Abstract
The purpose of this research was to study the effect of AudioVisual pattern on the muscle activity amplitude during mental imagery. For this purpose, 25 female students (20.73 ± 1.56 years old) engaged in mental imagery (internal, external, and kinesthetic) in three conditions: No pattern, Visual pattern, and AudioVisual pattern. The angular velocity of the elbow joint in the basketball jump shot skill was sonified and presented to the subjects as an auditory pattern. The results showed that the muscle activity amplitude in AudioVisual–kinesthetic and AudioVisual–internal (and not external) conditions is higher than for other conditions. Additionally, a positive correlation was observed between Visual–kinesthetic imagery ability and muscle activity amplitude in the AudioVisual pattern condition and in kinesthetic and internal imagery. In addition, the muscle activity amplitude of high and low Visual–kinesthetic imagery ability conditions were only different in the AudioVisual pattern. The superiority of the AudioVisual condition is most likely due to the auditory information presented in this research being closely related to the kinesthetic sense of movement.
1. Introduction
Imagery is referred to as a pseudo-sensory, pseudo-perceptual, and pseudo-emotional feature that is under the voluntary control of the imager and may occur in the absence of a real stimulus, and it is generally associated with actual experiences [1]. In fact, imagery is a specific mental process that can be practiced mentally [2], which includes creating and recreating any kind of experience in the mind, and it is not limited to motor performance [1]. Therefore, imagery is one of the most popular and common sports psychological strategies to improve performance and develop psychological skills. Cognitive sports psychology and neuroscience studies have proven that kinesthetic imagery is an effective way to improve motor skill performance [3] in many everyday motor activities [4].
Over a half-century ago, Jacobson [5] showed that changes in muscle excitation occurred during the imagination of movements. The psychoneuromuscular theory [6] held that muscle activation is the agent of the generated image and according to inflow processing theory [7], motor imagery activates muscular or peripheral structures that provide proprioceptive feedback to the central nervous system. In line with this explanation, many studies have shown that during mental imagery, the electrical activity of the muscles increases significantly [8,9,10]. Losana-ferrer et al. [10] showed that mental imagery similar to action observation leads to muscle activation.
However, outflow processing theory states that motor imagery produces changes in the central motor program and observed electromyographic activity is a consequence of imagery rather than a cause of imagery or imagery benefits [7]. Many studies have identified similarities between the brain mechanisms involved in mental imagery and the actual execution of movements (see the meta-analysis by Hardwick, Caspers, Eickhoff, and Swinnen, [11]). Oh and Choi [12] suggested that imagery training engages the same areas of the brain that are activated during physical training. For this reason, researchers have consistently reported beneficial effects of motor imagery on physical activities that require both acute (i.e., after a motor imagery session) and long-term (i.e., exercise) muscle force generation [3]. Lutz [13] also showed that motor imagery produced greater levels of covert excitation at the dominant biceps in comparison to control imagery and this covert excitation was associated with imaging ability and clarity. However, Lutz [13] showed that this covert excitation did not predict the acquisition and retention of the motor task and, therefore, the role of cortical contributions should also be considered [7,13,14].
It has been claimed that the use of different senses, including visual, auditory, kinesthetic, tactile, olfactory, and gustatory, in motor imagery may strengthen mental images [15]. However, it is worth mentioning that most of the research has only focused on visual imagery [16,17,18,19]. However, it has been found that non-visual forms of imagery are also common and useful in everyday life [20]. In recent years, research similar to visual imagery has been conducted for auditory, olfactory, and tactile imagery [21,22]. Past research has shown that the quality of the reported image is the highest for visual and auditory imagery and the lowest for olfactory and gustatory imagery [23,24,25]. In addition, it has been shown that the common components between auditory imagery (musical type) and motor imagery, in terms of the need for temporal skills, can have a higher cognitive importance than motor or auditory functions [18]. Therefore, it seems that the functions of auditory imagery in the development of movement are more important than what has been considered so far. The relationship between rhythmic sound and movement has been extensively studied and it has been shown that rhythmic movement, auditory acuity [26], as well as rhythmic sound, can affect the efficiency of movement [27]. However, the role of auditory imagery in perception and action has not been studied in detail. The research conducted in this area has often concentrated on the use of auditory imagery in the performance development of musicians [23,28,29,30], whereas sports skills have received less attention.
According to the definition provided by Intons-Peterson [31], auditory imagery is “the introspective persistence of an auditory experience made of its components in long-term memory, in the absence of direct sensory stimulation of that experience” [31]. In the few studies that have investigated the effect of auditory imagery on performance, audio tapes have been used to create an auditory experience containing the sound of people performing, including the sound of an athlete’s body or sports equipment hitting surfaces, environmental sounds, etc. [32,33,34]. Calmels et al. [32] demonstrated the positive effect of audiotape-based auditory imagery on the development of visual imagery vividness [32]. Smith and Holmes [34] showed that auditory imagery based on an audiotape of pattern improved putting performance in golfers [34]. Additionally, Debarnot and Guillot [35] showed that the use of rhythmic music related to movement increases the time matching between physical exercise and imagery exercise compared to movement without music, which can affect the effectiveness of imagery for time matching with physical exercise [4].
The use of audio tapes to create an auditory experience for auditory imagery may seem beneficial, but it is limited to sounds that are within the range of human hearing, such as sounds caused by the impact of the body or sports equipment on different surfaces. Such sounds usually cannot provide the learner with information about the mechanics of movement (the correct pattern of execution). Recent research has clearly shown that the use of hearing in perception related to movement can lead to a wider range of information, which subsequently increases the accuracy of received information to support motor learning [36]. Since vision has a greater spatial resolution, it is more proficient in spatial tasks [36,37]. However, since hearing has a more temporal resolution, it is, therefore, more dominant in temporal tasks. Considering that timing is an important part of motor skill execution, in the last two decades, using auditory information in order to provide movement patterns for learners has been attempted. Because, in many cases, the movement pattern does not create a sound in the human hearing range, sonification has been applied to create a sound related to the movement pattern. Sonification involves converting the kinetic or kinematic characteristics of human movement into audible patterns (for example, presenting the angular displacement or angular velocity of the elbow joint as an audible pattern to individuals). Such action-specific construction sounds are also called auditory kinematics of movement [38]. The research indicates that the use of sonification of movement characteristics in the form of simultaneous feedback (concurrent auditory feedback regarding how an individual performs based on their performance) or modeling (presenting another person’s movement pattern), alone or together with a visual pattern [22,39,40,41], can result in the development of perception and reproduction [39,41,42,43,44].
Although the research literature has confirmed the role of auditory kinematics of movement (sonification) in improving performance and learning motor skills, the effect of this type of auditory stimulation in mental imagery interventions has not yet been determined. So, this research addresses the question of whether visual imagery with the sounds related to the movement pattern (sonification) has a greater effect on muscle activation.
Another question investigated in this research is the type of auditory stimuli associated with which type of visual imagery (internal, external, or kinesthetic) is more effective. According to the PETTLEP model developed by Holmes and Collins [45], the imagery perspective is one of the seven components of mental imagery, and many kinds of research have been conducted regarding the adoption of the appropriate imagery [14,46,47,48]. Guillot et al. [14] stated that different types of mental imagery (internal and external) lead to specific and different dimensions of motor skill execution [14]. It has also been found that external imagery is more beneficial in the early stages of learning because it allows the learner to examine motor skills outside of their body and, as a result, gain a comprehensive perspective of the organs and visual cues associated with performance. In contrast, in tasks requiring kinesthetic awareness, internal imagery appears more useful because this type of imagery is more related to kinesthetic sense. It has been shown that while internal imagery has the potential to create kinesthetic images (sense of movement), external imagery is insufficient to create such a sense [46]. Since the auditory model used in this research is based on the kinematic characteristics of the movement, the main hypothesis of the present research is the use of auditory imagery along with Visual–internal and Visual–kinesthetic imagery, which is more effective compared to external visual imagery.
2. Materials and Methods
This study was semi-experimental and causal-comparative research (post-event survey) that was carried out in the Sports Sciences Laboratory of Damghan University.
