Infrared Fault Classification Based on the Siamese Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- A novel feature extraction method based on adaptive coordinate attention (ACA) is proposed, which dynamically adjusts the scope of module attention based on input images, thereby enhancing the ability of multi-scale feature extraction.
- (2)
- A novel feature fusion module (FFM) is designed to enhance feature learning ability and improve the accuracy of fault detection.
- (3)
- Advancements in terms of the average correct classification rate on an open-accessed infrared failure dataset. Experimental results show that the ACA-FFM Siamese network, compared to existing methods, demonstrates higher recognition rates in scenarios of high similarity.
2. Related Work
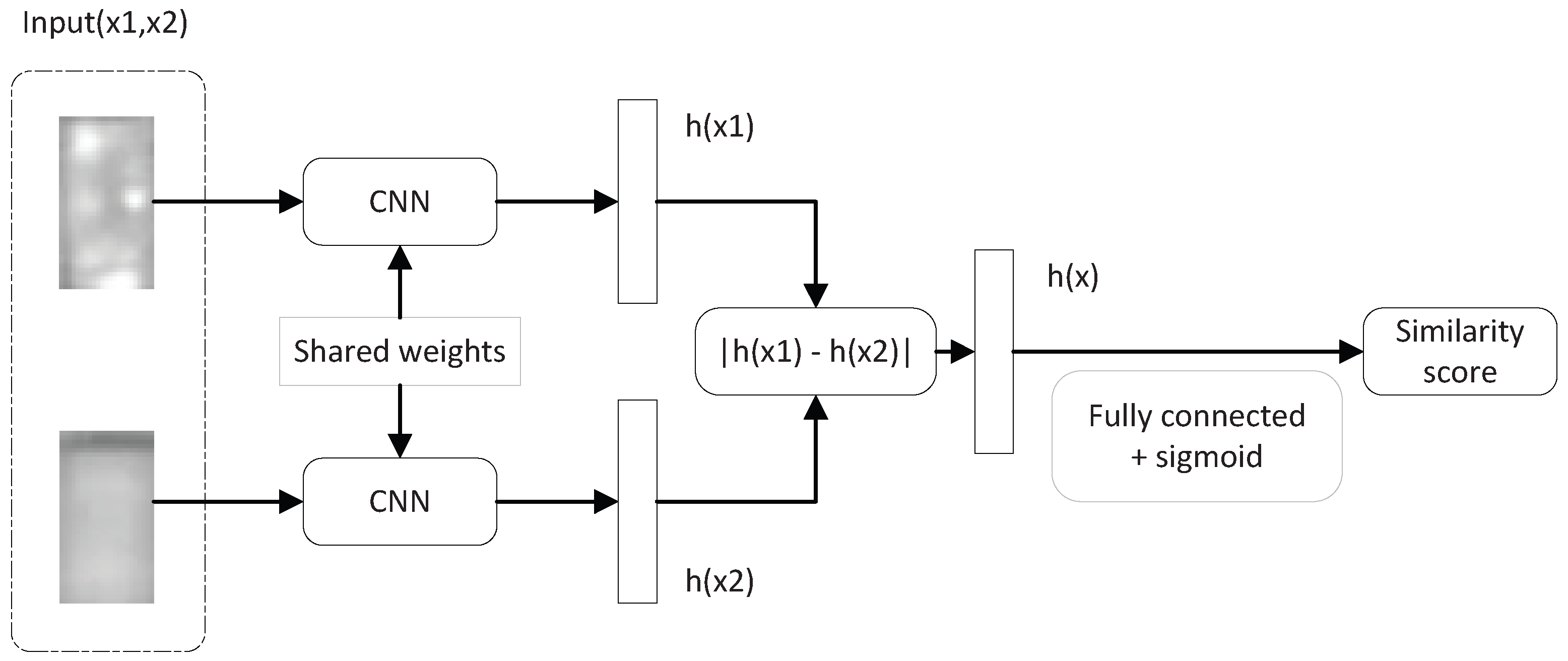
3. Methodology
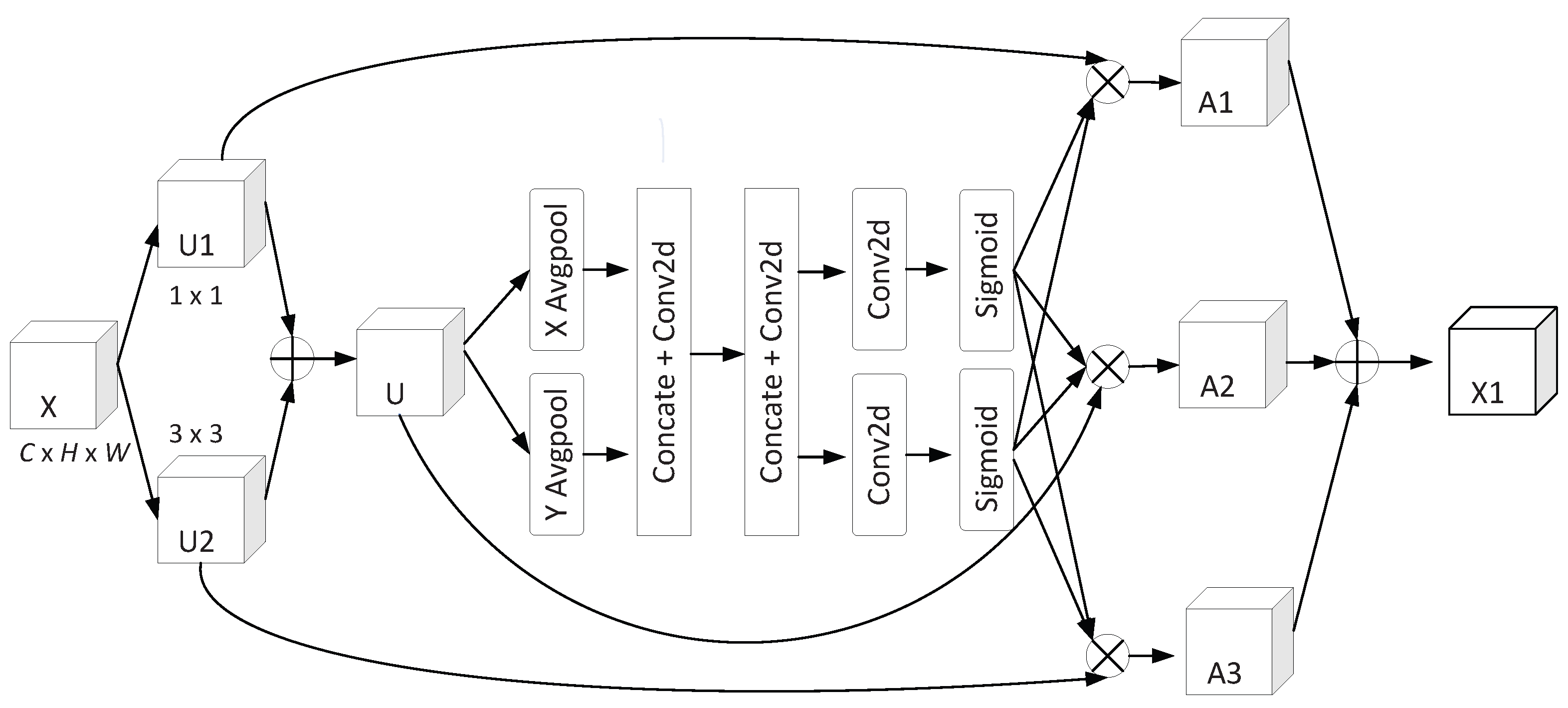
3.1. Adaptive Coordinate Attention
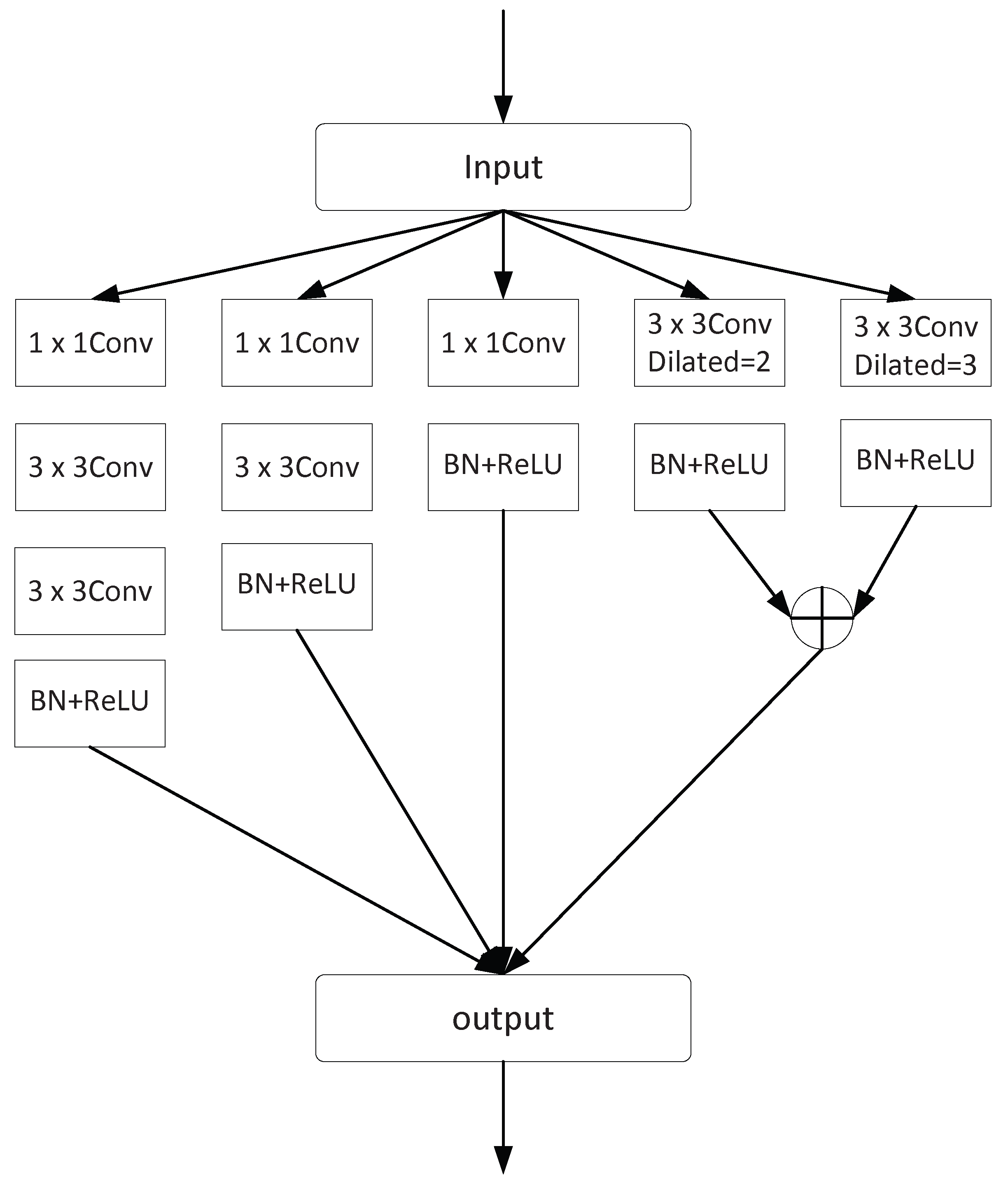
3.2. Feature Fusion Module
3.3. Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Various Attention Comparison Experiments
4.2. Comparative Experiments on Backbone Networks
4.3. Ablation Experiment
4.4. Classifying and Verifying Experiments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nebili, B.; Khellal, A.; Nemra, A.; Mascarilla, L. Augmented Convolutional Neural Network Models with Relative Multi-Head Attention for Target Recognition in Infrared Images. Unmanned Syst. 2023, 11, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Yang, Z.; Ren, X.; Wang, J.; Ku, Y. Infrared Small Target Detection Based on Smoothness Measure and Thermal Diffusion Flowmetry. