Does Exercise Testing with Arm Crank Ergometer Substitute for Cycle Ergometer to Evaluate Exercise Capacity?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Anthropometric Measurements
2.4. Assessment of Daily Training Status
2.5. Flow-Mediated Dilation (FMD)
2.6. Exercise Testing
2.7. Arm Crank Ergometer (ACE)
2.8. Cycle Ergometer (CE)
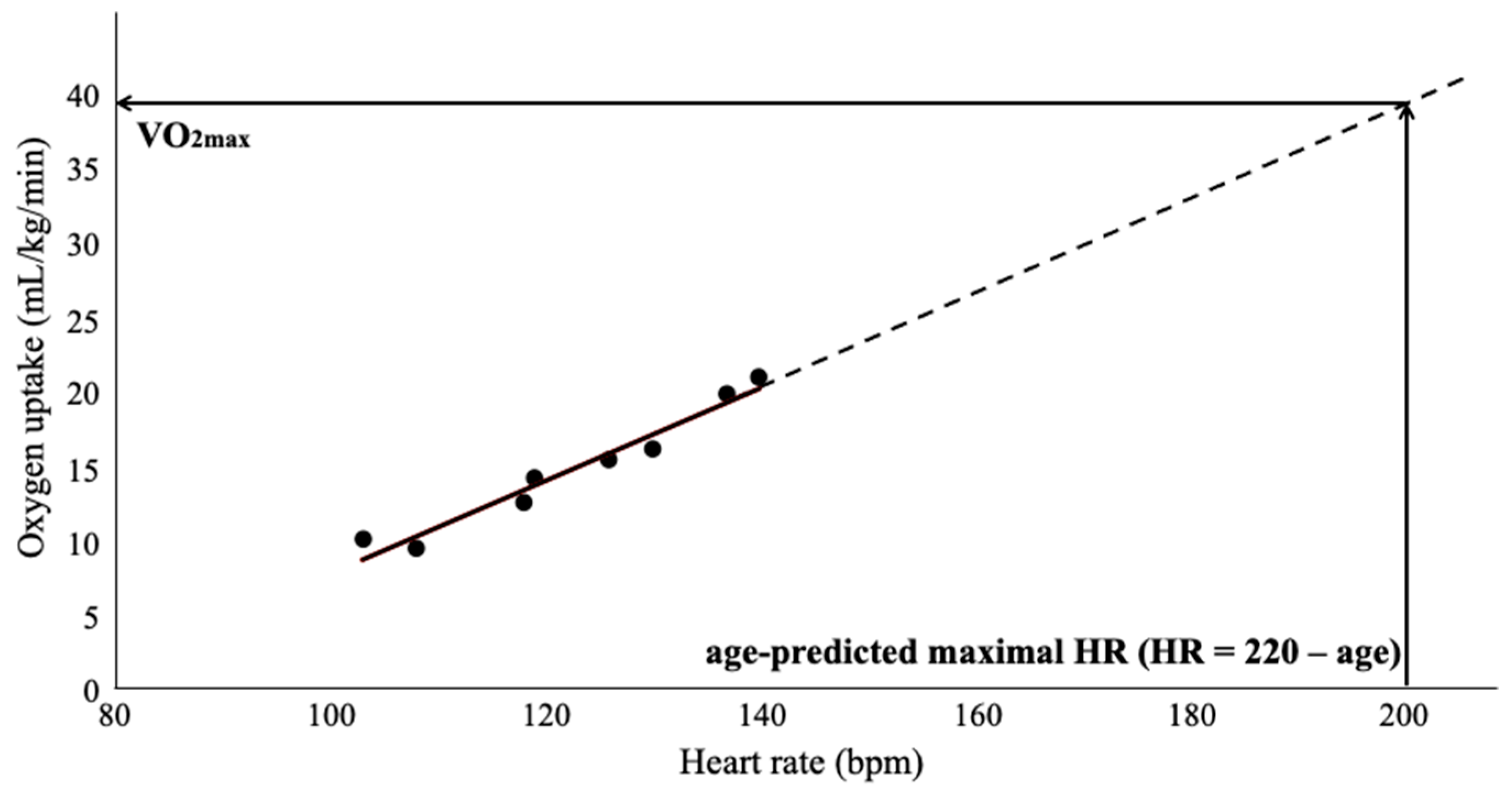
2.9. Estimation of VO2max from the Exercise Testing with ACE and CE
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Subjects
3.2. FMD of Brachial Artery
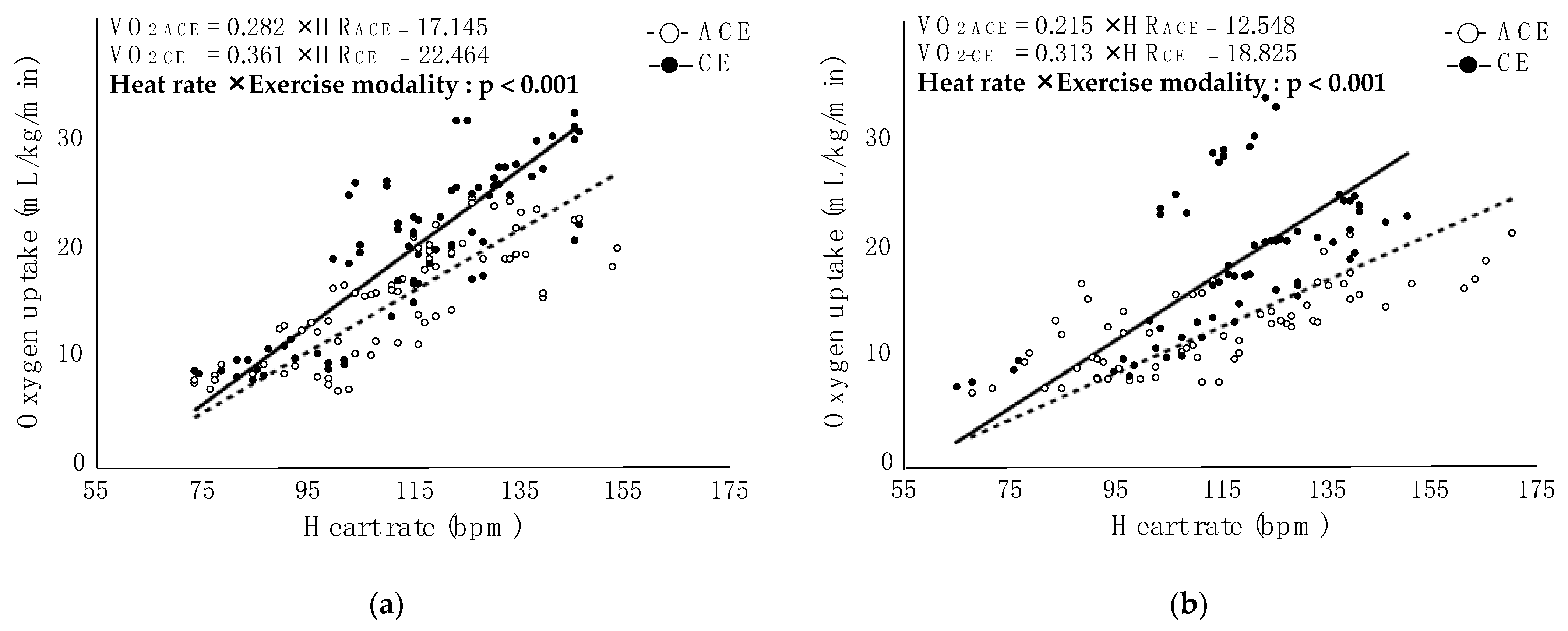
3.3. Correlation between HR and VO2 in Each Exercise Modality
3.4. Estimated VO2max from the Exercise Testing with ACE and CE
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakanishi, M.; Takaki, H.; Kumasaka, R.; Arakawa, T.; Noguchi, T.; Sugimachi, M.; Goto, Y. Targeting of high peak respiratory exchange ratio is safe and enhances the prognostic power of peak oxygen uptake for heart failure patients. Circ. J. 2014, 78, 2268–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keteyian, S.J.; Patel, M.; Kraus, W.E.; Brawner, C.A.; McConnell, T.R.; Piña, I.L.; Leifer, E.S.; Fleg, J.L.; Blackburn, G.; Fonarow, G.C.; et al. Variables Measured During Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing as Predictors of Mortality in Chronic Systolic Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzuto, B.; Agostoni, P. The Current Role of Cardiopulmonary Exercise Test in the Diagnosis and Management of Pulmonary Hypertension. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunelli, A.; Charloux, A.; Bolliger, C.T.; Rocco, G.; Sculier, J.P.; Varela, G.; Licker, M.; Ferguson, M.K.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Huber, R.M.; et al. ERS/ESTS clinical guidelines on fitness for radical therapy in lung cancer patients (surgery and chemo-radiotherapy). Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 34, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunelli, A.; Kim, A.W.; Berger, K.I.; Addrizzo-Harris, D.J. Physiologic evaluation of the patient with lung cancer being considered for resectional surgery: Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 2013, 143, e166S–e190S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palange, P.; Ward, S.A.; Carlsen, K.H.; Casaburi, R.; Gallagher, C.G.; Gosselink, R.; O’Donnell, D.E.; Puente-Maestu, L.; Schols, A.M.; Singh, S.; et al. Recommendations on the use of exercise testing in clinical practice. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 29, 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, N.; Asplund, C.A. Exercise Testing: Who, When, and Why? PM&R 2016, 8, S16–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.; Arena, R.; Franklin, B.; Pina, I.; Kraus, W.E.; McInnis, K.; Balady, G.J.; American Heart Association Committee on Exercise; Cardiac Rehabilitation; Prevention of the Council on Clinical Cardiology; et al. Recommendations for clinical exercise laboratories: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2009, 119, 3144–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulthuis, Y.; Drossaers-Bakker, W.; Oosterveld, F.; van der Palen, J.; van de Laar, M. Arm crank ergometer is reliable and valid for measuring aerobic capacity during submaximal exercise. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 2809–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrand, J.W.; Wagstaff, K.; Kasim, A.; Cawthorn, L.; Danjoux, G.R.; Kothmann, E. Reliability of repeated arm-crank cardiopulmonary exercise tests in patients with small abdominal aortic aneurysm. Anaesthesia 2018, 73, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seals, D.R.; Mullin, J.P. VO2max in variable type exercise among well-trained upper body athletes. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 1982, 53, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrieks, I.C.; Barnes, M.J.; Hodges, L.D. Comparison study of treadmill versus arm ergometry. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2011, 31, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitropoulos, A.; Gumber, A.; Crank, H.; Klonizakis, M. Validation of an Arm Crank Ergometer Test for Use in Sedentary Adults. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2017, 16, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Helgerud, J.; Øiestad, B.E.; Wang, E.; Hoff, J. Prediction of upper extremity peak oxygen consumption from heart rate during submaximal arm cycling in young and middle-aged adults. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 119, 2589–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achten, J.; Jeukendrup, A.E. Heart rate monitoring: Applications and limitations. Sports Med. 2003, 33, 517–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesch, P.A.; Karlsson, J. Muscle metabolite accumulation following maximal exercise. A comparison between short-term and prolonged kayak performance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1984, 52, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osaka Metropolitan University. Available online: https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Kyle, U.G.; Bosaeus, I.; De Lorenzo, A.D.; Deurenberg, P.; Elia, M.; Gómez, J.M.; Heitmann, B.L.; Kent-Smith, L.; Melchior, J.C.; Pirlich, M.; et al. Bioelectrical impedance analysis--part I: Review of principles and methods. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 1226–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, B.E.; Haskell, W.L.; Leon, A.S.; Jacobs, D.R.; Montoye, H.J.; Sallis, J.F.; Paffenbarger, R.S. Compendium of physical activities: Classification of energy costs of human physical activities. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1993, 25, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasikcioglu, E.; Oflaz, H.; Kasikcioglu, H.A.; Kayserilioglu, A.; Umman, S.; Meric, M. Endothelial flow-mediated dilatation and exercise capacity in highly trained endurance athletes. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2005, 205, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsch, M.A.; Blalock, P.; Credeur, D.P.; Parish, T.R. Comparison of brachial artery vasoreactivity in elite power athletes and age-matched controls. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, G.; Nottin, S.; Karpoff, L.; Pérez-Martin, A.; Dauzat, M.; Obert, P. Flow-mediated dilation and exercise-induced hyperaemia in highly trained athletes: Comparison of the upper and lower limb vasculature. Acta Physiol. 2008, 193, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, G.A. Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1982, 14, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liguori, G. “Exercise Testing and Prescription for Populations” in ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription, 11th ed.; Wolters Kluwer: Waltham, MA, USA, 2022; p. 354. [Google Scholar]
- Liguori, G. “Health-Related Physical Fitness Testing and Interpretation” In ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription, 11th ed.; Wolters Kluwer: Waltham, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 83–84. [Google Scholar]
