Abstract
Catheterization is a procedure used to diagnose and treat various cardiovascular diseases. Intracardiac echocardiography (ICE) is an emerging imaging modality that has gained popularity in these procedures due to its ability to provide high-resolution images of the heart and its surrounding structures in a minimally invasive manner. However, given its limited field of view, its orientation within the heart is difficult to judge simply from observing the acquired images. Therefore, ICE catheter tracking, which requires six degrees of freedom, would be useful to better guide interventionalists during a procedure. This work demonstrates a machine learning-based approach that has been trained to predict the roll angle of an ICE catheter using landmark scalar values extracted from bi-plane fluoroscopy images. The model consists of two fully connected deep neural networks that were trained on a dataset of bi-plane fluoroscopy images acquired from a 3D printed heart phantom. The results showed high accuracy in roll angle prediction, suggesting the ability to achieve 6 degrees of freedom tracking using bi-plane fluoroscopy that can be integrated into future navigation systems embedded into the c-arm, integrated within an AR/MR headset, or in other commercial navigation systems.
1. Introduction
The term “6-DOF” refers to the six degrees of freedom of motion that a mechanism or virtual object is capable of exhibiting. These degrees of freedom include movement in the vertical (up-down) plane, the horizontal (left-right) plane, the longitudinal (forward-back) plane, as well as rotation about the x (roll), y (pitch), and z (yaw) axes. The ability to move in these six distinct ways is crucial for a variety of applications, particularly in simulating the behavior of aircraft, robotics systems, and augmented/virtual reality (AR/VR) systems. The utilization of 6-DOF simulations is prevalent within the aerospace industry, serving as a valuable tool for both research and development, as well as for the training and evaluation of pilots and the assessment of aircraft designs [1]. It is also crucial for robotic applications, as it enables the capability of the robotic arm to effectively access and manipulate objects in various positions and orientations. In industries such as manufacturing, transportation, and surgical procedures, the implementation of 6-DOF robotic arms allows for the successful completion of intricate tasks that would be difficult or impossible for humans to perform. In recent years, the application of 6-DOF robotic systems has been an area of significant research interest, as it aims to develop robots that can perform complex tasks in various environments. For example, [2] presents new designs of 6-DOF robot manipulators for the transportation of building materials and 3D printing with concrete mixtures. In [3], Ma et al. proposed a system that uses augmented reality to assist in the autonomous view adjustment of a 6-DOF robotic stereo flexible endoscope. Torkaman et al. [4] proposed the use of a 6-DOF sensor-embedded soft robot for robotic-assisted minimally invasive surgery. The precise manipulation of objects is essential for tasks such as sorting, and 6-DOF robotic arms have been proven to be effective tools for such tasks. One example of this is the method presented in [5], which utilizes a 6-DOF robotic arm for cutlery sorting through object detection and grasping techniques.
In AR and VR as well as Mixed Reality (MR), 6-DOF allows for a greater level of realism, as the user is able to move and interact with virtual objects in a similar way to how they would in the real world [6]. For example, a 6-DOF controller allows the user to move their virtual hand in a natural, lifelike way, making it possible to grasp and manipulate virtual objects [7,8,9]. AR and MR technologies can enhance minimally invasive surgery by providing improved visualization and precision during procedures. AR overlays virtual images and data onto the patient’s body, while MR combines AR and VR to create an immersive experience for the surgeon [10,11,12]. These technologies can also be used to train surgeons and provide remote assistance [13]. They can improve patient outcomes by reducing the invasiveness of procedures and increasing the precision and skill of surgeons [12]. Specially, the utilization of AR and MR technology in cardiac catheterization has been demonstrated to potentially be a valuable tool in improving diagnostic and therapeutic capabilities [14]. The overlay of virtual images of the heart and its vasculature onto a real-time 3D representation of the patient’s anatomy allows for enhanced visualization of the heart’s structure, thereby facilitating the precise navigation and guidance of the catheter during the procedure [13,14]. This can result in an increase in the safety and efficiency of the procedure. Furthermore, the use of AR and MR technology can aid in the planning and execution of complex procedures such as transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) [15,16] and transcatheter mitral valve replacement (TMVR) [17,18].
Although many cardiac catheters are tube-like objects that require only 5-DOF, there are many that are rotationally asymmetric, and thus 6-DOF tracking is critical. In order to collect the necessary data for 6-DOF tracking of catheters, two options are available. The first option involves the integration of two receiving coil probes of electromagnetic (EM) sensors into the tip of the catheter. This method offers portability, but has a low accuracy of up to ~5 mm and may result in out-of-field data [13]. Additionally, the hardware required for this method is not readily available in catheterization labs, and manual integration of the probes into the catheter tip can introduce additional errors or the need for specialized equipment that is not scalable, given the FDA requirements for such procedures [19]. Furthermore, this method is limited to specific types of catheters and is not a general solution for 6-DOF tracking.
The second option for 6-DOF tracking involves the use of real-time bi-plane fluoroscopy imaging. This method offers a general tool that can be used for all types of catheters, and X-ray fluoroscopy machines are widely available in catheterization labs, although bi-plane c-arms are less common. However, this method only offers 5-DOF tracking and does not directly provide roll angle information, which is crucial for catheterization procedures. Roll angle is an essential parameter of 6-DOF tracking in catheterization, particularly when using Intracardiac Echocardiography (ICE) catheters. It provides precise navigation of the catheter by rotating it to access different parts of the heart and avoid obstacles, better visualization of the heart and surrounding structures by changing the view direction of the ultrasound transducer, increased flexibility in catheter positioning, and reduction in procedure time by easily obtaining the best imaging view.
To rectify the lack of roll angle sensing capabilities and to acquire complete 6-DOF tracking data for AR/MR systems, this paper has proposed a machine learning-based model to predict roll angles of an ICE catheter based on the positional tracking of the ICE catheter using bi-plane fluoroscopy imaging. The proposed model is a Multi-Input and Single Output (MISO) machine learning-based universal approximator that aims to accurately predict the roll angle of a catheter using inputs derived from the coordination of two intrinsic markers extracted from the synchronous frames of videos obtained from Antero Posterior (AP) and Left Anterior Oblique at 90 degrees (LAO90) planes of fluoroscopy imaging.