2.1. Participants
Regarding within-subject analysis, the sample size was calculated by G*Power software in which the first type error was 0.05, the statistical ability was 0.8, and the average effect size of previous studies was estimated. For this purpose, 25 students (M age = 20.35 years, SD = 1.6, female) voluntarily participated in the research. All subjects were right-handed and did not report any neurological, hearing, visual, motor, attention, or depression disorders. The subjects had no experience in the basketball jump shot and mental imagery of motor skills. The research protocol was approved by the ethics committee under the number IR.DU.REC.1400.003.
2.2. Measures
The mental rotation test, the visual imagery ability questionnaire (internal, external, kinesthetic), and the Bucknell auditory imagery scale (clarity and control) were used. Additionally, an eight-channel electromyography device was used to record the electrical activity of the elbow extensor muscles (triceps brachii).
2.2.1. Mental Rotation Test (MRT)
Mental rotation refers to the ability to rotate mental representations of two-dimensional and three-dimensional objects, which is related to the visual representation of such rotation in the human mind [49]. Mental rotation is a cognitive function that helps a person to understand the change in the state of the object. The mental rotation test has two forms: V, 20 questions; and K, 24 questions. In this study, the mental rotation test used was a set of 24 questions. Each problem consists of a target figure on the right and four stimulus figures on the left. Two of the four stimulus figures are the rotated version of the target figure, and the other two figures cannot be the same as the target figure [50]. In preliminary research, this test was conducted on a group of students other than the sample of the main research, and the reliability of the test, using the test–retest method, was calculated at 0.87. A cut-off point of 70% was used to select the subjects to participate in the research.
2.2.2. Movement Imagery Questionnaire-3 (External, Internal, Kinesthetic) (MIQ-3)
The third version of this questionnaire was developed by Williams et al. in 2012 [51]. This questionnaire measures internal imagery, external imagery, and kinesthetic imagery. This 24-question questionnaire was measured with a 5-point Likert scale. There were 8 questions to measure the imagery ability of each type of imagery (external, internal, kinesthetic). The results of Wilson et al. [52] confirmed that this questionnaire has very good construct validity (CFI = 0.98). They also reported a suitable validity for the subscales of this questionnaire including Visual–internal imagery (0.628), Visual–external imagery (0.679), and Visual–kinesthetic imagery (0.706). By examining the validity and reliability of the movement imagery vividness questionnaire, Sohrabi et al. [53]. reported that the questions accounted for 47% of the total variance related to visual, internal, and kinesthetic imagery vividness and the overall scale was equivalent to 0.86, 0.89, 0.91, and 0.95, respectively, which shows the high reliability of this subscale and the overall scale of motion visualization vividness. Additionally, the construct validity of the questionnaire was determined using the exploratory factor analysis method (KMO = 0.76) [53].
2.2.3. Bucknell Auditory Imagery Scale (Vividness and Control)
The Bucknell Auditory Imagery Scale (BAIS) is a short self-report scale including three main dimensions of auditory experience: musical, verbal, and environmental sounds. For each item in the BAIS, a situation is described and then the sound associated with that situation is presented [54]. Respondents are required to try to create an auditory image of that sound. For the vividness subscale (BAIS-V), subjects are asked to rate their image vividness of sound using a scale of 1 to 7, where 1 means no image, 4 means relatively vivid, and 7 means that the image is as vivid as real. No other scale points are labeled. For the control subscale (BAIS-C), each situation and sound is described again, but the main purpose of the rating is the ease of image change from the original sound to the new sound. To rate control, respondents use a different 7-point scale, where 1 means no image, 4 means one can change the image, but with effort, and 7 means it is very easy to change the image. The face and content validity of the Bucknell auditory imagery questionnaire (vividness and controllability) was confirmed by researchers with a content validity coefficient of 0.72.
2.3. Visual and Visual–Auditory Pattern
2.3.1. Visual Pattern
A skilled basketball player with 15 years of experience was used for the visual pattern. A skillful pattern was recorded from the front and at an angle of 20 degrees to the frontal plane. This selected model had three features: (1) it led to points; (2) it was confirmed by the skilled person themselves; and (3) it was confirmed by two basketball coaches.
2.3.2. Auditory Pattern
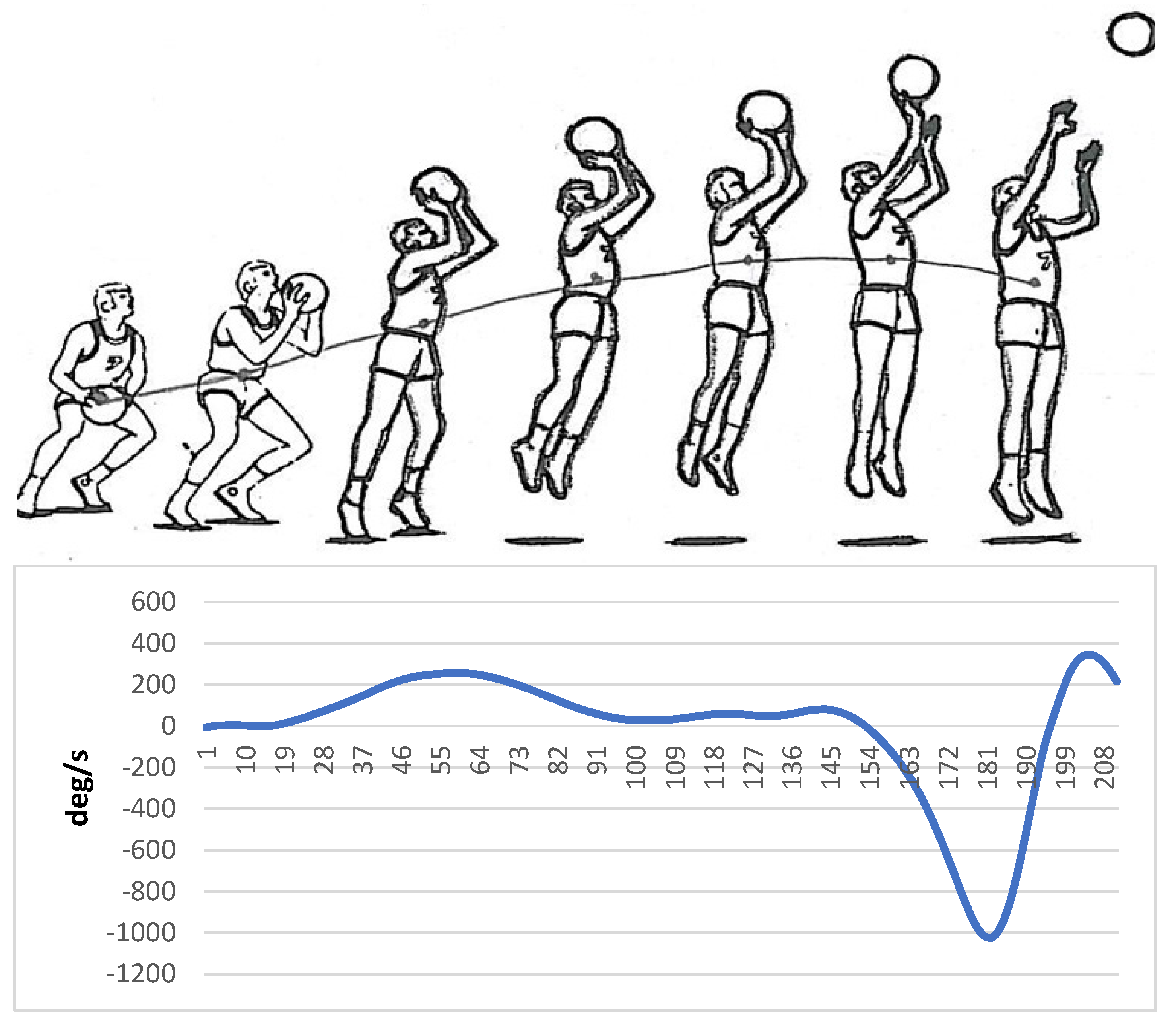
Markers were placed on specific areas of the hand, wrist, elbow, and shoulder before implementing a basketball jump shot by a skilled person. The information related to the movement of the model was collected by a motion analysis device (version 5.2, made by Motion Analysis Company, eight cameras, US, California, Santa Rosa) and then analyzed by Cortex software. Finally, the angular velocity of the elbow joint was used to create auditory patterns. Sandbox sonification software was used to sonify the data related to the angular velocity of the elbow joint. Figure 1 shows the angular velocity of the elbow joint regarding the different stages of the execution of basketball jump shots.
