Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Cement Blended with TEOS/PVP Nanofibers Containing CNTs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Materials
2.2. Polymer Solution
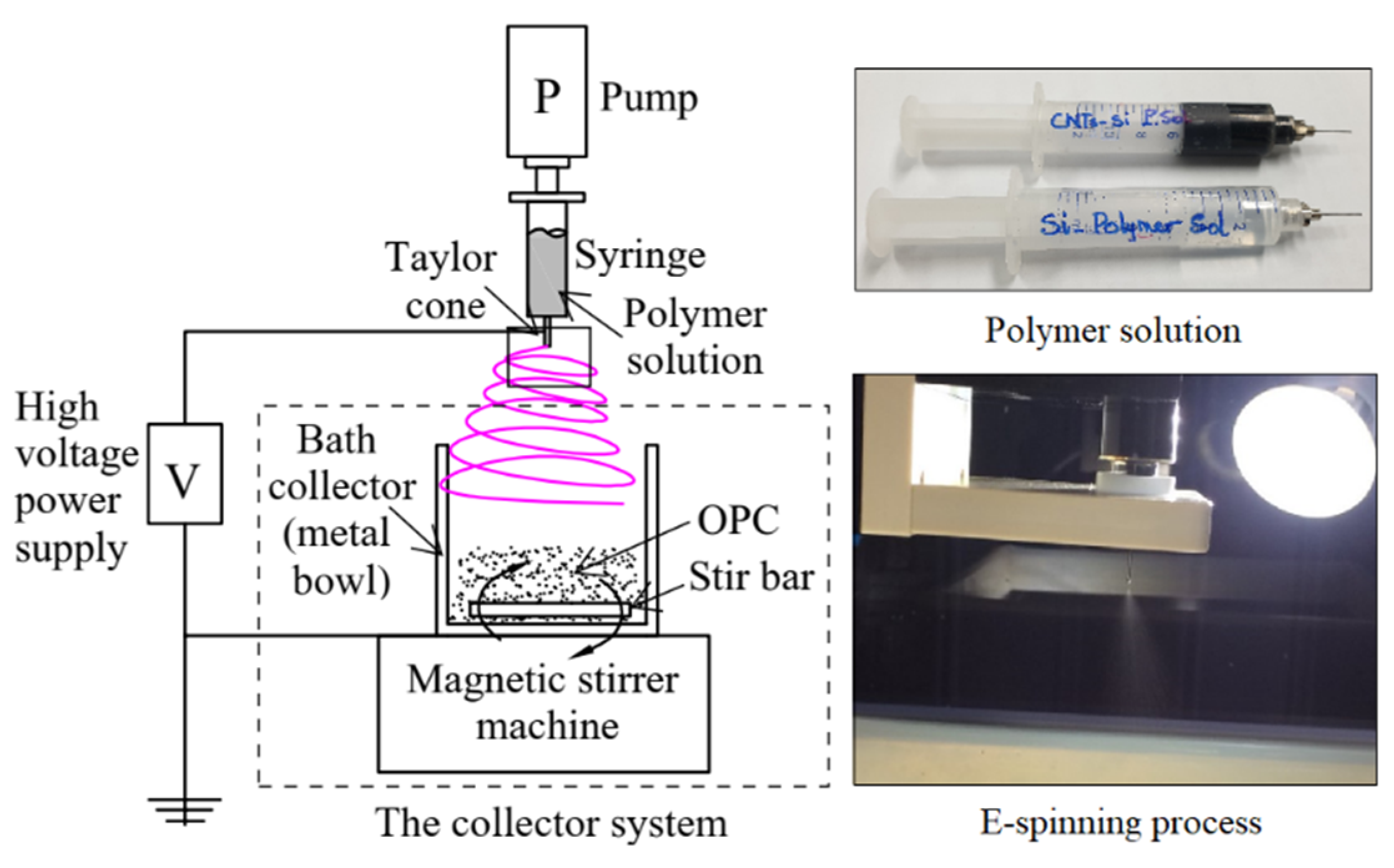
2.3. Electrospinning Process
2.4. Hardened Cement Pastes Preparation
2.5. Apparatus and Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
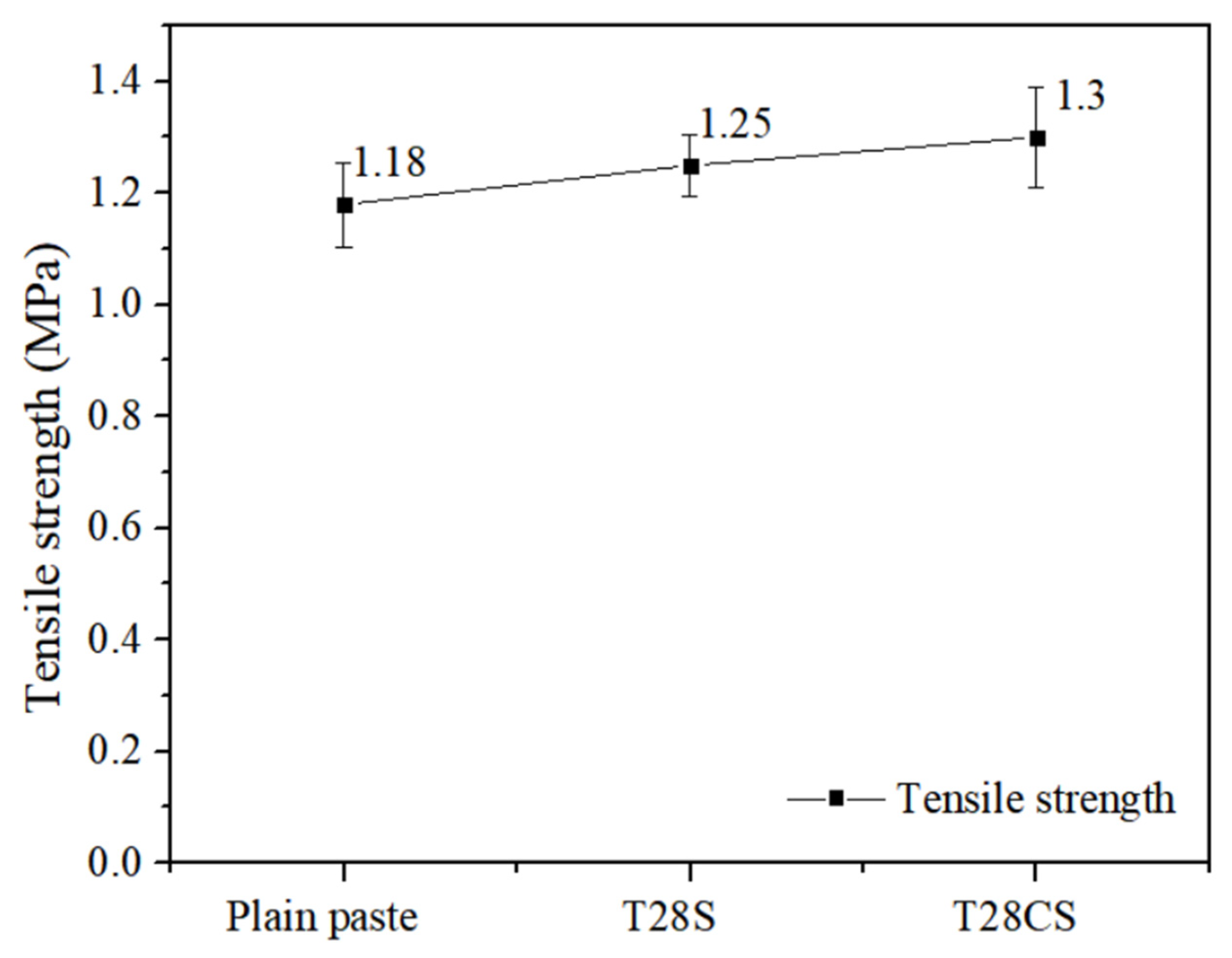
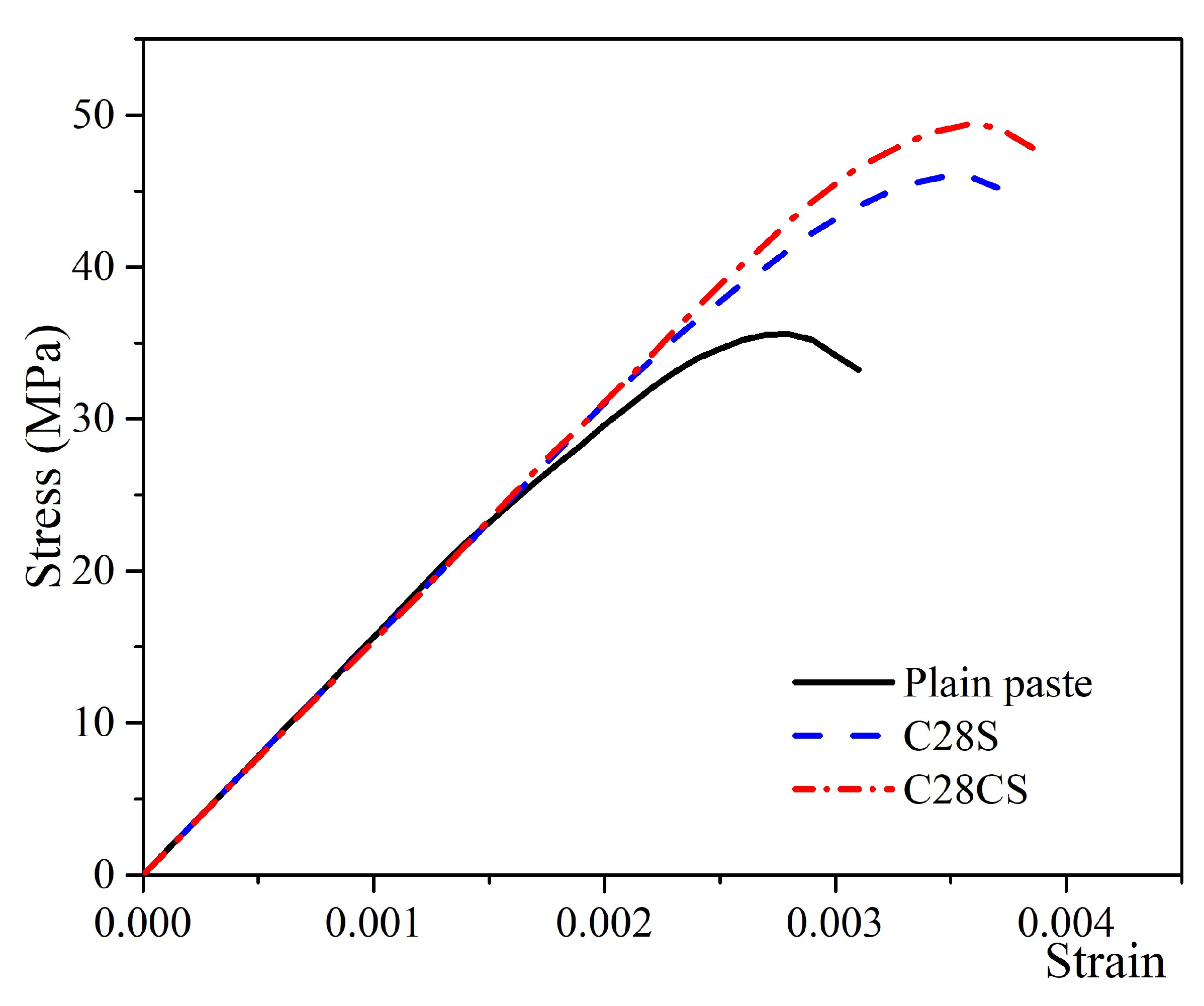
3.1. Tensile and Compressive Strength
3.2. Morphological Characteristics of Nanofibers
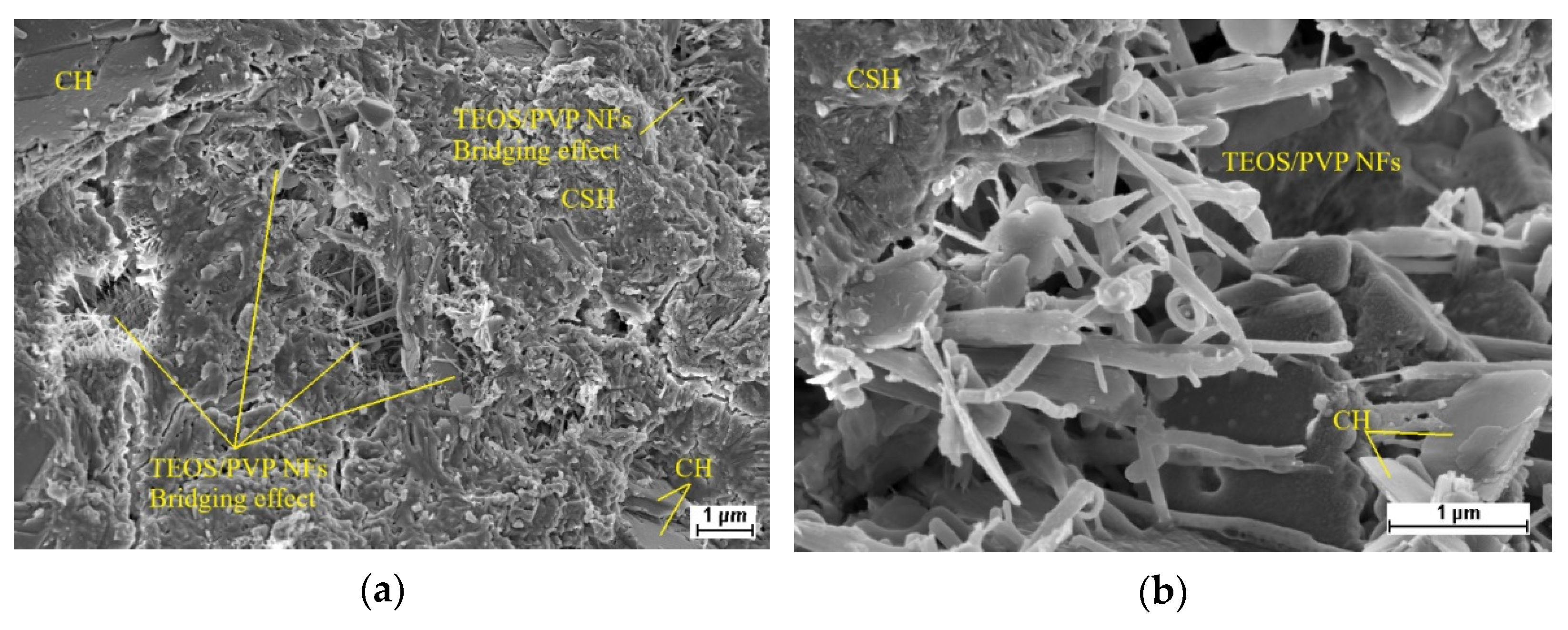
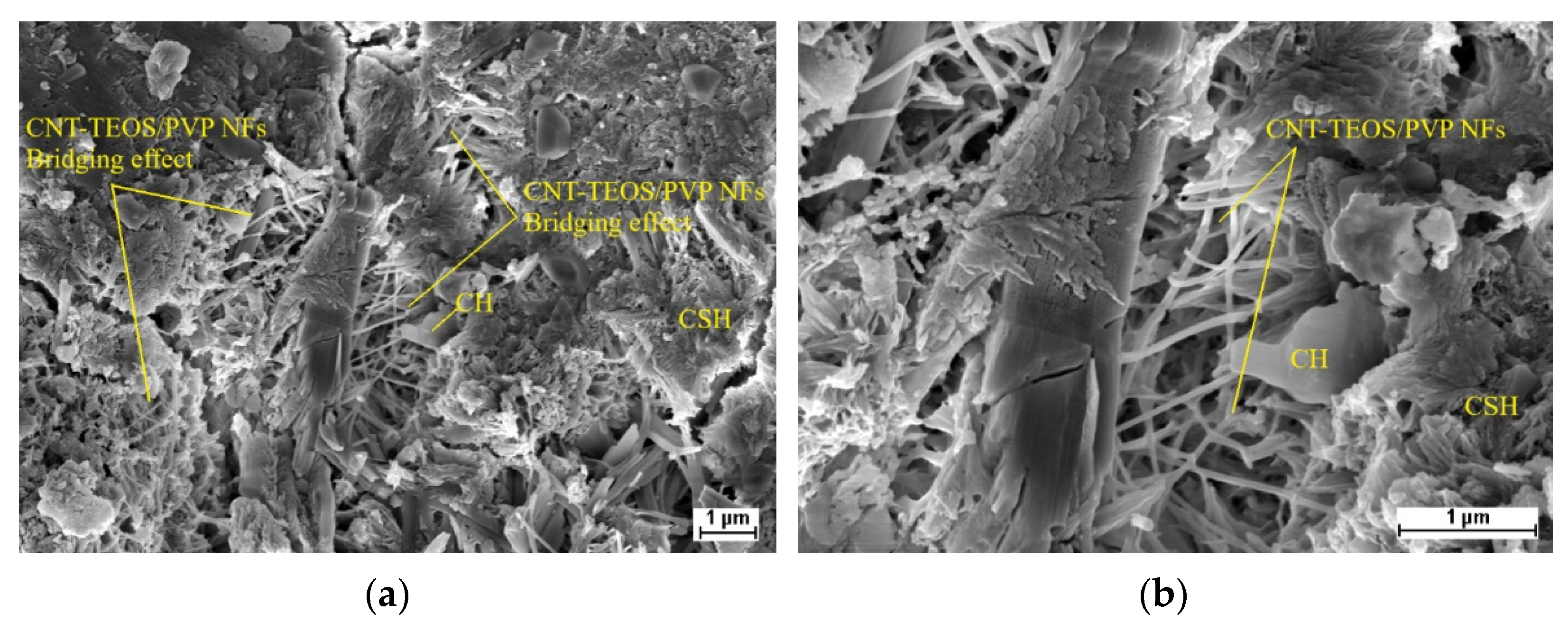
3.3. Microstructure of Hardened Cement Pastes
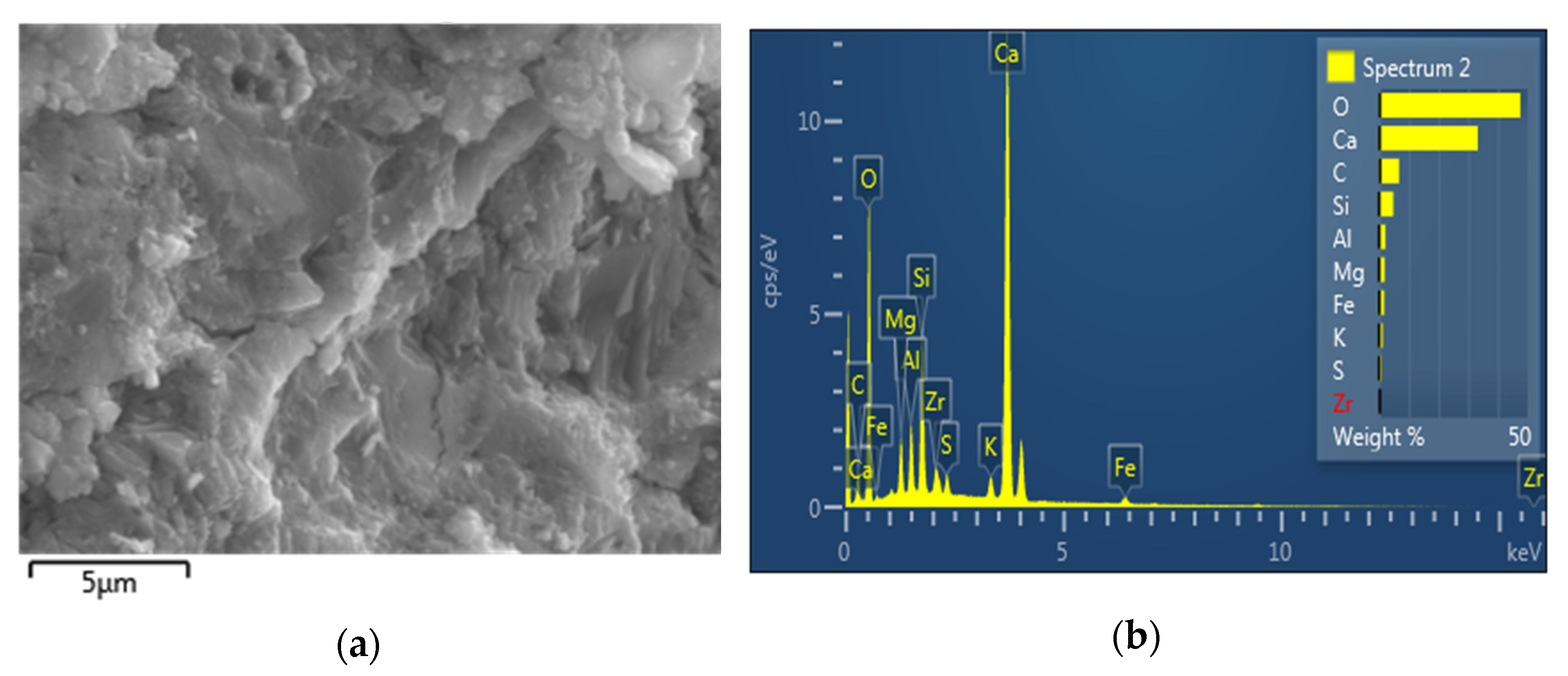
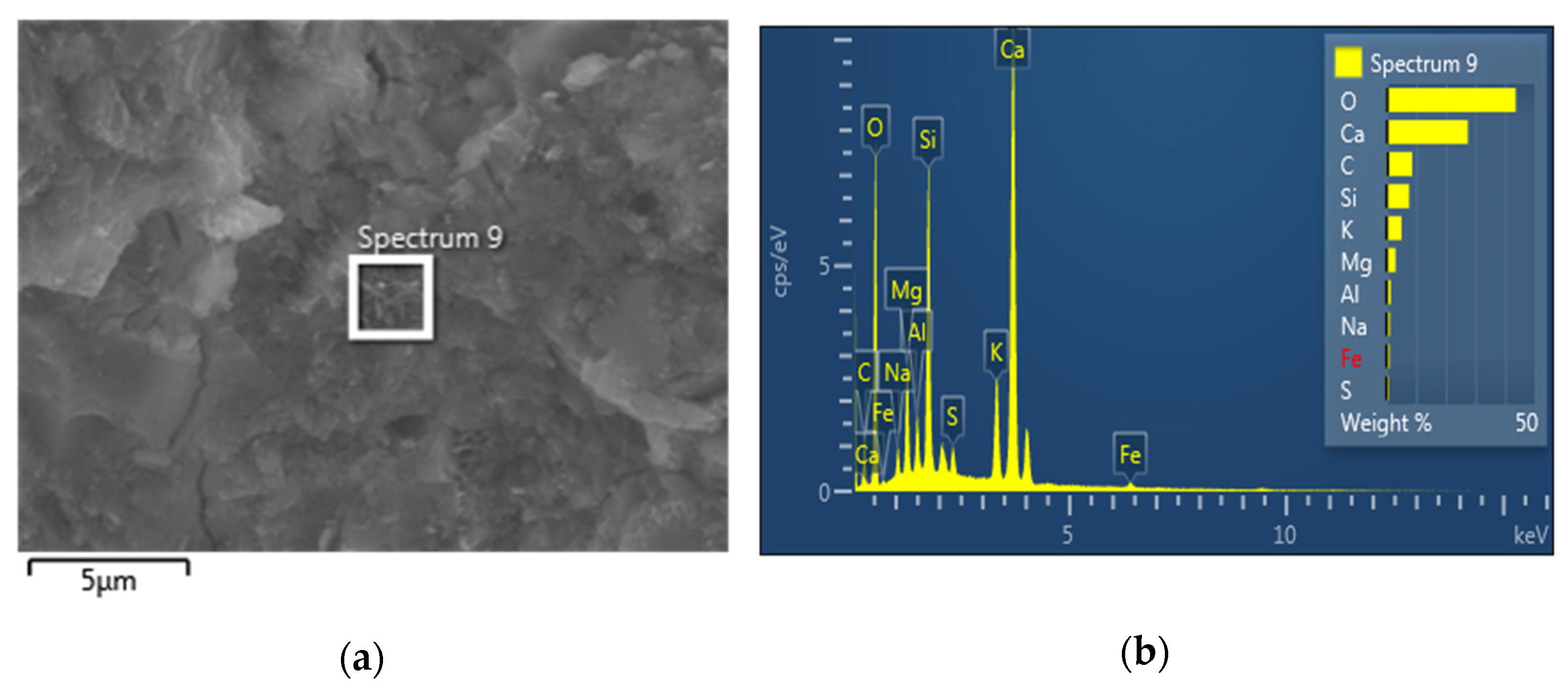
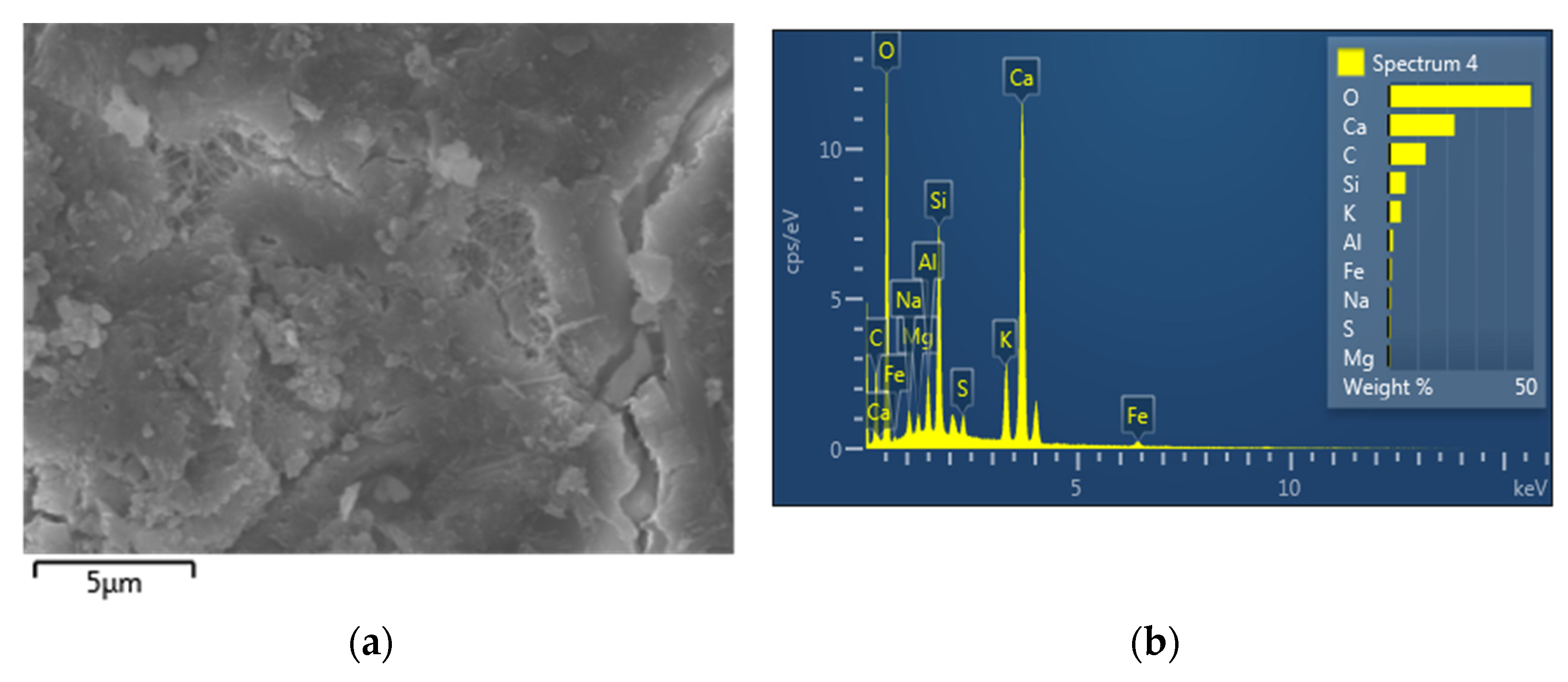
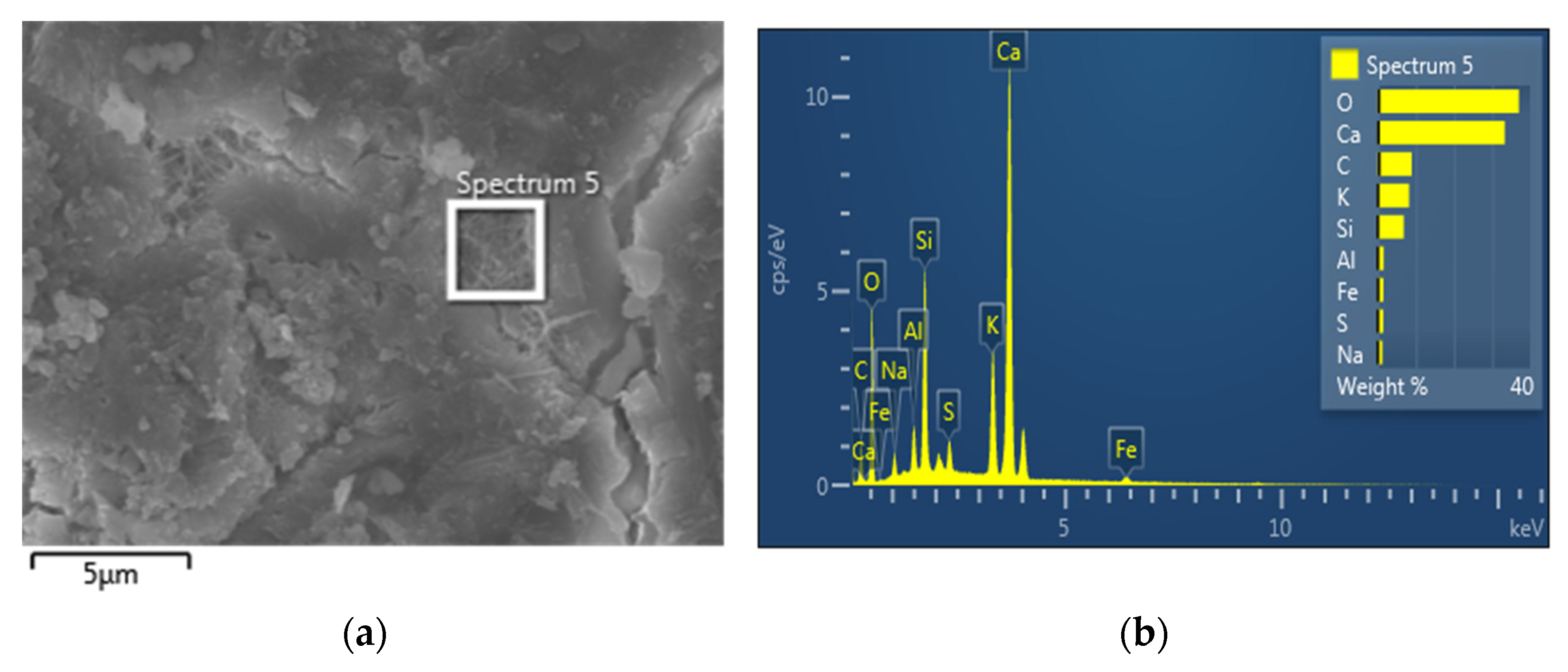
3.4. EDS Analysis
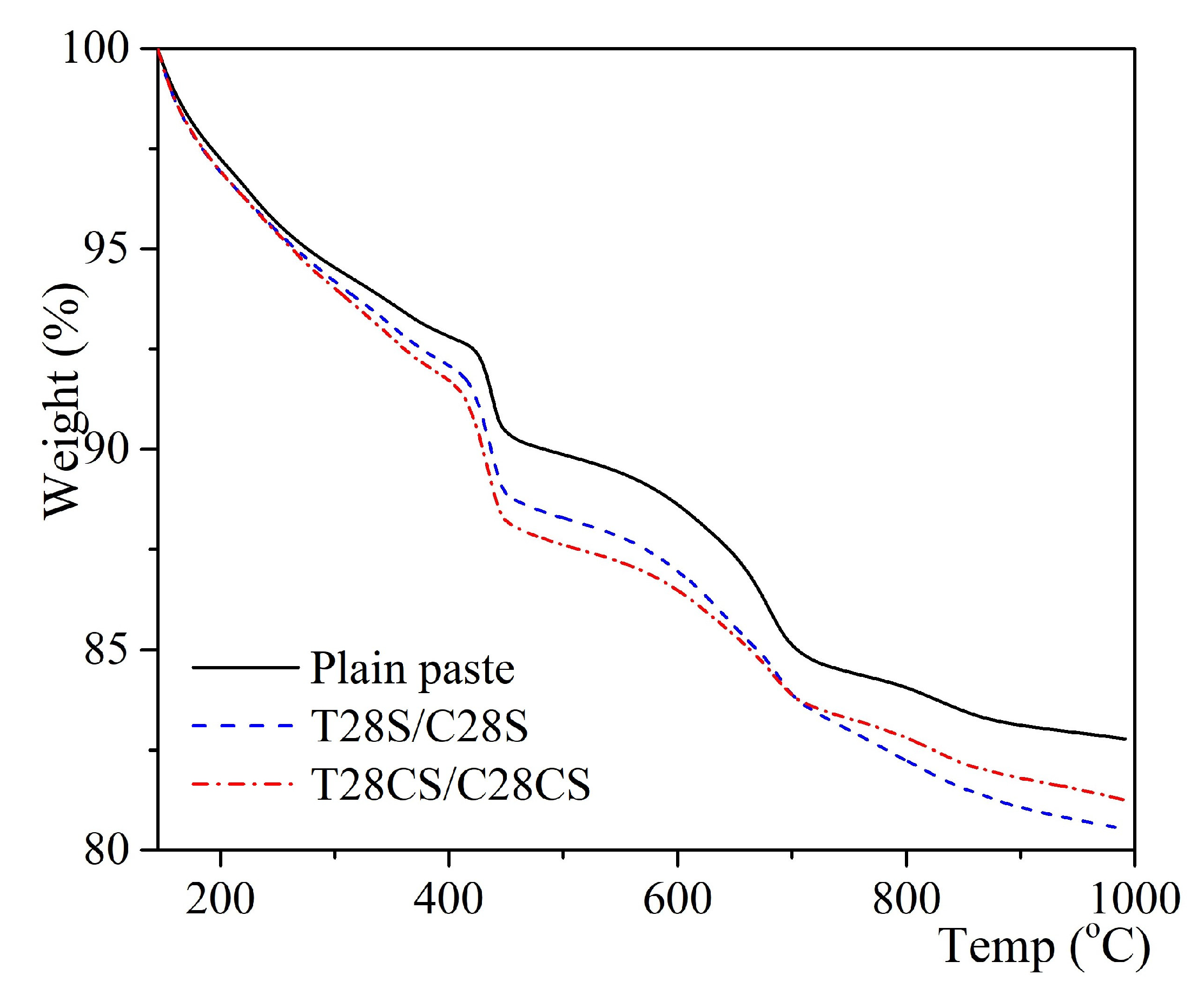
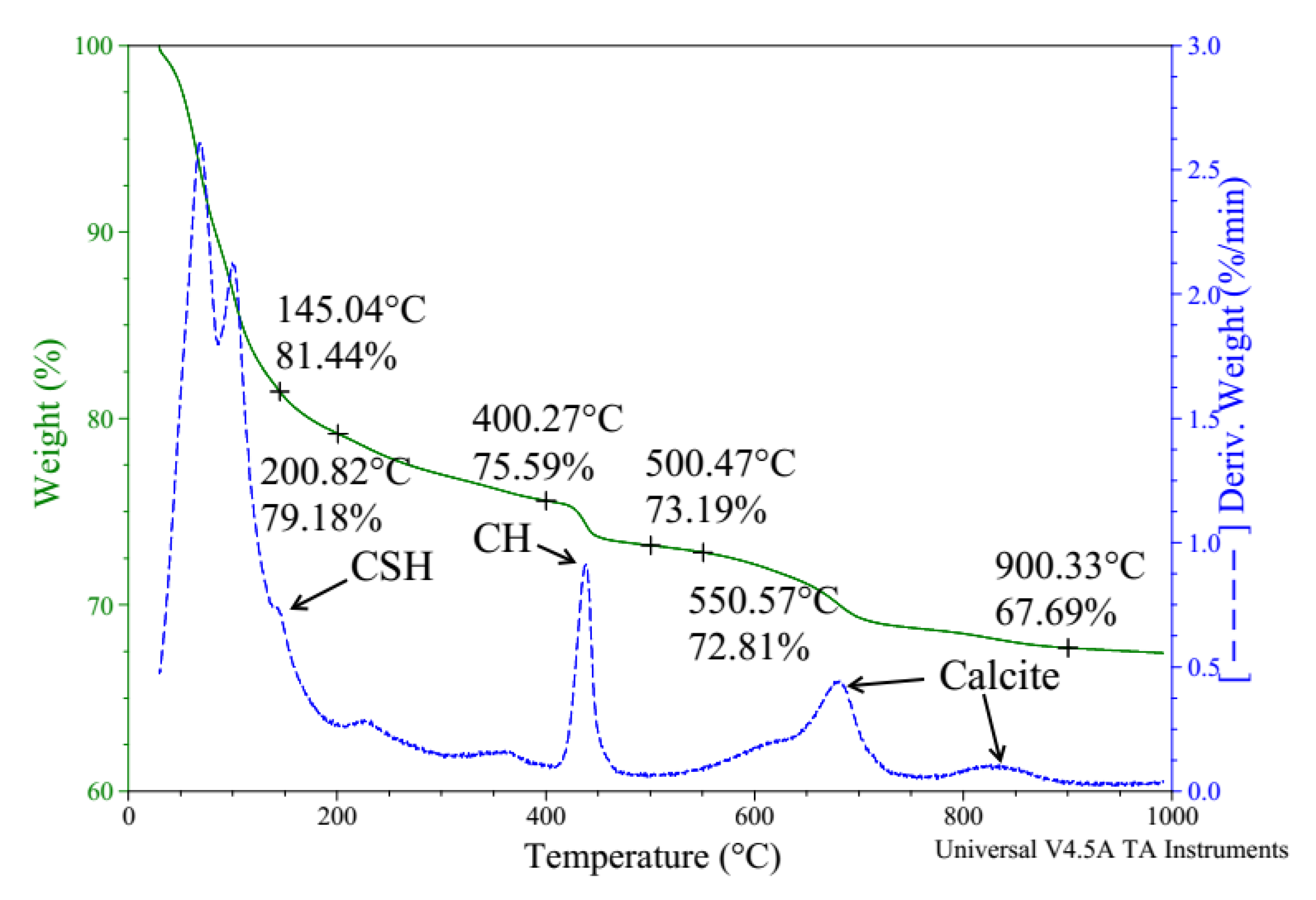
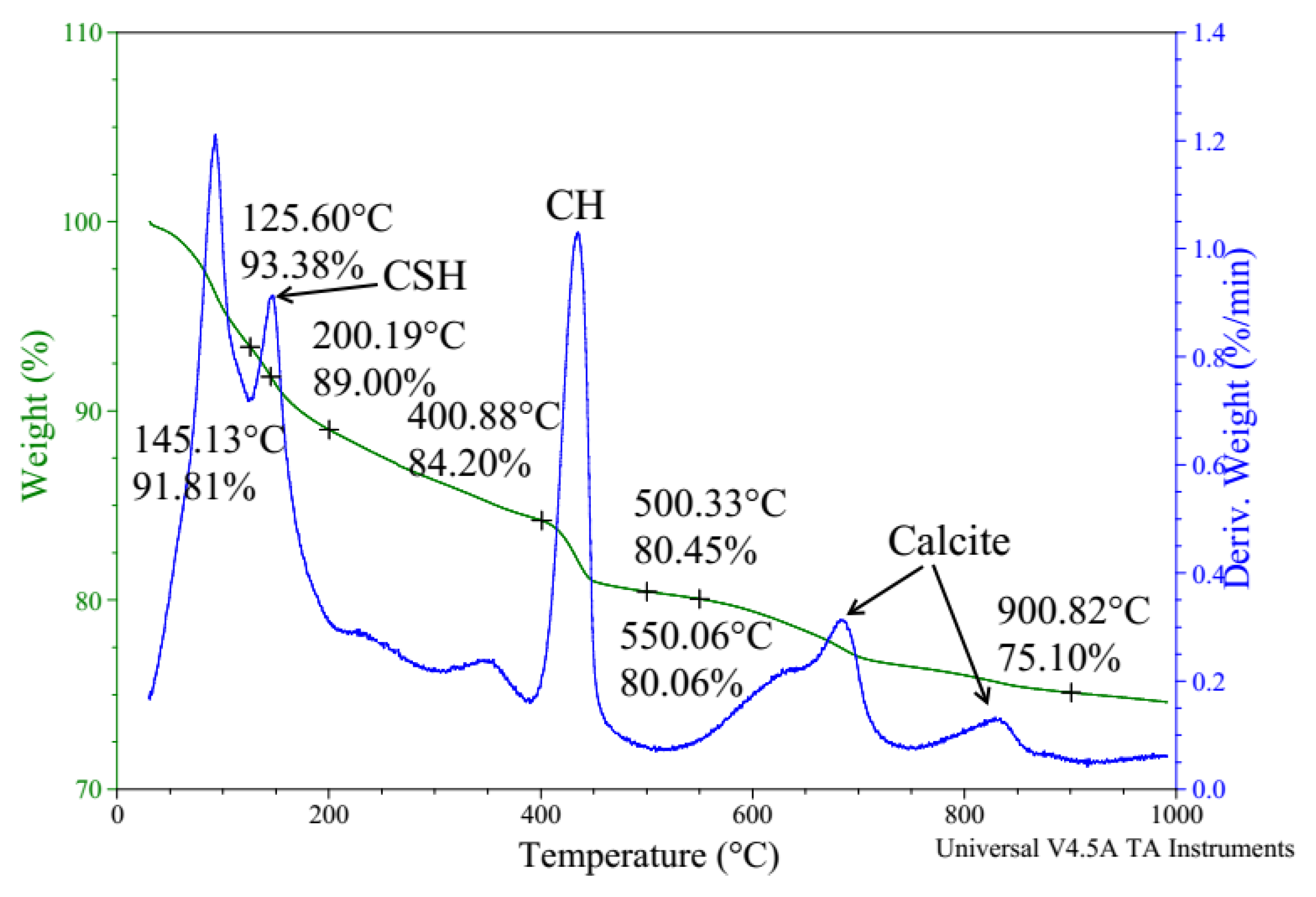
3.5. Thermal Analysis
4. Conclusions
- -
- According to results from mechanical strength testing, adding TEOS/PVP NFs and CNT-TEOS/PVP NFs to cementitious materials results in an increase in compressive strength of 28% and 38% and in toughness characteristics of 54% and 66%, respectively;
- -
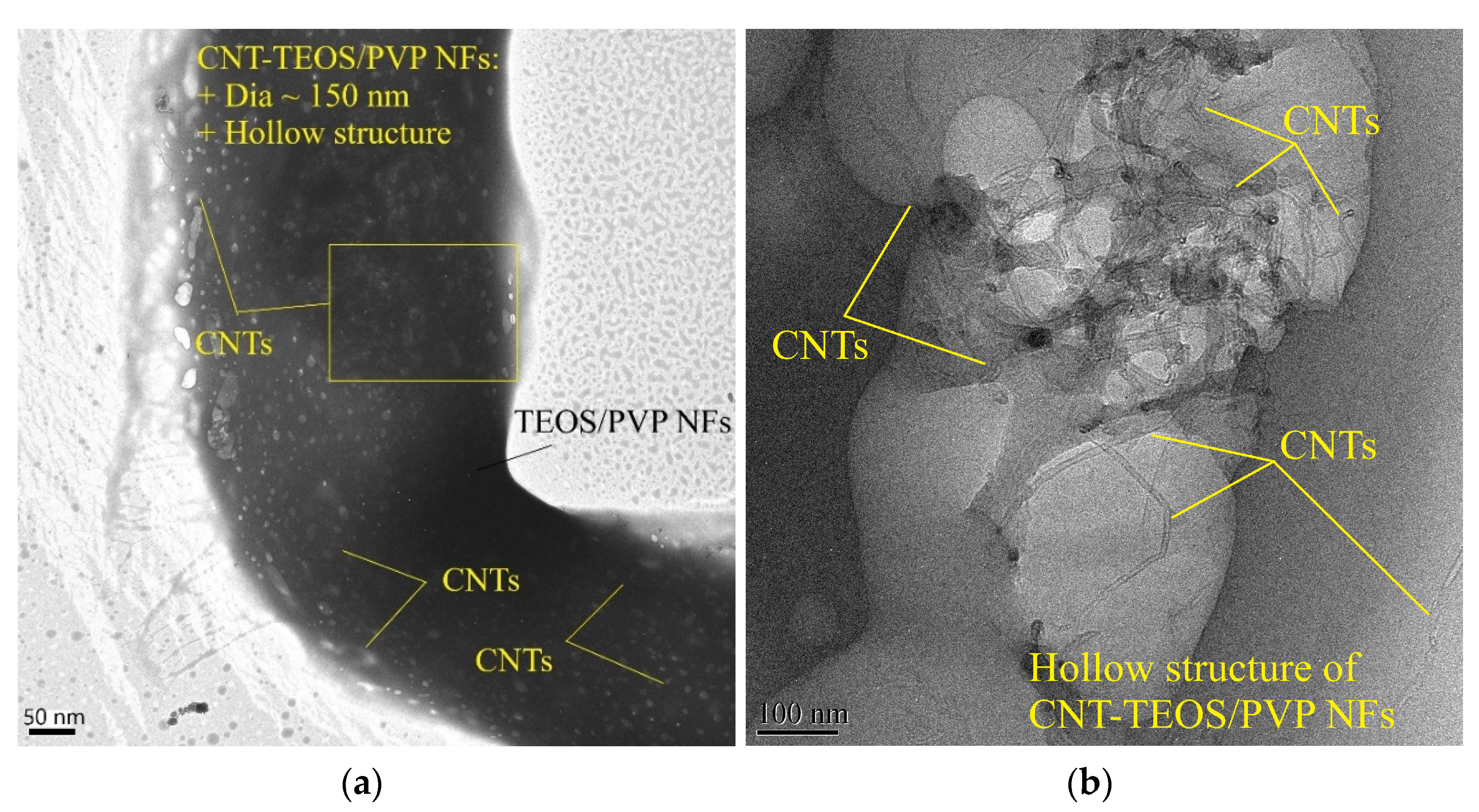
- We observed our proposed nanofibers’ morphology using SEM and TEM studies. We discovered that TEOS/PVP NFs had a hollow structure by examining TEM images. Additionally, the existence of CNTs was clear;
- -
- We discovered the bridging effect of fibers inside the matrix through SEM images. Additionally, through our EDS and TGA observations, we assessed the change in cement hydrates’ proportions and the more compacted structures of the modified cement pastes. Based on these microstructure observations, we showed that a higher percentage of cement hydrates combined with the more compacted structure is commensurate with, the higher compressive strength of our survey’s samples.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamada, H.M.; Al-Attar, A.; Shi, J.; Yahaya, F.; Al Jawahery, M.S.; Yousif, S.T. Optimization of sustainable concrete characteristics incorporating palm oil clinker and nano-palm oil fuel ash using response surface methodology. Powder Technol. 