Characterization and Degradation of Ancient Architectural Red Sandstone in a Natural Erosion Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
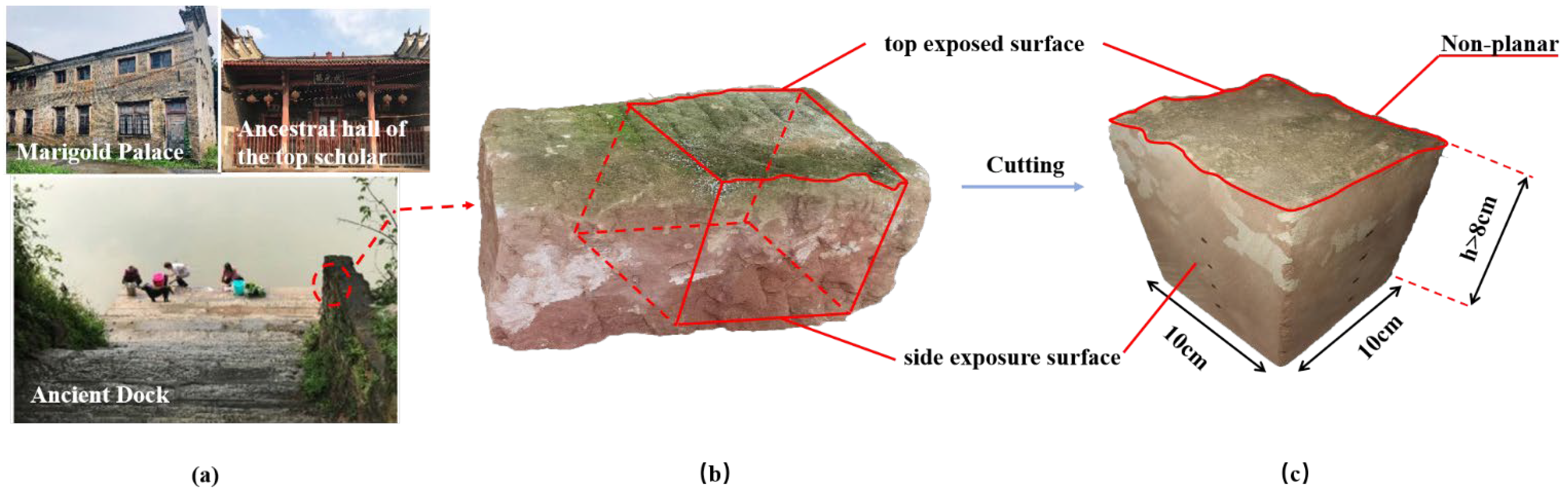
2.1.1. Background of the Project
2.1.2. Material Preparation
2.2. Detection Methods
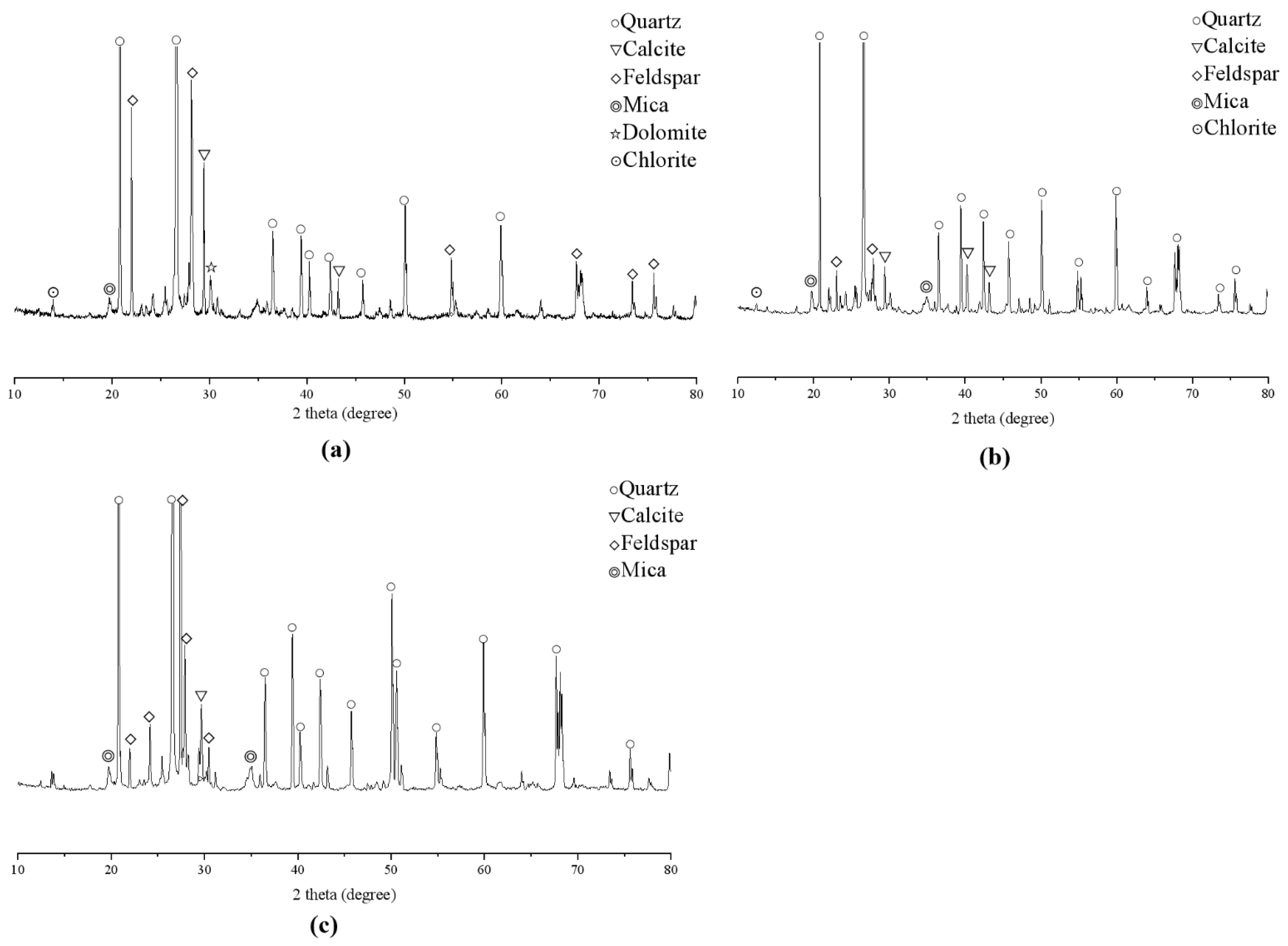
2.2.1. SEM and XRD
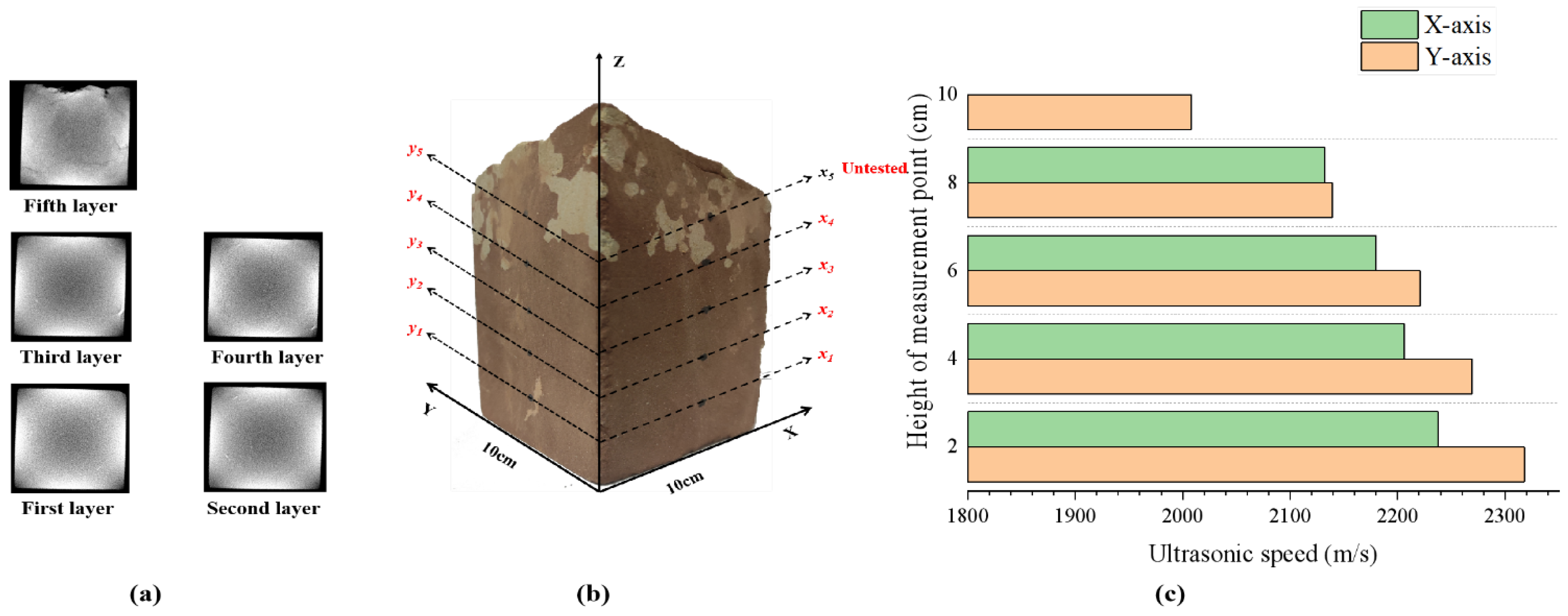
2.2.2. Ultrasonic Testing
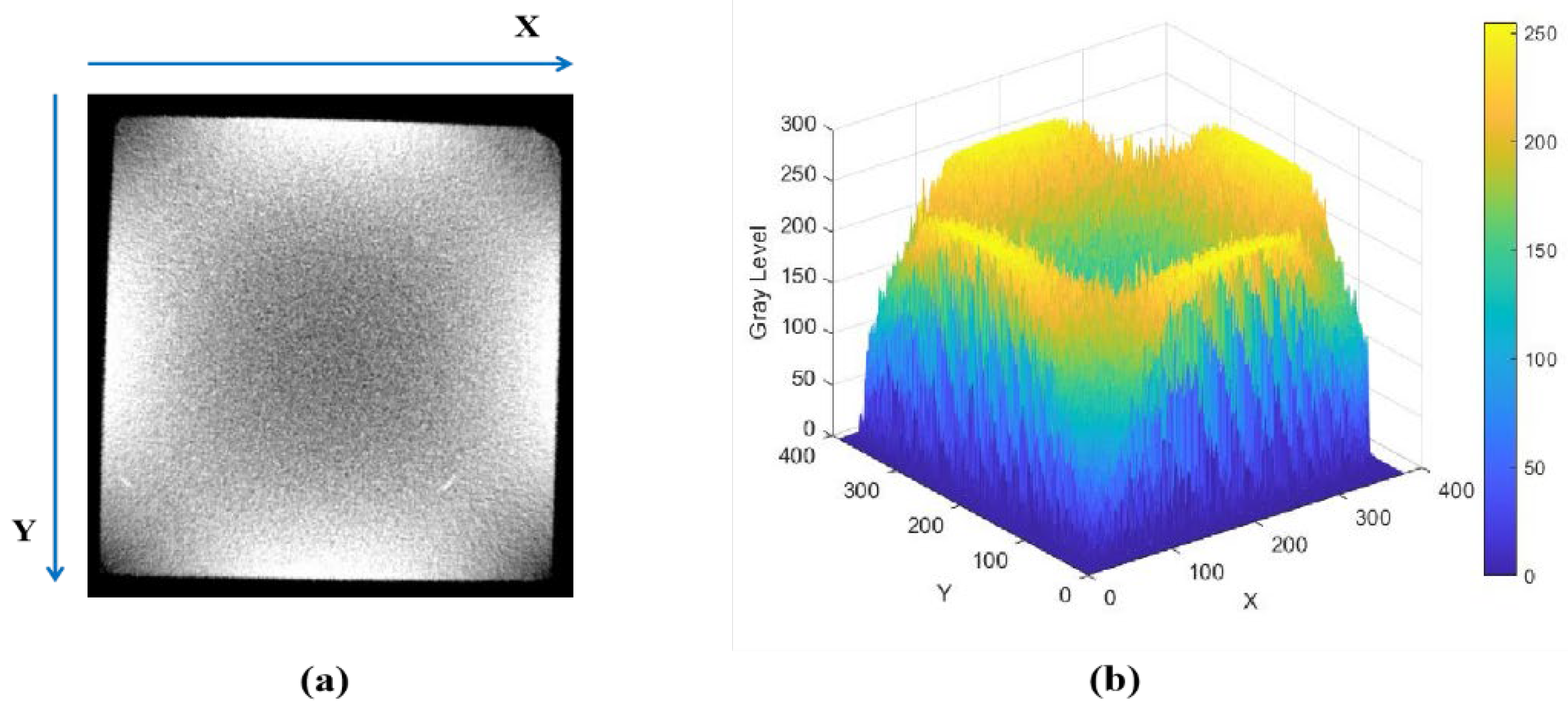
2.2.3. X-CT Scanning
2.3. Theoretical Basics
2.3.1. GM (1, 1) Gray Prediction Model
2.3.2. The Absolute Gray Correlation
3. Analysis of Results
3.1. Microscopic Inspection and Analysis of Red Sandstone Specimens
3.2. Analysis of Properties of Red Sandstone Specimens with Different Orientations
3.2.1. Ultrasonic Characterization of Red Sandstone Specimens
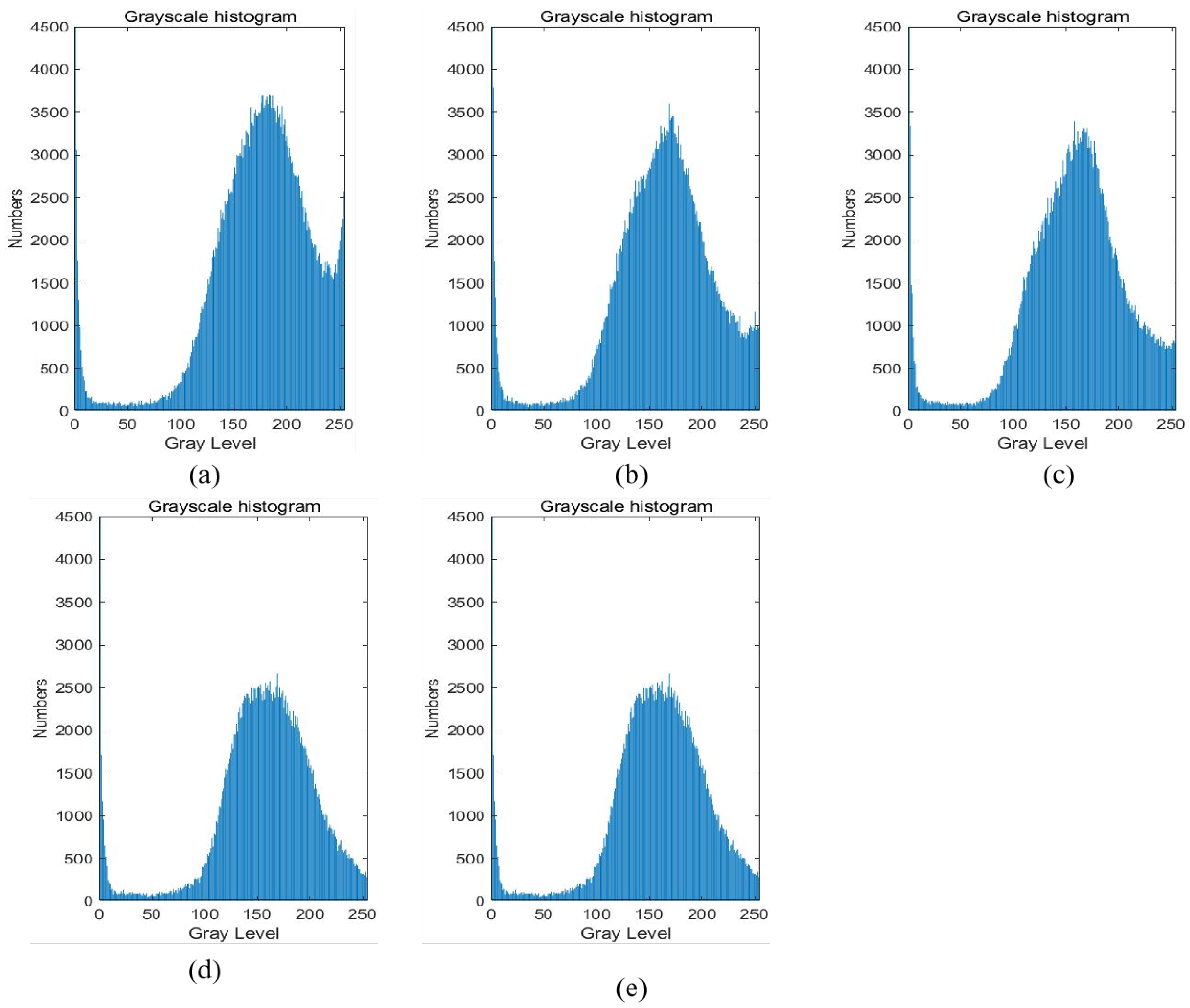
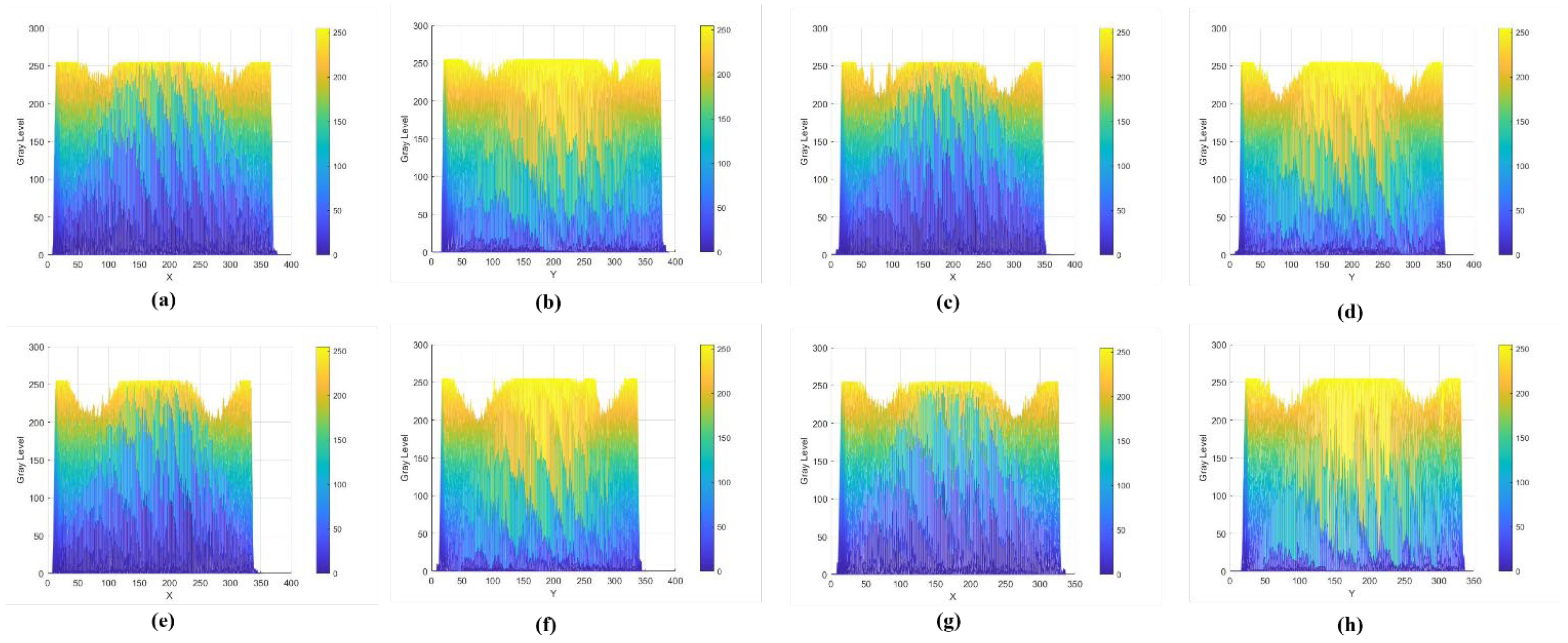
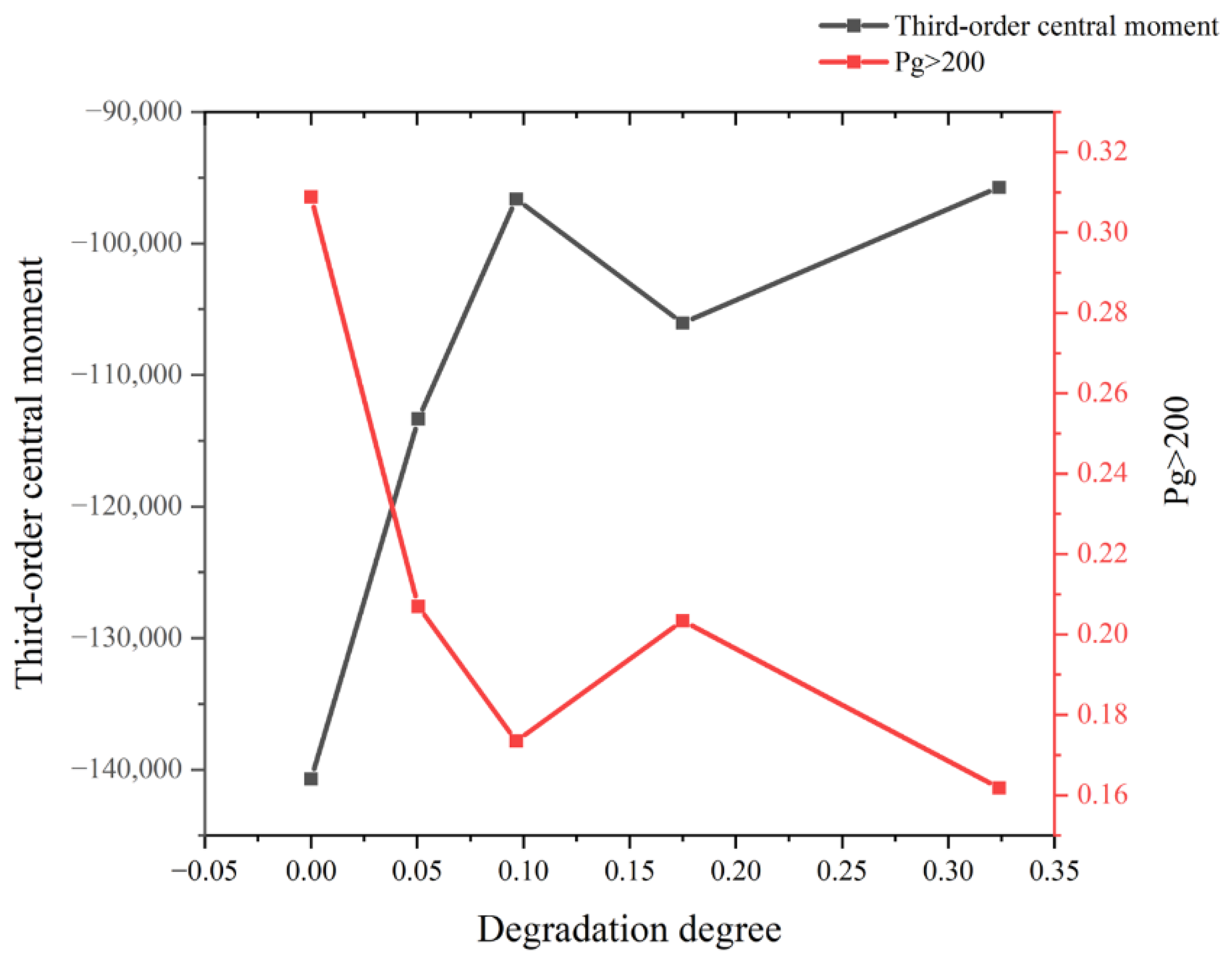
3.2.2. Differential Analysis of the Degradation Degree of Red Sandstone Specimens in Different Directions Based on CT Grayscale Images
- (1)
- Correlation analysis of longitudinal (Z direction) ultrasonic wave velocity values of red sandstone specimens with their CT grayscale distribution maps.
- (2)
- Specific analysis of the degree of degradation of horizontally oriented red sandstone specimens.
3.3. Comprehensive Assessment of the Extent of Structural Degradation of Red Sandstone
3.3.1. Overall Planar Ultrasonic Wave Velocity Analysis and Degradation Degree Evaluation
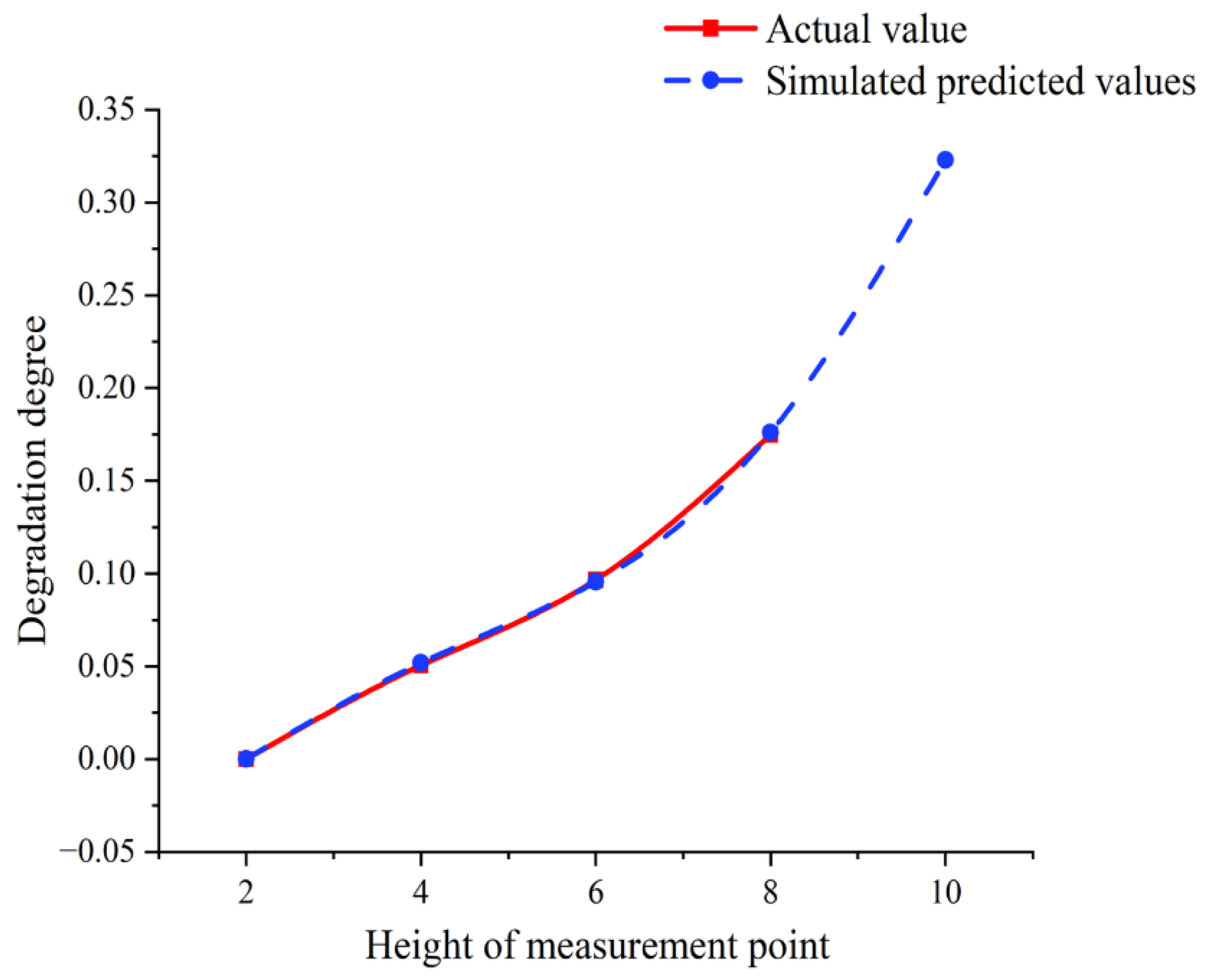
3.3.2. Analysis of Surface Degradation Degree of Red Sandstone Based on GM (1, 1) Gray Prediction Model
3.3.3. Correlation Analysis of the Degree of Red Sandstone Degradation with CT Grayscale Images