This paper is organized into three additional sections. Section 2 provides a definition of the ICE catheter and elaborates on the importance of roll angle prediction for its accurate tracking during cardiac catheterization; additionally, the proposed machine learning-based model for roll angle prediction is described. In Section 3, we present the results of our study, showcasing the accuracy of the proposed model through various error criteria. Finally, the key findings of this research are summarized and conclusions are drawn in Section 4.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ICE Imaging and the Necessity of Roll Angle Prediction
ICE is a real-time imaging modality that provides high-resolution visualizations of cardiac structures and allows for continuous monitoring of catheter positioning within the heart. It is well-tolerated by patients and has a reduced need for fluoroscopy and general anesthesia. It is commonly used for procedures, such as atrial septal defect closure and catheter ablation of cardiac arrhythmias and has an expanding role in other procedures [20]. ICE imaging uses ultrasound technology to produce images of the inside of the heart. A small, flexible catheter with a transducer at the tip is inserted into a blood vessel and guided to the heart. The transducer emits high-frequency sound waves, which bounce off the heart structures and return to the transducer as echoes [21]. These echoes are then converted into images that can be viewed on a monitor.
The roll angle is a crucial parameter that impacts the accuracy of the ICE imaging process during cardiac procedures. It influences the viewing orientation of the transducer, which will affect the speed, safety, and outcome of the procedure. The field of view of an ICE catheter is 90°, and thus, a 5–15° degree error will not significantly impact the physician’s ability to orient the catheter during the procedure, given that they are still able to visualize the live display of the ICE monitor. However, if the catheter is being used in a closed-loop robotic system, a wrong angle can lead to undesired consequences, such as a misdiagnosis, puncture, or improper delivery of a device. Similarly, the accurate prediction and display of the roll angle within an AR/MR system is imperative for providing the physician with the best possible representation of the catheter’s position and orientation during a procedure. Moreover, this technology can also provide an interactive platform for physicians to collaborate and discuss the patient’s condition and treatment plan, leading to improved patient outcomes.
2.2. Roll Angle Prediction
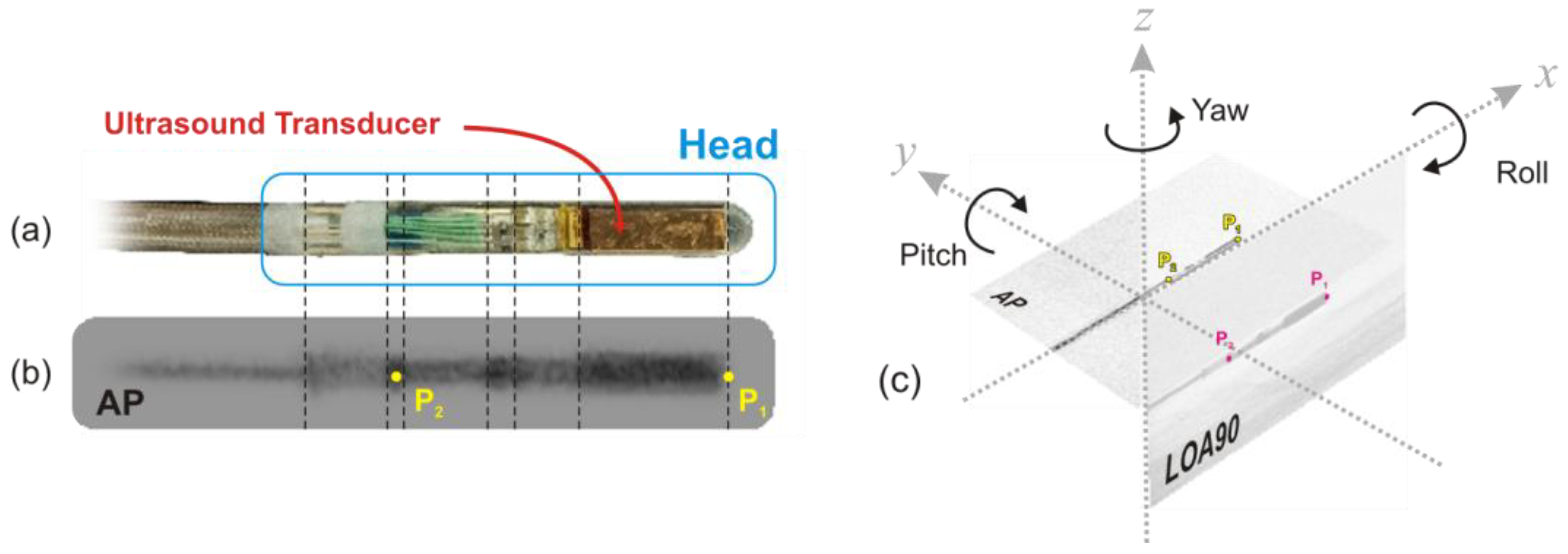
As illustrated in Figure 1a,b, the ICE catheter sensor head features three radiopaque markers which are clearly visible on fluoroscopy imaging (Figure 1b). Using the first marker in the AP (X-Y plane) and LAO90(X-Z plane) planes (Figure 1c), we can track the tip of catheter (P1) in both planes and determine the three positional degrees of freedom for the tip (X1, Y1, and Z1). Additionally, by calculating the angle of P1 around the center of one of the other markers (we chose P2 for this study) in the AP and LAO90 planes, we can determine the two angular degrees of freedom, Yaw (ψ) and Pitch (θ), respectively. However, to determine the roll angle (φ), a third plane perpendicular to the x-axis (Y-Z plane) is required. Unfortunately, this plane is not visible on bi-plane fluoroscopy.
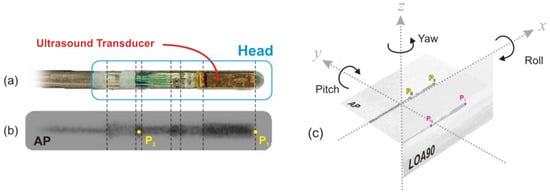
Figure 1.
(a) ICE catheter sensor head, (b) Fluoroscopy imaging of ICE catheter sensor head, (c) 3D representation of AP and LAO90 planes.