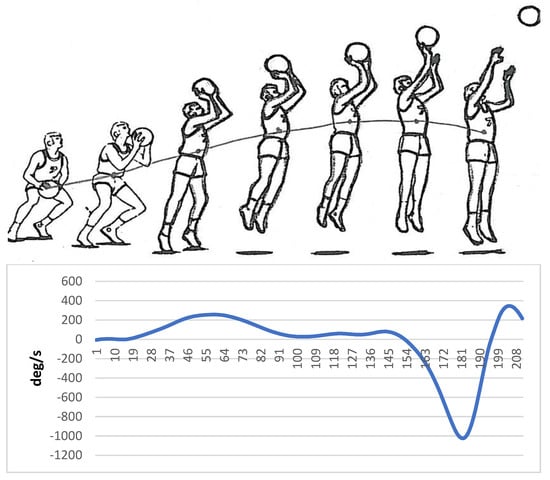
Figure 1.
Angular velocity of the elbow joint regarding the different stages of the basketball jump shot (Horizontal axis: Time frame, Vertical axis: Angular velocity (ω)).
2.4. Procedures
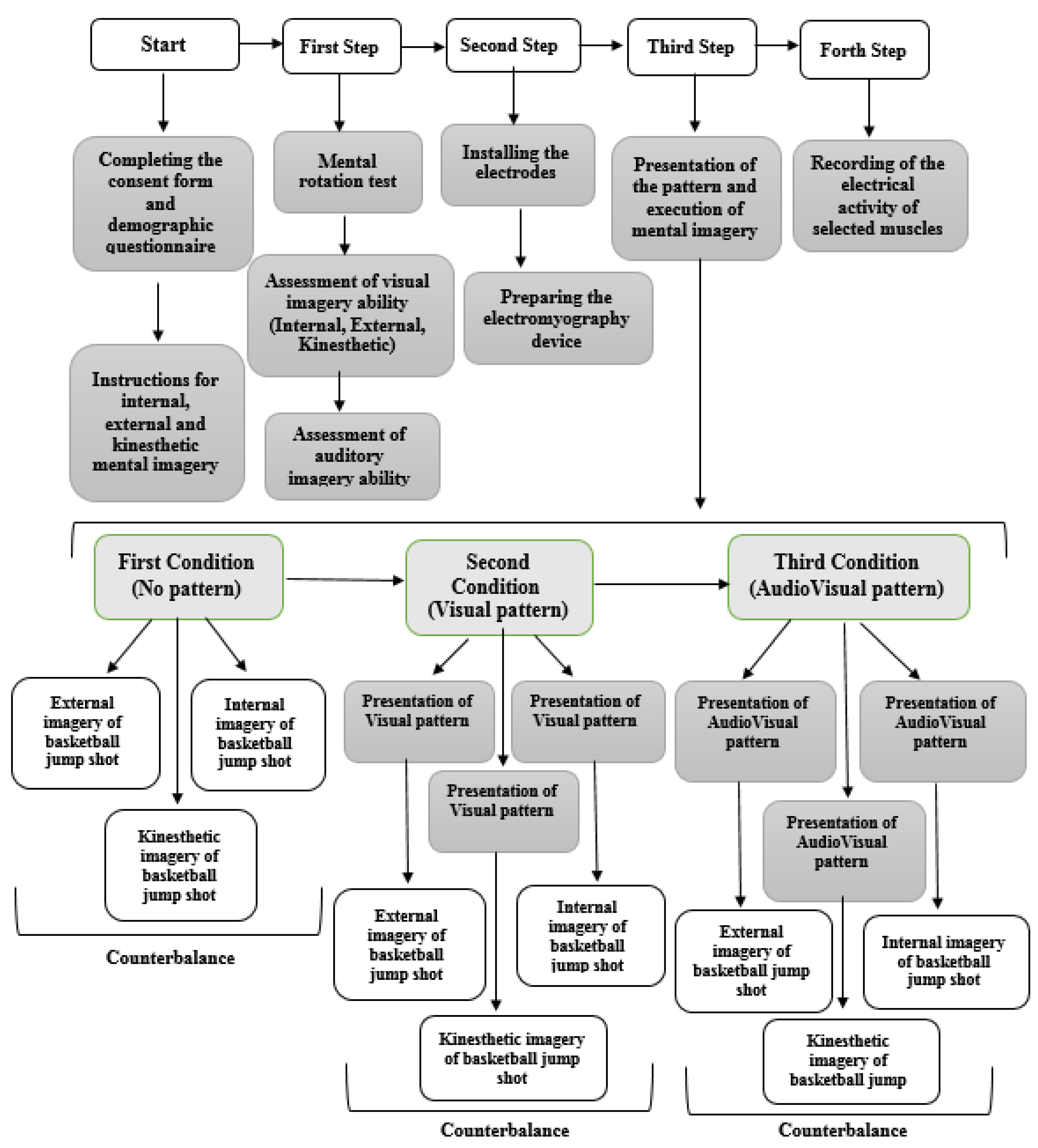
First, the aim of the research was fully explained to the subjects, after which they completed the consent form and the demographic questionnaire. In the next step, the subjects received sufficient information about imagery and its types, including internal, external and kinesthetic (two sessions), and finally took part in the mental rotation test. Subjects were asked to visualize themselves performing the task (basketball jump shot) in internal imagery, while in external imagery, they were asked to visualize themselves from a third person’s perspective. In kinesthetic imagery, subjects were asked to feel the effect of the mental images on their muscles without actually performing the movement. Those who scored above 70% on the mental rotation test were selected for the next step. They completed the visual imagery ability questionnaire (internal, external, and kinesthetic) and the Bucknell auditory imagery scale (vividness and control), and engaged in mental imagery in three different conditions of pattern presentation (no pattern, Visual pattern, and AudioVisual pattern), respectively. In order to control the possible effect of conditions on each other, three types of external, internal, and kinesthetic imagery were counterbalanced. Before each execution, the desired pattern was presented, and the subjects without time limitation engaged in mental imagery twice and the muscle activation was recorded both times. Figure 2 shows the steps of implementing the research plan.
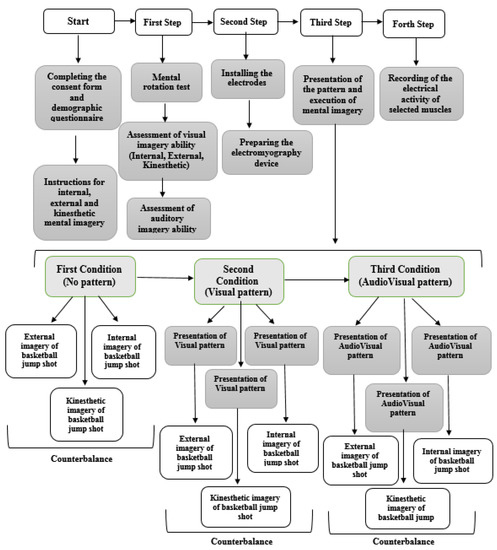
Figure 2.
Overview of research methodology.