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 7002505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, K.S.; Kim, J.; Na, Y.; Hwang, J.Y.Y. Local Similarity Siamese Network for Urban Land Change Detection on Remote Sensing Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 4139–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Zhang, H.; Liu, R.; Xiao, H. Accelerated sparse nonnegative matrix factorization for unsupervised feature learning. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2022, 156, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, F.; Ul Haq, A.; Ahmad, S.; Mahmoud, Y.; Jalal, M.; Ali, U. A Novel Convolutional Neural Network Based Approach for Fault Classification in Photovoltaic Arrays. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 41889–41904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta, A.; Pliego Marugán, A.; García Márquez, F.P. Photovoltaic plant condition monitoring using thermal images analysis by convolutional neural network-based structure. Renew. Energy 2020, 153, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alla Eddine, T.M.; Mouloudj, H.; Helaimi, M.; Rachid, T. Artificial Neural Network for Detection and Classification of Solar Panel Faults. In Proceedings of the First National Conference on Industrial Engineering and Sustainable Development (ICESD’23), Relizane, Algeria, 16 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Manno, D.; Cipriani, G.; Di Dio, V.; Giuseppina, C.; Guarino, S.; Lo Brano, V. Deep learning strategies for automatic fault diagnosis in photovoltaic systems by thermographic images. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 241, 114315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Goyal, D.; Letha, S.S. Infrared Thermography-Based Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motor Bearings Using Machine Learning. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, B.; Castanedo, C.I.; Maldague, X.P.V. Measuring Heterogeneous Thermal Patterns in Infrared-Based Diagnostic Systems Using Sparse Low-Rank Matrix Approximation: Comparative Study. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 4501209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Shu, X.; Liu, Q.; He, Z. Aligned Spatial-Temporal Memory Network for Thermal Infrared Target Tracking. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2023, 70, 1224–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiqbatcha, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, H.; Amrouch, H.; Henkel, J.; Tan, S.X.D. Post-Silicon Heat-Source Identification and Machine-Learning-Based Thermal Modeling Using Infrared Thermal Imaging. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2021, 40, 694–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, Q.T.; Wu, Y.K.; Phan, Q.D. Short-term Solar Power Forecasting Using XGBoost with Numerical Weather Prediction. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Future Energy Electronics Conference (IFEEC), Taipei, Taiwan, 16–19 November 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, P.; Subramaniam, U.; Babu, T.S.; Padmanaban, S.; Holm-Nielsen, J.B.; Mitolo, M.; Ravichandran, S. Improved Perturb and Observation Maximum Power Point Tracking Technique for Solar Photovoltaic Power Generation Systems. IEEE