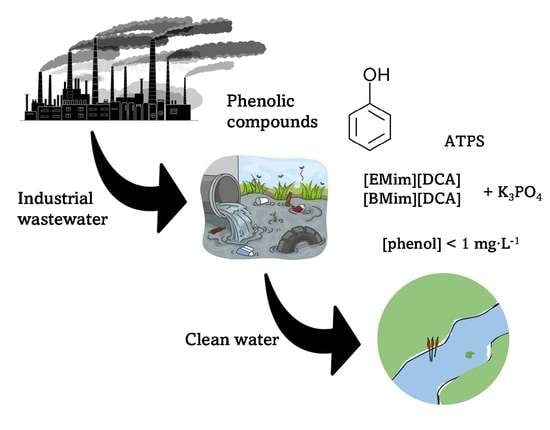
Cleaning Phenolic Compounds Present in Water Using Salting-Out Effect with DCA-Based Ionic Liquids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Determination of the Solubility Curves of Ternary Mixture: {Water + Salt + IL}
2.2.2. Liquid–Liquid Extraction
2.2.3. Phenolic Compound Mixture (PCM)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Initial Concentration in the Extraction Yield
3.2. Effect of the Cation Structure of the IL in the Extraction Yield
3.3. Effect of the Salt Concentration in the Extraction Yield
3.4. Extraction of Phenolic Compound Mixture (PCM)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banat, F.A.; Al-Bashir, B.; Al-Asheh, S.; Hayajneh, O. Adsorption of Phenol by Bentonite. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 107, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, N.K.; Singh, P.; Sarethy, I.P. Precipitation of Phenols from Paper Industry Wastewater Using Ferric Chloride. Rasayan J. Chem. 2011, 4, 452–456. [Google Scholar]
- Yaseen, D.A.; Scholz, M. Textile Dye Wastewater Characteristics and Constituents of Synthetic Effluents: A Critical Review; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 16, ISBN 0123456789. [Google Scholar]
- Gai, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, C.; Xiao, M.; Huang, T.; Wang, J.; Song, H. An Improved Tar–Water Separation Process of Low–Rank Coal Conversion Wastewater for Increasing the Tar Yield and Reducing the Oil Content in Wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, N.V.; Anupama, S.; Navya, K.; Shalini, H.N.; Idris, M.; Hampannavar, U.S. Biological Removal of Phenol from Wastewaters: A Mini Review. Appl. Water Sci. 2015, 5, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.S.; Ibrahim, T.H.; Jabbar, N.A.; Khamis, M.I.; Nancarrow, P.; Mjalli, F.S. Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Recovery of Phenolic Compounds: Effect of Ionic Liquids Structure and Process Parameters. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 12398–12422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Fan, Y.; Pei, Y.; Wu, K.; Wang, J.; Fan, M. Solvent Extraction of Selected Endocrine-Disrupting Phenols Using Ionic Liquids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 61, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuta, S.; Nakamura, K.I.; Kudo, Y.; Takeda, Y.; Kato, H. Partition Behavior of Chlorophenols and Nitrophenols between Hydrophobic Ionic Liquids and Water. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 4083–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Cao, H.; Descorme, C.; Xie, Y. Phenolic Compounds Removal by Wet Air Oxidation Based Processes. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2018, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Kargari, A.; Sanaeepur, H.; Abbassian, K.; Najafi, A.; Mofarrah, E. Phenol Removal from Industrial Wastewaters: A Short Review. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 53, 2215–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sas, O.G.; Domínguez, I.; González, B.; Domínguez, Á. Liquid-Liquid Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Water Using Ionic Liquids: Literature Review and New Experimental Data Using [C2mim]FSI. J. Environ. Manage. 2018, 228, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbassian, K.; Kargari, A.; Kaghazchi, T. Phenol Removal from Aqueous Solutions by a Novel Industrial Solvent. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2015, 202, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riveiro, E.; Villar, L.; Sas, O.G.; González, B.; Canosa, J.; Domínguez, Á. Extraction of Carboxylic Acids from Aqueous Solutions by Using [BMim][NTf2] and Salting-out Agents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 4717–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Bakaruddin, B.R.; Lethesh, K.C.; Mutalib, M.I.A.; Shah, S.N. Experimental and Theoretical Study on Extraction and Recovery of Naphthenic Acid Using Dicyanamide-Based Ionic Liquids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 213, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpińska, M.; Wlazło, M. Application of Dicyanamide-Based Ionic Liquid in Separation of Binary Mixtures Based on Gamma Infinity Data Measurements. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimura, K.; Amau, M.; Kume, R.; Suga, K.; Okamoto, Y.; Umakoshi, H. Characterization of Ionic Liquid Aqueous Two-Phase Systems: Phase Separation Behaviors and the Hydrophobicity Index between the Two Phases. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 5866–5874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaiahgari, A.; Gardas, R.L. Evaluation of Anion Chain Length Impact on Aqueous Two Phase Systems Formed by Carboxylate Anion Functionalized Ionic Liquids. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2018, 120, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Cheng, Z. Thermal Stability of Ionic Liquids: Current Status and Prospects for Future Development. Processes 2021, 9, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, N.; Khan, A.S.; Hassan, M.F.; Ibrahim, T.H.; Khamis, M.I.; Nancarrow, P. Ionic Liquid Agar–Alginate Beads as a Sustainable Phenol Adsorbent. Polymers 2022, 14, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.A.; Mulk, W.U.; Ullah, Z.; Khan, H.; Zahid, A.; Shah, M.U.H.; Shah, S.N. Recent Advances in the Synthesis, Application and Economic Feasibility of Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents for CO2 Capture: A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 9098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, C.M.S.S.; Dinis, T.B.V.; Carvalho, P.J.; Schröder, B.; Santos, L.M.N.B.F.