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, D.; Jian, Y.; Tang, Y.; Cao, K.; Zhang, W.; Chen, H.; Gong, C. Comprehensive Testing of Sulfate Erosion Damage of Concrete Structures and Analysis of Silane Coating Protection Effect. Sensors 2022, 22, 7991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.; Wang, F.; Mi, Q. Preservation planning of the qingcheng ancient city wall. Open House Int. 2018, 43, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kamh, G. Weathering at high latitudes on the carboniferous Old Red Sandstone, petrographic and geotechnical investigations, Jedburgh Abbey Church, Scotland, a case study. Environ. Geol. 2005, 47, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, M. Introduction: The state and historic buildings: Preserving ‘the national past’. Nations Natl. 2018, 24, 22–42. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, G.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.F. Assessment and retrofitting solutions for an historical wooden pavilion in China. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 105, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. The Recovery and Conservation of a Historic District Post-earthquake A Case Study of Zhaohua in Sichuan Province in China. J. Asian Archit. Build. 2012, 11, 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Cakir, H.K.; Aydin, D.; Arabulan, S. Adaptive reuse of open spaces in historical buildings. Int. J. Build. Pathol. 2020, 38, 703–719. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, F.; Tang, C.; Zuo, J.; Yu, R.; Zheng, T.; Niu, D. Water erosion control of undisturbed soil cores by near soil surface factors after 5-year vegetation restoration in red sandstone area from subtropical China. J. Soil. Sediment. 