Sorbets as Functional Food Products, Unexplored Food Matrices, Their Challenges, and Advancements
Abstract
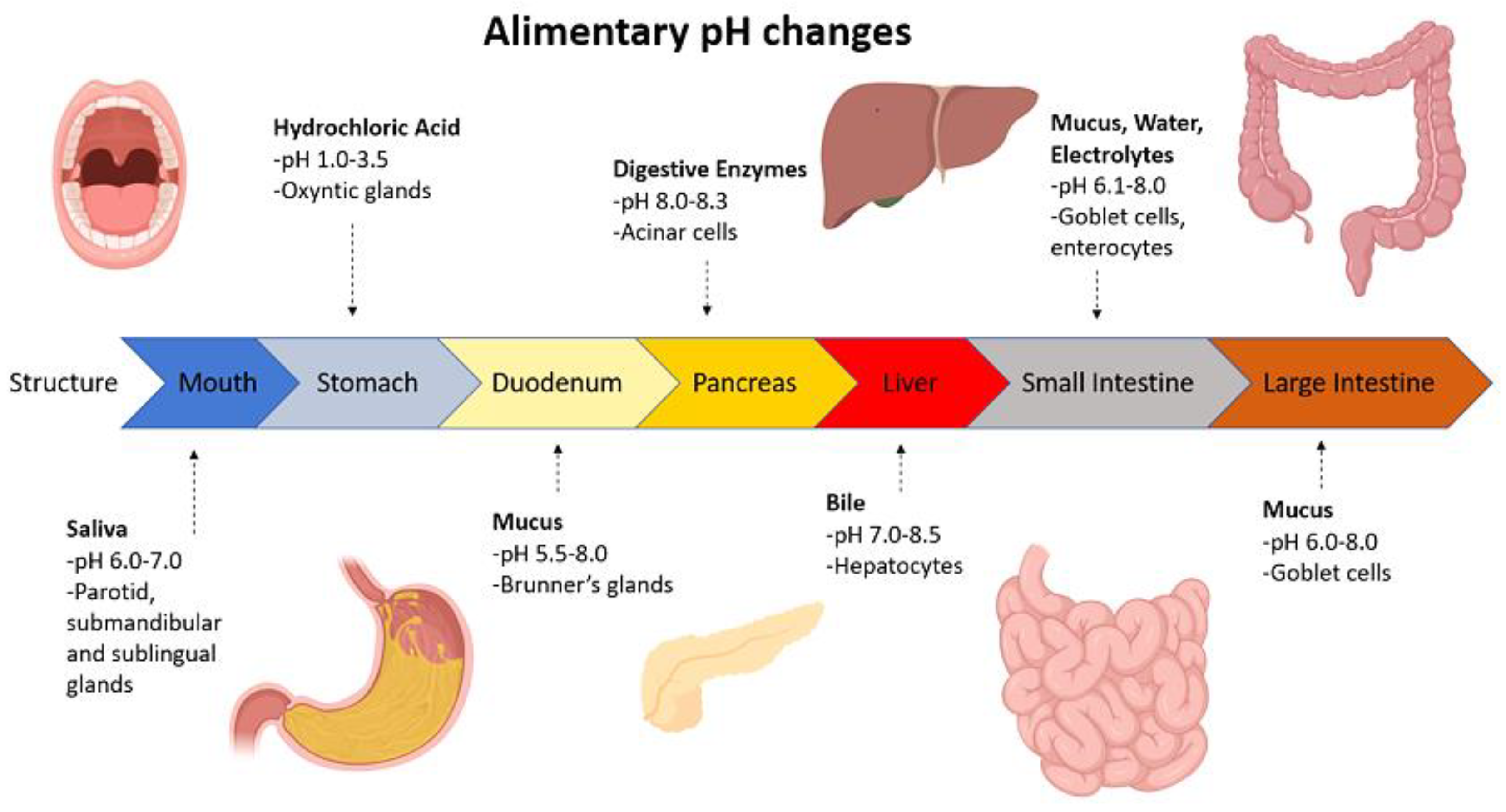
:1. Introduction
| Ingredient | Proposed Functional Food | Health Claim | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plant sterols and stanols | Margarine | Both plant sterols and stanols appear to lower blood LDL-C when consumed (1.5 to 3 g/day) with foods. | [23] |
| Folate/folic acid | Cereals | The prevention of embryological neural tube defects such as spina bifida and anencephaly. | [24] |
| Vitamin D and calcium | Milks and Juices | Fortification of Vitamin D and calcium potentially reduce future health burdens from osteoporotic fractures. | [25] |
| Iodine | Bread | Fortification of iodine in bread products in New Zealand positively contributes to 51% of iodine intake in developing children with a mean iodine intake of 35 μg/day. | [26] |
| Omega 3 | Eggs | Consumption of omega 3-enriched chicken eggs may provide extended health benefits to consumers by increasing total omega 3 status. | [27] |
2. Functional Food Vehicles
2.1. Sorbet as a Potential Functional Food
2.2. Developmental Considerations for a Functional Sorbet
2.2.1. Acidity
2.2.2. Moisture Content and Microbial Growth
2.2.3. Reduction of Microbial Growth
2.2.4. Stabilizers
3. Compound Interactions between the Sorbet Matrix and Digestive System
Metabolism of the Functional Ingredients
| Type of Interaction | Compounds | Type of Study | Finding | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug–food | Cyclosporine and grapefruit juice | Systematic review and meta-analysis | Seven studies (n = 98) indicated that administration of grapefruit juice increased the plasma concentrations of cyclosporine. | [65] |
| Drug–food | St John’s Wort and indinavir | Clinical trial | Fifteen-day oral administration of St John’s Wort significantly reduced plasma indinavir levels in male Wistar Rats. | [66] |
| Drug–food | Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and potassium | Review | Foods high in potassium must be considered by physicians prescribing angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors to reduce the incidence of hyperkalaemia. | [67] |
| Drug–food | Rupatadine and high-fat breakfast | Clinical trial | Rupatadine, an antiallergic medication with dual peripheral antihistamine H1 activity, in combination with food increased rupatadines bioavailability. | [68] |
| Food–food | Coffee and iron | Cross-sectional study | Data from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (n = 27,071) indicated that increased coffee intake was strongly associated with decreased serum ferritin concentrations. | [69] |
| Food–food | Vitamin C and iron | Review | Vitamin C consumption aids in regulating iron metabolism by increasing transferrin and non-transferrin uptake and decreases cellular iron efflux. | [70] |
| Food–food | Vitamin D and calcium | Systematic review | Vitamin D increases intestinal calcium absorption; however, the use of vitamin D in association with calcium shows inconsistent findings regarding health outcomes such as bone health, cardiovascular disease and cancer outcomes. | [71] |
4. Overcoming Absorption Issues
4.1. Nanoencapsulation
4.2. Lipid-Based Delivery Systems
5. Trends for Functional Sorbets
5.1. Improvements in Product Acceptance
5.2. Enhancing Taste
5.3. Health Trends
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Srikaeo, K. Biotechnological tools in the production of functional cereal-based beverages. In Biotechnological Progress and Beverage Consumption; Grumezescu, A.M., Holban, A.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 149–193. [Google Scholar]
- Research_and_Markets. Functional Foods Global Market Report 2023. Available online: https://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/5733821/functional-foods-global-market-report#:~:text=The%20global%20functional%20foods%20market,least%20in%20the%20short%20term (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Harrison, L.; Smith, R. Developing food products for consumers concerned with physical activity, sports, and fitness. In Developing Food Products for Consumers with Specific Dietary Needs; Osborn, S., Morley, W., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2016; pp. 215–239. [Google Scholar]
