Bioactive Compounds From Coffee By-Products on FGF21 Signaling Modulate Hepatic Mitochondrial Bioenergetics and Energy Metabolism in vitro. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 866233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebollo-Hernanz, M.; Kusumah, J.; Bringe, N.A.; Shen, Y.; Gonzalez de Mejia, E. Peptide release, radical scavenging capacity, and antioxidant responses in intestinal cells are determined by soybean variety and gastrointestinal digestion under simulated conditions. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ontawong, A.; Boonphang, O.; Pasachan, T.; Duangjai, A.; Pongchaidecha, A.; Phatsara, M.; Jinakote, M.; Amornlerdpison, D.; Srimaroeng, C. Hepatoprotective effect of coffee pulp aqueous extract combined with simvastatin against hepatic steatosis in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 54, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebollo-Hernanz, M.; Bringe, N.A.; Gonzalez de Mejia, E. Selected Soybean Varieties Regulate Hepatic LDL-Cholesterol Homeostasis Depending on Their Glycinin:β-Conglycinin Ratio. Antioxidants 2022, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norheim, F.; Gjelstad, I.; Hjorth, M.; Vinknes, K.; Langleite, T.; Holen, T.; Jensen, J.; Dalen, K.; Karlsen, A.; Kielland, A.; et al. Molecular Nutrition Research—The Modern Way of Performing Nutritional Science. Nutrients 2012, 4, 1898–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachenmeier, D.W.; Schwarz, S.; Rieke-Zapp, J.; Cantergiani, E.; Rawel, H.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A.; Martuscelli, M.; Gottstein, V.; Angeloni, S. Coffee by-products as sustainable novel foods: Report of the 2nd international electronic conference on foods—“future foods and food technologies for a sustainable world”. Foods 2022, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Xia, C.; Huang, Q. Using in vitro and in vivo models to evaluate the oral bioavailability of nutraceuticals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustin, M.A.; Sanguansri, L. Challenges and Solutions to Incorporation of Nutraceuticals in Foods. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonell-Capella, J.M.; Buniowska, M.; Barba, F.J.; Esteve, M.J.; Frígola, A. Analytical methods for determining bioavailability and bioaccessibility of bioactive compounds from fruits and vegetables: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, M.J.; Renouf, M.; Cruz-Hernandez, C.; Actis-Goretta, L.; Thakkar, S.K.; da Silva Pinto, M. Bioavailability of bioactive food compounds: A challenging journey to bioefficacy. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 588–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Herrero, A.M. Sensory Analysis and Consumer Research in New Product Development. Foods 2021, 10, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ferrero, C.; Sáiz-Abajo, M.J. Characterization and stability studies of bioactive compounds and food matrices as evidence in support of health claims. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 66, S4–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronyk, C.; Mazza, G. Design and scale-up of pressurized fluid extractors for food and bioproducts. J. Food Eng. 2009, 95, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, A.; Ponnuchamy, M.; Kumar, P.S.; Kapoor, A.; Vo, D.V.N.; Prabhakar, S. Techniques and modeling of polyphenol extraction from food: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, K.S.; Sridhar, A.; Vishali, S. Utilization of fruit and vegetable waste to produce value-added products: Conventional utilization and emerging opportunities—A review. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, D.; Nunes, D.S.; Barba, F.J. An integrated strategy between food chemistry, biology, nutrition, pharmacology, and statistics in the development of functional foods: A proposal. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 62, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-López, E.; Pérez-Guerrero, E.E.; Torres-Carrillo, N.M.; López-Quintero, A.; Betancourt-Núñez, A.; Gutiérrez-Hurtado, I.A. Methodological Aspects in Randomized Clinical Trials of Nutritional Interventions. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mena, P.; Tassotti, M.; Rosi, A.; Martini, D.; Righetti, L.; Antonini, M.; Dall’Asta, M.; Bresciani, L.; Fantuzzi, F.; Spigoni, V.; et al. A comprehensive approach to the bioavailability and cardiometabolic effects of the bioactive compounds present in espresso coffee and confectionery-derived coffee. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2020, 79, E123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhiravel, S.; Bekhit, A.E.D.A.; Mendis, E.; Jacobs, J.L.; Dunshea, F.R.; Rajapakse, N.; Ponnampalam, E.N. The Impact of Plant Phytochemicals on the Gut Microbiota of Humans for a Balanced Life. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, G.P.; Collins, F.S. Precision Nutrition—The Answer to “What to Eat to Stay Healthy”. JAMA 2020, 324, 735–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO Report on Functional Foods; Food Quality Standards Service: Rome, Italy, 2007.