Syst. J. 2021, 15, 3024–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Singh, H.K.; Niwareeba, R. Adaptive Control Technique for Portable Solar Powered EV Charging Adapter to Operate in Remote Location. IEEE Open J. Circuits Syst. 2023, 4, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Kim, C.O. Siamese Network-Based Health Representation Learning and Robust Reference-Based Remaining Useful Life Prediction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 5264–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Xu, T.B.; Wei, Z. IMSiam: IoU-aware Matching-adaptive Siamese network for object tracking. Neurocomputing 2022, 492, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, B.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Ren, M.; Xu, T. Learning Spatio-Temporal Attention Based Siamese Network for Tracking UAVs in the Wild. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Gong, M.; Liu, T.; Jiang, F.; Zhan, T.; Lu, D.; Zhang, M. HFA-Net: High frequency attention siamese network for building change detection in VHR remote sensing images. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 129, 108717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H. Smart Contract Vulnerability Detection Model Based on Siamese Network (SCVSN): A Case Study of Reentrancy Vulnerability. Energies 2022, 15, 9642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xiao, H.; Ou, J.; Chen, X. SiamSMDFFF: Siamese network tracker based on shallow-middle-deep three-level feature fusion and clustering-based adaptive rectangular window filtering. Neurocomputing 2022, 483, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Hui, Y.; Liang, Y.; Wu, X. Siamese Network Object Tracking Algorithm Combining Attention Mechanism and Correlation Filter Theory. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2022, 36, 2250003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D. Siamese Neural Networks: An Overview. Artif. Neural Netw. 2021, 2190, 73–94. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Du, X.; Wan, F.; Wang, X.; Yu, H. Rotating machinery fault diagnosis based on convolutional neural network and infrared thermal imaging. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2020, 33, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V, H.E.; Ghanekar, S. An Efficient Method for Generic Dsp Implementation of Dilated Convolution. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022–2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Singapore, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.; Zhao, Z.; Xiong, Q.; Guo, J. Lightweight the Focus module in YOLOv5 by Dilated Convolution. In Proceedings of the 2022 3rd International Conference on Computer Vision, Image and Deep Learning & International Conference on Computer Engineering and Applications, Changchun, China, 20–22 May 2022; pp. 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Attention | SE | ECA | CBAM | CA | ACA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACCR | 87.1 | 93.2 | 97.0 | 94.6 | 90.2 |
| Model | Params | Acc | Over Fitting | Predict Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mobilenetv2 | 1.9 M | 70.10% | No | 0.12 |
| EfficientNetV2_s | 22.3 M | 72.90% | Yes | 0.17 |
| Resnet18 | 11.1 M | 78.80% | Yes | 0.15 |
| Resnet34 | 21.2 M | 80.50% | Yes | 0.17 |
| CNN-AF | 0.9 M | 83.90% | No | 0.10 |
| CNN | ACA | FFM | ACC |
|---|---|---|---|
| ✓ | 67.70% | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | 75.30% | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 79.30% | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 83.90% |
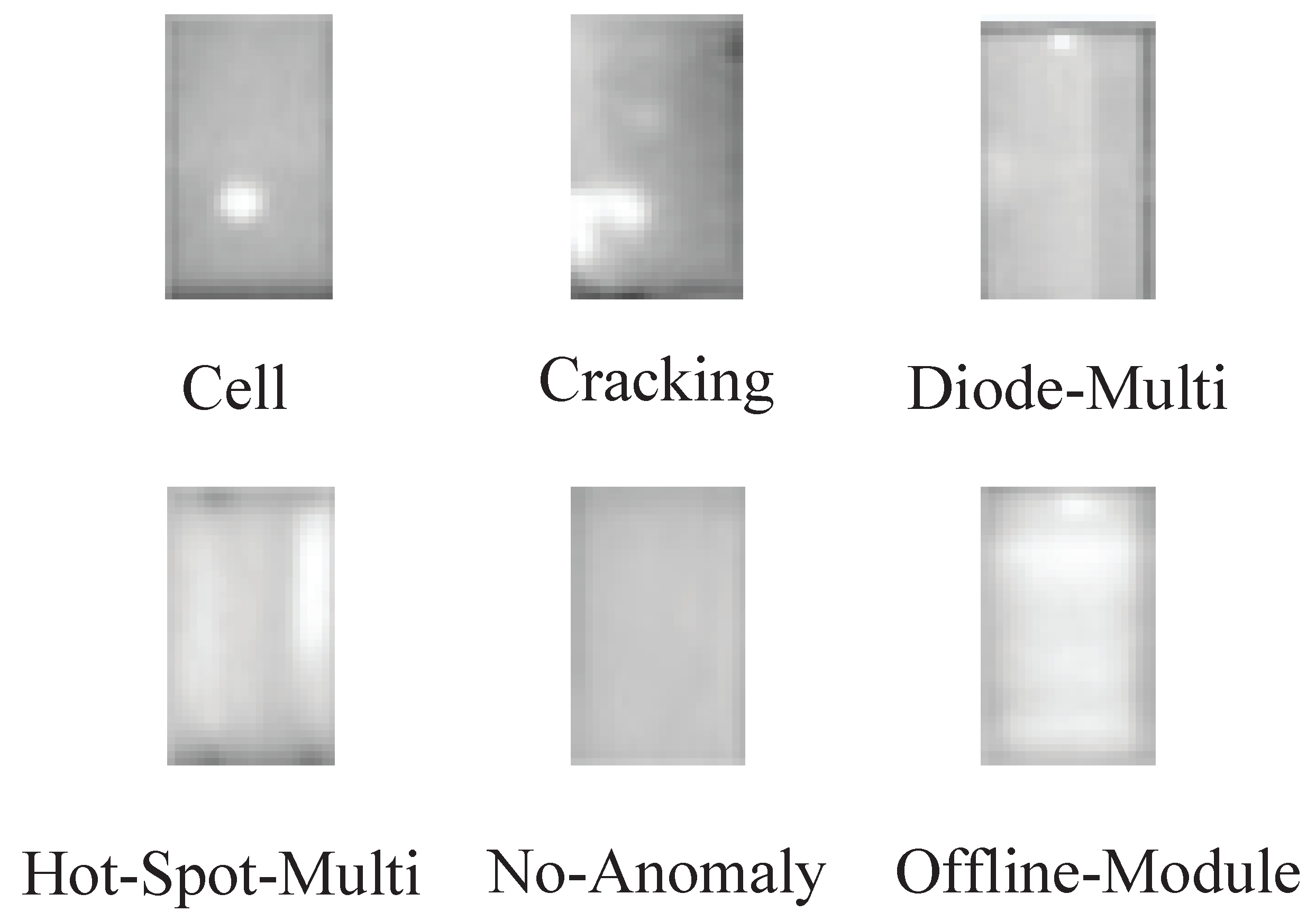
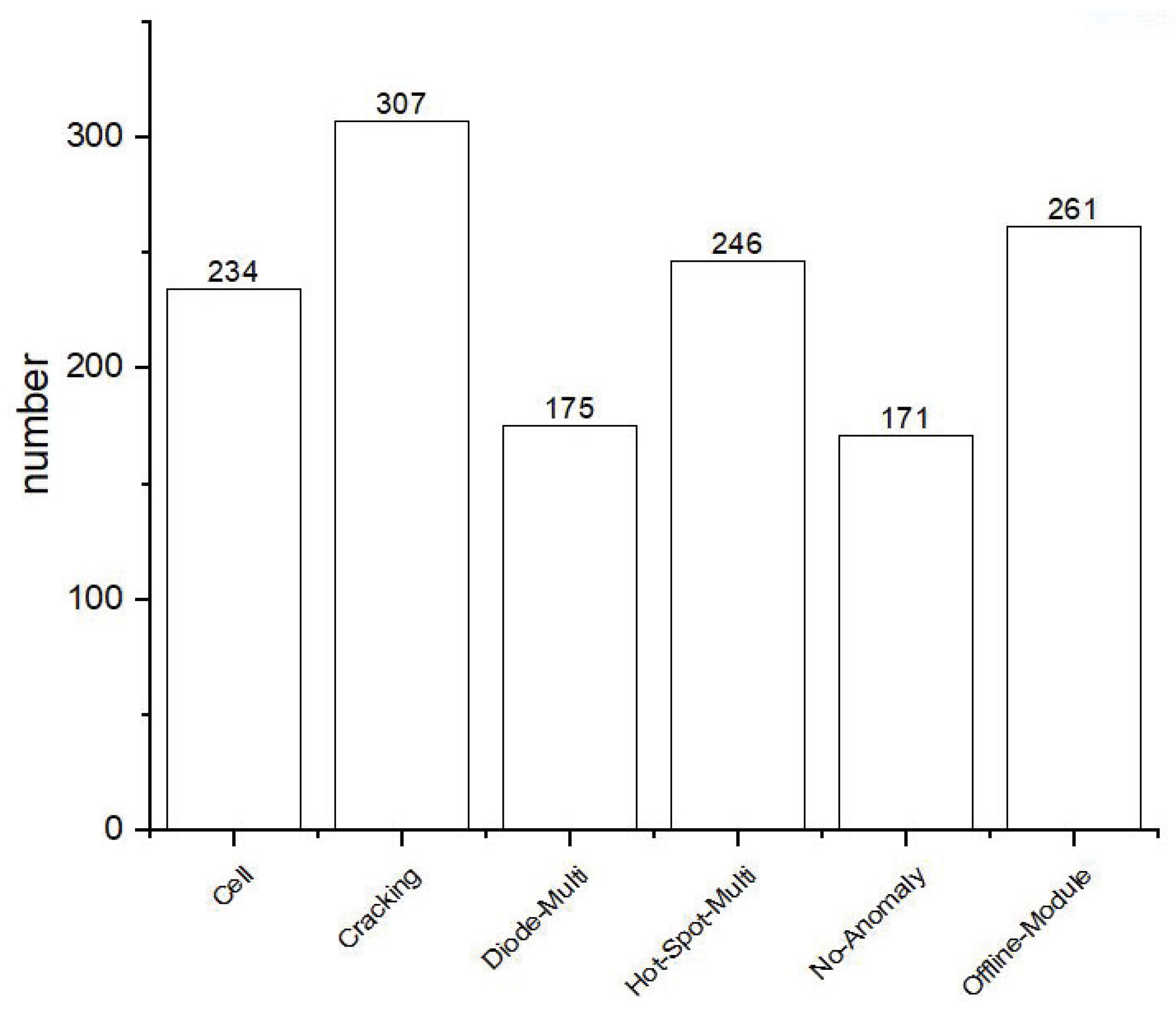
| Class | Cell | Cracking | Diode-Multi | Hot-Spot-Multi | No Anomaly | Offline-Module |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACCR | 76.6 | 86.7 | 72.8 | 98.2 | 91.3 | 93.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Bao, Q.; Jia, B.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. Infrared Fault Classification Based on the Siamese Network. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11457. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011457
Zhang L, Wang X, Bao Q, Jia B, Li X, Wang Y. Infrared Fault Classification Based on the Siamese Network. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(20):11457. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011457
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lili, Xiuhui Wang, Qifu Bao, Bo Jia, Xuesheng Li, and Yaru Wang. 2023. "Infrared Fault Classification Based on the Siamese Network" Applied Sciences 13, no. 20: 11457. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011457
APA StyleZhang, L., Wang, X., Bao, Q., Jia, B., Li, X., & Wang, Y. (2023). Infrared Fault Classification Based on the Siamese Network. Applied Sciences, 13(20), 11457. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011457






