Camphor-Soothed Banana Stem Biowaste in the Productivity and Sustainability of Solar-Powered Desalination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
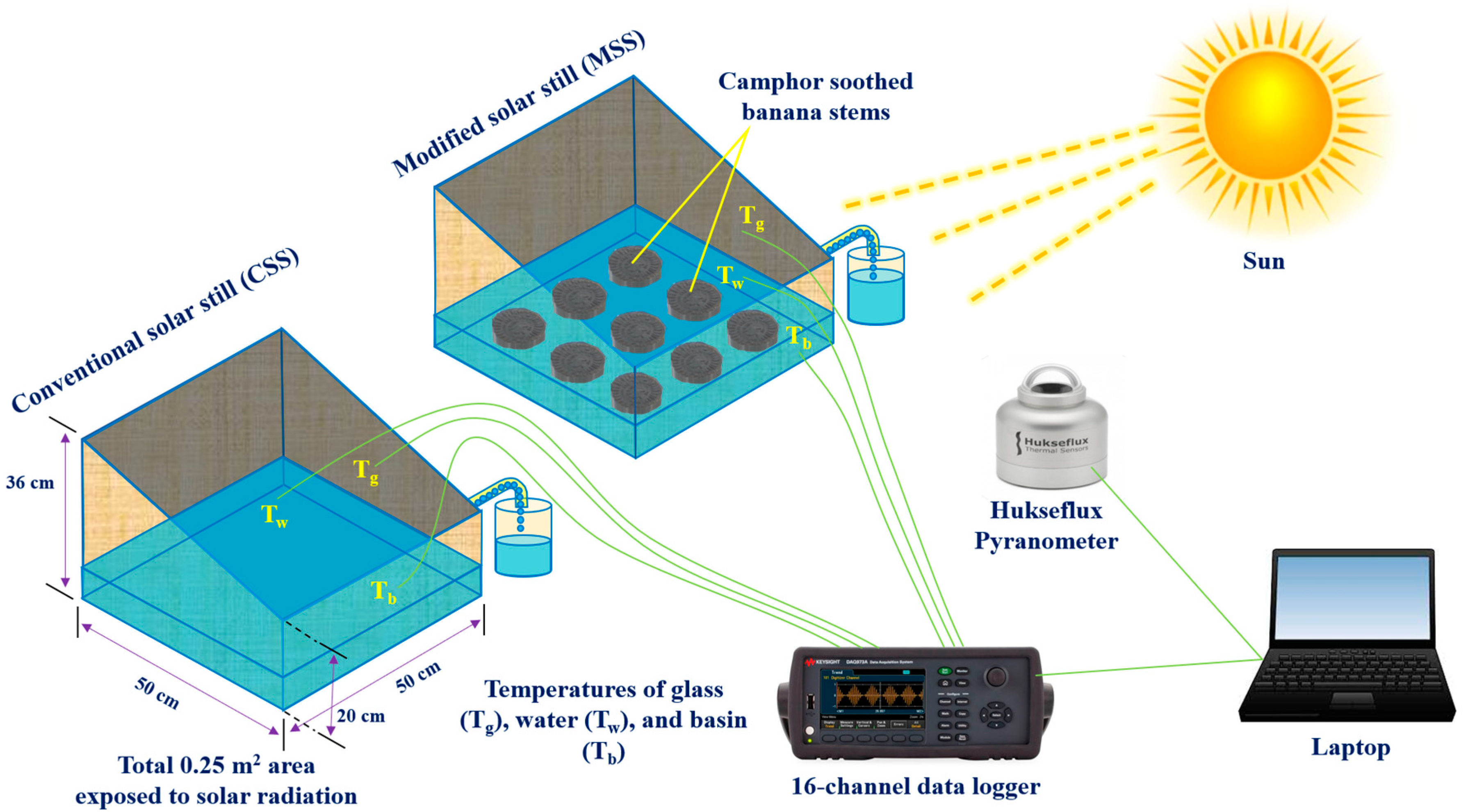
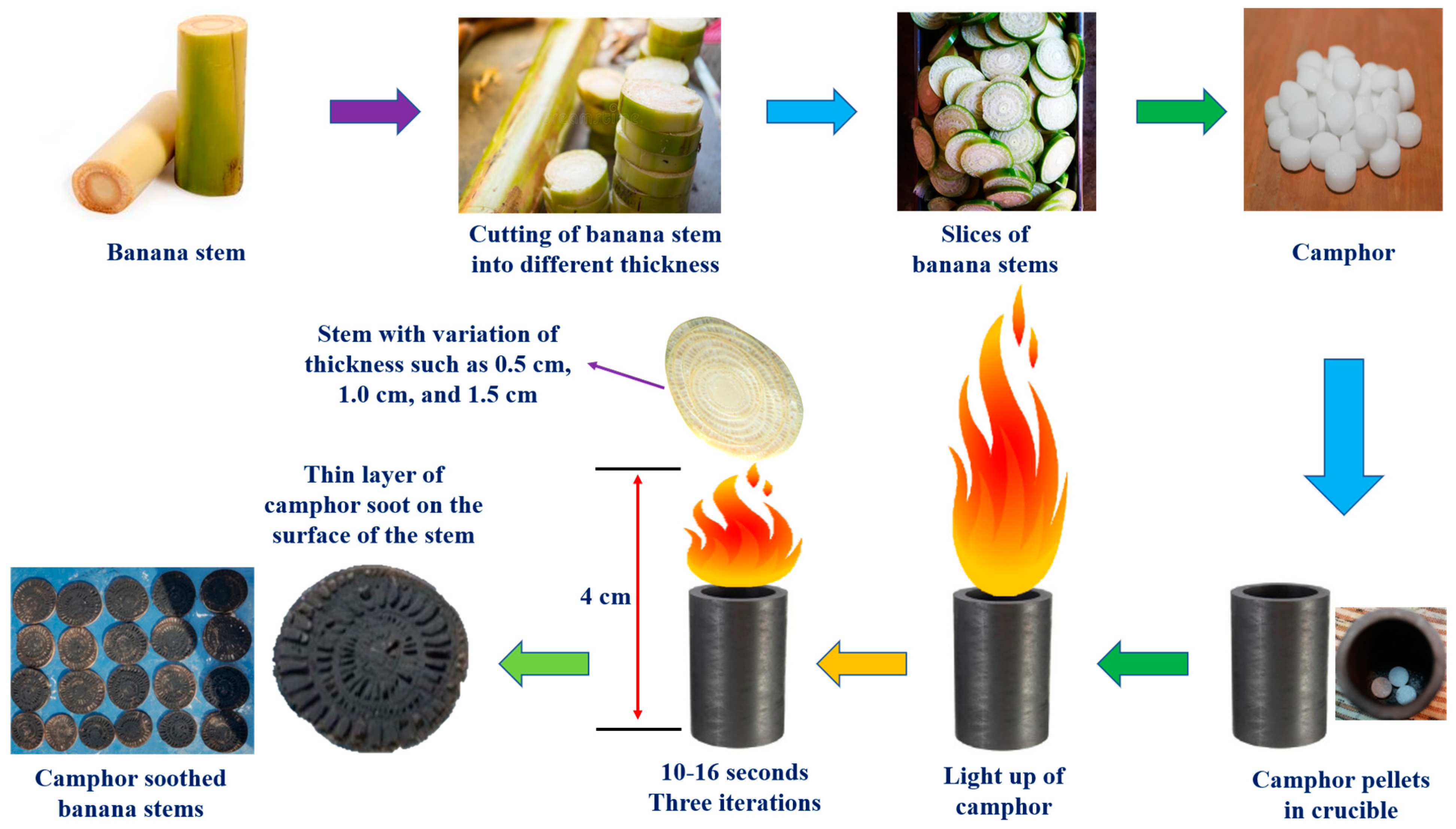
2. Experimentation
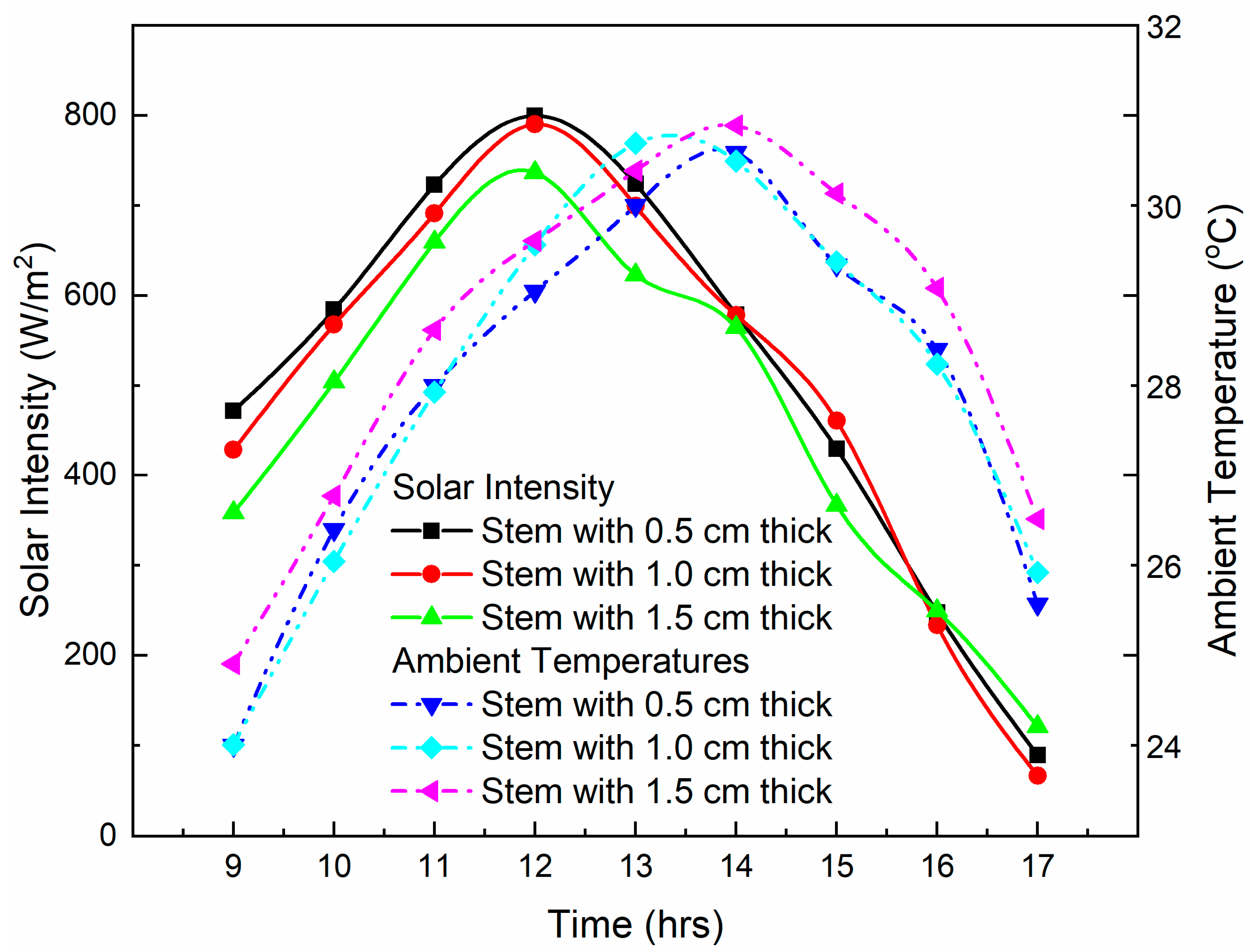
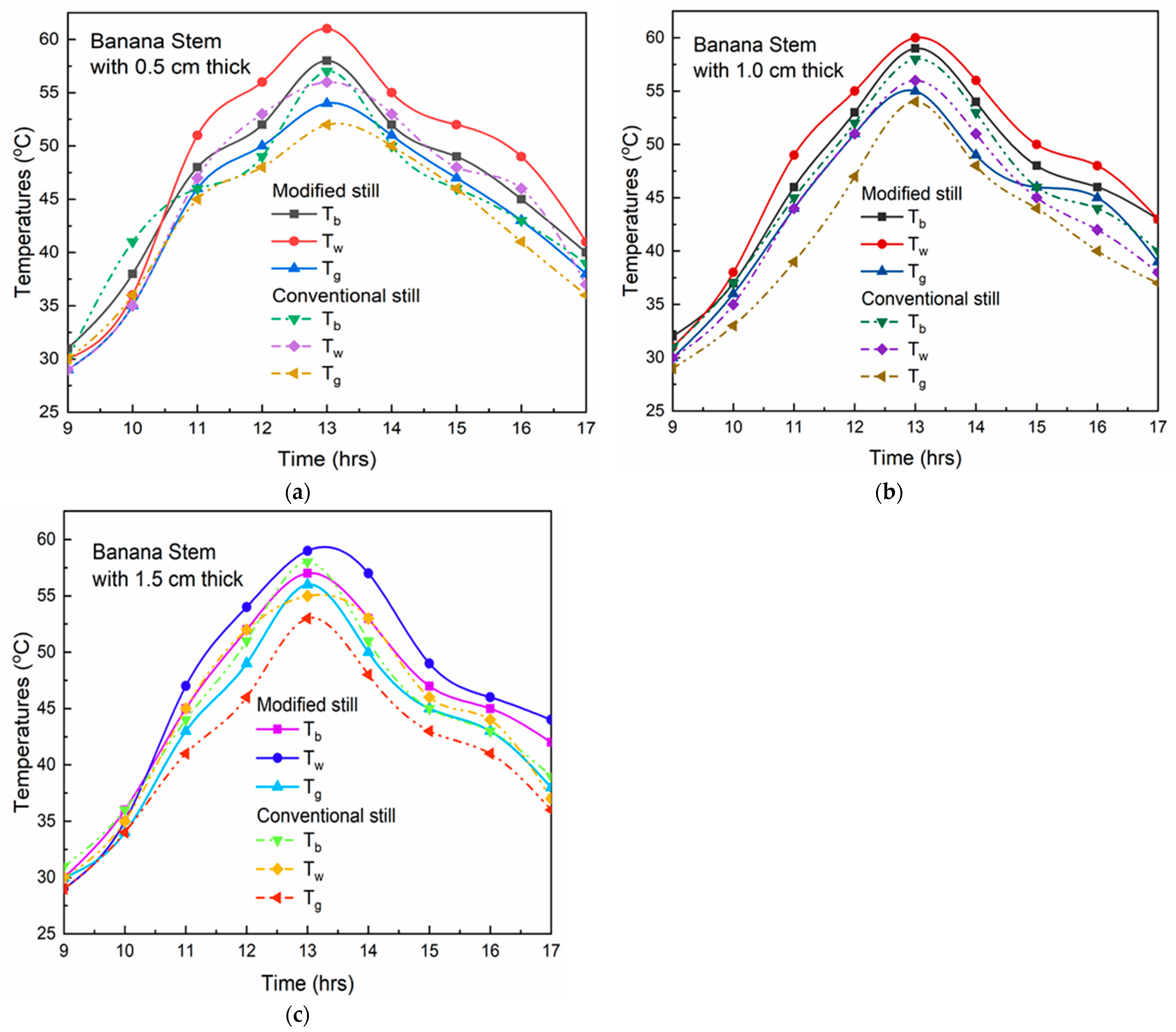
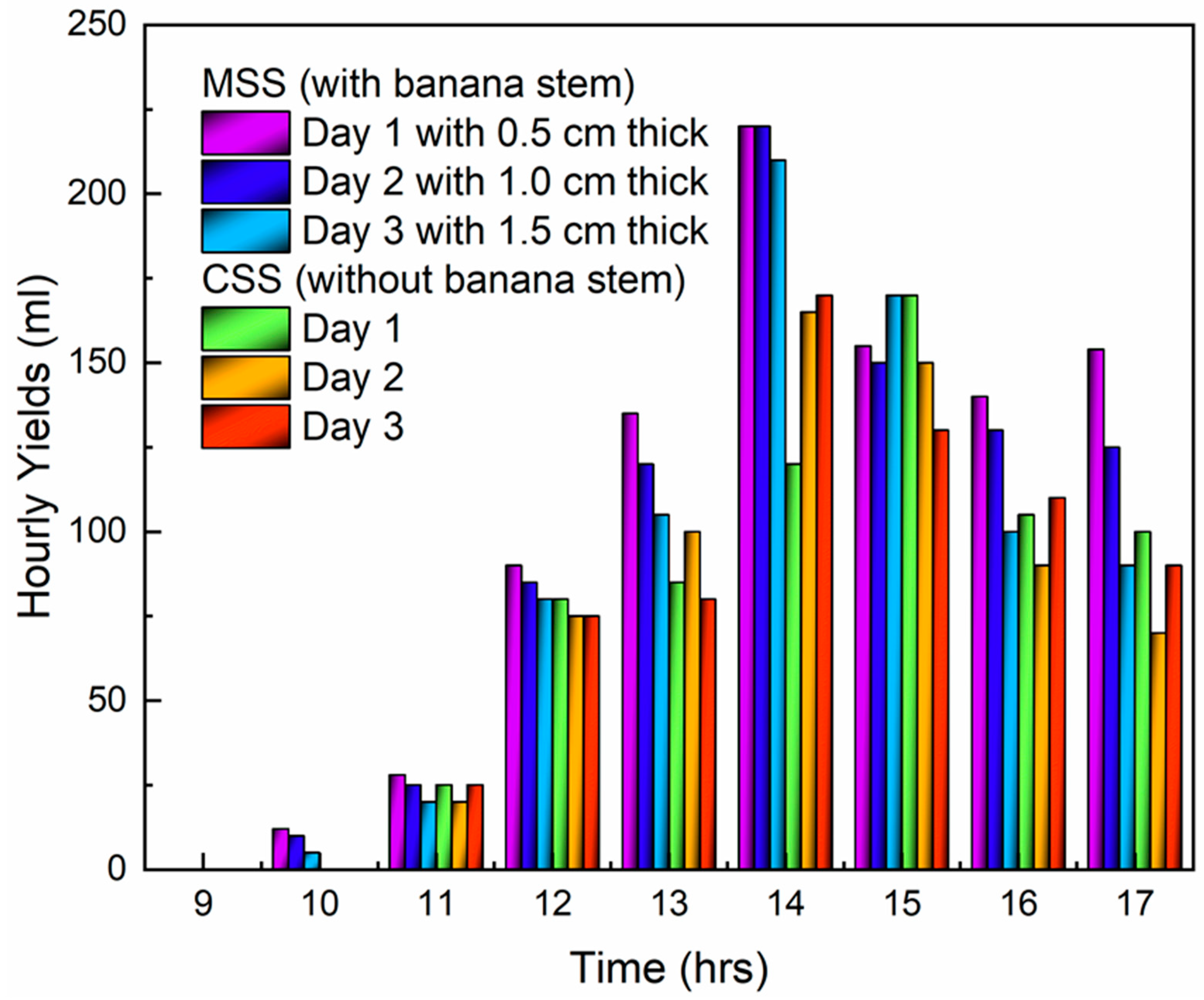
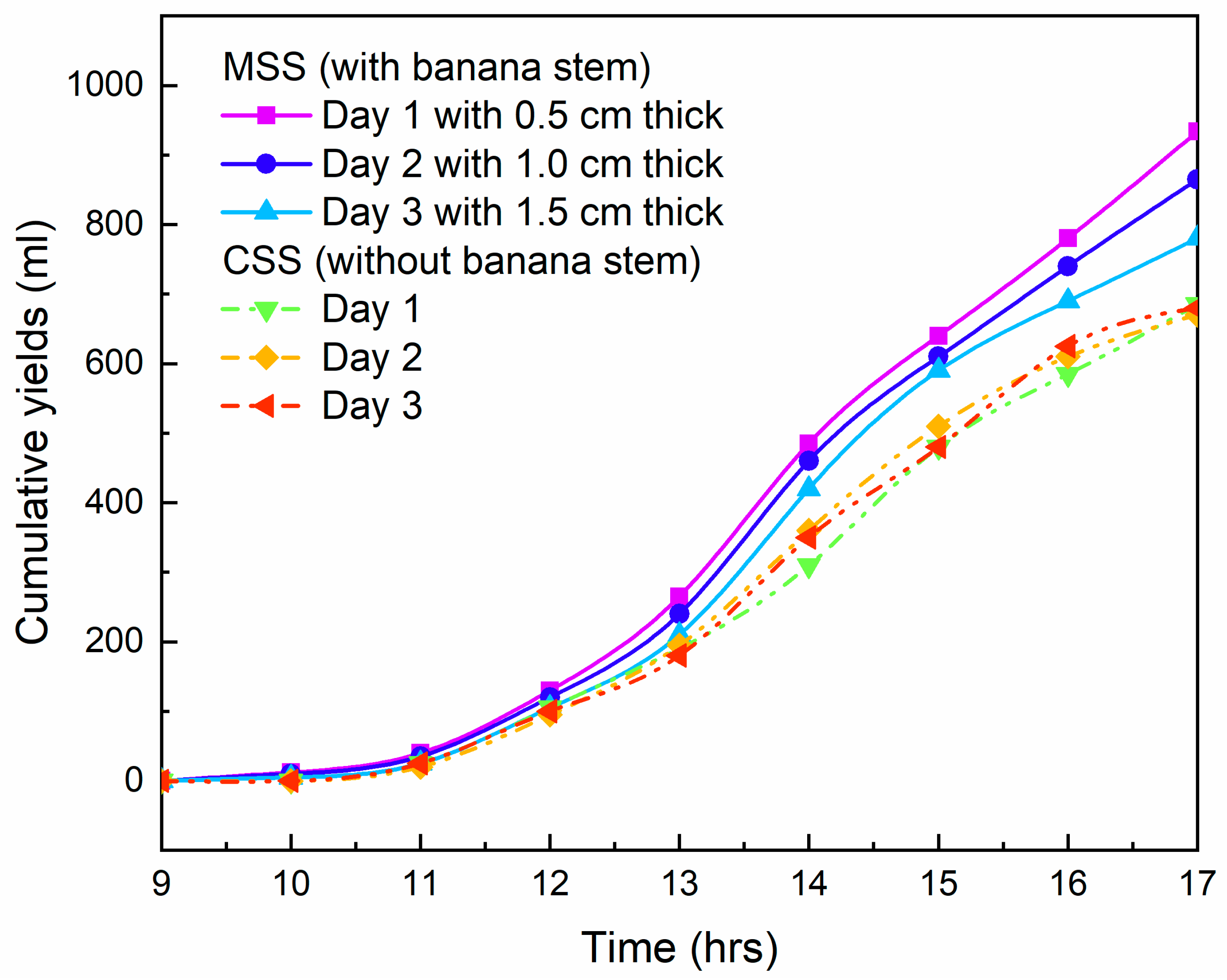
3. Results and Discussion
4. Monetary Analysis
5. Assessment of Water Quality
6. Enviro-Economic Investigation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Curto, D.; Franzitta, V.; Guercio, A. A Review of the Water Desalination Technologies. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, S.; Kumar, A.; Arunkumar, T.; Singh, V. Progress on Suspended Nanostructured Engineering Materials Powered Solar Distillation—A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 143, 110848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, M.A.; Zubo, R.H.A.; Rashid, F.L.; Dakkama, H.J.; Abd-Alhameed, R.; Mujtaba, I.M. Evaluation of Solar Energy Powered Seawater Desalination Processes: A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 6562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemeida, M.G.; Hemeida, A.M.; Senjyu, T. Renewable Energy Resources Technologies and Life Cycle Assessment: Review. Energies 2022, 15, 9417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkala, S.R.; Kumar Kaviti, A. Advanced Design Techniques in Passive and Active Tubular Solar Stills: A Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 