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Binary Mixtures of Ionic Liquids in Aqueous Solution: Towards an Understanding of Their Salting-In/Salting-Out Phenomena. J. Solut. Chem. 2019, 48, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Wei, X.; Xu, P. Aqueous Biphasic Systems Formed by Deep Eutectic Solvent and New-Type Salts for the High-Performance Extraction of Pigments. Talanta 2018, 181, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sas, O.G.; Domínguez, Á.; González, B. Recovery and Elimination of Phenolic Pollutants from Water Using [NTf2] and [Nf2]-Based Ionic Liquids. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thasneema, K.K.; Dipin, T.; Thayyil, M.S.; Sahu, P.K.; Messali, M.; Rosalin, T.; Elyas, K.K.; Saharuba, P.M.; Anjitha, T.; Hadda, T. Ben Removal of Toxic Heavy Metals, Phenolic Compounds and Textile Dyes from Industrial Waste Water Using Phosphonium Based Ionic Liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 323, 114645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sas, O.G.; Domínguez, I.; Domínguez, Á.; González, B. Using Bis(Trifluoromethylsulfonyl)Imide Based Ionic Liquids to Extract Phenolic Compounds. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2019, 131, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, E.J.; Díaz, I.; Gonzalez-Miquel, M.; Rodríguez, M.; Sueiras, A. On the Behavior of Imidazolium versus Pyrrolidinium Ionic Liquids as Extractants of Phenolic Compounds from Water: Experimental and Computational Analysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 201, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, N.J.; Gutowski, K.E.; Rogers, R.D. Investigation of Aqueous Biphasic Systems Formed from Solutions of Chaotropic Salts with Kosmotropic Salts (Salt–Salt ABS). Green Chem. 2007, 9, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Meng, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Liu, X. Phenol Distribution Behavior in Aqueous Biphasic Systems Composed of Ionic Liquids-Carbohydrate-Water. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2012, 57, 1910–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, H.; Sun, Y.T.; Xu, Y.J.; Wang, Q.W.; Yan, Y.S. Determination of Trace Chlorophenols Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in Water Sample Using [Bmim]BF4-NaH2PO4 Aqueous Two-Phase Extraction System Coupled with High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Fenxi Huaxue/ Chinese J. Anal. Chem. 2011, 39, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Blidi, L.; Saleh, J.; Ben Ghanem, O.; El-Harbawi, M.; Lévêque, J.M.; Hadj-Kali, M.K. Synthesis, Characterization, and Antimicrobial Toxicity Study of Dicyanamide-Based Ionic Liquids and Their Application to Liquid-Liquid Extraction. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2020, 65, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakereh, Z.; Zare, M.; Shakerzadeh, E. Exploring Enthalpies of Formation of Imidazolium-, Pyridinium-, and Pyrrolidinium-Based Ionic Liquids with Dicyanamide Anion Using Quantum Chemical Methods. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 308, 113137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, S.A.; Golding, J.; Deacon, G.B. Ionic Liquids Based on Imidazolium, Ammonium and Pyrrolidinium Salts of the Dicyanamide Anion. Green Chem. 2002, 4, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, M.; Arce, A.; Soto, A. Ionic Liquids on Desulfurization of Fuel Oils. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2010, 294, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domańska, U.; Królikowski, M. Extraction of Butan-1-Ol from Water with Ionic Liquids at T = 308.15 K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2012, 53, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, N.; Xu, S.; Zhu, Q.; Hu, J. The Influence of Temperature on the Phase Behavior of Ionic Liquid Aqueous Two-Phase Systems. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2019, 40, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, E.W.; Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D.; Clesceri, L.S. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewaster; American Water Works Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ventura, S.P.M.; Neves, C.M.S.S.; Freire, M.G.; Marrucho, I.M.; Oliveira, J.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Evaluation of Cation Influence on the Formation and Extraction Capacity of Ionic-Liquid-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 5194–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, I.; Ghorbanidehkordi, S.; Hallajisani, A. Assessment of Ionic Liquid-Based Aqueous Two-Phase System Abilities to Remove Sulfonamide Antibiotics from the Aquatic Environment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 11291–11300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 ), o-cresol (
), o-cresol (  ) and 2-chlorophenol (
) and 2-chlorophenol (  ) for the extraction using [EMim] [DCA] and 30% of K3PO4.