Recording and Analyzing the Electrical Activity of Muscles
In order to study the muscle activity during imagery, the electrodes of the electromyography device were connected to record the activity of the elbow extensor muscles. Then, an 8-channel surface electromyography device (Wireless EMG, Version V8.24) was used. The receiver system of this device had eight independent analog and digital inputs that displayed the received signals on an Asus laptop device. To determine the exact anatomical location for electrode placement, we performed the study according to the guidelines and previous studies. This was to collect and record the amplitude and latency of triceps muscle activity. First, the skin, where the electrodes were placed, was shaved, and then cleaned with alcohol and sanded to reduce skin resistance. The electrodes were connected to LEDs whose preamplifier had a high-pass filter with a cutoff frequency of 10 Hz. Then, the root mean square (RMS) of the EMG signal was calculated with a time window of 50 milliseconds for the duration of the imagery. Finally, it was normalized to the maximum range of activity during the imagery.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Repeated measures of analysis of variance were used to compare the range of muscle activity in different imagery conditions. Additionally, Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used to examine the relationship between imagery ability and muscle activity amplitude in different imagery conditions. Hierarchical cluster analysis was used to identify subgroups of participants based on visual imagery ability. Furthermore, an independent t-test was used to compare the amplitude of elbow extensor muscle activity in subgroups identified in each of the conditions: without a pattern, Visual pattern, and AudioVisual pattern.
3. Results
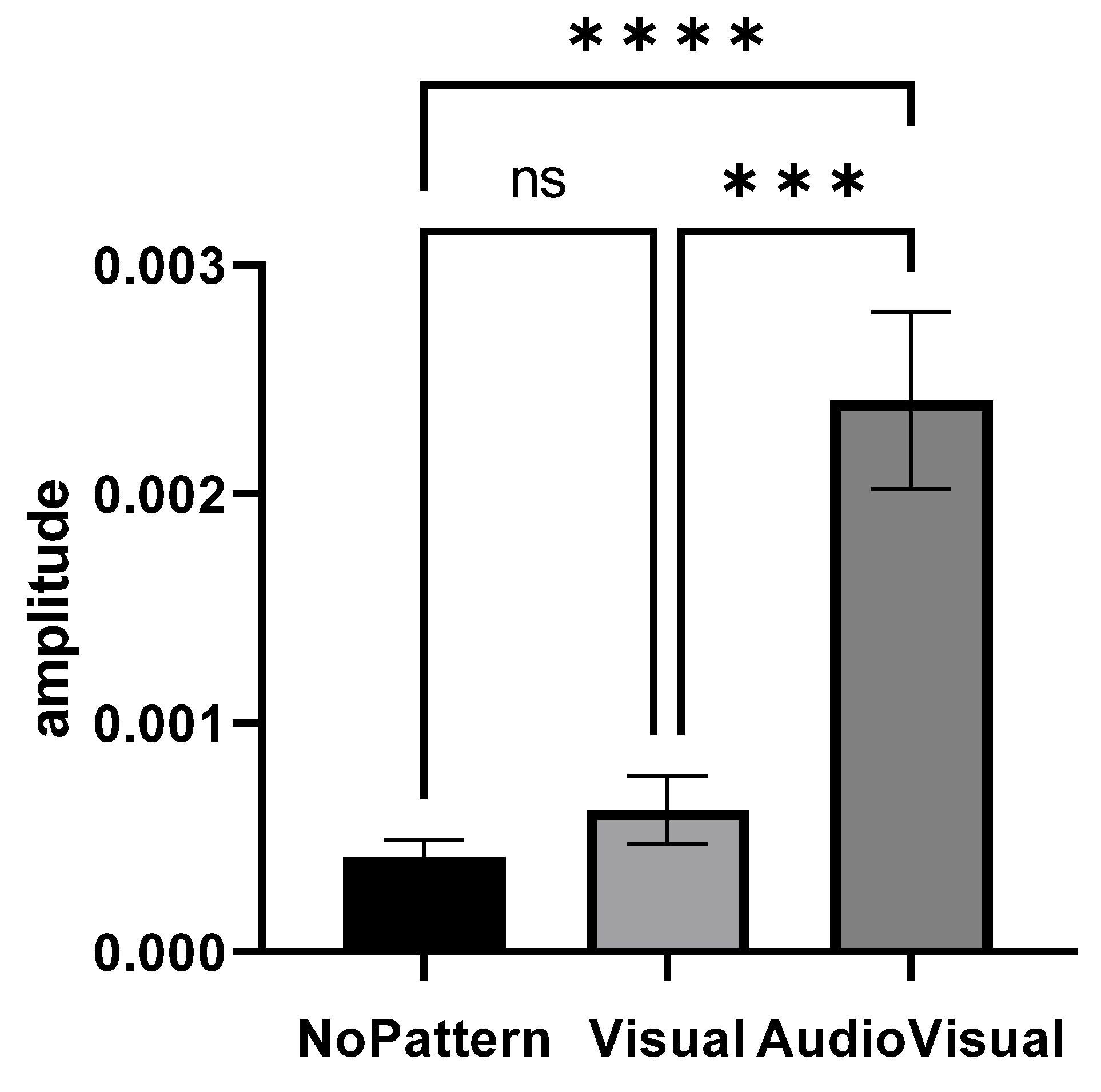
Figure 3 shows the elbow extensor muscle activity amplitude in different imagery conditions. The condition of AudioVisual pattern has a higher muscles activity amplitude than other conditions.
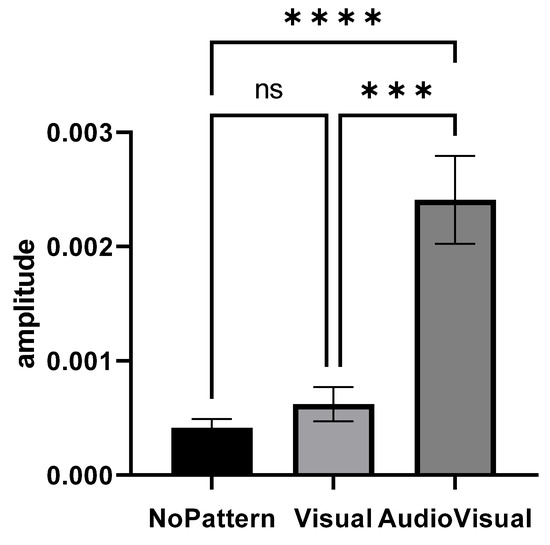
Figure 3.
Range of elbow extensor muscle activity in three conditions: No pattern, Visual pattern, and AudioVisual pattern; *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001.
Repeated measures of analysis of variance were used to compare the amplitude of muscle activity in different conditions (No pattern, Visual pattern, and AudioVisual pattern). Since the presumption of homogeneity of variance–covariance was not established (Mauchly’s W = 0.414, p = 0.001), the Greenhouse–Geisser method was used to analyze the data. The results showed that the effect of the condition is significant (F1.261, 30.274 = 22.213, p = 0.001, eta squared = 0.481) and there was a significant difference in the imagery in different conditions. The result of Bonferroni’s post hoc test also indicated that there are significant differences between conditions, so that the AudioVisual pattern had more activity than Visual (MD = 0.0017, p = 0.001) and No pattern (MD = 0.0019, p = 0.001) conditions. However, no significant difference was observed between the Visual pattern and No pattern conditions (MD = −0.0002, p = 0.615).
