Deep Learning-Based Acoustic Echo Cancellation for Surround Sound Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. First-Order Ambisonics (B-Format)
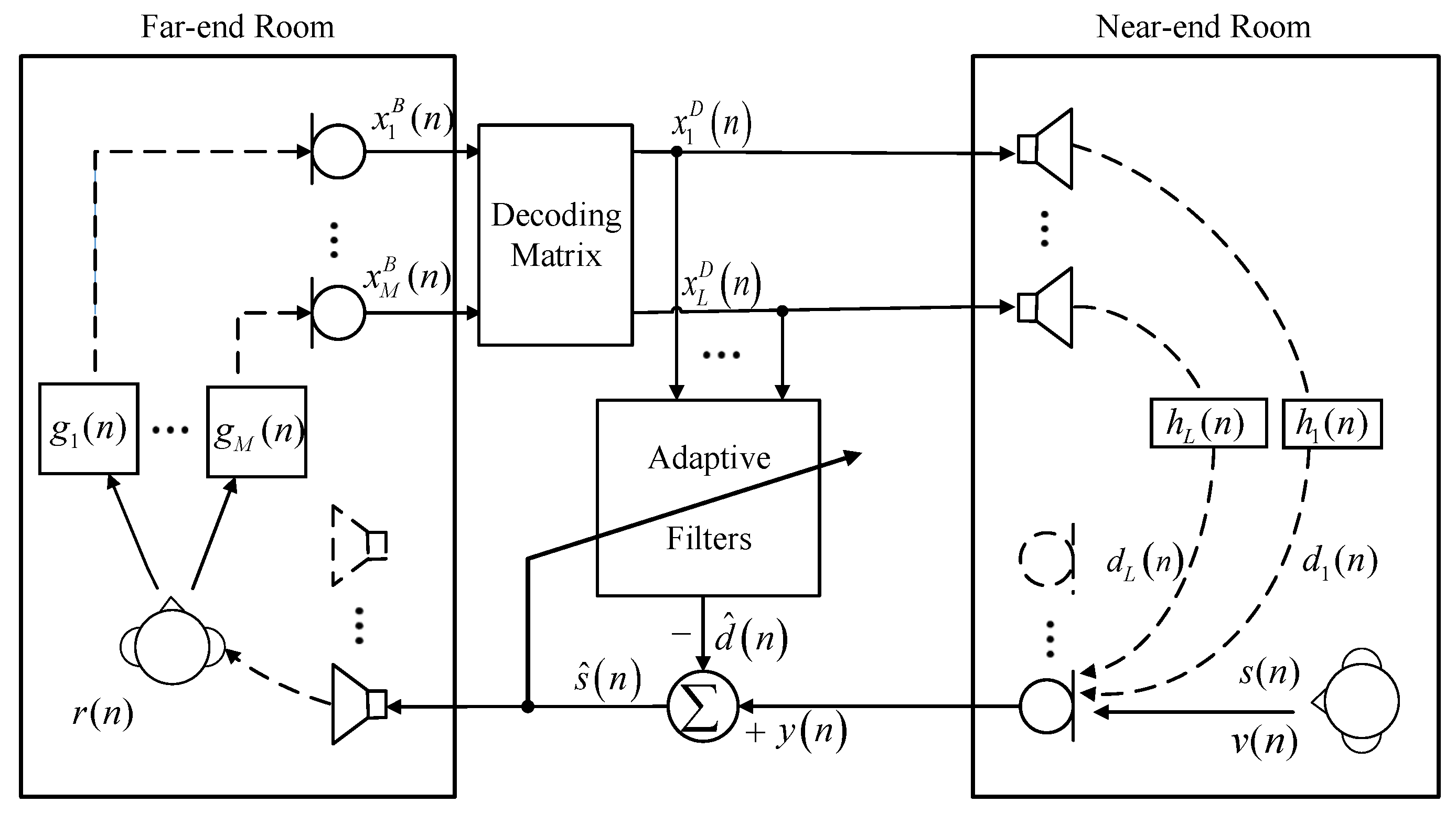
3. Signal Model
4. Proposed GCRN-Based Surround AEC
4.1. Feature Extraction and Signal Reconstruction
4.2. Model Architecture
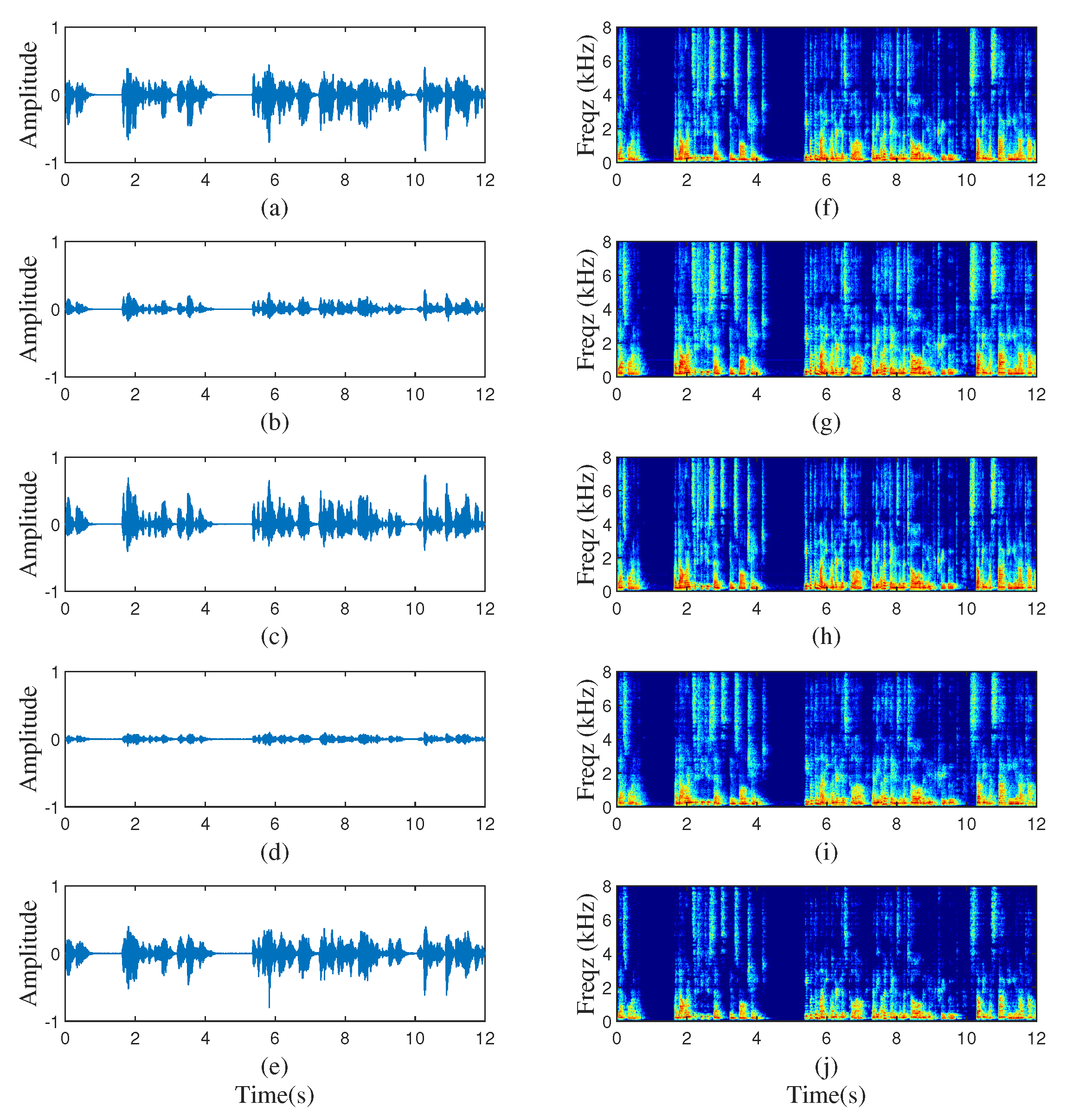
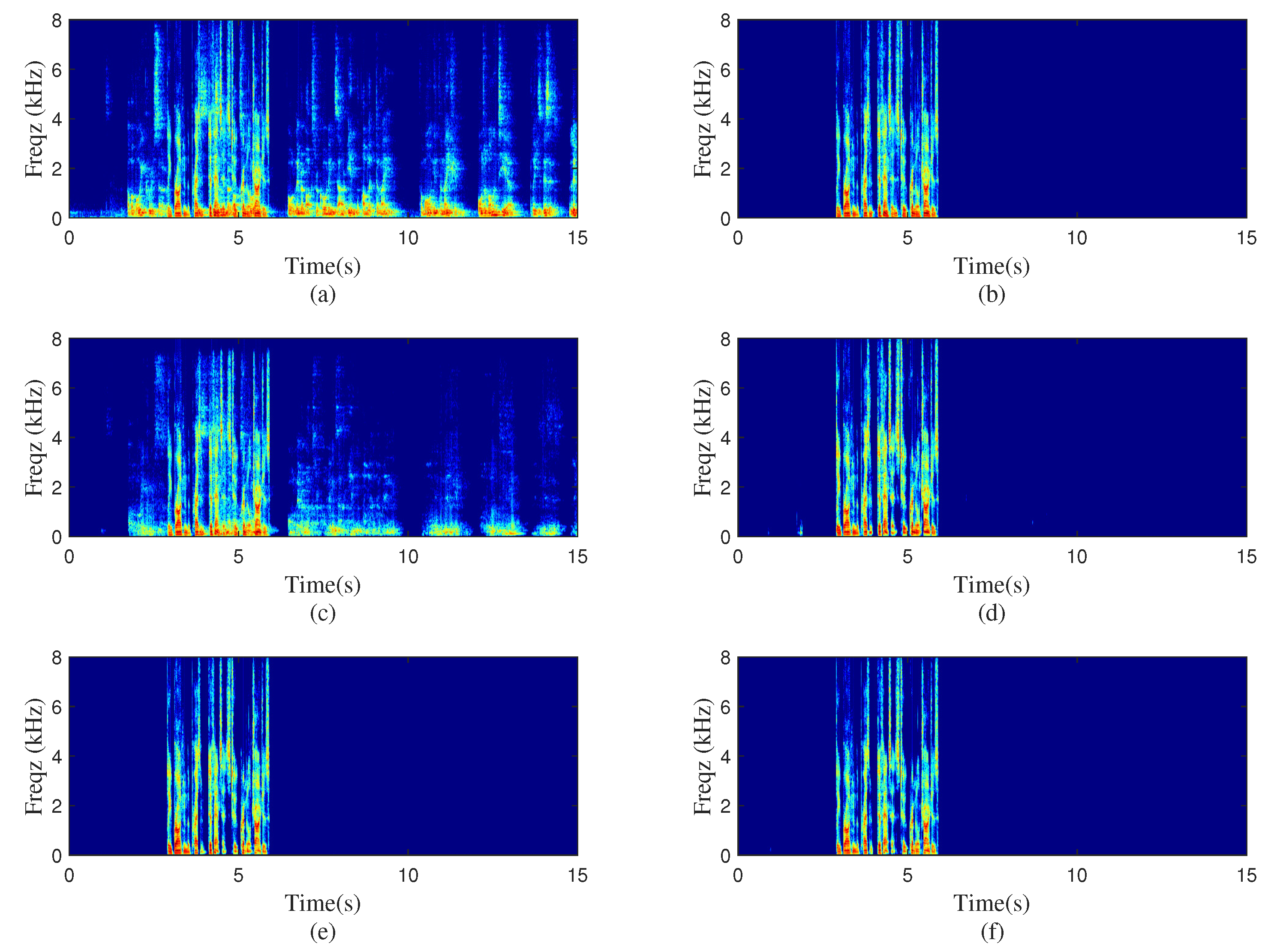
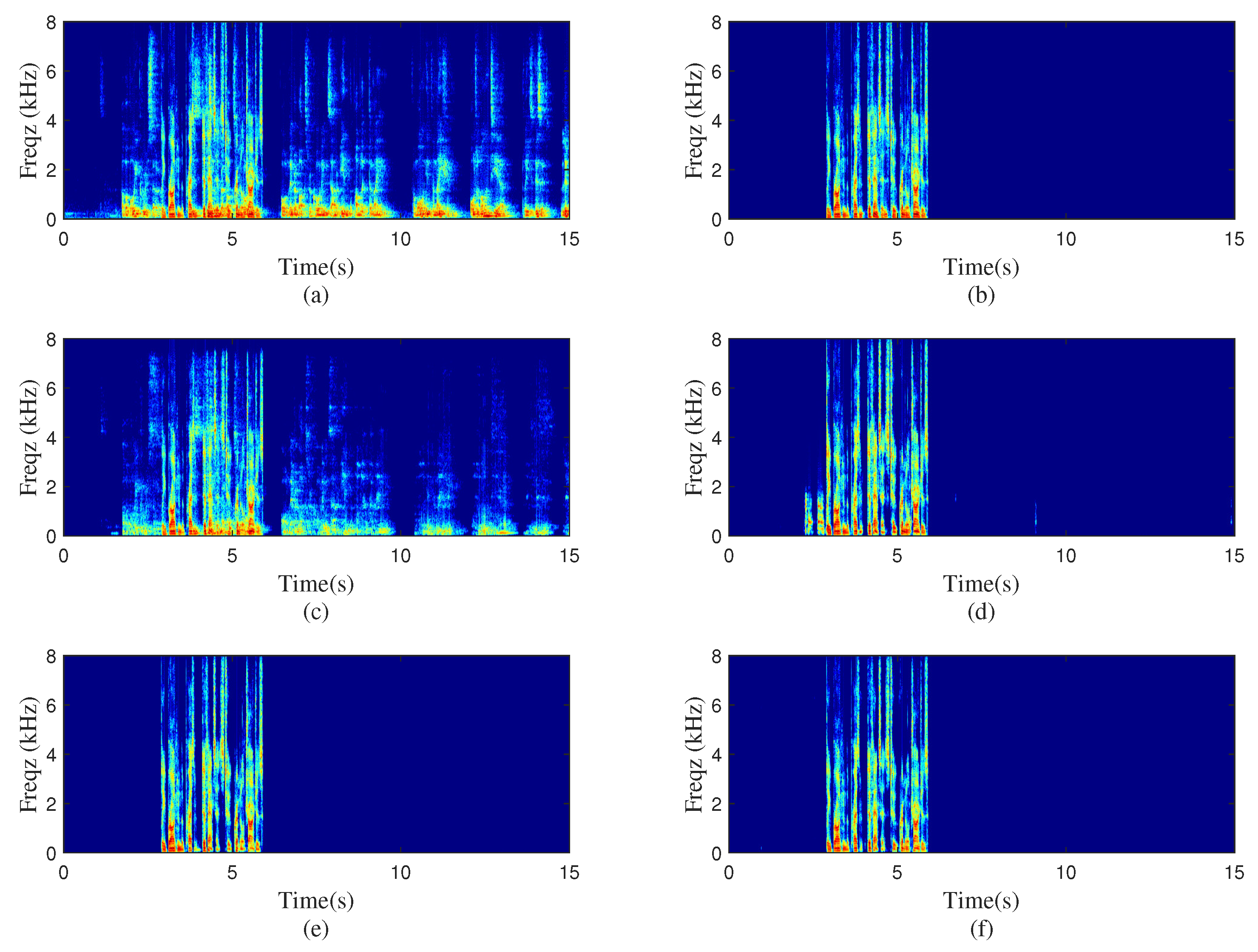
5. Experimental Results and Discussions
5.1. Experiment Settings
5.2. Performance and Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AEC | Acoustic echo cancellation |
| DNN | Deep neural network |
| BLSTM | Bidirectional long short-term memory |
| CRN | Convolutional recurrent network |
| PBFDLMS | Partitioned block frequency domain least mean square |
| GCRN | Gated convolutional recurrent network |
| PESQ | Perceptual evaluation of speech quality |
| ERLE | Echo return loss enhancement |
| STFT | Short-time Fourier transform |
| Conv-GLUs | Convolutional gated linear units |
| Deconv-GLUs | Deconvolutional gated linear units |
| BN | Batch normalization |
| ELU | Exponential linear unit |
| SER | Signal-to-echo ratio |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio |
| MSE | Mean squared error |
| RIRs | Room impulse responses |
References
- Poletti, M.A. Three-dimensional surround sound systems based on spherical harmonics. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2005, 53, 1004–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Buchner, H.; Spors, S. A general derivation of wave-domain adaptive filtering and application to acoustic echo cancellation. In Proceedings of the 2008 42nd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 26–29 October 2008; pp. 816–823. