The Duration Effect of Pulse-Type Near-Field Earthquakes on Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis and Damage Evaluation of Hydraulic Tunnels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Ground Motion Duration Index
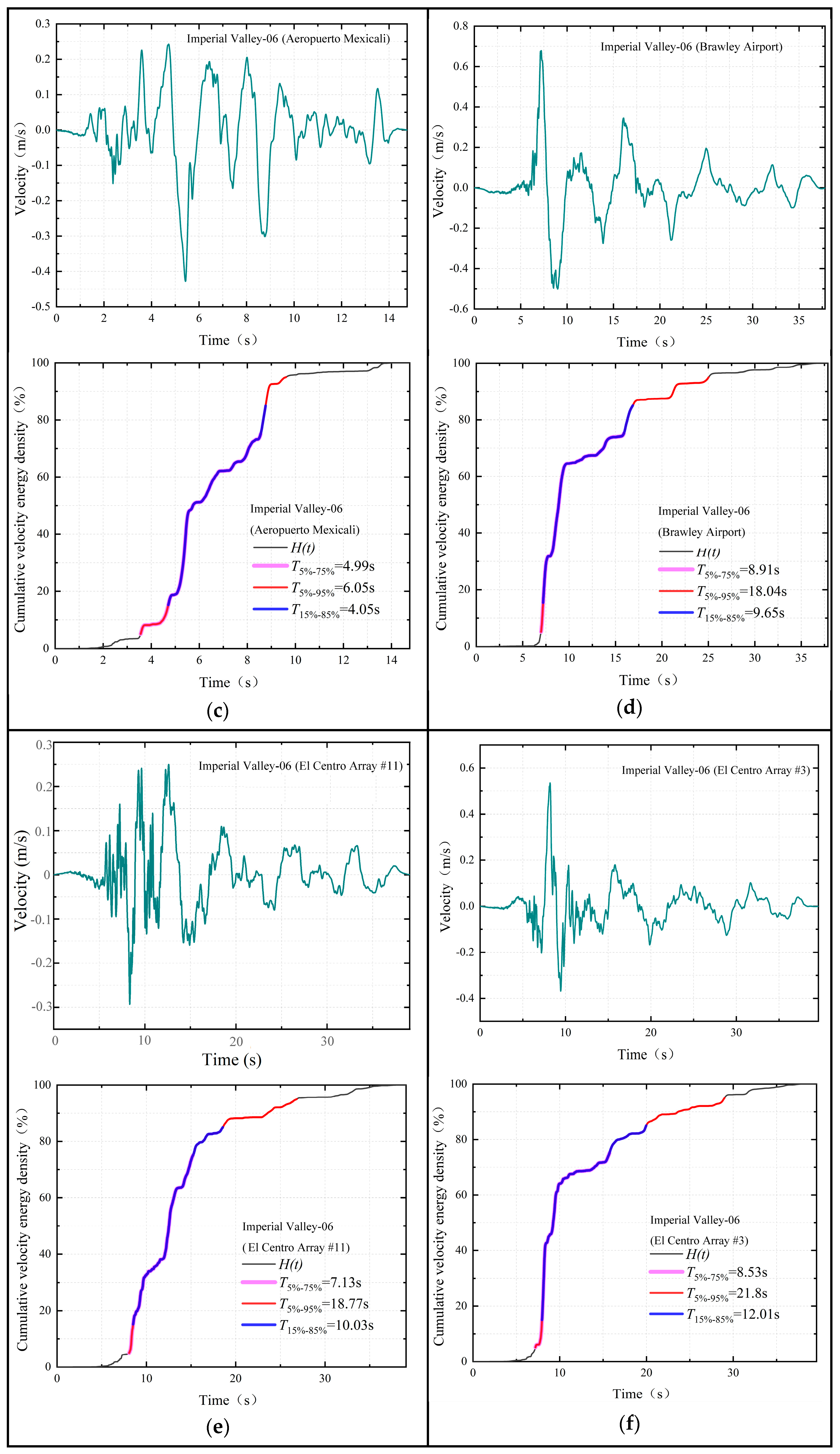
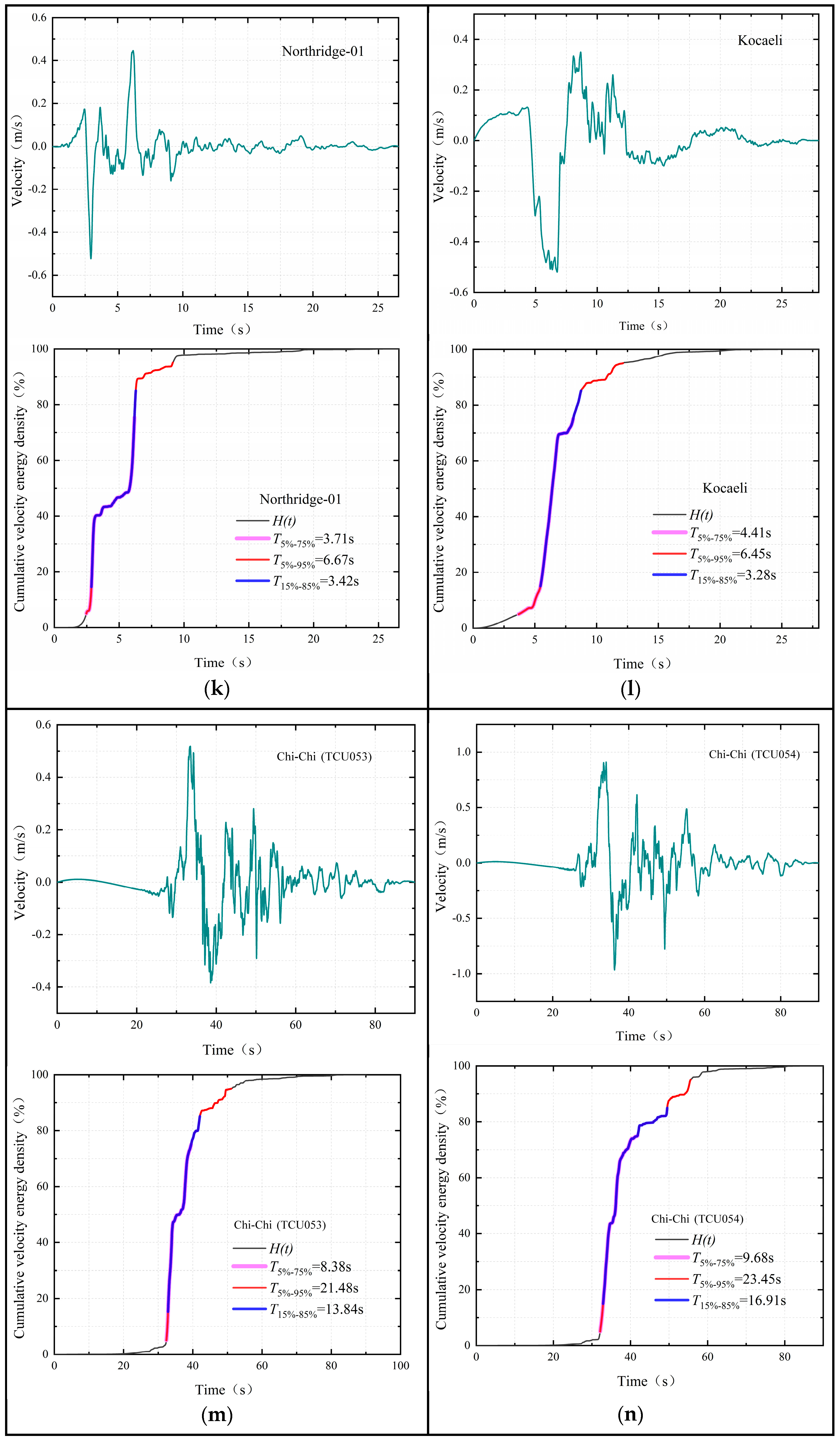
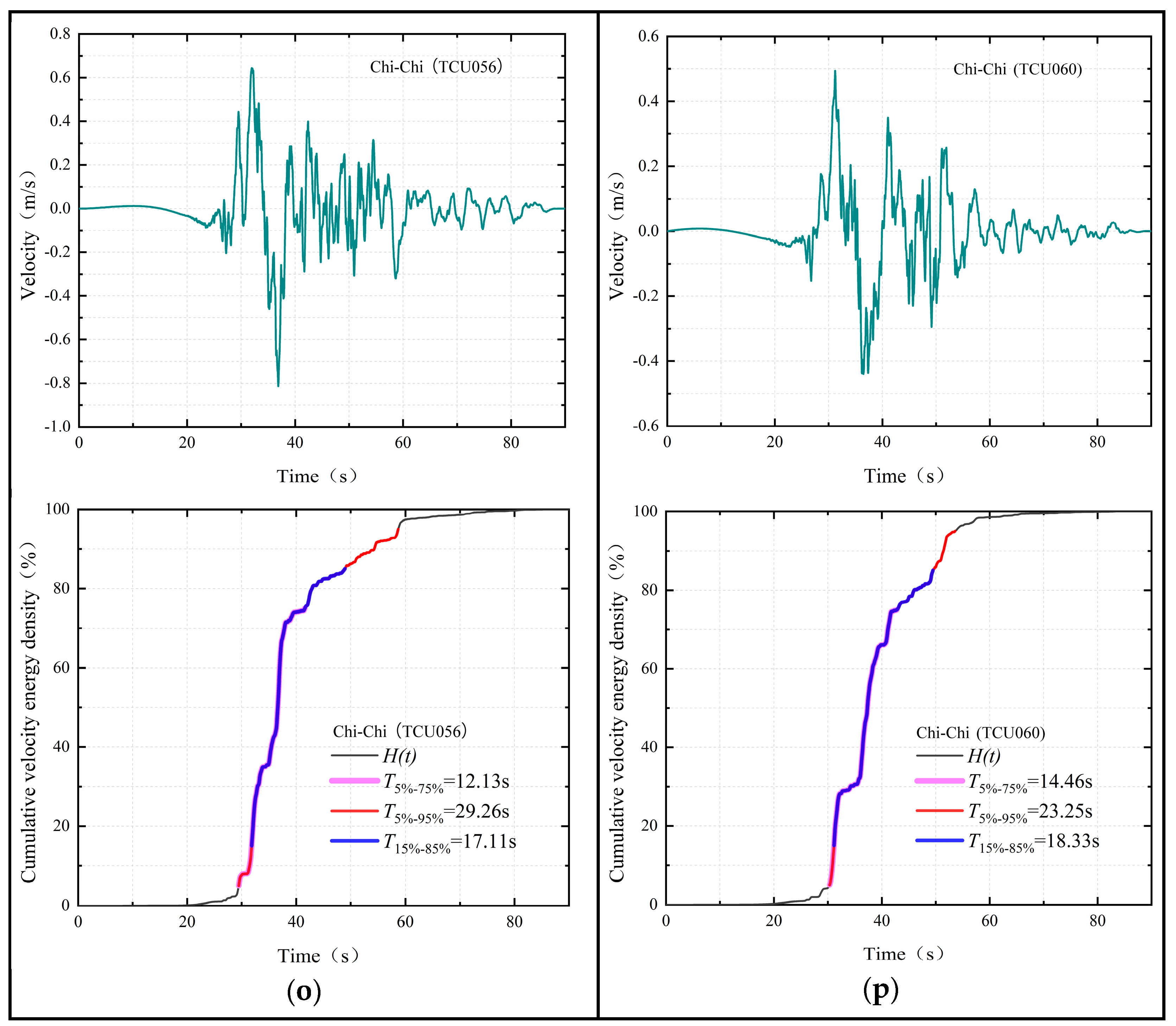
3. Near-Fault Ground Motion Database and Its Strong Duration
4. Model Establishment
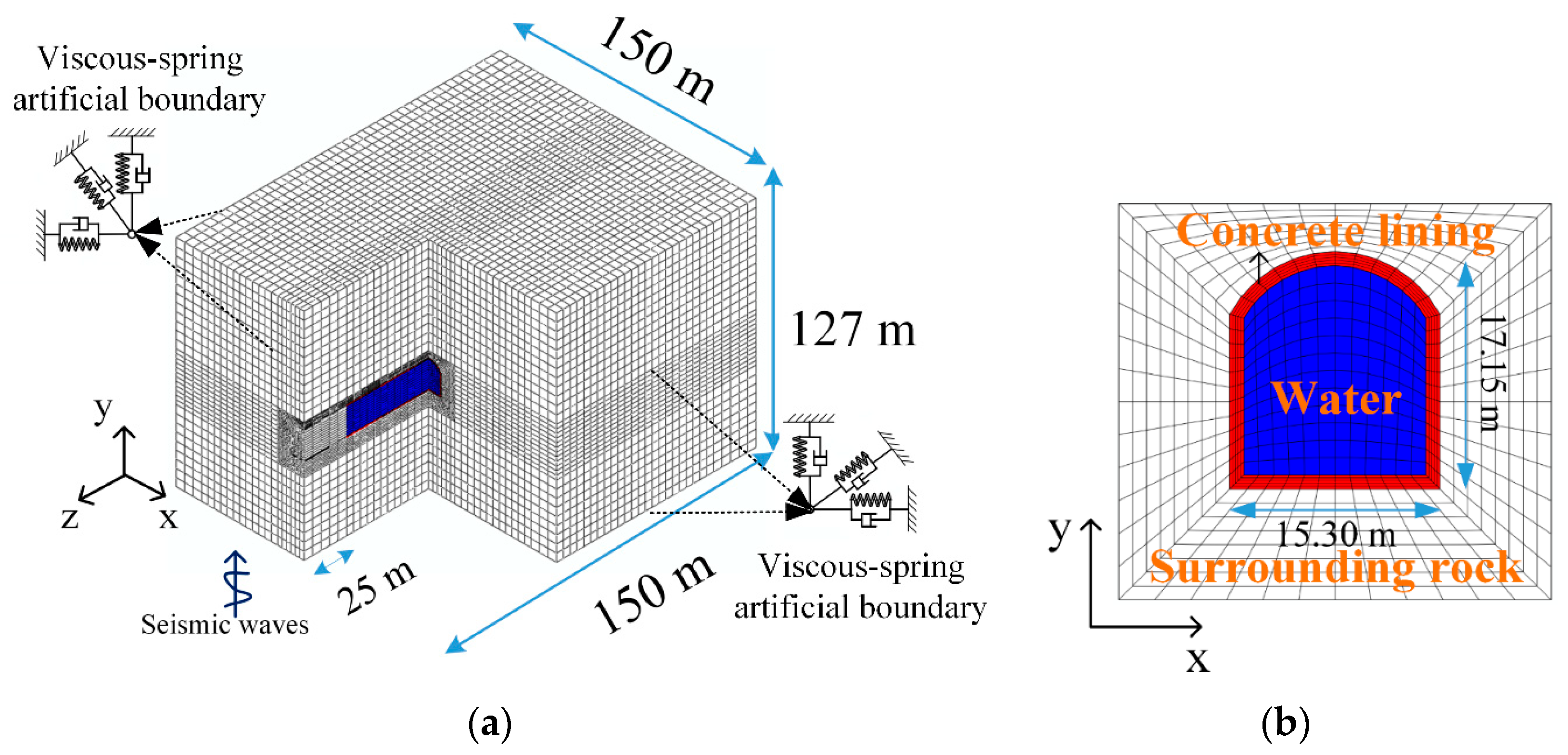
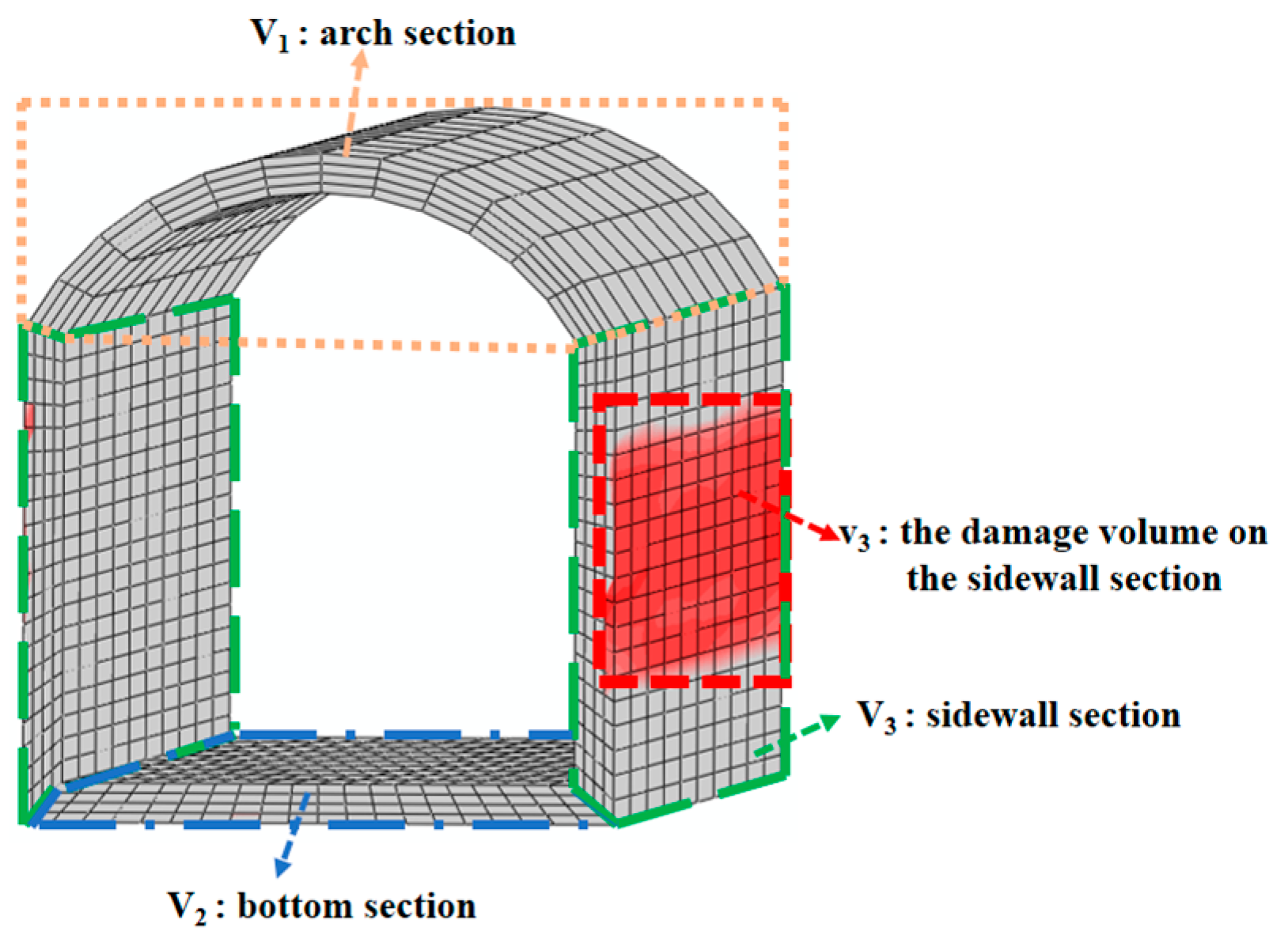
4.1. Finite Element Model
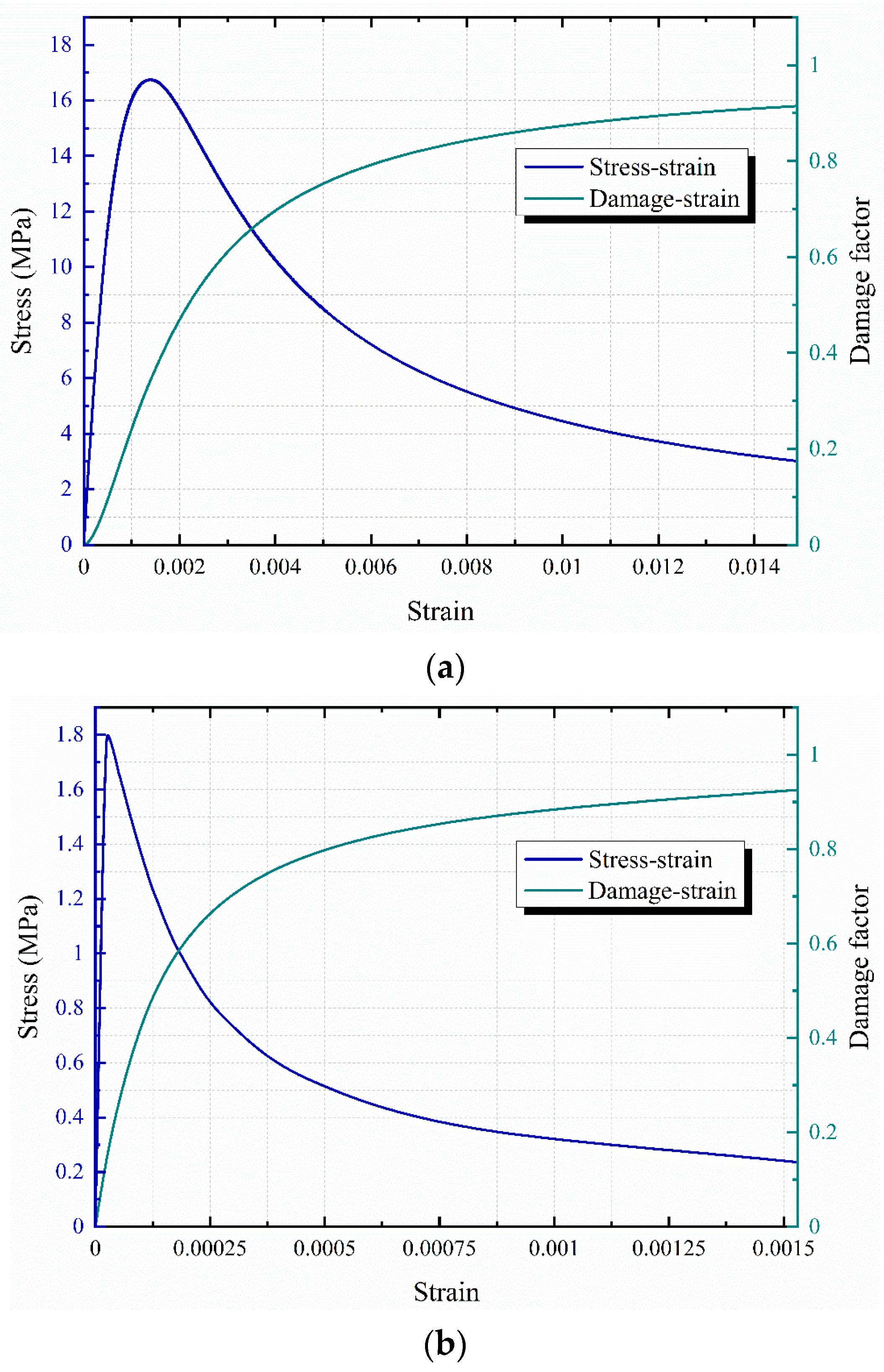
4.2. Constitutive Model and Fluid-Structure Interaction System
5. Numerical Results and Discussion
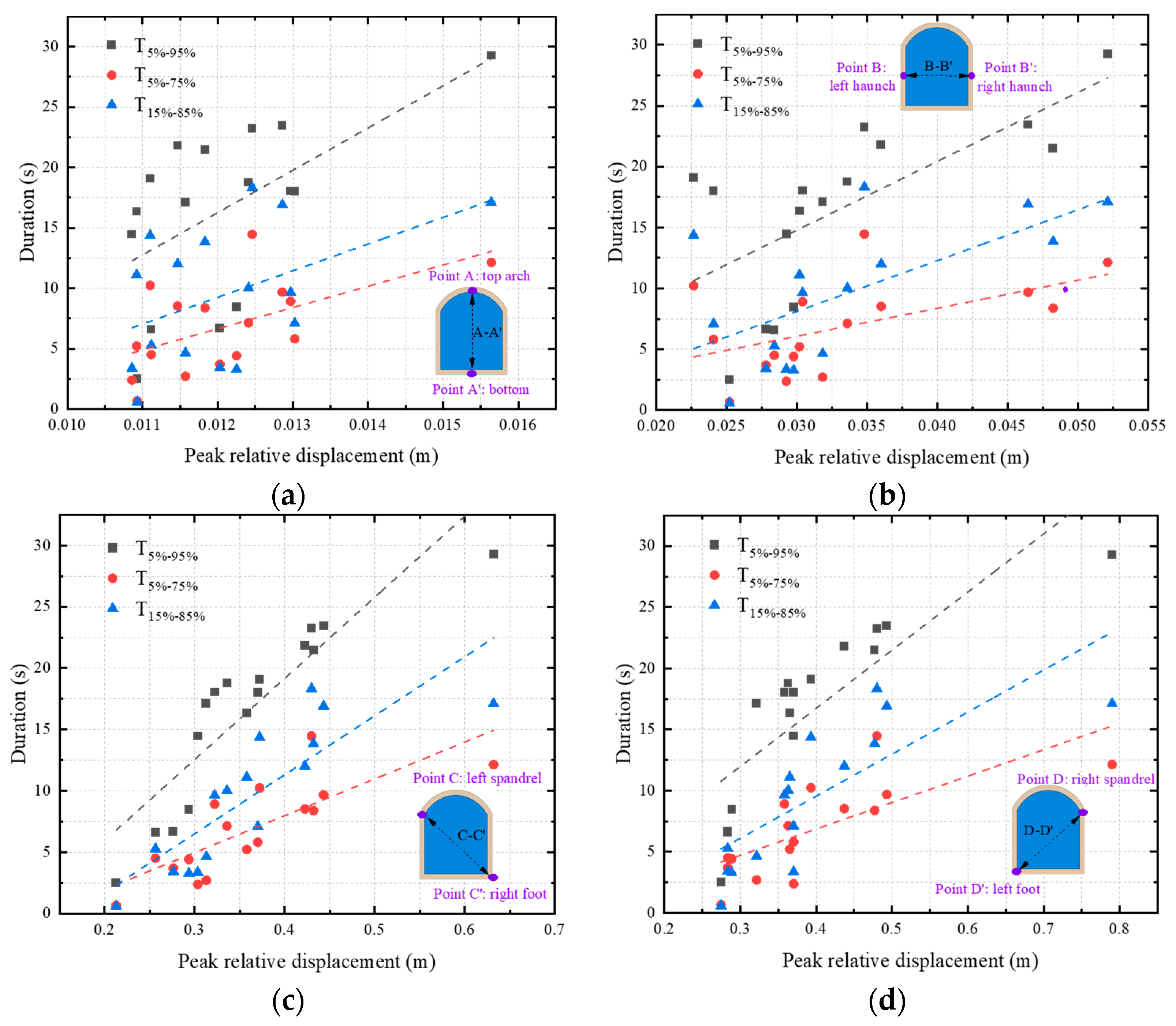
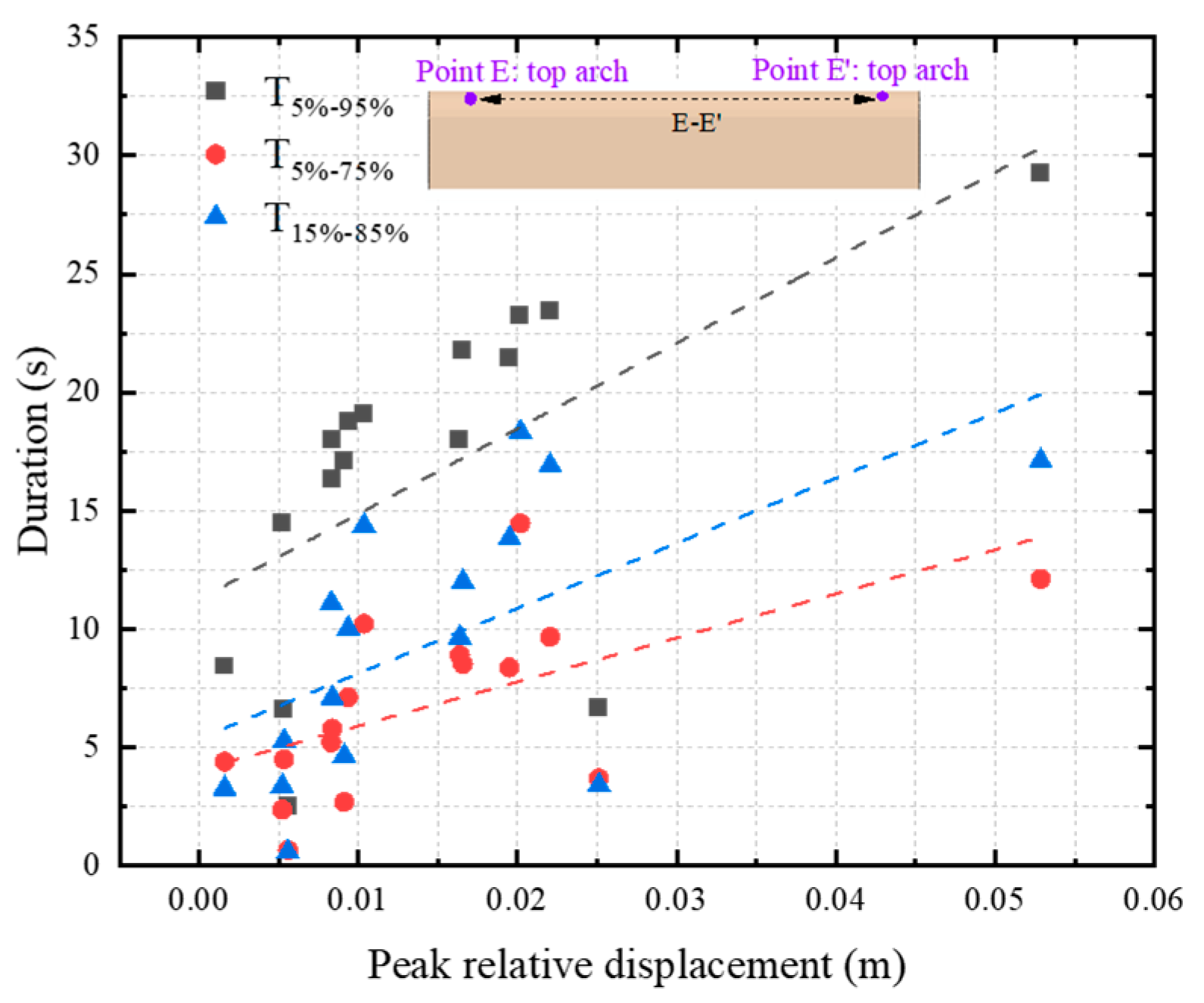
5.1. Identifying the Impact of Effective Velocity Duration on Maximum Relative Displacements
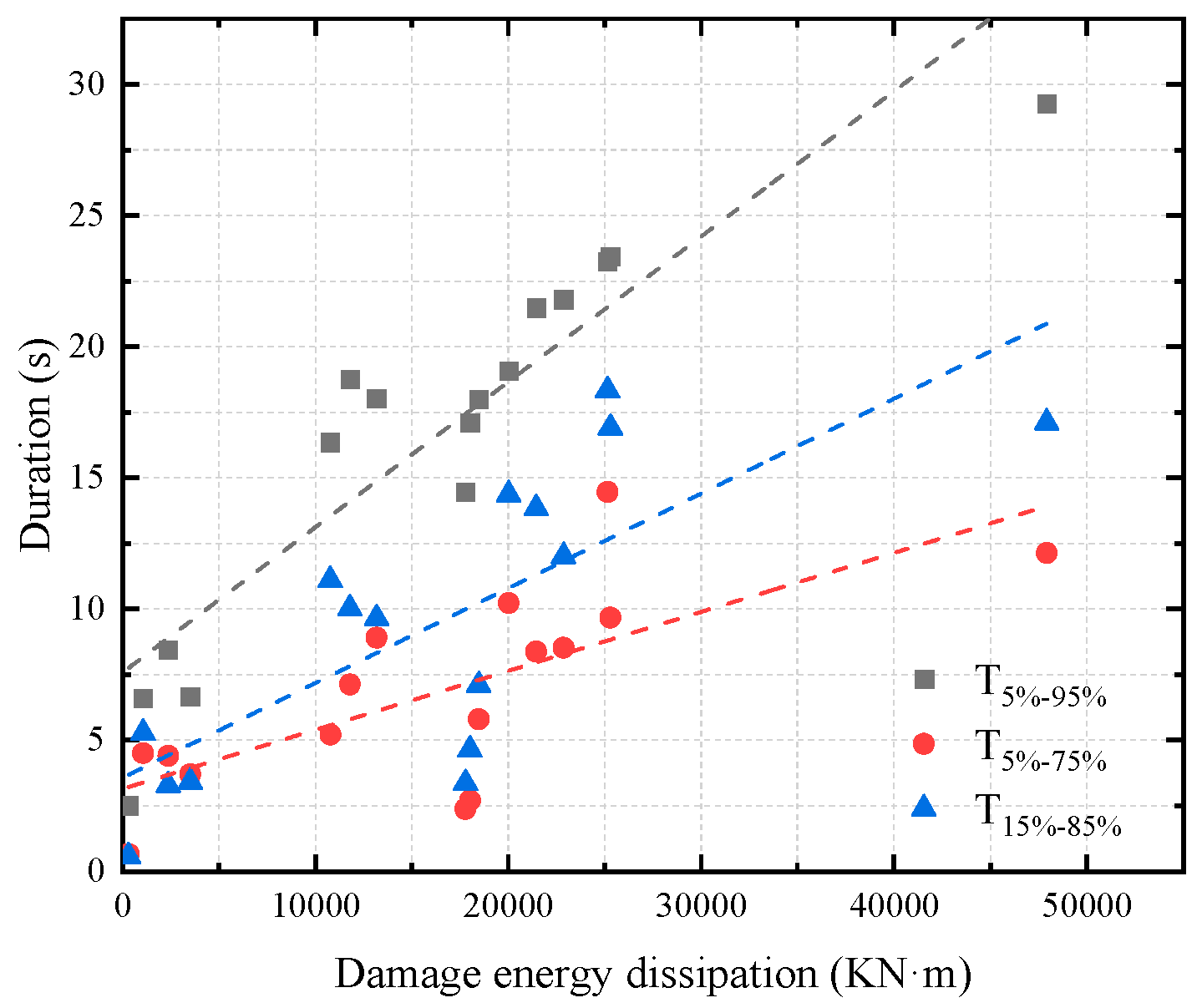
5.2. Identifying the Impact of Effective Velocity Duration on Accumulated Damage Patterns and Cumulative Damage Dissipation Energy
5.3. Identifying the Impact of Effective Velocity Duration on Damage Degree of Hydraulic Tunnels
6. The Applicability of a Strong Duration Index and Reduced Earthquake Record
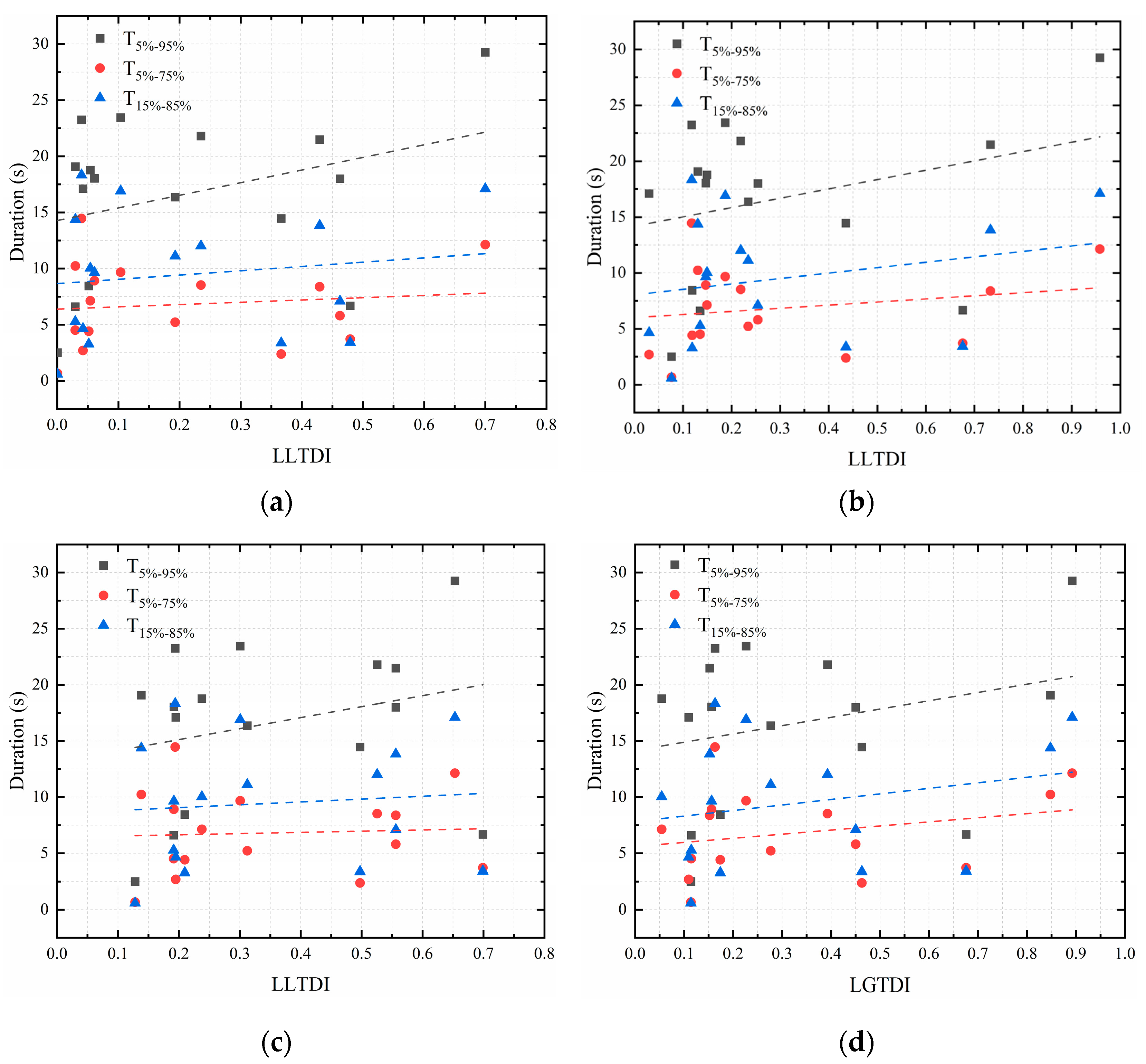
6.1. The Applicability of the Strong Acceleration Duration and Effective Velocity Duration with the Different Fixed Threshold Value
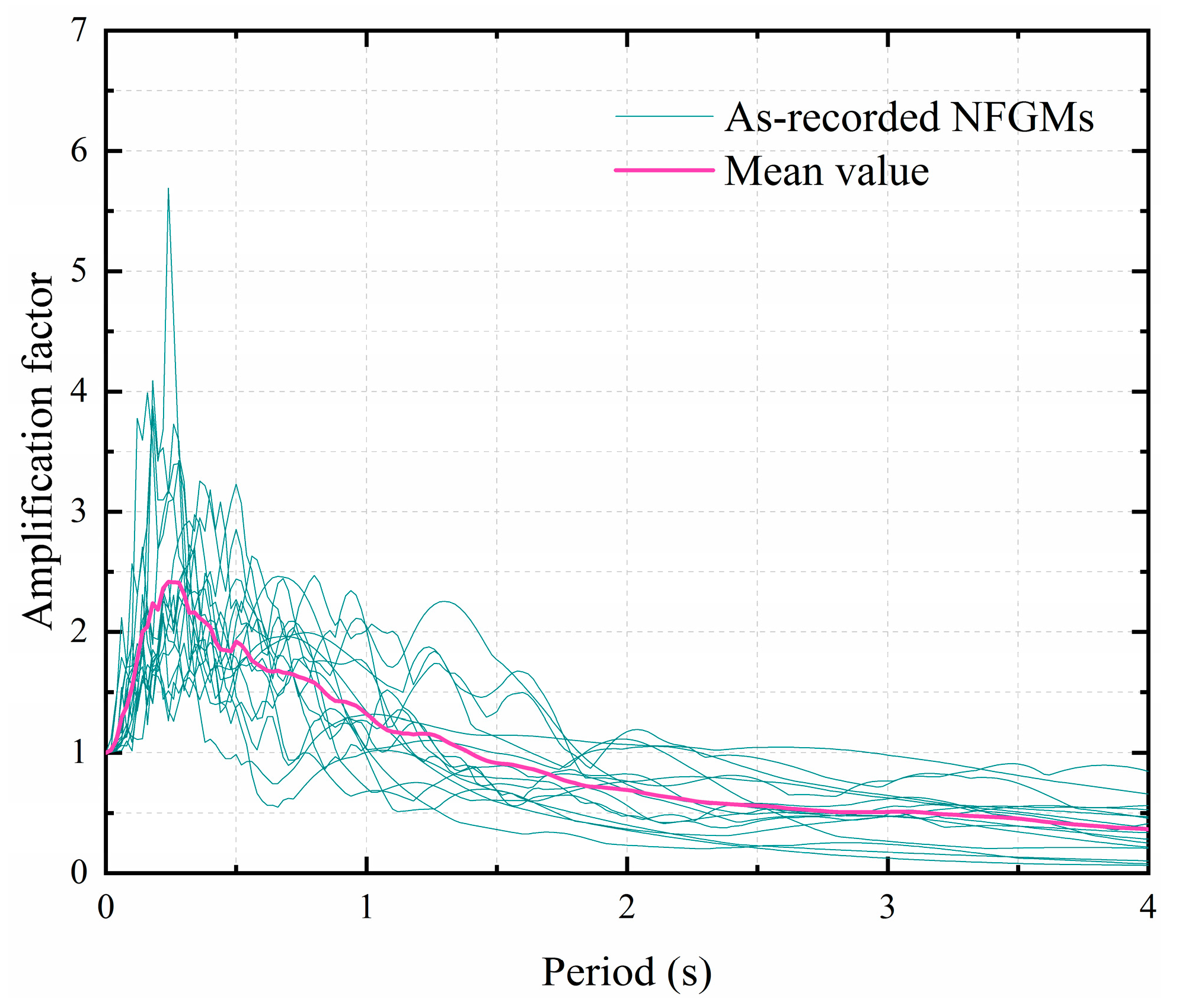
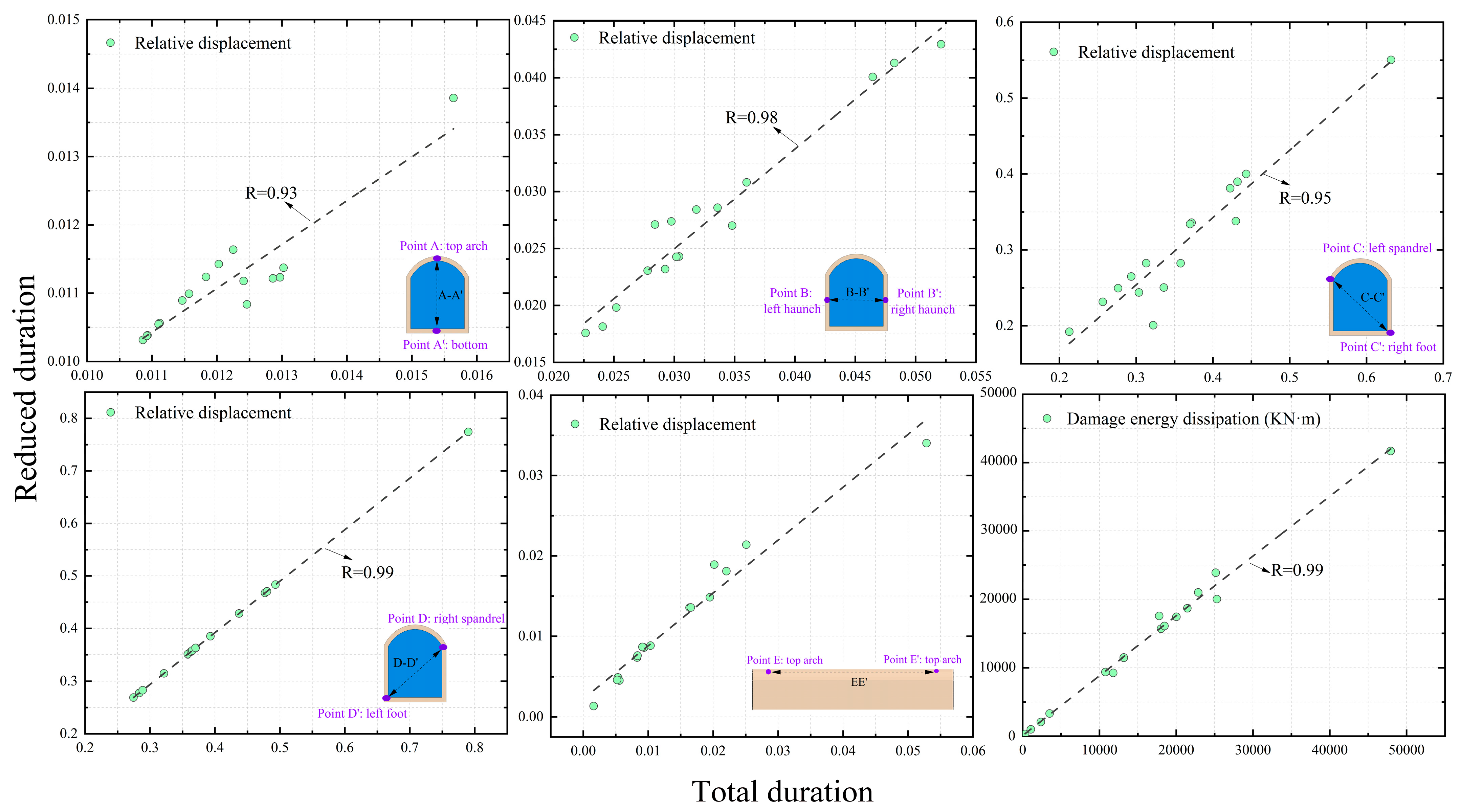
6.2. The Applicability of the Reduced Time-History Methodology of Earthquake Records
7. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| No. | Earthquake | Station Location | Year | Mw | Rrup (km) | TB (0.05 g) | TU (0.05 g) | TS (90%) | TE (90%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | San Fernando | Pacoima Dam (upper left abut) | 1971 | 6.61 | 1.81 | 14.6 | 35.65 | 7.3 | 7.0 |