Through analysis of data obtained from bi-plane fluoroscopy, an empirical nonlinear correlation between the current 5-DOF data (X1, Y1, Z1, ψ, and θ) and the remaining 6th degree of freedom (φ) was discovered. The goal of this research is to model this correlation in order to predict the value of φ. Based on the above-mentioned description, the relationship between φ and the variables X1, Y1, Z1, ψ, and θ is expressed mathematically as follows:
φ = f1 (X1, Y1, Z1, ψ, θ)
In order to calculate ψ and θ, the coordinates of P1 and P2 in both planes are utilized. ψ represents the angle of P1 around P2 on the AP plane, while θ represents the angle of P1 around P2 on the LAO90 plane. Mathematically, ψ is a function of X1, X2, Y1, and Y2, ( here we name it g1(X1, X2, Y1, Y2)) and θ is a function of X1, X2, Z1, and Z2 ( here we name it g2(X1, X2, Z1, Z2)). This results in the following equation:
where g1 and g2 are defined as follows:
φ = f1 (X1, Y1, Z1, g1(X1, X2, Y1, Y2), g2(X1, X2, Z1, Z2))
ψ = g1(X1, X2, Y1, Y2) = Atan2((Y1-Y2), (X1-X2))
θ = g2(X1, X2, Z1, Z2) = Atan2((Z1-Z2), (X1-X2))
The Atan2(a,b) function is an arctangent function that differs from the Atan(.) function in that it can handle all possible values of a and b, including negative values and zero. Unlike the Atan function, which is limited to the first and fourth quadrants, the Atan2 function can determine the angle of a point in all four quadrants.
Based on the above definition, it can be inferred that φ is solely a function of the positional coordinates of P1 and P2 in both planes, and can be expressed as follows:
where f2 is a nonlinear function that can be implemented by any universal approximator. In this study, we have employed a neural network-based universal approximator, which is detailed in the subsequent section.
φ = f2 (X1, Y1, Z1, X2, Y2, Z2)
2.3. Proposed ML-Based Model for Roll Angle Prediction
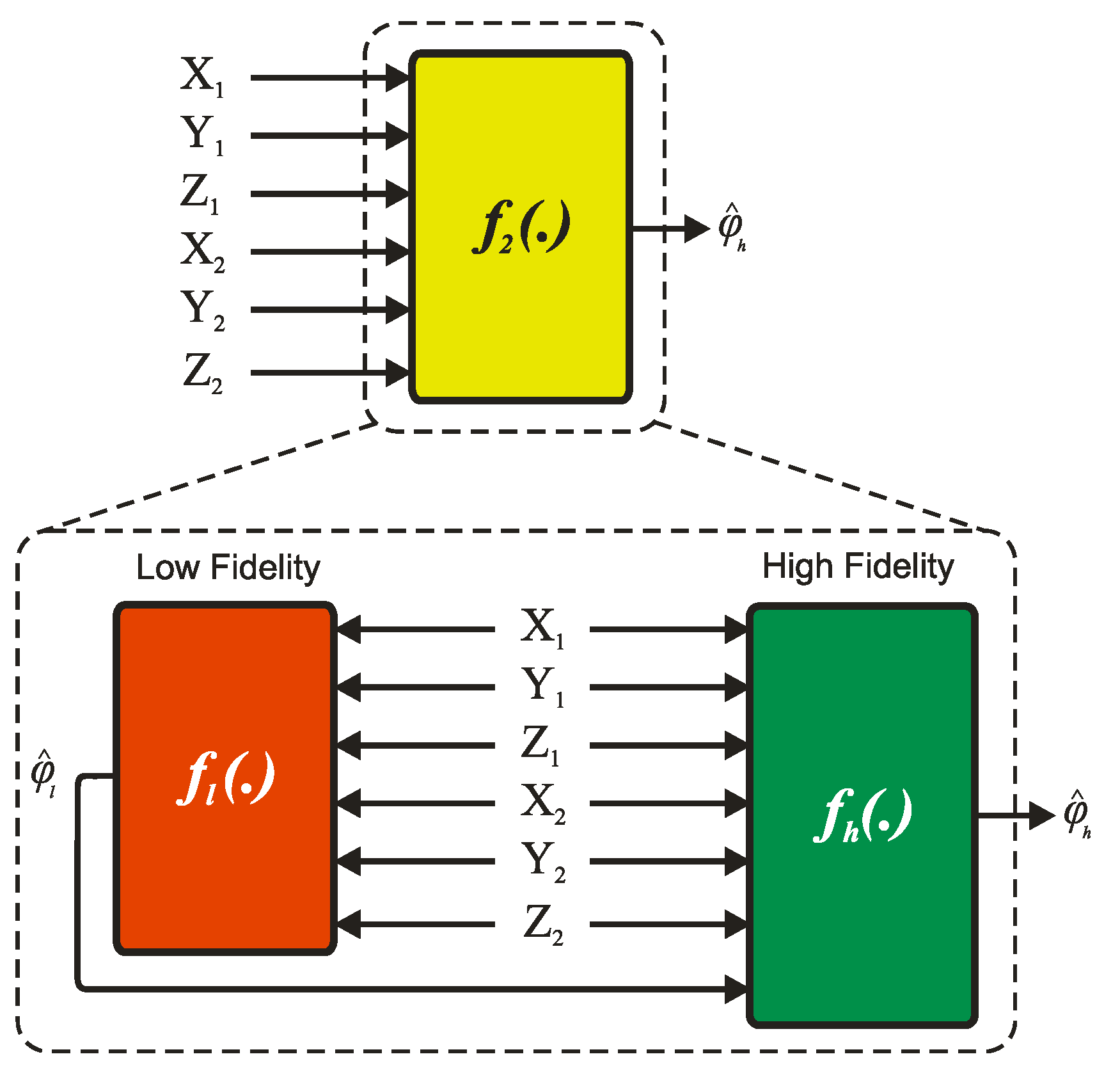
The objective of the proposed model is to identify the f2 functions in Equation (3). A variety of approaches, including neural networks, fuzzy systems, neuro-fuzzy systems, nonparametric Volterra-based models, wavelet models, etc., can be employ to realize f2 [22,23,24,25,26]. In this work, we propose a two-cascade-deep fully connected neural network, as depicted in Figure 2, for the prediction of roll angle in an ICE catheter. The arguments of the f2 functions serve as inputs for the proposed model, with the output being represented by φ. The model comprises two compartments: a low-fidelity model (LF) and a high-fidelity model (HF). All six inputs are inputted into the LF model, which produces a low-fidelity prediction of φ (denoted as ). Subsequently, all six inputs and are inputted into the HF model to produce a more accurate prediction of φ (denoted as ).
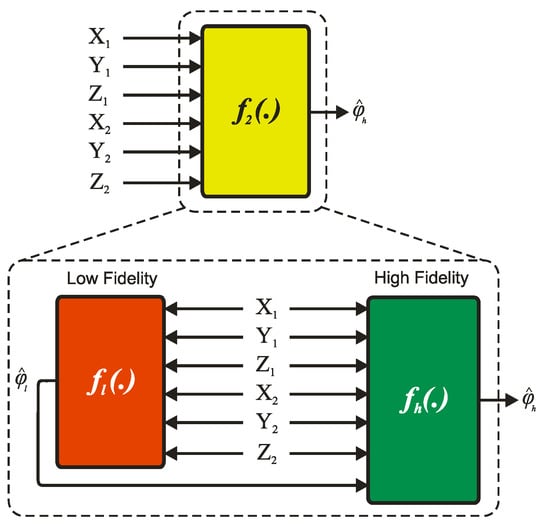
Figure 2.
