Studies of Organic Matter in Composting, Vermicomposting, and Anaerobic Digestion by 13C Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. 13C Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy for the Investigation of Organic Matter in Compost, Vermicompost, and Digestate
2.1. Experimental Techniques
2.2. Spectral Analysis
2.3. Experimental Conditions and Sample Preparation
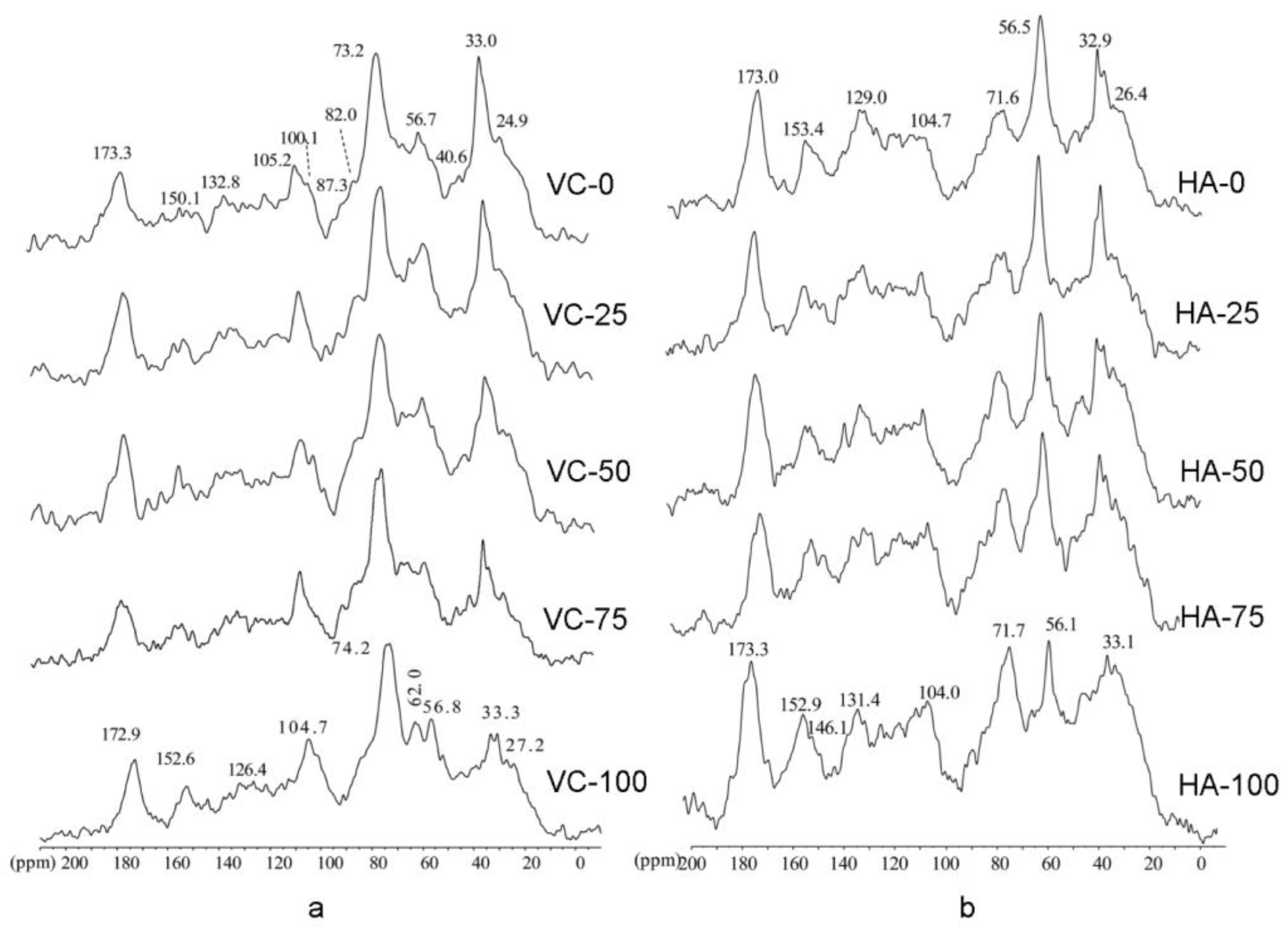
3. 13C Solid-State NMR Applications to Composting
| Ref. a | Feedstock b | Sample c | Alkyl C | O-Alkyl C | Aromatic C | Carboxyl/ Carbonyl C | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH3O/CHN | O-/Di-O-Alkyl C | Aryl C | O-Aryl C | Carboxyl C | Carbonyl C | ||||
| [88] | SM/poplar sawdust (5:3 w:w) | HA 60 d | 30.3 | 33.9 | 16.8 | 7.1 | 11.9 | ||
| +sepiolite 3 wt% | HA 60 d | 26.7 | 29.9 | 18.3 | 8.4 | 16.8 | |||
| +sepiolite 6 wt% | HA 60 d | 34.7 | 22.6 | 17.4 | 7.9 | 17.4 | |||
| +sepiolite 9 wt% | HA 60 d | 24.3 | 29.4 | 18.3 | 10.4 | 17.6 | |||
| +sepiolite 12 wt% | HA 60 d | 24.0 | 29.9 | 20.8 | 8.7 | 16.5 | |||
| [86] | CYN/corn straw and WC (70:30 w:w) | HS 100 d | 20.93 | 15.98 | 29.78 | 16.26 | 5.51 | 11.54 | |
| COF/corn straw and WC (70:30 w:w) | HS 100 d | 30.63 | 13.07 | 24.69 | 15.33 | 3.42 | 12.85 | ||
| PEP/corn straw and WC (70:30 w:w) | HS 100 d | 20.06 | 14.22 | 35.75 | 14.40 | 4.49 | 11.08 | ||
| [103] | CYN/WC (70:30 w:w) | HA 100 d | 22.2 | 13.8 | 27.5 | 20.0 | 5.7 | 10.9 | |
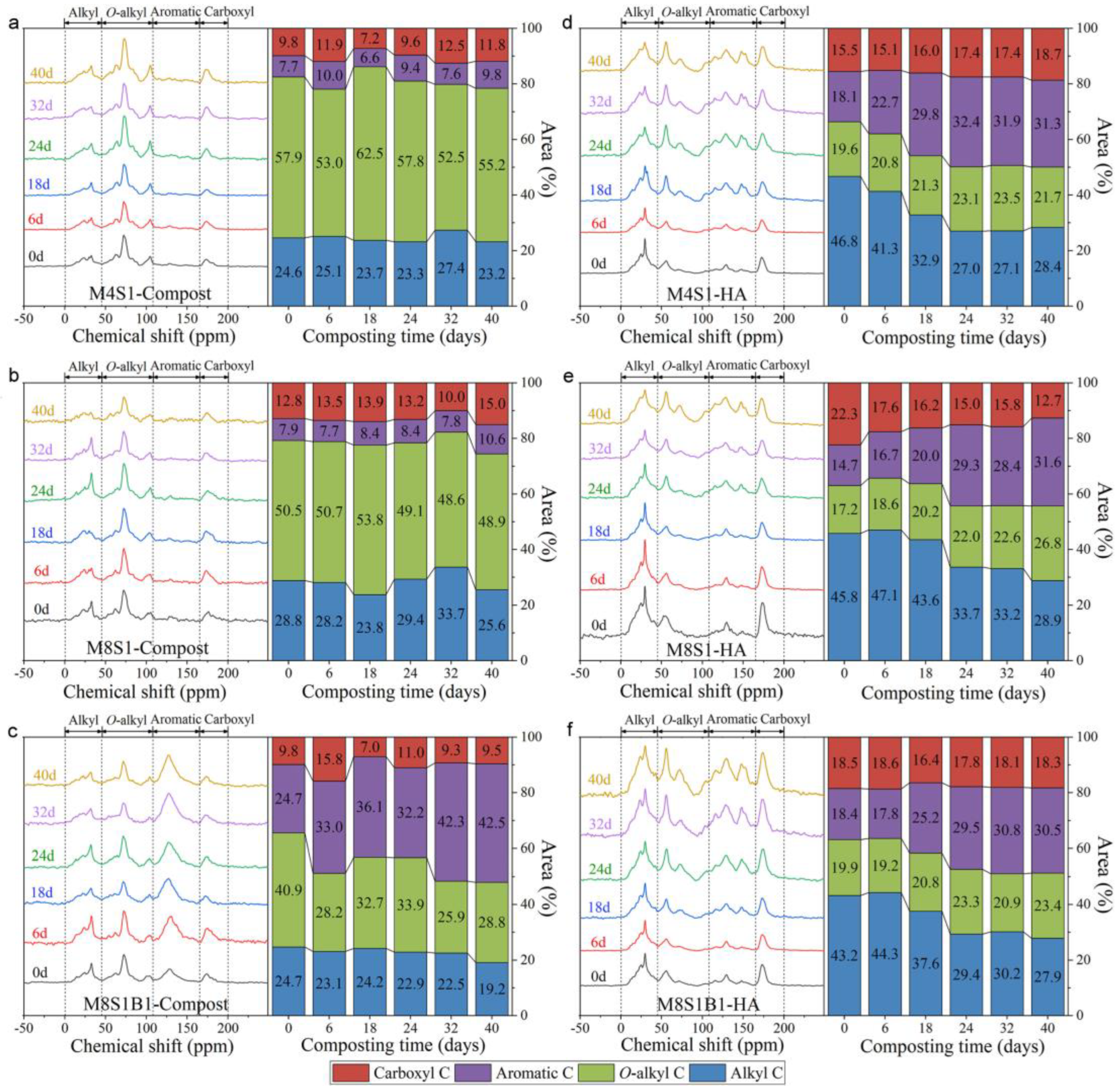
| [62] | SM/rice straw 4:1 SM/rice straw 8:1 SM/rice straw/biochar 8:1:1 | HA FS | 46.8 | 19.6 | 18.1 | 15.5 | |||
| HA 40d | 28.4 | 21.7 | 31.3 | 18.7 | |||||
| HA FS | 45.8 | 17.2 | 14.7 | 22.3 | |||||
| HA 40d | 28.9 | 26.8 | 31.6 | 12.7 | |||||
| HA FS | 43.2 | 19.9 | 18.4 | 18.5 | |||||
| HA 40d | 27.9 | 23.4 | 30.5 | 18.3 | |||||
| [37] | CYN/corn straw (70:30 w:w) | HS 100 d | 16.3 | 13.8 | 24.7 | 28.9 | 5.6 | 10.6 | |
| [104] | Coffee husks/lettuce residues at (60:40 w:w) | CT 100 d | 26.9 | 11.9 | 26.4 | 16.6 | 4.3 | 14 | |
| CYN with maize straw/WC (70:30 w:w) | CT 100 d | 27.6 | 12.1 | 27.3 | 15.0 | 4.2 | 13.9 | ||
| PEP with maize straw/WC (70:30 w:w) | CT 100 d | 17.4 | 14.3 | 31.1 | 19.2 | 5.8 | 12.3 | ||
| [85] | Agricultural crop plants/NH4NO3 (66:34 w:w) | HA 90 d | 41.63 | 24.89 | 19.31 | 14.16 | |||
| Date palm fronds/NH4NO3 (66:34 w:w) | HA 90 d | 36.39 | 29.05 | 23.85 | 10.70 | ||||
| Animal waste/NH4NO3 (66:34 w:w) | HA 90 d | 31.39 | 29.0 | 25.45 | 14.33 | ||||
| [35] | Tomato R/escarole R/WC/CS (17.5:20.5:60:2) | CT 105 d | 23.50 | 15.60 | 28.65 | 16.80 | 5.25 | 10.20 | |
| Tomato R/escarole R/WC/CS (37:11:50:2) | CT 105 d | 22.55 | 14.95 | 26.65 | 18.25 | 5.90 | 11.75 | ||
| Tomato R/escarole R/WC/CS (50:0:48:2) | CT 105 d | 23.40 | 14.70 | 26.80 | 17.10 | 6.90 | 11.15 | ||
| Commercial compost from biowaste | CT 105 d | 26.95 | 12.85 | 32.70 | 10.35 | 2.90 | 14.25 | ||
| [99] | DOW/COF/pine needles and WT (1:1:1) DOW/GT/FR (2:1:1) GT/COF/spent yeast (1:1:1) GT/COF/FR/sewage sludge (4:2:2.5:0.25) | DOM FS | 26.0 | 6.3 | 42.1 | 9.5 | 4.9 | 11.1 | |
| DOM 90 d | 30.8 | 7.4 | 27.1 | 13.4 | 7.3 | 14.0 | |||
| DOM FS | 31.8 | 6.2 | 38.5 | 7.9 | 4.3 | 11.4 | |||
| DOM 90 d | 34.6 | 7.3 | 25.9 | 13.1 | 4.9 | 14.2 | |||
| DOM FS | 30.8 | 5.3 | 41.2 | 6.2 | 2.8 | 13.6 | |||
| DOM 90 d | 35.2 | 8.4 | 22.7 | 11.8 | 5.8 | 16.2 | |||
| DOM FS | 30.8 | 6.2 | 38.2 | 8.6 | 4.9 | 11.3 | |||
| DO 90d | 33.9 | 7.8 | 25.0 | 13.2 | 5.4 | 14.7 | |||
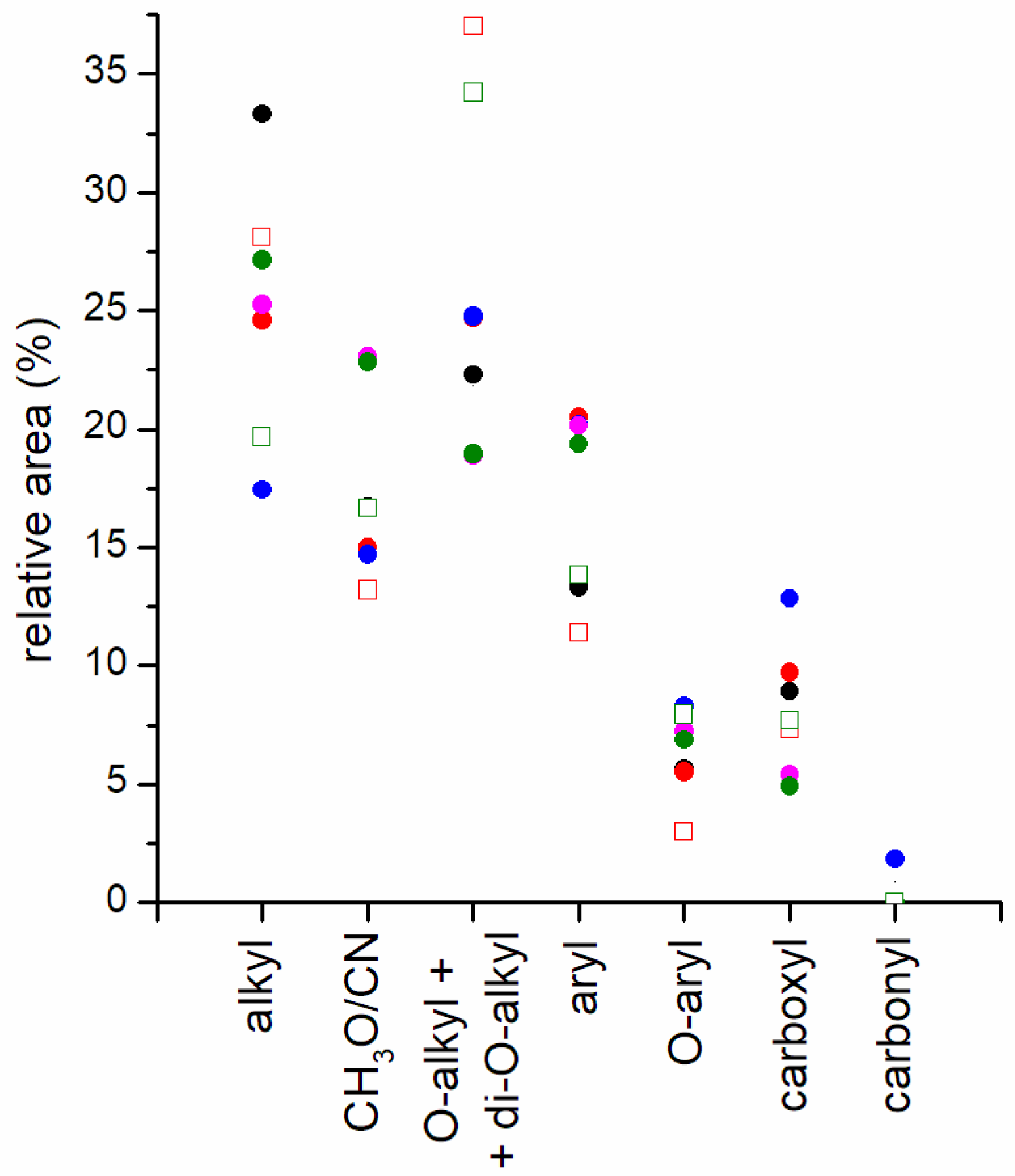
| [94] | DOW/GT/vegetal R from tobacco (50:30:20) | HA 60 d | 28.0 | 11.3 | 32.4 | 16.8 | 11.5 | ||
| HA 90 d | 34.9 | 10.8 | 28.6 | 15.7 | 10.0 | ||||
| HA 150 d | 34.5 | 9.3 | 23.1 | 19.8 | 13.4 | ||||
| [101] | OFMSW/GT/foliage R from tobacco (55:30:15) | CT 120 d | 31.0 | 9.0 | 23.1 | 13.3 | 23.6 | ||
| HoDOM 120 d | 34.6 | 12.6 | 19.5 | 19.3 | 14.0 | ||||
| HiDOM 120 d | 30.3 | 9.8 | 36.8 | 9.1 | 14.0 | ||||
| [87] | OvM/straw Mixture of animal manures Solid olive mill wastes Solid wastes of wineries Domestic wastes | HS FS | 18.6 | 49.7 | 8.2 | 23.5 | |||
| HS 120 d | 17.7 | 25.0 | 22.3 | 35.0 | |||||
| HS FS | 33.7 | 13.8 | 11.8 | 40.7 | |||||
| HS 120 d | 30.4 | 24.0 | 9.6 | 36.0 | |||||
| HS FS | 23.2 | 56.4 | 11.2 | 9.2 | |||||
| HS 120 d | 22.2 | 29.3 | 19.7 | 28.8 | |||||
| HS FS | 3.5 | 46.9 | 1.5 | 48.1 | |||||
| HS 120 d | 21.6 | 13.1 | 26.8 | 38.5 | |||||
| HS FS | 23.7 | 28.2 | 20.3 | 27.8 | |||||
| HS 120 d | 25.4 | 34.9 | 16.4 | 23.3 | |||||
| [95] | MSW/vegetal wastes (1:1 v:v) | HA FS | 43.4 | 25.9 | 10.3 | 16.4 | 4.0 | ||
| HA 28 d | 44.7 | 22.1 | 11.0 | 17.9 | 4.3 | ||||
| HA 100 d | 42.9 | 20.3 | 11.4 | 17.9 | 7.5 | ||||
| [79] | MSW | HA FS | 32 | 45 | 13 | 10 | |||
| HA 49 d | 48 | 26 | 16 | 10 | |||||
| [98] | MSW | HA 6 d | 38 | 31 | 13 | 5 | 11 | 2 | |
| HA 19 d | 45 | 23 | 15 | 5 | 11 | 1 | |||
| HA 33 d | 44 | 23 | 16 | 6 | 11 | 1 | |||
| HA 62 d | 42 | 24 | 15 | 6 | 12 | 2 | |||
| HA 105 d | 39 | 25 | 16 | 6 | 12 | 2 | |||
| HA 187 d | 38 | 26 | 17 | 6 | 12 | 3 | |||
| Core-HA 6 d | 34 | 24 | 21 | 8 | 12 | 2 | |||
| Core-HA 19 d | 33 | 23 | 23 | 9 | 11 | 2 | |||
| Core-HA 33 d | 34 | 23 | 23 | 9 | 11 | 1 | |||
| Core-HA 62 d | 38 | 23 | 19 | 7 | 11 | 3 | |||
| Core-HA 105 d | 43 | 21 | 19 | 7 | 10 | 0 | |||
| Core-HA 187 d | 35 | 22 | 20 | 8 | 13 | 3 | |||
| [97] | OFMSW | HA FS | 37.20 | 34.34 | 16.28 | 12.23 | |||
| HA C | 30.07 | 34.71 | 22.67 | 12.58 | |||||
4. 13C Solid-State NMR Applications to Vermicomposting
5. 13C Solid-State NMR Applications to Anaerobic Digestion
| Ref. a | Feedstock b | Sample c | Alkyl C | O-Alkyl C | Aromatic C | Carboxyl/Carbonyl C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [129] | Sewage sludge | D | 29.2 ± 6.7 | 54.8 ± 10 | 7.63 ± 2.5 | 8.37 ± 2.9 |
| [134] | Sludge | FS | 44.4 | 28.9 | 0.5 | 26.1 |
| D | 38.7 | 19.0 | 4.5 | 37.7 | ||
| Sludge hydrochar 125 °C | FS | 41.8 | 18.0 | 0.4 | 39.8 | |
| D | 38.7 | 10.0 | 3.9 | 47.4 | ||
| Sludge hydrochar 225 °C | FS | 43.8 | 10.1 | 2.9 | 43.2 | |
| D | 44.5 | 21.1 | 6.5 | 27.8 | ||
| SM | FS | 33.1 | 45.4 | 4.3 | 17.0 | |
| D | 41.1 | 29.9 | 2.4 | 26.6 | ||
| SM hydrochar 125 °C | FS | 32.7 | 44.6 | 4.9 | 17.5 | |
| D | 39.8 | 32.4 | 6.8 | 20.9 | ||
| SM hydrochar 225 °C | FS | 58.4 | 16.6 | 8.2 | 16.8 | |
| D | 45.7 | 14.1 | 17.4 | 22.8 | ||
| [128] | Organic fraction of household W/SW/industrial W (50:25:25) | FS | 25 | 60 | 8 | 7 |
| D | 33 | 42 | 13 | 9 | ||
| [132] | Starch/cereals/forage/corn silage | FS | 8–16 | 70–75 | 5–13 | 4–7 |
| D | 11–15 | 66–68 | 13–16 | 5–6 | ||
| Post-D | 14–15 | 64–65 | 14–15 | 6–7 | ||
| Cereals/sugar beets/crop/corn silage | FS | 8 | 81 | 9 | 2 | |
| D | 17–23 | 55–62 | 15 | 7–8 | ||
| Post-D | 19–24 | 52–57 | 17 | 7–8 | ||
| Pig slurry/ChM/HM/deep litter/cereals | FS | 16–27 | 55–65 | 9–12 | 7–8 | |
| D | 19–20 | 57–58 | 15–16 | 7 | ||
| MFW/SW/ food industry W | FS | 22 | 63 | 8 | 7 | |
| D | 38 | 39 | 11 | 12 | ||
| Post-D | 37 | 38 | 13 | 12 | ||
| MFW/vegetables/food package/SW/food industry W/SM/GSS | FS | 38–39 | 42–45 | 8–9 | 10 | |
| D | 30–35 | 47–49 | 11–13 | 8–9 | ||
| Post-D | 29–33 | 47–50 | 11–13 | 8–10 | ||
| MFW | FS | 19–22 | 61–64 | 9–10 | 7–8 | |
| D | 34–37 | 38–42 | 12–14 | 11–12 | ||
| Post-D | 35–38 | 37–40 | 13–14 | 11–12 | ||
| MFW | FS | 16–18 | 64–69 | 10–11 | 6–7 | |
| D | 21–22 | 52–54 | 17–18 | 7–8 | ||
| [133] | Green waste/food waste | FS | 21.19 | 63.6 | 7.49 | 7.72 |
| C | 17.48 | 65.8 | 13.63 | 3.09 | ||
| D | 16.74 | 63.06 | 14.27 | 5.93 | ||
| FS | 15.5 | 67.44 | 11.43 | 5.63 | ||
| C | 14.88 | 70.37 | 12.14 | 2.61 | ||
| D | 12.19 | 67.79 | 14.49 | 5.53 | ||
| FS | 12.35 | 69.12 | 14.05 | 4.48 | ||
| C | 10.27 | 71.11 | 14.97 | 3.65 | ||
| D | 12.24 | 65.17 | 15.99 | 6.59 | ||
| [131] | Corn/pig slurry (36.3:63.7) | FS | 12.4 | 75.6 | 6.9 | 5.1 |
| D | 22.3 | 58.5 | 10.3 | 8.9 | ||
| Giant cane/pig slurry (32.8:67.2) | FS | 9.7 | 78.4 | 7.9 | 4.0 | |
| D | 11.7 | 74.6 | 9.6 | 4.1 | ||
| [127] | Sorghum silage/OMW/organic R/agro-industrial R (7:1:1:1) | FS | 16.2 | 68.5 | 9.1 | 6.2 |
| D | 21.2 | 57.3 | 12.7 | 8.8 | ||