- Philbin, E.F.; Ries, M.D.; French, T.S. Feasibility of maximal cardiopulmonary exercise testing in patients with end-stage arthritis of the hip and knee prior to total joint arthroplasty. Chest 1995, 108, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Orr, J.L.; Williamson, P.; Anderson, W.; Ross, R.; McCafferty, S.; Fettes, P. Cardiopulmonary exercise testing: Arm crank vs cycle ergometry. Anaesthesia 2013, 68, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calbet, J.A.; González-Alonso, J.; Helge, J.W.; Søndergaard, H.; Munch-Andersen, T.; Saltin, B.; Boushel, R. Central and peripheral hemodynamics in exercising humans: Leg vs arm exercise. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 25 (Suppl. 4), 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volianitis, S.; Yoshiga, C.C.; Vogelsang, T.; Secher, N.H. Arterial blood pressure and carotid baroreflex function during arm and combined arm and leg exercise in humans. Acta Physiol. Scand. 2004, 181, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, H.; Yunoki, T.; Yano, T. Oxygen uptake/heart rate relationship during upper body and lower body exercise in a group of swimmers. Hokkaido Univ. Collect. Sch. Acad. Pap. 2000, 82, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, C.T.; Few, J.; Foster, K.G.; Sargeant, A.J. Plasma catecholamine concentration during dynamic exercise involving different muscle groups. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1974, 32, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijssen, D.H.; Cable, N.T.; Green, D.J. Impact of exercise training on arterial wall thickness in humans. Clin. Sci. 2012, 122, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.J.; Smith, K.J. Effects of Exercise on Vascular Function, Structure, and Health in Humans. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a029819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.J.; Rowley, N.; Spence, A.; Carter, H.; Whyte, G.; George, K.; Naylor, L.H.; Cable, N.T.; Dawson, E.A.; Thijssen, D.H.J. Why isn’t flow-mediated dilation enhanced in athletes? Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2013, 45, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundgren, K.M.; Karlsen, T.; Sandbakk, Ø.; James, P.E.; Tjønna, A.E. Sport-Specific Physiological Adaptations in Highly Trained Endurance Athletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 2150–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Data Set of Anthropometric Measurement, FMD, and Exercise Testing Obtained from Collegiate Student Athletes. Available online: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/Data_set_of_anthropometric_measurement_FMD_and_exercise_testing_obtained_from_collegiate_student_athletes/24441205 (accessed on 1 December 2023).