48020–48056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Prakash, O. Improving the Single-Slope Solar Still Performance Using Solar Air Heater with Phase Change Materials. Energies 2022, 15, 8013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khafaji, H.Q.A.; Abdul Wahhab, H.A.; Al-Maliki, W.A.K.; Alobaid, F.; Epple, B. Energy and Exergy Analysis for Single Slope Passive Solar Still with Different Water Depth Located in Baghdad Center. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaviti, A.K.; Ram, A.S.; Thakur, A.K. Influence of Fully Submerged Permanent Magnets in the Evaluation of Heat Transfer and Performance Analysis of Single Slope Glass Solar Still. J. Power Energy 2021, 236, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, A.; Jamil, B.; Haque, N.U.; Ansari, A. Investigating the Effect of Pumice Stones Sensible Heat Storage on the Performance of a Solar Still. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 9, 100228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaviti, A.K.; Akkala, S.R.; Sikarwar, V.S. Productivity Enhancement of Stepped Solar Still by Loading with Magnets and Suspended Micro Charcoal Powder. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2021, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Siva, A.; Kumari, A.A.; Hussain, S. Development of Hierarchical Structures for Enhanced Solar Desalination. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ram, S. Influence of Anodization Time on Al 2 O 3 Nanoporous Morphology and Optical Properties Using Energy Band Gap at Room Temperature. Results Eng. 2023, 17, 100816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanganeh, P.; Goharrizi, A.S.; Ayatollahi, S.; Feilizadeh, M. Productivity Enhancement of Solar Stills by Nano-Coating of Condensing Surface. Desalination 2019, 454, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, S.; Kumar, A.; Rao, S.; Sakthivel, S.; Harish, T.; Vinay, K.; Srinivasa, T.; Thaker, A.; Vishwanath, K.; Mohit, A.; et al. Performance Analysis of Non-Contact Nanostructure Solar Desalination System by Varying Water Depth at a Constant Air Gap. Sol. Energy 2022, 247, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, T.; Murugesan, D.; Raj, K.; Denkenberger, D.; Viswanathan, C.; Rufuss, D.D.W.; Velraj, R. Effect of Nano-Coated CuO Absorbers with PVA Sponges in Solar Water Desalting System. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 148, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaviti, A.K.; Naike, V.R.; Ram, A.S.; Thakur, A.K. Energy and Exergy Analysis of a Truncated and Parabolic Finned Double Slope Solar Stills. Int. J. Ambient. Energy 2021, 43, 6210–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Bai, W.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Duan, G.; Wu, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y. A Melanin-Inspired Robust Aerogel for Multifunctional Water Remediation. Mater. Horiz. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, D.; Duan, G.; Li, Y. Robust and Multifunctional Natural Polyphenolic Composites for Water Remediation. Mater. Horiz. 2022, 9, 2496–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Yang, F.; Bai, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Duan, G.