2023, 23, 1356–1369. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.; Duan, H.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Li, T. Effects of seepage-induced erosion on nonlinear hydraulic properties of broken red sandstones. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 91, 102993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xiao, T.; Liu, H.; Ge, P.; Xia, J.; Dai, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, X. Effects of AM Fungi and Grass Strips on Soil Erosion Characteristics in Red Sandstone Erosion Areas in Southern China. Forests 2022, 13, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Song, X.; Liu, F.; Li, D.; Zhang, G. Geophysical and geochemical characterization reveals topography controls on critical zone structure in a low hilly region. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2022, 47, 2796–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Yang, G. Field tests on mechanical characteristics and strength parameters of red-sandstone. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2010, 17, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Sun, Q.; Ye, J.; Zhang, W. Changes in color and roughness of red sandstone at high temperatures. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 1959–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Garcia, A.; Changani, H. Fragmentation and energy absorption characteristics of Red, Berea and Buff sandstones based on different loading rates and water contents. Geomech. Eng. 2018, 14, 151–159. [Google Scholar]
- Sirdesai, N.N.; Singh, T.N.; Ranjith, P.G.; Singh, R. Effect of Varied Durations of Thermal Treatment on the Tensile Strength of Red Sandstone. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2017, 50, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, J. A Study on the Dynamic Strength Deterioration Mechanism of Frozen Red Sandstone at Low Temperatures. Minerals 2021, 11, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wen, S.; Guo, H.; Fu, H. The Creep Test Study and Macro-Detail Analysis of Argillaceous Red Sandstone in Different Water-Containing States. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2022, 2022, 9698675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanlari, G.; Sahamieh, R.Z.; Abdilor, Y. The effect of freeze-thaw cycles on physical and mechanical properties of Upper Red Formation sandstones, central part of Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 5991–6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, J.; Tan, H.; Wang, J.; Shi, Z.; Li, K. Study on fatigue characteristics and thermal damage mechanism of red sandstone under high temperature-cyclic load coupling. Int. J. Fatigue 2023, 168, 107405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Jiang, A.; Zhang, F. Experimental investigation on damage and seepage of red sandstone subjected to cyclic thermal and cold treatment. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 222, 211461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yao, W.; Wang, X.; Zhu, W.; Lu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Huang, H. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of the Damage Characteristics of Rocks under Ballistic Penetration. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Qian, Z.; Wu, Z. Micro/macro physical and mechanical variation of red sandstone subjected to cyclic heating and cooling: An experimental study. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 1485–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J.; Wu, S.; Yan, C. Investigation into Macro- and Microcrack Propagation Mechanism of Red Sandstone under Different Confining Pressures Using 3D Numerical Simulation and CT Verification. Geofluids 2021, 2021, 2871687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, Q.; Jia, H.; Dong, Z.; Luo, T. Effects of high-temperature thermal treatment on the porosity of red sandstone: An NMR analysis. Acta Geophys. 2021, 69, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Yang, W.; Yu, H. Study on the permeability of red sandstone via image enhancement. Fractals 2017, 25, 1750055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Li, X.; Ying, P.; Dong, Y.; Deng, S. Study on the microscopic damage evolution and dynamic fracture properties of sandstone under freeze-thaw cycles. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2021, 191, 103328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobadi, M.H.; Babazadeh, R. An investigation on the effect of accelerated weathering on strength and durability of Tertiary sandstones (Qazvin province, Iran). Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 4237–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Cai, L.; Shao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Huang, C. Prediction of Shear Strength of Fully Weathered Coastal Red Sandstone: Influence of Water Content, Fine Content, and Relative Compaction. J. Coast. Res. 2021, 37, 827–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludovico-Marques, M.; Chastre, C.; Vasconcelos, G. Modelling the compressive mechanical behaviour of granite and sandstone historical building stones. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 28, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, A.; Al-Hajeri, M.; Najem, A.; Al-Qattan, F. Facies architecture of Lower Fars Formation at Jal Az-Zor escarpment, Kuwait. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y. Energy demand forecasting using a novel remnant GM (1, 1) model. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 13903–13912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Ma, X.; Shi, J. Modeling Method of the Grey GM (1, 1) Model with Interval Grey Action Quantity and Its Application. Complexity 2020, 2020, 6514236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, S.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, X. City Traffic Flow Prediction Based on Improved GM (1, 1) Model. J. Grey Syst. 2012, 24, 337–346. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, W.; Zeng, B.; Li, S. A Novel Fractional-Order Grey Prediction Model and Its Modeling Error Analysis. Information 2019, 10, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, B. An Improved T-GM (1, 1) and It’s Application. J. Grey Syst. 2018, 30, 186–193. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, D.; Li, Q.; Li, C. Histogram-based image segmentation using variational mode decomposition and correlation coefficients. Signal Image Video Process. 2017, 11, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Gu, G.; Qian, W.; Ren, K.; Chen, Q.; Maldague, X. Infrared Image Enhancement Using Adaptive Histogram Partition and Brightness Correction. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acharya, U.K.; Kumar, S. Directed searching optimized mean-exposure based sub-image histogram equalization for grayscale image enhancement. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 24005–24025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

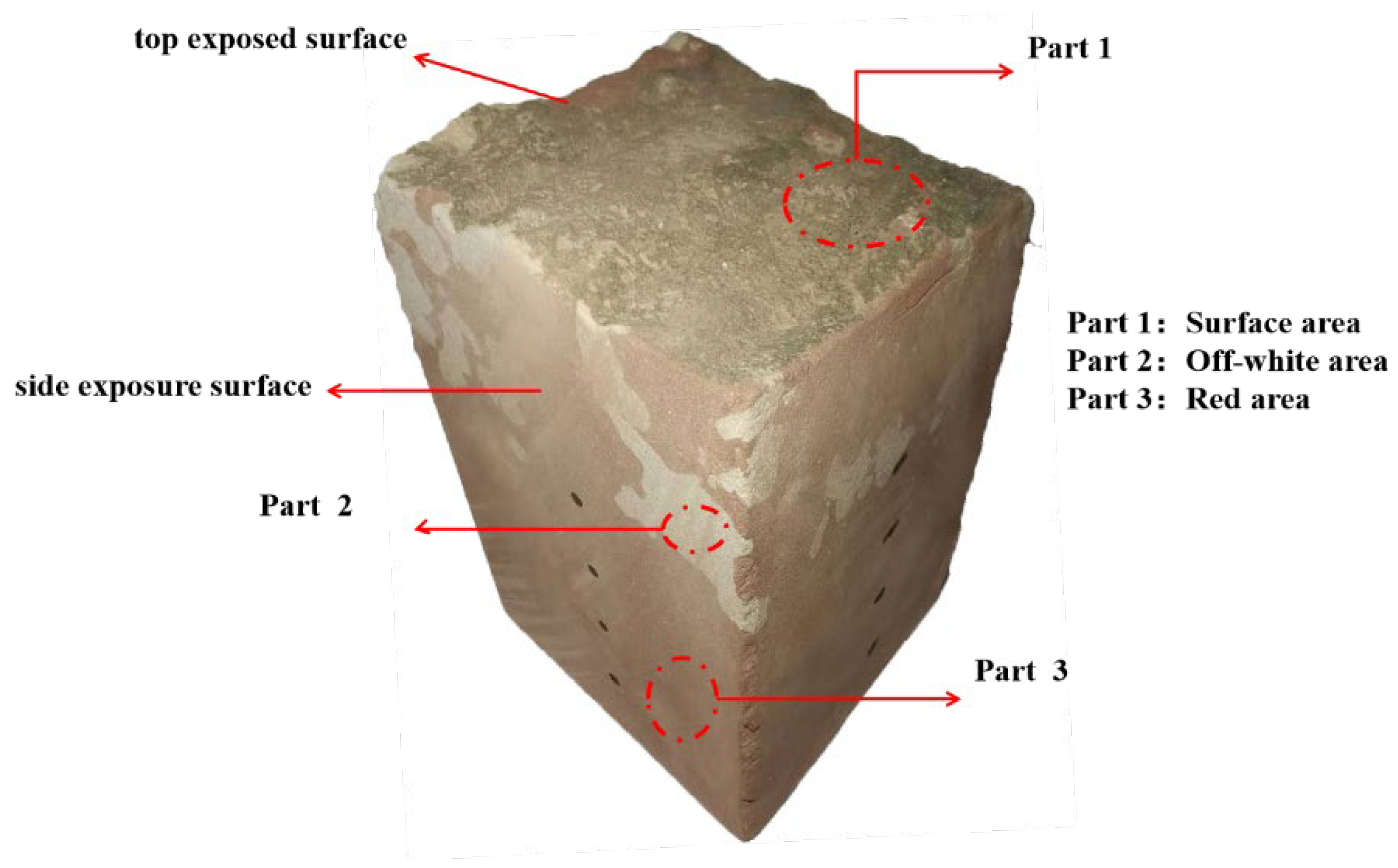


| Main Substances | Microscopic Distribution | |
|---|---|---|
| Part 1 | Chlorite, dolomite, quartz, calcite, feldspar and mica | Dissolved flocculent, fissure, disorderly pore distribution |
| Part 2 | Dolomite, quartz, calcite, feldspar and mica | Broken and messy, with microscopic cracks |
| Part 3 | Quartz, calcite, feldspar and mica | Well-angled micro-grain structure, no significant defects |
| Feature Name | Calculation Formula |
|---|---|
| Average gray level | |
| Standard deviation | |
| Third-order central moment | |
| Homogeneity | |
| Average message size | |
| Maximum probability gray level | |
| Probability of a gray level greater than 200 (Pg > 200) |
| First Layer | Second Layer | Third Layer | Fourth Layer | Fifth Layer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average gray level | 175 | 162 | 158 | 160 | 157 |
| Standard deviation | 668 | 676 | 676 | 688 | 651 |
| Third-order central moment | −140,720 | −113,330 | −96,618 | −106,040 | −95,730 |
| Homogeneity | 0.0068 | 0.0067 | 0.0067 | 0.0066 | 0.0072 |
| Average message size | 2.2200 | 2.2345 | 2.2370 | 2.2426 | 2.2153 |
| Maximum probability gray level | 187 | 169 | 158 | 171 | 169 |
| (Pg > 200) | 0.3089 | 0.2070 | 0.1735 | 0.2034 | 0.1618 |
| GM (1, 1) Model | Predicted Value of | Average Relative Error | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EGM | 0.2947 | 4.9155% | |
