Analysis of Surface and Building Deformation by Shield Tunneling through Geology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model Establishment and Parameter Determination
2.1. Project Overview
2.2. Physical and Mechanical Indexes of Rock Mass and Segments
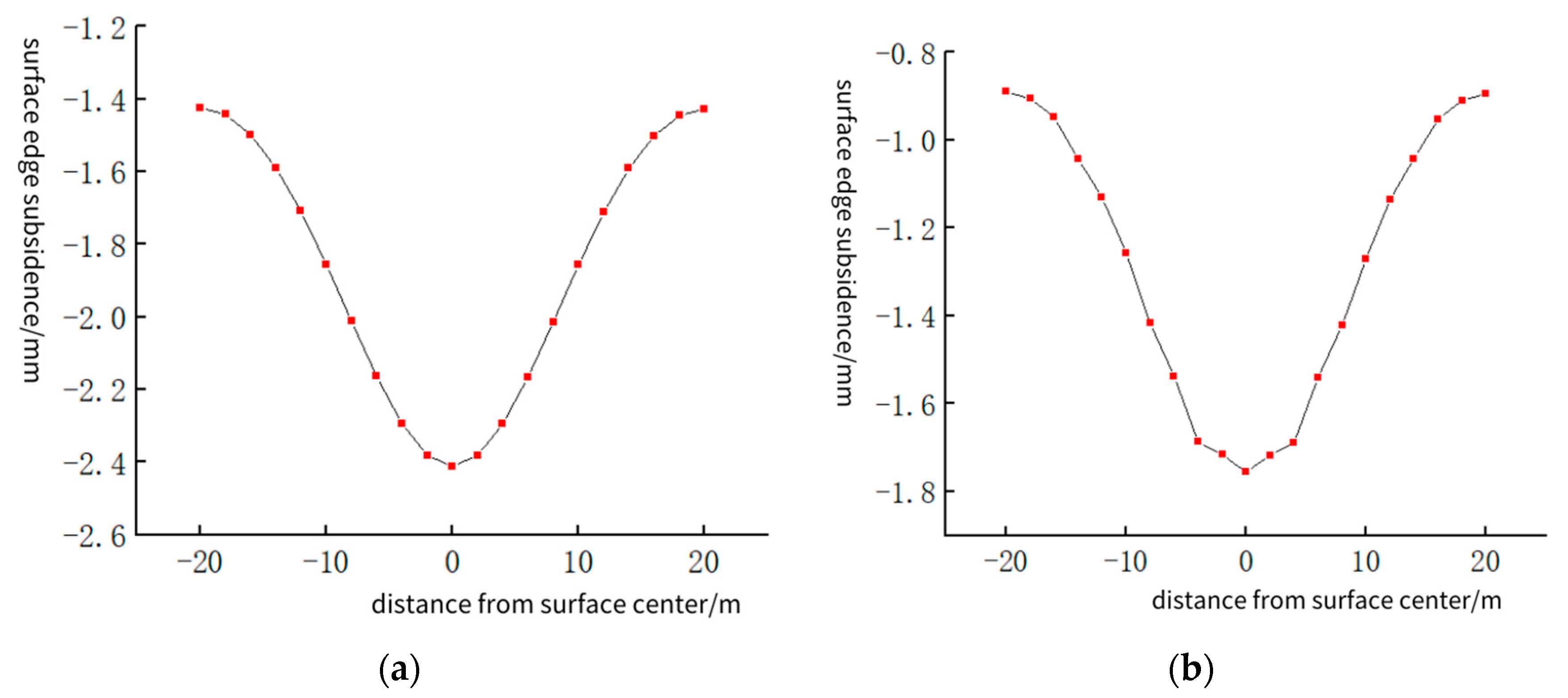
3. Influence of Shield Tunnel Excavation on Surface Settlement
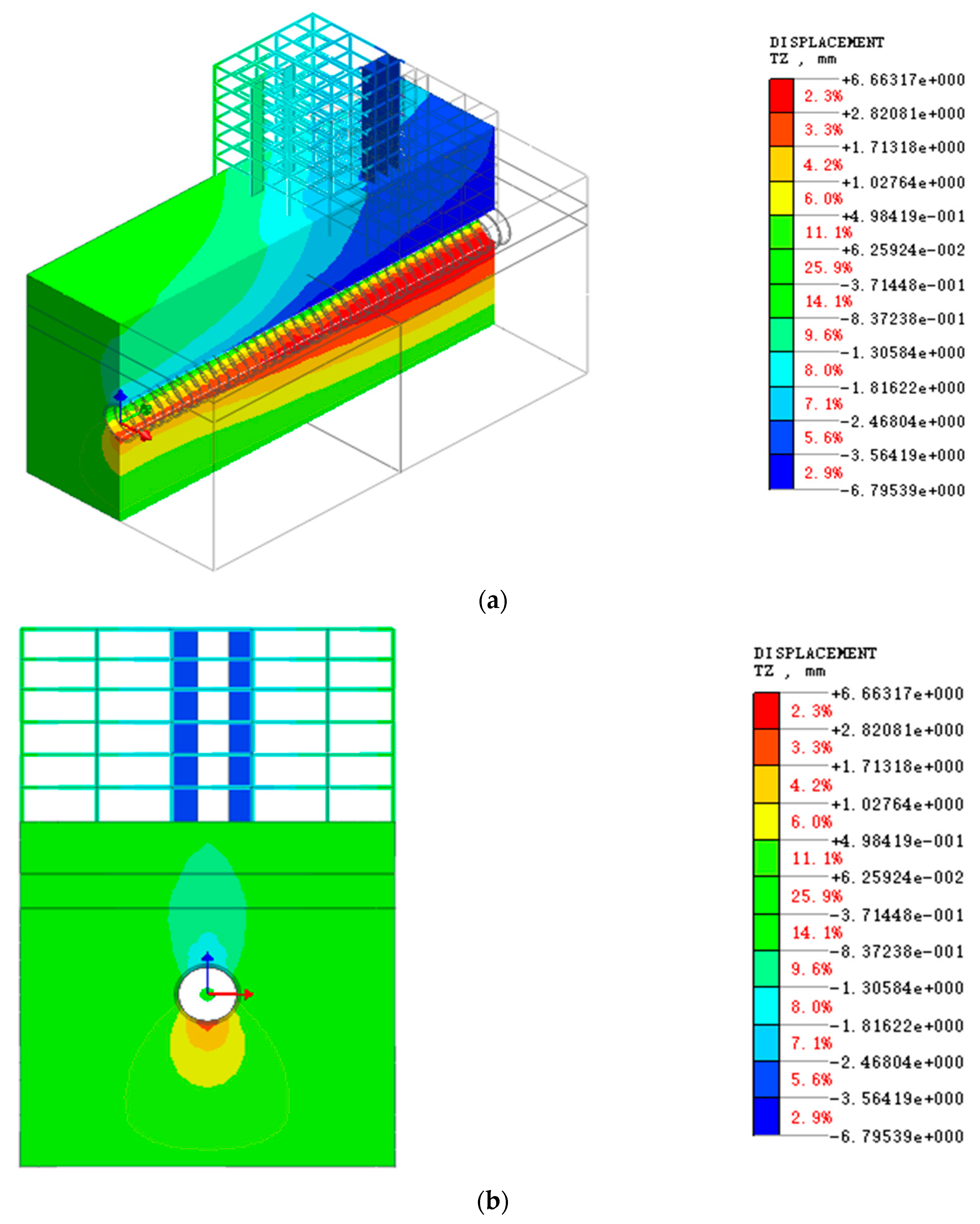
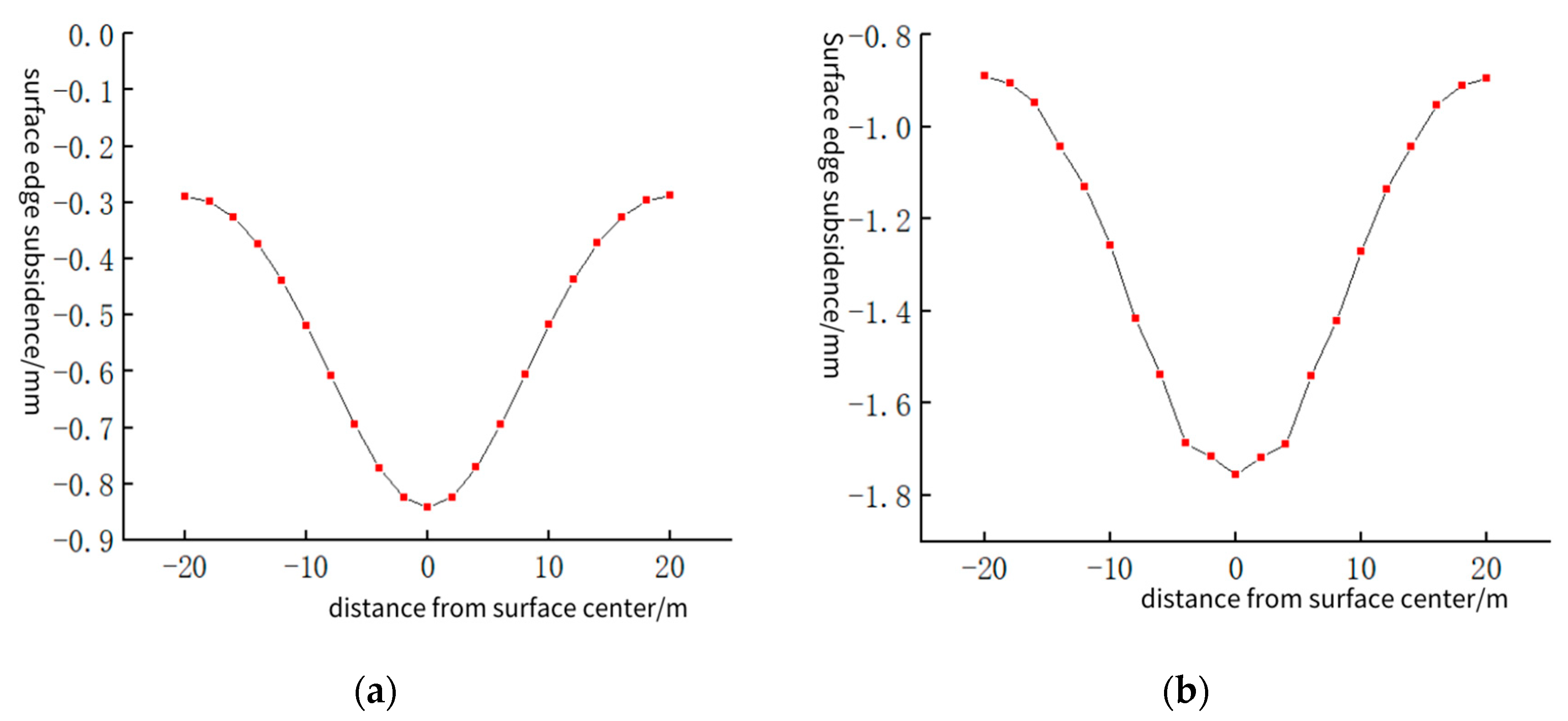
3.1. Shield Tunnel Excavation from Hard Rock to Soft Rock
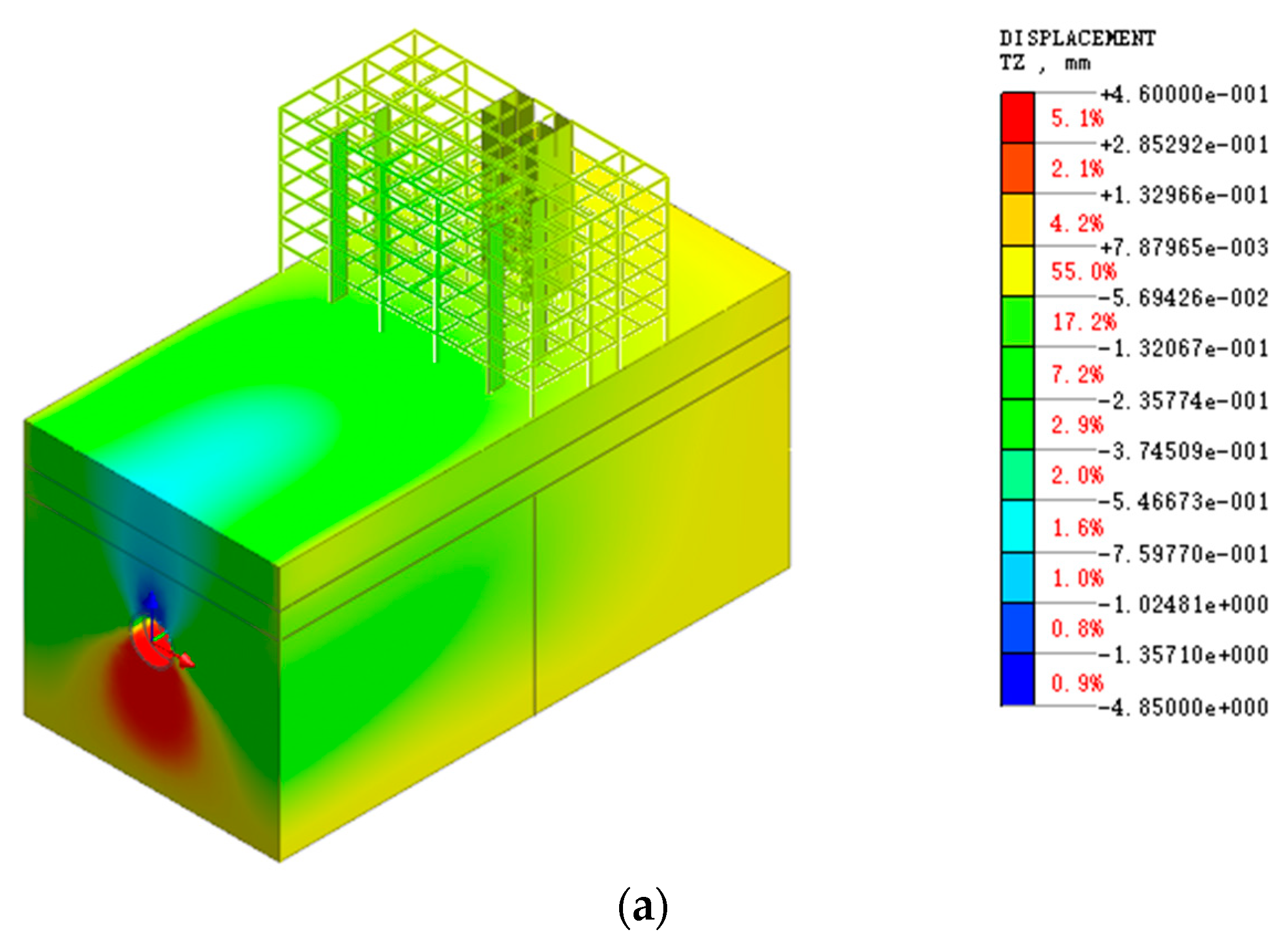
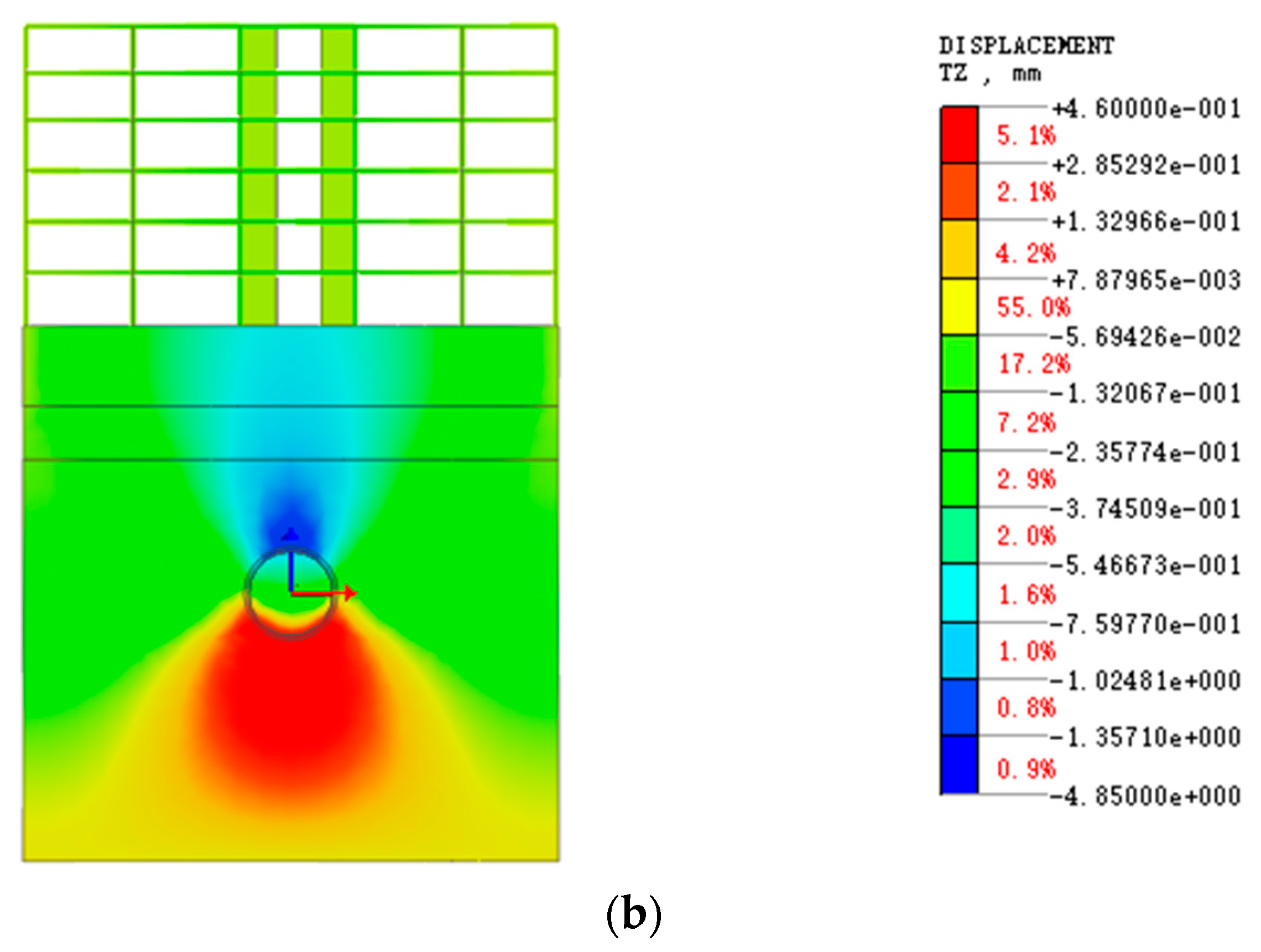
3.2. Shield Tunnel Excavation from Soft Rock to Hard Rock
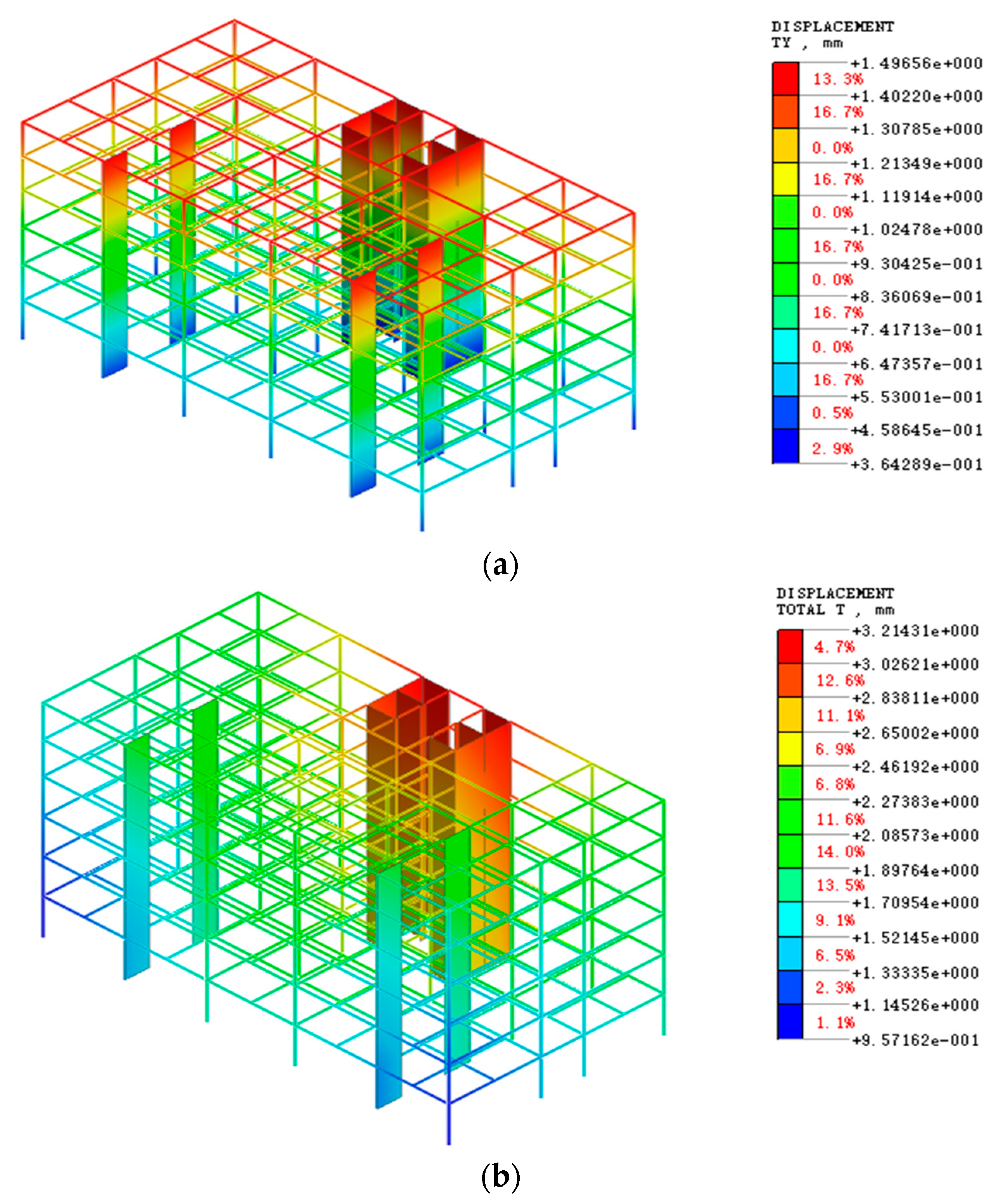
4. Influence of Shield Tunnel Excavation on Building Deformation
5. Control and Monitoring Measures for Abrupt Geological Deformation of Shield Crossing
5.1. Deformation Control Measures
5.1.1. Surface Settlement and Engineering Measures
5.1.2. Deformation of Buildings and Engineering Measures
5.2. Monitoring Measures
5.2.1. Monitoring of Surface Deformation
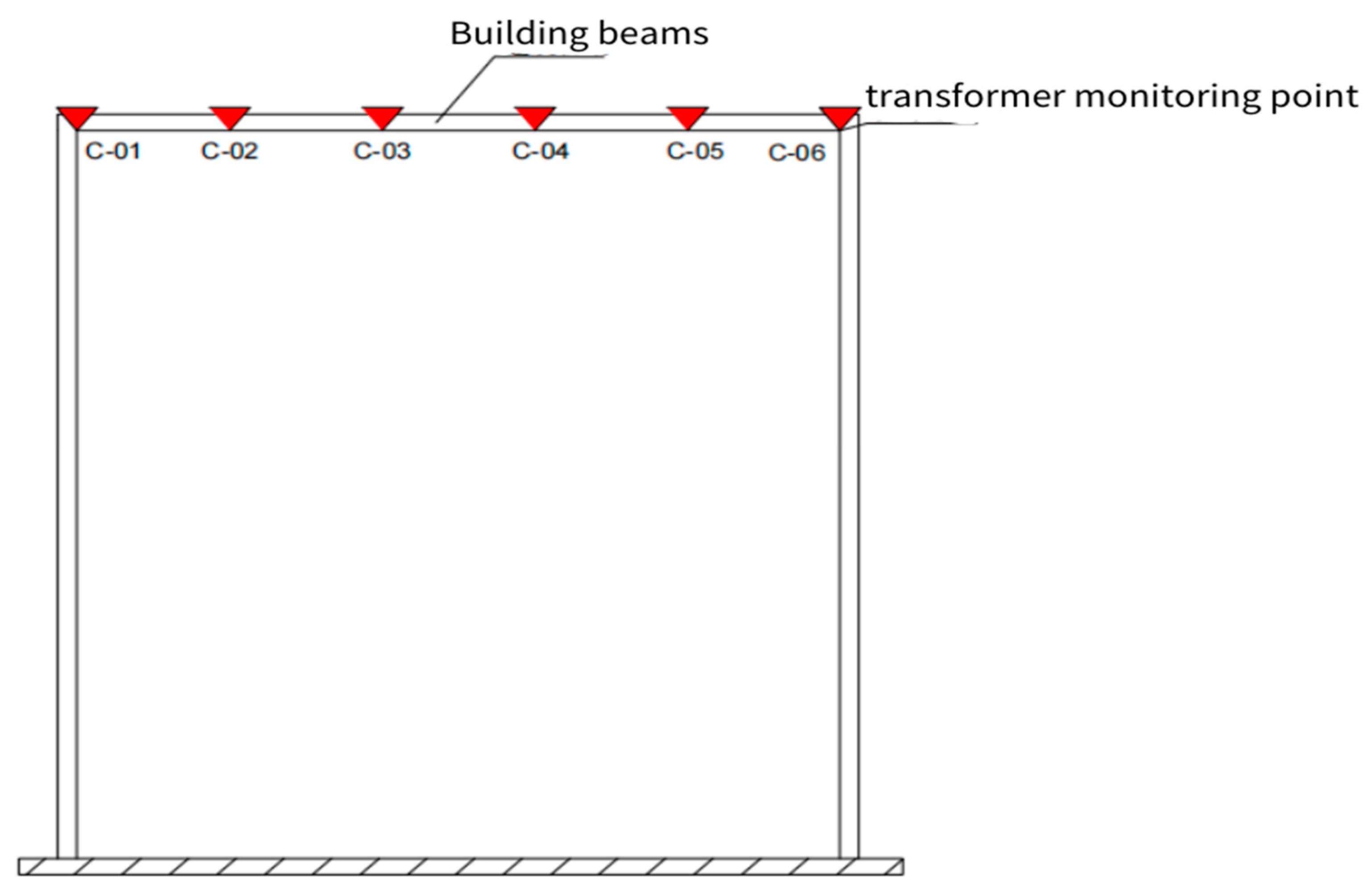
5.2.2. Monitoring of Building Deformation
6. Conclusions
7. Recommendations for Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, F.; Zhao, H. Research on key technology of open TBM construction under complex geological conditions of Gaoligongshan tunnel. Tunn. Constr. 2017, 37, 128–133. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, J.; Jia, R. Analysis of railway tunnel construction under complex geological conditions. Jiangxi Build. Mater. 2021, 143–145. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. Application of shield technology in soft and hard interbedded strata of Nanjing Metro. J. Chang. Inst. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2020, 21, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Ju, S. Shield Construction Technology in Composite Stratum; China Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, G.; Wang, D. Settlement analysis and prevention measures of shield construction on upper soft and lower hard strata. Guangdong Civ. Eng. Archit. 2019, 26, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W. Elastic-Plastic Analysis of Tunnel Excavation Face Approaching Different Geological Interfaces; National Taiwan Province University of Science and Technology: Taiwan, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z. Study on the Loosening Characteristics and the Calculation Method of the Loosening Pressure of Underground Caverns in Jointed Rock Mass with Soft Upper and Hard Lower; Beijing Jiaotong University: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, L.; Yang, L. Analysis of displacement characteristics of surrounding rock and its influencing factors when the tunnel excavation face is close to the geological interface. China Railw. Sci. 2009, 30, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q. Study on the Support Pressure of Shield Tunnel Excavation Face in Upper Soft and Lower Hard Stratum; Huazhong University of Science and Technology: Wuhan, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G. Application and process improvement of EPB shield in complex geology. Archit. Constr. 2016, 38, 218–220. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D. Impact and Control Measures of Shield Construction on Adjacent Buildings in Rich Water and Soft Soil Areas. Constr. Technol. Chin. Engl. 2022, 51, 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Gan, P.; Yan, Z.; Liu, W. Model test study on the stability of excavation face of shallow clay tunnel. J. Xi’an Univ. Archit. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2017, 49, 478–484. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Zeng, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Li, B. Study on the ground settlement caused by shield construction in upper soft stratum and lower hard stratum in xiamen metro. J. Railw. Sci. Eng. 2018, 15, 444–449. [Google Scholar]
- Hesami, S.; Ahmadi, S.; Taghavi Ghalesari, A.; Hasanzadeh, A. Ground surface settlement prediction in urban areas due to tunnel excavation by the NATM. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. EJGE 2013, 18, 1961–1972. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Miao, L.; Lin, H. Numerical simulation of the stability of excavation face of shield tunnel with different buried depth. J. Southeast Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2017, 47, 164–169. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, S.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of Surface Deformation and Settlement Characteristics Caused by Tunnel Excavation and Unloading. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 5383257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, J.; Zou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Gan, P.; Liu, W.; Pan, C. Model test of instability development process of shallow shield tunnel excavation face. J. Zhejiang Univ. Eng. Ed. 2017, 51, 863–869. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Yin, X.; Tang, L. Centrifugal test study on instability of excavation face considering seepage. Geotech. Mech. 2015, 36, 225–229. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Liu, W.; Zou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, X. Large-scale model test study on instability of excavation face of shallow shield tunnel. J. Geotech. Eng. 2018, 40, 562–567. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Study on mechanical behavior of subway shield tunnel under complex conditions. J. Railw. 2016, 38, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Cao, C.; Lei, M. An analysis of the ground deformation caused by shield tunnel construction combining an elastic half-space model and stochastic medium theory. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2017, 21, 1933–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Guo, Z.; Ding, P.; Chen, W.; Li, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, B. Summary of Research on the Impact of Shield Construction Vibration on Adjacent Buildings and Control Methods. Tunn. Constr. Chin. Engl. 2021, 41, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, T. The Impact of Shield Tunnel Construction on Surrounding Surface and Building Settlement in Soft Soil Regions. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2022, 49, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Lv, Y. Study on the Impact of Shield Tunnel Construction on Ground Structures in Tianjin Coastal Soft Soil Site. Constr. Technol. Chin. Engl. 2022, 51, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J. Research on the Application of HS and HSS Models in Foundation Pit Calculation by Back Analysis Method. Shanxi Archit. 2011, 37, 34–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeke, E.; Brown, E.T. Practical Estimates of Rock Mass Strength. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 1997, 34, 1165–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Geologic Parameter | First Layer: Miscellaneous Fill | Second Layer: Silty Clay | Hard Rock | Soft Rock |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit weight/(kN/m3) | 19.1 | 20.5 | 25 | 22 |
| Uniaxial compressive strength/MPa | 1.66 | 3 | 60 | 15 |
| Deformation modulus/GPa | 1.54 | 2.11 | 13 | 7 |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.25 | 0.3 |
| Cohesive force/kPa | 45 | 56 | 1400 | 600 |
| Angle of internal friction/(°) | 16 | 20 | 50 | 30 |
| Density (kg/m3) | Material Model | Modulus of Elasticity (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Bulk Density (kN/m3) | The Bulk Modulus (GPa) | Shear Modulus (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2400 | The elastic | 38 | 0.2 | 25 | 15.12 | 12.65 |
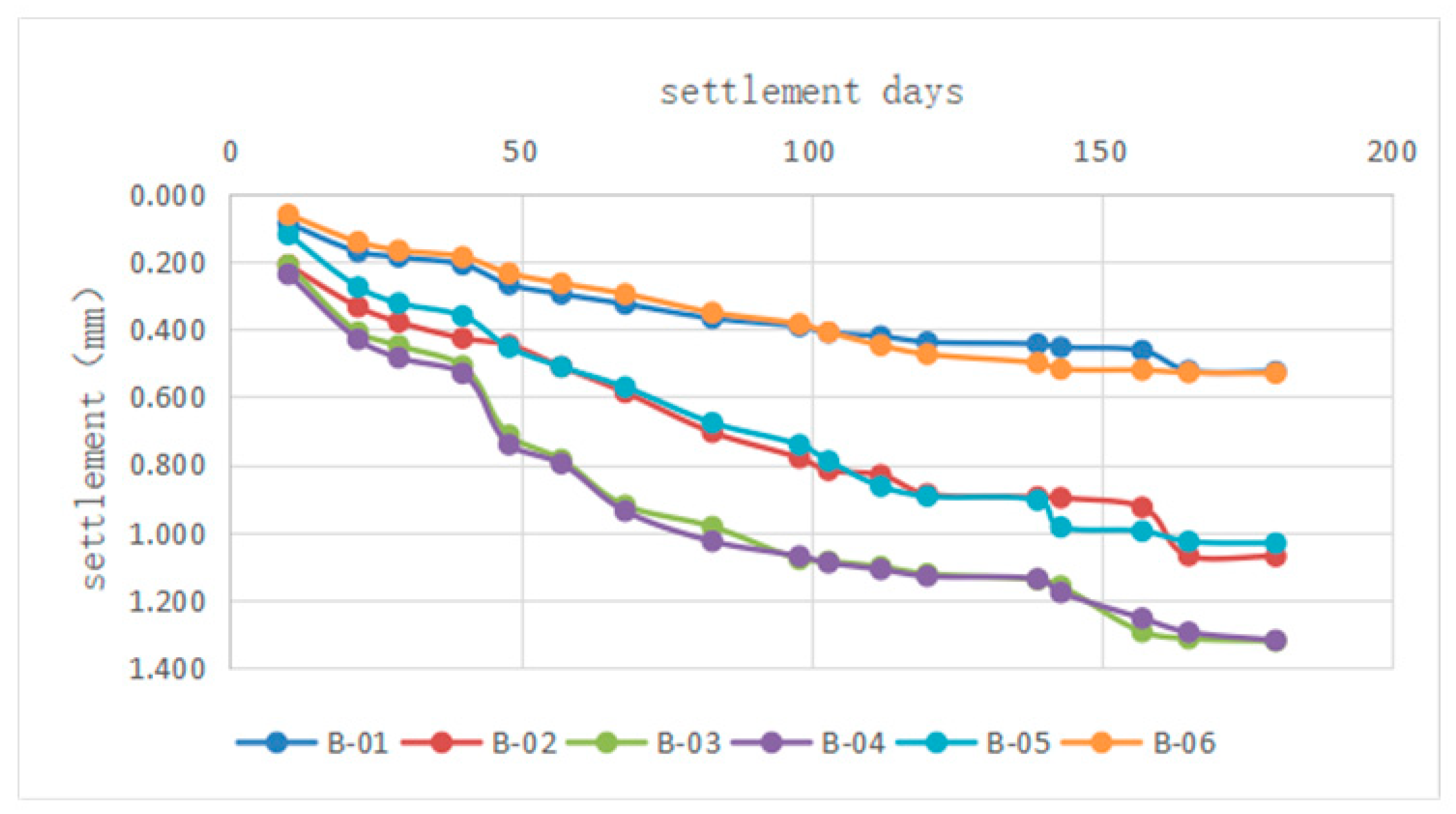