- Truong, V.K.; Dupont, M.; Elbourne, A.; Gangadoo, S.; Rajapaksha Pathirannahalage, P.; Cheeseman, S.; Chapman, J.; Cozzolino, D. From Academia to Reality Check: A Theoretical Framework on the Use of Chemometric in Food Sciences. Foods 2019, 8, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco-Ramell, A.; Palau-Rodriguez, M.; Alay, A.; Tulipani, S.; Urpi-Sarda, M.; Sanchez-Pla, A.; Andres-Lacueva, C. Evaluation and comparison of bioinformatic tools for the enrichment analysis of metabolomics data. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, D.; Yang, P.; Feng, H. Utilization of text mining as a big data analysis tool for food science and nutrition. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 875–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Moraes Lopes, M.H.B.; Ferreira, D.D.; Ferreira, A.C.B.H.; da Silva, G.R.; Caetano, A.S.; Braz, V.N. Use of artificial intelligence in precision nutrition and fitness. In Artificial Intelligence in Precision Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 465–496. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.T.; Hsueh, M.C.; Hung, S.P.; Lu, J.M.; Peng, J.H.; Chen, S.F. Prediction of specialty coffee flavors based on near-infrared spectra using machine- and deep-learning methods. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 4705–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, A.; Wall, A.; Khaldi, N.; Kussmann, M. Artificial Intelligence in Functional Food Ingredient Discovery and Characterisation: A Focus on Bioactive Plant and Food Peptides. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 768979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagrasta, F.P.; Pontrandolfo, P.; Scozzi, B. Circular economy business models for the Tanzanian coffee sector: A teaching case study. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho Neto, D.P.D.; Gonot-Schoupinsky, X.P.; Gonot-Schoupinsky, F.N. Coffee as a Naturally Beneficial and Sustainable Ingredient in Personal Care Products: A Systematic Scoping Review of the Evidence. Front. Sustain. 2021, 2, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Sarsaiya, S.; Kumar Awasthi, M.; Singh, R.; Rajput, R.; Mishra, U.C.; Chen, J.; Shi, J. Bioenergy and bio-products from bio-waste and its associated modern circular economy: Current research trends, challenges, and future outlooks. Fuel 2022, 307, 121859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasoki, T.; Nurmalia, A. Analysis Of Robusta Coffee Supply Chain through the Food Supply Chain Network Approach. Agritepa J. Ilmu Dan Teknol. Pertan. 2021, 8, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, H.; Loschelder, D.D.; Lang, D.J.; Wiek, A. Connecting consumers to producers to foster sustainable consumption in international coffee supply—A marketing intervention study. J. Mark. Manag. 2021, 37, 1148–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePaula, J.; Cunha, S.C.; Cruz, A.; Sales, A.L.; Revi, I.; Fernandes, J.; Ferreira, I.M.P.L.V.O.; Miguel, M.A.L.; Farah, A. Volatile Fingerprinting and Sensory Profiles of Coffee Cascara Teas Produced in Latin American Countries. Foods 2022, 11, 3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qishr the Coffee Fruit Tea You Need to Try—Baba Seed Coffee Roasters. Available online: https://babaseedcoffee.com/blogs/blog/qishr-the-coffee-fruit-tea-you-need-to-try (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Cascara | Nescafé Nativ | Nestlé Australia. Available online: https://www.nestle.com.au/en/brands/cascara (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Starbucks Starbucks First New Beverage of 2017, the Cascara Latte|Starbucks Newsroom. Available online: https://news.starbucks.com/news/starbucks-cascara-latte (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Supracafé ¿Conoces la Infusión de Cáscara de Café? Supracafé Maximiza su Sostenibilidad con Tabifruit. Available online: http://www.supracafe.com/press-releases/conoces-la-infusion-de-cascara-de-cafe-supracafe-maximiza-su-sostenibilidad-con-tabifruit/ (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I.; Lordan, R. Functional foods: Growth, evolution, legislation, and future perspectives. In Functional Foods and Their Implications for Health Promotion; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, A.S.; Lordan, R.; Horbańczuk, O.K.; Atanasov, A.G.; Chopra, I.; Horbańczuk, J.O.; Jóźwik, A.; Huang, L.; Pirgozliev, V.; Banach, M.; et al. The current use and evolving landscape of nutraceuticals. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 175, 106001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.N.; Chan, M. An Overview of Functional Food Regulation in North America, European Union, Japan and Australia. In Functional Food Product Development; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 257–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 November 2015 on novel foods, amending Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council and repealing Regulation (EC) No 258/97 etc. Off. J. Eur. Union 2015, 327, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Iwatani, S.; Yamamoto, N. Functional food products in Japan: A review. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C. Historical Change of Raw Materials and Claims of Health Food Regulations in China. In Nutraceutical and Functional Food Regulations in the United States and Around the World, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 363–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, J.P.; Farrell, M.; McMullin, C.; Retik, L.; White, J. Regulation of dietary supplements and functional foods in Canada. In Nutraceutical and Functional Food Regulations in the United States and around the World, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, D. Nutraceutical and Functional Food Regulations in the United States and Around the World; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780128164679. [Google Scholar]
- The European Comission. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2017/2468 of 20 December 2017 laying down administrative and scientific requirements concerning traditional foods from third countries in accordance with Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 of the European Parliament and of the European Parliament and of the Council on novel foods. Off. J. Eur. Union 2017, 351, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- The European Comission. European Union Commission implementing regulation (EU) 2017/2469 of 20 December 2017 laying down administrative and scientific requirements for applications referred to in Article 10 of Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 of the European Parliament. Off. J. Eur. Union 2017, 351, 64–71. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products; Nutrition and Allergies (NDA); Turck, D.; Bresson, J.L.; Burlingame, B.; Dean, T.; Fairweather-Tait, S.; Heinonen, M.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Mangelsdorf, I. Guidance on the preparation and presentation of an application for authorisation of a novel food in the context of Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 2016, 14, 4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Comission. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2022/47 of 13 January 2022 authorising the placing on the market of Coffea arabica L. and/or Coffea canephora Pierre ex A. Froehner dried cherry pulp and its infusion as a traditional food from a third country under. Off. J. Eur. Union 2022, 9, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). Scientific Opinion on acrylamide in food. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chon, K.; Shin, J.; Lee, Y.G.; Kim, S.; Kwak, J.; Son, C. A Method for Preparing Organic Adsorbent Based on Coffee Wastes and Steel Making Slag for Selective Recovery or Removal of Phosphorus a Organic Adsorbent Therefrom and use of the Same. Patent KR20220129225A, 26 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.Y.; Jurng, J.; Ahn, Y.; Lee, M.; Ahmad, W. Formaldehyde Removal Adsorption Comprising Coffee Waste and Acid Mine Drainage Sludge and Method for Manufacturing the Same. Patent KR102348305B1, 4 January 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Luo, Y.; Cui, X.; Zhang, C.; Shan, Z.; Ma, J.; Xie, E.; Zhao, W. Composting Method for Improving Utilization Rate of Coffee Pericarp. Patent CN202111211719.6, 22 February 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, J.; Hayashi, M.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Y.; Sheng, D.; You, H. Method for Producing High-Aroma Instant Coffee Powder from Cold Extraction Coffee Processing Byproducts. Patent CN202210189401.0, 10 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji, S.; Fujiwara, H.; Nakashima, K. Extracted and Fermented Composition of Coffee Cherry Pulp and Skin and Method for Producing Same. Patent CN201980086419.4, 13 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; You, H.; Huang, C.; Jiang, A. Production Method of Coffee Fresh Fruit Extract. Patent CN202210292688.X, 3 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.W.; Choi, I.S.; Kim, H.M.; Jeong, S.G.; Yang, J.E.; Ko, S.H. Method for Microorganism Cryoprotectant using Coffee Residue. Patent KR102364057B1, 14 February 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Appaiah, S. A Method for Extracting Phytochemicals from Coffee Waste. Patent WO2022113120A1, 13 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Taborda Valencia, N.J.; Naranjo, C.M. Coffee Pulp Extract and Production Method. Patent US2022125067A1, 6 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Luo, B.; Cheng, J.; Hu, R.; He, H.; Long, Y.; Huang, J.; Zong, Y.; Fu, X. Coffee Pericarp Superfine Powder Crisp Biscuit and Preparation Method Thereof. Patent CN114651850A, 24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.S. Pellet Manufacturing Method. Patent KR102358649B1, 27 January 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Li, Z.; Fu, X.; Feng, L. Processing Technology for Ice Cream Containing Coffee Pulp Pigment Powder. Patent CN201710992664.4, 12 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nabeiro, R.M.; Figueira, B.D.R.C.; Rodriguez, C. Container made of compo-site material with affinity between substances. Patent CN115379990A, 22 