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, M.; Kellermann, W. The generalized frequency-domain adaptive filtering algorithm as an approximation of the block recursive least-squares algorithm. Eurasip. J. Adv. Sign. Process. 2016, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hänsler, E. The hands-free telephone problem-An annotated bibliography. Signal Process 1992, 27, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondhi, M.M.; Morgan, D.R.; Hall, J.L. Stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation-an overview of the fundamental problem. IEEE Signal Process Lett. 1995, 2, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romoli, L.; Cecchi, S.; Piazza, F. A combined approach for channel decorrelation in stereo acoustic echo cancellation exploiting time-varying frequency shifting. IEEE Signal Process Lett. 2013, 20, 717–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gansler, T.; Eneroth, P. Influence of audio coding on stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation. In Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–15 May 1998; pp. 3649–3652. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M. Stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation system using time-varying all-pass filtering for signal decorrelation. In Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–15 May 1998; pp. 3689–3692. [Google Scholar]
- Herre, J.; Buchner, H.; Kellermann, W. Acoustic echo cancellation for surround sound using perceptually motivated convergence enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Honolulu, HI, USA, 15–20 April 2007; pp. 17–120. [Google Scholar]
- Emura, S.; Haneda, Y. A method of coherence-based step-size control for robust stereo echo cancellation. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Accoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Hong Kong, China, 6–10 April 2003; pp. 592–595. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.M.; Shin, J.W.; Kim, N.S. DNN-based residual echo suppression. In Proceedings of the 16th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication, Dresden, Germany, 6–10 September 2015; pp. 1775–1779. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, D. Deep learning for acoustic echo cancellation in noisy and double-talk scenarios. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018; pp. 3239–3243. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Peng, R.; Li, A.; Zheng, C.; Li, X. Deep learning-based stereophonic acoustic echo suppression without decorrelation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 150, 816–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, R.; Cheng, L.; Zheng, C.; Li, X. ICASSP 2021 acoustic echo cancellation challenge: Integrated adaptive echo cancellation with time alignment and deep learning-based residual echo plus noise suppression. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, ICASSP 2021, Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 146–150. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, D. Neural Cascade Architecture for Multi-Channel Acoustic Echo Suppression. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2022, 30, 2326–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Zheng, C.; Li, A.; Peng, R.; Li, X. A deep complex network with multi-frame filtering for stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation. In Proceedings of the 23rd INTERSPEECH Conference, Songdo Convension, Incheon, Korea, 18–22 September 2022; pp. 2508–2512. [Google Scholar]
- Gerzon, M.A. Ambisonics in multichannel broadcasting and video. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1985, 33, 859–871. [Google Scholar]
- Malham, D.G.; Myatt, A. 3-D sound spatialization using ambisonic techniques. Comput. Music J. 1995, 19, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noisternig, M.; Musil, T.; Sontacchi, A.; Holdrich, R. 3D binaural sound reproduction using a virtual ambisonic approach. In Proceedings of the 2003 International Symposium on Virtual Environments, Human-Computer Interfaces and Measurement Systems, VECIMS 2003, Lugano, Switzerland, 27–29 July 2003; pp. 174–178. [Google Scholar]
- Rix, A.W.; Beerends, J.G.; Hollier, M.P.; Hekstra, A.P. Perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ)-a new method for speech quality assessment of telephone networks and codecs. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 7–11 May 2001; pp. 749–752. [Google Scholar]
- Politis, A. Microphone Array Processing for Parametric Spatial Audio Techniques. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Signal Processing and Acoustics, Aalto University, Espoo, Finland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, J.; Rault, J.B.; Polack, J.D. Ambisonics encoding of other audio formats for multiple listening conditions. In Proceedings of the 105th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, San Francisco, CA, USA, 26–29 September 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Arteaga, D. Introduction to Ambisonics; Escola Superior Politècnica Universitat Pompeu Fabra: Barcelona, Spain, 2015; pp. 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zotter, F.; Pomberger, H.; Noisternig, M. Energy-preserving ambisonic decoding. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2012, 98, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zheng, C.; Peng, R.; Li, X. On the importance of power compression and phase estimation in monaural speech dereverberation. JASA Exp. Lett. 2021, 1, 014802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Peng, R.; Zheng, C.; Li, X. A supervised speech enhancement approach with residual noise control for voice communication. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, K.; Wang, D. Learning complex spectral mapping with gated convolutional recurrent networks for monaural speech enhancement. IEEE ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2020, 28, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2015, Lile, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 448–456.
- Clevert, D.A.; Unterthiner, T.; Hochreiter, S. Fast and accurate deep network learning by exponential linear units (elus). arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.07289. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, C.K.; Dubey, H.; Koishida, K.; Nair, A.; Gopal, V.; Cutler, R.; Srinivasan, S. Interspeech 2021 deep noise suppression challenge. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.01902. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, J.B.; Berkley, D.A. Image method for efficiently simulating small-room acoustics. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1979, 65, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neukom, M. Decoding second order ambisonics to 5.1 surround systems. In Proceedings of the 121st Convention Papers 2006, San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–8 October 2006; pp. 1399–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Gänsler, T.; Benesty, J. The fast normalized cross-correlation double-talk detector. Signal Process 2006, 86, 1124–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchner, H.; Benesty, J.; Gansler, T.; Kellermann, W. Robust extended multidelay filter and double-talk detector for acoustic echo cancellation. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2006, 14, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, NIPS 2017, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5999–6009. [Google Scholar]


| Layer Name | Input Size | Hyperparameters | Output Size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Encoder | ||||
| - | ||||
| 1024 | ||||
| 1024 | ||||
| - | ||||
| Decoder1(2) | - | |||
| - | ||||
| - | ||||
| - | ||||
| - | ||||
| - | ||||
| 161 | ||||
| Algorithms | ERLE (dB) | PESQ | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SER(dB) | - | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 |
| = 0.3 s | Unprocessed | - | - | - | - | 1.85 | 2.15 | 2.46 | 2.71 |
| PBFDLMS | 14.54 | 16.13 | 16.00 | 13.89 | 2.46 | 2.71 | 2.85 | 2.93 | |
| Singlechn Model | 57.94 | 58.88 | 56.44 | 51.96 | 2.66 | 3.02 | 3.27 | 3.51 | |
| D-format Model | 62.30 | 60.72 | 58.40 | 53.60 | 2.81 | 3.15 | 3.37 | 3.63 | |
| B-format Model | 61.49 | 59.91 | 57.57 | 52.30 | 2.85 | 3.18 | 3.34 | 3.63 | |
| = 0.6 s | Unprocessed | - | - | - | - | 1.79 | 2.18 | 2.39 | 2.71 |
| PBFDLMS | 13.63 | 12.54 | 13.04 | 14.08 | 2.44 | 2.57 | 2.74 | 2.97 | |
| Singlechn Model | 56.32 | 57.66 | 56.25 | 52.36 | 2.66 | 3.02 | 3.27 | 3.44 | |
| D-format Model | 58.53 | 59.68 | 57.62 | 53.83 | 2.63 | 2.95 | 3.27 | 3.50 | |
| B-format Model | 57.34 | 58.56 | 56.34 | 52.44 | 2.67 | 3.02 | 3.31 | 3.53 | |
| = 0.9 s | Unprocessed | - | - | - | - | 1.86 | 2.09 | 2.42 | 2.72 |
| PBFDLMS | 11.31 | 13.02 | 12.75 | 13.55 | 2.23 | 2.44 | 2.76 | 2.99 | |
| Singlechn Model | 57.26 | 56.18 | 56.53 | 52.14 | 2.46 | 2.82 | 3.18 | 3.46 | |
| D-format Mode | 58.82 | 58.59 | 56.98 | 53.62 | 2.52 | 2.89 | 3.23 | 3.50 | |
| B-format Model | 57.56 | 56.86 | 56.88 | 52.63 | 2.57 | 2.95 | 3.26 | 3.52 | |
| Algorithms | ERLE (dB) | PESQ | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SER(dB) | - | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 |
| = 0.3 s | Unprocessed | - | - | - | - | 1.85 | 2.12 | 2.46 | 2.70 |
| PBFDLMS | 13.74 | 13.89 | 15.00 | 14.01 | 2.36 | 2.69 | 2.82 | 3.00 | |
| Singlechn Model | 59.54 | 59.53 | 56.92 | 52.43 | 2.69 | 3.03 | 3.25 | 3.50 | |