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y. A Bioinspired Antibacterial and Photothermal Membrane for Stable and Durable Clean Water Remediation. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, Y.; Li, N.; Yang, P.; Yang, Y.; Duan, G.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y. A Robust and 3D-Printed Solar Evaporator Based on Naturally Occurring Molecules. Sci. Bull. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; He, P.; Hao, L.; Fan, Z.; Niu, R.; Tang, T.; Gong, J. Waste-Treating-Waste: Upcycling Discarded Polyester into Metal–Organic Framework Nanorod for Synergistic Interfacial Solar Evaporation and Sulfate-Based Advanced Oxidation Process. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 456, 140994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ren, J.; Gong, J.; Qu, J.; Niu, R. Cost-Effective, Scalable Fabrication of Self-Floating Xerogel Foam for Simultaneous Photothermal Water Evaporation and Thermoelectric Power Generation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraparaju, S.K.; Natarajan, S.K. Combined Enhancement of Evaporation and Condensation Rates in the Solar Still for Augmenting the Freshwater Productivity Using Energy Storage and Natural Fibres. Aqua Water Infrastruct. Ecosyst. Soc. 2022, 71, 628–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraparaju, S.K.; Natarajan, S.K. Augmentation of Freshwater Productivity in Single Slope Solar Still Using Luffa Acutangula Fibres. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 2943–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suraparaju, S.K.; Natarajan, S.K. Effect of Natural Sisal Fibre on Enhancing the Condensation Rate of Solar Still for Sustainable Clean Water Production. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2022, 36, 101527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraparaju, S.K.; Natarajan, S.K. Performance Analysis of Single Slope Solar Desalination Setup with Natural Fiber. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 193, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraparaju, S.K.; Dhanusuraman, R.; Natarajan, S.K. Performance Evaluation of Single Slope Solar Still with Novel Pond Fibres. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 154, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dsilva Winfred Rufuss, D.; Suganthi, L.; Iniyan, S.; Davies, P.A. Effects of Nanoparticle-Enhanced Phase Change Material (NPCM) on Solar Still Productivity. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 192, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fath, H.E.S.; El-Samanoudy, M.; Fahmy, K.; Hassabou, A. Thermal-Economic Analysis and Comparison between Pyramid-Shaped and Single-Slope Solar Still Configurations. Desalination 2003, 159, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiuddin, S.A.; Kaviti, A.K.; Rao, T.S.; Atchuta, S.R. Experimental Assessment of Productivity and Sustainability of Nanoporous Cr-Mn-Fe Oxide Nanocoating in Solar-Powered Desalination. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 162, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Samsher. Material Conscious Energy Matrix and Enviro-Economic Analysis of Passive ETC Solar Still. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 38, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.S.; Sharon, H. Active Multi-Effect Vertical Solar Still: Mathematical Modeling, Performance Investigation and Enviro-Economic Analyses. Desalination 2016, 395, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datt, P.; Singh, V.P.; Singh, P.H. Latent Heat of Vaporization/Condensation. In Encyclopedia of Snow, Ice and Glaciers; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 5, pp. 248–253. [Google Scholar]
- Hammond, G.P.; Jones, C.I. Embodied Energy and Carbon in Construction Materials. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Energy 2008, 161, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joshi, P.; Tiwari, G.N. Energy Matrices, Exergo-Economic and Enviro-Economic Analysis of an Active Single Slope Solar Still Integrated with a Heat Exchanger: A Comparative Study. Desalination 2018, 443, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Measuring Device | Standard Uncertainty | % Error | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hukseflux pyranometer (SR05-D1A3) | 5.77 W/m2 | 10 | ±10 W/m2 |
| RTD sensors | 0.5 ℃ | 0.25 | ±0.8 ℃ |
| Data logger | 0.06 ℃ | 1.3 | ±0.1 ℃ |
| Measuring jars | 3 mL | 5 | ±5 mL |
| Anemometer | 0.06 m/s | 10 | ±0.1 m/s |
| S. No | Material/Service | Area/Quantity per Still | CSS (USD) | MSS (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Glasses | 2.5 m2 | 15 | 15 |
| 2. | PVC collecting channel | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 3. | Black powder coating | 1 m2 | 4 | 4 |
