Camellia oleifera Fruit Detection Algorithm in Natural Environment Based on Lightweight Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A dataset containing 4750 images of Camellia oleifera fruit was created and expanded to 19,000 images by data enhancement means.
- The original YOLOV5s was improved, including the backbone and the neck network lightweight improvements, activation function optimization to improve the nonlinear expressivity, and loss function optimization to improve the ability to localize objects.
- The effectiveness of the improved method is verified by ablation experiments, and the overall performance of the improved model is evaluated and compared with mainstream algorithms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets Acquisition
2.2. Images Filtrating and Preprocessing
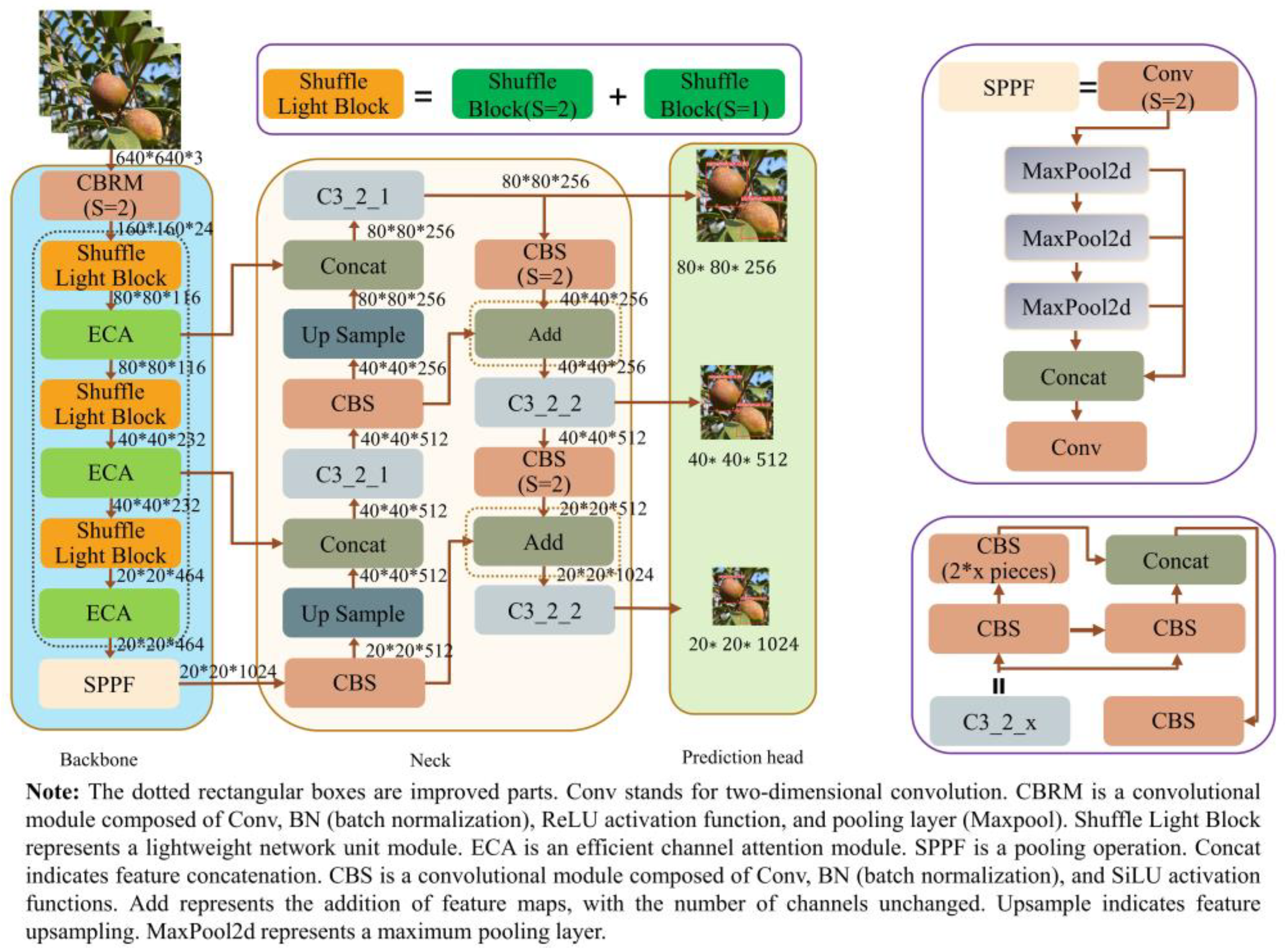
2.3. Camellia Oleifera Fruit Object Detection Algorithm
2.3.1. YOLOv5s-Camellia Detection Model
2.3.2. Lightweight Improvements to the Backbone Network for YOLOv5
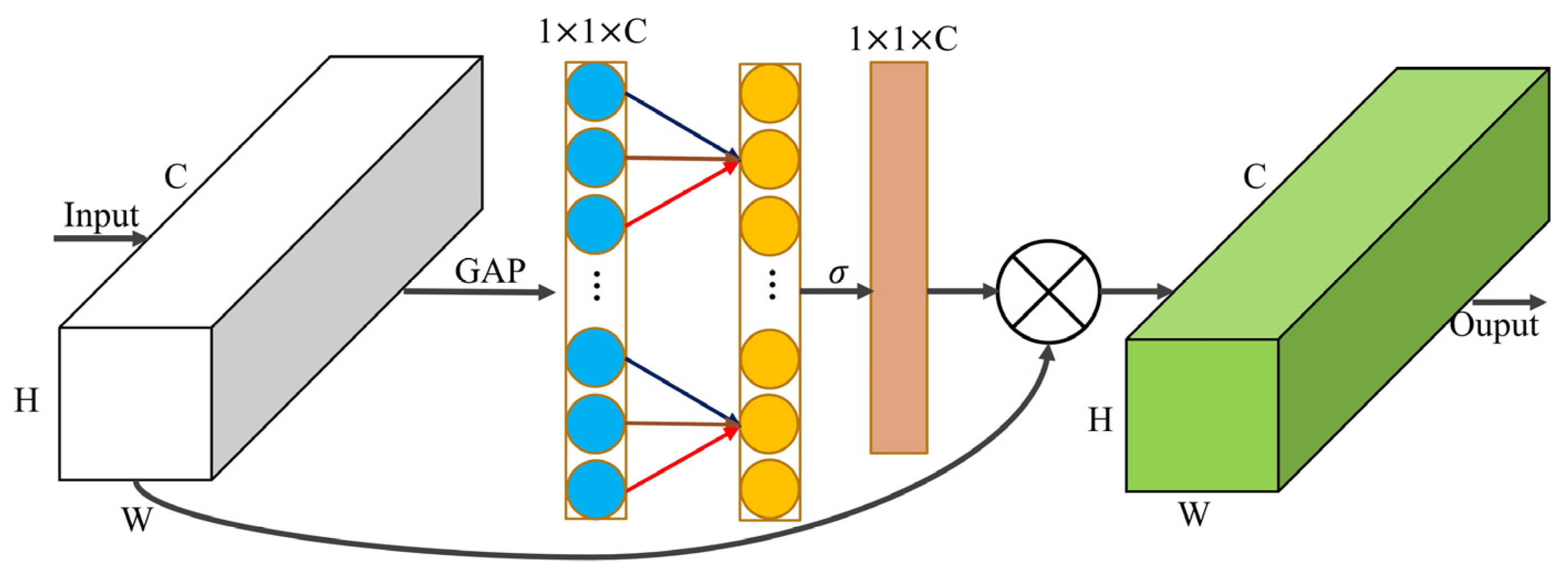
2.3.3. Efficient Channel Attention Mechanism
2.3.4. Improved PAN of the Neck Network
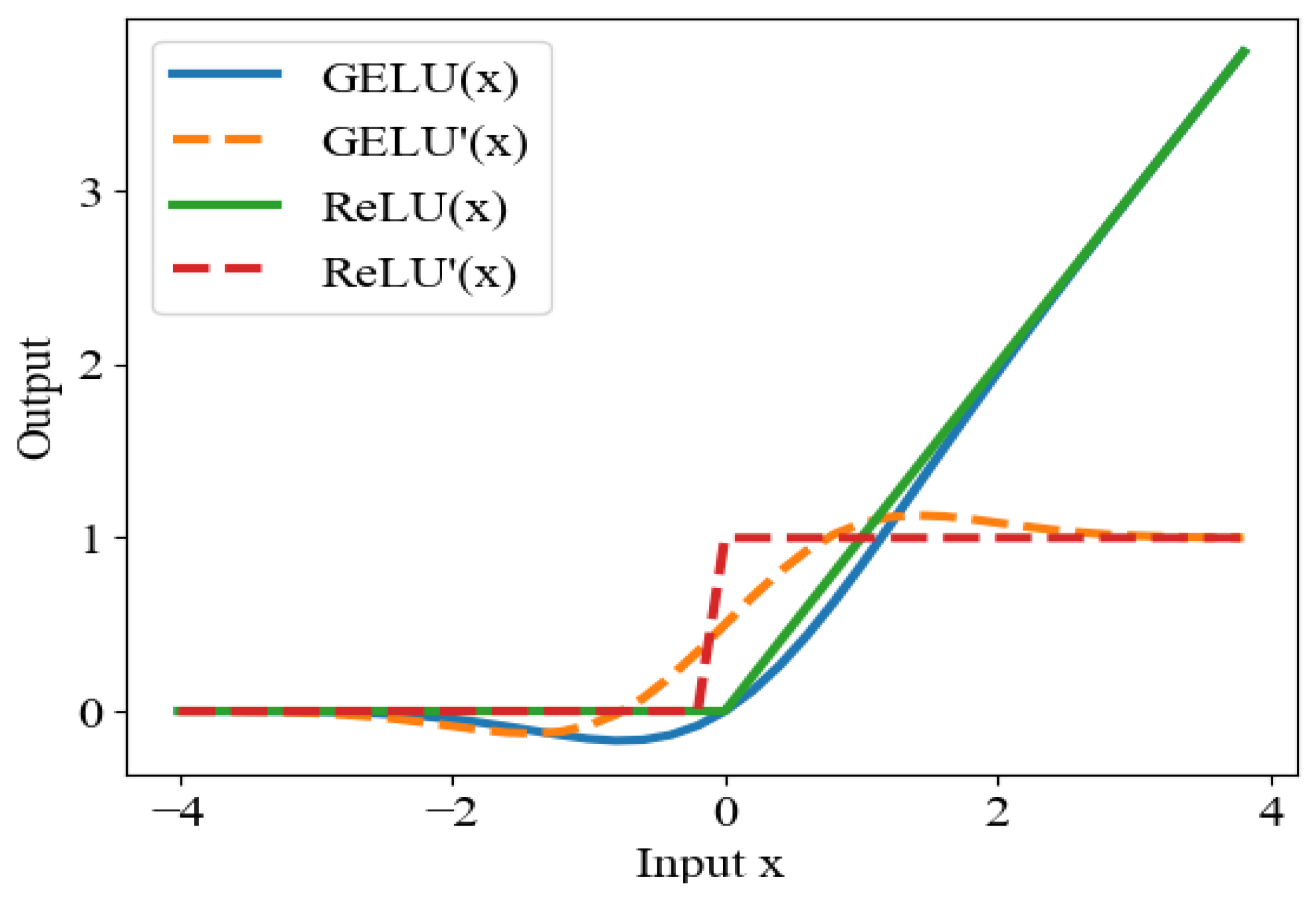
2.3.5. Activation Function Optimization
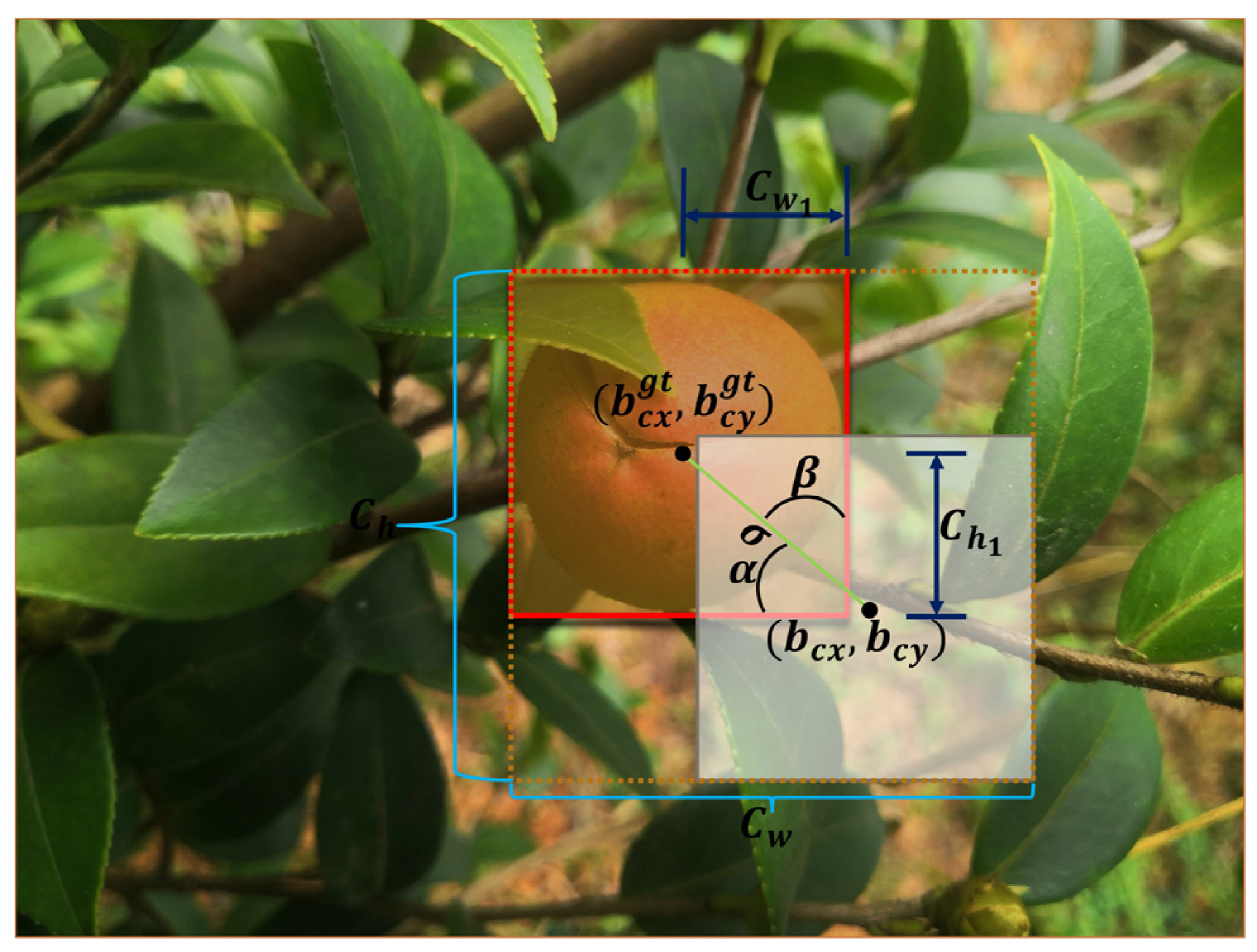
2.3.6. Loss Function Improvement
3. Experiments and Analyses
3.1. Experimental Platform Construction
3.2. Evaluation Indicators
3.3. Ablation Experiments
3.4. Analysis of Improved Model Results
3.5. Performance Comparison of Different Object Detection Algorithms
4. Conclusions
- The unit of the ShuffleNetV2 was introduced as the basic unit of the backbone network, which significantly reduced the number of parameters, computation, and size of the model while saving computational resources and cache space.
- After the model was lightened, the feature extraction ability of Camellia oleifera fruit details was weakened, and the detection performance was improved by embedding three efficient channel attention modules in the backbone network while increasing the number of partial parameters.
- To enhance the neck network’s ability and refine the granularity of feature maps, the Concat dimensional stitching in the PAN was replaced with Add dimensional fusion, which increased the amount of information under each dimension while reducing the number of parameters and maintaining the dimension of the feature map tensor.
- The better nonlinearity of the GELU activation function was used to optimize the model, which improved the characterization ability of the deep neural network. Compared with the ReLU activation function, the nonzero gradient is better able to maintain a smaller negative value, avoiding the problems of gradient disappearance and gradient explosion.