) for the extraction using [EMim] [DCA] and 30% of K3PO4.
 ), o-cresol (
), o-cresol (  ) and 2-chlorophenol (
) and 2-chlorophenol (  ) for the extraction using [EMim] [DCA] and 30% of K3PO4.
) for the extraction using [EMim] [DCA] and 30% of K3PO4.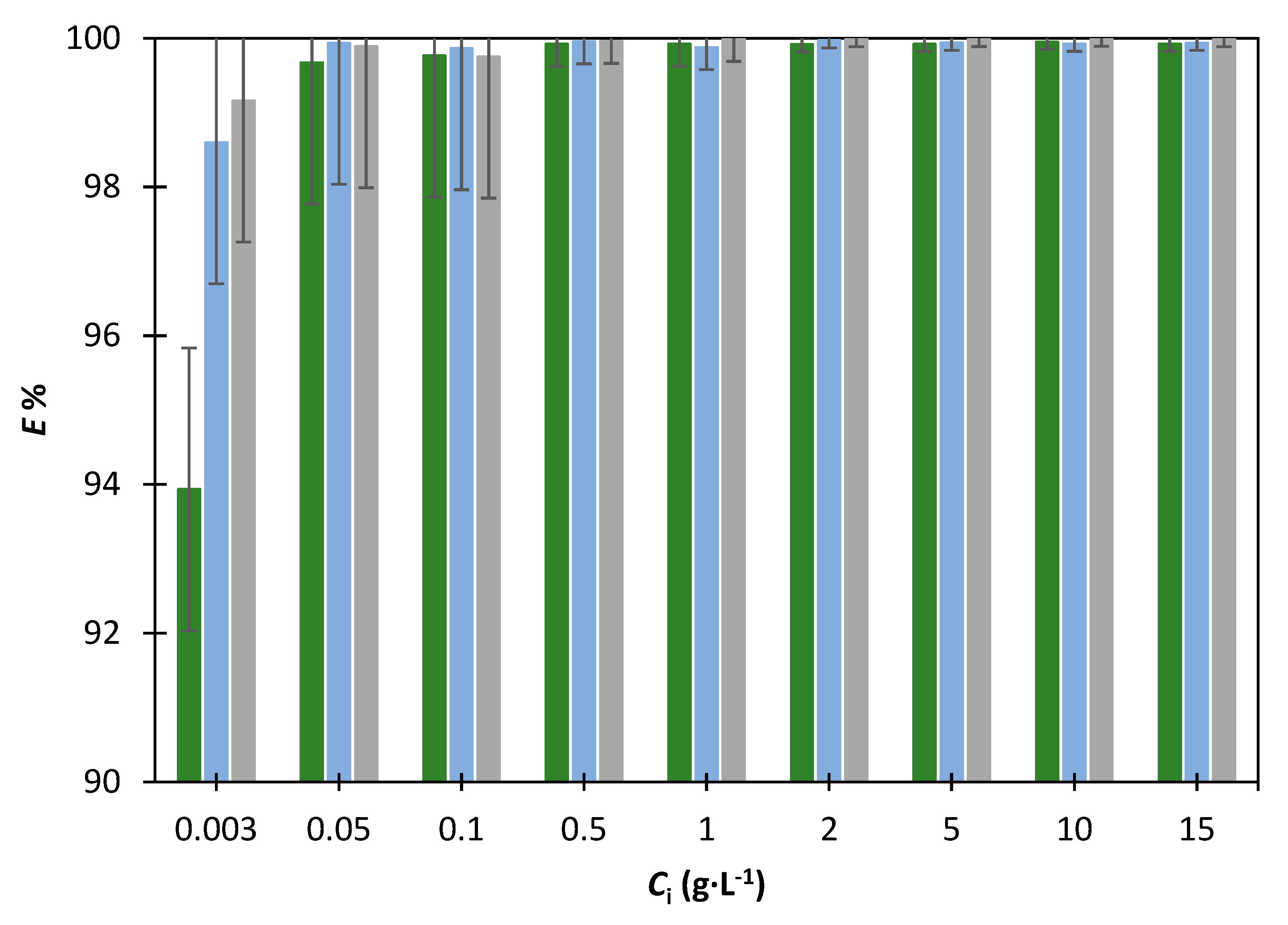
 ), o-cresol (
), o-cresol (  ) and 2-chlorophenol (
) and 2-chlorophenol (  ) for the extraction using [EMim] [DCA] and 20% of K3PO4.