Proposed LF/HF model block diagram.
The proposed model consists of two fully connected deep neural networks (LF and HF) with five hidden layers, each containing ten neurons. No dropout was applied to the networks during the training process. The LF compartment was trained first to meet one of the early stopping criteria, which include a maximum of 1000 epochs, a minimum performance gradient of 1 × 10−6, zero mean squared error, and six consecutive validation failures. After training the LF model, its output was used as the input to the HF compartment, which was then trained with the same early stopping criteria. This sequential training method resulted in low error; however, it may have resulted in a lack of generalization for rare samples, resulting in a larger standard deviation in absolute error. To address this issue, both training procedures were placed in a while loop, allowing the models to be trained multiple times with different initial random weights to achieve low error and low standard deviation. The Levenberg–Marquardt back-propagation training method was used to train the LF and HF compartments using 70% of the shuffled dataset, and the models were validated using the remaining 20% to minimize overfitting. Finally, the entire LF/HF model was tested on the remaining 10% of the dataset that was not seen during the training process.
2.4. Input Feature Extraction
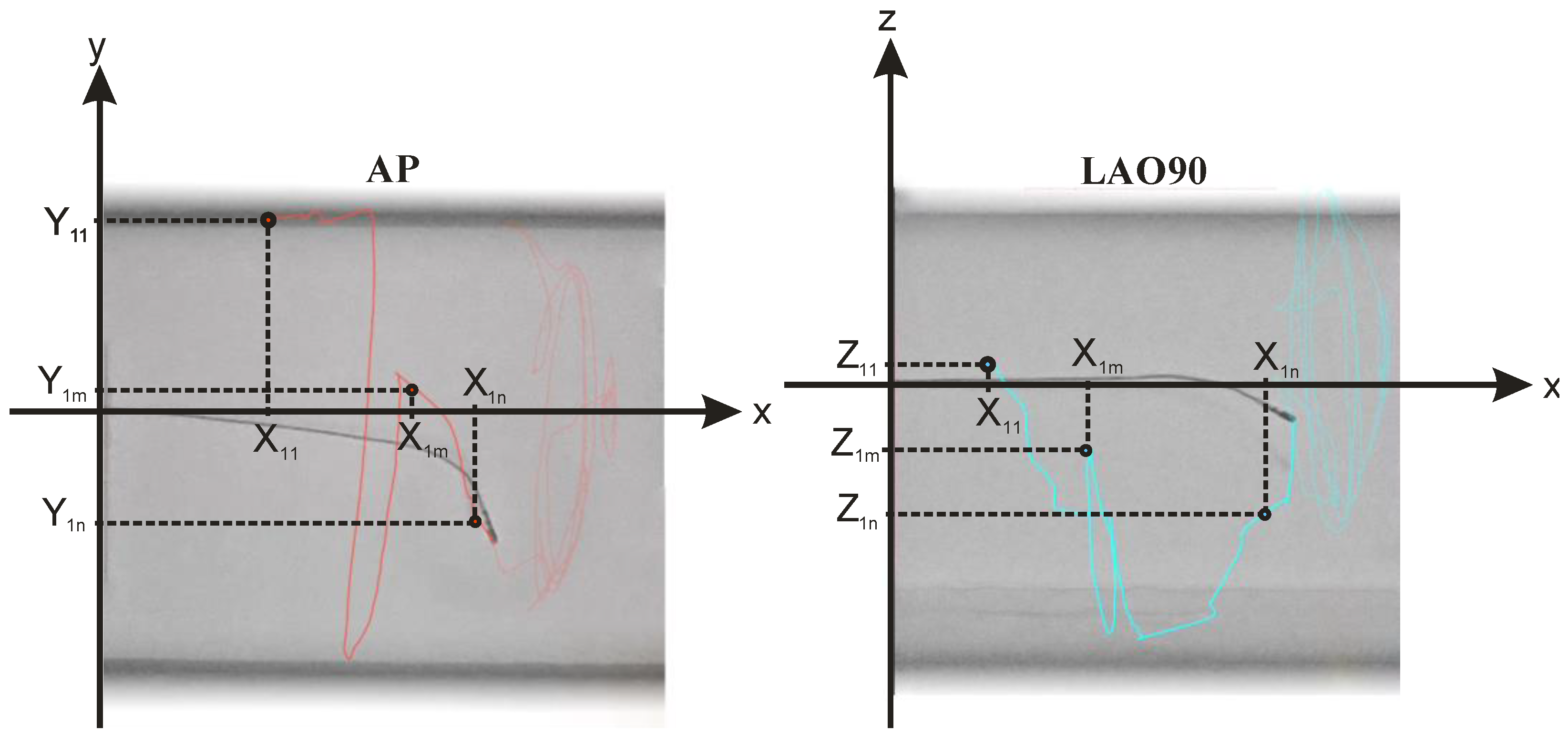
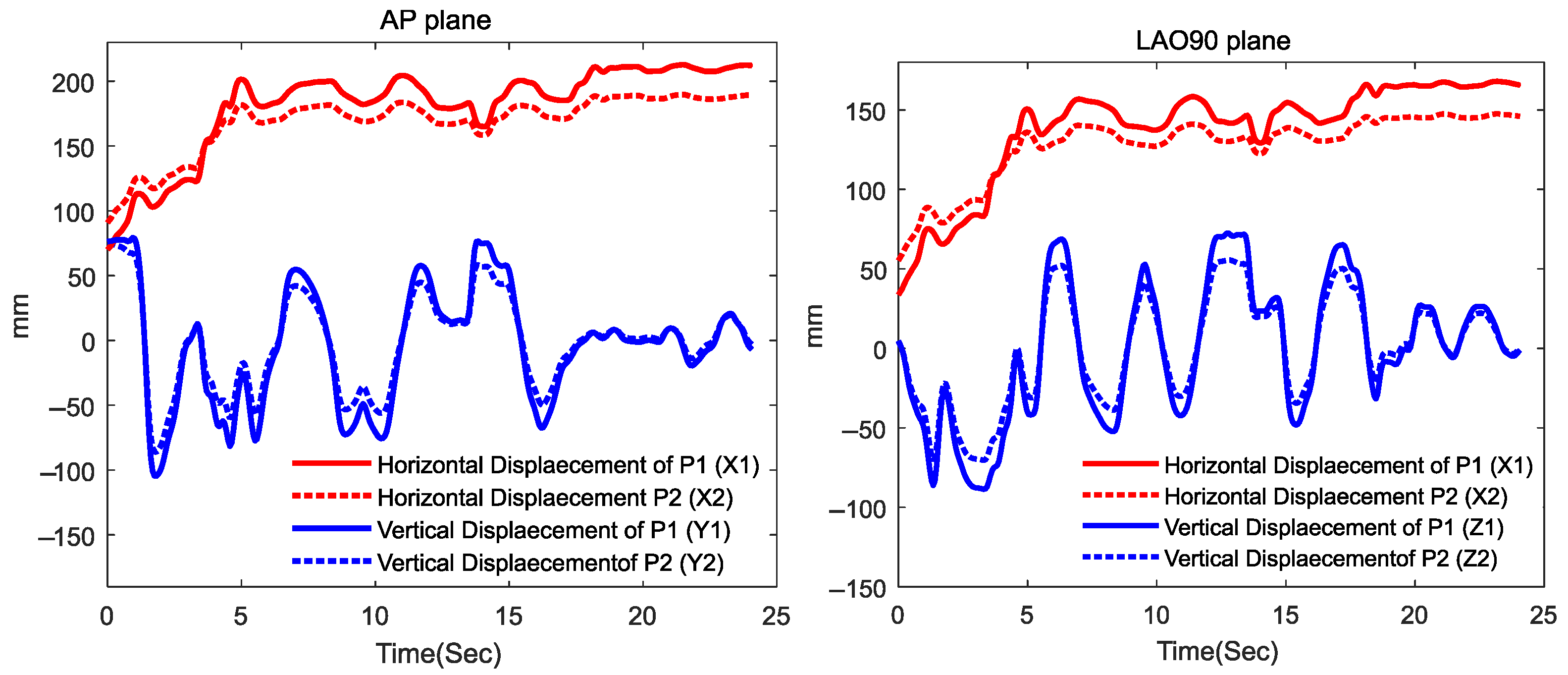
The f2 function, as specified in Equation (3), employs six input features (X1, Y1, Z1, X2, Y2, Z2) derived from both the AP and LAO90 views of the saved fluoroscopy video. The procedure for extracting these features for three samples (the first, mth and nth frames) at point P1 has been depicted in Figure 3. The same process can be applied to point P2. As shown in the figure, vectors for P1 (X1, Y1, Z1) and