Enhancing Surface Characteristics and Combustion Behavior of Black Poplar Wood through Varied Impregnation Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Wood Material
2.1.2. Impregnation Material (Calcium Hydroxide (Ca(OH)2))
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Impregnation Methods (Immersion Method and Vacuum Method)
2.2.2. Preparation of Samples
2.2.3. Testings of Surface and Burning Properties
- Surface roughness test
- Water contact angle test
- FTIR analysis
- DTG/TGA analysis
- LOI analysis
- SEM analysis
- Statistical analysis
3. Results and Discussion
- The physical properties
- The surface roughness, contact angle, and LOI properties
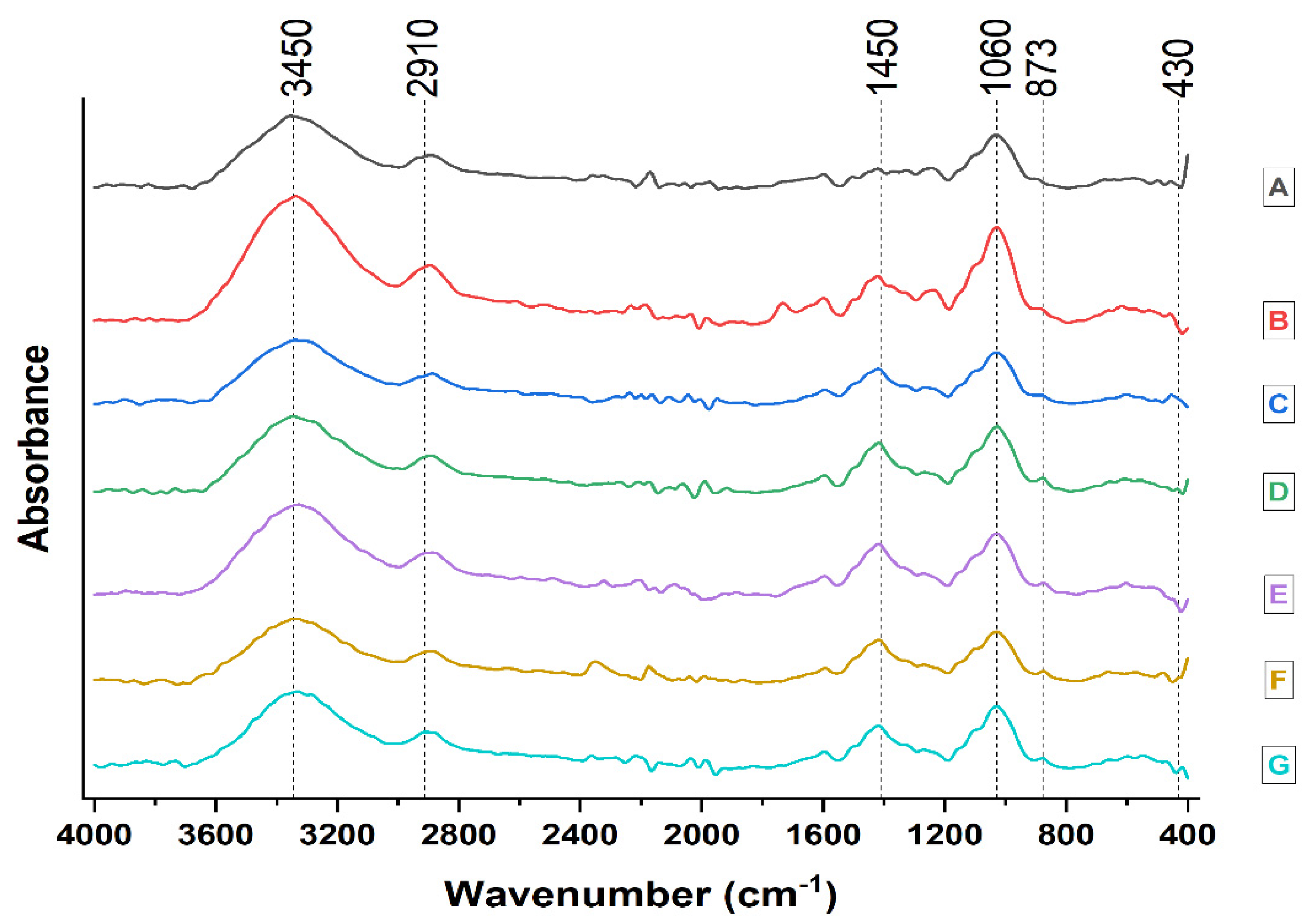
- FTIR analysis
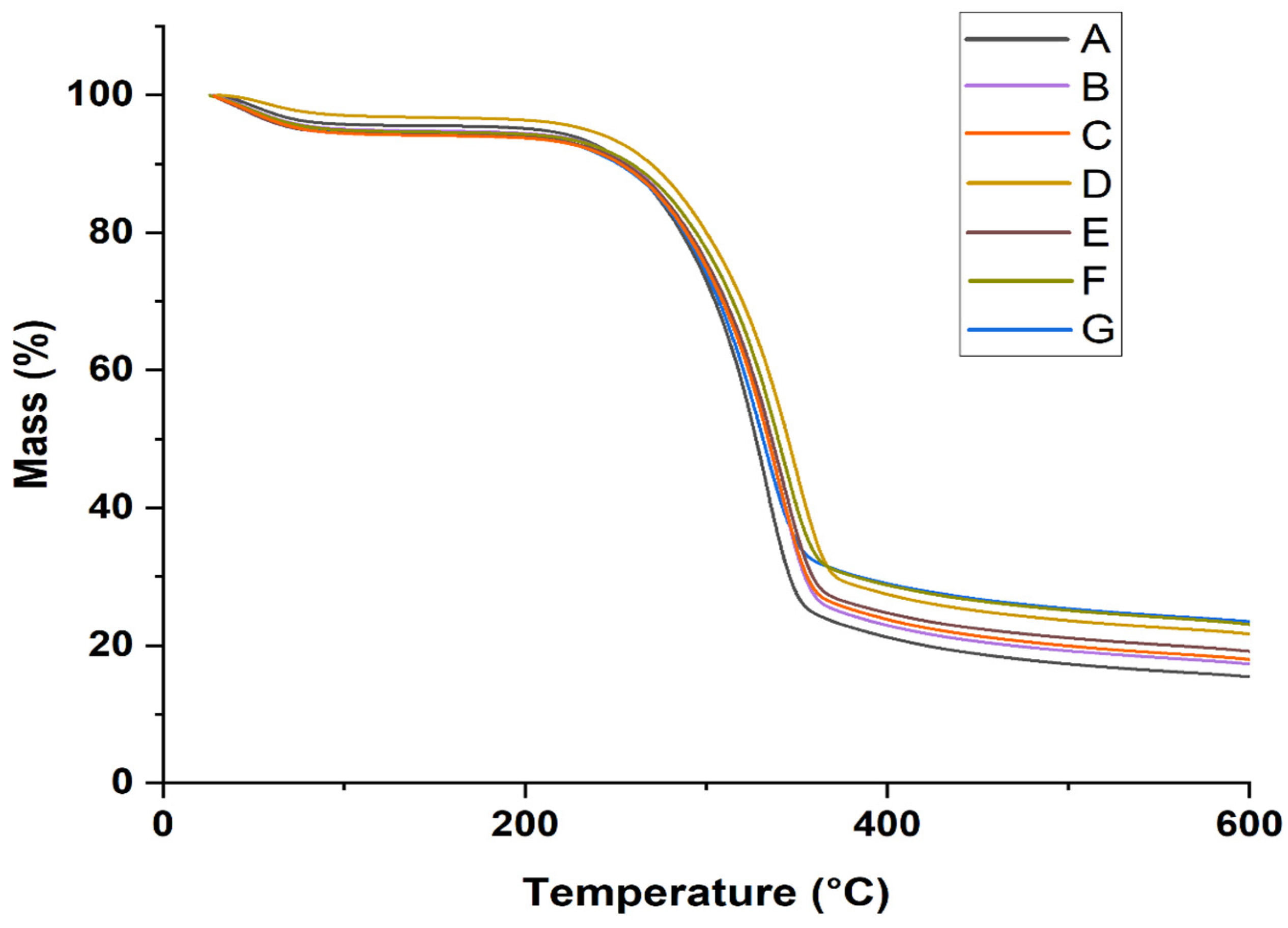
- DTG/TGA analysis
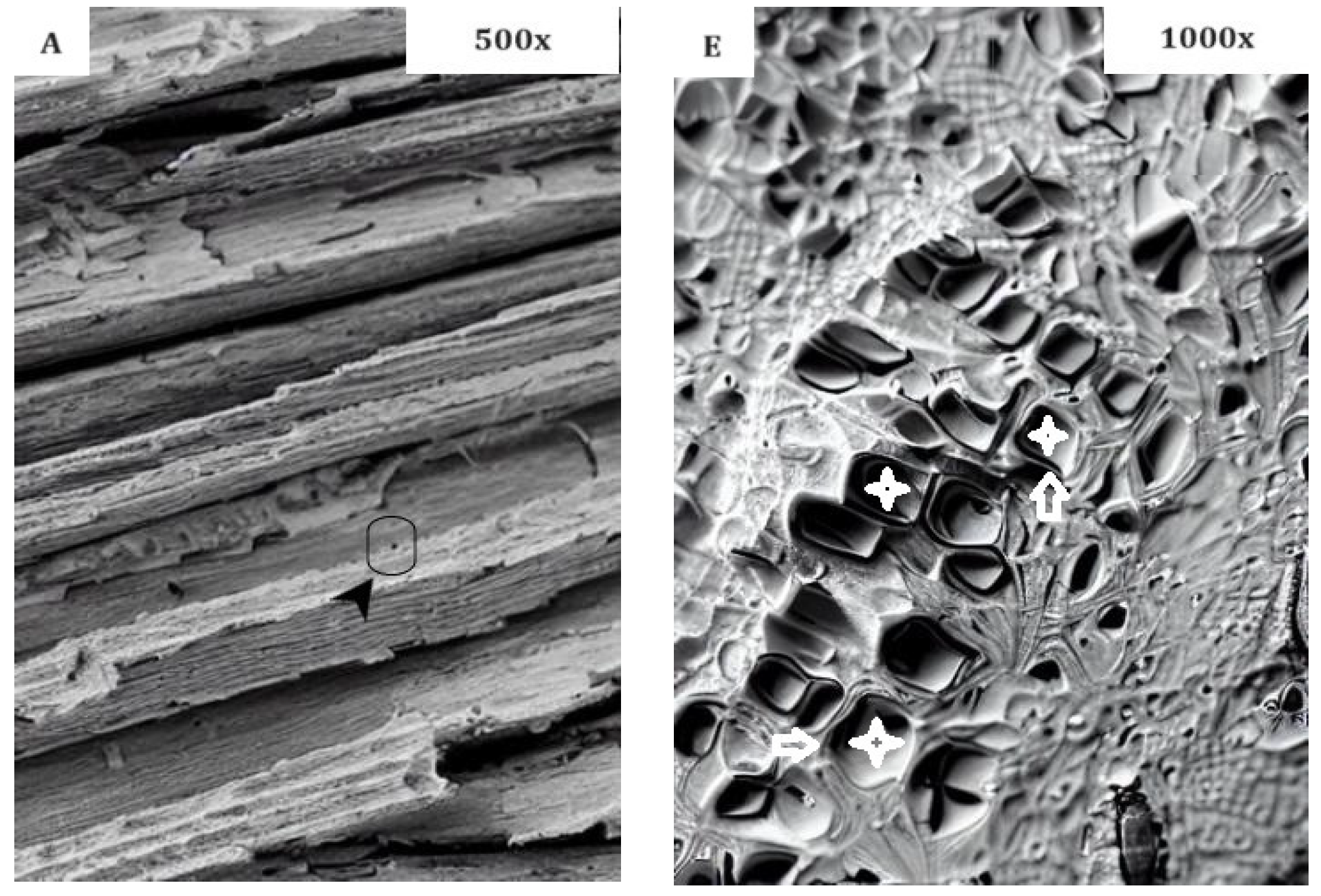
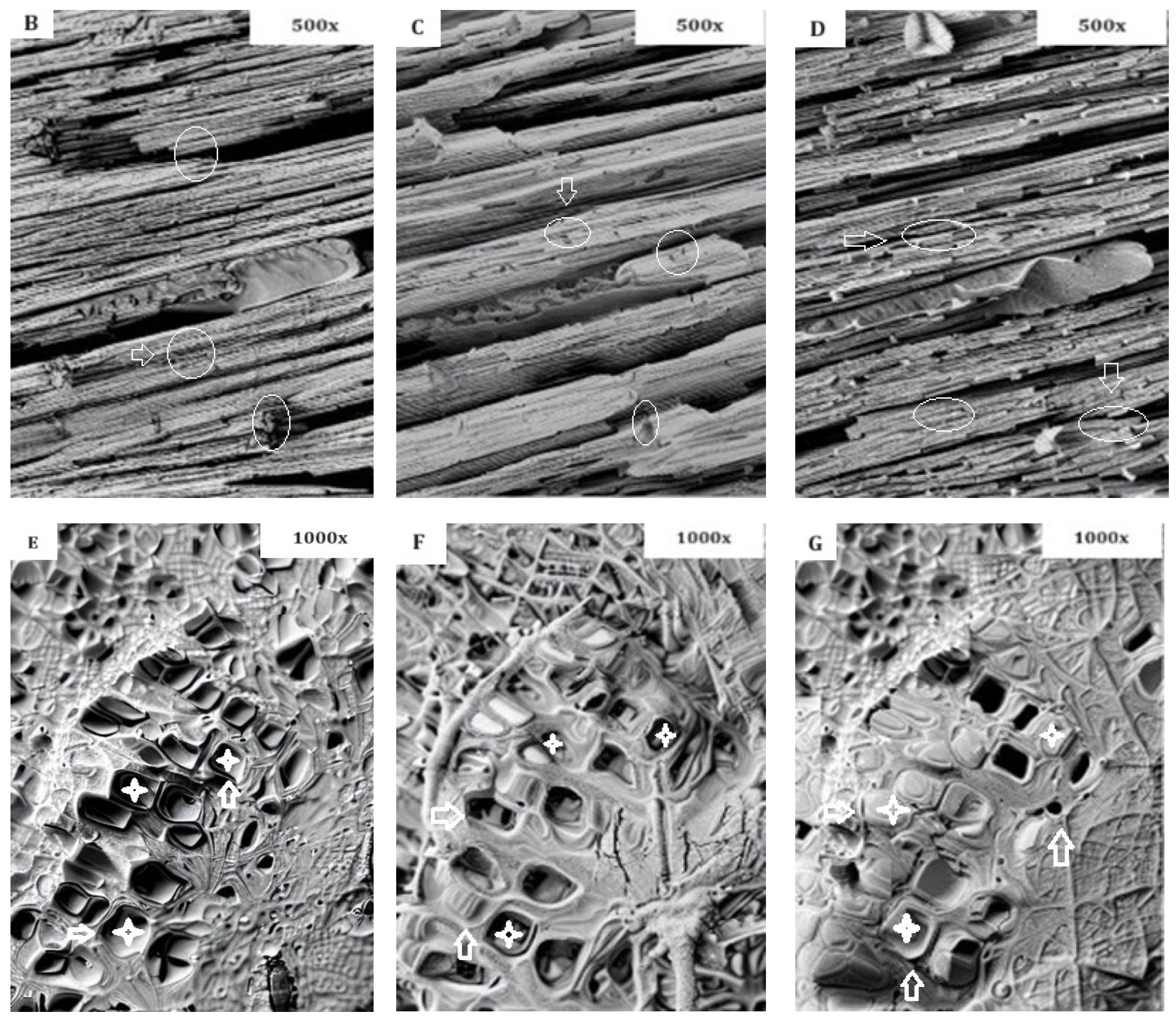
- SEM analysis