| 2 | Coyote Lake | Gilroy Array #6 | 1979 | 5.74 | 3.11 | 2.4 | 5.03 | 4.0 | 4.2 |
| 3 | Imperial Valley-06 | Aeropuerto Mexicali | 1979 | 6.53 | 0.34 | 12.44 | 5.96 | 7.5 | 7.26 |
| 4 | Imperial Valley-06 | Brawley Airport | 1979 | 6.53 | 10.42 | 4.7 | 16.9 | 14.9 | 15.2 |
| 5 | Imperial Valley-06 | El Centro Array #11 | 1979 | 6.53 | 12.56 | 5.1 | 11.4 | 9.0 | 9.4 |
| 6 | Imperial Valley-06 | El Centro Array #3 | 1979 | 6.53 | 12.85 | 5.5 | 14.8 | 14.1 | 11.7 |
| 7 | Imperial Valley-06 | El Centro Differential Array | 1979 | 6.53 | 5.09 | 4.6 | 11.8 | 7.0 | 6.9 |
| 8 | Cape Mendocino | Petrolia | 1992 | 7.01 | 8.18 | 5.1 | 18.7 | 17.7 | 17.7 |
| 9 | Landers | Barstow | 1992 | 7.28 | 34.86 | 6.4 | 29.6 | 21.3 | 21.1 |
| 10 | Landers | Yermo Fire Station | 1992 | 7.28 | 23.62 | 7.6 | 23.0 | 18.9 | 17.4 |
| 11 | Northridge-01 | LA Dam | 1994 | 6.69 | 5.92 | 3.8 | 8.0 | 6.5 | 6.5 |
| 12 | Kocaeli | Gebze | 1999 | 7.51 | 10.92 | 3.9 | 7.9 | 8.2 | 7.5 |
| 13 | Chi-Chi | TCU053 | 1999 | 7.62 | 5.95 | 9.4 | 28.5 | 27.7 | 21.8 |
| 14 | Chi-Chi | TCU054 | 1999 | 7.62 | 5.28 | 16.7 | 31.8 | 25.5 | 24.0 |
| 15 | Chi-Chi | TCU056 | 1999 | 7.62 | 10.48 | 18.0 | 34.5 | 31.8 | 26.2 |
| 16 | Chi-Chi | TCU060 | 1999 | 7.62 | 8.51 | 8.6 | 28.6 | 26.7 | 21.3 |
References
- Sun, B.; Zhang, S.; Deng, M.; Wang, C. Nonlinear dynamic analysis and damage evaluation of hydraulic arched tunnels under mainshock–aftershock ground motion sequences. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 98, 103321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Xiao, M. Seismic damage assessment and mechanism analysis of underground powerhouse of the Yingxiuwan Hydropower Station under the Wenchuan earthquake. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 113, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitayama, S.; Constantinou, M.C. Implications of strong earthquake ground motion duration on the response and testing of seismic isolation systems. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 50, 290–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Lu, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, C. Integrated duration effects on seismic performance of concrete gravity dams using linear and nonlinear evaluation methods. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2015, 79, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.-C.; Song, J.; Wang, P.-H.; Adidharma, L.; Chang, K.-C.; Lee, G.C. Ground Motion Duration Effects on Hysteretic Behavior of Reinforced Concrete Bridge Columns. Eng. Struct. 2014, 140, 04013065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R.A.; Terri, G.A. Number of Equivalent Cycles Concept for Liquefaction Evaluations—Revisited. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2005, 131, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T. Damage to mountain tunnels related to the Wenchuan earthquake and some suggestions for aseismic tunnel construction. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2011, 71, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Gao, B.; Yang, X.; Tao, S. Seismic damage mechanism and dynamic deformation characteristic analysis of mountain tunnel after Wenchuan earthquake. Eng. Geol. 2014, 180, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, T.; Su, J.; Lin, C.; Seng, C.; Huang, T. Assessment of damage in mountain tunnels due to the Taiwan Chi-Chi Earthquake. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2001, 16, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z. Seismic damage classification and risk assessment of mountain tunnels with a validation for the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2013, 45, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chen, J.; Bobet, A.; Yuan, Y. Damage observation and assessment of the Longxi tunnel during the Wenchuan earthquake. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 54, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J. Quantitative Classification of Near-Fault Ground Motions Using Wavelet Analysis. Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 2007, 97, 1486–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahari, S.F.; Jahankhah, H.; Ghannad, M.A. Study on elastic response of structures to near-fault ground motions through record decomposition. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2010, 30, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Panagiotou, M. Characterization and Representation of Near-Fault Ground Motions Using Cumulative Pulse Extraction with Wavelet Analysis. Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 2013, 104, 410–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghmaei-Sabegh, S. Detection of pulse-like ground motions based on continues wavelet transform. J. Seism. 2010, 14, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashash, Y.M.; Hook, J.J.; Schmidt, B.; Yao, J.I.-C. Seismic design and analysis of underground structures. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2001, 16, 247–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.R.; Ribeiro, F.L.A.; Neves, L.A.C. Influence of earthquake ground-motion duration on damage estimation: Application to steel moment resisting frames. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2016, 46, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommer, J.J.; Martínez-Pereira, A. The Effective Duration Of Earthquake Strong Motion. J. Earthq. Eng. 1999, 3, 127–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommer, J.; Stafford, P.; Alarcon, J.E. Empirical Equations for the Prediction of the Significant, Bracketed, and Uniform Duration of Earthquake Ground Motion. Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 2009, 99, 3217–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Lu, W.; Yan, P.; Zhou, W.; Chen, M. A general definition of integrated strong motion duration and its effect on seismic demands of concrete gravity dams. Eng. Struct. 2016, 125, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Cui, W. Ground motion duration effect on responses of hydraulic shallow-buried tunnel under SV-waves excitations. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 2020, 19, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repapis, C.C.; Mimoglou, P.P.; Dimakopoulou, V.V.; Psycharis, I.N.; Taflampas, I.M. Efficient strong motion duration of pulse-like records for nonlinear structural analyses. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 49, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pilato, M.; Perotti, F.; Fogazzi, P. 3D dynamic response of submerged floating tunnels under seismic and hydrodynamic excitation. Eng. Struct. 2008, 30, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzigeorgiou, G.D.; Beskos, D.E. Soil–structure interaction effects on seismic inelastic analysis of 3-D tunnels. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2010, 30, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-Q.; Du, X.-L.; Jin, L.; Zhao, M. Impact of incident angles of P waves on the dynamic responses of long lined tunnels. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2016, 45, 2435–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-Q.; Du, X.-L.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, X. Impact of incident angles of earthquake shear (S) waves on 3-D non-linear seismic responses of long lined tunnels. Eng. Geol. 2017, 222, 168–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakbaz, M.C.; Yareevand, A. 2-D analysis of circular tunnel against earthquake loading. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2005, 20, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Chen, J.; Xu, Q. 3-D numerical analysis on seismic responses of the underground large scale frame structure under near-fault ground motions. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 91, 103020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Qi, C.; Zhao, B.; Qu, X. Seismic response of the subway station due to a specific active fault. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 85, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Gu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, X. Seismic analysis of a long tunnel based on multi-scale method. Eng. Struct. 2013, 49, 572–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkus, D.S.; Hughes, T.J. Mixed finite element methods-Reduced and selective integration techniques: A unification of concepts. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1978, 15, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, G. Effects of near-fault and far-fault ground motions on nonlinear dynamic response and seismic damage of concrete gravity dams. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2013, 53, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.K.; Yang, K.S. An evaluation of strong motion records and a new parameterA95. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1987, 15, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husid, R.L. Analisis de Terremoros: Analisis General; Universidad de Chile: Santiago, Chile, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Lysmer, J.; Kuhlemeyer, R.L. Finite Dynamic Model for Infinite Media. J. Eng. Mech. Div. 1969, 95, 859–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, S.; Cui, W.; Deng, M.; Wang, C. Nonlinear dynamic response and damage analysis of hydraulic arched tunnels subjected to P waves with arbitrary incoming angles. Comput. Geotech. 2019, 118, 103358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Deng, M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Cui, W.; Li, Q.; Zhao, X.; Yan, H. Optimal selection of scalar and vector-valued intensity measures for improved fragility analysis in cross-fault hydraulic tunnels. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 132, 104857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Liu, W.; Deng, M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, J. Compound intensity measures for improved seismic performance assessment in cross-fault hydraulic tunnels using partial least-squares methodology. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 132, 104890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Du, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J. 3D viscous-spring artificial boundary in time domain. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 2006, 5, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, S.; Deng, M.; Wang, C. Inelastic dynamic response and fragility analysis of arched hydraulic tunnels under as-recorded far-fault and near-fault ground motions. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 132, 106070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, G.; Xue, B.; Kou, L.; Hu, L.; Liu, W. The analysis of the optimal scalar and vector intensity measurements for seismic performance assessment of deep-buried hydraulic arched tunnels. Undergr. Space 2023, 9, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubliner, J.; Oliver, J.; Oller, S.; Oñate, E. A plastic-damage model for concrete. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1989, 25, 299–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiff, A.J.; Tang, A.K.; Kieffer, D.S.; Mcrae, C.M.; Chern, J.C.; Kao, H.C.; Lee, J.C. Lifeline Performance. Earthq. Spectra 2001, 17, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Constitutive Model | Parameter | Unit | Magnitude |