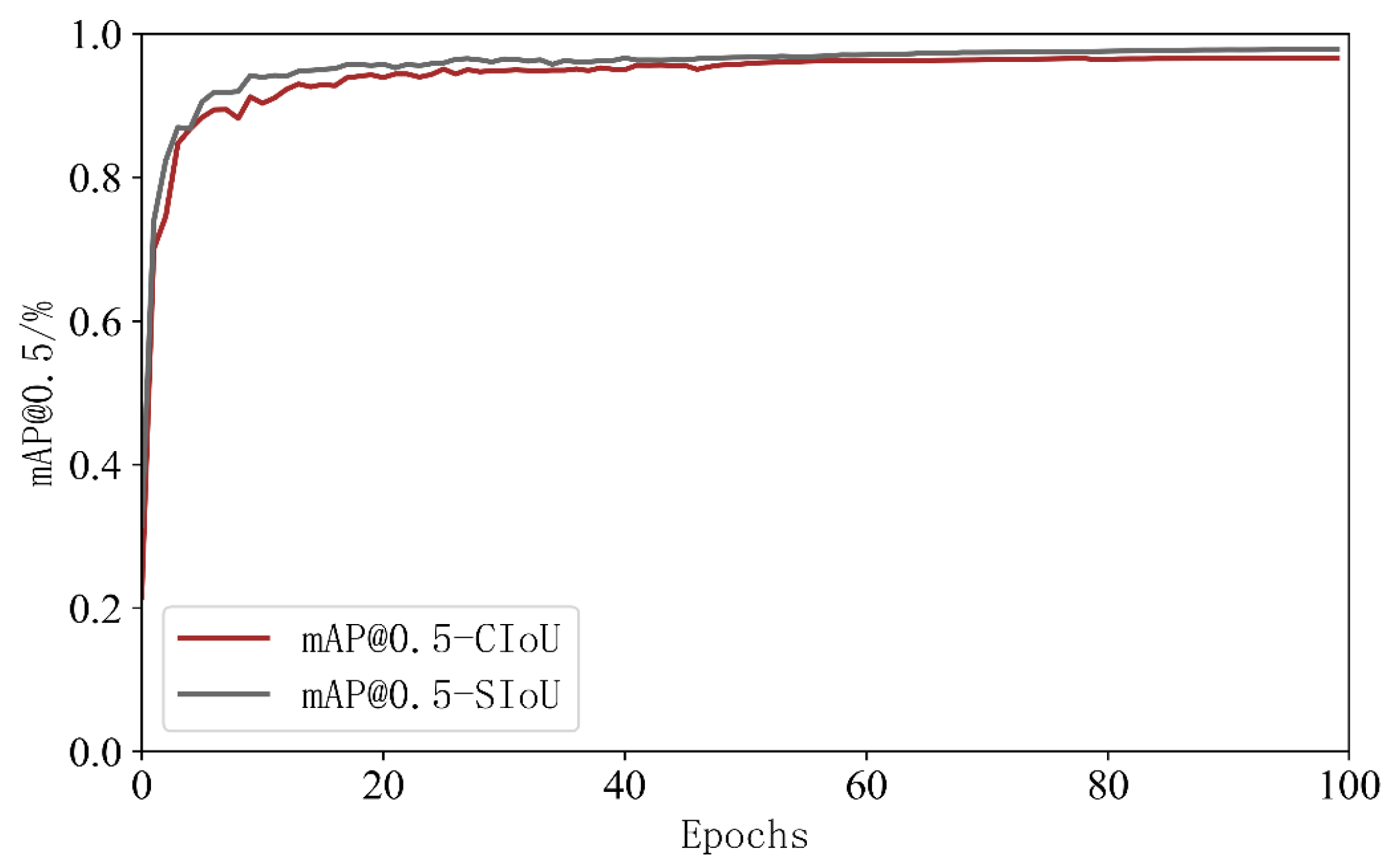
- By introducing the SIoU loss function, the vector angle loss between the ground truth box and the predicted box was added to the bounding box regression loss, which reduced the model error and improved the convergence speed and bounding box regression accuracy. The final average detection accuracy of the model reached 98.8% and the detection speed was 60.98 frame/s. Compared with other object detection algorithms, the comprehensive performance of the YOLOv5s-Camellia was better and can meet the real-time detection requirements.
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rao, H.H.; Wang, Y.L.; Li, Q.S.; Wang, B.Y.; Yang, J.L.; Liu, M.H. Design and Experiment of Camellia oleifera Fruit Layered Harvesting Device. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric Mac. 2021, 52, 203–212. Available online: http://www.j-csam.org/jcsam/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20211021&journal_id=jcsam (accessed on 5 October 2022.).