| Sorghum silage/beef cattle slurry/agro-industrial R (7:1:2) | FS | 18.4 | 65.6 | 8.2 | 7.8 | |
| D | 21.3 | 60.4 | 10.9 | 7.4 | ||
| Pig slurry | FS | 38.5 | 44.4 | 7.0 | 10.1 | |
| D | 29.5 | 38.5 | 6.9 | 25.1 | ||
| DSF | 16.2 | 71.1 | 7.4 | 5.3 | ||
| [126] | OFMSW/pig slurry (80:20) | FS | 25.9 | 59.1 | 5.1 | 9.8 |
| D | 44.5 | 35.4 | 7.9 | 12.2 | ||
| Pig slurry/milk serum/cow slurry/maize silage/rice R (48:24:10:4) | FS | 18.6 | 66.9 | 7.0 | 7.5 | |
| D | 26.8 | 57.4 | 8.0 | 7.8 | ||
| Pig slurry/blood industry residues/maize silage (65:20:15) | FS | 19.8 | 65.8 | 8.0 | 6.3 | |
| D | 32.5 | 51.2 | 8.1 | 8.1 | ||
| Slurries from municipal wastewater | D | 37.3 | 43.8 | 6.9 | 12.1 | |
| Ligno-cellulosic residues | C | 25.0 | 53.4 | 12.8 | 8.8 | |
| Ligno-cellulosic residues/OFMSW (33:67) | C | 20.1 | 56.5 | 14.4 | 9.0 | |
| [125] | Energetic crops/cow slurry/agro-industrial waste/OFMSW | FS | 21.77 | 65.5 | 4.81 | 7.92 |
| D | 39.08 | 42.01 | 9.07 | 9.84 | ||
| Post-D | 43.76 | 36.75 | 8.17 | 11.32 | ||
| [9] | Green waste/pine bark/DMSS (1:1:1 v:v) | C 4 d | 22.4 | 54.8 | 14.5 | 8.3 |
| C 18 d | 19.0 | 58.7 | 14.1 | 8.3 | ||
| C 31 d | 22.2 | 56.6 | 13.3 | 7.8 | ||
| C 40 d | 19.8 | 57.9 | 14.3 | 8.1 | ||
| C 57 d | 21.0 | 54.9 | 15.4 | 8.7 | ||
| C 67 d | 19.7 | 57.6 | 14.3 | 8.4 | ||
| C 84 d | 19.4 | 55.8 | 16.0 | 8.7 | ||
| C 101 d | 18.5 | 56.9 | 15.8 | 8.9 | ||
| C 114 d | 17.9 | 56.5 | 16.4 | 9.3 | ||
| C 128 d | 19.6 | 57.1 | 14.8 | 8.5 | ||
| C 146 d | 18.5 | 57.4 | 16.3 | 7.8 | ||
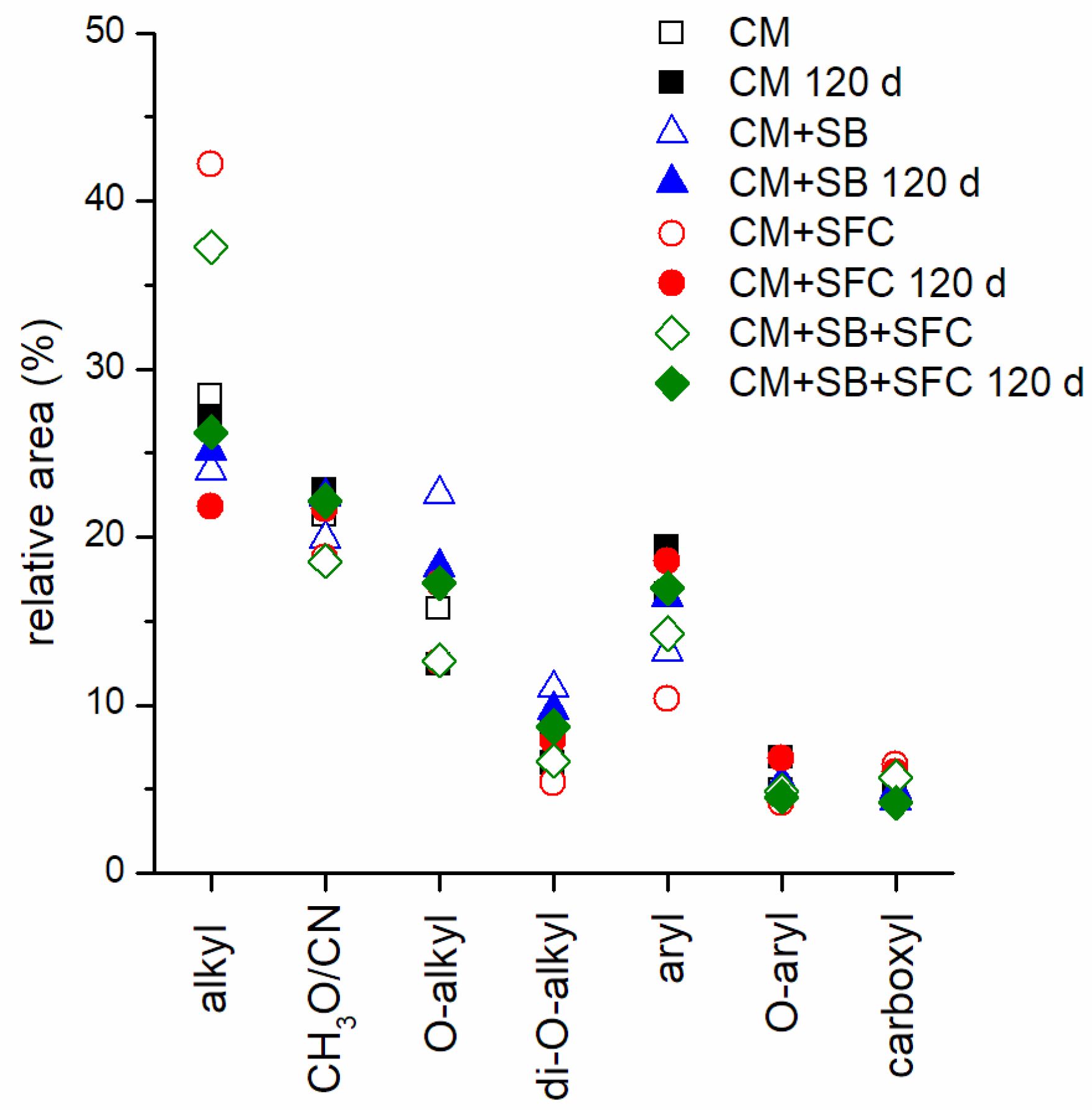
| [124] | CM (+straw) | FS | 20.3 | 61.1 | 5.6 | 11.1 |
| D | 24.7 | 52.6 | 7.2 | 14.4 | ||
| C | 18.0 | 53.6 | 10.0 | 16.8 | ||
| Mixed | 20.4 | 51.8 | 10.2 | 15.7 | ||
| PM (+straw) | FS | 21.9 | 62.0 | 4.8 | 8.6 | |
| D | 28.2 | 45.8 | 7.6 | 14.1 | ||
| Mixed | 17.7 | 65.6 | 5.2 | 10.4 | ||
| [130] | Municipal solid waste | FS | 50 | 34 | 7 | 9 |
| D | 51 | 26 | 13 | 10 | ||
| FS | 30 | 56 | 11 | 3 | ||
| C | 39 | 36 | 20 | 5 | ||
| FS | 23 | 59 | 13 | 5 | ||
| C | 32 | 43 | 20 | 5 | ||
| FS | 23 | 62 | 10 | 4 | ||
| C | 36 | 34 | 24 | 6 | ||
| FS | 23 | 62 | 10 | 4 | ||
| C | 28 | 41 | 24 | 7 | ||
| FS | 23 | 62 | 10 | 4 | ||
| C | 32 | 37 | 25 | 7 | ||
| FS | 30 | 55 | 12 | 3 | ||
| Alt | 46 | 35 | 15 | 5 | ||
| FS | 19 | 53 | 20 | 8 | ||
| Alt | 26 | 45 | 22 | 7 | ||
| FS | 23 | 62 | 10 | 5 | ||
| Mixed | 34 | 38 | 24 | 5 |
| Ref. a | Feedstock b | Sample c | A/OA | ARM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [132] | Starch/cereals/forage/corn silage | FS | 0.1–0.3 | |
| D | 0.2–0.3 | |||
| Post-D | 0.3 | |||
| Cereals/sugar beets/crop/corn silage | FS | 0.1 | ||
| D | 0.3–0.5 | |||
| Post-D | 0.4–0.6 | |||
| Pig slurry/ChM/HM/deep litter/cereals | FS | 0.3–0.6 | ||
| D | 0.4 | |||
| MFW/SW/food industry W | FS | 0.4 | ||
| D | 1.1 | |||
| Post-D | 1.1 | |||
| MFW/vegetables/food package/SW/food industry W/SM/GSS | FS | 0.9–1.1 | ||
| D | 0.7–0.9 | |||
| Post-D | 0.7–0.8 | |||
| Municipal food waste | FS | 0.4 | ||
| D | 0.9–1.1 | |||
| Post-D | 1.1–1.2 | |||
| Municipal food waste | FS | 0.3 | ||
| D | 0.5 | |||
| [133] | Green waste/food waste | FS | 8.12 | |
| C | 14.07 | |||
| D | 15.17 | |||
| FS | 12.11 | |||
| C | 12.46 | |||
| D | 15.34 | |||
| FS | 14.71 | |||
| C | 15.54 | |||
| D | 17.12 | |||
| [9] | Green waste/pine bark/DMSS (1:1:1 v:v) | C 4 d | 15.8 | |
| C 18 d | 15.4 | |||
| C 31 d | 14.5 | |||
| C 40 d | 15.5 | |||
| C 57 d | 16.9 | |||
| C 67 d | 15.6 | |||
| C 84 d | 17.6 | |||
| C 101 d | 17.3 | |||
| C 114 d | 18.1 | |||
| C 128 d | 16.2 | |||
| C 146 d | 17.6 | |||
| [124] | CM (+straw) | FS | 6.2 | |
| D | 9.5 | |||
| C | 13.0 | |||
| Mixed | 15.2 | |||
| PM (+straw) | FS | 6.3 | ||
| D | 13.8 | |||
| Mixed | 6.9 | |||
| [130] | Municipal solid waste | FS | 1.45 | |
| D | 1.93 | |||
| FS | 0.53 | |||
| C | 1.08 | |||
| FS | 0.39 | |||
| C | 0.75 | |||
| FS | 0.37 | |||
| C | 1.05 | |||
| FS | 0.37 | |||
| C | 0.68 | |||
| FS | 0.37 | |||
| C | 0.85 | |||
| FS | 0.55 | |||
| Alt | 1.53 | |||
| FS | 0.37 | |||
| Alt | 0.57 | |||
| FS | 0.36 | |||
| Mixed | 0.89 |
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bandini, F.; Taskin, E.; Bellotti, G.; Vaccari, F.; Misci, C.; Guerrieri, M.C.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Puglisi, E. The treatment of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste (OFMSW) as a possible source of micro- and nano-plastics and bioplastics in agroecosystems: A review. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2022, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://datatopics.worldbank.org/what-a-waste/trends_in_solid_waste_management.html (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Tejaswini, M.S.S.R.; Pathak, P.; Gupta, D.K. Sustainable approach for valorization of solid wastes as a secondary resource through urban mining. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coma, M.; Martinez-Hernandez, E.; Abeln, F.; Raikova, S.; Donnelly, J.; Arnot, T.C.; Allen, M.J.; Hong, D.D.; Chuck, C.J. Organic waste as a sustainable feedstock for platform chemicals. Faraday Discuss. 2017, 202, 175–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lohri, C.R.; Diener, S.; Zabaleta, I.; Mertenat, A.; Zurbrügg, C. Treatment technologies for urban solid biowaste to create value products: A review with focus on low- and middle-income settings. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 16, 81–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, V.; Singh, A.; Mohanty, S.S.; Srivastava, V.K.; Varjani, S. Organic solid waste: Biorefinery approach as a sustainable strategy in circular bioeconomy. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 349, 126835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Corato, U.; De Bari, I.; Viola, E.; Pugliese, M. Assessing the main opportunities of integrated biorefining from agro-bioenergy co/by-products and agroindustrial residues into high-value added products associated to some emerging markets: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 88, 326–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Khanal, S.; Lü, F.; Wong, J.W.C.; Wu, D.; Oechsner, H. Anaerobic digestion beyond biogas. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, R.; Ziarelli, F.; Alarcón-Gutiérrez, E.; Le Petit, J.; Terrom, G.; Perissol, C. 13C solid-state NMR assessment of decomposition pattern during co-composting of sewage sludge and green wastes. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 59, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papale, M.; Romano, I.; Finore, I.; Lo Giudice, A.; Piccolo, A.; Cangemi, S.; Di Meo, V.; Nicolaus, B.; Poli, A. Prokaryotic diversity of the composting thermophilic phase: The case of ground coffee compost. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhiar, A.; Zamri, M.F.M.A.; Torrijos, M.; Shamsuddin, A.H.; Battimelli, A.; Roslan, E.; Marzuki, M.H.M.; Carrere, H. Anaerobic digestion industries progress throughout the world. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 476, 012074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, S.; Ehimen, E.; Pillai, S.C.; Black, A.; Tormey, D.; Bartlett, J. Biogas production from small-scale anaerobic digestion plants on European farms. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 139, 110580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigkou, K.; Zagklis, D.; Tsafrakidou, P.; Zapanti, P.; Manthos, G.; Karamitou, K.; Zafiri, C.; Kornaros, M. Expired food products and used disposable adult nappies mesophilic anaerobic co-digestion: Biochemical methane potential, feedstock pretreatment and two-stage system performance. Renew. Energy 2021, 168, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamri, M.F.M.A.; Hasmady, S.; Akhiar, A.; Ideris, F.; Shamsuddin, A.H.; Mofijur, M.; Rizwanul Fattah, I.M.; Mahlia, T.M.I. A comprehensive review on anaerobic digestion of organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, B.; Mazumder, D. Anaerobic digestion for the stabilization of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste: A review. Environ. Rev. 2016, 24, 426–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehariya, S.; Patel, A.K.; Obulisamy, P.K.; Punniyakotti, E.; Wong, J.W.C. Co-digestion of food waste and sewage sludge for methane production: Current status and perspective. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jara-Samaniego, J.; Perez-Murcia, M.D.; Bustamante, M.A.; Perez-Espinosa, A.; Paredes, C.; Lopez, M.; López-Lluch, D.B.; Gavilanes-Teráne, I.; Moral, R. Composting as sustainable strategy for municipal solid waste management in the Chimborazo Region, Ecuador: Suitability of the obtained composts for seedling production. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 141, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesaro, A.; Conte, A.; Belgiorno, V.; Siciliano, A.; Guida, M. The evolution of compost stability and maturity during the full-scale treatment of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palaniveloo, K.; Amran, M.A.; Norhashim, N.A.; Mohamad-Fauzi, N.; Peng-Hui, F.; Hui-Wen, L.; Kai-Lin, Y.; Jiale, L.; Chian-Yee, M.G.; Jing-Yi, L.; et al. Food waste composting and microbial community structure profiling. Processes 2020, 8, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.compostnetwork.info/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/ECN-rapport-2022.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Ducasse, V.; Capowiez, Y.; Peigné, J. Vermicomposting of municipal solid waste as a possible lever for the development of sustainable agriculture. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 42, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aira, M.; Sampedro, L.; Monroy, F.; Domínguez, J. Detritivorous earthworms directly modify the structure, thus altering the functioning of a microdecomposer food web. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 2511–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.L.; Lee, L.H.; Wu, T.Y. Sustainability of using composting and vermicomposting technologies for organic solid waste biotransformation: Recent overview, greenhouse gases emissions and economic analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 111, 262–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.A.; Singh, J.; Vig, A.P. Instrumental characterization of organic wastes for evaluation of vermicompost maturity. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.; Ma, L.Q.; Martinez, G.A. Comparison of methods for evaluating stability and maturity of biosolids compost. J. Environ. Qual. 2000, 29, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouatmane, A.; Provenzano, M.R.; Hafidi, M.; Senesi, N. Compost maturity assessment using calorimetry, spectroscopy and chemical analysis. Compost Sci. Util. 2000, 8, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, T.A.; Sikora, L.J.; Steinhilber, P.M.; Douglass, L.W. Compost age and sample storage effects on maturity indicators of biosolids compost. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 2141–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Nuclear magnetic resonance, infra-red and pyrolysis: Application of spectroscopic methodologies to maturity determination of composts. Compost Sci. Util. 2003, 11, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francou, C.; Poitrenaud, M.; Houot, S. Stabilization of organic matter during composting: Influence of process and feedstocks. Compost Sci. Util. 2005, 13, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichuk, K.M.; McCartney, D. Compost stability and maturity evaluation—A literature review. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2010, 37, 1505–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo-Ocaña, E.R.; Torres-Lozada, P.; Marmolejo-Rebellon, L.F.; Hoyos, L.V.; Gonzales, S.; Barrena, R.; Komilis, D.; Sanchez, A. Stability and maturity of biowaste composts derived by small municipalities: Correlation among physical, chemical and biological indices. Waste Manag. 2015, 44, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simpson, A.J.; Simpson, M.J. Nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of natural organic matter. In Biophysico-Chemical Processes Involving Natural Nonliving Organic Matter in Environmental Systems; Senesi, N., Xing, B., Huang, P.M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 589–651. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, A.J.; McNally, D.J.; Simpson, M.J. NMR spectroscopy in environmental research: From molecular interactions to global processes. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2011, 58, 97–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldock, J.A.; Oades, J.M.; Nelson, P.N.; Skene, T.M.; Golchin, A.; Clarke, P. Assessing the extent of decomposition of natural organic materials using solid-state 13C NMR spectroscopy. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1997, 35, 1061–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pane, C.; Palese, A.M.; Spaccini, R.; Piccolo, A.; Celano, G.; Zaccardelli, M. Enhancing sustainability of a processing tomato cultivation system by using bioactive compost teas. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 202, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaccini, R.; Cozzolino, V.; Di Meo, V.; Savy, D.; Drosos, M.; Piccolo, A. Bioactivity of humic substances and water extracts from compost made by ligno-cellulose wastes from biorefinery. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrillo, M.; Cozzolino, V.; Spaccini, R.; Piccolo, A. Humic substances from green compost increase bioactivity and antibacterial properties of essential oils in basil leaves. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2021, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Férnandez-Domínguez, D.; Guilayn, F.; Patureau, D.; Jimenez, J. Characterising the stability of the organic matter during anaerobic digestion: A selective review on the major spectroscopic techniques. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 21, 691–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meija, J.; Coplen, T.B.; Berglund, M.; Brand, W.A.; De Bièvre, P.; Gröning, M.; Holden, N.E.; Irrgeher, J.; Loss, R.D.; Walczyk, T.; et al. Isotopic compositions of the elements 2013 (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2016, 88, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holden, N.E.; Coplen, T.B.; Böhlke, J.K.; Tarbox, L.V.; Benefield, J.; de Laeter, J.R.; Mahaffy, P.G.; O’Connorr, G.; Roth, E.; Tepper, D.H.; et al. IUPAC periodic table of the elements and isotopes (IPTEI) for the education community (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2018, 90, 1833–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knicker, H. Solid state CPMAS 13C and 15N NMR spectroscopy in organic geochemistry and how spin dynamics can either aggravate or improve spectra interpretation. Org. Geochem. 2011, 42, 867–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichler, M.; Knicker, H.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Changes in the chemical structure of municipal solid waste during composting as studied by solid-state dipolar dephasing and PSRE 13C NMR and solid-state 15N NMR spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 4034–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Cao, X.; Olk, D.C.; Chu, W.; Schmidt-Rohr, K. Advanced solid-state NMR spectroscopy of natural organic matter. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2017, 100, 17–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conte, P.; Spaccini, R.; Piccolo, A. State of the art of CPMAS 13C-NMR spectroscopy applied to natural organic matter. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2004, 44, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, C.M.; Cade-Menun, B.J.; Sayer, B.G. Characterization of Canadian backyard composts: Chemical and spectroscopic analyses. Compost Sci. Util. 1998, 6, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yu, Z.; Gao, H.; Yan, X.; Chang, J.; Wang, C.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L. Chemical structures and characteristics of animal manures and composts during composting and assessment of maturity indices. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Réveillé, V.; Mansuy, L.; Jardé, E.; Garnier-Sillam, E. Characterization of sewage–sludge derived organic matter: Lipids and humic acids. Org. Geochem. 2003, 34, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.A.; Pires, O.C.; Mota, M.; Alves, M.M. Anaerobic biodegradation of oleic and palmitic acids: Evidence of mass transfer limitations caused by long chain fatty acid accumulation onto the anaerobic sludge. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 92, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dignac, M.F.; Derenne, S.; Ginestet, P.; Bruchet, A.; Kniker, H.; Largeau, C. Determination of structure and origin of refractory organic matter in biodepurated wastewater via spectroscopic methods. Comparison of conventional and ozonation treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 3389–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kögel-Knabner, I. The macromolecular organic composition of plant and microbial residues as inputs to soil organic matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ussiri, A.A.N.; Johnson, C.E. Characterization of organic matter in a northern hardwood forest soil by 13C NMR spectroscopy and chemicals methods. Geoderma 2003, 11, 123–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalla, R.H.; VanderHart, D.L. The role of solid state 13C NMR spectroscopy in studies of the nature of native cellulose. Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson. 1999, 15, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatcher, P.G. Chemical structural studies of natural lignin by dipolar dephasing solid-state 13C nuclear magnetic resonance. Org. Geochem. 1987, 11, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manu, M.K.; Kumar, R.; Garg, A. Performance assessment of improved composting system for food waste with varying aeration and use of microbial inoculum. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 234, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustamante, M.A.; Paredes, C.; Marhuenda-Egea, F.C.; Perez-Espinosa, A.; Bernal, M.P.; Moral, R. Co-composting of distillery wastes with animal manures: Carbon and nitrogen transformations in the evaluation of compost stability. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Selvam, A.; Wong, J.W.C. Evaluation of humic substances during co-composting of food waste, sawdust and Chinese medicinal herbal residues. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 168, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chefetz, B.; Hadar, Y.; Chen, Y. Dissolved organic carbon fractions formed during composting of municipal solid waste: Properties and significance. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 1998, 26, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eudoxie, G.; Martin, M. Compost tea quality and fertility. In Organic Fertilizers: History, Production and Applications; Larramendy, M., Soloneski, S., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romero, C.M.; Redman, A.-A.P.H.; Owens, J.; Terry, S.A.; Ribeiro, G.O.; Gorzelak, M.A.; Oldenburg, T.B.P.; Hazendonk, P.; Larney, F.J.; Hao, X.; et al. Effects of feeding a pine-based biochar to beef cattle on subsequent manure nutrients, organic matter composition and greenhouse gas emissions. Sci. Total Environ 2022, 812, 152267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacomino, G.; Sarker, T.C.; Ippolito, F.; Bonanomi, G.; Vinale, F.; Staropoli, A.; Idbella, M. Biochar and compost application either alone or in combination affects vegetable yield in a volcanic Mediterranean soil. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, S.M.; Chen, C.R.; Xu, Z.H.; Nelson, P.N.; Boyd, S.E.; Meszaros, I.; Chan, K.Y. Molecular composition of recycled organic wastes, as determined by solid-state 13C NMR and elemental analyses. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 2157–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Guo, X.; Wu, S. Probing changes in humus chemical characteristics in response to biochar addition and varying bulking agents during composting: A holistic multi-evidence-based approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeken, A.H.M.; Adani, F.; Nierop, K.G.J.; de Jager, P.A.; Hamelers, H.V.M. Degradation of biomacromolecules during high-rate composting of wheat straw–amended feces. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Mata, J.; Lahoz-Ramos, C.; Bustamante, M.A.; Marhuenda-Egea, F.C.; Moral, R.; Santos, A.; Sáez, J.A.; Bernal, M.P. Thermal and spectroscopic analysis of organic matter degradation and humification during composting of pig slurry in different scenarios. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17357–17369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.-C.; Maie, N.; Tada, Y.; Katayama, A. Characterization of the maturing process of cattle manure compost. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inbar, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hadar, Y. Solid-state carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance and infrared spectroscopy of composted organic matter. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1989, 53, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Inbar, Y.; Hadar, Y.; Malcolm, R.L. Chemical properties and solid-state CPMAS 13C-NMR of composted organic matter. Sci. Total Environ. 1989, 81–82, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; He, C.; You, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Qi, H.; Ren, N. Transformation of organic matters in animal wastes during composting. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Climent, A.; Gomis, P.; Martín-Mata, J.; Bustamante, M.A.; Marhuenda-Egea, F.C.; Pérez-Murcia, M.D.; Pérez-Espinosa, A.; Paredes, C.; Moral, R. Chemical, thermal and spectroscopic methods to assess biodegradation of winery-distillery wastes during composting. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spaccini, R.; Todisco, D.; Drosos, M.; Nebbioso, A.; Piccolo, A. Decomposition of bio-degradable plastic polymer in a real on-farm composting process. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2016, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-Z.; Lin, Y.-H. Preliminary design for establishing compost maturity by using the spectral characteristics of five organic fertilizers. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaccini, R.; Piccolo, A. Spectroscopic characterization of compost at different maturity stages. Clean 2008, 36, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knicker, H.; Lüdemann, H.-D. N-15 and C-13 CPMAS and solution NMR studies of N-15 enriched plant material during 600 days of microbial degradation. Org. Geochem. 1995, 23, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spaccini, R.; Piccolo, A. Molecular characterization of compost at increasing stages of maturity. 2. Thermochemolysis-GC-MS and 13C-CPMAS-NMR spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 2303–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anda, M.; Syed Omar, S.R.; Shamshuddin, J.; Fauziah, C.I. Changes in properties of composting rice husk and their effects on soil and cocoa growth. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2008, 39, 2221–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caricasole, P.; Provenzano, M.R.; Hatcher, P.G.; Senesi, N. Evolution of organic matter during composting of different organic wastes assessed by CPMAS 13C NMR spectroscopy. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pane, C.; Spaccini, R.; Caputo, M.; De Falco, E.; Zaccardelli, M. Multi-parameter characterization of disease-suppressive bio-composts from aromatic plant residues evaluated for garden cress (Lepidium sativum L.) cultivation. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inbar, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hadar, Y. Carbon-13 CPMAS NMR and FTIR spectroscopic analysis of organic matter transformations during composting of solid wastes from wineries. Soil Sci. 1991, 152, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Vila, F.J.; Almendros, G.; Madrid, F. Molecular alterations of organic fractions from urban waste in the course of composting and their further transformation in amended soil. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 236, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chefetz, B.; Hatcher, P.G.; Hadar, Y.; Chen, Y. Chemical and biological characterization of organic matter during composting of municipal solid waste. J. Environ. Qual. 1996, 25, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.N.; Baldock, J.A. Estimating the molecular composition of a diverse range of natural organic materials from solid-state 13C NMR and elemental analyses. Biogeochemistry 2005, 72, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmora-Nahum, S.; Hadar, Y.; Chen, Y. Physico-chemical properties of commercial composts varying in their source materials and country of origin. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 1263–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haw, J.F.; Maciel, G.E.; Schroeder, H.A. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometric study of wood and wood pulping with cross polarization and magic-angle spinning. Anal. Chem. 1984, 56, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skene, T.M.; Skjemstad, J.O.; Oades, J.M.; Clarke, P.J. The influence of inorganic matrices on the decomposition of straw. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1996, 34, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Faiyz, Y.S.S. CPMAS 13C NMR characterization of humic acids from composted agricultural Saudi waste. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 5839–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrillo, M.; Salzano, M.; Savy, D.; di Meo, V.; Valentini, M.; Cozzolino, V.; Piccolo, A. Antibacterial and antioxidant properties of humic substances from composted agricultural biomasses. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2022, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, M.; Baigorri, R.; González-Gaitano, G.; García-Mina, J.M. The complementary use of 1H NMR, 13C NMR, FTIR and size exclusion chromatography to investigate the principal structural changes associated with composting of organic materials with diverse origin. Org. Geochem. 2007, 38, 2012–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Yang, Z.; Huang, L.; Chen, Y. Roles of organic matter transformation in the bioavailability of Cu and Zn during sepiolite-amended pig manure composting. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 314, 115046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J. The role of biochar in organic waste composting and soil improvement: A review. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 884–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, P.; Rumpel, C.; Ngo, Q.; Alexis, M.; Vargas, G.V.; Mora Gil, M.D.L.L.; Dang, D.; Jouquet, P. Biological and chemical reactivity and phosphorus forms of buffalo manure compost, vermicompost and their mixture with biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 148, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, X.; Han, Z.; Huang, X.; Hu, B.; Shi, D.; Wu, W. Effects of bamboo charcoal and bamboo vinegar on nitrogen conservation and heavy metals immobility during pig manure composting. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, M.M.; Suárez-Estrella, F.; López, M.J.; Vargas-García, M.C.; López-González, J.A.; Moreno, J. Enhanced turnover of organic matter fractions by microbial stimulation during lignocellulosic waste composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 186, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, H.; Wu, S. Humic substances developed during organic waste composting: Formation mechanisms, structural properties, and agronomic functions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaccini, R.; Piccolo, A. Molecular characteristics of humic acids extracted from compost at increasing maturity stages. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1164–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldi, P.; Alberti, G.; Merella, R.; Melis, P. Study of the organic matter evolution during municipal solid waste composting aimed at identifying suitable parameters for the evaluation of compost maturity. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almendros, G.; Dorado, J.; González-Vila, F.J.; Blanco, M.J.; Lankes, U. 13C NMR assessment of decomposition patterns during composting of forest and shrub biomass. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, C.; Hernández, T.; Costa, F. Comparison of humic acids derived from city refuse with more developed humic acids. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1992, 38, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chefetz, B.; Adani, F.; Genevini, P.; Tambone, F.; Hadar, Y.; Chen, Y. Humic-acid transformation during composting of municipal solid waste. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caricasole, P.; Provenzano, M.R.; Hatcher, P.G.; Senesi, N. Chemical characteristics of dissolved organic matter during composting of different organic wastes assessed by 13C CPMAS NMR spectroscopy. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8232–8236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinceslas-Akpa, M.; Loquet, M. Organic matter transformations in lignocellulosic waste products composted or vermicomposted (Eisenia Fetida Andrei): Chemical analysis and 13C CPMAS NMR spectroscopy. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1997, 29, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaccini, R.; Baiano, S.; Gigliotti, G.; Piccolo, A. Molecular characterization of a compost and its water-soluble fractions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Açıkgöz, M.A. Evaluation of phytochemical compositions and biological properties of Achillea gypsicola at different phenological stages. Chem. Biodivers. 2019, 16, e1900373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrillo, M.; Parisi, M.; Savy, D.; Caiazzo, G.; di Caprio, R.; Luciano, M.A.; Cacciapuoti, S.; Fabbrocini, G.; Piccolo, A. Antiflammatory activity and potential dermatological applications of characterized humic acids from a lignite and a green compost. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrillo, M.; Salzano, M.; Cozzolino, V.; Spaccini, R.; Piccolo, A. Bioactivity and antimicrobial properties of chemically characterized compost teas from different green composts. Waste Manag. 2021, 120, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canellas, L.P.; Piccolo, A.; Dobbss, L.B.; Spaccini, R.; Olivares, F.L.; Zandonadi, D.B.; Façanha, A.R. Chemical composition and bioactivity properties of size-fractions separated from a vermicompost humic acid. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthod, J.; Dignac, M.-F.; Le Mer, G.; Bottinelli, N.; Watteau, F.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Rumpel, C. How do earthworms affect organic matter decomposition in the presence of clay-sized minerals? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 143, 107730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Mer, G.; Barthod, J.; Dignac, M.-F.; Barré, P.; Baudin, F.; Rumpel, C. Inferring the impact of earthworms on the stability of organo-mineral associations by Rock-Eval thermal analysis and 13C NMR spectroscopy. Org. Geochem. 2020, 144, 104016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Aquino, A.M.; Canellas, L.P.; da Silva, A.P.S.; Canellas, N.O.; da S Lima, L.; Olivares, F.L.; Piccolo, A.; Spaccini, R. Evaluation of molecular properties of humic acids from vermicompost by 13C-CPMAS-NMR spectroscopy and thermochemolysis–GC–MS. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2019, 141, 104634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayans, B.; Pérez-Esteban, J.; Escolástico, C.; Eymar, E.; Masaguer, A. Evaluation of commercial humic substances and other organic amendments for the immobilization of copper through 13C CPMAS NMR, FT-IR, and DSC analyses. Agronomy 2019, 9, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguiar, N.O.; Olivares, F.L.; Novotny, E.H.; Dobbss, L.B.; Balmori, D.M.; Santos-Júnior, L.G.; Chagas, J.G.; Façanha, A.R.; Canellas, L.P. Bioactivity of humic acids isolated from vermicomposts at different maturation stages. Plant Soil 2013, 362, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinceslas-Akpa, M.; Loquet, M. 13C CPMAS NMR spectroscopy of organic matter transformation in ligno-cellulosic waste products composted and vermicomposted (Eisenia Fetida Andrei). Eur. J. Soil Biol. 1994, 30, 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Busato, J.D.; dos Santos, L.F.; Monteiro de Paula, A.; Sodré, F.F.; de Oliveira, A.L.; Dobbss, L.B.; de Souza Martins, E.; Jindo, K. Can co-application of silicate rock powder and humic-like acids increase nutrient uptake and plant growth in weathered tropical soil? Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B 2022, 72, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Balmori, D.; Spaccini, R.; Aguiar, N.O.; Novotny, E.H.; Olivares, F.L.; Canellas, L.P. Molecular characteristics of humic acids isolated from vermicomposts and their relationship to bioactivity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 11412–11419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.C.; Tavares, O.C.H.; Martínez Balmori, D.; dos Santos Almeida, V.; Canellas, L.P.; García-Mina, J.M.; Berbara, R.L.L. Structure-function relationship of vermicompost humic fractions for use in agriculture. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, N.O.; Novotny, E.H.; Oliveira, A.L.; Rumjanek, V.M.; Olivares, F.L.; Canellas, L.P. Prediction of humic acids bioactivity using spectroscopy and multivariate analysis. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 129, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaglia, B.; Nunes, R.R.; Rezende, M.O.O.; Tambone, F.; Adani, F. Investigating organic molecules responsible of auxin-like activity of humic acid fraction extracted from vermicompost. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Gómez, M.J.; Nogales, R.; Plante, A.; Plaza, C.; Fernández, J.M. Application of a set of complementary techniques to understand how varying the proportion of two wastes affects humic acids produced by vermicomposting. Waste Manag. 2015, 35, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- dos Santos, T.L.; Huertas Tavares, O.C.; de Abreu Lopes, S.; Sánchez Elias, S.; Louro Berbara, R.L.; García, A.C. Environmental implications of the organic matter structure for white-rot fungus Pleurotus eryngii growth in a tropical climate. Fungal. Biol. 2021, 125, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Balmori, D.; Domínguez, C.Y.A.; Carreras, C.R.; Rebatos, S.M.; Farías, L.B.P.; Izquierdo, F.G.; Berbara, R.L.L.; García, A.C. Foliar application of humic liquid extract from vermicompost improves garlic (Allium Sativum L.) production and fruit quality. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2019, 8, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canellas, L.P.; Dobbss, L.B.; Oliveira, A.L.; Chagas, J.G.; Aguiar, N.O.; Rumjanek, V.M.; Novotny, E.H.; Olivares, F.L.; Spaccini, R.; Piccolo, A. Chemical properties of humic matter as related to induction of plant lateral roots. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2012, 63, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbss, L.B.; Canellas, L.P.; Olivares, F.L.; Aguiar, N.O.; Peres, L.E.P.; Azevedo, M.; Spaccini, R.; Piccolo, A.; Façanha, A.R. Bioactivity of chemically transformed humic matter from vermicompost on plant root growth. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3681–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, B.; Chandra, T.S. Chemolytic and solid-state spectroscopic evaluation of organic matter transformation during vermicomposting of sugar industry wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 1680–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, K.; Lal, R.; Preston, C.M.; Nierop, K.G.J. Strengthening the soil organic carbon pool by increasing contributions from recalcitrant aliphatic bio(macro)molecules. Geoderma 2007, 142, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez, X.; Diaz, M.C.; Cooper, M.; Blanco, D.; Morán, A.; Snape, C.E. Study of biological stabilization processes of cattle and poultry manure by thermogravimetric analysis and 13C NMR. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 1889–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambone, F.; Genevini, P.; D’Imporzano, G.; Adani, F. Assessing amendment properties of digestate by studying the organic matter composition and the degree of biological stability during the anaerobic digestion of the organic fraction of MSW. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3140–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tambone, F.; Scaglia, B.; D’Imporzano, G.; Schievano, A.; Orzi, V.; Salati, S.; Adani, F. Assessing amendment and fertilizing properties of digestates from anaerobic digestion through a comparative study with digested sludge and compost. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tambone, F.; Adani, F.; Gigliotti, G.; Volpe, D.; Fabbri, C.; Provenzano, M.R. Organic matter characterization during the anaerobic digestion of different biomasses by means of CPMAS 13C NMR spectroscopy. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 48, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laera, A.; Shakeri Yekta, S.; Hedenstrom, M.; Buzier, R.; Guibaud, G.; Dario, M.; van Hullebusch, E.D. A simultaneous assessment of organic matter and trace elements bio-accessibility in substrate and digestate from an anaerobic digestion plant. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pigoli, A.; Zilio, M.; Tambone, F.; Mazzini, S.; Schepis, M.; Meers, E.; Schoumans, O.; Giordano, A.; Adani, F. Thermophilic anaerobic digestion as suitable bioprocess producing organic and chemical renewable fertilizers: A full scale approach. Waste Manag. 2021, 124, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, M.; Knicker, H.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Solid-state 13C NMR spectroscopic, chemolytic and biological assessment of pretreated municipal solid waste. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 26, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corno, L.; Pilu, R.; Tambone, F.; Scaglia, B.; Adani, F. New energy crop giant cane (Arundo donax L.) can substitute traditional energy crops increasing biogas yield and reducing costs. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 191, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri Yekta, S.; Hedenström, M.; Svensson, B.H.; Sundgren, I.; Dario, M.; Enrich-Prast, A.; Hertkorn, N.; Bjorn, A. Molecular characterization of particulate organic matter in full scale anaerobic digesters: An NMR spectroscopy study. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Bayo, J.D.; Yazdani, R.; Simmons, C.W.; Vander Gheynst, J.S. Comparison of thermophilic anaerobic and aerobic treatment processes for stabilization of green and food wastes and production of soil amendments. Waste Manag. 2018, 77, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Huang, R.; Dykstra, C.M.; Jiang, R.; Pavlostathis, S.G.; Tang, Y. Energy and nutrient recovery from sewage sludge and manure via anaerobic digestion with hydrothermal pretreatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambone, F.; Terruzzi, L.; Scaglia, B.; Adani, F. Composting of the solid fraction of digestate derived from pig slurry: Biological processes and compost properties. Waste Manag. 2015, 35, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, R.; Sebag, D.; Verrecchia, A. Organic matter decomposition: Bridging the gap between Rock–Eval pyrolysis and chemical characterization (CPMAS 13C NMR). Biogeochemistry 2015, 122, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Chemical Shift Range | Assignment | Conventional Region Name |
|---|---|---|
| 0–28 ppm | CH3 and CH2 in short chain and simple aliphatics | Alkyl C |
| 28–45 ppm | CH2 and CH in long aliphatic chains | |
| 45–60 ppm | O-CH3; CH-N; aliphatic quaternary C | O-Alkyl C |
