Sentinel-2 Observation of Water Color Variations in Inland Water across Guangzhou and Shenzhen after the Establishment of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Bay Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Research Data
- (1)
- Sentinel-2
- (2)
- Auxiliary data
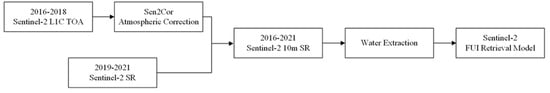
2.3. Image Pre-Processing
2.4. Waterbody Extraction Method
2.5. Calcualtion
2.6. Temporal and Spatial Aggregation
2.7. Evaluation Index
3. Results
3.1. Accuracy Evaluation of the FUI
3.2. Spatial Distribution
3.3. Seasonal Variations
3.4. Inter-Annual Variations
4. Discussion
4.1. Meteorological Factors
4.2. Human Factors
4.3. Model Adaptability
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, R.; Junwu, T.; Duan, H.; Delu, P. Progress in Lake Water Color Remote Sensing. J. Lake Sci. 2009, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Shen, Q.; Wu, Y.; Wang, G.; Zou, L.; Wang, S. Validation of a Synthetic Chlorophyll Index for Remote Estimates of Chlorophyll-a in a Turbid Hypereutrophic Lake. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Liu, G.; Wang, Q.; Wen, Z.; Lyu, L.; Du, Y.; Sha, L.; Fang, C. Quantification of Lake Clarity in China Using Landsat OLI Imagery Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 243, 111800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Li, J.; Xiao, C.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Yin, Z.; Wang, C. A Classification-Based, Semianalytical Approach for Estimating Water Clarity From a Hyperspectral Sensor Onboard the ZY1-02D Satellite. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, B. Water Clarity Changes in Lake Taihu over 36 Years Based on Landsat TM and OLI Observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupana, R.S.; Odermatt, D.; Cesana, I.; Giardino, C.; Nedbal, L.; Damm, A. Remote Sensing of Sun-Induced Chlorophyll-a Fluorescence in Inland and Coastal Waters: Current State and Future Prospects. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 262, 112482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Steele, C.; Simis, S.; Warren, M.; Tyler, A.; Spyrakos, E.; Selmes, N.; Hunter, P. Retrieval of Chlorophyll-a Concentration and Associated Product Uncertainty in Optically Diverse Lakes and Reservoirs. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 267, 112710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werther, M.; Odermatt, D.; Simis, S.G.H.; Gurlin, D.; Lehmann, M.K.; Kutser, T.; Gupana, R.; Varley, A.; Hunter, P.D.; Tyler, A.N.; et al. A Bayesian Approach for Remote Sensing of Chlorophyll-a and Associated Retrieval Uncertainty in Oligotrophic and Mesotrophic Lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 283, 113295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Matsushita, B.; Pahlevan, N.; Gurlin, D.; Lehmann, M.K.; Fichot, C.G.; Schalles, J.; Loisel, H.; Binding, C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Remotely Estimating Total Suspended Solids Concentration in Clear to Extremely Turbid Waters Using a Novel Semi-Analytical Method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 258, 112386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramski, D.; Constantin, S.; Reynolds, R.A. Adaptive Optical Algorithms with Differentiation of Water Bodies Based on Varying Composition of Suspended Particulate Matter: A Case Study for Estimating the Particulate Organic Carbon Concentration in the Western Arctic Seas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 286, 113360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houskeeper, H.F.; Hooker, S.B.; Kudela, R.M. Spectral Range within Global ACDOM(440) Algorithms for Oceanic, Coastal, and Inland Waters with Application to Airborne Measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 253, 112155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Jun-Sheng, L.I.; Yuan-Feng, W.U.; Zhang, B. Review of Spectral Curve Fitting and Analysis of Inherent Optical Parameters in Lakes. Remote Sens. Inf. 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Feng, S.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, M.; Qin, B. A Study of Absorption Characteristics of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter and Particles in Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 2007, 592, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratyev, K.Y.; Pozdnyakov, D.V.; Pettersson, L.H. Water Quality Remote Sensing in the Visible Spectrum. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 957–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alföldi, T.T.; Munday, J. Water Quality Analysis by Digital Chromaticity Mapping of Landsat Data. Can. J. Remote Sens. 1978, 4, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukata, R.P.; Jerome, J.H.; Kondratyev, K.Y.; Pozdnyakov, D.V.; Kotykhov, A.A. Modelling the Radiometric Color of Inland Waters: Implications to a) Remote Sensing and b) Limnological Color Scales. J. Gt. Lakes Res. 1997, 23, 254–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F.; Shen, Q.; Peng, D.; Tian, L. MODIS Observations of Water Color of the Largest 10 Lakes in China between 2000 and 2012. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2016, 9, 788–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, J.; Bing, Z.; Evangelos, S.; Tyler, A.N.; Qian, S.; Zhang, F.; Tiit, K.; Lehmann, M.K.; Wu, Y. Trophic State Assessment of Global Inland Waters Using a MODIS-Derived Forel-Ule Index. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 444–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Cao, C.; Zhang, B. A Dataset of Remote-Sensed Forel-Ule Index for Global Inland Waters during 2000–2018. Sci. Data 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Shen, Q.; Li, J. Retrieval and Spatio-Temporal Variations Analysis of Yangtze River Water Clarity from 2017 to 2020 Based on Sentinel-2 Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Lee, Z.; Spyrakos, E.; Feng, L.; Liu, C.; Zhao, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, L.; et al. Changes of Water Clarity in Large Lakes and Reservoirs across China Observed from Long-Term MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Shen, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, F. Remote Sensing-Based Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Water Colour Variations in Baiyangdian Lake after the Establishment of the Xiong’an New Area. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shen, Q.; Wang, Q.; Yang, F.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Yao, Y. Recognition of Water Colour Anomaly by Using Hue Angle and Sentinel 2 Image. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Junsheng, L.; Bing, Z.; Qian, S.; Fangfang, Z.; Zhaoyi, L. A Simple Correction Method for the MODIS Surface Reflectance Product over Typical Inland Waters in China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 6076–6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B.; Hu, T.; Liu, X.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Annual Maps of Global Artificial Impervious Area (GAIA) between 1985 and 2018. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C.; Guo, H.; Du, J.; Duan, Z. A Robust Multi-Band Water Index (MBWI) for Automated Extraction of Surface Water from Landsat 8 OLI Imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 68, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Woerd, H.J.; Wernand, M.R. Hue-Angle Product for Low to Medium Spatial Resolution Optical Satellite Sensors. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novoa, S.; Marcel, W.H.; Woerd, H.J.V.D. The Forel-Ule Scale Revisited Spectrally: Preparation Protocol, Transmission Measurements and Chromaticity. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. Rapid Publ. 2013, 8, 13057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woerd, H.; Wernand, M. True Colour Classification of Natural Waters with Medium-Spectral Resolution Satellites: SeaWiFS, MODIS, MERIS and OLCI. Sensors 2015, 15, 25663–25680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Shen, Q.; Wu, Y.; Mei, Y.; Qiu, R.; Li, J. Analysis of the Water Color Transitional Change in Qinghai Lake during the Past 35 Years Observed from Landsat and MODIS. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 42, 101154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H.; Ramachandra Rao, A. A Modified Mann-Kendall Trend Test for Autocorrelated Data. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Test against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Feng, L.; Hou, X.; Wang, J.; Tang, J. Four-Decade Dynamics of the Water Color in 61 Large Lakes on the Yangtze Plain and the Impacts of Reclaimed Aquaculture Zones. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Ji, H.; Ke, Y.; Fu, Y. Combining Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 to Investigate Seasonal Changes of Suspended Particulate Matter off the Abandoned Distributary Mouths of Yellow River Delta. Mar. Geol. 2021, 441, 106622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Barnes, B.B.; Hu, C.; Carlson, P.R.; Yarbro, L.A. Water Clarity Monitoring in Complex Coastal Environments: Leveraging Seagrass Light Requirement toward More Functional Satellite Ocean Color Algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 286, 113418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Pan, D. Deteriorating Water Clarity in Shallow Waters: Evidence from Long Term MODIS and in-Situ Observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 68, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmanson; LG; Bauer; ME; Brezonik; PL A 20-Year Landsat Water Clarity Census of Minnesota’s 10,000 Lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 4086–4097. [CrossRef]