) for the extraction using [EMim] [DCA] and 20% of K3PO4.
 ), o-cresol (
), o-cresol (  ) and 2-chlorophenol (
) and 2-chlorophenol (  ) for the extraction using [EMim] [DCA] and 20% of K3PO4.
) for the extraction using [EMim] [DCA] and 20% of K3PO4.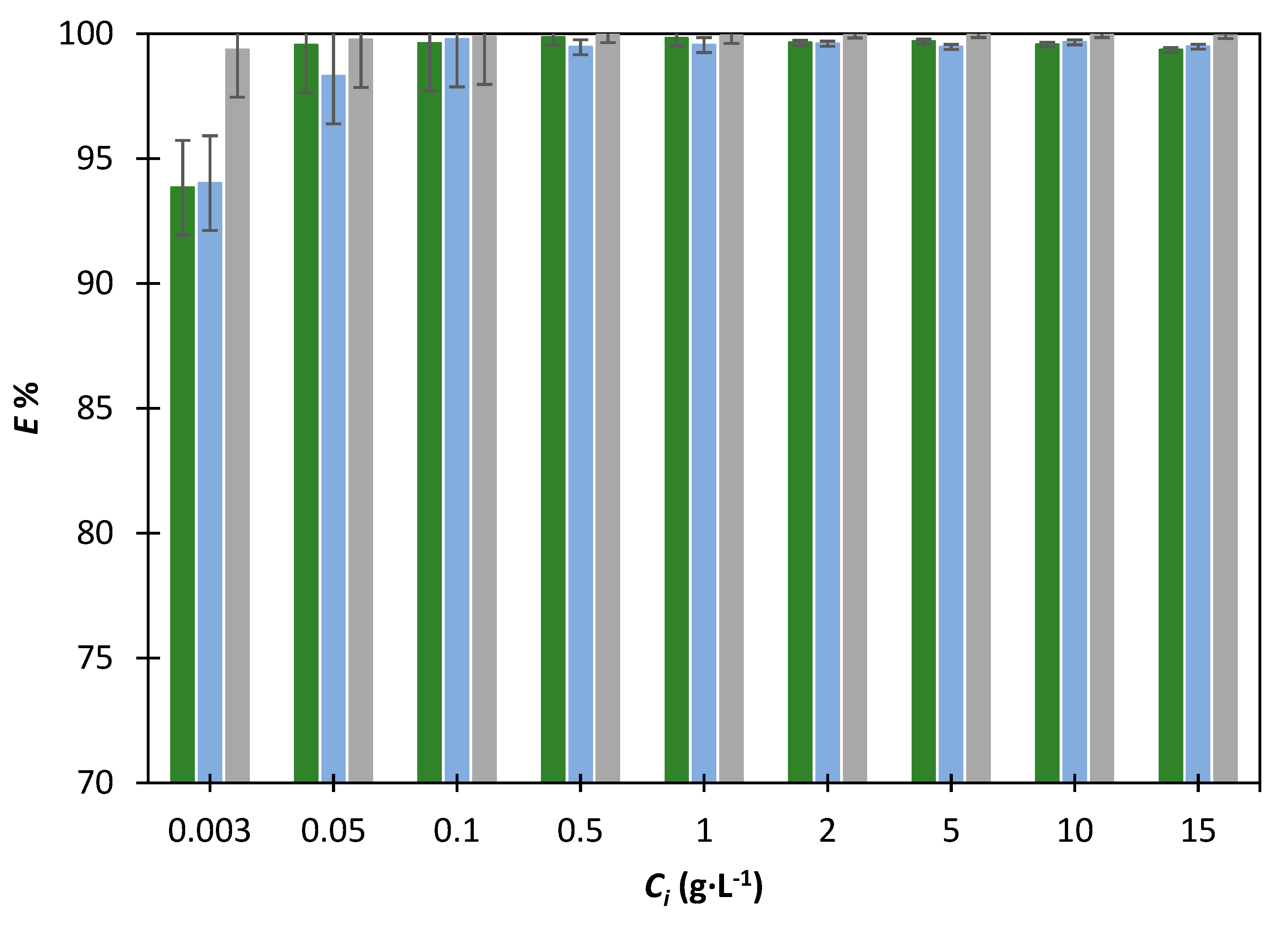
 ) and [BMim][DCA] (
) and [BMim][DCA] (  ) with 20% of salt.