| Monitoring the Number of Days | Surface Monitoring Point Settlement Value/mm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-01 | B-02 | B-03 | B-04 | B-05 | B-06 | |
| 10 | 0.090 | 0.213 | 0.213 | 0.240 | 0.123 | 0.064 |
| 22 | 0.174 | 0.336 | 0.411 | 0.432 | 0.278 | 0.144 |
| 29 | 0.189 | 0.381 | 0.450 | 0.486 | 0.325 | 0.169 |
| 40 | 0.211 | 0.428 | 0.510 | 0.532 | 0.363 | 0.189 |
| 48 | 0.270 | 0.448 | 0.714 | 0.742 | 0.455 | 0.237 |
| 57 | 0.298 | 0.512 | 0.786 | 0.798 | 0.513 | 0.267 |
| 68 | 0.328 | 0.588 | 0.921 | 0.938 | 0.573 | 0.298 |
| 83 | 0.370 | 0.706 | 0.984 | 1.027 | 0.678 | 0.352 |
| 98 | 0.393 | 0.781 | 1.080 | 1.071 | 0.743 | 0.386 |
| 103 | 0.412 | 0.818 | 1.086 | 1.090 | 0.790 | 0.411 |
| 112 | 0.423 | 0.832 | 1.102 | 1.110 | 0.865 | 0.450 |
| 120 | 0.440 | 0.888 | 1.123 | 1.130 | 0.894 | 0.476 |
| 139 | 0.445 | 0.897 | 1.140 | 1.138 | 0.906 | 0.501 |
| 143 | 0.455 | 0.899 | 1.159 | 1.178 | 0.985 | 0.520 |
| 157 | 0.465 | 0.927 | 1.294 | 1.254 | 0.997 | 0.522 |
| 165 | 0.524 | 1.070 | 1.314 | 1.295 | 1.028 | 0.530 |
| 180 | 0.527 | 1.071 | 1.321 | 1.319 | 1.033 | 0.532 |
| The Dot | Field Monitoring | The Numerical Simulation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Biggest Uplift/mm | The Largest Settlement/mm | The Biggest Uplift/mm | The Largest Settlement/mm | |
| B-01 | 0 | 0.53 | 0 | 0.85 |
| B-02 | 0 | 1.07 | 0 | 1.16 |
| B-03 | 0 | 1.32 | 0 | 1.62 |
| B-04 | 0 | 1.33 | 0 | 1.61 |
| B-05 | 0 | 1.03 | 0 | 1.14 |
| B-06 | 0 | 0.54 | 0 | 0.87 |
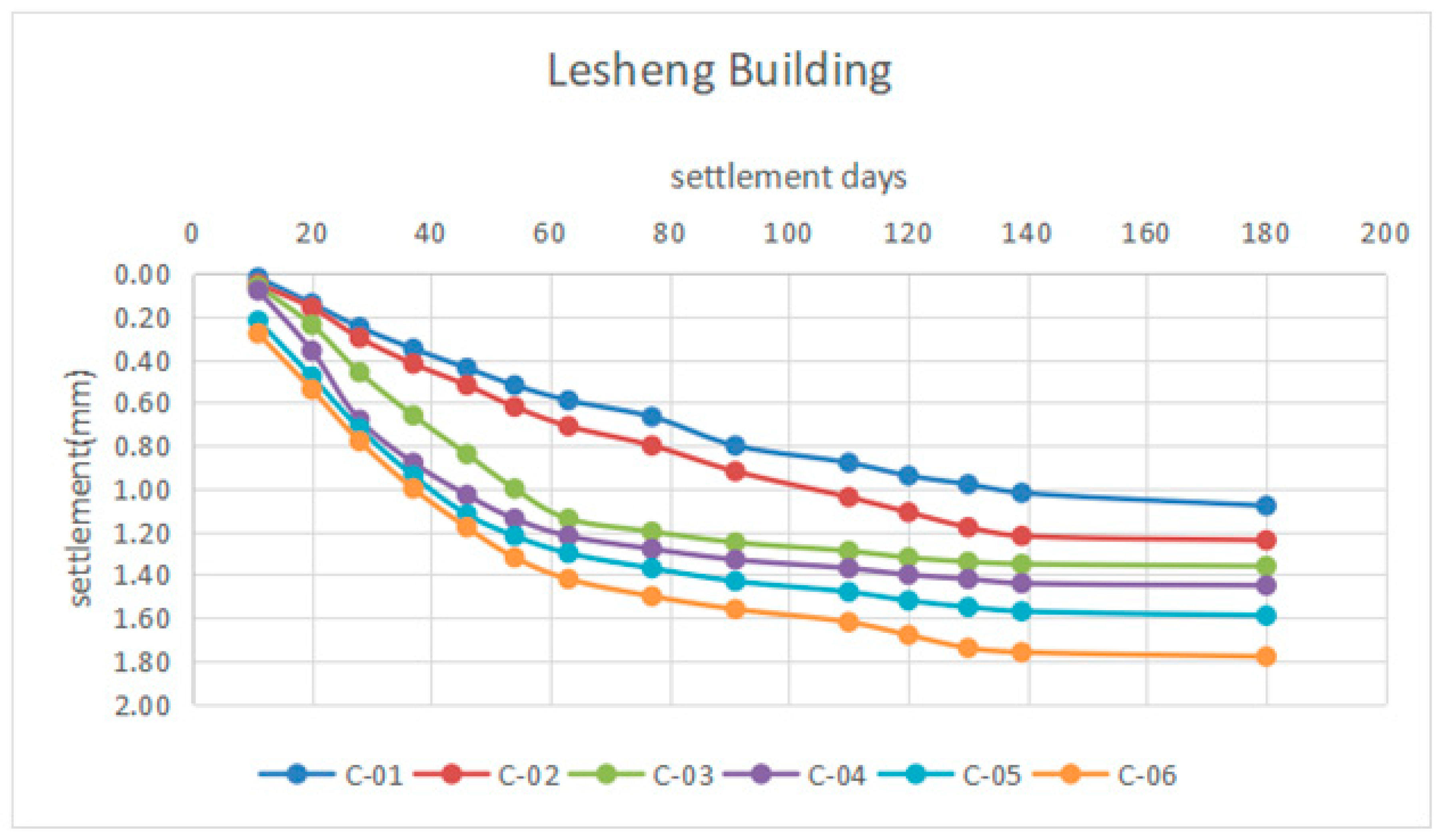
| Number of Days | Deformation Value of Building Beam/mm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-01 | C-02 | C-03 | C-04 | C-05 | C-06 | |
