Heterogeneous Fenton Oxidation with Natural Clay for Textile Levafix Dark Blue Dye Removal from Aqueous Effluent
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wastewater
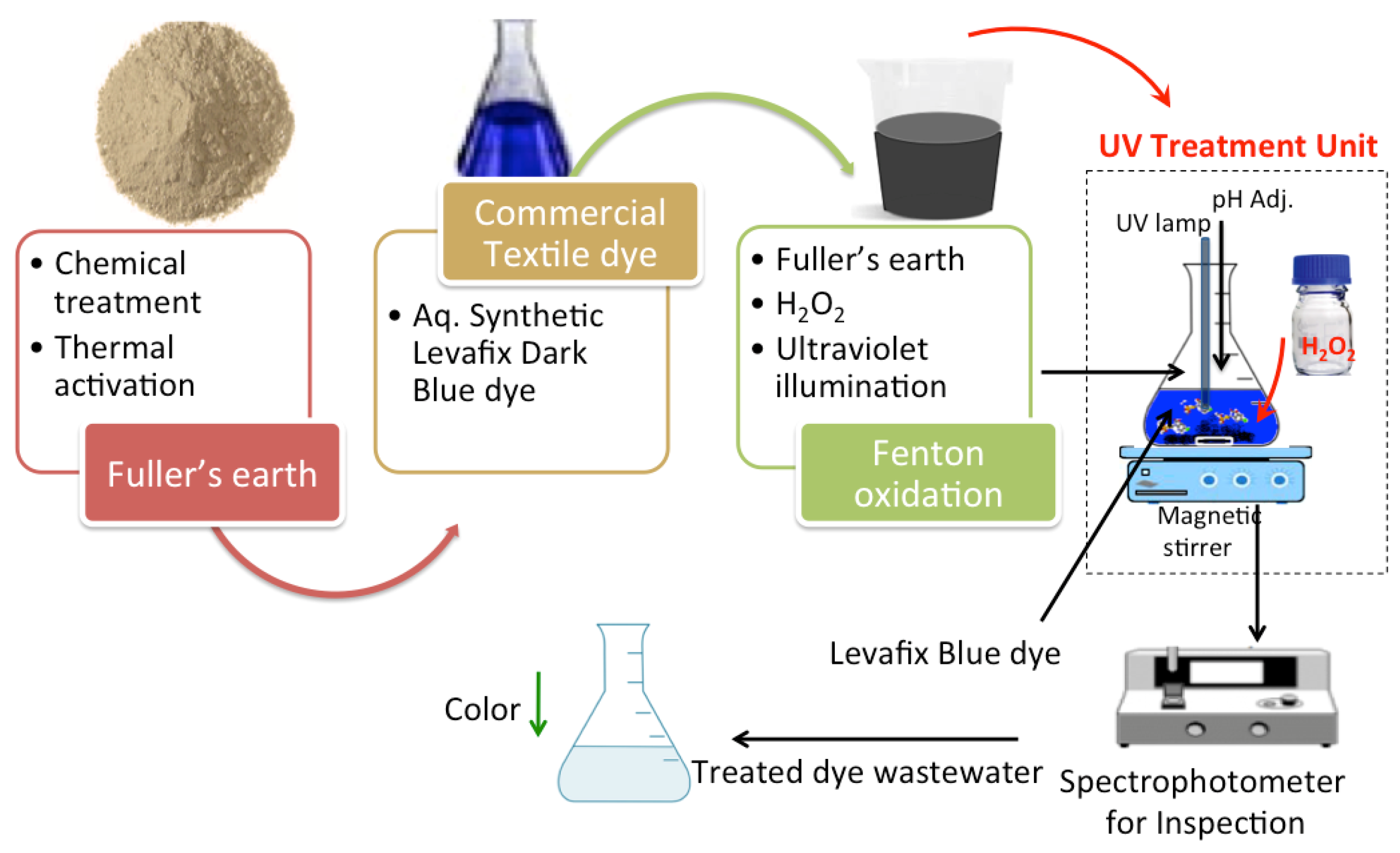
2.2. Preparation of Fuller’s Earth-Based Fenton Catalyst
2.3. Photocatalytic Test
2.4. Characterization Study
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
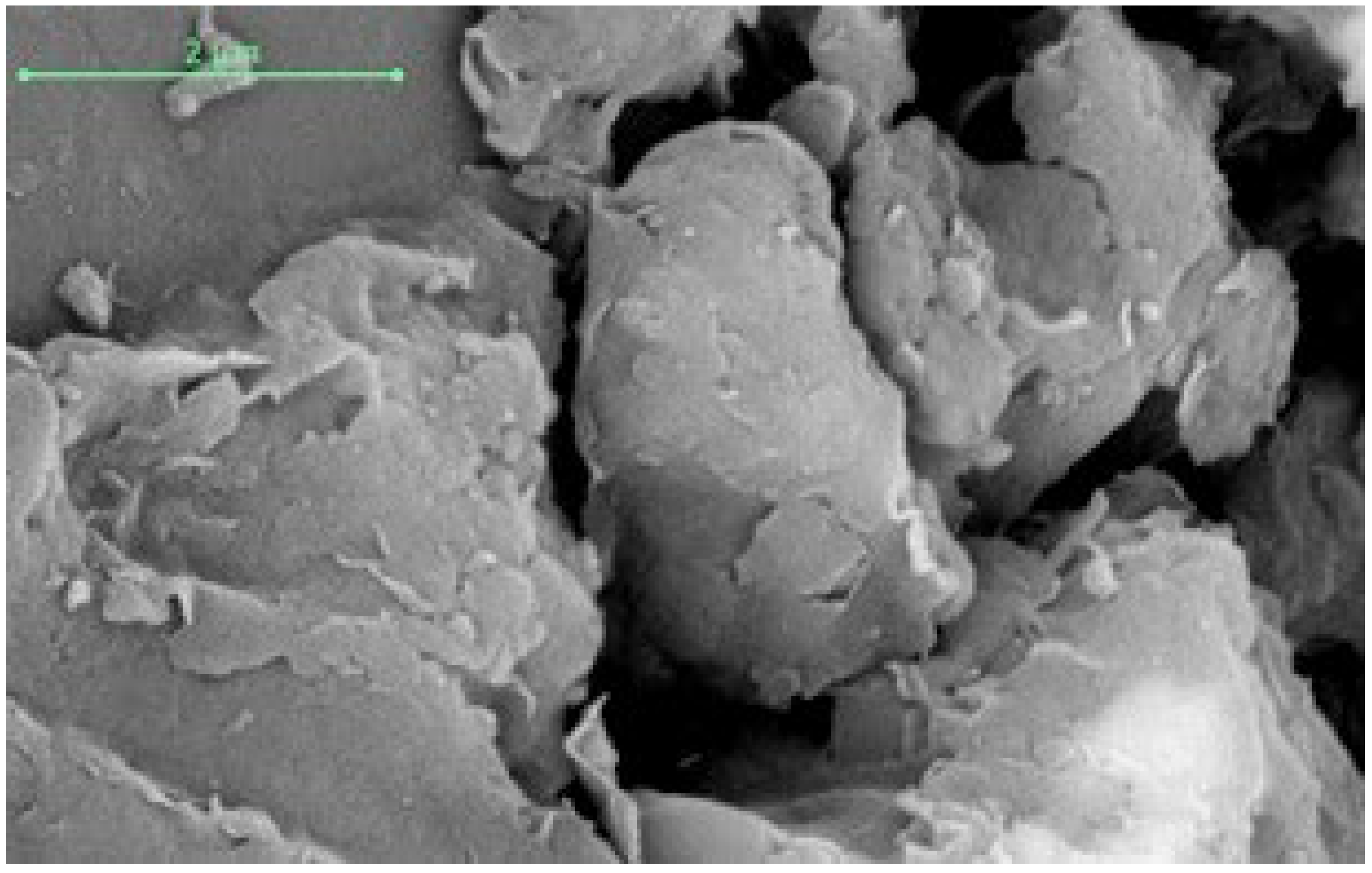
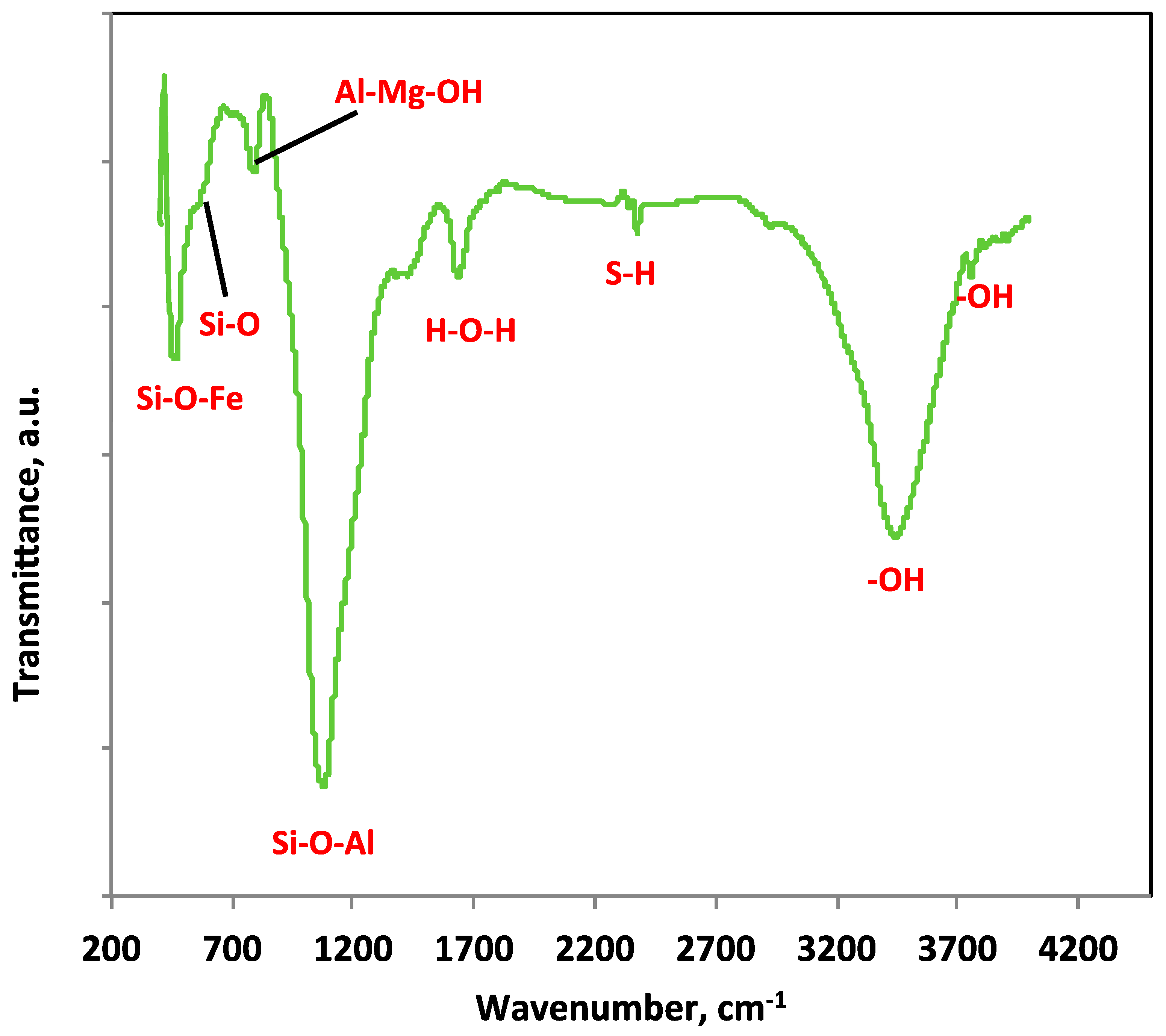
3.1. Characterization of the Prepared Fuller’s Earth Material
3.2. Reactive Azo Dye Oxidation
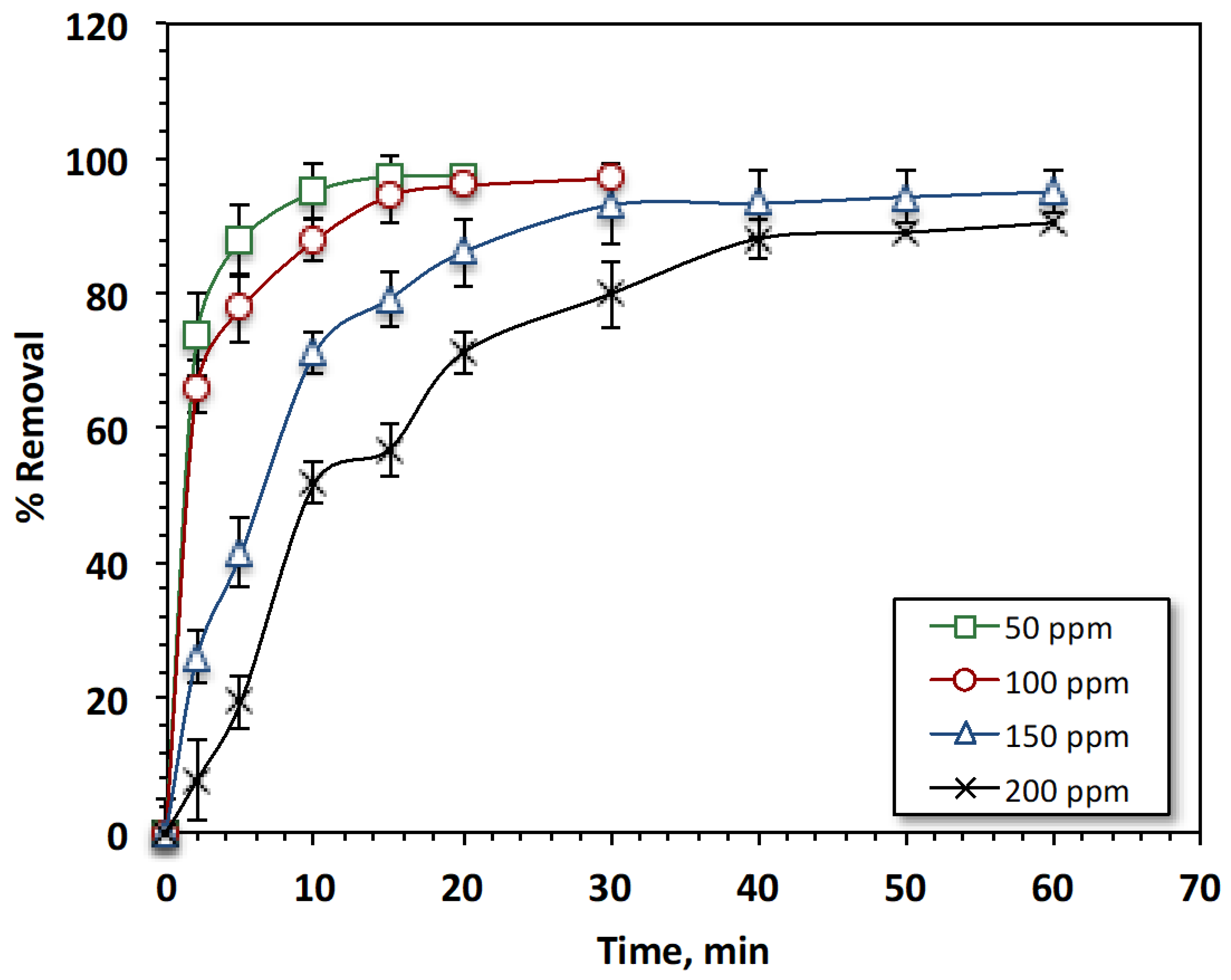
3.2.1. Effects of Reaction Time and Reactive Azo Dye Loading
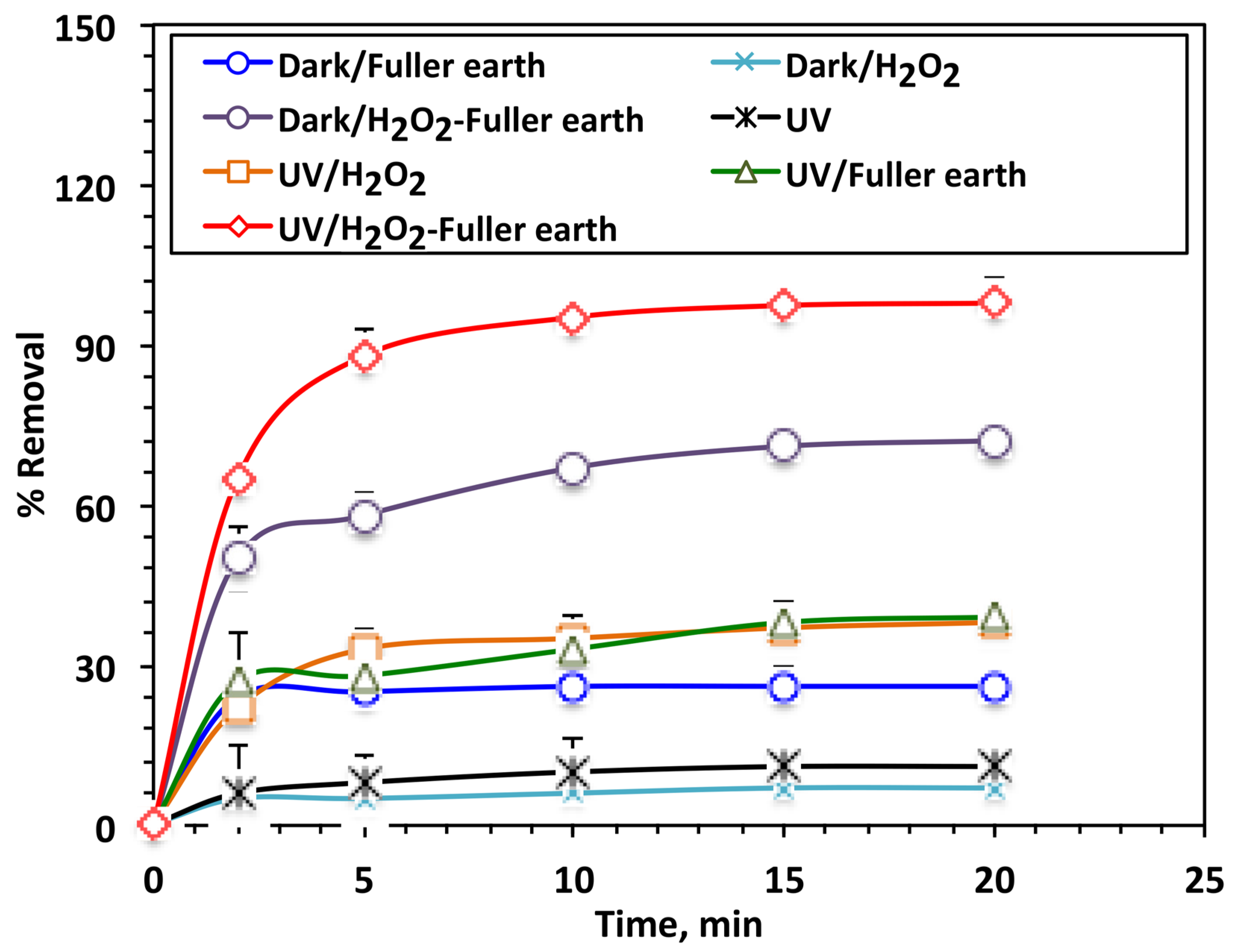
3.2.2. Effects of Various Treatment Systems
3.2.3. Effects of Photo-Fenton Parameters
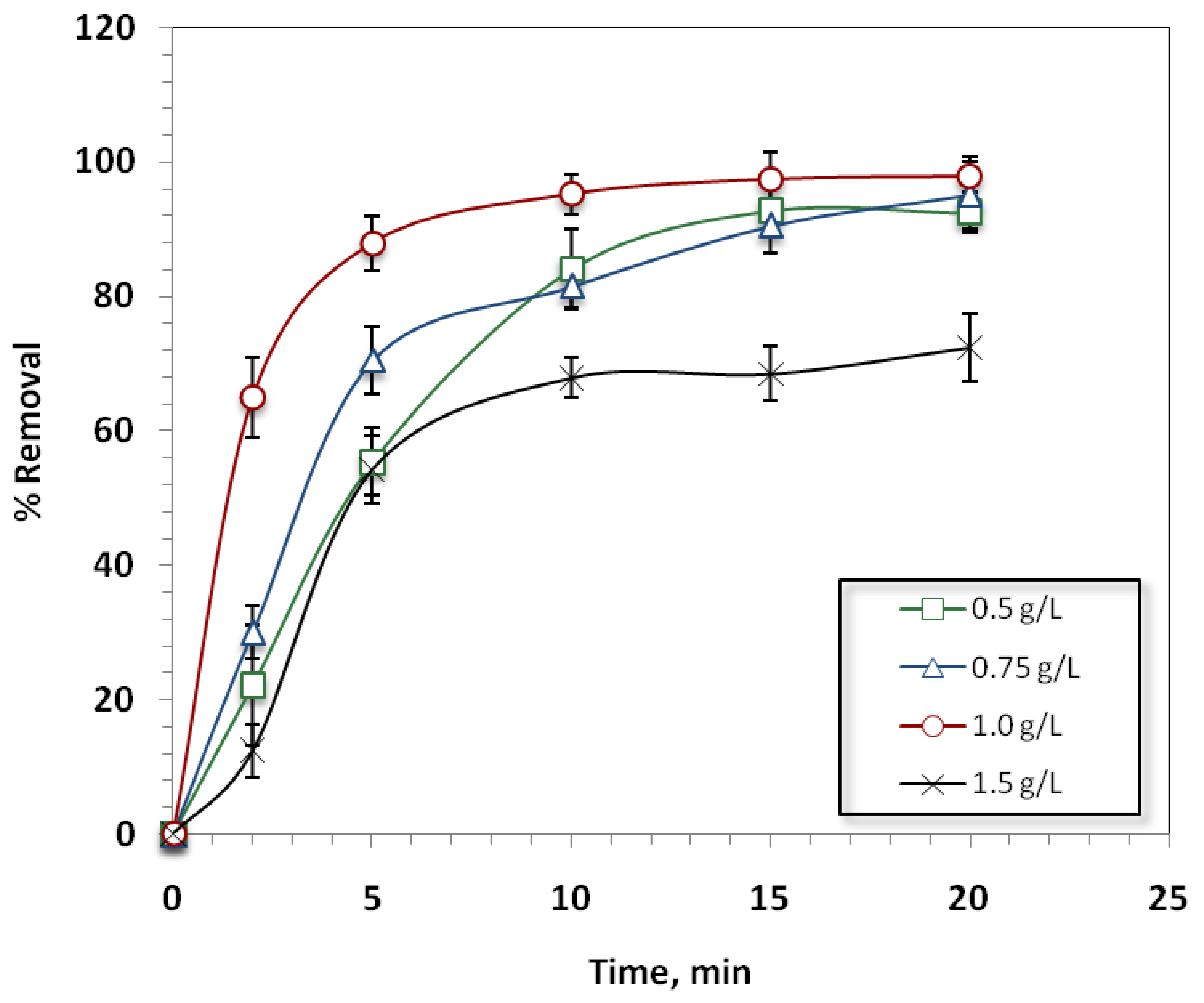
Effect of Fuller’s Earth Dose
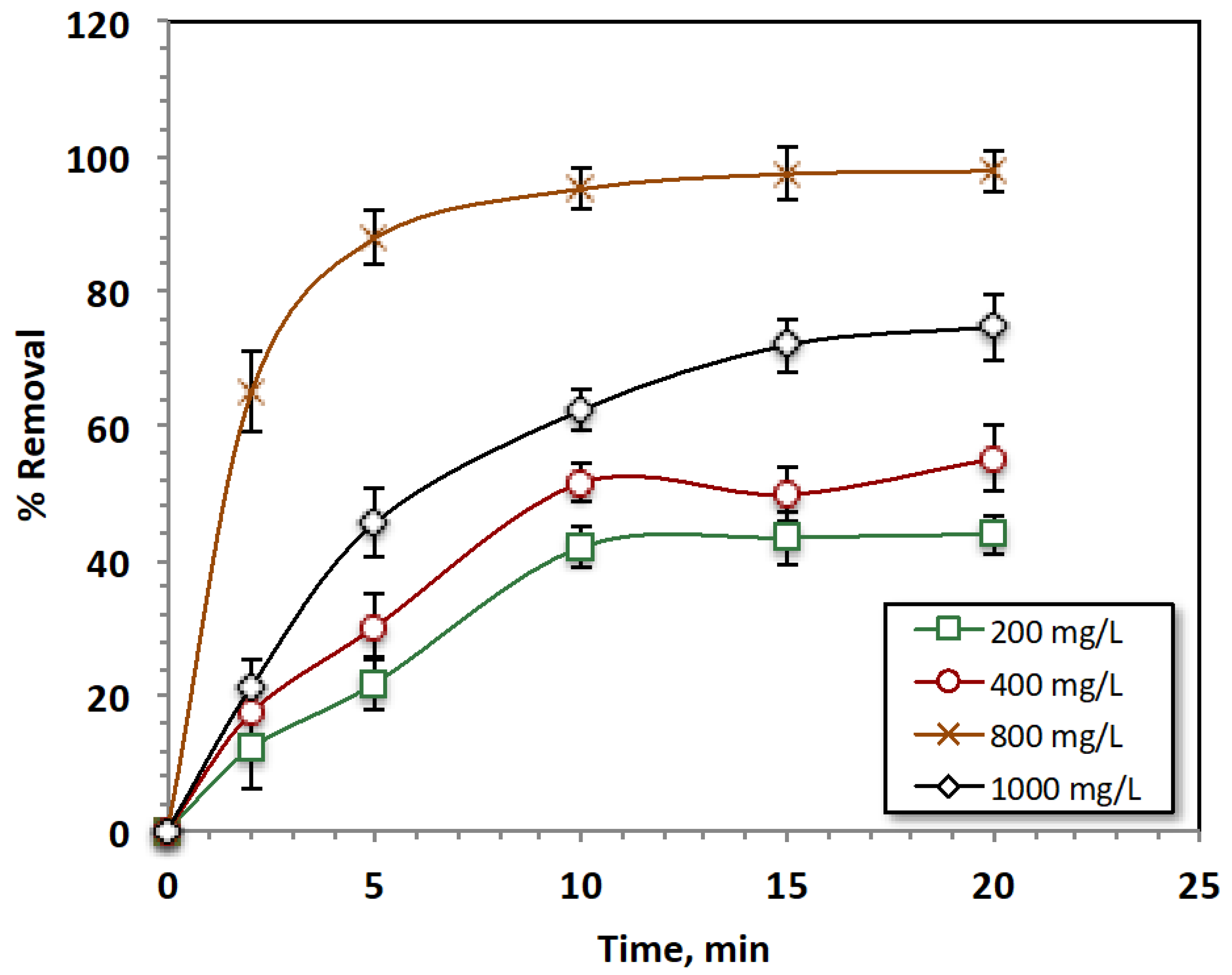
Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide Reagent Concentration
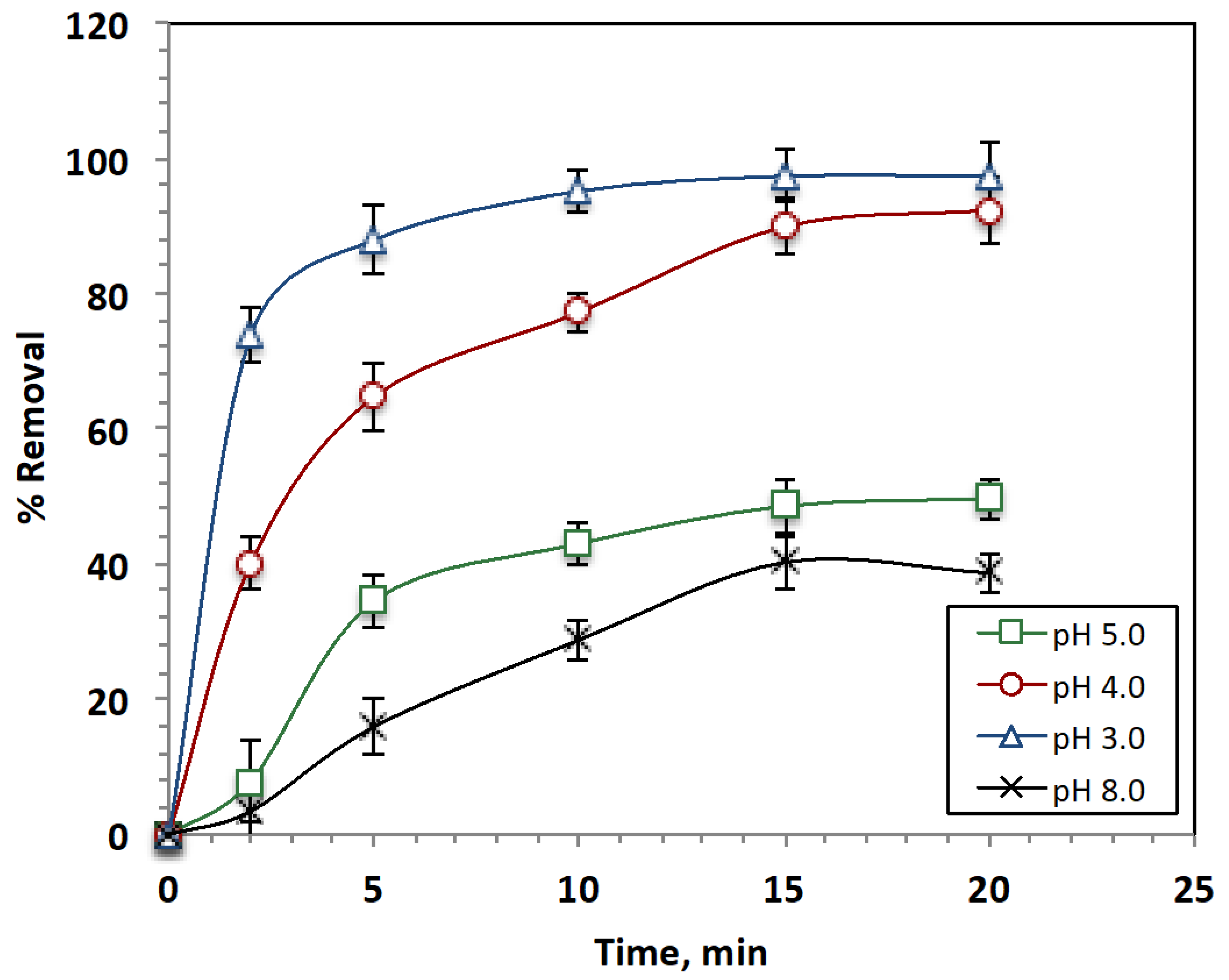
Effect of pH Value on the Treatment Efficiency
Box–Behnken Regression Design Fitting
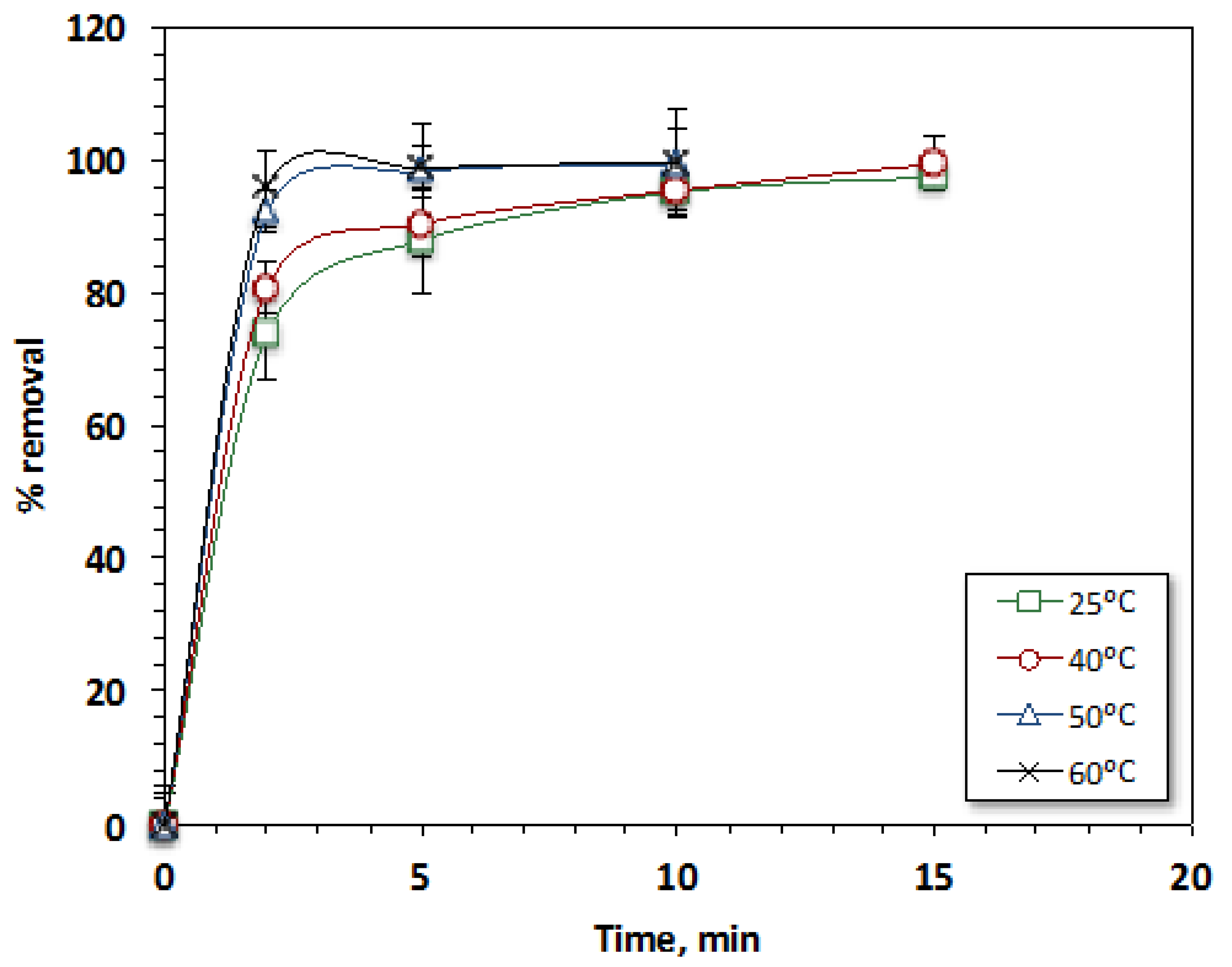
3.2.4. Effect of Temperature
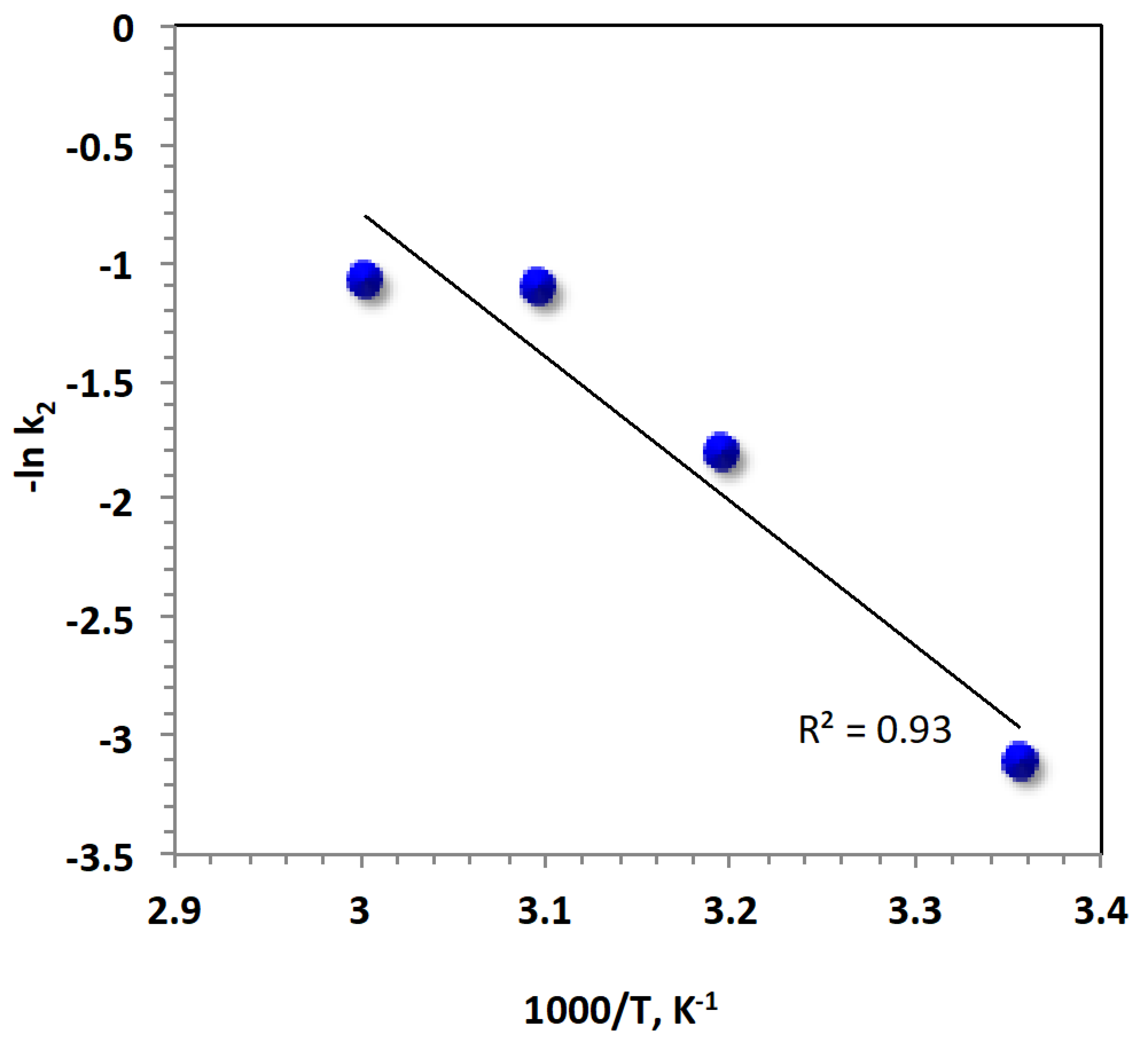
3.2.5. Kinetics and Thermodynamics
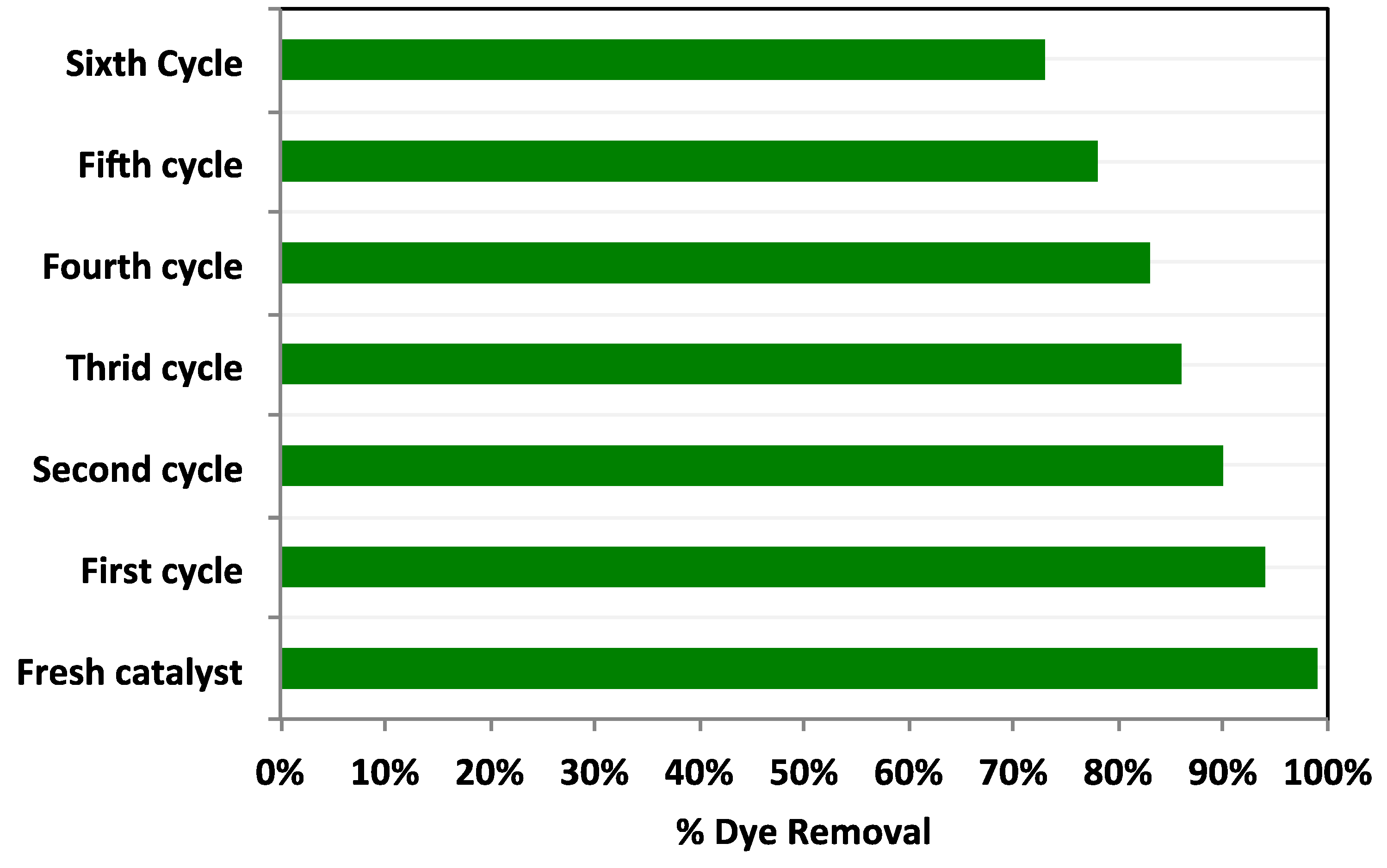
3.2.6. Catalyst Stability and Reusability
3.2.7. Data Comparison with Previous Fenton Studies
3.2.8. Validation of Reclaimed Water
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shimi, A.K.; Parvathiraj, C.; Kumari, S.; Dalal, J.; Kumar, V.; Wabaidur, S.M.; Alothman, Z.A. Green synthesis of SrO nanoparticles using leaf extract of Albizia julibrissin and its recyclable photocatalytic activity: An eco-friendly approach for treatment of industrial wastewater. Environ. Sci. 2022, 1, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, F. Clays, nanoclays, and montmorillonite minerals. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2008, 39, 2804–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, F. Montmorillonite: An Introduction to Properties and Utilization; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rohilla, S.; Gupta, A.; Kumar, V.; Kumari, S.; Petru, M.; Amor, N.; Noman, M.T.; Dalal, J. Excellent UV-light triggered photocatalytic performance of ZnO. SiO2 nanocomposite for water pollutant compound methyl orange dye. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safwat, S.M.; Medhat, M.; Abdel-Halim, H. Phenol adsorption onto kaolin and fuller’s earth: A comparative study with bentonite. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 155, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nour, M.; Tony, M.A.; Nabawy, H. Immobilization of magnetic nanoparticles on cellulosic wooden sawdust for competitive Nudrin elimination from environmental waters as a green strategy: Box-Behnken Design optimization. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Li, G.; Sun, H.; Kong, L.; Lu, H.; Gao, X. Preparation of magnetic core/shell structured γ-Fe2O3@ Ti-tmSiO2 and its application for the adsorption and degradation of dyes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 186, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Chai, L.; Tang, C.; Li, B.; Yang, Z. Comparison of the degradation of molecular and ionic ibuprofen in a UV/H2O2 system. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 2174–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, J.; Jan, M.R.; Muhammad, M.; Ara, B.; Fahmeeda. Kinetic and equilibrium profile of the adsorptive removal of Acid Red 17 dye by surfactant-modified fuller’s earth. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Dai, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Ouyang, D. Metronidazole degradation by UV and UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation processes: Kinetics, mechanisms, and effects of natural water matrices. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, X.; Chen, G.; Li, D.; Meng, S.; Chen, S. Synthesis of BiPO4 by Crystallization and Hydroxylation with Boosted Photocatalytic Removal of Organic Pollutants in Air and Water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 122999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Wang, T.; Qu, G.; Deng, F.; Liang, D.; Yang, W.; Liu, M. In Situ Synthesis of g-C3N4/TiO2Heterojunction Nanocomposites as a Highly Active Photocatalyst for the Degradation of Orange II under Visible Light Irradiation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 19122–19133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabet, R.H.; Fouad, M.K.; El Sherbiny, S.A.; Tony, M.A. Identifying optimized conditions for developing dewatered alum sludge based photocatalyst to immobilize a wide range of dye contamination. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran-Pérez, O.D.; Hormaza-Anaguano, A.; Zuluaga-Diaz, B.; Cardona-Gallo, S.A. Structural modification of regenerated fuller earth and its application, in the adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes. Dyna 2015, 82, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Huynh, K.A.; Padungthon, S.; Pranudta, A.; Amonpattaratkit, P.; Tran, L.B.; Phan, P.T.; Nguyen, N.H. Synthesis of natural flowerlike iron-alum oxide with special interaction of Fe-Si-Al oxides as an effective catalyst for heterogeneous Fenton process. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosallanejad, S.; Dlugogorski, B.Z.; Kennedy, E.M.; Stockenhuber, M. On the Chemistry of Iron Oxide Supported on γ-Alumina and Silica Catalysts. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, G.; Yang, Y.; Huang, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, H. A Multifunctional Platform by Controlling of Carbon Nitride in the Core-Shell Structure: From Design to Construction, and Catalysis Applications. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 258, 117957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tony, M.A. Valorization of undervalued aluminum-based waterworks sludge waste for the science of The 5 Rs’ criteria. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Jin, Y. The adsorption and reaction of a titanate coupling reagent on the surfaces of different nanoparticles in supercritical CO2. J. Colloid. Intermol. Sci. 2006, 304, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourali, P.; Behzad, M.; Arfaeinia, H.; Ahmadfazeli, A.; Afshin, S.; Poureshgh, Y.; Rashtbari, Y. Removal of acid blue 113 from aqueous solutions using low-cost adsorbent: Adsorption isotherms, thermodynamics, kinetics and regeneration studies. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut-Jadhav, S.; Pinjari, D.V.; Saini, D.R.; Sonawane, S.H.; Pandit, A.B. Intensification of degradation of methomyl (carbamate group pesticide) by using the combination of ultrasonic cavitation and process intensifying additives. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2016, 31, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar, W.; Chirchi, L.; Santosb, E.; Ghorhel, A. Kinetic study of 2-nitrophenol photodegradation on Al-pillared montmorillonite doped with copper. J. Environ. Monit. 2001, 3, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, S.; Yang, H.; Sun, X.; Xian, T. Preparation and promising application of novel LaFeO3/BiOBr heterojunction photocatalysts for photocatalytic and photo-Fenton removal of dyes. Opt. Mater. 2020, 100, 109644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tony, M.A.; Lin, L.S. Performance of acid mine drainage sludge as an innovative catalytic oxidation source for treating vehicle-washing wastewater. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2020, 43, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W. Enhanced Photocatalytic Performance of ZnTi-LDHs with Morphology Control. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 7025–7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markandeya; Shukla, S.P.; Dhiman, N.; Mohan, D.; Kisku, G.C.; Roy, S. An efficient removal of disperse dye from wastewater using zeolite synthesized from cenospheres. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2017, 21, 04017017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M.N.; El Taher, M.A.D.; Fadlalla, S.M. Photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine-B dye using composite prepared from drinking water treatment sludge and nano TiO2. Environ. Quality Manag. 2022, 31, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, S.A.; El-Sayed, E.; Tony, M. Impregnated chitin biopolymer with magnetic nanoparticles to immobilize dye from aqueous media as a simple, rapid and efficient composite photocatalyst. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichela, D.A.; Berkovic, A.M.; Costante, M.R.; Juliarena, M.P.; Einschlag, F.S.G. Nitrobenzene degradation in Fenton-like systems using Cu (II) as catalyst. Comparison between Cu (II)- and Fe (III)-based systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buthiyappan, A.; Raman, A.A.; Daud, W.M.W. Development of an advanced chemical oxidation wastewater treatment system for the batik industry in Malaysia. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 25222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Lopez, C.; Martín-Pascual, J.; Martínez-Toledo, M.V.; González-López, J.; Hontoria, E.; Poyatos, J.M. Effect of the operative variables on the treatment of wastewater polluted with phthalo blue by H2O2/UV process. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, C.S.; Ramos, M.D.N.; Velloso, C.C.V.; Aguiar, A. Kinetic evaluation of dye decolorization by Fenton processes in the presence of 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, J.; Hu, X.; Yue, P.L.; Zhu, H.Y.; Lu, G.Q. Discoloration and mineralization of Reactive Red HE-3B by heterogeneous photo-Fenton reaction. Water Res. 2003, 37, 3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, H.L.; Budarin, V.L.; Clark, J.H.; Hunt, A.J. Use of Starbon for the Adsorption and Desorption of Phenols. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sum, O.S.; Feng, J.; Hu, X.; Yue, P.L. Pillared laponite clay-based Fe nanocomposites as heterogeneous catalysts for photo-Fenton degradation of acid black. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2004, 59, 5269. [Google Scholar]
- Kalam, A.; Al-Sehemi, A.G.; Assiri, M.; Du, G.; Ahmad, T.; Ahmad, I.; Pannipara, M. Modified solvothermal synthesis of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) magnetic nanoparticles photocatalysts for degradation of methylene blue with H2O2/visible light. Results Phys. 2018, 8, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, H.B.; Hathiya, L.; Joshi, H.; Tanna, A. Synthesis and characterization of photocatalytic MnFe2O4 nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 21, 1905–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, K.; Xu, Y. Tartaric acid enhanced CuFe2O4-catalyzed heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like degradation of methylene blue. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 245, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghwal, K.; Agrawal, R.; Kumawat, S.; Jangid, N.K.; Ameta, C. Chemical and Biological Treatment of Dyes. In Impact of Textile Dyes on Public Health and the Environment; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghwal, K.; Kumawat, S.; Ameta, C.; Jangid, N.K. Effect of dyes on water chemistry, soil quality, and biological properties of water. In Impact of Textile Dyes on Public Health and the Environment; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 90–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
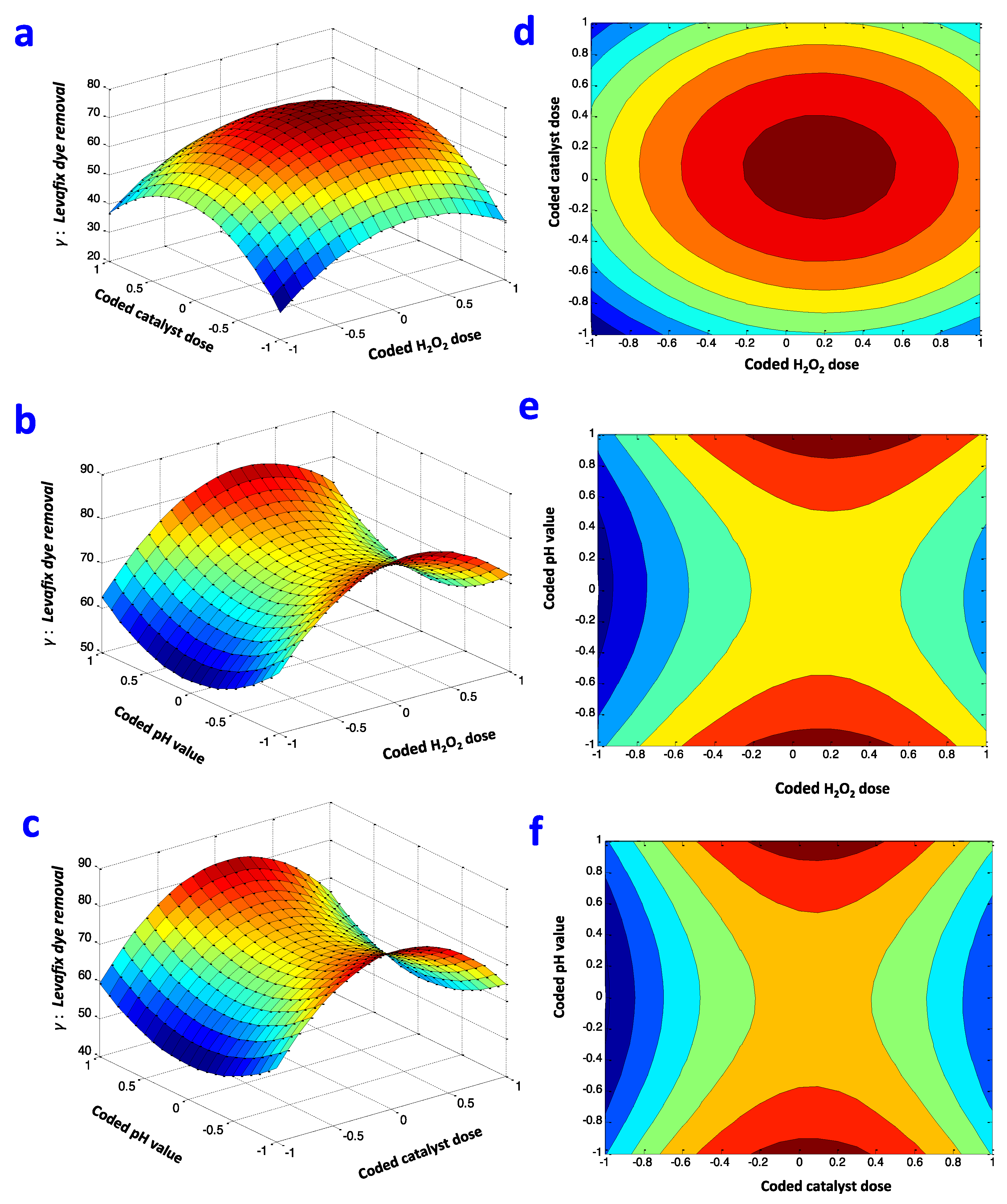
| Experimental Variables | Symbols | Range and Levels | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uncoded | Coded | −1 | 0 | 1 | |
| H2O2 (mg/L) | ε1 | ζ1 | 700 | 800 | 900 |