- Sapra, L.; Sandhu, J.K.; Goyal, N. Intelligent Method for Detection of Coronary Artery Disease with Ensemble Approach. J. Adv. Commun. Comput. Technol. 2021, 668, 11–18. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40747-017-0048-6 (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- Rana, P.; Batra, I.; Malik, A.; Imoize, A.L.; Kim, Y.; Pani, S.K.; Goyal, N.; Kumar, A.; Rho, S. Intrusion Detection Systems in Cloud Computing Paradigm: Analysis and Overview. Complexity 2022, 2022, 3999039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Gupta, D.; Gupta, S.; Uppal, M.; Anand, D.; Ortega-Mansilla, A.; Alharithi, F.S.; Almotiri, J.; Goyal, N. A Deep Learning-Based Intelligent Garbage Detection System Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Symmetry. 2022, 14, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.C.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H.J.; Zhang, Y.Q. Fruit detection and positioning technology for a Camellia oleifera C. Abel orchard based on improved YOLOv4-tiny model and binocular stereo vision. J. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 211, 118573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.C.; Ma, B.L.; Song, L.; Wang, Y.N.; Duan, Y.C.; Song, H.B. Nighttime detection method of polymorphic Camellia oleifera fruits based on YOLON network. J. N. W. A&F Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 51, 1–14. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C45S0n9fL2suRadTyEVl2pW9UrhTDCdPD66SiUpAuf8Bk08bs0aFBNWmLyxqJGMvQZI-DYFmge5uZAFqqnoOxDZN&uniplatform=NZKPT (accessed on 22 February 2023).
- WANG, L.; Hou, Y.F.; He, J. Target Recognition and Detection of Camellia oleifera Fruit in Natural Scene Based on Mask-RCNN. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2022, 43, 148–154. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C44YLTlOAiTRKibYlV5Vjs7iJTKGjg9uTdeTsOI_ra5_XWoeTkBDDiZyEr12KcpOhrgb9KsyIs7KlfowkNwkNRx5&uniplatform=NZKPT (accessed on 24 October 2022).
- Song, H.B.; Wang, Y.N.; Wang, Y.F.; Lv, S.C.; Jiang, M. Camellia oleifera Fruit Detection in Natural Scene Based on YOLO v5s. Trans. Chin Soc Agric Mach. 2022, 53, 234–242. Available online: http://www.j-csam.org/jcsam/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20220724&journal_id=jcsam (accessed on 24 October 2022).
- Chen, B.; Wang, Y.L.; Li, Q.S.; Wang, B.Y.; Yang, J.L.; Liu, M.H. Study on Detection of Camellia oleifera Fruit in Natural Environment Based on Faster R CNN. Acta. Agric. JX 2021, 33, 67–70. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C44YLTlOAiTRKibYlV5Vjs7iy_Rpms2pqwbFRRUtoUImHa_XfV1B1hbSSmFX7alT4YCqO1eVRcLO9JnimIKxHru-&uniplatform=NZKPT (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Hu, G.R.; Zhou, J.G.; Chen, C.; Li, C.; Sun, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J. Fusion of The Lightweight Network and Visual Attention Mechanism to Detect Apples in Orchard Environment. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 131–142. Available online: http://www.tcsae.org/nygcxb/article/abstract/20221915?st=search (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.X.; Shi, J.; Bai, X.P.; Zhou, Y.J. Lightweight Real-time Apple Detection Method Based on Improved YOLOv4. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2022, 53, 294–302. Available online: http://www.j-csam.org/jcsam/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20220831&journal_id=jcsam (accessed on 27 December 2022).
- Wang, Y.T.; Xue, J.R. Lightweight Object Detection Method for Lingwu Long Jujube Images Based on Improved SSD. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 173–182. Available online: http://www.tcsae.org/nygcxb/article/abstract/20211920?st=search (accessed on 17 December 2022).
- Zhang, X.M.; Zhu, D.L.; Yu, M.S. Lightweight Detection Model of Maize Tassel in UAV Remote Sensing Image. Acta. Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2022, 44, 461–472. Available online: https://www.sciengine.com/JXNYDXXB/doi/10.13836/j.jjau.2022048 (accessed on 16 April 2023).
