Multi-Indicator Weighted Robustness Analysis of Planktonic Community Systems under Different Destructive Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methodology
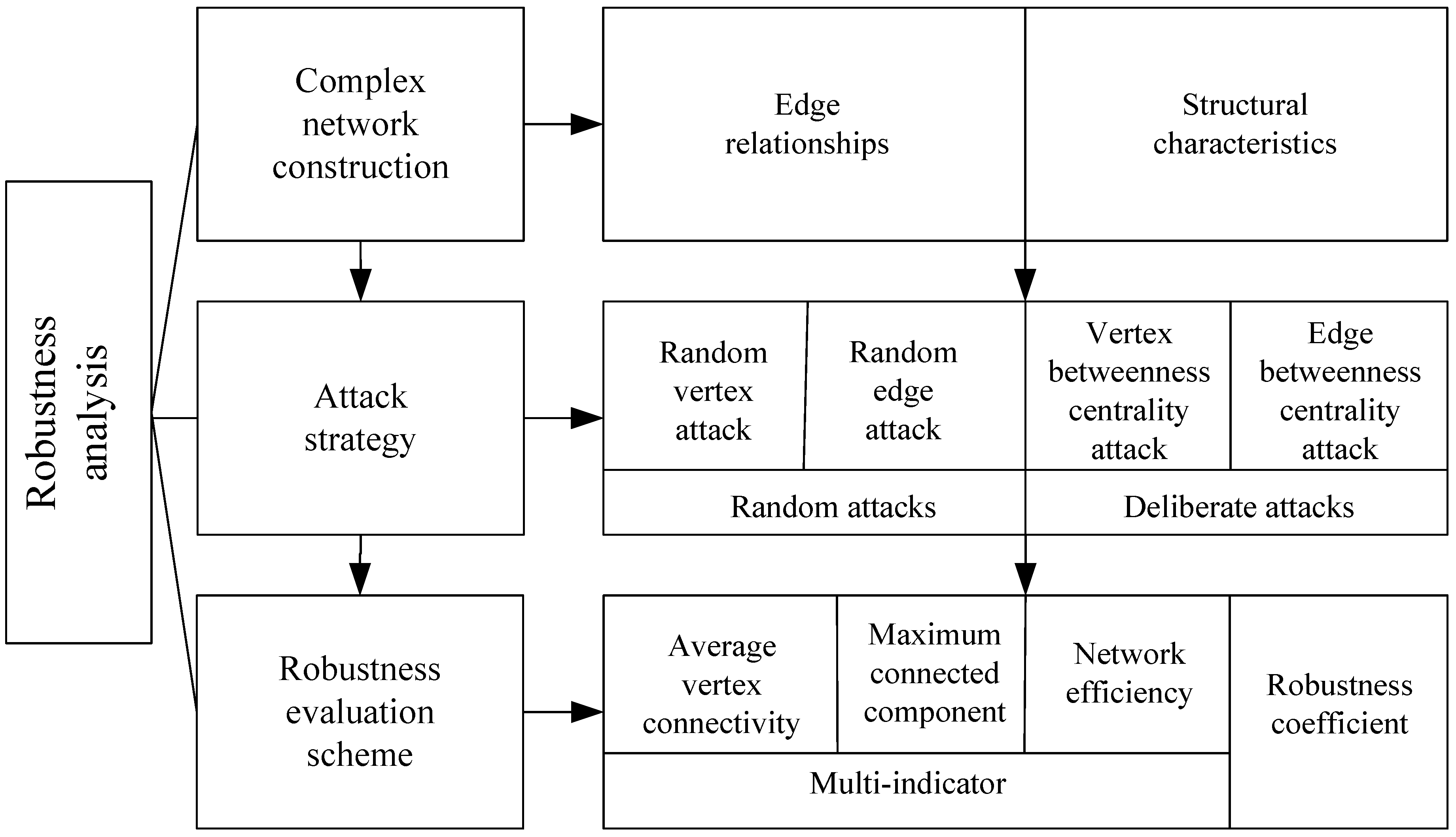
2.2.1. Complex Network Construction
2.2.2. Attack Strategies
2.2.3. Robustness Evaluation Scheme
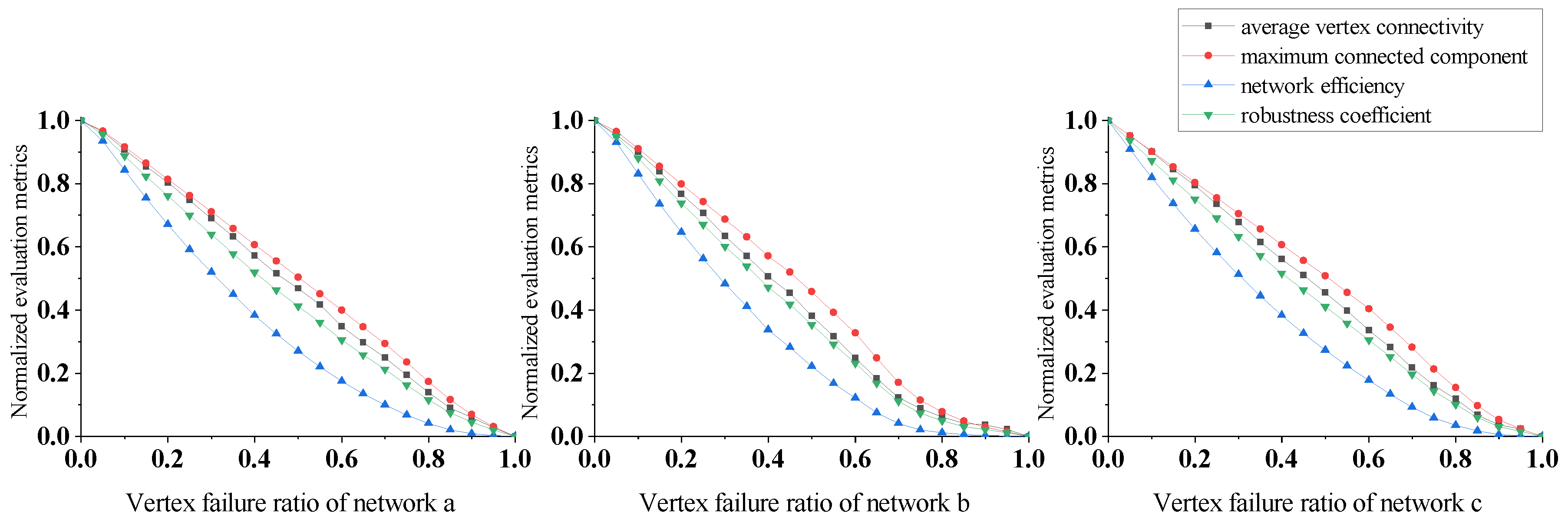
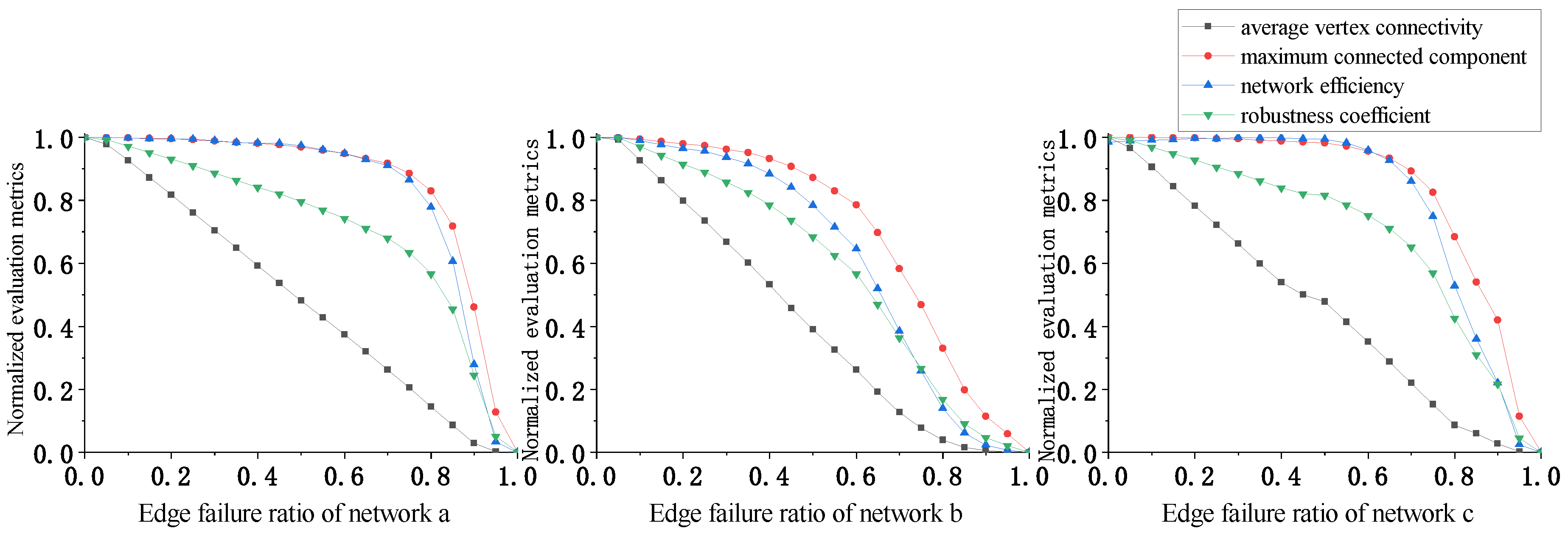
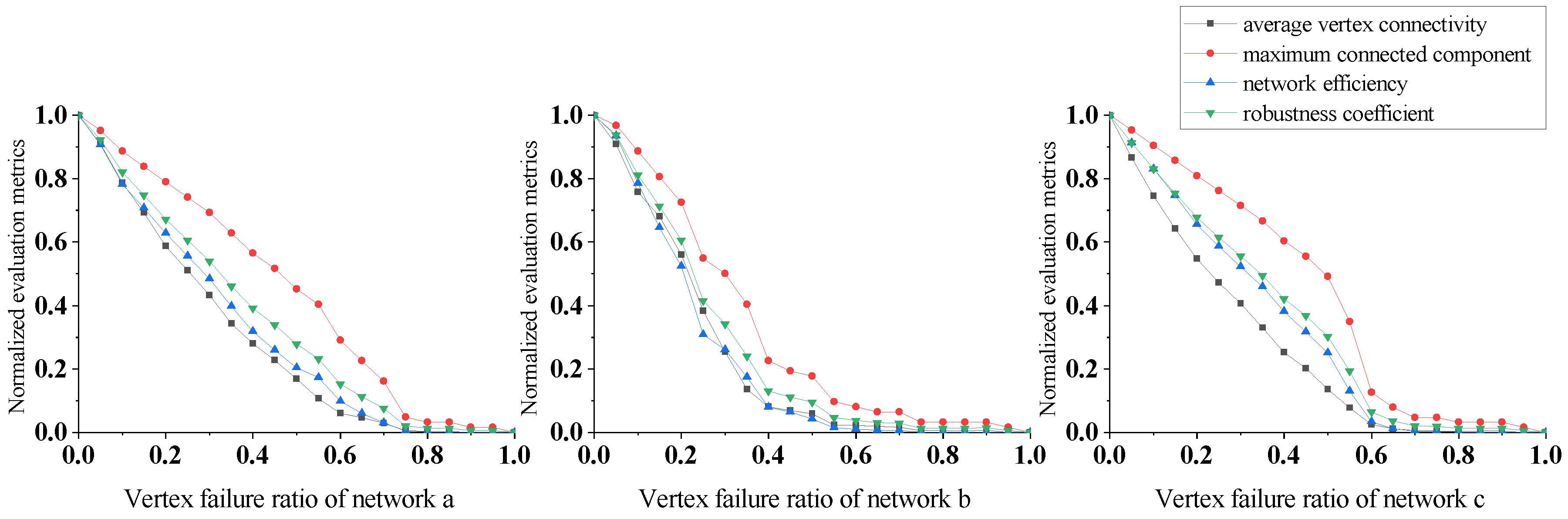
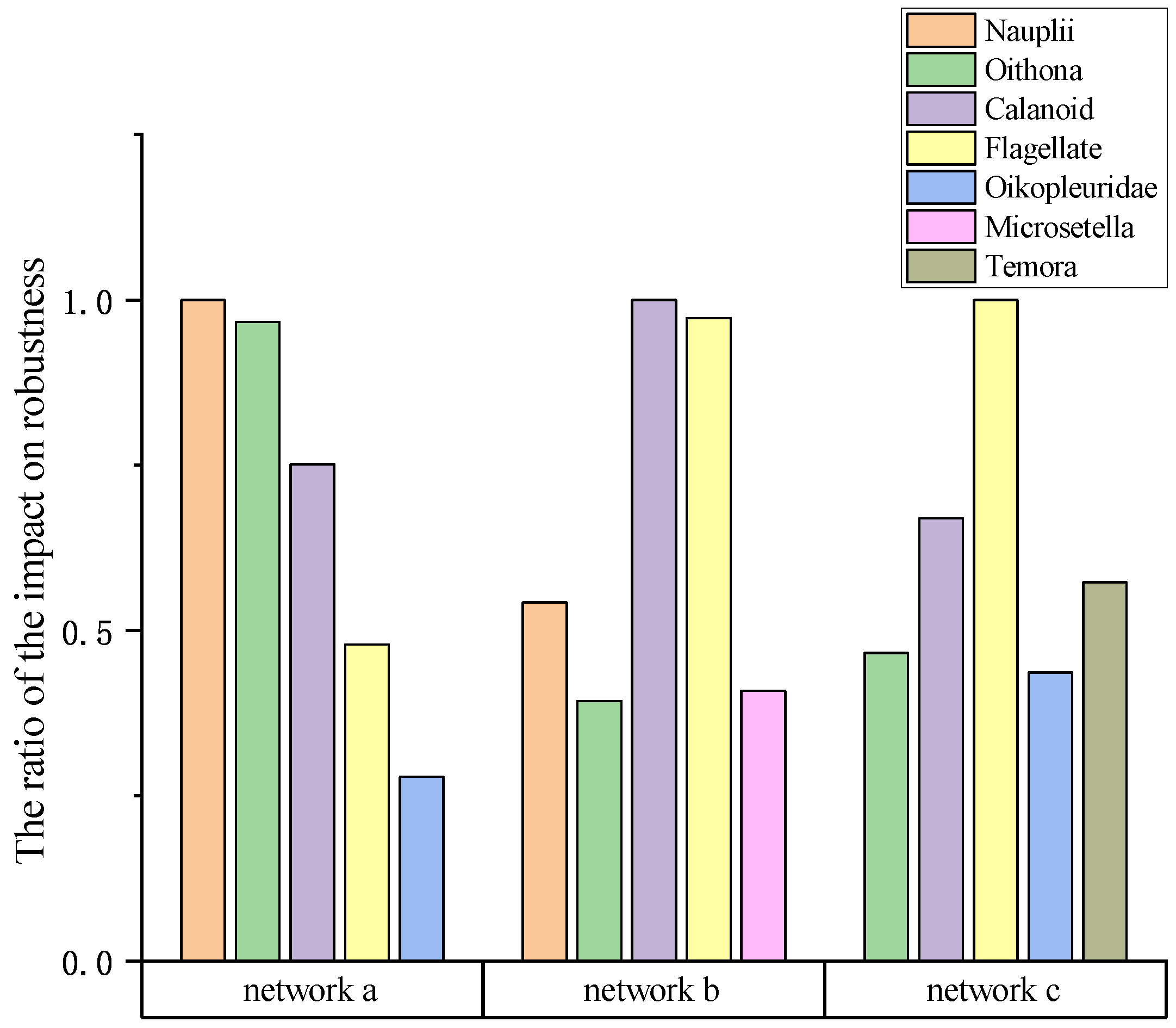
3. Results
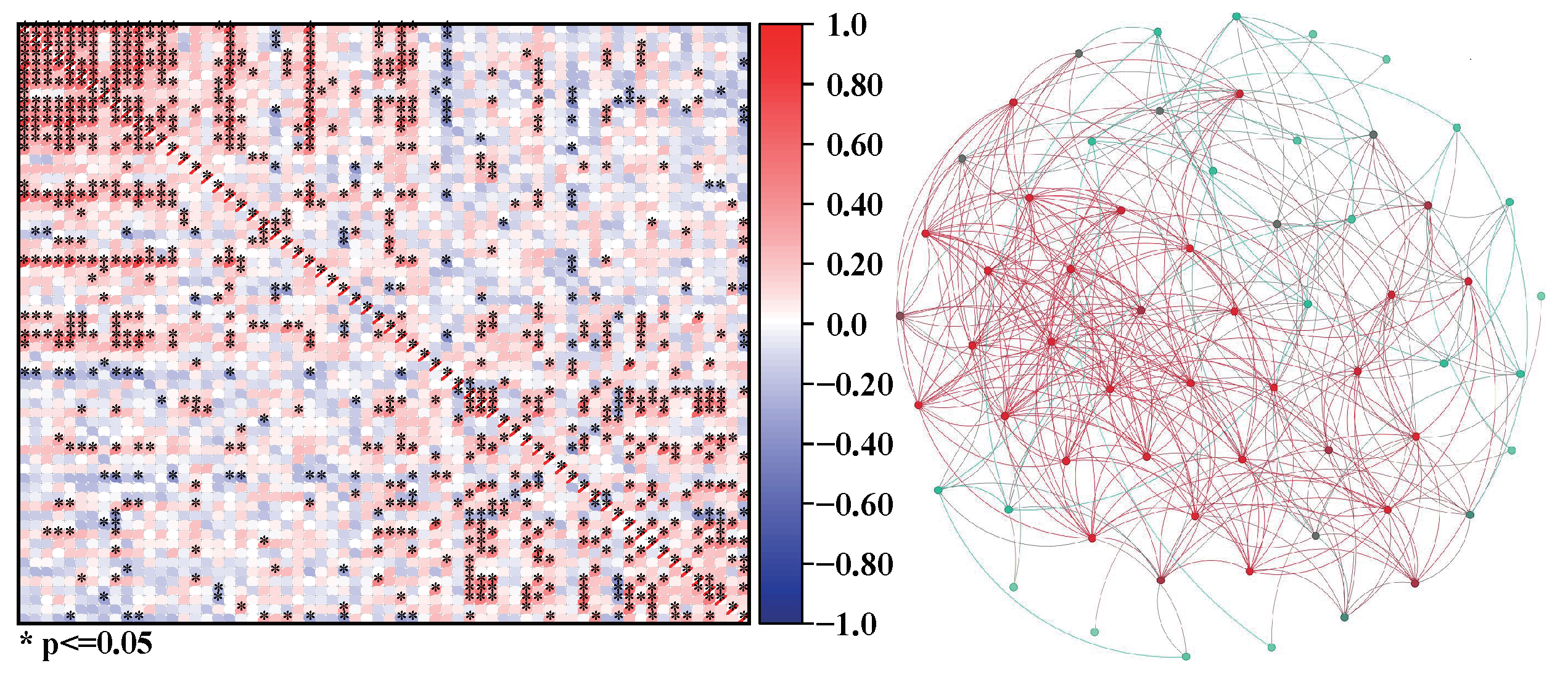
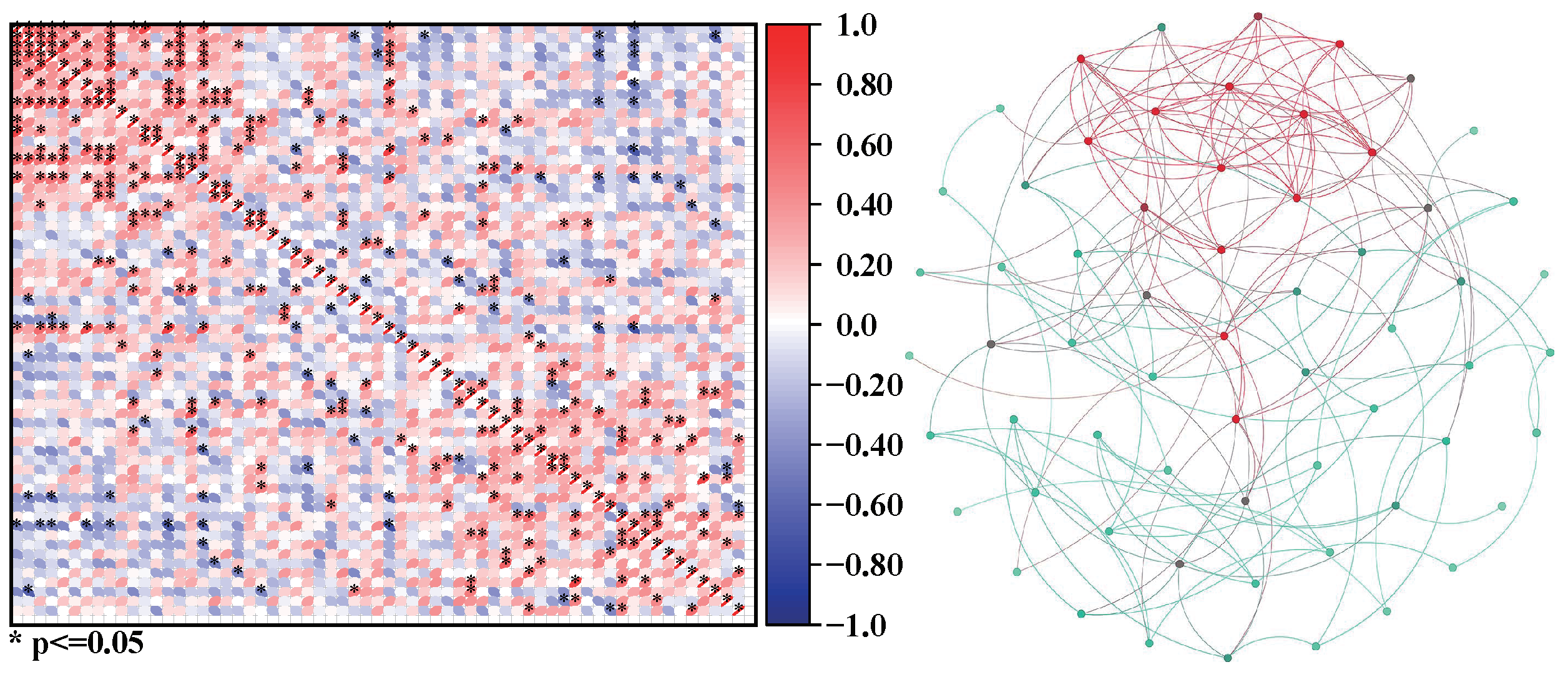
3.1. Network Construction
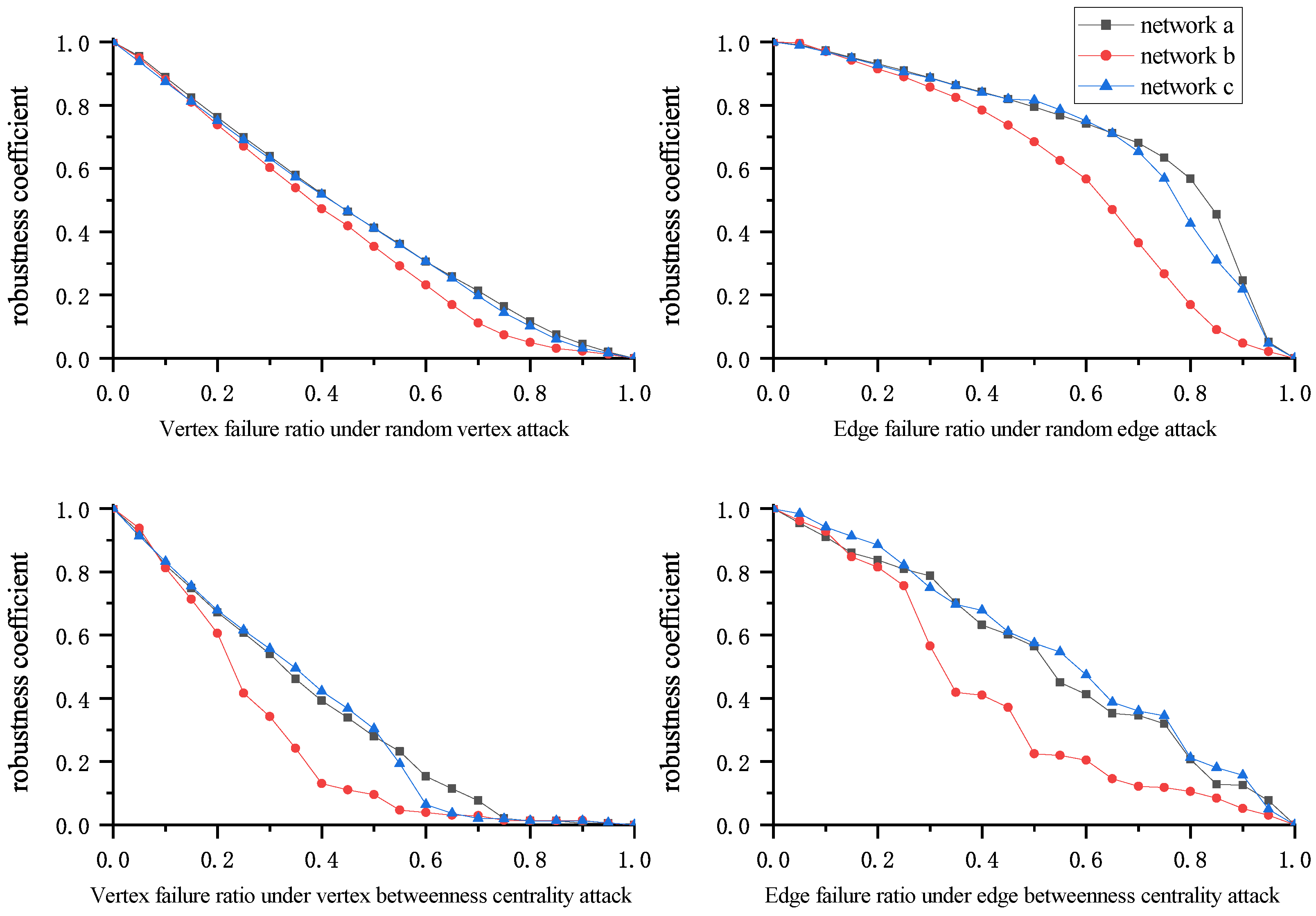
3.2. Network Robustness Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Ecological Significance of the Results
4.2. Methodological Advantages
- -
- It captures the intricate relationships between plankton types, rather than treating genera in isolation, helping to assess robustness at the ecosystem scale;
- -
- It can simulate community dynamics during response to perturbations through different attack strategies;
- -
- Its computational efficiency allows rapid investigation of multiple scenarios;
- -
- The proposed multi-metric evaluation enables more nuanced measurement of robustness;
- -