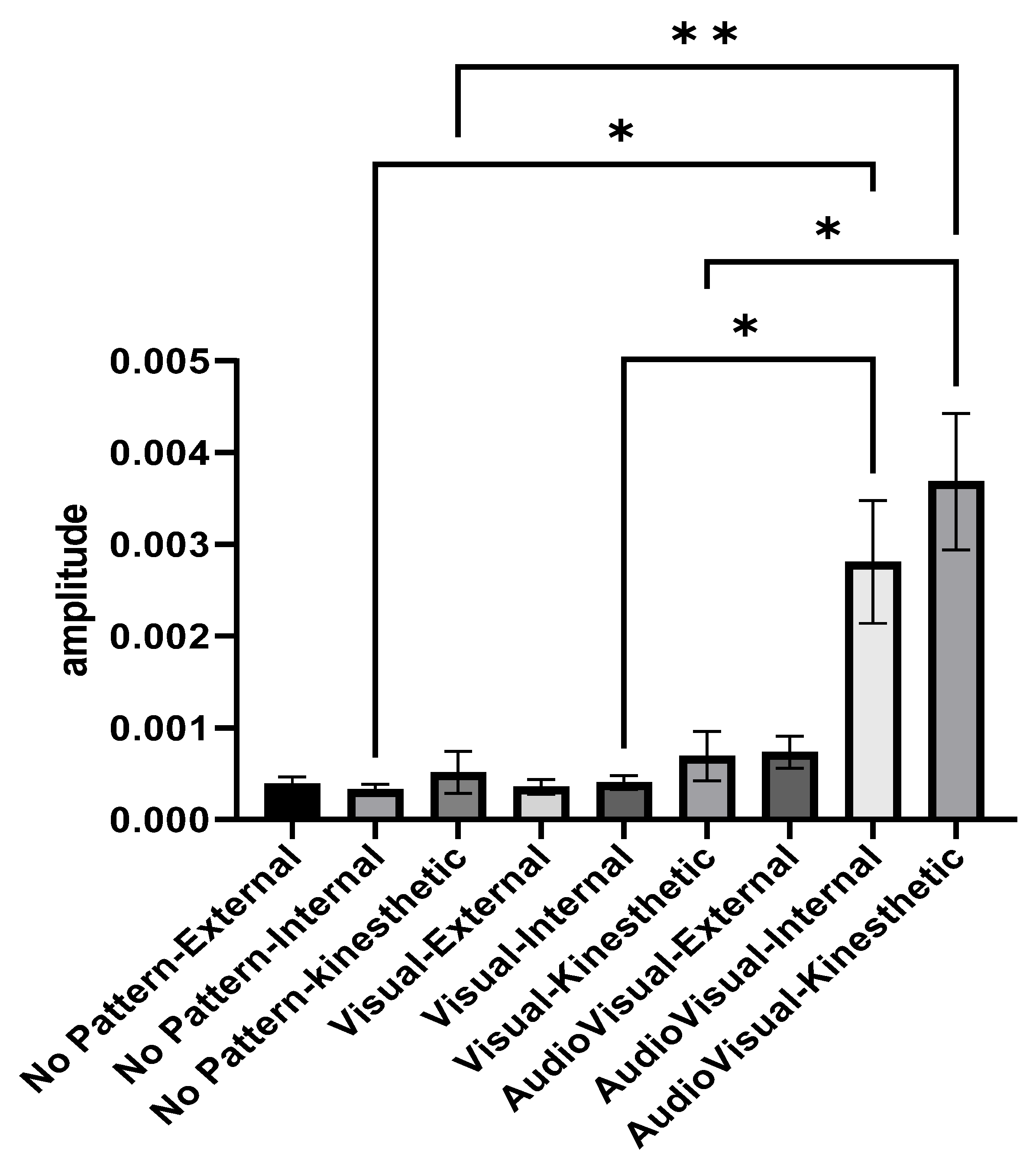
Figure 4 illustrates the activity amplitude of elbow joint extensor muscles in different imagery conditions and perspectives. The average activity amplitude of the elbow extensor muscles in the conditions of AudioVisual–internal imagery and AudioVisual–kinesthetic imagery was higher than other conditions. In the two conditions of Visual pattern and AudioVisual pattern, internal and kinesthetic imagery results in more muscle activity than external imagery. As shown in Figure 3, the average activity amplitude of the elbow extensor muscles in the conditions of AudioVisual–internal imagery and AudioVisual–kinesthetic imagery is more than in other conditions. In the two other conditions of Visual pattern and AudioVisual pattern, internal and kinesthetic imagery results in more muscle activity than external imagery.
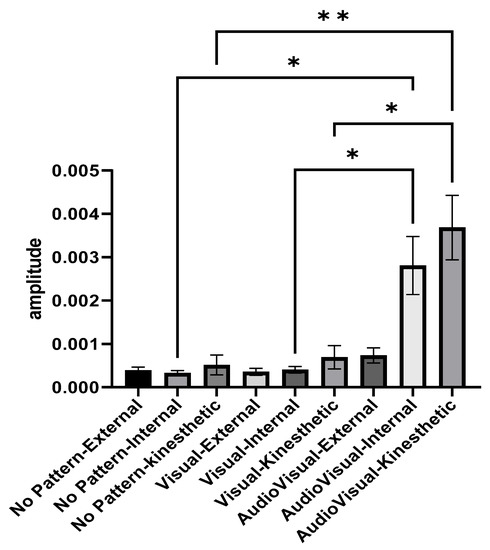
Figure 4.
Activity range of elbow extensor muscles in three different conditions of No pattern, Visual pattern, and AudioVisual pattern and in three different perspectives of external, internal, and kinesthetic imagery; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
Repeated measures ANOVA was used to compare the amplitude of muscle activity in different conditions. Since the presumption of homogeneity of variance–covariance was not established (Mauchly’s W = 0.0015, p = 0.001), the Greenhouse–Geisser method was used to analyze the data. The results indicated that the effect of the test is significant (F2.876, 69.029 = 11.178, p = 0.001, eta Squared = 0.318) and there was a significant difference between different imagery conditions. In the following, Bonferroni’s post hoc test indicated that AudioVisual–kinesthetic imagery is better than other conditions (except for AudioVisual–internal imagery). Additionally, the results showed that the AudioVisual–internal condition is significantly better than the Visual–internal and No pattern conditions.
In addition, the present study investigated the relationship between the participants’ auditory mental imagery ability and muscle activity amplitude. The results showed that there is a significant positive relationship between the auditory mental imagery ability and the muscle activity amplitude only in the AudioVisual pattern condition (r = 0.541, p = 0.005). The results also revealed that there is a significant positive relationship between Visual imagery ability and muscle activity amplitude in all three conditions: in No pattern (r = 0.410, p = 0.42), Visual pattern (r = 0.481, p = 0.015) and AudioVisual pattern condition (r = 0.459, p = 0.021), respectively.
Furthermore, in AudioVisual pattern conditions, there was a significant relationship between Visual–kinesthetic imagery ability and muscle activity amplitude (r = 0.576, p = 0.003), while this relationship was not observed in Visual pattern conditions and No pattern conditions (p > 0.05).
Finally, the results showed the positive and significant relationship between Visual–kinesthetic imagery ability and muscle activity amplitude in the AudioVisual–internal pattern (r = 0.517, p = 0.008) and AudioVisual–kinesthetic pattern (r = 0.470, p = 0.018) conditions, while there was no significant relationship between Visual–kinesthetic imagery ability and muscle activity amplitude in the AudioVisual–external pattern condition (r = 0.173, p = 0.408).