- Bozkurt, F.; Ergen, A.; İnci, B. The impact of attitude, consumer innovativeness and interpersonal influence on functional food consumption. Int. Bus. Res. 2016, 9, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Siró, I.; Kápolna, E.; Kápolna, B.; Lugasi, A. Functional food. Product development, marketing and consumer acceptance—A review. Appetite 2008, 51, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiPietro, R.B.; Remar, D.; Parsa, H.G. Health consciousness, menu information, and consumers’ purchase intentions: An empirical investigation. J. Foodserv. Bus. Res. 2016, 19, 497–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesías, M.; Seiquer, I.; Navarro, M.P. Calcium nutrition in adolescence. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.-F. The joint moderating effect of health consciousness and healthy lifestyle on consumers’ willingness to use functional foods in Taiwan. Appetite 2011, 57, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Pieniak, Z.; Verbeke, W. Consumers’ attitudes and behaviour towards safe food in China: A review. Food Control 2013, 33, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Bai, L.; Zhang, X.; Gong, S. Re-understanding the antecedents of functional foods purchase: Mediating effect of purchase attitude and moderating effect of food neophobia. Food Qual. Prefer. 2019, 73, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roddy, G.; Cowan, C.A.; Hutchinson, G. Consumer attitudes and behaviour to organic foods in Ireland. J. Int. Consum. Mark. 1996, 9, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, C.J. Functional foods. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 657–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Driessche, J.J.; Plat, J.; Mensink, R.P. Effects of superfoods on risk factors of metabolic syndrome: A systematic review of human intervention trials. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 1944–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.L.Y.; Ling, K.H.; El-Nezami, H.; Wang, M.F. Influence of functional food components on gut health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 1927–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.X.; He, J.F.; Zhang, Y.C.; Bing, D.J. Composition, physicochemical properties of pea protein and its application in functional foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2593–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, M.; Bunt, C.R.; Mason, S.L.; Hussain, M.A. Non-dairy probiotic food products: An emerging group of functional foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2626–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Cunha, N.M.; Georgousopoulou, E.N.; Dadigamuwage, L.; Kellett, J.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Thomas, J.; McKune, A.J.; Mellor, D.D.; Naumovski, N. Effect of long-term nutraceutical and dietary supplement use on cognition in the elderly: A 10-year systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 280–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seddon, N.; D’Cunha, N.; Mellor, D.; McKune, A.; Georgousopoulou, E.; Panagiotakos, D.; Kellett, J.; Naumovski, N. Effects of curcumin on cognitive function—A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Explor. Res. Hypothesis Med. 2019, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Fujihashi, A.; Govindarajulu, M.; Ramesh, S.; Deruiter, J.; Majrashi, M.; Almaghrabi, M.; Nadar, R.M.; Moore, T.; Agrawal, D.C.; et al. Role of mushrooms in neurodegenerative diseases. In Medicinal Mushrooms: Recent Progress in Research and Development; Agrawal, D.C., Dhanasekaran, M., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 223–249. [Google Scholar]
- Onaolapo, A.Y.; Obelawo, A.Y.; Onaolapo, O.J. Brain ageing, cognition and diet: A review of the emerging roles of food-based nootropics in mitigating age-related memory decline. Curr. Aging Sci. 2019, 12, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; Kellett, J.; Roach, P.D.; McKune, A.; Mellor, D.; Thomas, J.; Naumovski, N. L-theanine as a functional food additive: Its role in disease prevention and health promotion. Beverages 2016, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.L.; Everett, J.M.; D’Cunha, N.M.; Sergi, D.; Georgousopoulou, E.N.; Keegan, R.J.; McKune, A.J.; Mellor, D.; Anstice, N.; Naumovski, N. The effects of green tea amino acid l-theanine consumption on the ability to manage stress and anxiety levels: A systematic review. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2019, 75, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trautwein, E.A.; Vermeer, M.A.; Hiemstra, H.; Ras, R.T. Ldl-cholesterol lowering of plant sterols and stanols—Which factors influence their efficacy? Nutrients 2018, 10, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesia, I.; Mouratidou, T.; González-Gross, M.; Huybrechts, I.; Breidenassel, C.; Santabárbara, J.; Díaz, L.