- Fleming-Lehtinen, V.; Laamanen, M. Long-Term Changes in Secchi Depth and the Role of Phytoplankton in Explaining Light Attenuation in the Baltic Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 102–103, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuzzo, E.; Stephens, D.; Silva, T.; Barry, J.; Forster, R.M. Decrease in Water Clarity of the Southern and Central North Sea during the 20th Century. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 2206–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


















| Guangzhou City | Shenzhen City | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Area | Station | Area | Station |
| Conghua Area | Taipingpu Station | Baoan Area | Shiyan Station |
| Huanglongdai Station | Luotian Station | ||
| Huadu Area | Jiuwantan Station | Tiegang Station | |
| Futian Area | Xili Station | ||
| Huangpu Area | Huangpu Station | Longgang Area | Qinglinjing Station |
| Dapeng New Area | Nanao Station | ||
| Zengcheng Area | Paitan Station | Yantian Area | Sanzhoutian Station |
| Luohu Area | Shenzhen Station | ||
| Sentinel-2 | Landsat 8 OLI | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Central Wavelength (nm) | Bands | Central Wavelength (nm) | Bands |
| 443 | Coastal Blue | 443 | Coastal Blue |
| 490 | Blue | 483 | Blue |
| 560 | Green | 561 | Green |
| 665 | Red | 661 | Red |
| 705 | Vegetation Red Edge | ||
| FUI | x | y | (°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.191363 | 0.166919 | 40.467 |
| 2 | 0.198954 | 0.199871 | 45.19626 |
| 3 | 0.210015 | 0.2399 | 52.85273 |
| 4 | 0.226522 | 0.288347 | 67.16945 |
| 5 | 0.245871 | 0.335281 | 91.29804 |
| 6 | 0.266229 | 0.37617 | 122.5852 |
| 7 | 0.290789 | 0.411528 | 151.4792 |
| 8 | 0.315369 | 0.440027 | 170.4629 |
| 9 | 0.336658 | 0.461684 | 181.4983 |
| 10 | 0.363277 | 0.476353 | 191.8352 |
| 11 | 0.386188 | 0.486566 | 199.0383 |
| 12 | 0.402416 | 0.4811 | 205.0622 |
| 13 | 0.416243 | 0.47368 | 210.5766 |
| 14 | 0.431336 | 0.465513 | 216.5569 |
| 15 | 0.445679 | 0.457605 | 222.1153 |
| 16 | 0.460605 | 0.449426 | 227.6293 |
| 17 | 0.475326 | 0.440985 | 232.8302 |
| 18 | 0.488676 | 0.43285 | 237.3523 |
| 19 | 0.503316 | 0.424618 | 241.7592 |
| 20 | 0.515498 | 0.416136 | 245.5513 |
| 21 | 0.528252 | 0.408319 | 248.9529 |
| Month | Season |
|---|---|
| March, April, May | Spring |
| June, July, August | Summer |
| September, October, November | Autumn |
| December, January, February | Winter |
| Z | Significance | |
|---|---|---|
| ≥2.58 | ≤0.01 | Extremely significant |
| ≥1.96 | ≤0.05 | Significant |
| <1.96 | >0.05 | Not significant |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, X. Sentinel-2 Observation of Water Color Variations in Inland Water across Guangzhou and Shenzhen after the Establishment of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Bay Area. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9039. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13159039
Zhao Y, Chen J, Li X. Sentinel-2 Observation of Water Color Variations in Inland Water across Guangzhou and Shenzhen after the Establishment of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Bay Area. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(15):9039. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13159039
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yelong, Jinsong Chen, and Xiaoli Li. 2023. "Sentinel-2 Observation of Water Color Variations in Inland Water across Guangzhou and Shenzhen after the Establishment of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Bay Area" Applied Sciences 13, no. 15: 9039. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13159039
APA StyleZhao, Y., Chen, J., & Li, X. (2023). Sentinel-2 Observation of Water Color Variations in Inland Water across Guangzhou and Shenzhen after the Establishment of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Bay Area. Applied Sciences, 13(15), 9039. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13159039