Sliding-Mode Active Disturbance Rejection Control for Electromagnetic Driven Compliant Micro-Positioning Platform
Abstract
1. Introduction
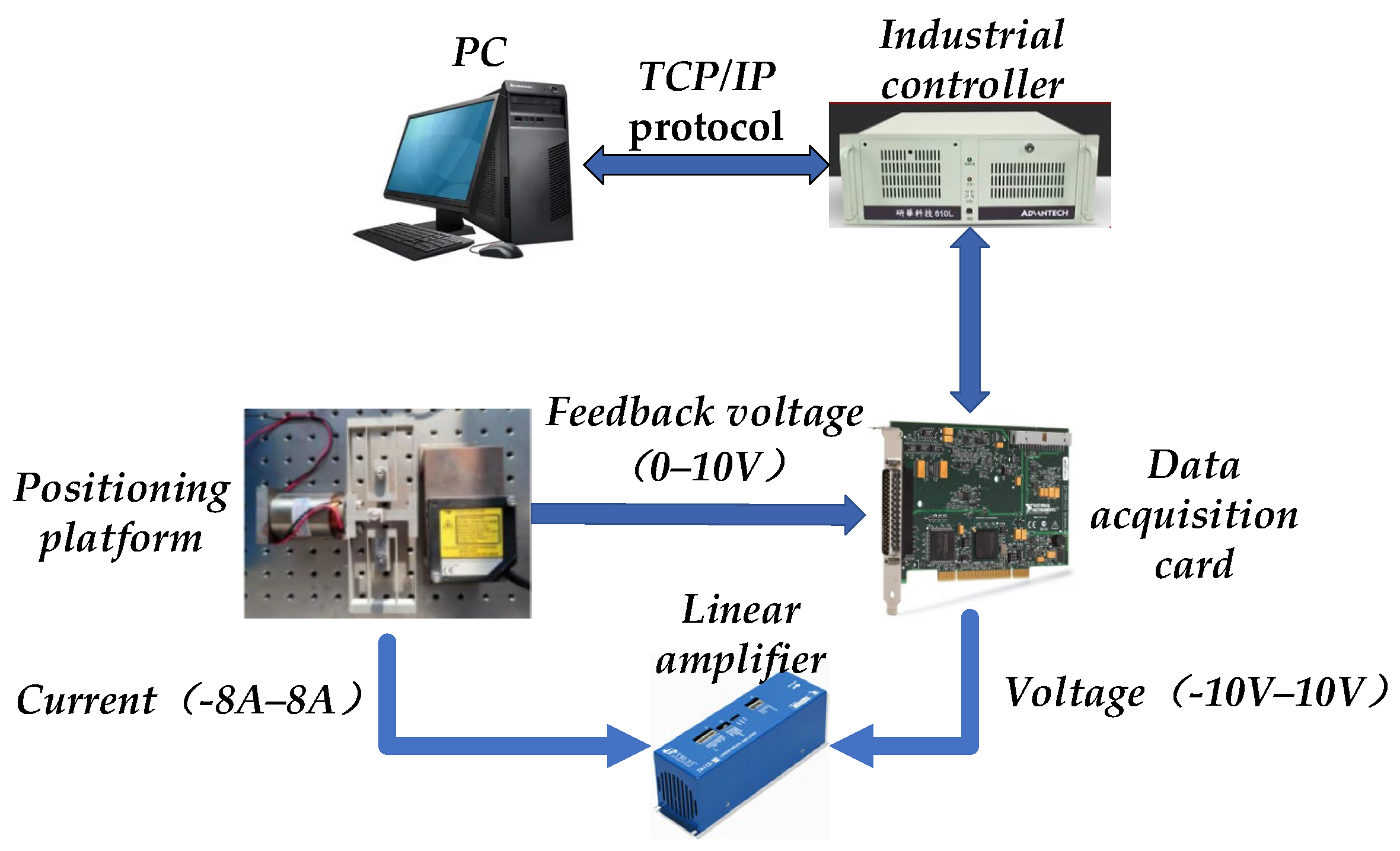
2. Mathematical Modelling for the Micro-Positioning Platform
3. Design of the Sliding-Mode Active Disturbance Rejection Controllers
4. Stability Analysis
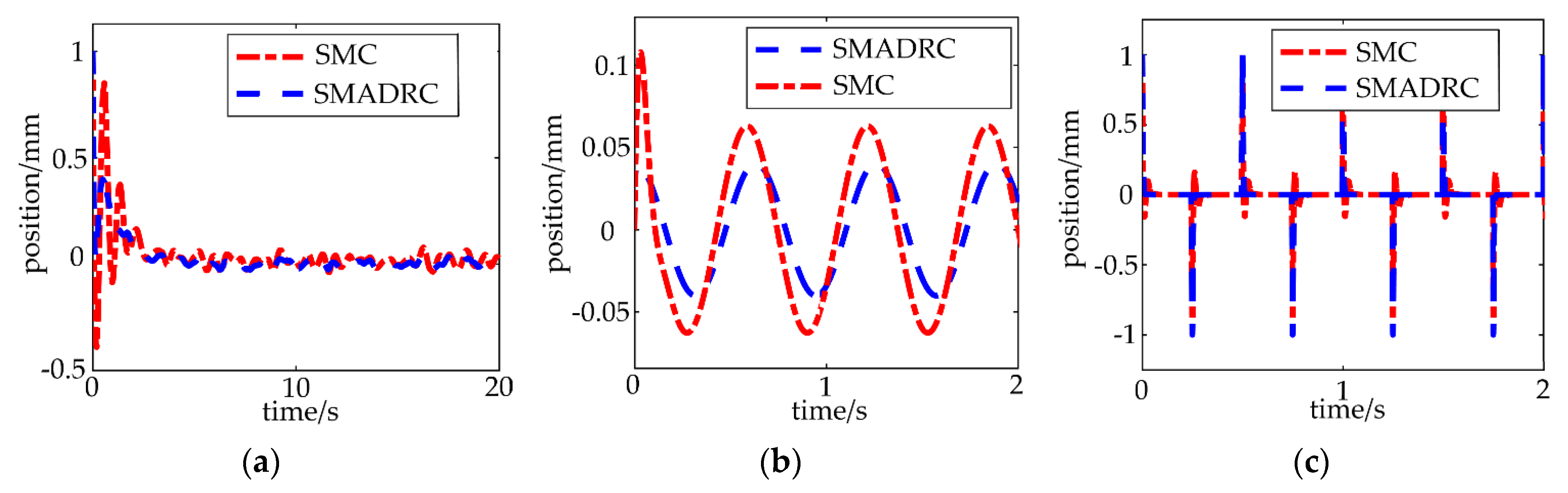