| 60–95 ppm a | C2-C6 in cellulose and hemicellulose; alcohols; ethers | |
| 95–110 ppm b | C1 of cellulose and hemicellulose; anomeric carbon of polysaccharides | |
| 110–145 ppm c | unsubstituted or alkyl-substituted aromatic C | Aromatic C |
| 145–160 ppm d | O,N-substituted aromatics | |
| 160–190 ppm | Carboxylic acids; esters; amides | Carboxyl/carbonyl C |
| 190–220 ppm | ketones; aldehydes |
| Ref. a | Feedstock b | Sample c | Alkyl C | O-Alkyl C | Aromatic C | Carboxyl/ Carbonyl C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH3O/CHN | O-/Di-O-alkyl C | Aryl C | O-Aryl C | |||||
| [60] | Olive mill waste/orchard pruning residues | C 200 d | 17.39 | 11.63 | 45.86 | 12.31 | 5.75 | 7.06 |
| Olive mill waste/animal manure/wool residues | C 200 d | 26.82 | 15.32 | 38.59 | 6.93 | 4.0 | 8.34 | |
| [71] | ChM/saw dust (3:1 w:w) | C 56 d | 28.38 | 32.26 | 16.51 | |||
| CM/saw dust (3:1 w:w) | C 56 d | 22.13 | 32.20 | 10.49 | ||||
| SM/saw dust (3:1 w:w) | C 56 d | 31.62 | 41.36 | 17.71 | ||||
| Soybean meal/saw dust (3:1 w:w) | C 56 d | 37.94 | 43.16 | 18.40 | ||||
| Lemon peel/saw dust (3:1 w:w) | C 56 d | 36.23 | 41.10 | 17.43 | ||||
| [77] | Wood chips/vegetable R/aromatic plant R | C1 | 33.9 | 13.0 | 31.3 | 12.6 | 2.1 | 7.2 |
| C2 | 38.2 | 12.3 | 26.8 | 11.5 | 2.9 | 8.2 | ||
| C3 | 23.4 | 11.7 | 44.0 | 12.1 | 3.7 | 5.1 | ||
| C4 | 21.0 | 11.8 | 41.1 | 14.3 | 3.8 | 8.1 | ||
| C5 | 19.0 | 11.4 | 42.4 | 15.5 | 3.8 | 7.9 | ||
| C6 | 24.6 | 10.9 | 38.7 | 15.1 | 3.3 | 7.4 | ||
| C7 | 35.7 | 11.8 | 31.0 | 11.8 | 2.5 | 7.2 | ||
| C8 | 37.8 | 12.0 | 30.1 | 11.4 | 2.2 | 6.5 | ||
| C9 | 43.6 | 10.5 | 28.0 | 9.5 | 2.2 | 6.3 | ||
| C10 | 34.7 | 11.5 | 30.7 | 10.4 | 3.1 | 9.5 | ||
| C11 | 30.2 | 11.3 | 33.6 | 12.0 | 5.3 | 7.7 | ||
| [62] | SM/ rice straw (4:1 w:w) SM/ rice straw (8:1 w:w) SM/rice straw/biochar (8:1:1 w:w) | FS | 24.6 | 57.9 | 7.7 | 9.8 | ||
| C 40 d | 23.2 | 55.2 | 9.8 | 11.8 | ||||
| FS | 28.8 | 50.5 | 7.9 | 12.8 | ||||
| C 40 d | 25.6 | 48.9 | 10.6 | 15.0 | ||||
| FS | 24.7 | 40.9 | 24.7 | 9.8 | ||||
| C 40 d | 19.2 | 28.8 | 42.5 | 9.5 | ||||
| [10] | COF/fresh grass/mature compost (18:80:2 w:w) | C 6 d | 33.5 | 15.2 | 23.3 | 14.8 | 3.2 | 10 |
| [64] | Solid pig slurry/cotton gin waste (4:3 v:v) Solid pig slurry/cotton gin waste (3:4 v:v) Solid pig slurry/cotton gin waste (3:7 v:v) | FS | 13.5 | 5.9 | 74.9 | 3.7 | 0.9 | 1.1 |
| BT | 17.5 | 8.2 | 62.7 | 5.3 | 1.8 | 4.5 | ||
| AT | 26.0 | 12.3 | 51.2 | 4.2 | 2.5 | 3.9 | ||
| EB | 30.1 | 10.5 | 48.1 | 4.4 | 1.9 | 5.0 | ||
| AM | 35.5 | 13.1 | 43.8 | 3.6 | 0.7 | 3.4 | ||
| FS | 19.4 | 9.3 | 71.6 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| BT | 13.6 | 7.1 | 71.6 | 5.5 | 1.0 | 1.2 | ||
| AT | 18.7 | 4.7 | 61.9 | 7.4 | 3.2 | 4.1 | ||
| EB | 26.4 | 11.4 | 53.8 | 5.7 | 4.5 | 6.8 | ||
| AM | 34.1 | 12.5 | 44.3 | 3.8 | 1.3 | 4.1 | ||
| FS | 22.9 | 7.4 | 63.6 | 2.3 | 1.1 | 2.7 | ||
| BT | 24.9 | 9.3 | 59.1 | 0.9 | 2.0 | 3.9 | ||
| AT | 21.0 | 9.3 | 65.5 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 2.2 | ||
| EB | 18.4 | 8.1 | 69.7 | 2.1 | 1.4 | 0.3 | ||
| AM | 21.8 | 9.0 | 58.8 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 5.2 | ||
| [70] | BM/CM/maize straw/PT (70:30 w:w) +bioplastic (1 wt%) +bioplastic (2 wt%) | FS | 15.4 | 10.5 | 58.4 | 8.6 | 3.0 | 4.1 |
| C 108 d | 18.5 | 11.4 | 48.0 | 12.0 | 3.4 | 6.7 | ||
| C 108 d | 17.6 | 11.1 | 47.9 | 12.3 | 4.0 | 7.1 | ||
| C 108 d | 18.9 | 11.0 | 49.2 | 11.6 | 3.6 | 5.7 | ||
| [68] | SM/pumice CM/pumice ChM/pumice | FS | 34.6 | 48.5 | 7.3 | 9.7 | ||
| C 10 d | 21.5 | 60.4 | 10.5 | 7.7 | ||||
| C 20 d | 23.6 | 57.7 | 10.9 | 7.7 | ||||
| C60 d | 26.2 | 48.3 | 12.9 | 12.7 | ||||
| FS | 14.6 | 64.8 | 12.4 | 8.3 | ||||
| C 10 d | 9.0 | 70.4 | 12.9 | 7.7 | ||||
| C 20 d | 10. | 69.2 | 12.7 | 7.7 | ||||
| C60 d | 11.7 | 66.6 | 13.3 | 8.5 | ||||
| FS | 29.5 | 52.3 | 8.2 | 10.1 | ||||
| C 10 d | 21.5 | 66.0 | 6.4 | 6.1 | ||||
| C 20 d | 21.7 | 61.6 | 9.3 | 7.4 | ||||
| C60 d | 26.8 | 52.0 | 10.5 | 10.7 | ||||
| [69] | Exhausted grape marc/CM (76:24 w:w) Grape marc/CM (72:28 w:w) Exhausted grape marc/PM (67:33 w:w) | FS | 30.7 | 17.0 | 39.5 | 3.3 | 3.5 | 6.1 |
| C 28 d | 36.4 | 15.9 | 31.2 | 5.7 | 3.7 | 7.3 | ||
| C105 d | 37.9 | 16.1 | 28.9 | 6.3 | 3.9 | 6.9 | ||
| C 168 d | 37.3 | 14.3 | 22.4 | 7.1 | 4.8 | 14.2 | ||
| FS | 33.6 | 15.3 | 37.1 | 2.9 | 3.7 | 7.4 | ||
| C 28 d | 34.3 | 13.7 | 37.3 | 3.6 | 3.6 | 7.5 | ||
| C105 d | 33.3 | 14.8 | 38.6 | 3.8 | 3.0 | 6.6 | ||
| C 168 d | 34.9 | 15.2 | 34.4 | 3.3 | 4.0 | 8.2 | ||
| FS | 30.8 | 14.2 | 41.0 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 7.0 | ||
| C 28 d | 34.4 | 14.6 | 35.4 | 3.2 | 4.0 | 8.5 | ||
| C105 d | 33.9 | 15.5 | 35.7 | 3.7 | 3.9 | 7.5 | ||
| C 168 d | 34.3 | 15.5 | 31.5 | 3.4 | 5.0 | 10.2 | ||
| [61] | CM | CC | 18.2 | 7.6 | 48.8 | 8.9 | 5.0 | 11.6 |
| Broiler litter | CC | 17.9 | 9.1 | 48 | 8.0 | 5.2 | 11.7 | |
| Green waste | CC | 22.4 | 10.7 | 40.4 | 8.2 | 6.3 | 12.0 | |
| Nitro-humus | CC | 19.6 | 8.8 | 43 | 9.6 | 6.7 | 12.4 | |
| MSW | CC | 23.0 | 7.6 | 48.7 | 7.3 | 3.6 | 9.8 | |
| [75] | Rice husk/rice bran/BEM/molasses | FS | 2.15 | 25.8 | 67.4 | 2.98 | 0.99 | |
| C 13 d | 1.98 | 25.6 | 68.9 | 3.07 | 0.51 | |||
| C 34 d | 0.66 | 25.6 | 70.8 | 2.98 | - | |||
| C 53 d | 1.10 | 22.6 | 73.1 | 3.29 | - | |||
| C 61 d | 1.03 | 24.0 | 71.9 | 3.09 | - | |||
| C 116 d | 0.88 | 25.7 | 69.9 | 2.63 | 0.88 | |||
| [74] | DOW/plant trimming/vegetal R (50:40:10 w:w) | C 60 d | 37.6 | 50.8 | 7.2 | 4.3 | ||
| C 90 d | 30.6 | 56.1 | 7.3 | 6.1 | ||||
| C 150 d | 45.3 | 37.6 | 9.6 | 7.4 | ||||
| [65] | CM/rice straw | FS | 14.9 | 54.9 | 20.3 | 10.0 | ||
| C 60 d | 17.4 | 57.4 | 20.9 | 10.6 | ||||
| C 120 d | 17.4 | 48.6 | 18.6 | 9.9 | ||||
| C 240 d | 15.2 | 34.1 | 16.1 | 9.2 | ||||
| C 365 d | 13.9 | 25.7 | 12.4 | 6.5 | ||||
| C 548 d | 12.8 | 22.8 | 11.3 | 6.6 | ||||
| FS | 13.5 | 56.7 | 20.1 | 9.7 | ||||
| C 148 d | 15.2 | 39.6 | 18.7 | 10.0 | ||||
| FS | 15.2 | 56.4 | 18.8 | 9.6 | ||||
| C 60 d | 13.4 | 47.5 | 16.5 | 8.4 | ||||
| C 120 d | 12.6 | 42.0 | 17.5 | 8.5 | ||||
| C 240 d | 12.1 | 37.2 | 15.9 | 8.1 | ||||
| C 365 d | 12.6 | 35.6 | 15.3 | 7.7 | ||||
| [63] | SM/wheat straw (95:5 w:w) | FS | 27.2 | 55.6 | 9.2 | 8.0 | ||
| C 7 d | 18.6 | 66.1 | 9.8 | 5.5 | ||||
| C 14 d | 15.2 | 65.3 | 12.2 | 7.3 | ||||
| C 21 d | 16.8 | 65.2 | 11.5 | 6.5 | ||||
| C 28 d | 14.7 | 63.3 | 13.6 | 8.3 | ||||
| [79] | MSW (composted in spring) MSW (composted in summer) | FS | 15.8 | 59.5 | 14.9 | 7.9 | ||
| C 28 d | 17.7 | 59.2 | 13.6 | 7.4 | ||||
| C 42 d | 17.5 | 55.5 | 16.2 | 7.2 | ||||
| C 49 d | 17.3 | 55.5 | 17.7 | 5.4 | ||||
| FS | 16.2 | 60.4 | 12.1 | 7.8 | ||||
| C 28 d | 16.8 | 60.2 | 13.9 | 6.9 | ||||
| C 42 d | 18.0 | 56.1 | 15.3 | 6.8 | ||||
| C 49 d | 18.2 | 56.9 | 15.8 | 6.0 | ||||
| [45] | Kitchen waste/garden waste | C1 | 28.4 | 45.6 | 7.4 | 4.6 | 14.0 | |
| C2 | 25.4 | 48.6 | 9.8 | 4.8 | 11.4 | |||
| C3 | 30.3 | 32.5 | 11.1 | 6.3 | 19.8 | |||
| C4 | 32.4 | 38.2 | 7.9 | 4.9 | 16.6 | |||
| C5 | 19.2 | 53.0 | 12.8 | 8.2 | 6.8 | |||
| C6 | 25.5 | 40.8 | 12.6 | 6.6 | 14.5 | |||
| C7 | 27.4 | 42.8 | 11.3 | 6.3 | 12.2 | |||
| C8 | 26.7 | 42.6 | 9.0 | 7.9 | 13.8 | |||
| C9 | 14.1 | 43.6 | 8.1 | 12.0 | 22.2 | |||
| [80] | MSW | FS | 26.9 | 47.9 | 11.6 | 4.3 | 8.3 | |
| C 34 d | 25.5 | 52.1 | 10.5 | 3.6 | 8.2 | |||
| C 76 d | 24.7 | 46.5 | 13.6 | 4.9 | 10.3 | |||
| C 90 d | 23.6 | 42.4 | 19.0 | 6.6 | 11.4 | |||
| C132 d | 23.6 | 40.4 | 16.9 | 7.6 | 11.4 | |||
| [78] | Grape skin Grape seeds Grape skin and seeds | FS | 8.7 | 53.4 | 17.5 | 18.7 | ||
| C 160 d | 10.9 | 51.8 | 18.9 | 17.0 | ||||
| FS | 25.0 | 41.3 | 13.1 | 18.7 | ||||
| C 160 d | 21.7 | 38.4 | 15.7 | 22.3 | ||||
| FS | 16.2 | 49.7 | 13.2 | 18.8 | ||||
| C 160 d | 18.6 | 43.7 | 15.9 | 20.3 | ||||
| Ref. a | Feedstock b | Sample c | Alkyl C | O-Alkyl C | Aromatic C | Carboxyl/ Carbonyl C | HB/HI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH3O/CHN | O-Alkyl C | Di-O-Alkyl C | Aryl C | O-Aryl C | ||||||
| [106] | OMx | VC 196 d | 24.1 | 51.8 | 12.4 | 3.1 | 8.6 | |||
| C 196 d | 27.6 | 48.2 | 11.7 | 2.7 | 9.8 | |||||