|---|---|---|---|
| DP model | Cohesion | MPa | 1.1 |
| Friction angle | ° | 41 | |
| Poisson’s ratio | - | 0.25 | |
| Mass density | kg/m3 | 2625 | |
| Elastic modulus | GPa | 4.0 | |
| CPM | Compressive yield stress | MPa | 16.7 |
| Tensile yield stress | MPa | 1.78 | |
| Poisson’s ratio | - | 0.167 | |
| Mass density | kg/m3 | 2450 | |
| Elastic modulus | GPa | 28 | |
| Linear elasticity | Bulk modulus | GPa | 2.07 |
| Mass density | kg/m3 | 1000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Sun, B.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Cui, W.; Zhao, X. The Duration Effect of Pulse-Type Near-Field Earthquakes on Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis and Damage Evaluation of Hydraulic Tunnels. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13042041
Liu W, Sun B, Zhang S, Wang C, Cui W, Zhao X. The Duration Effect of Pulse-Type Near-Field Earthquakes on Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis and Damage Evaluation of Hydraulic Tunnels. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(4):2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13042041
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Weiying, Benbo Sun, Sherong Zhang, Chao Wang, Wei Cui, and Xiaohua Zhao. 2023. "The Duration Effect of Pulse-Type Near-Field Earthquakes on Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis and Damage Evaluation of Hydraulic Tunnels" Applied Sciences 13, no. 4: 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13042041
APA StyleLiu, W., Sun, B., Zhang, S., Wang, C., Cui, W., & Zhao, X. (2023). The Duration Effect of Pulse-Type Near-Field Earthquakes on Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis and Damage Evaluation of Hydraulic Tunnels. Applied Sciences, 13(4), 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13042041