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asif, M. Sustainability of timber, wood and bamboo in construction. In Sustainability of Construction Materials; Khatib, J.M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosillo-Calle, F.; Woods, J. The Biomass Assessment Handbook; Routledge: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Aristri, M.A.; Lubis, M.A.R.; Yadav, S.M.; Antov, P.; Papadopoulos, A.N.; Pizzi, A.; Fatriasari, W.; Ismayati, M.; Iswanto, A.H. Recent developments in lignin-and tannin-based non-isocyanate polyurethane resins for wood adhesives—A review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimak, K.M.; Slimak, R.A. Enhancing the Strength, Moisture Resistance, and Fire-Resistance of Wood, Timber, Lumber, Similar Plant-Derived Construction and Building Materials, and Other Cellulosic Materials. U.S. Patent No. 6,146,766, 21 March 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Östman, B.; Voss, A.; Hughes, A.; Jostein Hovde, P.; Grexa, O. Durability of fire-retardant treated wood products at humid and exterior conditions review of literature. Fire Mater. 2001, 25, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereyra, A.M.; Giudice, C.A. Flame-retardant impregnants for woods based on alkaline silicates. Fire Saf. J. 2009, 44, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.Y.; Kang, C.W.; Park, H.J. Impregnation and mechanical properties of three softwoods treated with a new fire-retardant chemical. J. Wood Sci. 2014, 60, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Medina, L.; Li, Y.; Carosio, F.; Hajian, A.; Berglund, L.A. Nanostructured wood hybrids for fire-retardancy prepared by clay impregnation into the cell wall. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 36154–36163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madyaratri, E.W.; Ridho, M.R.; Aristri, M.A.; Lubis, M.A.R.; Iswanto, A.H.; Nawawi, D.S.; Antov, P.; Kristak, L.; Majlingová, A.; Fatriasari, W. Recent advances in the development of fire-resistant biocomposites—A review. Polymers 2022, 14, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.L.; Ma, Z.Y.; Yao, H.X.; Qin, B.; Gao, Y.C.; Xia, Z.J.; Huang, Z.H.; Yin, Y.C.; Tu, H.; Ye, H.; et al. Economical architected foamy aerogel coating for energy conservation and flame resistance. ACS Mater. Lett. 2022, 4, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercan, M. Poplar Research Institute from its Establishment to the Present 1962–2014; (T.R. Ministry of Forestry and Water Affairs, General Directorate of Forestry, Poplar and Fast-Growing Forest Trees Research Institute. Directorate Publication No: 270); Various Publications Series No: 25: Izmit, Türkiye, 2014. Available online: https://kutuphane.tarimorman.gov.tr/vufind/Record/10258 (accessed on 5 August 2023).