) with 20% of salt.
 ) and [BMim][DCA] (
) and [BMim][DCA] (  ) with 20% of salt.
) with 20% of salt.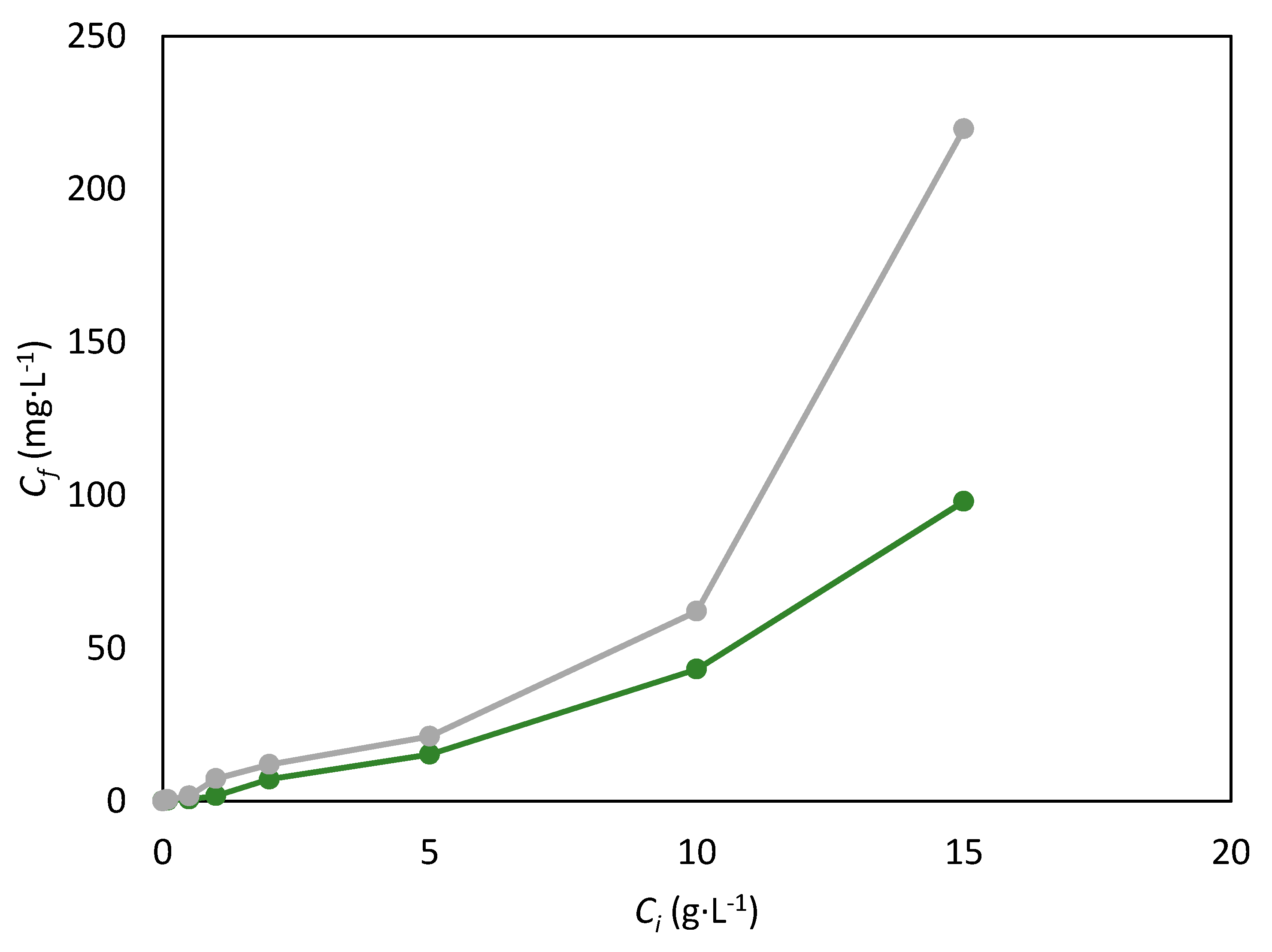
 ), 30% (
), 30% (  ) and 40% (
) and 40% (  ) of K3PO4.