-E.; Hällström, L.; De Henauw, S.; Gottrand, F.; et al. Foods contributing to vitamin b6, folate, and vitamin b12 intakes and biomarkers status in european adolescents: The HELENA study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 1767–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandmann, A.; Amling, M.; Barvencik, F.; König, H.-H.; Bleibler, F. Economic evaluation of vitamin d and calcium food fortification for fracture prevention in germany. Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 1874–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.; McLean, R.; Davies, B.; Hawkins, R.; Meiklejohn, E.; Ma, Z.F.; Skeaff, S. Adequate iodine status in New Zealand school children post-fortification of bread with iodised salt. Nutrients 2016, 8, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, B.; Brothersen, C.; McMahon, D.J. Fortification of foods with omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 98–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gool, J.D.; Hirche, H.; Lax, H.; De Schaepdrijver, L. Folic acid and primary prevention of neural tube defects: A review. Reprod. Toxicol. 2018, 80, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, N.; Sneddon, J.; Densem, J.; Frost, C.; Stone, R. Prevention of neural tube defects: Results of the medical research council vitamin study. Lancet 1991, 338, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterhues, A.; Ali, N.S.; Michels, K.B. The role of folic acid fortification in neural tube defects: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 1180–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malgor, M.; Sabbione, A.C.; Scilingo, A. Amaranth lemon sorbet, elaboration of a potential functional food. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2020, 75, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumovski, N.; Blades, B.L.; Roach, P.D. Food inhibits the oral bioavailability of the major green tea antioxidant epigallocatechin gallate in humans. Antioxidants 2015, 4, 373–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topdas, E.F.; Cakmakci, S.; Çakıroğlu, K. The antioxidant activity, vitamin c contents, physical, chemical and sensory properties of ice cream supplemented with cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.) paste. J. Fac. Vet. Med. Kafkas Univ. 2017, 23, 691–697. [Google Scholar]
- Bahramparvar, M.; Mazaheri Tehrani, M. Application and functions of stabilizers in ice cream. Food Rev. Int. 2011, 27, 389–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; McKune, A.J.; Georgousopoulou, E.N.; Kellett, J.; D’Cunha, N.M.; Sergi, D.; Mellor, D.; Naumovski, N. The effect of l-theanine incorporated in a functional food product (mango sorbet) on physiological responses in healthy males: A pilot randomised controlled trial. Foods 2020, 9, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CODEX. Dairy-based desserts (e.g., pudding, fruit or flavoured yoghurt). In General Standards for Food Additives; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Palka, A.; Skotnicka, M. The health-promoting and sensory properties of tropical fruit sorbets with inulin. Molecules 2022, 27, 4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudette, N.; Pickering, G. Modifying bitterness in functional food systems. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 464–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Shalini, R. Effect of hurdle technology in food preservation: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Ma, M.; Li, C.; Luo, L. Stability of tea polyphenols solution with different ph at different temperatures. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontoin, H.; Saucier, C.; Teissedre, P.-L.; Glories, Y. Effect of pH, ethanol and acidity on astringency and bitterness of grape seed tannin oligomers in model wine solution. Food Qual. Prefer. 2008, 19, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.P.; Jenkins, B.M.; Vandergheynst, J. The critical moisture range for rapid microbial decomposition of rice straw during storage. Trans. ASABE 2009, 52, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Húngaro, H.M.; Peña, W.E.L.; Silva, N.B.M.; Carvalho, R.V.; Alvarenga, V.O.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Food microbiology. In Encyclopedia of Agriculture and Food Systems; Van Alfen, N.K., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 213–231. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, F.; Vandergheynst, J.S. Critical moisture content for microbial growth in dried food-processing residues. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 2000–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, D.L. Freezing: An underutilized food safety technology? Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 90, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirife, J.; Herszage, L.; Joseph, A.; Kohn, E.S. In vitro study of bacterial growth inhibition in concentrated sugar solutions: Microbiological basis for the use of sugar in treating infected wounds. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1983, 23, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbyshire, B.; Muirhead, W.A.; Henry, R. Water-soluble polysaccharide in nine commercial sweet corn cultivars and its suitability for estimating kernel maturity. Anim. Prod. Sci. 1979, 19, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez-Cock, J.; Serpa, A.; Vélez, L.; Gañán, P.; Gómez Hoyos, C.; Castro, C.; Duizer, L.; Goff, H.D.; Zuluaga, R. Influence of cellulose nanofibrils on the structural elements of ice cream. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, R.A.; Jones, J.M.; Kern, M.; Lee, S.-Y.; Mayhew, E.J.; Slavin, J.L.; Zivanovic, S. Functionality of sugars in foods and health. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 433–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshima, H.; Kinoshita, M. Effects of sugars on the thermal stability of a protein. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 138, 245101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Timasheff, S.N. The thermodynamic mechanism of protein stabilization by trehalose. Biophys. Chem. 1997, 64, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Manabe, Y.; Minamoto, N.; Saiki, N.; Fukase, K. Development of a simple assay system for protein-stabilizing efficiency based on hemoglobin protection against denaturation and measurement of the cooperative effect of mixing protein stabilizers. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 1874–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensink, M.A.; Frijlink, H.W.; van der Voort Maarschalk, K.; Hinrichs, W.L.J. How sugars protect proteins in the solid state and during drying (review): Mechanisms of stabilization in relation to stress conditions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 114, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushra, R.; Aslam, N.; Khan, A.Y. Food-drug interactions. Oman Med. J. 2011, 26, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, A.M.; Dang, C.H. Basic review of the cytochrome p450 system. J. Adv. Pr. Oncol. 2013, 4, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.R. The cytochrome p450 homepage. Hum. Genom. 2009, 4, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, H.; Pipingas, A.; Pase, M.P. Multivitamin-multimineral supplementation and mortality: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 97, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelo, G.; Drake, V.J.; Frei, B. Efficacy of multivitamin/mineral supplementation to reduce chronic disease risk: A critical review of the evidence from observational studies and randomized controlled trials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 1968–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Choi, J.; Kwon, S.Y.; McEvoy, J.W.; Blaha, M.J.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Guallar, E.; Zhao, D.; Michos, E.D. Association of multivitamin and mineral supplementation and risk of cardiovascular disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2018, 11, e004224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrowman, J.A.; D’Mello, A.; Herxheimer, A. A single dose of neomycin impairs absorption of vitamin a (retinol) in man. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1973, 5, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, M.; Booth, S.L.; Possidente, C.J.; Davidson, K.W.; Sadowski, J.A.; Bovill, E.G. The association of vitamin k status with warfarin sensitivity at the onset of treatment. Br. J. Haematol. 2001, 112, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidelbaugh, J.J. Proton pump inhibitors and risk of vitamin and mineral deficiency: Evidence and clinical implications. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2013, 4, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonstad, S.; Knudtzon, J.; Sivertsen, M.; Refsum, H.; Ose, L. Efficacy and safety of cholestyramine therapy in peripubertal and prepubertal children with familial hypercholesterolemia. J. Pediatr. 