2023, 413, 118054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhu, X.; Liu, B.; Shi, J.; Gencel, O.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Mechanical property and durability of engineered cementitious composites (ECC) with nano-material and superabsorbent polymers. Powder Technol. 2022, 409, 117839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shen, J.; Liu, J.; Lu, S.; He, G. Influence of carbon nanofiber content and sodium chloride solution on the stability of resistance and the following self-sensing performance of carbon nanofiber cement paste. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2019, 11, e00247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gao, X.; Wang, R. The influence of rheological parameters of cement paste on the dispersion of carbon nanofibers and self-sensing performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 134, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, H.M.; El-Sheikh, S.M.; Elshereafy, E.E.; Essa, A.K. Performance of cement-slag-titanate nanofibers composite immobilized radioactive waste solution through frost and flooding events. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 223, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, H.M.; El-Sheikh, S.M.; Elshereafy, E.E.; Essa, A.K. Mechanical and physical characterization of cement reinforced by iron slag and titanate nanofibers to produce advanced containment for radioactive waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 200, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinchillas-Chinchillas, M.J.; Gaxiola, A.; Alvarado-Beltrán, C.G.; Orozco-Carmona, V.M.; Pellegrini-Cervantes, M.J.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, M.; Castro-Beltrán, A. A new application of recycled-PET/PAN composite nanofibers to cement–based materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElroy, P.; Emadi, H.; Surowiec, K.; Casadonte, D.J. Mechanical, rheological, and stability performance of simulated in-situ cured oil well cement slurries reinforced with alumina nanofibers. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 183, 106415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Azevedo, N.H.; Gleize, P.J.P. Effect of silicon carbide nanowhiskers on hydration and mechanical properties of a Portland cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 169, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Al-Rub, R.; Tyson, B.M.; Yazdanbakhsh, A.; Grasley, Z. Mechanical Properties of Nanocomposite Cement Incorporating Surface-Treated and Untreated Carbon Nanotubes and Carbon Nanofibers. J. Nanomech. Micromech. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.M.; Yoo, D.-Y.; Kim, J.J. Cementitious material reinforced by carbon nanotube-Nylon 66 hybrid nanofibers: Mechanical strength and microstructure analysis. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 23, 100845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.M.; Moon, J.; Kim, J.J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of hardened cement paste including Nylon 66 nanofibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 232, 117134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Nguyen, T.N.M.; Nguyen, X.T.; Ta, D.H. Reinforcing cementitious material using single-walled carbon nanotube—nylon 66 nanofibers. Transp. Commun. Sci. J. 2020, 71, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenmozhi, S.; Dharmaraj, N.; Kadirvelu, K.; Kim, H.Y. Electrospun nanofibers: New generation materials for advanced applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2017, 217, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Xie, J.; Liu, W.; Xia, Y. Electrospun Nanofibers: New Concepts, Materials, and Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 1976–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arinstein, A. Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers, chapter 1; Pan Stanford Publishing Pte. Ltd.: Stanford, CA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, A.C.; Li, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Wei, Y. Electrospinning of Porous Silica Nanofibers Containing Silver Nanoparticles for Catalytic Applications. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, P.-H.; Chou, C.-K.; Saldana, S.M.; Hung, M.-C.; Kameoka, J. The fabrication and testing of electrospun silica nanofiber membranes for the detection of proteins. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 445714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veverková, I.; Lovětinská-Šlamborová, I. Modified Silica Nanofibers with Antibacterial Activity. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 2837197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henry, N.; Clouet, J.; Le Visage, C.; Weiss, P.; Gautron, E.; Renard, D.; Cordonnier, T.; Boury, F.; Humbert, B.; Terrisse, H.; et al. Silica nanofibers as a new drug delivery system: A study of the protein–silica interactions. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 2908–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepekiran, B.N.; Calisir, M.D.; Polat, Y.; Akgul, Y.; Kilic, A. Centrifugally spun silica (SiO2) nanofibers for high-temperature air filtration. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-S.; Lee, S.G.; Im, S.S.; Kim, S.H.; Joo, Y.L. Silica nanofibers from electrospinning/sol-gel process. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2003, 22, 891–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, T.E.; Olesik, S.V. Silica-based nanofibers for electrospun ultra-thin layer chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1364, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freyer, A.; Savage, N.O. Effects of Sol Viscosity and Application to Thin Layer Chromatography. In The Science and Function of Nanomaterials: From Synthesis to Application; American Chemical Society: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahhosseininia, M.; Bazgir, S.; Joupari, M.D. Fabrication and investigation of silica nanofibers via electrospinning. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Debnath, S.; Gregan, E.; Byrne, H.J. Ultrasound-Assisted SWNTs Dispersion: Effects of Sonication Parameters and Solvent Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 8821–8827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Terentjev, E.M. Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubes: Mixing, Sonication, Stabilization, and Composite Properties. Polymers 2012, 4, 275–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, K.; Yi, Z.; Jing, Q.; Yue, R.; Jiang, W.; Lin, D. Sonication-assisted dispersion of carbon nanotubes in aqueous solutions of the anionic surfactant SDBS: The role of sonication energy. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 2082–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabet, S.M.; Mahfuz, H.; Hashemi, J.; Nezakat, M.; Szpunar, J.A. Effects of sonication energy on the dispersion of carbon nanotubes in a vinyl ester matrix and associated thermo-mechanical properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 4729–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C150; Standard Specification for Portland Cement. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Rao, A.M.; Chen, J.; Richter, E.; Schlecht, U.; Eklund, P.C.; Haddon, R.; Venkateswaran, U.D.; Kwon, Y.-K.; Tomanek, D. Effect of van der Waals Interactions on the Raman Modes in Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 3895–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabba, Y.; Thomas, E.L. High-Concentration Dispersion of Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 4815–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.; Wu, K.; Lin, Y.; Wang, K.; Fu, Q. Largely improved thermal conductivity of HDPE/expanded graphite/carbon nanotubes ternary composites via filler network-network synergy. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 99, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C307; Standard Test Method for Tensile Strength of Chemical-Resistant Mortar, Grouts, and Monolithic Surfacings. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- ASTM C109; Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50 mm] Cube Specimens). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Mohammed, S.; Elhem, G.; Mekki, B. Valorization of pozzolanicity of Algerian clay: Optimization of the heat treatment and mechanical characteristics of the involved cement mortars. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 132–133, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevielle, A.M. Properties of Concrete, 5th ed.; Pearson, Prentice Hall: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Vedalakshmi, R.; Raj, A.S.; Srinivasan, S.; Babu, K.G. Quantification of hydrated cement products of blended cements in low and medium strength concrete using TG and DTA technique. Thermochim. Acta 2003, 407, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, H.F.W. Cement Chemistry; Thomas Telford: London, UK, 1997; Chapter 5. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, P.K.; Monteiro, P.J.M. Concrete: Microstructure, Properties, and Materials; The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Chapter 6; pp. 203–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.; Zhu, W.; Howind, T.; Sharma, U. Quantification and characterization of C-S-H in silica nanoparticles incorporated cementitious system. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 79, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrade, D.D.S.; Rêgo, J.H.D.S.; Morais, P.C.; Lopes, A.N.D.M.; Rojas, M.F. Investigation of C-S-H in ternary cement pastes containing nanosilica and highly-reactive supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs): Microstructure and strength. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 198, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Foley, E.M.; Taha, M.M.R. Nano-mechanical characterization of synthetic calcium–silicate–hydrate (C–S–H) with varying CaO/SiO2 mixture ratios. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 36, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, E.M.; Kim, J.J.; Taha, M.M.R. Synthesis and nano-mechanical characterization of calcium-silicate-hydrate (C-S-H) made with 1.5 CaO/SiO2 mixture. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkeo, W.; Thongsanitgarn, P.; Chindaprasirt, P.; Chaipanich, A. Thermogravimetry of ternary cement blends—Effect of different curing methods. J. Therm. Anal. 2013, 113, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.K.; Monteiro, P.J.M. Concrete: Microstructure, Properties, and Materials, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bom, D.; Andrews, R.; Jacques, D.; Anthony, J.; Chen, B.; Meier, M.S.; Selegue, J.P. Thermogravimetric Analysis of the Oxidation of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes: Evidence for the Role of Defect Sites in Carbon Nanotube Chemistry. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| CaO | 61.33 |
| SiO2 | 21.01 |
| Al2O3 | 6.40 |
| SO3 | 2.30 |
| MgO | 3.02 |
| Fe2O3 | 3.12 |
| Ig. loss | 1.40 |
| Compressive strength at 28 days (MPa) | 36 |
| Specific surface area (cm2/g) | 2800 |