| OMx/montmorillonite (7:3 w:w) | VC 196 d | 19.9 | 57.0 | 11.8 | 3.0 | 8.3 | ||||
| C 196 d | 21.6 | 56.7 | 10.0 | 2.5 | 9.1 | |||||
| OMx/kaolinite (7:3 w:w) | VC 196 d | 22.6 | 47.2 | 14.6 | 3.8 | 11.8 | ||||
| C 196 d | 18.4 | 58.2 | 11.5 | 3.0 | 9.0 | |||||
| OMx/goethite (8.5:1.5 w:w) | VC 196 d | 22.5 | 42.2 | 15.3 | 5.2 | 14.7 | ||||
| C 196 d | 19.2 | 55.0 | 11.7 | 3.6 | 10.5 | |||||
| [107] | OMx/montmorillonite (7:3 w:w) | FS | 9.1 | 76.9 | 7.0 | 1.7 | 5.3 | |||
| F1 VC 196 d | 17.6 | 56.7 | 14.8 | 3.9 | 7.0 | |||||
| F1 C 196 d | 28.0 | 47.4 | 12.0 | 3.0 | 9.7 | |||||
| F2 VC 196 d | 21.9 | 53.4 | 12.1 | 3.2 | 9.3 | |||||
| F2 C 196 d | 22.9 | 51.8 | 12.0 | 3.1 | 10.2 | |||||
| F3 VC 196 d | 19.0 | 57.5 | 10.7 | 3.0 | 9.8 | |||||
| F3 C 196 d | 21.1 | 58.8 | 9.0 | 2.3 | 8.8 | |||||
| [108] | CM d | VC 120 d | 28.1 | 13.2 | 37.0 | 11.4 | 3.0 | 7.3 | 1.0 | |
| CM/flock cotton residues d (75:25 v:v) | VC 120 d | 29.5 | 11.8 | 35.8 | 11.3 | 3.7 | 7.8 | 1.0 | ||
| CM/flock cotton residues d (50:50 v:v) | VC 120 d | 24.1 | 11.9 | 39.0 | 13.7 | 4.2 | 7.1 | 0.9 | ||
| CM/flock cotton residues d (25:75 v:v) | VC 120 d | 20.1 | 11.2 | 44.5 | 13.3 | 4.0 | 7.0 | 0.8 | ||
| Flock cotton residues d | VC 120 d | 19.4 | 11.5 | 44.4 | 13.7 | 4.5 | 6.6 | 0.8 | ||
| [109] | CM/garden green waste e | VC 70 d | 17.8 | 11.1 | 31.1 | 8.9 | 13.3 | 7.8 | 10.0 | |
| [110] | CM d | FS | 23.16 | 17.70 | 24.97 | 9.99 | 11.45 | 6.39 | 6.34 | 0.69 |
| VC 120 d | 19.67 | 16.64 | 23.70 | 10.51 | 13.85 | 7.94 | 7.69 | 0.71 | ||
| CM/SCB d (1:1 w:w) | FS | 14.46 | 16.58 | 31.90 | 12.39 | 12.00 | 6.94 | 5.73 | 0.50 | |
| VC 120 d | 19.22 | 16.68 | 24.49 | 10.91 | 13.46 | 7.82 | 7.42 | 0.68 | ||
| CM/SC d (1:1 w:w) | FS | 15.04 | 17.29 | 33.35 | 12.48 | 10.50 | 5.36 | 5.99 | 0.45 | |
| VC 120 d | 13.88 | 17.13 | 29.80 | 12.19 | 13.44 | 7.95 | 5.60 | 0.54 | ||
| CM/SCB/SC d(1:1:1 w:w) | FS | 15.85 | 17.65 | 32.74 | 11.26 | 9.93 | 5.33 | 7.25 | 0.45 | |
| VC 120 d | 15.77 | 16.53 | 25.23 | 11.10 | 14.94 | 9.16 | 7.26 | 0.66 | ||
| [111] | Maple pruning waste | FS | 79.26 | 8.28 | 4.75 | 6.04 | ||||
| VC 30 d | 76.87 | 9.83 | 5.24 | 6.54 | ||||||
| VC 150 d | 75.45 | 10.07 | 5.73 | 6.79 | ||||||
| VC 180 d | 74.62 | 10.25 | 5.72 | 7.80 | ||||||
| VC 240 d | 74.43 | 10.43 | 5.65 | 7.56 | ||||||
| VC 300 d | 75.40 | 12.12 | 5.45 | 5.90 | ||||||
| C 30 d | 77.94 | 10.56 | 4.84 | 5.76 | ||||||
| C 150 d | 72.11 | 12.37 | 5.98 | 7.51 | ||||||
| C 180 d | 72.19 | 11.63 | 6.21 | 7.80 | ||||||
| C 240 d | 73.10 | 11.59 | 6.03 | 7.85 | ||||||
| C 300 d | 72.54 | 11.88 | 6.21 | 7.79 | ||||||
| Ref. a | Feedstock b | Sample c | Alkyl C | O-Alkyl C | Aromatic C | Carboxyl/ Carbonyl C | HB/HI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH3O/CHN | O-Alkyl C | Di-O-Alkyl C | Aryl C O-Aryl C | Carboxyl C Carbonyl C | |||||||
| [112] | CM | HA 120 d | 33.3 | 16.7 | 16.7 | 5.6 | 13.3 | 5.6 | 8.9 | 0.98 | |
| [108] | CM | HA 120 d | 24.6 | 15.0 | 24.7 | 20.5 | 5.5 | 9.7 | 1.4 h | ||
| CM/flock cotton residues d (25:75 v:v) | HA 120 d | 24.2 | 13.8 | 25.6 | 18.4 | 6.8 | 11.3 | 1.3 h | |||
| CM/flock cotton residues d (50:50 v:v) | HA 120 d | 26.8 | 13.1 | 25.7 | 18.1 | 6.5 | 9.9 | 1.4 h | |||
| CM/flock cotton residues d (75:25 v:v) | HA 120 d | 24.1 | 12.9 | 28.1 | 19.0 | 7.0 | 9.0 | 1.3 h | |||
| Flock cotton residues d | HA 120 d | 22.1 | 12.2 | 29.4 | 17.6 | 7.6 | 11.1 | 1.2 h | |||
| [114] | CM | HAw 120 d | 37.63 | 11.82 | 10.75 | 4.3 | 11.82 | 3.22 | 12.90 | 7.52 | 1.32 |
| HA 120 d | 17.43 | 14.68 | 15.60 | 9.17 | 20.18 | 8.26 | 12.84 | 1.83 | 0.88 | ||
| HR 120 d | 33.68 | 11.57 | 26.31 | 7.36 | 8.42 | 2.10 | 8.42 | 2.10 | 0.82 | ||
| [119] | CM | HS | 21.21 | 15.15 | 14.14 | 9.09 | 16.16 | 10.10 | 14.14 | ||
| [116] | CM/SD (85:15 v:v) | HA 0–30 d | 20.38 | 47.94 | 21.06 | 10.61 | |||||
| HA 45–60 d | 20.58 | 49.75 | 19.50 | 10.17 | |||||||
| HA 90–135 d | 19.93 | 49.22 | 20.45 | 10.39 | |||||||
| CM/SD/TWS (72.5:12.5:15 v:v) | HA 0–30 d | 21.54 | 47.69 | 20.64 | 10.12 | ||||||
| HA 45–60 d | 21.33 | 47.81 | 20.44 | 10.42 | |||||||
| HA 90–135 d | 20.54 | 47.85 | 21.53 | 10.08 | |||||||
| CM/SD/TWC (70:10:20 v:v) | HA 0–30 d | 21.57 | 48.18 | 19.90 | 10.35 | ||||||
| HA 45–60 d | 23.76 | 46.65 | 19.62 | 9.97 | |||||||
| HA 90–135 d | 20.74 | 49.11 | 20.14 | 10.00 | |||||||
| CM/SD/TWS/TWC (70:10:7.5:12.5 v:v) | HA 0–30 d | 20.33 | 46.61 | 21.23 | 11.83 | ||||||
| HA 45–60 d | 22.07 | 48.41 | 19.41 | 10.11 | |||||||
| HA 90–135 d | 20.31 | 47.80 | 21.15 | 10.74 | |||||||
| [117] | Tomato plant /PMS (2:1 w:w) Tomato plant/PMS (1:1 w:w) | HA FS | 49.4 | 26.5 | 11.1 | 13.0 | |||||
| HA 180 d | 33.1 | 39.3 | 15.9 | 11.7 | |||||||
| HA FS | 50.9 | 21.1 | 13.1 | 14.9 | |||||||
| HA 180 d | 29.1 | 38.2 | 19.3 | 13.4 | |||||||
| [113] | CM d | HA 90 d | 25.25 | 23.07 | 12.38 | 6.53 | 20.15 | 7.22 | 5.41 | 1.11 | |
| CM/SCB d (1:1 w:w) | HA 90 d | 20.77 | 21.31 | 19.61 | 9.53 | 17.62 | 5.86 | 5.30 | 0.79 | ||
| CM/SC d (1:1 w:w) | HA 90 d | 22.68 | 22.24 | 18.96 | 8.87 | 17.31 | 5.13 | 4.81 | 0.82 | ||
| CM/SCB/SC d (1:1:1 w:w) | HA 90 d | 19.08 | 22.81 | 20.46 | 8.96 | 18.53 | 5.51 | 4.65 | 0.76 | ||
| Sugar cane filter cake residue d | HA 90 d | 21.91 | 17.94 | 14.64 | 9.35 | 20.39 | 7.48 | 8.30 | 0.99 | ||
| [115] | CM e | HA FS | 28.41 | 21.29 | 15.74 | 8.58 | 16.62 | 4.97 | 4.39 | 1.00 | |
| HA 60 d | 25.55 | 19.45 | 14.28 | 7.53 | 18.42 | 7.54 | 7.23 | 1.06 | |||
| HA 120 d | 27.12 | 22.82 | 12.40 | 6.55 | 19.36 | 6.87 | 4.88 | 1.14 | |||
| CM/SCB e (1:1 w:w) | HA FS | 23.79 | 19.9 | 22.56 | 10.99 | 13.17 | 5.31 | 4.29 | 0.73 | ||
| HA 60 d | 25.40 | 21.36 | 17.52 | 8.94 | 16.23 | 5.11 | 5.43 | 0.87 | |||
| HA 120 d | 25.01 | 22.37 | 18.20 | 9.68 | 16.37 | 5.39 | 4.98 | 0.88 | |||
| CM/SC e (1:1 w:w) | HA FS | 42.22 | 18.76 | 12.57 | 5.4 | 10.39 | 4.16 | 6.49 | 1.31 | ||
| HA 60 d | 27.00 | 21.34 | 17.93 | 8.73 | 16.12 | 4.34 | 4.54 | 0.90 | |||
| HA 120 d | 21.83 | 21.64 | 17.22 | 7.90 | 18.57 | 6.83 | 6.01 | 0.90 | |||
| CM/SCB/SC e (1:1:1 w:w) | HA FS | 37.27 | 18.56 | 12.66 | 6.67 | 14.25 | 4.88 | 5.71 | 1.29 | ||
| HA 60 d | 21.24 | 22.68 | 21.27 | 9.80 | 16.12 | 4.36 | 4.52 | 0.71 | |||
| HA 120 d | 26.23 | 22.15 | 17.25 | 8.71 | 16.95 | 4.51 | 4.19 | 0.91 | |||
| [121] | CM/plant residues (1:5 v:v) | HS 45 d g | 23.20 | 42.90 | 23.90 | 10.00 | 0.89 | ||||
| [105] | CM/plant residues (1:5 v:v) | HA 90 d | 26.3 | 26.0 | 6.0 | 30.6 | 11.2 | ||||
| SF1 | 26.9 | 41.8 | 5.4 | 18.4 | 7.5 | ||||||
| SF2 | 25.1 | 38.9 | 5.8 | 21.1 | 9.0 | ||||||
| SF3 | 28.0 | 47.9 | 4.3 | 13.0 | 6.9 | ||||||
| SF4 | 31.3 | 52.0 | 4.2 | 9.0 | 3.5 | ||||||
| SF5 | 36.2 | 49.6 | 2.2 | 5.2 | 6.8 | ||||||
| SF6 | 35.8 | 48.6 | 3.7 | 6.8 | 5.2 | ||||||
| [122] | CM/pressmud/trash/bagasse f (1:7:1:1 w:w) | HA FS | 17.0 | 71.7 | 1.3 | 10.0 | |||||
| HA 20 d | 34.1 | 47.3 | 7.1 | 11.3 | |||||||
| HA 40 d | 14.8 | 50.4 | 21.6 | 12.8 | |||||||
| HA 60 d | 26.9 | 60.1 | 6.1 | 6.6 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pizzanelli, S.; Calucci, L.; Forte, C.; Borsacchi, S. Studies of Organic Matter in Composting, Vermicomposting, and Anaerobic Digestion by 13C Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2900. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13052900
Pizzanelli S, Calucci L, Forte C, Borsacchi S. Studies of Organic Matter in Composting, Vermicomposting, and Anaerobic Digestion by 13C Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(5):2900. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13052900
Chicago/Turabian StylePizzanelli, Silvia, Lucia Calucci, Claudia Forte, and Silvia Borsacchi. 2023. "Studies of Organic Matter in Composting, Vermicomposting, and Anaerobic Digestion by 13C Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy" Applied Sciences 13, no. 5: 2900. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13052900
APA StylePizzanelli, S., Calucci, L., Forte, C., & Borsacchi, S. (2023). Studies of Organic Matter in Composting, Vermicomposting, and Anaerobic Digestion by 13C Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy. Applied Sciences, 13(5), 2900. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13052900