) of K3PO4.
 ), 30% (
), 30% (  ) and 40% (
) and 40% (  ) of K3PO4.
) of K3PO4.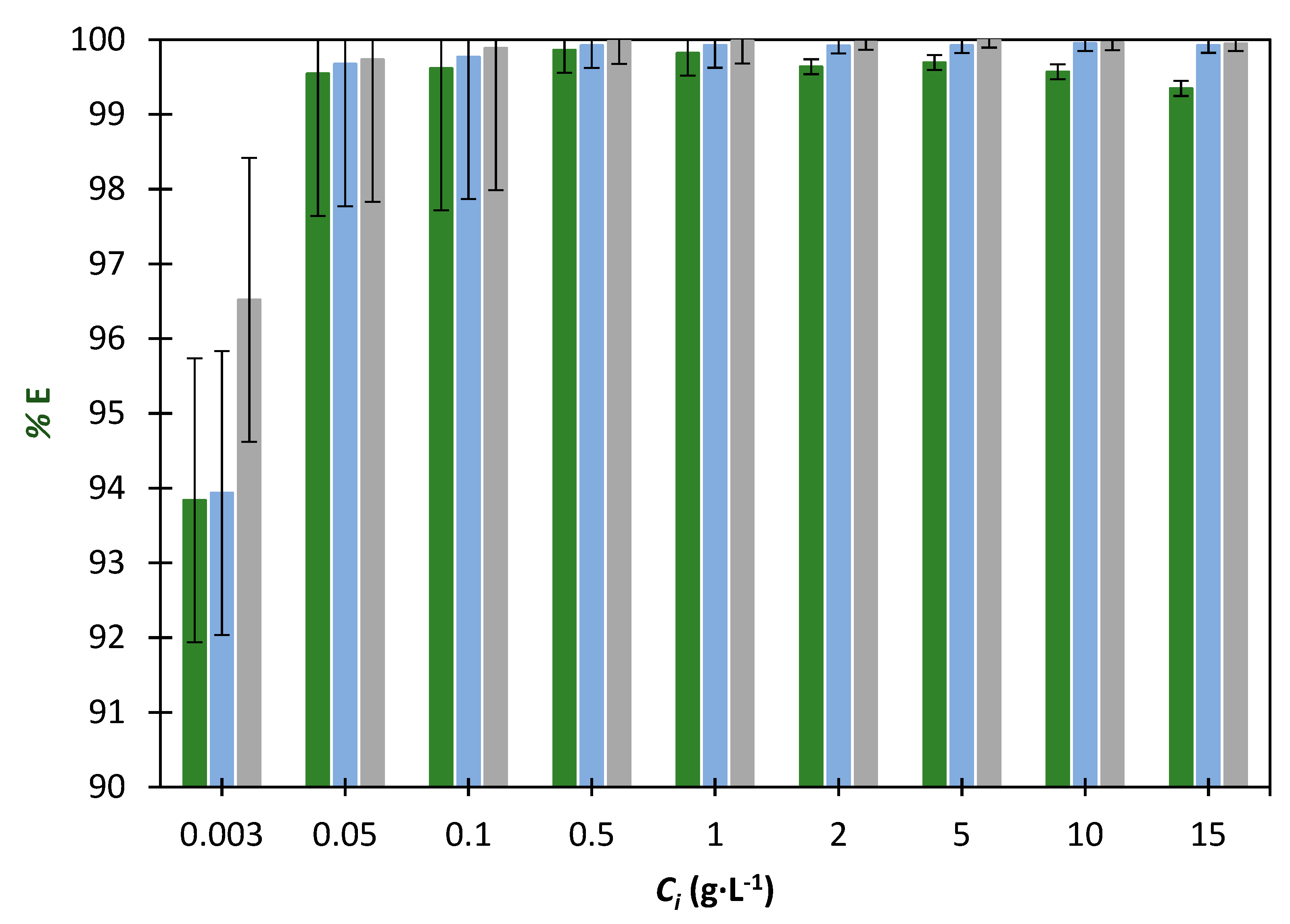
 ), 30% (
), 30% (  ) and 40% (
) and 40% (  ) of K3PO4.
) of K3PO4.
 ), 30% (
), 30% (  ) and 40% (
) and 40% (  ) of K3PO4.