| Rowers (n = 9) | Cyclists (n = 8) | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 19.4 | ± | 0.9 | 20.3 | ± | 1.0 | 0.104 |
| Height (cm) | 173.6 | ± | 7.4 | 174.5 | ± | 9.1 | 0.830 |
| Weight (kg) | 66.7 | ± | 7.2 | 66.2 | ± | 6.2 | 0.885 |
| Body fat (%) | 8.3 | ± | 3.1 | 12.4 | ± | 3.1 | 0.015 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.1 | ± | 1.5 | 21.8 | ± | 2.0 | 0.732 |
| Brachium Mmusc (kg/m2) | 0.58 | ± | 0.10 | 0.46 | ± | 0.07 | 0.012 |
| Forearm Mmusc (kg/m2) | 0.40 | ± | 0.04 | 0.36 | ± | 0.08 | 0.230 |
| UL Mmusc (kg/m2) | 0.97 | ± | 0.14 | 0.82 | ± | 0.12 | 0.026 |
| Thigh Mmusc (kg/m2) | 3.33 | ± | 0.57 | 3.06 | ± | 0.28 | 0.238 |
| Lower leg Mmusc (kg/m2) | 1.02 | ± | 0.14 | 0.95 | ± | 0.11 | 0.271 |
| LL Mmusc (kg/m2) | 4.36 | ± | 0.62 | 4.02 | ± | 0.30 | 0.184 |
| Trunk Mmusc (kg/m2) | 5.19 | ± | 0.61 | 4.52 | ± | 0.59 | 0.035 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 111.9 | ± | 12.3 | 114.6 | ± | 14.0 | 0.673 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 73.2 | ± | 11.6 | 77.0 | ± | 12.6 | 0.528 |
| Years of competition (months) | 14.1 | ± | 9.9 | 18.8 | ± | 6.9 | 0.285 |
| Training volume (METs-hour/week) | 90.6 | ± | 86.2 | 92.2 | ± | 109.2 | 0.973 |
| Rowers (n = 9) | Cyclists (n = 8) | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dbase (mm) | 4.3 | ± | 0.7 | 3.8 | ± | 0.3 | 0.151 |
| Dmaxpostdefl (mm) | 4.6 | ± | 0.7 | 4.1 | ± | 0.4 | 0.119 |
| FMD (%) | 7.9 | ± | 4.2 | 8.0 | ± | 2.7 | 0.976 |
| Rowers (n = 9) | p | Cyclists (n = 8) | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VO2max-ACE (mL/kg/min) | 41.7 | ± | 7.3 | 0.010 | 35.5 | ± | 14.2 | 0.011 |
| VO2max-CE (mL/kg/min) | 52.6 | ± | 8.6 | 50.4 | ± | 13.4 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deguchi, M.; Yokoyama, H.; Hongu, N.; Toya, A.; Matsutake, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Imai, D.; Yamazaki, Y.; Emoto, M.; Okazaki, K. Does Exercise Testing with Arm Crank Ergometer Substitute for Cycle Ergometer to Evaluate Exercise Capacity? Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12926. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132312926
Deguchi M, Yokoyama H, Hongu N, Toya A, Matsutake T, Suzuki Y, Imai D, Yamazaki Y, Emoto M, Okazaki K. Does Exercise Testing with Arm Crank Ergometer Substitute for Cycle Ergometer to Evaluate Exercise Capacity? Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(23):12926. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132312926
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeguchi, Miwako, Hisayo Yokoyama, Nobuko Hongu, Atsuya Toya, Takahiro Matsutake, Yuta Suzuki, Daiki Imai, Yuko Yamazaki, Masanori Emoto, and Kazunobu Okazaki. 2023. "Does Exercise Testing with Arm Crank Ergometer Substitute for Cycle Ergometer to Evaluate Exercise Capacity?" Applied Sciences 13, no. 23: 12926. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132312926
APA StyleDeguchi, M., Yokoyama, H., Hongu, N., Toya, A., Matsutake, T., Suzuki, Y., Imai, D., Yamazaki, Y., Emoto, M., & Okazaki, K. (2023). Does Exercise Testing with Arm Crank Ergometer Substitute for Cycle Ergometer to Evaluate Exercise Capacity? Applied Sciences, 13(23), 12926. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132312926