| ODGM | 0.3241 | 1.4720% | |
| EDGM | 0.3239 | 1.4591% | |
| DGM | 0.3241 | 1.4802% |
| Feature Parameters of CT Grayscale Images | Degradation Degree | |
|---|---|---|
| True Value + L5 Layer Predicted Value | Simulated Predicted Values | |
| Average gray level | 0.7268 | 0.7821 |
| Standard deviation | 0.7035 | 0.7620 |
| Third-order central moment | 0.7934 | 0.8409 |
| Homogeneity | 0.7024 | 0.7625 |
| Average message size | 0.7020 | 0.7599 |
| Maximum probability gray level | 0.7339 | 0.7912 |
| (Pg > 200) | 0.8581 | 0.8999 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Ao, T.; Cao, K.; Meng, X. Characterization and Degradation of Ancient Architectural Red Sandstone in a Natural Erosion Environment. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9159. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169159
Liu D, Ao T, Cao K, Meng X. Characterization and Degradation of Ancient Architectural Red Sandstone in a Natural Erosion Environment. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(16):9159. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169159
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Dunwen, Tao Ao, Kunpeng Cao, and Xianqing Meng. 2023. "Characterization and Degradation of Ancient Architectural Red Sandstone in a Natural Erosion Environment" Applied Sciences 13, no. 16: 9159. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169159
APA StyleLiu, D., Ao, T., Cao, K., & Meng, X. (2023). Characterization and Degradation of Ancient Architectural Red Sandstone in a Natural Erosion Environment. Applied Sciences, 13(16), 9159. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169159