1996, 129, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Xu, S.; Xu, H.; Chen, S.; Xia, Z. Effects of phenytoin on serum levels of homocysteine, vitamin b12, folate in patients with epilepsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis (prisma-compliant article). Medicine 2019, 98, e14844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, K.; Sivaramakrishnan, G. Interaction of citrus juices with cyclosporine: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2016, 41, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.-F.; Huang, D.-K.; Hsueh, W.-C.; Lai, M.-Y.; Yu, H.-Y.; Tsai, T.-H. Effects of St. John’s wort extract on indinavir pharmacokinetics in rats: Differentiation of intestinal and hepatic impacts. Life Sci. 2009, 85, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, B.F. Managing hyperkalemia caused by inhibitors of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solans, A.; Carbó, M.l.; Peña, J.; Nadal, T.; Izquierdo, I.; Merlos, M. Influence of food on the oral bioavailability of rupatadine tablets in healthy volunteers: A single-dose, randomized, open-label, two-way crossover study. Clin. Ther. 2007, 29, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, E.S.; Choi, C.K.; Kim, N.R.; Kim, S.A.; Shin, M.-H. Association of coffee and tea with ferritin: Data from the Korean national health and nutrition examination survey (IV and V). Chonnam Med. J. 2018, 54, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, D.J.R.; Richardson, D.R. The active role of vitamin c in mammalian iron metabolism: Much more than just enhanced iron absorption! Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 75, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.; Balk, E.M.; Brendel, M.; Ip, S.; Lau, J.; Lee, J.; Lichtenstein, A.; Patel, K.; Raman, G.; Tatsioni, A.; et al. Vitamin d and calcium: A systematic review of health outcomes. Evid. Rep. Technol. Assess. 2009, 183, 1–420. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, A.; Kesisoglou, F. Impaired drug absorption due to high stomach ph: A review of strategies for mitigation of such effect to enable pharmaceutical product development. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 3970–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouge, N.; Buri, P.; Doelker, E. Drug absorption sites in the gastrointestinal tract and dosage forms for site-specific delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 136, 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assadpour, E.; Mahdi Jafari, S. A systematic review on nanoencapsulation of food bioactive ingredients and nutraceuticals by various nanocarriers. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 3129–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, L.; Stevenson, L.; Lane, K.E. The oxidative stability of omega-3 oil-in-water nanoemulsion systems suitable for functional food enrichment: A systematic review of the literature. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 1154–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.O.; Diosady, L.L.; Wesley, A.S. Folic acid fortification through existing fortified foods: Iodized salt and vitamin A—Fortified sugar. Food Nutr. Bull. 2011, 32, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Del Prado-Audelo, M.L.; Cortés, H.; Leyva-Gómez, G.; Stojanović-Radić, Z.; Singh, Y.D.; Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Martins, N.; Martorell, M.; et al. Therapeutic applications of curcumin nanomedicine formulations in cardiovascular diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafiee, Z.; Nejatian, M.; Daeihamed, M.; Jafari, S.M. Application of different nanocarriers for encapsulation of curcumin. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 3468–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, H.; Bala, R.; Arora, S. Lipid-based drug delivery systems. J. Pharm. 2014, 2014, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökmen, V.; Mogol, B.A.; Lumaga, R.B.; Fogliano, V.; Kaplun, Z.; Shimoni, E. Development of functional bread containing nanoencapsulated omega-3 fatty acids. J. Food Eng. 2011, 105, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigger, I.; Dubernet, C.; Couvreur, P. Nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, M.J.; Renouf, M.; Cruz-Hernandez, C.; Actis-Goretta, L.; Thakkar, S.K.; da Silva Pinto, M. Bioavailability of bioactive food compounds: A challenging journey to bioefficacy. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 588–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palka, A.; Wilczynska, A. Storage quality changes in craft and industrial blueberry, strawberry, raspberry and passion fruit-mango sorbets. Foods 2023, 12, 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneha, K.; Kumar, A. Nanoemulsions: Techniques for the preparation and the recent advances in their food applications. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 76, 102914. [Google Scholar]