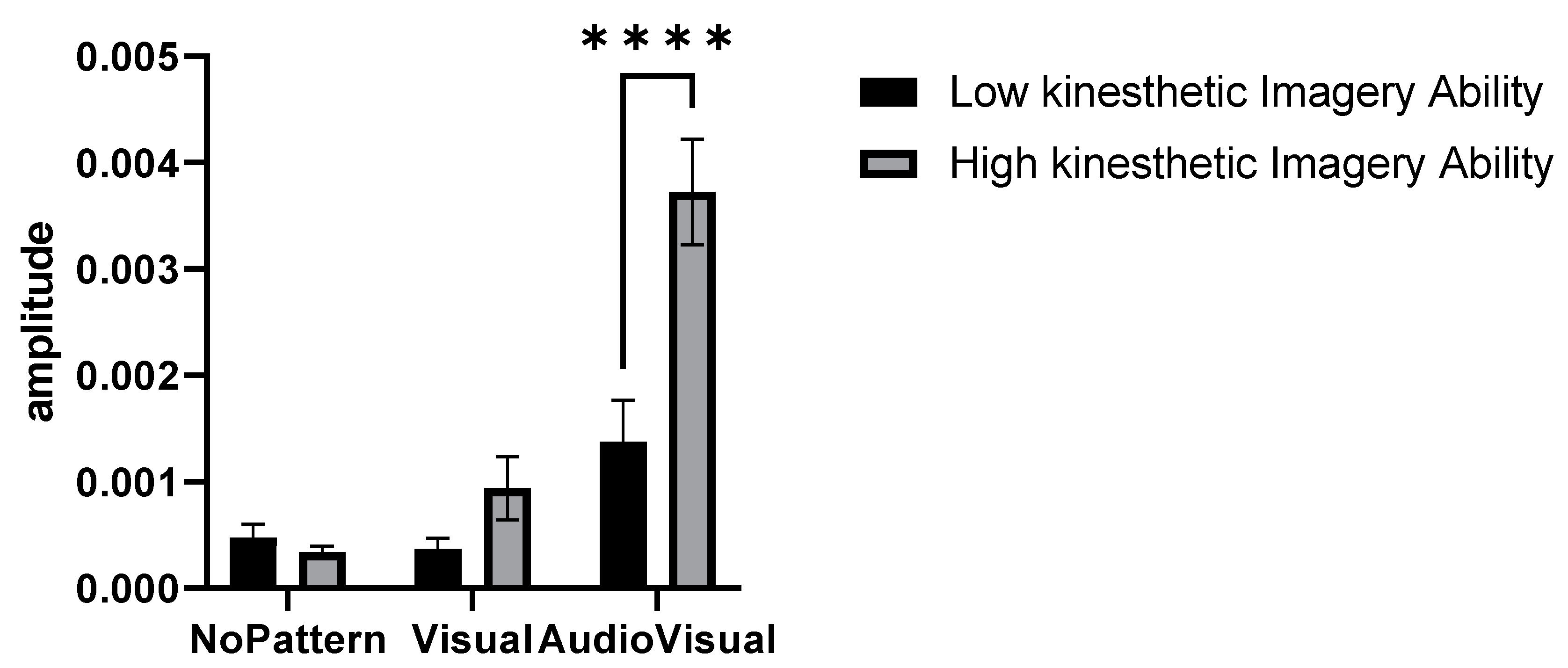
In this research, a hierarchical cluster analysis was performed according to the perspective of accumulation, by the method of “Between-group linkage” and based on the “Squared Euclidean distance” on the variable of Visual–kinesthetic imagery ability level of the subjects, and finally, two cluster solutions under titles of High Visual–kinesthetic imagery ability and low Visual–kinesthetic imagery ability were determined. Figure 5 compares the activity amplitude of elbow extensor muscles in two identified clusters and different conditions of No pattern, Visual pattern, and AudioVisual pattern.
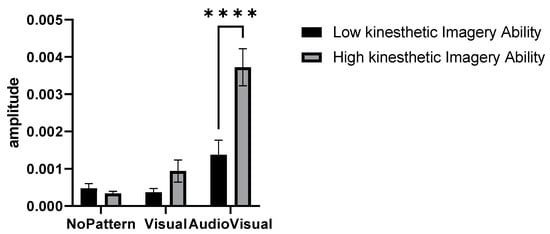
Figure 5.
Amplitude of muscle activity in three conditions of No pattern, Visual pattern, and AudioVisual pattern, and in two categories of high and low Visual–kinesthetic imagery ability **** p < 0.0001.
4. Discussion
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of presenting an AudioVisual pattern on the intensity of muscle activity during mental imagery. For this purpose, 25 female students with an average age of 20.73 years were engaged in mental imagery in three different conditions: No pattern, Visual pattern, and AudioVisual pattern. The subjects were asked to perform all three types of external, internal, and kinesthetic imagery. Before each performance, the desired pattern was presented to them twice and the subjects could imagine the task. Additionally, the visual mental imagery ability (internal, external, and kinesthetic) and auditory imagery ability of the subjects were assessed.
The results revealed that there is a significant difference between the intensity of elbow extensor muscle activity in different imagery conditions (No pattern, Visual pattern, and AudioVisual pattern) in favor of AudioVisual pattern conditions. After comparing different types of imagery (i.e., external, internal, and kinesthetic) in different conditions (No pattern, Visual pattern, and AudioVisual pattern), it was found that the intensity of muscle activity is significantly higher in AudioVisual–kinesthetic than in other conditions (except for AudioVisual–internal imagery). The similar performance of subjects in the AudioVisual–kinesthetic and AudioVisual–internal imagery conditions can be explained based on the results of research that has studied the neural basis of imagery. Filgueiras, Francisco, Conde and Hall [55] showed that visual and kinesthetic imagery share similar neural networks. However, some studies have observed destinations in neurophysiological brain mechanisms in kinesthetic and visual imagery [56,57]. Chholack et al. [57] showed that kinesthetic imagery leads to event-related desynchronization of motor-associated brain rhythms. By contrast, visual imagery results in event-related synchronization of α- and β-wave activity. They also showed that in all kinesthetic imagery subjects, the activity in the frontal cortex is suppressed during motor imagery, while in the visual imagery subjects, the frontal cortex is always active. Another important result of this research was that there is a significant positive relationship between Visual–kinesthetic imagery ability and the intensity of muscle activity in AudioVisual pattern conditions in kinesthetic and internal (and not external) perspectives. This relationship was not observed in the condition of Visual pattern and No pattern conditions. These results are in line with the research of Lutz [13] and Lebon, Horn, Domin and Lotze [58]. Lotze [13] showed that covert muscle excitation (muscle activation) was associated with imaging ability and clarity. Lebon et al. [58] found that high kinesthetic imagery vividness predicted a high performance after training. Higher muscle activity in subjects with higher kinesthetics in visual imagery and AudioVisual conditions in the present study is in line with the research of Lebon et al. [58].
The results of this research also determined that the use of sound related to the movement pattern (sound related to changes in the speed of the elbow joint during the performance) can affect the intensity of the elbow extensor muscles during mental imagery (at least in kinesthetic and internal imagery). Although past research has confirmed the positive effect of auditory imagery on imagery vividness [33,59] and performance [34], the sounds used in these studies were often auditory cues (in music) [59] or sound caused by the one’s movement (hitting the ground or sound from sports equipment) [34] and not related to one’s movement pattern. However, the sound used in this research is an auditory pattern through which the kinematic variable of the angular speed of the joint involved in the movement (elbow joint) was presented to the subjects. Since past research has indicated that the prediction of movement timing and the ability of musical imagery are related [28,29], it is likely that in the conditions of the AudioVisual pattern, the concurrency of the Auditory pattern and the Visual pattern results in the development of movement pattern timing in the mental imagery of the subjects and, consequently, creates higher quality images. In this regard, Schaefer [18] has stated that the commonalities between music imagery and movement may be more related to internal timing mechanisms. Although this study did not examine the temporal adaptation of muscle activity in the conditions of imagery and real performance, various researchers in the field of music have suggested that auditory imagery maintains the temporal characteristics of the auditory stimulus [31,60]. Keller, Bella and Koch [61] and Debarnot and Guillot [35] also showed that auditory imagery can accommodate movement timing and it is assumed that auditory imagery can at least create a similarity between the temporal structure of the visualized action and the actual movement. According to Scheffer [18], this temporal relationship between kinesthetic and musical processes is transferred to the imaged stimuli or imaged actions. Therefore, further studying the impact of this type of imagery on the temporal structure of mental images and actual performance is suggested in order to determine the effective mechanisms of auditory imagery concerning kinesthetic skills. Other research has also emphasized the sensory motor synchronization caused by auditory imagery [62]. In addition, movement sonification has been found to develop the activity of the action observation system [63]. Such a development may be based partly on auditory and audiovisual mirror neurons that form a “listen–act” system as part of the perceptual system [64]. On the other hand, various researchers have confirmed that in auditory imagery, the structural characteristics of auditory stimuli and, in particular, the sound frequency changes (used in this research), are preserved [31,60,65,66]. Therefore, it seems that auditory imagery can not only independently affect the timing of movement execution, but also develop one’s overall understanding by affecting visual perception. Ramezanzade et al. [41] and Effenberg [39] also showed that auditory information can develop perception and recognition of the observed movement components. Recent research has also confirmed that the use of artificial movement sounds possibly presents the mechanisms of biological perception of movement and allows people to assess the quality and quantity of the characteristics of large body movements [63,67]. It seems that the results of the present study conflict with the study of Castro et al. [68]. In their research, they investigated the effect of action observation-motor imagery with and without an auditory pattern (sonification) on cortico-spinal excitability, and showed that there is no difference between the two groups. The simple motor task used in Castro et al.’s study makes it difficult to generalize the results to complex sports skills. It seems that, at least for simple actions, adding sonification to action observation-motor imagery did not affect cortico-spinal excitability and may have even acted as a distractor in this condition.