P2 (X2, Y2, Z2) are comprised of scalar values extracted from the video frames. These scalars can be obtained through custom image processing-based point tracking or utilizing open-source software. In this case, Kinovea open-source software was utilized to automatically track P1 and P2, returning the horizontal and vertical displacement of both points over time. It should be noted that the horizontal displacement in both AP and LAO90 views corresponds to the X axis in the 3D representation of Figure 1c, with one view omitted, as the displacement by the catheter in the two views exhibit nearly 99% correlation. Additionally, vertical displacement in the AP plane represents the Y axis, while vertical displacement in the LAO90 plane represents the Z axis. The extracted input features have been shown in Figure 4.
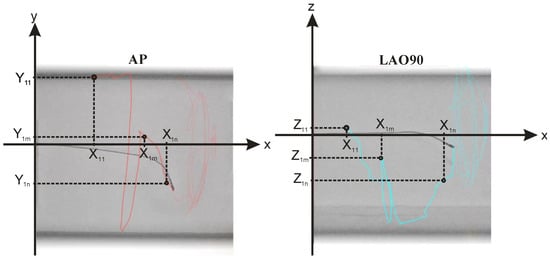
Figure 3.
The procedure for extracting these features for three samples (the first, mth and nth frames) at point P1 of both AP and LAO90 planes. Red and blue lines represent the catheter tip movement.
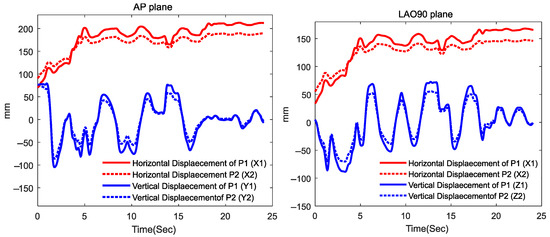
Figure 4.
Horizontal and Vertical Displacement of P1 and P2 in AP and LAO90 planes.
2.5. Output Feature Extraction
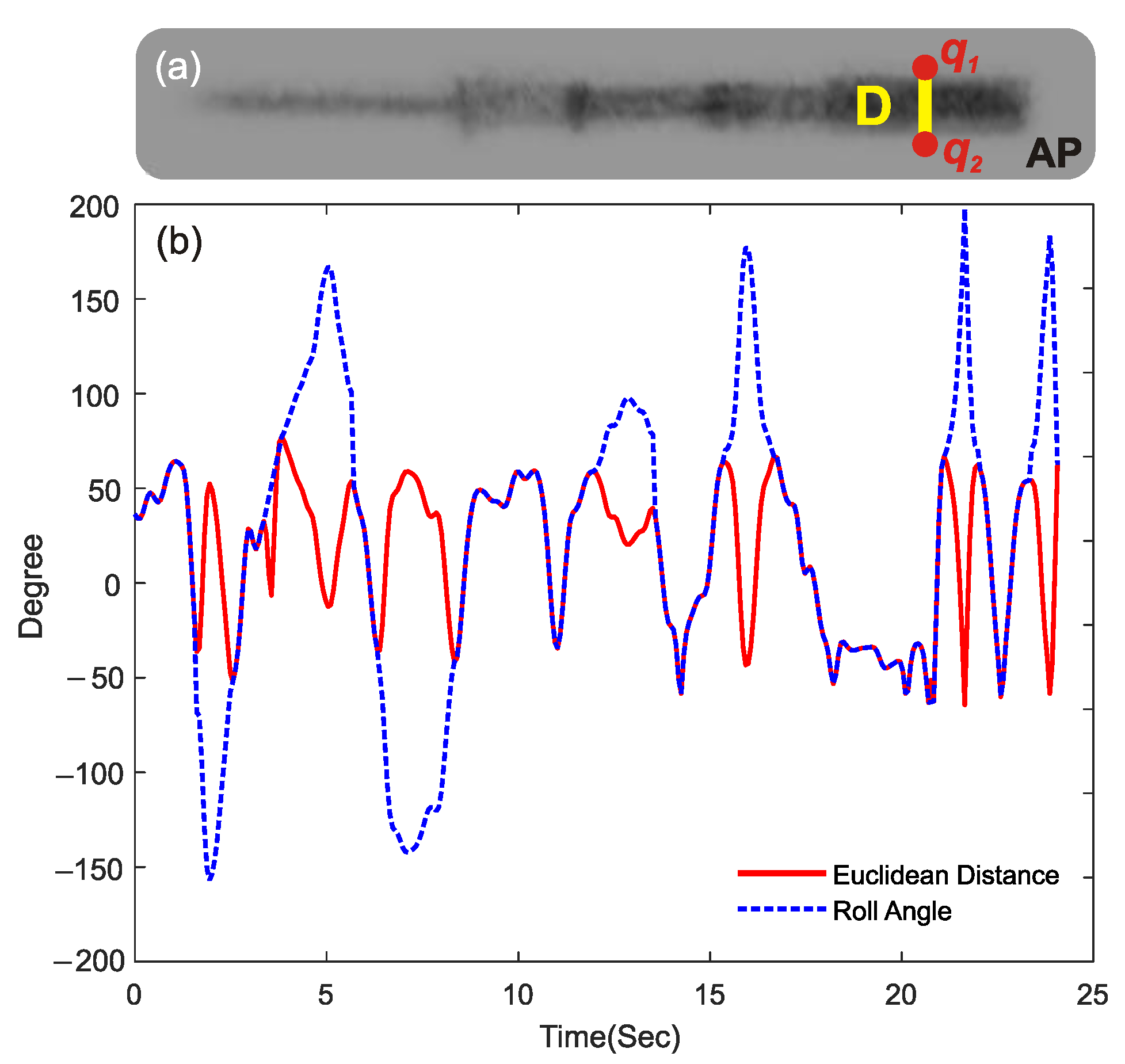
The output feature of the proposed LF/HF model is Roll Angle (φ), which needs to be predicted using the proposed model. To train the model, ground truth data for φ is required, for which the human-in-the-loop labeling (HITLL) method was utilized. The length of the black area of the ICE catheter tip on the AP view can be extracted by calculating the Euclidean distance (D) between two tracked points at the edges of this region (q1, and q2), as shown in Figure 5a. These points can be tracked using the Kinovea open-source software, but with manual effort. This step is performed only once to extract ground truth data and