| D-format Model | 53.16 | 55.80 | 55.75 | 52.57 | 2.72 | 3.05 | 3.31 | 3.56 | |
| B-format Model | 63.67 | 61.09 | 58.11 | 52.80 | 2.87 | 3.17 | 3.37 | 3.63 | |
| = 0.6 s | Unprocessed | - | - | - | - | 1.74 | 2.18 | 2.39 | 2.71 |
| PBFDLMS | 12.44 | 14.04 | 14.23 | 14.38 | 2.41 | 2.55 | 2.75 | 2.89 | |
| Singlechn Model | 59.47 | 58.62 | 56.40 | 53.34 | 2.58 | 2.92 | 3.23 | 3.40 | |
| D-format Model | 54.83 | 53.77 | 54.75 | 53.61 | 2.56 | 2.92 | 3.24 | 3.51 | |
| B-format Model | 60.32 | 59.49 | 57.97 | 53.72 | 2.72 | 3.05 | 3.32 | 3.50 | |
| = 0.9 s | Unprocessed | - | - | - | - | 1.86 | 2.09 | 2.42 | 2.72 |
| PBFDLMS | 12.15 | 13.10 | 12.41 | 14.10 | 2.38 | 2.44 | 2.80 | 2.96 | |
| Singlechn Model | 57.44 | 58.54 | 57.31 | 52.76 | 2.51 | 2.87 | 3.21 | 3.47 | |
| D-format Model | 52.27 | 57.94 | 57.32 | 53.26 | 2.51 | 2.87 | 3.21 | 3.49 | |
| B-format Model | 59.30 | 59.68 | 57.65 | 53.52 | 2.65 | 2.98 | 3.29 | 3.54 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Zheng, C.; Ke, Y.; Li, X. Deep Learning-Based Acoustic Echo Cancellation for Surround Sound Systems. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031266
Li G, Zheng C, Ke Y, Li X. Deep Learning-Based Acoustic Echo Cancellation for Surround Sound Systems. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(3):1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031266
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guoteng, Chengshi Zheng, Yuxuan Ke, and Xiaodong Li. 2023. "Deep Learning-Based Acoustic Echo Cancellation for Surround Sound Systems" Applied Sciences 13, no. 3: 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031266
APA StyleLi, G., Zheng, C., Ke, Y., & Li, X. (2023). Deep Learning-Based Acoustic Echo Cancellation for Surround Sound Systems. Applied Sciences, 13(3), 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031266