) of K3PO4.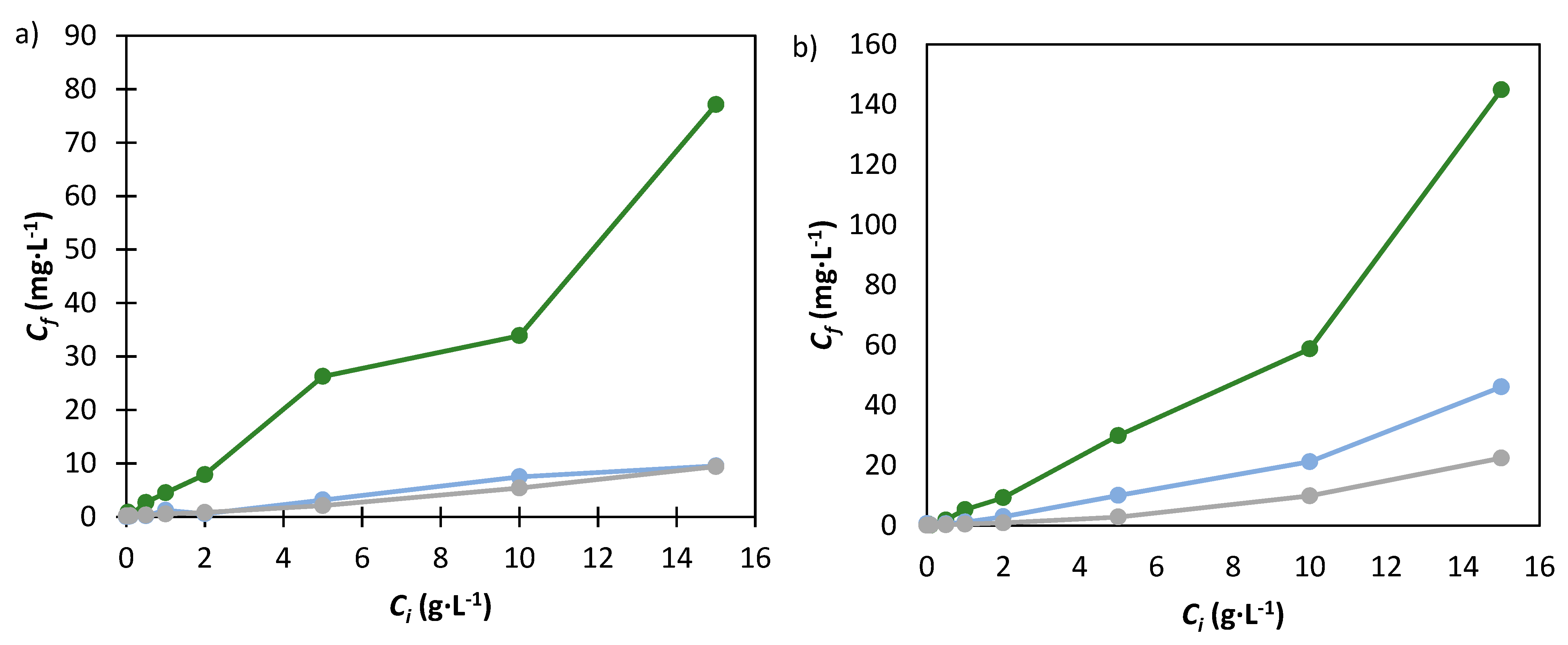
 ), 30% (
), 30% (  ) and 40% (
) and 40% (  ) of K3PO4.
) of K3PO4.
 ), 30% (
), 30% (  ) and 40% (
) and 40% (  ) of K3PO4.
) of K3PO4.