is not required later when using the trained model. A visual inspection of the video in the AP view reveals a direct relationship between D and φ. While D is highly correlated with the magnitude of φ, it does not contain information about its direction, which needs to be manually determined. By analyzing the D graph and observing the recorded video in the AP plane, it can be determined that in some frames, D is equal to φ, while in the rest of the frames, φ is equal to the vertically flipped version of D. As a result, as shown in Figure 5b, the human-in-the-loop feature extraction process involves vertically flipping the D graph in selected samples to obtain ground truth data for φ.
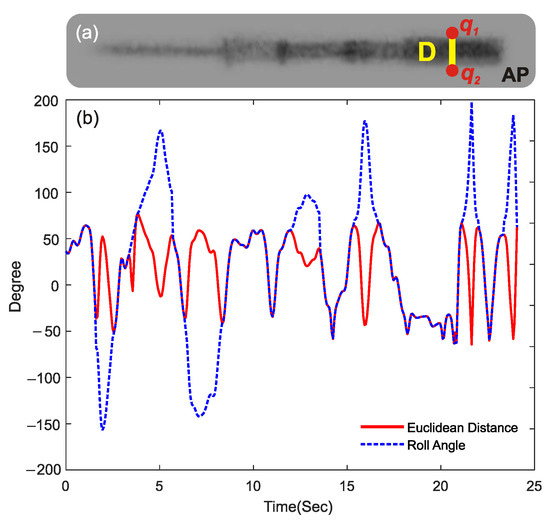
Figure 5.
(a) Euclidean distance (D) of the black width (between points q1 and q2) of the ICE catheter tip on the AP plane. (b) Distance “D” and the extracted Roll angle of the ICE catheter as the ground truth data for the ML model.
3. Results
The proposed model was trained using 360 paired bi-plane fluoroscopic images obtained during mock procedures in the catheterization lab at New York Presbyterian Hospital. These images depict the maneuvering of a VersiSight Pro ICE catheter (Philips) in both AP and LAO90 planes. As was described previously, the data was partitioned into three subsets, with 70% (252 images) allocated as the training set, 20% (72 images) as the validation set, and 10% (36 images) as the testing set. The training and validation sets were utilized during the model training phase, while the testing set was reserved for evaluating the model’s performance at the conclusion of the training phase. To ensure a representative distribution of the ICE catheter’s movement in both the training and testing datasets and prevent overfitting, the data was randomly shuffled prior to being divided into the training and testing sets.