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.D.; Byun, D.W.; Byun, W.S.; Shin, K.S. Bio Plastic Using Coffee Residual Products and Method Making the Same. Patent KR101344471B1, 24 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Von Staden, H. Composite Material Having Components Obtained from the Solver Sheet of Coffee. Patent CN115515866A, 23 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Miozzo, V.; Planchard, H.; Vidal, F.; Roux, M. Beverage Capsule and Method for Sealing Coffee Beverage Capsule. Patent CN115583435A, 10 January 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S. Pellet Using Coffee Waste. Patent KR20220062702A, 17 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Son, C.G.; Lee, S.B. Composition Comprising Coffee, Coffee Extract, and Byproduct as Active Ingredient for Prevention of Cancer Metastasis or for Alleviation or Treatment of Cancer. Patent WO2022158885A1, 28 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Son, C.G.; Lee, S.B. Composition for Preventing Improving or Treating Metastasis of Cancer Comprising Coffee Coffee Extract and Byproduct as Effective Components. Patent KR20220108263A, 3 August 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Cao, X.; Wang, J. Preparation and modification of high dietary fiber flour: A review. Food Res. Int. 2018, 113, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandeponseele, A.; Draye, M.; Piot, C.; Chatel, G. Subcritical water and supercritical carbon dioxide: Efficient and selective eco-compatible solvents for coffee and coffee by-products valorization. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 8544–8571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Senthamaraikannan, R.; Padamati, R.B.; Sun, D.W.; Tiwari, B.K. Green extraction of soluble dietary fibre from coffee silverskin: Impact of ultrasound/microwave-assisted extraction. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 2242–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías-Garbett, R.; Sosa-Hernández, J.E.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Contreras-Esquivel, J.C.; Chen, W.N.; Melchor-Martínez, E.M.; Parra-Saldívar, R. Combined Pulsed Electric Field and Microwave-Assisted Extraction as a Green Method for the Recovery of Antioxidant Compounds with Electroactive Potential from Coffee Agro-Waste. Plants 2022, 11, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favaro, C.P.; Baraldi, I.J.; Casciatori, F.P.; Farinas, C.S. β-Mannanase Production Using Coffee Industry Waste for Application in Soluble Coffee Processing. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugebo, B. A review on enhanced biofuel production from coffee by-products using different enhancement techniques. Mater. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2022, 11, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, I.; Riemma, S.; Iannone, R. Life cycle assessment of supercritical CO2 extraction of caffeine from coffee beans. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 133, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varangis, P.; Siegel, P.; Giovannucci, D.; Lewin, B. Dealing with the Coffee Crisis in Central America: Impacts and Strategies; World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espro, C.; Paone, E.; Mauriello, F.; Gotti, R.; Uliassi, E.; Bolognesi, M.L.; Rodríguez-Padrón, D.; Luque, R. Sustainable production of pharmaceutical, nutraceutical and bioactive compounds from biomass and waste. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 11191–11207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capanoglu, E.; Nemli, E.; Tomas-Barberan, F. Novel Approaches in the Valorization of Agricultural Wastes and Their Applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 6787–6804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez Díaz, L.; Fernández-Ruiz, V.; Cámara, M. An international regulatory review of food health-related claims in functional food products labeling. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 68, 103896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayson, S.; Williams, I.D. Resources, Conservation & Recycling Applying a circular economy approach to valorize spent coffee grounds. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 172, 105659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, L.C.; Barbosa, J.R.; da Costa, A.L.C.; Bezerra, F.W.F.; Pinto, R.H.H.; Carvalho Junior, R.N. de From waste to sustainable industry: How can agro-industrial wastes help in the development of new products? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 169, 105466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristizábal-Marulanda, V.; Chacón-Perez, Y.; Cardona Alzate, C.A. The biorefinery concept for the industrial valorization of coffee processing by-products. In Handbook of Coffee Processing By-Products: Sustainable Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 9780128112915. [Google Scholar]
- Serna-Jiménez, J.A.; Siles, J.A.; de los Ángeles Martín, M.; Chica, A.F. A Review on the Applications of Coffee Waste Derived from Primary Processing: Strategies for Revalorization. Processes 2022, 10, 2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).