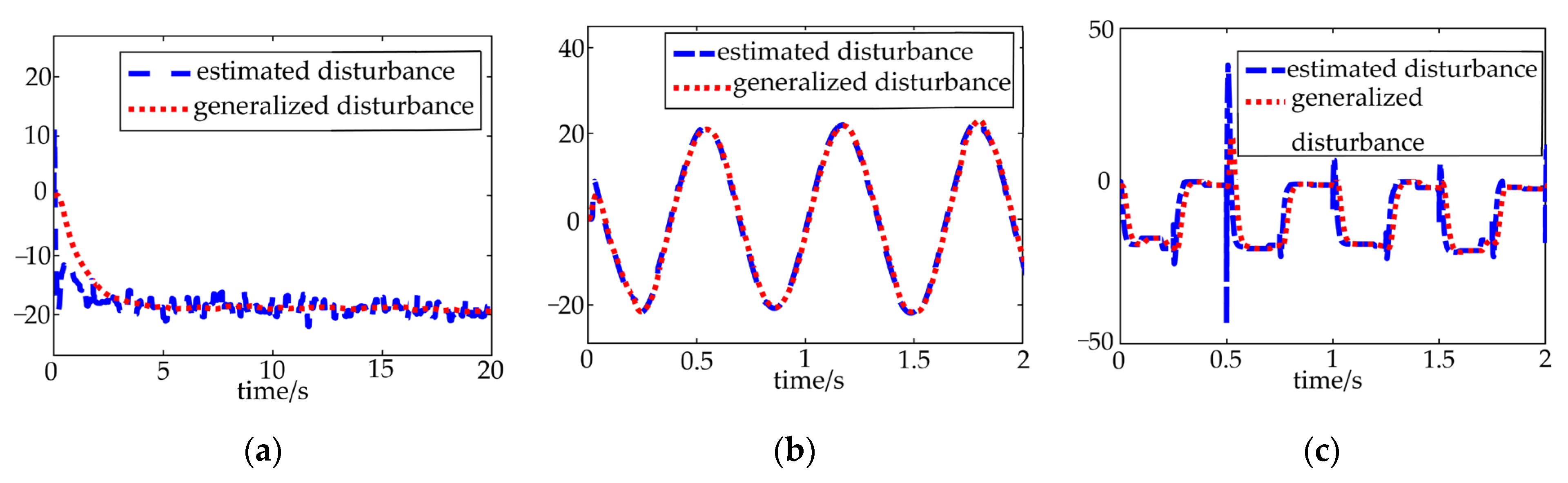
5. Simulation
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The proposed sliding-mode active disturbance rejection control can ensure smaller tracking errors and faster tracking speed than the sliding-mode control in the pre-control period (best for the signal tracking, the first 0.5 s) and without jitter.