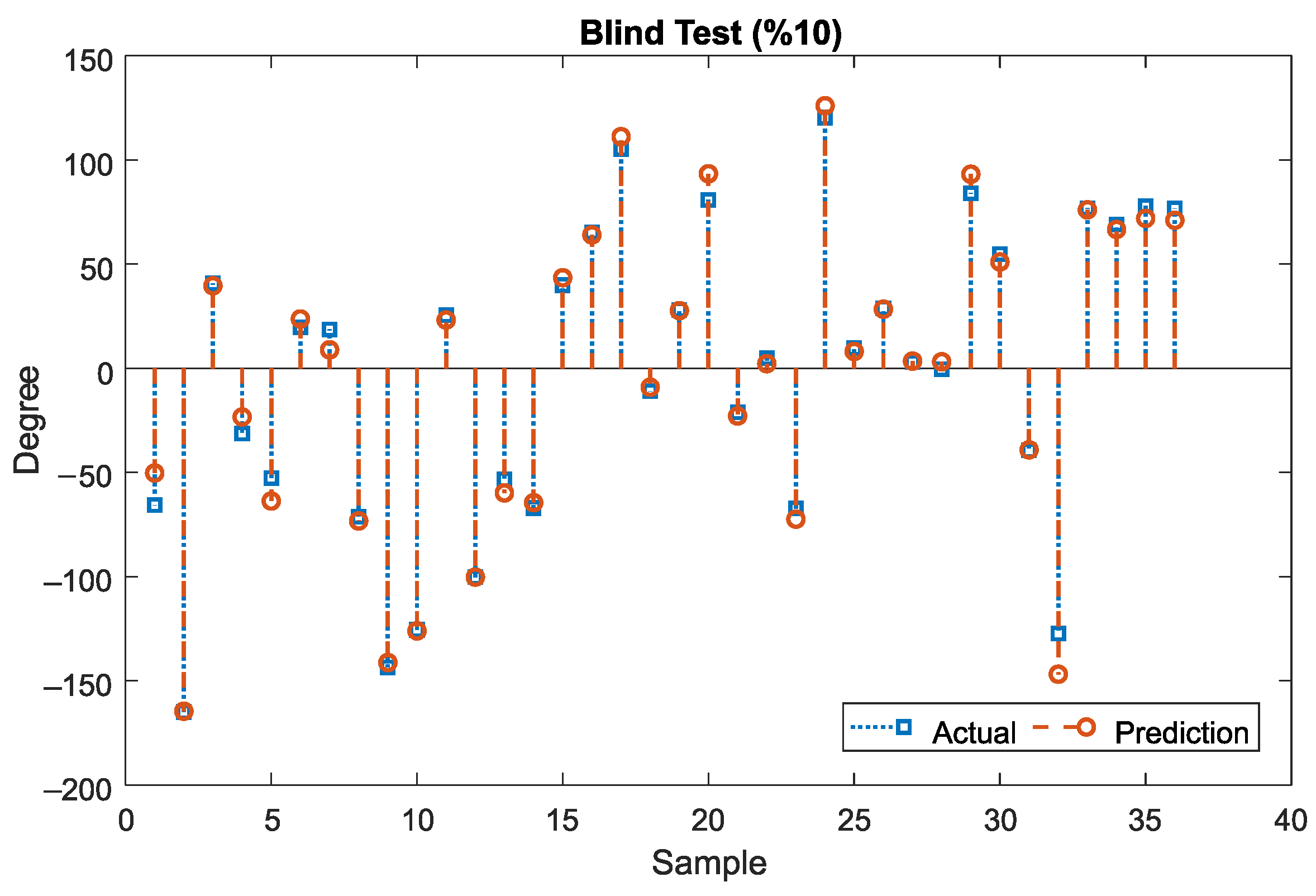
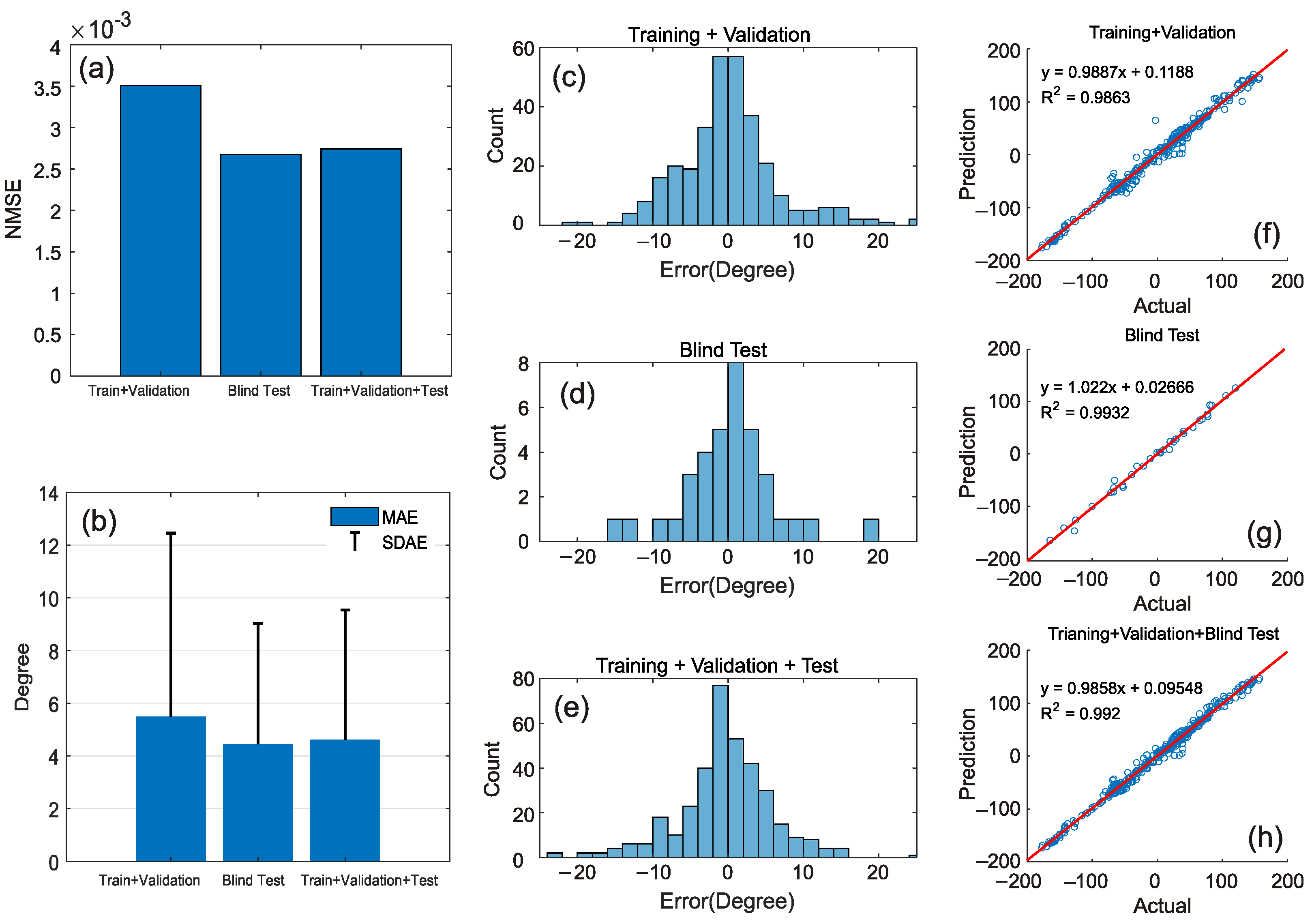
The standard process of system identification consists of three stages: data creation (feature extraction), model determination, and validation [27]. The first two stages are described in Section 2. In this section, the focus is on the validation stage, where the model is tested on a portion of the dataset that it has not seen before. The results, as depicted in Figure 6, indicate that the proposed model closely follows the output with high accuracy. To quantitatively assess the performance of the method, three metrics are selected: Normalized Mean Square Error (NMSE), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), and Standard Deviation of Absolute Error (SDAE). In Figure 7a,b, the values of NMSE, MAE, and SDAE are depicted for three sample groups: Training and Validation samples, Blind test samples, and all samples (Training, Validation, and Blind test). As displayed, the NMSE values are of the order of ~, indicating a low error and a high level of fitting. The MAE values are of the order of ~4.5 degrees of error in the prediction of the roll angle, corresponding to ~1.25% error on average (~4.5/360 degree), which is considered acceptable for practical purposes. Finally, the SDAE values show a standard deviation of less than five degrees, implying that the model is capable of predicting the roll angle of the ICE catheter with a deviation of approximately 1.39% or 5/360 degree, which is also acceptable for surgeons. In Figure 7c–e, the absolute error histograms of the model are displayed for the same three sample groups. All three histograms exhibit a normal distribution centered around zero, indicating that the majority of errors are less than five degrees, which is acceptable for catheterization procedures. To demonstrate the linear correlation between the predicted and actual outputs of the model, a line was fitted over the data for each of the three sample groups in Figure 7f–h. The R-squared values for all three groups are approximately 0.99, indicating a high degree of accuracy in replicating the actual output by the proposed model.