| Properties | TEOS | PVP | Butanol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear formula | (C2H5O)4Si | (C6H9NO)n | C4H10O |
| Molecular weight (g/mol) | 208.329 | 1,300,000 | 74.12 |
| Purity (%) | 98 | 98 | 99.9 |
| Density at 25 °C (g/mL) | 0.934 | 1.2 | 0.81 |
| Solvent | PVP | CNTs | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TEOS/PVP polymer solution | 90 | 10 | - |
| CNT-TEOS/PVP polymer solution | 90 | 9.6 | 0.4 |
| Voltage (kV) | 12 |
| Syringe (mL) | 12 |
| Needle | 20 |
| Working distance (mm) | 60 |
| Pump speed (µL/min) | 30 |
| Samples | Binder (B) | Water/B | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPC | TEOS/PVP NFs | CNTs | ||
| Plain paste | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0.5 |
| T28S/C28S | 99.7 | 3.3 | 0 | 0.5 |
| T28CS/C28CS | 99.7 | 3.3 | 0.02 | 0.5 |
| Previous Works [11,12] | Present Work | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N66 NFs MCP (1) | N66 NFs MCP (2) | SWCNT-N66 NFs MCP | MWCNT-N66 NFs MCP | T28S/C28S | T28CS/C28CS | |
| CNTs content (wt% in the cement-based materials) | 0 | 0 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0 | 0.02 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 32 | 28 | 43 | 57 | 6 | 10 |
| Compressive strength (MPa) | 6 | 8 | 10 | 14 | 28 | 38 |
| Toughness (J/m3) | 42 | 49 | 30 | 12 | 54 | 66 |
| Toughness (J/m3) | |
|---|---|
| Plain paste | 67,898.5 |
| T28S/C28S | 104,537.7 |
| T28CS/C28CS | 112,933.9 |
| Element | Wt% | Wt% Sigma | Atomic % | Standard Label | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plain paste | C | 6.70 | 0.41 | 11.69 | C Vit |
| O | 47.48 | 0.33 | 62.21 | SiO2 | |
| Mg | 1.90 | 0.05 | 1.64 | MgO | |
| Al | 2.17 | 0.05 | 1.69 | Al2O3 | |
| Si | 4.78 | 0.07 | 3.57 | SiO2 | |
| S | 0.82 | 0.04 | 0.54 | FeS2 | |
| K | 1.23 | 0.05 | 0.66 | KBr | |
| Ca | 33.19 | 0.24 | 17.36 | Wollastonite | |
| Fe | 1.73 | 0.11 | 0.65 | Fe | |
| T28S/C28S | C | 9.54 | 0.39 | 16.40 | C Vit |
| O | 45.00 | 0.32 | 58.08 | SiO2 | |
| Na | 0.92 | 0.05 | 0.83 | Albite | |
| Mg | 0.55 | 0.04 | 0.47 | MgO | |
| Al | 1.60 | 0.05 | 1.22 | Al2O3 | |
| Si | 5.54 | 0.07 | 4.07 | SiO2 | |
| S | 0.76 | 0.04 | 0.49 | FeS2 | |
| K | 4.46 | 0.07 | 2.36 | KBr | |
| Ca | 30.14 | 0.22 | 15.53 | Wollastonite | |
| Fe | 1.47 | 0.11 | 0.54 | Fe | |