| 11 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.22 | 0.28 |
| 20 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.24 | 0.36 | 0.48 | 0.54 |
| 28 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.46 | 0.68 | 0.72 | 0.78 |
| 37 | 0.35 | 0.42 | 0.66 | 0.88 | 0.94 | 1.00 |
| 46 | 0.44 | 0.52 | 0.84 | 1.03 | 1.12 | 1.18 |
| 54 | 0.52 | 0.62 | 1.00 | 1.14 | 1.22 | 1.32 |
| 63 | 0.59 | 0.71 | 1.14 | 1.22 | 1.30 | 1.42 |
| 77 | 0.67 | 0.80 | 1.20 | 1.28 | 1.37 | 1.50 |
| 91 | 0.80 | 0.92 | 1.25 | 1.33 | 1.43 | 1.56 |
| 110 | 0.88 | 1.04 | 1.29 | 1.37 | 1.48 | 1.62 |
| 120 | 0.94 | 1.11 | 1.32 | 1.40 | 1.52 | 1.68 |
| 130 | 0.98 | 1.18 | 1.34 | 1.42 | 1.55 | 1.74 |
| 139 | 1.02 | 1.22 | 1.35 | 1.44 | 1.57 | 1.76 |
| 180 | 1.08 | 1.24 | 1.36 | 1.45 | 1.59 | 1.78 |
| The Dot | Field Monitoring | The Numerical Simulation |
|---|---|---|
| The Maximal Displacement/mm | The Maximal Displacement/mm | |
| C-01 | 1.08 | 1.22 |
| C-02 | 1.24 | 1.36 |
| C-03 | 1.36 | 1.51 |
| C-04 | 1.45 | 1.73 |
| C-05 | 1.59 | 1.88 |
| C-06 | 1.78 | 2.02 |
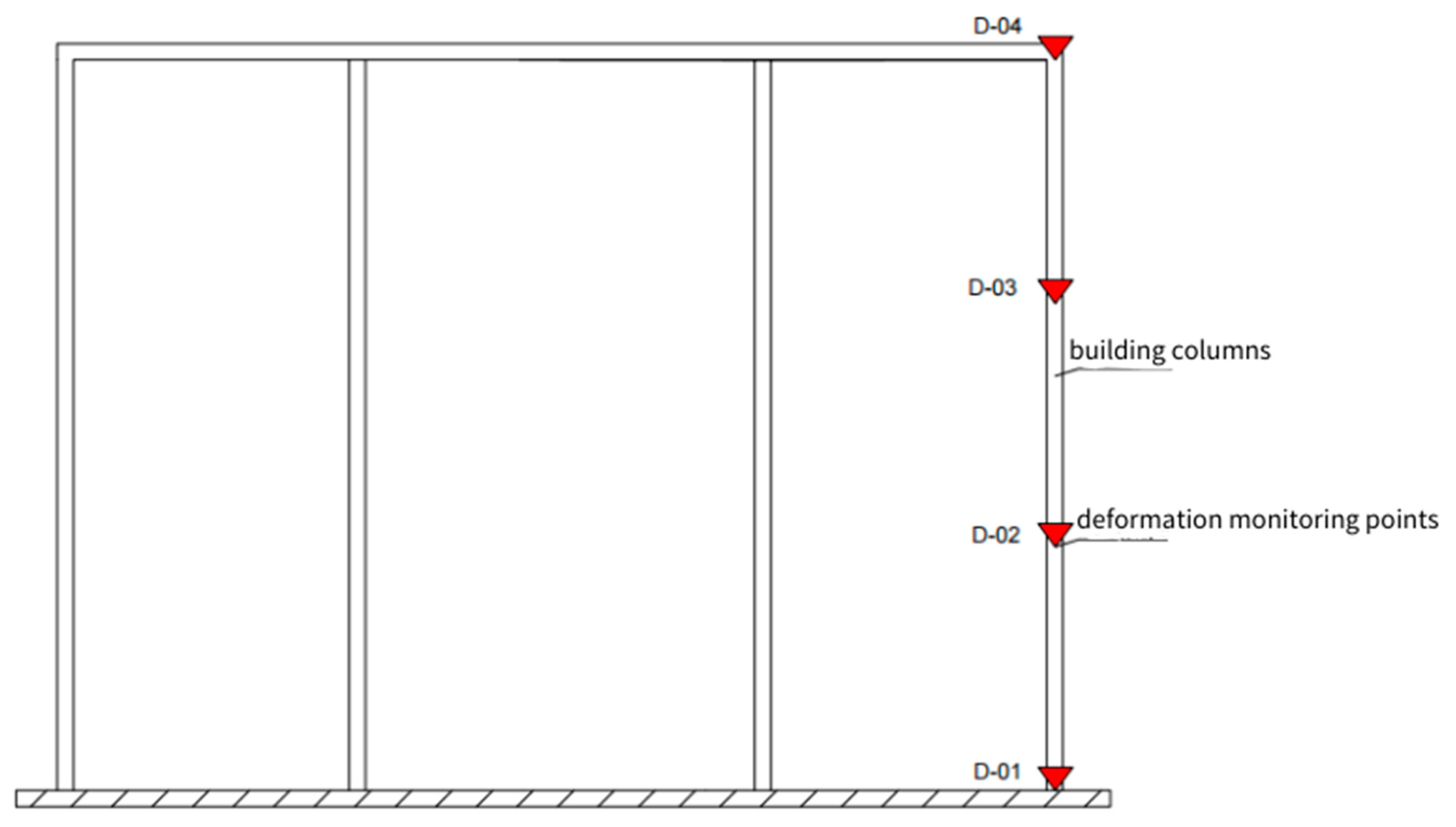
| Number of Days | Deformation Value of Building Column/mm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D-01 | D-02 | D-03 | D-04 | |
| 11 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.29 |
| 20 | 0.15 | 0.28 | 0.41 | 0.54 |
| 28 | 0.21 | 0.39 | 0.57 | 0.75 |
| 37 | 0.26 | 0.48 | 0.70 | 0.84 |
| 46 | 0.30 | 0.55 | 0.80 | 0.96 |
| 54 | 0.34 | 0.58 | 0.82 | 1.02 |
| 63 | 0.37 | 0.60 | 0.83 | 1.03 |