Another interesting finding of the present study was that although the intensity of the electrical activity of the muscles is higher in AudioVisual–kinesthetic and AudioVisual–internal pattern conditions compared to other conditions, the intensity of the electrical activity of the muscles in the AudioVisual–external conditions is not different from other conditions. The difference between internal and external imagery has been studied extensively in the research literature, which shows that certain dimensions of motor skill implementation are developed through different types of imagery [14,47]. Internal imagery has the potential to create kinesthetic images (sense of movement), while external imagery seems insufficient to create such a feeling [69]. Additionally, the auditory pattern used in this research (elbow joint angular velocity sonification) is a way of developing auditory movement information for silent phases of actions (for example, actions or limb movements). Action-specific construction sounds contain information about movement-related kinematics, which can lead to the creation of a special type of information called auditory kinematics [38]. It seems that the auditory pattern used in the current research provides individuals with information about the movement which is very similar to the information from the sense of movement. Therefore, the use of this type of auditory imagery in the conditions of Visual–auditory-kinesthetic and Visual–auditory-internal patterns results in a higher level of activation of the muscles involved in the movement. The positive correlation between Visual–kinesthetic and Visual–internal imagery ability with the intensity of elbow extensor muscle activity is in line with the explanation provided. Of course, it should be kept in mind that the idea of similarity of the auditory information presented in the current research with the information related to the sense of movement is based on the observed relationships between the type of imagery, perspective of imagery and the electrical activity of the muscles. Other studies with experimental designs should be implemented to support this idea. In generalizing the results of this research, another important issue should be considered. Recent research has shown that the effect of internal or external imagery depends on the type of skill. Dana and Gozalzadeh [70] showed that internal imagery and external imagery are more effective in serve accuracy and forehand accuracy, respectively.
5. Conclusions
This research showed that the use of the AudioVisual pattern in the conditions of kinesthetic and internal imagery, compared to the No pattern or Visual pattern conditions, results in more intense activity of the muscles involved in the execution of movement. Additionally, based on the results obtained in this research, auditory imagery ability is related to the intensity of muscle activity in the conditions of AudioVisual pattern. In addition, Visual–kinesthetic imagery ability is related to the intensity of muscle activity in AudioVisual–kinesthetic and AudioVisual–internal conditions. The findings of this research emphasize the effective role of the auditory pattern used in activating more muscles involved in the movement. However, an analysis of the temporal structure of muscle contractions related to the movement pattern during imagery and its comparison with the timing of the presented movement pattern was not carried out in this study. Therefore, in order to develop external validity, it is necessary to further study the role of AudioVisual patterns and their related imagery in motor skill acquisition and learning. Based on past research, the relationship between muscle activity (covert muscle excitations) and the acquisition and retention of motor tasks is not clear [7,9,13]. Although some studies have shown the role of motor imagery in learning motor skills [71], Lutz [13] concluded that covert muscle excitation is a byproduct of the central generation of the image that does not relate meaningfully to motor skill acquisition or retention gains. Therefore, one should be careful in generalizing the results of the present study to the learning of the basketball jump shot, and other studies are needed to investigate the relationship between the increased activation of AudioVisual imagery (especially of kinesthetic type) with the acquisition and retention of motor skills.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.R. and G.B.; methodology, H.R., S.H.Z.S. and S.M.; software, S.M. and H.R.; validation, H.R., S.H.Z.S. and M.M.; formal analysis, H.R.; investigation, S.M.; resources, M.M. and S.C.; data curation, F.P. and M.M; writing—original draft preparation, H.R.; writing—review and editing, G.B., S.C., S.H.Z.S. and G.G.; visualization, F.P.; supervision, S.C. and G.G.; project administration, H.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Damghan University (protocol code: IR.DU.REC.1400.003; date of approval: 12 July 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to show appreciation to the participants in this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Simonsmeier, B.A.; Andronie, M.; Buecker, S.; Frank, C. The effects of imagery interventions in sports: A meta-analysis. Int. Rev. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2021, 14, 186–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.M.; Martin, K.A. The use of imagery in sport. In Advances in Sport Psychology; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Iacono, A.D.; Ashcroft, K.; Zubac, D. Ain’t Just Imagination! Effects of Motor Imagery Training on Strength and Power Performance of Athletes during Detraining. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 2324–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrendt, F.; Zumbrunnen, V.; Brem, L.; Suica, Z.; Gäumann, S.; Ziller, C.; Gerth, U.; Schuster-Amft, C. Effect of Motor Imagery Training on Motor Learning in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, E. Electrical measurements of neuromuscular states during mental activities: V. Variation of specific muscles contracting during imagination. Am. J. Physiol. 1931, 96, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A. Mental practice: A review and discussion part I. Res. Q. Am. Assoc. Health Phys. Educ. 1967, 38, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decety, J.; Ingvar, D.H. Brain structures participating in mental simulation of motor behavior: A neuropsychologiacal interpretation. Acta Psychol. 1990, 73, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobelt, M.; Wirth, B.; Schuster-Amft, C. Muscle Activation during Grasping with and without Motor Imagery in Healthy Volunteers and Patients after Stroke or with Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebon, F.; Guillot, A.; Collet, C. Increased Muscle Activation Following Motor Imagery During the Rehabilitation of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2011, 37, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losana-Ferrer, A.; Manzanas-López, S.; Cuenca-Martínez, F.; Paris-Alemany, A.; La Touche, R. Effects of motor imagery and action observation on hand grip strength, electromyographic activity and intramuscular oxygenation in the hand gripping gesture: A randomized controlled trial. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2018, 58, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardwick, R.M.; Caspers, S.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Swinnen, S.P. Neural correlates of action: Comparing meta-analyses of imagery, observation, and execution. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 94, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.; Choi, J. Effects of Motor Imagery Training on Balance and Gait in Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, R.S. Covert muscle excitation is outflow from the central generation of motor imagery. Behav. Brain Res. 2003, 140, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillot, A.; Nadrowska, E.; Collet, C. Using Motor Imagery to Learn Tactical Movements in Basketball. J. Sport Behav. 2009, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Vealey, R.S.; Greenleaf, C.A. Seeing is believing: Understanding and using imagery in sport. Appl. Sport Psychol. Pers. Growth Peak Perform. 2010, 4, 247–272. [Google Scholar]
- Finks, R.A.; Pinker, S.; Farah, M.J. Reinterpreting visual patterns in mental imagery. Cogn. Sci. 1989, 13, 51–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisberg, D.; Heuer, F. Visuospatial Images; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer, R.S. Images of time: Temporal aspects of auditory and movement imagination. Front. Media SA 2014, 5, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, R.J.; Case, T.I. Olfactory imagery: A review. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2005, 12, 244–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eardley, A.F.; Pring, L. Remembering the past and imagining the future: A role for nonvisual imagery in the everyday cognition of blind and sighted people. Memory 2006, 14, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plailly, J.; Delon-Martin, C.; Royet, J.-P. Experience induces functional reorganization in brain regions involved in odor imagery in perfumers. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2011, 33, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.T.; Ostwald, D.; Blankenburg, F. Imaging tactile imagery: Changes in brain connectivity support per-ceptual grounding of mental images in primary sensory cortices. Neuroimage 2014, 98, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, R.S.; Vlek, R.J.; Desain, P. Music perception and imagery in EEG: Alpha band effects of task and stimulus. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2011, 82, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, K.D.; Ashton, R.; Brown, R.M.D. The measurement of imagery vividness: Normative data and their relationship to sex, age, and modality differences. Br. J. Psychol. 