- Peng, H.X.; Xu, H.M.; Liu, H.N. Lightweight Agricultural Crops Pest Identification Model Using Improved ShuffleNetV2. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 161–170. Available online: http://www.tcsae.org/nygcxb/article/abstract/20221118?st=search (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- Li, Z.T.; Sun, J.B.; Yang, K.W.; Xiong, D.H. A Review of Adversarial Robustness Evaluation for Image Classification. J. Comp. Res. Dev. 2022, 59, 2164–2189. Available online: https://crad.ict.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.7544/issn1000-1239.20220507 (accessed on 8 September 2023).
- Nanni, L.; Paci, M.; Brahnam, S.; Lumini, A. Comparison of Different Image Data Augmentation Approaches. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, N.E.; Loey, M.; Mirjalili, S. A comprehensive survey of recent trends in deep learning for digital images augmentation. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 2351–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.K.; Zhu, Y.C.; Liu, L.P.; Huang, Q. Research Review of Space-Frequency Domain Image Enhancement Methods. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2022, 58, 23–32. Available online: http://cea.ceaj.org/CN/Y2022/V58/I11/23 (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- Zhou, T.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, J.; Wang, C.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, Y. Detection of Residual Film on the Field Surface Based on Faster R-CNN Multiscale Feature Fusion. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cui, J.; Liu, H.; Han, Y.; Ai, H.; Dong, C.; Zhang, J.; Chu, Y. Weed Identification in Soybean Seedling Stage Based on Optimized Faster R-CNN Algorithm. Agriculture 2023, 13, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Huang, Y.; Yin, Y. SE-Mask R-CNN: An Improved Mask R-CNN for Apple Detection and Segmentation. J. Intell. Fuzzy. Syst. 2021, 41, 6715–6725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; He, Z.; Fan, H.; Sun, K. Detection of Cattle Key Parts Based on the Improved Yolov5 Algorithm. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Qi, J.; Zhang, J.; Shao, H.; Yang, J.; Li, X. A Real-Time Detection Algorithm for Kiwifruit Defects Based on YOLOv5. Electronics 2021, 10, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, R.; Lin, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, S.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, S.; Zou, X. Plant Disease Recognition Model Based on Improved YOLOv5. Agronomy 2022, 12, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Ma, Z.; Ye, B.; Yu, G.; Tang, T.; Zheng, M. Detection of Green Asparagus in Complex Environments Based on the Improved YOLOv5 Algorithm. Sensors 2023, 23, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Lu, X.; Huang, J.; Zhou, J.; Jiao, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, F.; Su, B.; Gu, P. A Multi-Source Data Fusion Decision-Making Method for Disease and Pest Detection of Grape Foliage Based on ShuffleNet V2. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Fu, C.; Zhai, Y.; Li, J.; Jin, Z.; Xu, Y. Identification of Rice Leaf Disease Using Improved ShuffleNet V2. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2023, 75, 4501–4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, L.; Shen, J.; Xiao, X.; Liu, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Li, D. Improved Neural Network with Spatial Pyramid Pooling and Online Datasets Preprocessing for Underwater Target Detection Based on Side Scan Sonar Imagery. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Pang, Y.; Nie, J.; Cao, J.; Han, J. Latent Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2022, 25, 2153–2163. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9684715 (accessed on 2 April 2023). [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Li, X.; Feng, Y.; Han, S. Multiple attentional path aggregation network for marine object detection. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 2434–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, Q. Fast 3D-CNN Combined with Depth Separable Convolution for Hyperspectral Image Classification. J. Front. Comp. Sci. Technol. 2022, 16, 2860–2869. Available online: http://fcst.ceaj.org/CN/10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2103051 (accessed on 4 March 2023).
- Chu, K.; Wang, L.; Ma, D.; Zhang, Z.N. Research on Application of Depthwise Separable Convolution in Android Malware Classification. Appl. Res. Comp. 2022, 39, 1534–1540. Available online: https://www.arocmag.com/article/01-2022-05-043.html (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Jang, J.-G.; Quan, C.; Lee, H.D.; Kang, U. Falcon: Lightweight and accurate convolution based on depthwise separable convolution. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2023, 65, 2225–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.B.; Ma, B.L.; Shang, Y.Y.; Wen, Y.C.; Zhang, S.J. Detection of Young Apple Fruits Based on YOLOv7-ECA Model. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric Mac. 2023, 54, 233–242. Available online: http://www.j-csam.org/jcsam/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20230624&journal_id=jcsam (accessed on 11 September 2023).