| 77 | 0.39 | 0.62 | 0.85 | 1.07 |
| 91 | 0.41 | 0.64 | 0.87 | 1.09 |
| 110 | 0.43 | 0.66 | 0.89 | 1.11 |
| 120 | 0.45 | 0.67 | 0.89 | 1.11 |
| 130 | 0.47 | 0.68 | 0.89 | 1.12 |
| 139 | 0.49 | 0.70 | 0.90 | 1.12 |
| 180 | 0.53 | 0.72 | 0.92 | 1.14 |
| The Dot | Field Monitoring | The Numerical Simulation |
|---|---|---|
| The Biggest Deformation/mm | The Biggest Deformation/mm | |
| D-01 | 0.53 | 0.64 |
| D-02 | 0.72 | 1.04 |
| D-03 | 0.91 | 1.17 |
| D-04 | 1.14 | 1.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, Z.; Yu, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, Z. Analysis of Surface and Building Deformation by Shield Tunneling through Geology. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11155. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011155
Tian Z, Yu C, Zhang B, Zhao Q, Wang Z. Analysis of Surface and Building Deformation by Shield Tunneling through Geology. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(20):11155. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011155
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Zhongxi, Chao Yu, Baoliang Zhang, Qingshuang Zhao, and Zhiwei Wang. 2023. "Analysis of Surface and Building Deformation by Shield Tunneling through Geology" Applied Sciences 13, no. 20: 11155. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011155
APA StyleTian, Z., Yu, C., Zhang, B., Zhao, Q., & Wang, Z. (2023). Analysis of Surface and Building Deformation by Shield Tunneling through Geology. Applied Sciences, 13(20), 11155. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011155