- Marchi, M.; Bergante, S.; Ray, D.; Barbetti, R.; Facciotto, G.; Chiarabaglio Pier, M.; Nervo, G. Universal reaction norms for the sustainable cultivation of hybrid poplar clones under climate change in Italy. Iforest Biogeosciences For. 2022, 15, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmaca, C. Performance of Various Poplar Clones in the Early Years. Master’s Thesis, Düzce University, Institute of Science and Technology, Düzce, Türkiye, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Birler, A.S. Poplar Cultivation in Türkiye: Nursery-Afforestation-Protection-Revenue-Economy-Wood Characteristics; Poplar and Fast-Growing Forest Trees Research Directorate of the Ministry of Environment and Forestry: Ankara, Türkiye, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bozkurt, Y.; Erdin, N. Wood Anatomy; İstanbul University, Publishing of Faculty of Forestry: Istanbul, Türkiye, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gaudet, M.; Jorge, V.; Paolucci, I.; Beritognolo, I.; Scarascia Mugnozza, G.; Sabatti, M. Genetic linkage maps of Populus nigra L. including AFLPs, SSRs, SNPs, and sex trait. Tree Genet. Genomes 2008, 4, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, B.; Yapıcı, F.; Kol, H.Ş.; Özcan, C.; Esen, R.; Korkmaz, M. Determination of thermal conductivity finished on impregnated wood material. In Proceedings of 6th International Advanced Technologies Symposium (IATS’11), Elazığ, Türkiye, 6–18 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kesik, H.İ.; Keskin, H.; Temel, F.; Öztürk, Y. Bonding Strength and Surface Roughness Properties of Wood Materials Impregnated with VacsolAqua. Kastamonu Univ. J. For. Fac. 2016, 16, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, A.; Aydin, İ. Effects of Treatment with Fire Retardant Chemicals on Technologic Properties of Wood and Wooden Materials. Duzce Univ. Fac. For. J. For. 2016, 12, 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- Göker, Y.; Ayrılmış, N. Performance characteristicsand thermal degredation of wood and wood-based products in fire. J. Fac. For. Istanb. Univ. 2002, 52, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Li, X.J.; Zhong, Z.; Mou, Q.; Yan, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, L. Effectiveness of impregnation of ammonium polyphosphate fire retardant in poplar wood using microwave heating. Fire Mater. 2016, 40, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Guan, H.; Wang, X. In situ polymerization of furfuryl alcohol with ammonium dihydrogen phosphate in poplar wood for improved dimensional stability and flame retardancy. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3349–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chai, Y.; Ni, L.; Lyu, W. Flame retardant properties and thermal decomposition kinetics of wood treated with boric acid modified silica sol. Materials 2020, 13, 4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuai, B.; Wang, Z.; Gao, J.; Tong, J.; Zhan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J.; Cai, L. Development of densified wood with high strength and excellent dimensional stability by impregnating delignified poplar by sodium silicate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 344, 128282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Lu, D.; Yue, K.; Lu, W.; Zhang, Z. Fire resistance improvement of fast-growing poplar wood based on combined modification using resin impregnation and compression. Polymers 2022, 14, 3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- As, N.; Akbulut, T. Odunun fiziksel özelliklerini iyileştiren işlemler ve mekanik özellikler üzerine olan etkisi. J. Fac. For. Istanb. Univ. 1989, 39, 98–112. [Google Scholar]
- LeVan, S.L.; Winandy, E.J. Effect of fire retardant treatment on wood strenght: A Rewiev. Wood Fiber Sci. 1990, 22, 113–131. [Google Scholar]
- Ayrılmış, N. Effects of Various Fire Retardants on Fire and Technological Properties of Some Wood Based Panel Products. Ph.D. Thesis, Istanbul University, Institute of Science, İstanbul, Türkiye, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Demir, A. The Effects of Fire Retardant Chemicals on Thermal Conductivity of Plywood Produced from Different Wood Species. Master’s Thesis, Karadeniz Technical University, Institute of Science, Trabzon, Türkiye, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gökmen, K. The Effect of Heat Treatment with Tall Oil Impregnation on the Properties of Wood Material. Master’s Thesis, Bartın University, Institute of Science and Technology, Bartın, Türkiye, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, T. Effect of vacuum impregnation on mechanical properties of fast-growing poplar. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2019, 47, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.; Cai, J.; Wu, M.; Zhou, N.; Huang, Z.; Cai, L.; Zhang, Y. Surface properties of poplar wood after heat treatment, resin impregnation, or both modifications. BioResources 2021, 16, 7562–7577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Gao, M.; Wang, J.; Mu, H.; Qi, D. Fast Preparation of high-performance wood materials assisted by ultrasonic and vacuum impregnation. Forests 2021, 12, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guan, P.; Zuo, Y.; Li, P.; Bi, X.; Li, X. Preparation of highly-densified modified poplar wood by evacuating the micro-pores of wood through a gas expansion method. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 194, 116374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; Rafique, I.; Anwar, Z.; Muhammad, B. Recent developments in different types of flame retardants and effect on fire retardancy of epoxy composite. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2016, 55, 1512–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, P.; Pepin, S. Trends in chemical wood surface improvements and modifications: A review of the last five years. Coatings 2021, 11, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawalerczyk, J.; Walkiewicz, J.; Dziurka, D.; Mirski, R. Nanomaterials to Improve Fire Properties in Wood and Wood-Based Composite Panels. In Emerging Nanomaterials: Opportunities and Challenges in Forestry Sectors; Taghiyari, H., Morrell, J.J., Husen, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 65–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Şirin, M.; Baltaş, H. Ecological structure: Production of organic impregnation material from mussel shell and combustion. Polímeros 2022, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumdahl, S.S.; DeCoste, D.J. Chemical Principles, 7th ed.; Cengage Learning: Belmont, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, W.M. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 95th ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- TS 2470; Methods and General Properties of Sampling from Wood for Physical and Mechanical Experiments. TSE: Ankara, Türkiye, 1976.