- Zennoune, A.; Latil, P.; Flin, F.; Perrin, J.; Weitkamp, T.; Scheel, M.; Geindreau, C.; Benkhelifa, H.; Ndoye, F.T. Investigating the influence of freezing rate and frozen storage conditions on a model sponge cake using synchrotron X-rays micro-computed tomography. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 112116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanWees, S.R.; Rankin, S.A.; Hartel, R.W. Shrinkage in frozen desserts. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 780–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blahovec, J. Role of water content in food and product texture. Int. Agrophysics 2007, 21, 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, R.; Kimizuka, N.; Watanabe, M.; Suzuki, T. The effect of supercooling on ice structure in tuna meat observed by using X-ray computed tomography. Int. J. Refrig. 2015, 60, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamińska-Dwórznicka, A.; Kot, A.; Jakubczyk, E.; Buniowska-Olejnik, M.; Nowacka, M. Effect of ultrasound-assisted freezing on the crystal structure of mango sorbet. Crystals 2023, 13, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobowski, N. Shifting human salty taste preference: Potential opportunities and challenges in reducing dietary salt intake of americans. Chemosens. Percept. 2015, 8, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.S.; Tang, X.H.; Yang, W.Y.; Ong, S.H.; Naumovski, N.; Jani, R. Taste sensitivity and taste preference among Malay children aged 7 to 12 years in kuala lumpur-a pilot study. Pediatr. Rep. 2021, 13, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.Y.; Ong, S.H.; De Lee, Y.; Yen, P.L.; Lim, K.Y.; Naumovski, N.; Jani, R. Exploration of Malaysian school-children’s food preferences: What do we know? J. Trop. Pediatr. 2022, 68, fmac075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, T.A.; Alarcon, S.; Thomas, A.; Berdougo, E.; Doranz, B.J.; Breslin, P.A.; Rucker, J.B. Probenecid inhibits the human bitter taste receptor tas2r16 and suppresses bitter perception of salicin. Public Libr. Sci. One 2011, 6, e20123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravina, S.A.; McGregor, R.A.; Nossoughi, R.; Kherlopian, J.; Hofmann, T. Biomimetic in vitro assay for the characterization of bitter tastants and identification of bitter taste blockers. In Challenges in Taste Chemistry and Biology; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; Volume 867, pp. 91–101. [Google Scholar]
- Spielman, A.I. Gustducin and its role in taste. J. Dent. Res. 1998, 77, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christenson, J.; Whitby, S.J.; Mellor, D.; Thomas, J.; McKune, A.; Roach, P.D.; Naumovski, N. The effects of resveratrol supplementation in overweight and obese humans: A systematic review of randomized trials. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2016, 14, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liem, D.G.; Miremadi, F.; Keast, R.S.J. Reducing sodium in foods: The effect on flavor. Nutrients 2011, 3, 694–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, S.S.-C.; Egan, J.M. The endocrinology of taste receptors. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.M.W.; Jenkins, D.J.A. Carbohydrate digestibility and metabolic effects. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 2539S–2546S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, R. Sweet proteins—Potential replacement for artificial low calorie sweeteners. Nutr. J. 2005, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petkova, T.; Doykina, P.; Alexieva, I.; Mihaylova, D.; Popova, A. Characterization of fruit sorbet matrices with added value from Zizyphus jujuba and Stevia rebaudiana. Foods 2022, 11, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldfein, K.R.; Slavin, J.L. Why sugar is added to food: Food science 101. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunert, K.G.; Wills, J.M.; Fernández-Celemín, L. Nutrition knowledge, and use and understanding of nutrition information on food labels among consumers in the UK. Appetite 2010, 55, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Document 32006R1924; Consolidated Text: Regulation (ec) no 1924/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 December 2006 on Nutrition and Health Claims Made on Foods. EUR-Lex: Brussels, Belgium, 2014.