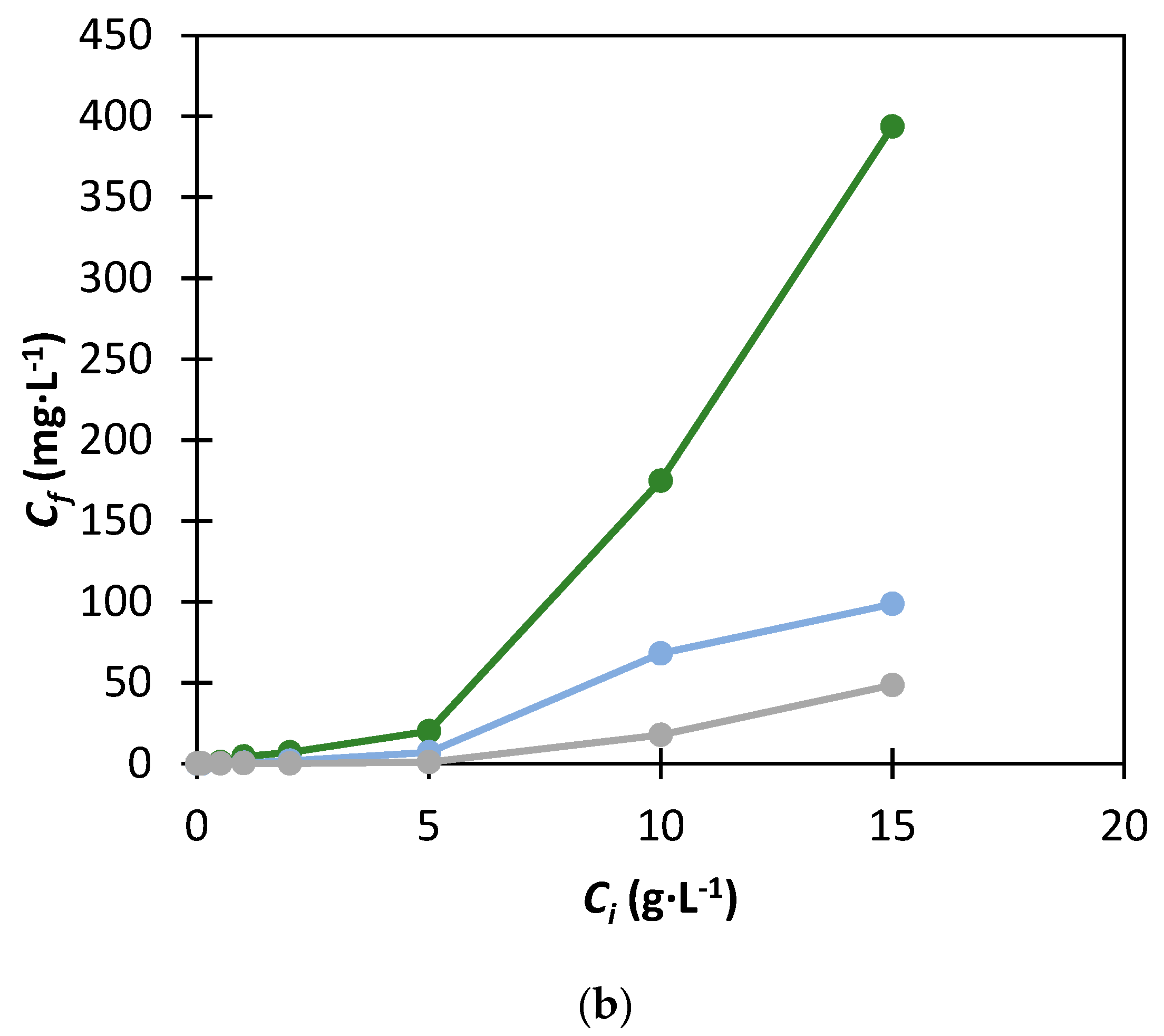
| Industry | Phenol Concentration (mg·L−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Paper | 79.5 | [2] |
| Textile | 155 | [3] |
| Coal | 551 | [4] |
| Coke | 200 | [5] |
| Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Biological degradation | Substitution of chemicals by microorganisms | Growth control, use of co-solvent for low phenol concentrations |
| Oxidative process | Simple process | Expensive, hazardous substances, high pressure, and temperature |
| Electrochemical | Not an expensive chemical | High consumption of energy, toxic chemicals |
| Adsorption | Economic process, simple equipment | Difficult to regenerate, not suitable for low concentrations |
| Liquid–liquid extraction | Easy operation, extraction agents can be recycled | Volatile organic solvents, low selectivity |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
G. Sas, O.; Domínguez, Á.; González, B. Cleaning Phenolic Compounds Present in Water Using Salting-Out Effect with DCA-Based Ionic Liquids. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2009. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13032009
G. Sas O, Domínguez Á, González B. Cleaning Phenolic Compounds Present in Water Using Salting-Out Effect with DCA-Based Ionic Liquids. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(3):2009. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13032009
Chicago/Turabian StyleG. Sas, Olalla, Ángeles Domínguez, and Begoña González. 2023. "Cleaning Phenolic Compounds Present in Water Using Salting-Out Effect with DCA-Based Ionic Liquids" Applied Sciences 13, no. 3: 2009. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13032009
APA StyleG. Sas, O., Domínguez, Á., & González, B. (2023). Cleaning Phenolic Compounds Present in Water Using Salting-Out Effect with DCA-Based Ionic Liquids. Applied Sciences, 13(3), 2009. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13032009