- Kılıç, Ö.; Anıl, M. The effects of limestone characteristic properties and calcination temperature to the lime quality. Asian J. Chem. 2006, 18, 655–666. [Google Scholar]
- Ropp, R.C. Encyclopedia of the Alkaline Earth Compounds; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Duchesne, J.; Reardon, E.J. Measurement and prediction of portlandite solubility in alkali solutions. Cem. Concr. Res. 1995, 25, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D 1413-99; Standard Method of Testing Wood Preservatives by Laboratory Soil Block Cultures. Annual Book of ASTM Standards: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1995.
- TS EN 2472; Wood—Determination of Density for Physical and Mechanical Tests. Turkish Standards Institution: Ankara, Türkiye, 1972.
- TS 4084; Wood—Determination of Radial and Tangential Swelling. Turkish Standard Institution: Ankara, Türkiye, 1983.
- TS EN 317; Particleboards and Fibreboards–Determination of Swelling in Thickness after Immersion in Water. TSE: Ankara, Türkiye, 1999.
- DIN 4768; Determination of Values of Surface Roughness Parameters, Ra, Rz, Rmax, Using Electrical Contact (Stylus) Instruments. Concepts and Measuring Conditions. Deutsches Institut für Norming: Berlin, Germany, 1990.
- ASTM D 2863; Standard Test Method for Measuring the Minimum Oxygen Concentration to Support Candle-Like Combustion of Plastics (Oxygen Index). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2006.
- Habibzade, S.; Taghiyari, H.R.; Omidvar, A.; Roudi, H.R. Effects of impregnation with styrene and nano-zinc oxide on fire-retarding, physical, and mechanical properties of poplar wood. Cerne 2016, 22, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Cao, J.; Wang, W. Forming textured hydrophobic surface coatings via mixed wax emulsion impregnation and drying of poplar wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 421–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holy, S.; Temiz, A.; Köse Demirel, G.; Aslan, M.; Amini, M.H.M. Physical properties, thermal and fungal resistance of Scots pine wood treated with nano-clay and several metal-oxides nanoparticles. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 17, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogutlu, C.; Dongel, N. The effect of the impregnate process of wooden material to color changes and surface roughness. J. Polytech. 2009, 12, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Keskin, H.; Bülbül, R. Impacts of impregnation with Tanalith-E on surface roughness of solid wood materials. Furnit. Wooden Mater. Res. J. 2019, 2, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aykaç, S.; Sofuoğlu, S.D. A study on the comparison of surface roughness parameters in bamboo material applied with cellulosic, synthetic, polyurethane and water-based varnishes. Furnit. Wooden Mater. Res. J. 2020, 3, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, S. Wettebality, water absorption and thickness swelling of particleboard made from remediated CCA-treated wood. J. Fac. For. Istanb. Univ. 2001, 51, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, M.R.; Calderon, J.U.; Lennox, B.R. Surface energy of modified nanoclays and its effect on polymer/clay nanocomposites. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2009, 23, 663–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.J.; Fadhillah, F.; Saleem, H.; Hawari, A.; Benamor, A. Organically modified nanoclay filled thin-film nanocomposite membranes for reverse osmosis application. Materials 2019, 12, 3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emampour, M.; Khademieslam, H.; Faezipour, M.M.; Talaeipour, M. Effects of coating Populus nigra wood with nanoclay. Bioresources 2020, 15, 8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhuthali, A.; Low, I.M.; Dong, C. Characterisation of the water absorption, mechanical and thermal properties of recycled cellulose fibre reinforced vinyl-ester eco-nanocomposites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 43, 2772–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.; Maji, T.K. Comparative study on the properties of wood polymer composites based on different modified soybean oils. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2017, 37, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, A.I. Fire performance of thermally modified wood impregnated with clay nanomaterials. Feb. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2022, 31, 5292–5296. [Google Scholar]