- Visual network representations provide intuitive understanding of topological vulnerabilities.
4.3. Limitations
4.4. Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paerl, H.W. Marine Plankton; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 127–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, A.S. Plankton. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R478–R483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, G.S.; Pacheco, D.; Cotas, J.; da Silva, J.W.A.; Saboya, J.; Moreira, R.T.; Pereira, L. Plankton: Environmental and Economic Importance for a Sustainable Future; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Falkowski, P. Ocean Science: The power of plankton. Nature 2012, 483, S17–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierella Karlusich, J.J.; Ibarbalz, F.M.; Bowler, C. Phytoplankton in the Tara Ocean. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2020, 12, 233–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gökçe, A.; Yazar, S.; Sekerci, Y. Stability of spatial patterns in a diffusive oxygen–plankton model with time lag effect. Math. Comput. Simul. 2022, 194, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallina, S.M.; Cermeno, P.; Dutkiewicz, S.; Loreau, M.; Montoya, J.M. Phytoplankton functional diversity increases ecosystem productivity and stability. Ecol. Model. 2017, 361, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.K.; Ojha, A.; Tiwari, P.K.; Upadhyay, R.K. An investigation of delay induced stability transition in nutrient-plankton systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 142, 110474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, A.; Arashkevich, E.; Nikishina, A.; Solovyev, K. Nutrient-rich plankton communities stabilized via predator—Prey interactions: Revisiting the role of vertical heterogeneity. Math. Med. Biol. 2011, 28, 185–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, R.; Barabási, A.L. Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, R.; Jeong, H.; Barabási, A.L. Error and attack tolerance of complex networks. Nature 2000, 406, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellens, W.; Kooij, R.E. Graph measures and network robustness. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1311.5064. [Google Scholar]
- Bascompte, J. Disentangling the web of life. Science 2009, 325, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, J.; Williams, R.; Martinez, N. Network structure and biodiversity loss in food webs: Robustness increases with connectance. Ecol. Lett. 2002, 5, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, K.; Raes, J. Microbial interactions: From networks to models. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tylianakis, J.; Laliberte, E.; Nielsen, A.; Bascompte, J. Conservation of species interaction networks. Biol. Conserv. 2010, 143, 2270–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitacre, J.M. Biological robustness: Paradigms, mechanisms, and systems principles. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, H. Biological robustness. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrend, P.; Collet, P. A Review on Complex System Engineering. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 2020, 33, 1755–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huang, J.; Xu, X.; Xiao, Y. Damage attack on complex networks. Phys. A 2014, 408, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y. Subgraph robustness of complex networks under attacks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. Syst. 2017, 49, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, J. A memetic algorithm for enhancing the robustness of scale-free networks against malicious attacks. Phys. A 2014, 410, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béthoux, J.P.; Morin, P.; Ruiz-Pino, D.P. Temporal trends in nutrient ratios: Chemical evidence of Mediterranean ecosystem changes driven by human activity. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2002, 49, 2007–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Xu, X.; Liao, Y.; Shou, L.; Liu, J.; Chen, Q.; Zeng, J. Advance in the toxic effects of petroleum water accommodated fraction on marine plankton. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crucitti, P.; Latora, V.; Marchiori, M.; Rapisarda, A. Error and attack tolerance of evolving networks with local preferential attachment. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2004, 340, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgatti, S.P. Centrality and network flow. Soc. Netw. 2005, 27, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.M.; Lenz, P.H. Predator-prey interactions in the plankton: Larval fish feeding on evasive copepods. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, T.B.; Wolkovich, E.M.; Scheuerell, M.D.; Katz, S.L.; Holmes, E.E.; Hampton, S.E. Shifting regimes and changing interactions in the Lake Washington, USA, plankton community from 1962–1994. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.; Bala, S. Plankton predation rates in turbulence: A study of the limitations imposed on a predator with a non-spherical field of sensory perception. J. Theor. Biol. 2006, 242, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, H.; Frisch, I. Analysis and design of survivable networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. Technol. 1970, 18, 501–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesch, F.; Frisch, I. On the Smallest Disconnecting Set in a Graph. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 1968, 15, 286–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazit, H. An optimal randomized parallel algorithm for finding connected components in a graph. SIAM J. Comput. 1991, 20, 1046–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.l.; Fu, Y.j.; Cheng, L.; Yang, Y.y. Identifying multiple influential spreaders based on maximum connected component decomposition method. Phys. A 2021, 571, 125791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latora, V.; Marchiori, M. Efficient behavior of small-world networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 198701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, V.H.; Cheong, S.A.; Bui, N.D. Complex Network Analysis of the Robustness of the Hanoi, Vietnam Bus Network. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 2019, 32, 1251–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cropp, R.; Norbury, J. Parameterizing plankton functional type models: Insights from a dynamical systems perspective. J. Plankton Res. 2009, 31, 939–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Plankton Community ID | Number of the Genus | Average Biomass (mg/m3) |
|---|---|---|
| a | 62 | 29,872.03 |
| b | 62 | 12,055.91 |
| c | 63 | 76,150.55 |
| Network ID | Number of Vertices | Number of Edges | Average Path Length | Average Degree | Network Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 62 | 388 | 12.52 | 2.05 | 4 |
| b | 62 | 172 | 5.55 | 2.93 | 5 |
| c | 63 | 333 | 10.57 | 2.15 | 4 |
| Name | Average Vertex Connectivity | Maximum Connected Component | Network Efficiency | Robustness Coefficient (Ours) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random vertex attack | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| Random edge attack | 0.34 | 0.30 | 0.35 | 0.32 |
| Vertex betweenness centrality attack | 0.33 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.33 |
| Edge betweenness centrality attack | 0.34 | 0.31 | 0.35 | 0.32 |
| Mean standard deviation | 0.335 | 0.325 | 0.343 | 0.325 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, D.; Zhang, T.; Chen, T.; He, Q.; Huang, D. Multi-Indicator Weighted Robustness Analysis of Planktonic Community Systems under Different Destructive Factors. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8742. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13158742
Zhao D, Zhang T, Chen T, He Q, Huang D. Multi-Indicator Weighted Robustness Analysis of Planktonic Community Systems under Different Destructive Factors. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(15):8742. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13158742
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Danfeng, Tao Zhang, Tianwen Chen, Qi He, and Dongmei Huang. 2023. "Multi-Indicator Weighted Robustness Analysis of Planktonic Community Systems under Different Destructive Factors" Applied Sciences 13, no. 15: 8742. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13158742
APA StyleZhao, D., Zhang, T., Chen, T., He, Q., & Huang, D. (2023). Multi-Indicator Weighted Robustness Analysis of Planktonic Community Systems under Different Destructive Factors. Applied Sciences, 13(15), 8742. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13158742