| 4. | Glass cover, 0.4 cm | 0.5 m2 | 1 | 1 |
| 5. | Double side foam tape | 1.5 m | 1 | 1 |
| 6. | Silicon glue | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| 7. | Camphor sooth | 200 gm | - | 2 |
| 8. | Banana stem | 0.9 kg | - | - |
| 9. | Fabrication charges | - | 30 | 30 |
| Total cost | - | 59 | 61 |
| Parameters in USD | Conventional Still | Modified Still |
|---|---|---|
| P | 59 | 61 |
| CRF | 0.177 | 0.177 |
| FAC | 10.45 | 10.80 |
| S | 11.8 | 12.2 |
| SFF | 0.05698 | 0.05698 |
| ASV | 0.6723 | 0.6951 |
| AMC | 1.5675 | 1.6200 |
| AC | 11.34 | 11.72 |
| M | 171 | 233 |
| CPL | 0.0665 | 0.0503 |
| Water Quality Metrics | Prior to Desalination | After Desalination (CSS) | After Desalination (MSS) | Maximum Allowable Levels in Drinking Water (WHO and BIS Standards) [30] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.16 | 7.50 | 7.25 | 8.5 |
| Fluoride (mg/L) | 0.579 | 0.426 | 0.348 | 1.5 |
| Hardness (mg/L) | 330 | 160 | 125 | 200 |
| TDS (ppm) | 440 | 30 | 18.6 | 500 |
| Chloride (mg/L) | 57.6 | 10.45 | 7.68 | 250 |
| Components | Weight/Volume | Energy Density (kWh/kg or kWh/m3) | Embodied Energy (kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Galvanized iron sheet (0.1 cm thickness) | 8 kg | 10.83 | 86.64 |
| Plywood sheet (1.8 cm thickness) | 8 kg | 4.167 | 33.34 |
| Glass cover | 0.51 m × 0.6 m × 0.004 m | 11,127.8 | 13.62 |
| Foam tape on two sides and silicon glue | 0.25 kg | 3.3 | 0.83 |
| PVC channel | 0.2 kg | 18.75 | 3.75 |
| Banana stem + Camphor soothing | 0.9 kg | 0.95 | 0.85 |
| Total embodied energy | 139.03 | ||