- Janotka, I.; Madejova, J.; Števula, L.; Frt’Alová, D.M. Behaviour of Ca(OH)2 in the presence of the set styrene-acrylate dispersion. Cem. Concr. Res. 1996, 26, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodirlau, R.; Teaca, C.A. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and thermal analysis of lignocellulose fillers treated with organic anhydrides. Rom. J. Phys. 2009, 54, 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Esteves, B.; Velez Marques, A.; Domingos, I.; Pereira, H. Chemical changes of heat-treated pine and eucalypt wood monitored by FTIR. Maderas Cienc. Y Tecnol. 2013, 15, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, K. A structural scheme of soil allophane. Am. Mineral. 1967, 52, 690–708. [Google Scholar]
- Bellamy, L.J. The Infra-Red Spectra of Complex Molecules; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Romero, M.Q.; Zhang, X.Q.; Wang, R.; Wang, D.Y. Intumescent multilayer hybrid coating for flame retardant cotton fabrics based on layer-by-layer assembly and sol–gel process, RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 10647–10655. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 10647–10655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beram, A.; Yaşar, S. Performance of brutian pine (Pinus brutia Ten.) particles modified with NaOH in board production. J. Grad. Sch. Nat. Appl. Sci. Mehmet Akif Ersoy Univ. 2018, 9, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faix, O.; Meier, D.; Fortmann, I. Thermal degradation products of wood. A collection of electron-impact (EI) mass spectra of monomeric lignin derived products. Holz. Als. Roh. Werkst. 1990, 48, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotilainen, R.; Toivannen, T.; Alén, R. FTIR monitoring of chemical changes in softwood during heating. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2000, 20, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windeisen, E.; Strobel, C.; Wegener, G. Chemical changes during the production of thermotreated beech wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, F.; Trautz, M.; Beger, A.L.; Löwer, M.; Jacobs, G.; Hillringhaus, F.; Wormit, A.; Usadel, B.; Reimer, J. Fungal mycelium as a building material. In Proceedings of the Annual Symposium of the International Associationfor Shell and Spatial Structures, IASS 2017, Hamburg, Germany, 25–28 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Zhong, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, P.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, G. Novel high-efficiency casein-based P–N-containing flame retardants with multiple reactive groups for cotton Fabrics. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 13999–14008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, Z.; Matsue, N.; Henmi, T. Nanometer-scale chemical modification of nanoball allophane. Clays Clay Miner. 2007, 55, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, J.; Hu, J.; Fan, D. Effect of nitrogen phosphorus flame retardants on thermal degradation of wood. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2633–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowden, L.A.; Hull, T.R. Flammability behaviour of wood and a review of the methods for its reduction. Fire Sci. Rev. 2013, 2, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Xu, J.S.; Shen, H.Y.; Xu, J.Q.; Cao, J.Z. Montmorillonite-catalyzed furfurylated wood for flame retardancy. Fire Saf. J. 2021, 121, 103297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Siddhanta, S.K.; Chakrabarti, A. Characterization of poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) modified polyaniline prepared in stable aqueous medium. Eur. Polym. J. 1999, 35, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.X.; Xu, F.; Sun, X.F.; Xiao, B.; Sun, R.C. Physico-chemical and thermal characterization of cellulose from barley straw. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 88, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, A.; Foresti, M.L.; Cerrutti, P.; Galvagno, M. Bacterial cellulose from simple and low cost production media by Gluconacetobacter xylinus. J. Polym. Environ. 2013, 21, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakiewicz, P.; Drożdżek, M.; Laskowska, A.; Grześkiewicz, M.; Bytner, O.; Radomski, A.; Zawadzki, J. Effects of thermal modification on selected physical properties of sapwood and heartwood of black poplar (Populus nigra L.). BioResources 2019, 14, 8391–8404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaşar, S.; Güler, G. Chemical characterization of black poplar (Populus nigra L.) sawdust hemicelluloses esterified with acyl chlorides. Turk. J. For. 2021, 22, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydemir, D.; Çivi, B.; Alsan, M.; Can, A.; Sivrikaya, H.; Gündüz, G.; Wang, A. Mechanical, morphological and thermal properties of nano-boron nitride treated wood materials. Maderas. Cienc. Y Tecnol. 2016, 18, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| CAS number | 1305-78-8 |