- Sarkar, A.K.; Tan, Z.-H. On Training Targets and Activation Functions for Deep Representation Learning in Text-Dependent Speaker Verification. Acoustics 2023, 5, 693–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.L.; Liu, F.H.; Wu, W.Y.; Li, C.; Xiao, P.; Liu, C. Wood Surface Defect Recognition Based on ViT Convolutional Neural Network. Comp. Sci. 2022, 49, 609–614. Available online: https://www.jsjkx.com/CN/10.11896/jsjkx.211100090 (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Gevorgyan, Z. SIoU Loss: More Powerful Learning for Bounding Box Regression. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.12740. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhan, R.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J. LMSD-YOLO: A Lightweight YOLO Algorithm for Multi-Scale SAR Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Yang, Z.; He, M. Recognizing apple targets before thinning using improved YOLOv7. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. (Trans. CSAE) 2023, 39, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Designation | Environment Configuration |
|---|---|
| Operating System | Windows11 |
| CPU | Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-9400F |
| GPU | GeForceRTX3070Ti(8GB) |
| Development Framework | Pytorch1.7.1 |
| Development Environment | Anaconda, Python3.9, CUDA11.3, OpenCV4.5.2 |
| Model | FLOPs/(G) | Parameters | Size/MB | Layers | mAP@0.5/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5s | 15.8 | 7,012,822 | 14.5 | 213 | 98.4 |
| YOLOv5s + ShuffleNet | 5.3 | 2,898,610 | 6.2 | 184 | 96.9 |
| YOLOv5s + ShuffleNet + ECA | 5.7 | 3,137,679 | 6.7 | 187 | 98.1 |
| YOLOv5s + ShuffleNet + ECA + Add | 5.5 | 2,973,839 | 6.3 | 187 | 98.2 |
| YOLOv5s + ShuffleNet+ECA + Add + GELU | 5.5 | 2,973,839 | 6.3 | 187 | 98.5 |
| Model | Improvement Factors | Evaluation Indicators | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Backbone Improvement | SIoU | PAN Improvement | P/% | R/% | mAP@0.5/% | F1 Score | |
| YOLOv5s | × | × | × | 98.2 | 97.7 | 98.4 | 97.94 |
| YOLOv5s-B | √ | × | × | 96.3 | 95.4 | 98.1 | 95.84 |
| YOLOv5s-B-P | √ | × | √ | 97.2 | 95.1 | 98.5 | 96.14 |
| YOLOv5s-Camellia | √ | √ | √ | 98.6 | 97.4 | 98.8 | 97.99 |
| Model | Evaluation Indicators | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP@0.5/% | Average Single Image Detection Time/s | Speed/ (Fame/s) | Size/MB | |
| YOLO v5s | 98.4 | 0.035 | 25.77 | 14.5 |
| YOLO v4-tiny | 89.9 | 0.025 | 40.45 | 23.1 |
| YOLO v5s-EfficientNet | 98.3 | 0.027 | 33.56 | 6.3 |
| Faster R CNN | 94.3 | 3.6 | 0.03 | 108 |
| YOLOv5s-Camellia | 98.8 | 0.014 | 60.98 | 6.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Kang, L.; Rao, H.; Nie, G.; Tan, Y.; Liu, M. Camellia oleifera Fruit Detection Algorithm in Natural Environment Based on Lightweight Convolutional Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10394. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131810394
Li Z, Kang L, Rao H, Nie G, Tan Y, Liu M. Camellia oleifera Fruit Detection Algorithm in Natural Environment Based on Lightweight Convolutional Neural Network. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(18):10394. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131810394
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zefeng, Lichun Kang, Honghui Rao, Ganggang Nie, Yuhan Tan, and Muhua Liu. 2023. "Camellia oleifera Fruit Detection Algorithm in Natural Environment Based on Lightweight Convolutional Neural Network" Applied Sciences 13, no. 18: 10394. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131810394
APA StyleLi, Z., Kang, L., Rao, H., Nie, G., Tan, Y., & Liu, M. (2023). Camellia oleifera Fruit Detection Algorithm in Natural Environment Based on Lightweight Convolutional Neural Network. Applied Sciences, 13(18), 10394. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131810394