| T28S/C28S–nanofibers spectrum | C | 8.70 | 0.43 | 15.06 | C Vit |
| O | 43.63 | 0.33 | 56.67 | SiO2 | |
| Na | 1.10 | 0.05 | 0.99 | Albite | |
| Mg | 3.09 | 0.06 | 2.64 | MgO | |
| Al | 1.44 | 0.05 | 1.11 | Al2O3 | |
| Si | 7.62 | 0.09 | 5.64 | SiO2 | |
| S | 0.92 | 0.05 | 0.60 | FeS2 | |
| K | 5.05 | 0.08 | 2.68 | KBr | |
| Ca | 27.44 | 0.22 | 14.23 | Wollastonite | |
| Fe | 1.01 | 0.11 | 0.38 | Fe | |
| T28CS/C28CS | C | 12.78 | 0.42 | 20.49 | C Vit |
| O | 49.00 | 0.33 | 58.98 | SiO2 | |
| Na | 1.00 | 0.05 | 0.84 | Albite | |
| Mg | 0.62 | 0.04 | 0.49 | MgO | |
| Al | 1.64 | 0.04 | 1.17 | Al2O3 | |
| Si | 5.94 | 0.07 | 4.07 | SiO2 | |
| S | 0.81 | 0.04 | 0.49 | FeS2 | |
| K | 4.34 | 0.07 | 2.14 | KBr | |
| Ca | 22.75 | 0.18 | 10.93 | Wollastonite | |
| Fe | 1.14 | 0.09 | 0.39 | Fe | |
| T28CS/C28CS–nanofibers spectrum | C | 8.92 | 0.41 | 16.42 | C Vit |
| O | 37.01 | 0.34 | 51.15 | SiO2 | |
| Na | 1.19 | 0.05 | 1.14 | Albite | |
| Al | 1.58 | 0.05 | 1.29 | Al2O3 | |
| Si | 6.83 | 0.08 | 5.38 | SiO2 | |
| S | 1.44 | 0.05 | 0.99 | FeS2 | |
| K | 8.22 | 0.11 | 4.65 | KBr | |
| Ca | 33.30 | 0.25 | 18.37 | Wollastonite | |
| Fe | 1.51 | 0.12 | 0.60 | Fe |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.N.M.; Han, T.H.; Park, J.K.; Kim, J.J. Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Cement Blended with TEOS/PVP Nanofibers Containing CNTs. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020714
Nguyen TNM, Han TH, Park JK, Kim JJ. Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Cement Blended with TEOS/PVP Nanofibers Containing CNTs. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(2):714. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020714
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Tri N. M., Taek Hee Han, Jun Kil Park, and Jung J. Kim. 2023. "Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Cement Blended with TEOS/PVP Nanofibers Containing CNTs" Applied Sciences 13, no. 2: 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020714
APA StyleNguyen, T. N. M., Han, T. H., Park, J. K., & Kim, J. J. (2023). Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Cement Blended with TEOS/PVP Nanofibers Containing CNTs. Applied Sciences, 13(2), 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020714