- (2)
- The proposed sliding-mode active disturbance rejection control has better robustness. Using the designed observer, the unmolded dynamic and environmental disturbances are estimated and compensated, which can reduce the impact of disturbances on the control process and improve the control accuracy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, B.C.; Shi, R.; Wang, F.J. Design of an adaptive feedforward/feedback combined control for piezoelectric actuated micro positioning stage. Precis. Eng. J. Int. Soc. Precis. Eng. Nanotechnol. 2022, 78, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.F.; Ding, B.X.; Li, Y.M. Design, Assembly, and Simulation of Flexure-Based Modular Micro-Positioning Stages. Machines 2022, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.G.; Zhi, Y.L.; Liao, C.; Shen, J.; Wang, X. A Nano Positioning Platform for STM and Its Compound Control Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Hao, Y.; Xu, F.; Jin, J.; Li, Q.; Tong, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X. Proposal of an Equal-Stiffness and Equal-Stroke 2D Micro-Positioning Platform Driven by Piezoelectric Actuators. Actuators 2020, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Lai, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, L. Fractional order zero phase error tracking control of a novel decoupled 2-DOF compliant micro-positioning stage. J. Micromechanics Microengineering 2021, 31, 105006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cai, A.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y. Precise geometric error model based on z-axis motion platform of micro v-groove machine tools. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 92, 3219–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakjun, L.; Dahoon, A. Ultra-precision Magnetic Levitation Stage Utilizing Voice Coil Motors. J. Korean Soc. Manuf. Technol. Eng. 2022, 31, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, Z.K.; Xu, Q.S. Design of a New Bio-Inspired Dual-Axis Compliant Micromanipulator with Millimeter Strokes. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lai, L.J. Closed-loop inverse iterative learning control in frequency-domain for electromagnetic driven compliant micro-positioning platform. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2021, 29, 2149–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.Y.; Zhu, L.M.; Su, C.Y.; Ding, H.; Fatikow, S. Proxy-Based Sliding-Mode Tracking Control of Piezoelectric-Actuated Nanopositioning Stages. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Wang, K.C.; Wu, L. Positional Regulation of Electrostatic Micro-electromechanical Actuator via Adaptive Two-stage Sliding Mode Control. Sens. Mater. 2020, 32, 3343–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, J.; Yang, B.; Chen, X. Event-Triggered Adaptive Control Design with Prescribed Performance for Macro-Micro Composite Positioning Stage. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 9963–9971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Hirata, K.; Asai, Y. Experimental verification of disturbance compensation control of linear resonant actuator. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2016, 52, 1637–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, J.K.; Kim, S.K. VCM controller design with enhanced disturbance decoupling for precise automated manufacturing processes. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2012, 6, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.X.; Chen, Y.Q. Extended state observer design with fractional order Bode′s ideal cut-off filter in a linear motor motion control system. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control. Eng. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, L.; Huang, M.; Han, W.; Wang, Z.; Lu, X.; Bai, Y.; Gao, H. Improved Active Disturbance Rejection Double Closed-Loop Control of a Rotary-Type VCM in a Moving Mirror Control System. Sensors 2022, 22, 3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.D.; Bai, J.; Zhang, J. Full-order adaptive observer for interior permanent-magnet synchronous motor based on novel fast super-twisting algorithm. Meas. Control. 2022, 00202940221122235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.W.; Cao, W.H.; She, J.H. Analysis and Design of Active Disturbance Rejection Control with an Improved Extended State Observer for Systems with Measurement Noise. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Cheng, T.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Z.; Han, C.; Wang, R.; Liu, E. Modified active disturbance rejection control scheme with sliding mode compensation for airborne star tracker driven by Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. Control. Eng. Pract. 2022, 127, 105267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Gong, D.; Liu, J. Global Integral Sliding-Mode Control with Improved Nonlinear Extended State Observer for Rotary Tracking of a Hydraulic Roof bolter. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Sun, X.M. A Linear-Nonlinear Switching Active Disturbance Rejection Voltage Controller of PMSG. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.09295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, C. Motion Control of Autonomous Underwater Glider with Sliding Variable Structure Control. In International Conference on Autonomous Unmanned Systems; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1484–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Tian, W.; Jin, G.; Chen, E.; Li, S. Active control of nonlinear suspension with fractional order based on a differential geometry method. J. Vib. Shock. 2022, 40, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Duan, C.; Yao, W.; Zeng, P.; Jiang, L. Adaptive Lyapunov Function Method for Power System Transient Stability Analysis; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, A.; Song, J.; Lai, L. Sliding-Mode Active Disturbance Rejection Control for Electromagnetic Driven Compliant Micro-Positioning Platform. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031309
Zhang A, Song J, Lai L. Sliding-Mode Active Disturbance Rejection Control for Electromagnetic Driven Compliant Micro-Positioning Platform. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(3):1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031309
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Aihua, Jiqiang Song, and Leijie Lai. 2023. "Sliding-Mode Active Disturbance Rejection Control for Electromagnetic Driven Compliant Micro-Positioning Platform" Applied Sciences 13, no. 3: 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031309
APA StyleZhang, A., Song, J., & Lai, L. (2023). Sliding-Mode Active Disturbance Rejection Control for Electromagnetic Driven Compliant Micro-Positioning Platform. Applied Sciences, 13(3), 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031309