1977, 68, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivetti Belardinelli, M.; Palmiero, M.; Sestieri, C.; D’Ausilio, A.; Di Matteo, R.; Londei, A.; D’Ausilio, A.; Ferretti, A.; Del Gratta, C.; Romani, G.L. An fMRI investigation on image generation in different sensory modalities: The influence of vividness. Acta Psycholl. 2007, 132, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.-H.; Pöppel, E. Body movement enhances the extraction of temporal structures in auditory sequences. Psychol. Res. 2011, 76, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bood, R.J.; Nijssen, M.; van der Kamp, J.; Roerdink, M. The Power of Auditory-Motor Synchronization in Sports: Enhancing Running Performance by Coupling Cadence with the Right Beats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, P.E.; Appel, M. Individual Differences, Auditory Imagery, and the Coordination of Body Movements and Sounds in Musical Ensembles. Music. Percept. 2010, 28, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecenka, N.; Keller, P.E. Auditory Pitch Imagery and Its Relationship to Musical Synchronization. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2009, 1169, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repp, B.H. Effects of music perception and imagery on sensorimotor synchronization with complex timing patterns. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2001, 930, 409–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intons-Peterson, M.J. Components of auditory imagery. Audit. Imag. 1992, 45–72. [Google Scholar]
- Hale, B.; Crisfield, P. Imagery Training: A Guide for Sports Coaches and Performers; Coachwise 1st4sport: Leeds, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Calmels, C.; Holmes, P.S.; Berthoumieux, C.; Singer, R.N. The development of movement imagery vividness through a structured intervention in softball. J. Sport Behav. 2004, 27, 307–322. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.; Holmes, P. The Effect of Imagery Modality on Golf Putting Performance. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2004, 26, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debarnot, U.; Guillot, A. When music tempo affects the temporal congruence between physical practice and motor imagery. Acta Psychol. 2014, 149, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann, T.; Hunt, A.; Neuhoff, J.G. The Sonification Handbook; Logos Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, R.B.; Warren, D.H. Immediate perceptual response to intersensory discrepancy. Psychol. Bull. 1980, 88, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinken, P.M.; Kröger, D.; Fehse, U.; Schmitz, G.; Brock, H.; Effenberg, A.O. Auditory Coding of Human Movement Kinematics. Multisensory Res. 2013, 26, 533–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effenberg, A.O. Movement Sonification: Effects on Perception and Action. IEEE MultiMed. 2005, 12, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, R.; Medeiros, C.B.; Wanderley, M.M.; Schönwiesner, M. The effect of movement-complexity on perceived audio-visual synchronicity. J. Vis. 2014, 14, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanzade, H.; Abdoli, B.; Farsi, A.; Sanjari, M.A. The effect of sonification modelling on perception and accuracy of performing jump shot basketball. Int. J. Sport. Stud. 2014, 4, 1388–1392. [Google Scholar]
- Effenberg, A.O.; Fehse, U.; Schmitz, G.; Krueger, B.; Mechling, H. Movement Sonification: Effects on Motor Learning beyond Rhythmic Adjustments. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effenberg, A.; Fehse, U.; Weber, A. Movement Sonification: Audiovisual benefits on motor learning. BIO Web Conf. 2011, 1, 00022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanzade, H.; Abdoli, B.; Farsi, A.; Sanjari, M.A. The effect of audiovisual integration on performance accuracy and learning in motor task. J. Res. Rehabil. Sci. 2015, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, P.S.; Collins, D.J. The PETTLEP Approach to Motor Imagery: A Functional Equivalence Model for Sport Psychologists. J. Appl. Sport Psychol. 2001, 13, 60–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.R.; Rodgers, W.M.; Barr, K.A. The Use of Imagery by Athletes in Selected Sports. Sport Psychol. 1990, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, L.; Callow, N. Efficacy of external and internal visual imagery perspectives for the enhancement of per-formance on tasks in which form is important. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 1999, 21, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, M.J.; Avener, M. Psychology of the elite athlete: An exploratory study. Cogn. Ther. Res. 1977, 1, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, R.N.; Metzler, J. Mental Rotation of Three-Dimensional Objects. Science 1971, 171, 701–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.; Laeng, B.; Latham, K.; Jackson, M.; Zaiyouna, R.; Richardson, C. A Redrawn Vandenberg and Kuse Mental Rotations Test—Different Versions and Factors that Affect Performance. Brain Cogn. 1995, 28, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.E.; Cumming, J.; Ntoumanis, N.; Nordin-Bates, S.M.; Ramsey, R.; Hall, C. Further validation and de-velopment of the movement imagery questionnaire. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2012, 34, 621–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.; Smith, D.; Burden, A.; Holmes, P. Participant-generated imagery scripts produce greater EMG activity and imagery ability. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2010, 10, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, M.; Farsi, A.; Foladian, J. Determining the validity and reliability of the Persian version of the revised movement imaging questionnaire. Mot. Behav. 2010, 2, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Halpern, A.R. Differences in auditory imagery self-report predict neural and behavioral outcomes. Psychomusicol. Music. Mind Brain 2015, 25, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filgueiras, A.; Francisco, E.; Conde, Q.; Hall, C.R. The neural basis of kinesthetic and visual imagery in sports: An ALE meta-analysis. Brain Imaging Behav. 2018, 12, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callow, N.; Jiang, D.; Roberts, R.; Edwards, M.G. Kinesthetic Imagery Provides Additive Benefits to Internal Visual Imagery on Slalom Task Performance. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2017, 39, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chholak, P.; Niso, G.; Maksimenko, V.A.; Kurkin, S.A.; Frolov, N.S.; Pitsik, E.N.; Hramov, A.E.; Pisarchik, A.N. Visual and kinesthetic modes affect motor imagery classification in untrained subjects. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebon, F.; Horn, U.; Domin, M.; Lotze, M. Motor imagery training: Kinesthetic imagery strategy and inferior parietal fMRI activation. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heremans, E.; Helsen, W.F.; De Poel, H.J.; Alaerts, K.; Meyns, P.; Feys, P. Facilitation of motor imagery through movement-related cueing. Brain Res. 2009, 1278, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halpern, A.R.; Zatorre, R.J. When that tune runs through your head: A PET investigation of auditory imagery for familiar melodies. Cereb. Cortex 1999, 9, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, P.E.; Bella, S.D.; Koch, I. Auditory imagery shapes movement timing and kinematics: Evidence from a musical task. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2010, 36, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colley, I.D.; Keller, P.E.; Halpern, A.R. Working memeory and auditory imagery predict sensorimotor synchro-nization with expressively timed music. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 2018, 71, 1781–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, G.; Mohammadi, B.; Hammer, A.; Heldmann, M.; Samii, A.; Münte, T.F.; Effenberg, A.O. Observation of sonified movements engages a basal ganglia frontocortical network. BMC Neurosci. 2013, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahav, A.; Saltzman, E.; Schlaug, G. Action Representation of Sound: Audiomotor Recognition Network While Listening to Newly Acquired Actions. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, T.L. Auditory imagery: Empirical findings. Psychol. Bull. 2010, 136, 302–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zatorre, R.J.; Halpern, A.R.; Bouffard, M. Mental Reversal of Imagined Melodies: A Role for the Posterior Parietal Cortex. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2010, 22, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, G.; Effenberg, A.O. Perceptual effects of auditory information about own and other movements. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Auditory Display, Atlanta, GA, USA, 18–21 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, F.; Bryjka, P.A.; Pino, G.D.; Vuckovic, A.; Nowicky, A.; Bishop, D. Sonification of combined action obser-vation and motor imagery: Effect on corticospinal exitability. Brain Cogn. 2021, 152, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, W.; Hall, C.; Buckolz, E. The effect of an imagery training program on imagery ability, imagery use, and figure skating performance. J. Appl. Sport Psychol. 1991, 3, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, A.; Gozalzadeh, E. Internal and External Imagery Effects on Tennis Skills Among Novices. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2017, 124, 1022–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobierajewicz, J.; Przekoracka-Krawczyk, A.; Jaśkowski, W.; Verwey, W.B.; van der Lubbe, R. The influence of motor imagery on the learning of a fine hand motor skill. Exp. Brain Res. 2016, 235, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).