- Vella, M.N.; Stratton, L.M.; Sheeshka, J.; Duncan, A.M. Functional food awareness and perceptions in relation to information sources in older adults. Nutr. J. 2014, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskaran, S.; Hardley, F. Buyer beliefs, attitudes and behaviour: Foods with therapeutic claims. J. Consum. Mark. 2002, 19, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.K. Dietary salt intake and hypertension. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2014, 12, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.L.; Arcand, J.; Mendoza, J.; Henson, S.J.; Qi, Y.; Lou, W.; L’Abbe, M.R. Consumer attitudes and understanding of low-sodium claims on food: An analysis of healthy and hypertensive individuals. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 1288–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrar, I.; Schmitting, S.; Della Corte, K.W.; Buyken, A.E.; Alexy, U. Age and time trends in sugar intake among children and adolescents: Results from the donald study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 59, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestle. Nestlé’s Groundbreaking Material Science Makes Less Sugar Taste Just as Good. Available online: https://www.nestle.com.au/media/newsandfeatures/nestle-research-discovery-sugar-reduction (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- Yasueda, A.; Urushima, H.; Ito, T. Efficacy and interaction of antioxidant supplements as adjuvant therapy in cancer treatment:A systematic review. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifirad, S.; Ghaffari, A.; Amoli, M.M. The antioxidants dilemma: Are they potentially immunosuppressants and carcinogens? Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conn, V.S.; Ruppar, T.M. Medication adherence outcomes of 771 intervention trials: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Prev. Med. 2017, 99, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Vitamin/Mineral | Drug | Type of Study | Finding | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | Protein pump Inhibitors | Literature review | Vitamin C bioavailability is decreased when taken alongside protein pump inhibitors such as omeprazole. | [62] |
| Vitamin A | Neomycin | Clinical trial | The single dose (2 g) neomycin sulphate in combination with 30,000 i.u. Vitamin A decreased plasma retinol levels 4 h post-food consumption. | [60] |
| Vitamin K | Warfarin | Clinical trial | Patients with lower vitamin K status showed greater sensitivity to warfarin than those with high vitamin K status. | [61] |
| Vitamin D | Cholestyramine | Clinical trial | Adolescents with familial hypercholesterolemia consuming cholestyramine 8 g/day for one year showed significant decreases in serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations. | [63] |
| Vitamin B9 (folate) | Phenytoin | Systematic review | The administration of the anticonvulsant drug phenytoin showed significant decreases in serum folate levels in epileptic patients. | [64] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Williams, J.; McKune, A.J.; Naumovski, N. Sorbets as Functional Food Products, Unexplored Food Matrices, Their Challenges, and Advancements. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11945. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132111945
Williams J, McKune AJ, Naumovski N. Sorbets as Functional Food Products, Unexplored Food Matrices, Their Challenges, and Advancements. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(21):11945. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132111945
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilliams, Jackson, Andrew J. McKune, and Nenad Naumovski. 2023. "Sorbets as Functional Food Products, Unexplored Food Matrices, Their Challenges, and Advancements" Applied Sciences 13, no. 21: 11945. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132111945
APA StyleWilliams, J., McKune, A. J., & Naumovski, N. (2023). Sorbets as Functional Food Products, Unexplored Food Matrices, Their Challenges, and Advancements. Applied Sciences, 13(21), 11945. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132111945