| Fuller’s earth (mg/L) | ε2 | ζ2 | 0.75 | 1.0 | 1.25 |
| pH | ε3 | ζ3 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 3.5 |
| Element | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| weight % | 79.16 | 12.81 | 5.26 | 0.53 | 0.96 | 0.08 | 0.24 | 0.96 |
| Kinetic Model | Parameter | Temperature, °C | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 40 | 50 | 60 | ||
| Zero-order | k0 (mg.min−1) | 2.673 | 2.62 | 2.459 | 2.403 |
| t1/2 (min) | 72.171 | 70.794 | 66.393 | 64.881 | |
| R2 | 0.54 | 0.49 | 0.39 | 0.37 | |
| First-order | k1 (min−1) | 0.223 | 0.293 | 0.33 | 0.317 |
| t1/2 (min) | 3.107 | 2.365 | 2.100 | 2.186 | |
| R2 | 0.90 | 0.94 | 0.81 | 0.72 | |
| Second-order | k2 (L.mg−1 min−1) | 0.044 | 0.164 | 0.328 | 0.341 |
| t1/2 (min) | 0.4208 | 0.1129 | 0.0564 | 0.0543 | |
| R2 | 0.97 | 0.90 | 0.98 | 0.97 | |
| Parameters Thermodynamic Parameters | Temperature (°C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 40 | 50 | 60 | |
| ∆G′ (kJ/mol) | 80,720.78 | 81,487.94 | 82,314.45 | 84,839.69 |
| ∆H′ (kJ/mol) | −2426.76 | −2551.47 | −2634.61 | −2717.75 |
| ∆S′ (J/mol) | −279.02 | −268.49 | −263.00 | −262.93 |
| Ea (kJ/mol) | 50.8 | |||
| Fenton System | Target Dye Pollutant | Initiation Source | Operating Conditions | Oxidation Time | Efficiency | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O2/Fullers’ earth | Levafix blue | Ultraviolet illumination | Catalyst 1.02 g/L; H2O2 818 mg/L; pH 3.0; Temperature 298 K | 20 min | 99% | Current work |
| H2O2/Clay-Fe3O4 | Levafix blue | Ultraviolet illumination | Catalyst 1 g/L; H2O2 400 mg/L; pH 3.0; Temperature 300 K | 30 min | 100% | [13] |
| H2O2/Fe-laponite | Acid Black 1 | Ultraviolet illumination | Catalyst 1 g/L; H2O2 218 mg/L; pH 3.0; Temperature 298 K | 120 min | 100% | [34] |
| H2O2/Fe-zeolite | Acid Blue 74 | Ultraviolet illumination | Catalyst 0.3 g/L; H2O2 228 mg/L; pH 5.0; Temperature 298 K | 120 min | 55% | [35] |