| S. No | Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Embodied energy (out) | 146.58 kWh |
| 2. | Lifespan CO2 emission | 219.62 kg |
| 3. | Lifespan SO2 emission | 1.67 kg |
| 4. | Lifespan NO emission | 0.69 kg |
| 5. | Embodied energy | 139 kWh |
| 6. | Net CO2 reduction for 10 years | 2.09 tonnes |
| 7. | Earned carbon credit for 10 years | USD 20.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaviti, A.K.; Akkala, S.R.; Sikarwar, V.S.; Sai Snehith, P.; Mahesh, M. Camphor-Soothed Banana Stem Biowaste in the Productivity and Sustainability of Solar-Powered Desalination. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031652
Kaviti AK, Akkala SR, Sikarwar VS, Sai Snehith P, Mahesh M. Camphor-Soothed Banana Stem Biowaste in the Productivity and Sustainability of Solar-Powered Desalination. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(3):1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031652
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaviti, Ajay Kumar, Siva Ram Akkala, Vineet Singh Sikarwar, Pilli Sai Snehith, and Moodapelly Mahesh. 2023. "Camphor-Soothed Banana Stem Biowaste in the Productivity and Sustainability of Solar-Powered Desalination" Applied Sciences 13, no. 3: 1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031652
APA StyleKaviti, A. K., Akkala, S. R., Sikarwar, V. S., Sai Snehith, P., & Mahesh, M. (2023). Camphor-Soothed Banana Stem Biowaste in the Productivity and Sustainability of Solar-Powered Desalination. Applied Sciences, 13(3), 1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031652