| PubChem CID | 14778 |
| UN number | 1910 |
| Molecule formula | CaO |
| Molecular mass | 56.0774 g/mol |
| Appearance | White to yellow/brown powder |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 3.34 gr/cm³ |
| Melting point | 2613 °C |
| Boiling point | 3850 °C (100 hPa) |
| Solubility | (in water) reacts to form calcium hydroxide |
| Acidity (pKa) | 12.8 |
| Method | Sample Type | Concentration of Solution (%) | Impregnation Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | A | - | - |
| Immersion | B | 1 | 120 |
| C | 3 | 120 | |
| D | 5 | 120 | |
| Vacuum | E | 1 | 30 + 30 |
| F | 3 | 30 + 30 | |
| G | 5 | 30 + 30 |
| Sample Type | D0 (g/cm3) | WA-2 h | WA-24 h | TS-2 h | TS-24 h | WPG (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.36 (0.09) 1 a 2 | 38.21 (3.57) a | 72.89 (5.88) a | 14.86 (2.43) a | 17.26 (3.45) a | - |
| B | 0.41 (0.13) b | 33.83 (3.26) b | 67.86 (6.11) b | 13.23 (1.31) b | 15.08 (3.04) b | 0.62 (0.09) a |
| C | 0.44 (0.09) c | 29.42 (2.61) c | 63.22 (5.67) c | 11.38 (1.14) c | 13.77 (2.14) c | 0.73 (0.21) b |
| D | 0.45 (0.11) c | 26.55 (1.93) d | 59.49 (4.93) d | 10.75 (0.81) cd | 12.13 (1.86) cd | 0.91 (0.18) b |
| E | 0.42 (0.12) b | 31.26 (2.79) c | 63.92 (4.55) c | 11.49 (1.05) c | 14.86 (2.11) b | 1.12 (0.30) c |
| F | 0.46 (0.14) c | 24.12 (2.44) d | 58.32 (5.22) d | 9.08 (1.27) d | 12.22 (1.37) cd | 1.79 (0.35) d |
| G | 0.49 (0.09) d | 22.07 (1.66) e | 54.11 (4.83) e | 8.83 (0.95) d | 11.45 (1.96) d | 2.28 (0.51) e |
| Sample Type | Surface Roughness (Ra) (║) | Changes (%) | Contact Angle (°) | Changes (%) | LOI (%) | Changes (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2.77 (0.31) 1 a 2 | - | 41 (4.66) a | - | 23.16 (2.55) b | - |
| B | 3.36 (0.99) b | 21.3 | 54 (4.34) b | 31.7 | 26.75 (3.07) b | 15.5 |
| C | 3.90 (0.83) c | 40.8 | 59 (5.27) c | 43.9 | 28.44 (2.43) b | 22.8 |
| D | 4.12 (0.46) d | 48.7 | 62 (4.02) d | 51.2 | 30.08 (1.94) b | 29.8 |
| E | 3.58 (0.60) c | 29.2 | 61 (3.95) c | 48.8 | 28.27 (1.64) b | 22.0 |
| F | 4.35 (0.97) d | 57.0 | 66 (6.26) e | 60.9 | 30.62 (2.44) b | 32.2 |
| G | 5.22 (0.44) e | 88.4 | 68 (6.31) e | 65.8 | 31.23 (2.74) b | 34.8 |
| Spectrum Band Position, cm−1 | Active Wood Mass Group | Type of Vibration |
|---|---|---|
| 3450–3400 | O-H of alcohols, phenols and acids | O-H stretching |
| 2970–2850 | CH2, CH- and CH3 | C-H stretching |
| 1462–1425 | CH2 cellulose, lignin | C-H deformations |
| 1060–1025 | C-O-C | Deformation |
| 876 | Anti-symmetric out-of-phase stretching in pyranose ring | Stretching in pyranose ring |
| Sample Type | T0 (°C) | Tmax (°C) | Tf (°C) | RW at 600 °C (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 140 | 329 | 476 | 16.2 |
| B | 140 | 332 | 494 | 18.3 |
| C | 140 | 337 | 503 | 18.5 |
| D | 140 | 338 | 531 | 22.3 |
| E | 140 | 339 | 532 | 19.8 |
| F | 140 | 342 | 576 | 24.4 |
| G | 140 | 347 | 584 | 24.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beram, A. Enhancing Surface Characteristics and Combustion Behavior of Black Poplar Wood through Varied Impregnation Techniques. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11482. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011482
Beram A. Enhancing Surface Characteristics and Combustion Behavior of Black Poplar Wood through Varied Impregnation Techniques. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(20):11482. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011482
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeram, Abdullah. 2023. "Enhancing Surface Characteristics and Combustion Behavior of Black Poplar Wood through Varied Impregnation Techniques" Applied Sciences 13, no. 20: 11482. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011482
APA StyleBeram, A. (2023). Enhancing Surface Characteristics and Combustion Behavior of Black Poplar Wood through Varied Impregnation Techniques. Applied Sciences, 13(20), 11482. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011482