| H2O2/Fe2.46Ni0.54O4 | Methylene blue | Dark Fenton | Catalyst 1.0 g/L; H2O2 340 mg/L; pH 7.0; Temperature 298 K | 50 min | 10% | [36] |
| H2O2/Co- Fe2O4 | Methylene blue | Natural solar radiation | Catalyst 0.2 g/L; H2O2 0.68 mg/L; pH 5.0; Temperature 298 K | 150 min | 79% | [35] |
| H2O2/Mn-Fe2O4 | Methylene blue | Natural solar radiation | Catalyst 1.0 g/L; H2O2 2720 mg/L; pH 7.0; Temperature 298 K | 80 min | 100% | [36] |
| H2O2/Cu-Fe2O4 | Methylene blue | Ultraviolet illumination | Catalyst 0.2 g/L; H2O2 0.68 mg/L; pH 5.0; Temperature 298 K | 80 min | 90% | [37] |
| Parameter (Unit) | Suspended Solids (mg/L) | Turbidity (NTU) | pH | DO (mg/L) | COD (mg-COD/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wastewater | 120 | 34 | 5.0 | 2.4 | 420 |
| Treated water | 38 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 2.3 | 28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nour, M.M.; Tony, M.A.; Nabwey, H.A. Heterogeneous Fenton Oxidation with Natural Clay for Textile Levafix Dark Blue Dye Removal from Aqueous Effluent. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8948. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13158948
Nour MM, Tony MA, Nabwey HA. Heterogeneous Fenton Oxidation with Natural Clay for Textile Levafix Dark Blue Dye Removal from Aqueous Effluent. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(15):8948. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13158948
Chicago/Turabian StyleNour, Manasik M., Maha A. Tony, and Hossam A. Nabwey. 2023. "Heterogeneous Fenton Oxidation with Natural Clay for Textile Levafix Dark Blue Dye Removal from Aqueous Effluent" Applied Sciences 13, no. 15: 8948. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13158948
APA StyleNour, M. M., Tony, M. A., & Nabwey, H. A. (2023). Heterogeneous Fenton Oxidation with Natural Clay for Textile Levafix Dark Blue Dye Removal from Aqueous Effluent. Applied Sciences, 13(15), 8948. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13158948