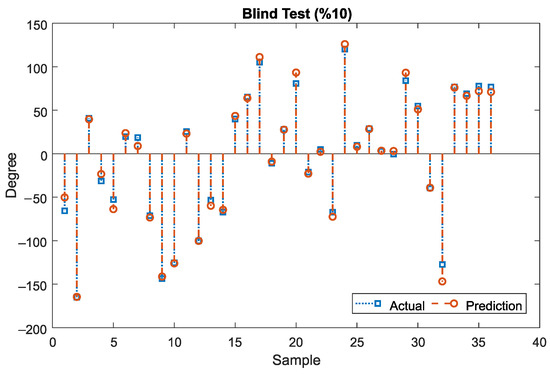
Figure 6.
Actual Prediction of Blind test dataset using the proposed LF/HF ML model.
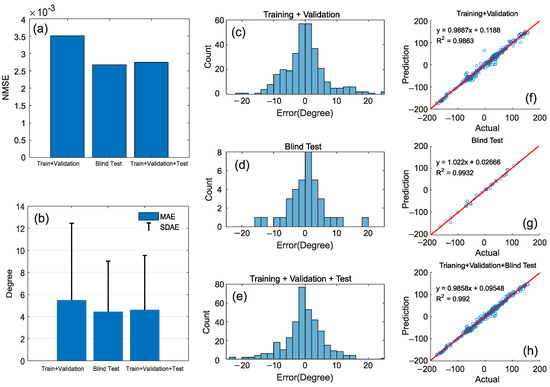
Figure 7.
Error criteria for three sample groups: Training and Validation samples, Blind test samples, and all samples (Training, Validation, and Blind test). (a) Normalized Mean Square Error (NMSE), (b) Mean Absolute Error (MAE), and Standard Deviation of Absolute Error (SDAE), (c–e) Error histograms, (f–h) Linear correlation and R-squared.
4. Conclusions and Future Plan
Catheterization is a procedure used to diagnose and treat various cardiovascular diseases. Intracardiac echocardiography (ICE) is an emerging imaging modality that has gained popularity in cardiac catheterization procedures due to its ability to provide high-resolution images of the heart and its surrounding structures in a minimally invasive manner. However, given its limited field of view, understanding its orientation within the heart is difficult simply from observing the acquired images. Therefore, ICE catheter tracking would be useful as a guide during the procedure. There are two traditional tracking methods for 3D tracking, (1) Electro-Magnetic (EM) sensors and (2) Bi-plane fluoroscopy. EM sensors offer the convenience of portability and real-time tracking, but their accuracy is limited to approximately 5 mm and they are restricted to certain types of catheters. Hence, they may not be well-suited for all cardiac catheterization procedures. For the second option, we have bi-plane fluoroscopy, and although it is more accurate than EM sensors and compatible with all catheter types, it provides only 5-DOF tracking, thereby omitting information about the roll angle of the catheter.
To overcome these limitations, the current study presented a machine learning-based approach to predict the roll angle of an ICE catheter using bi-plane fluoroscopy images to have a full 6 DOF tracking system. The innovative approach of using machine learning models to track the catheter has several advantages over traditional EM sensors. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data and identify complex patterns that may be difficult for traditional sensors to detect. Additionally, this approach does not require any additional hardware, making it a cost-effective solution for catheter tracking.
The results of the study showed that the developed model has a low error rate and a high degree of accuracy with Normalized Mean Square Error values of ~, an average error of ~1.25% with Mean Absolute Error values of ~4.5 degrees, and a standard deviation of less than 5 degrees. Additionally, the model demonstrated a high degree of accuracy with R-squared values of approximately 0.99. While the results of the study are promising, there are some limitations that need to be addressed in future research. Firstly, the model should be trained on clinical images with a greater complexity of background features to improve its accuracy in real-world scenarios. Secondly, it needs to be combined with co-registration algorithms that align the ICE catheter to the patient’s anatomy for VR/AR/MR applications. Finally, a larger dataset that extracts values from images acquired from various machines, sites, and settings needs to be used to validate the model’s generalizability.
The results suggest that the developed model has the potential to provide 6-DOF tracking of an ICE catheter, enhancing the accuracy of VR/AR/MR-based real-time guidance systems that provide visualization and navigation during clinical procedures. This has significant implications for cardiac catheterization procedures, which are increasingly relying on these advanced imaging modalities. Accurate tracking of the catheter during the procedure will not only improve the accuracy of the diagnosis and treatment but also reduce the risks and complications associated with the procedure.
In our future plan, the focus will be on incorporating feature extraction through image analysis of clinical data. The current study’s predictive model employs scalar data obtained via open-source tracking software as its inputs, which does not necessitate feature extraction via image analysis. However, to facilitate the operation of the current model, the team is working on the development of a deep learning-based model that automatically extracts the relevant features from clinical images. As the final goal of this study, multiple modules—including the automatic feature extraction module, predictive model, and VR/AR/MR unit—will be integrated into a real-time 6DOF tracking and visualization system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.M.; Methodology, M.A.; Software, M.A.; Investigation, M.A., A.C. and S.C.W.; Resources, S.C.W.; Data curation, M.A.; Writing—original draft, M.A. and B.M.; Supervision, B.M.; Project administration, B.M.; Funding acquisition, B.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data related to this study can be requested from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank Philips for providing the VeriSight ICE catheter supported by a research grant.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zipfel, P.H. Fundamentals of Six Degrees of Freedom Aerospace Simulation and Analysis in C++, 2nd ed.; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Inc.: Reston, VA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.H.; Kuralbay, Y.; Aitmaganbet, A.; Kamal, M.A.S. Design of a 6-DOF robot manipulator for 3D printed construction. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 49, 1462–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Song, C.; Qian, L.; Liu, W.; Chiu, P.W.; Li, Z. Augmented Reality-Assisted Autonomous View Adjustment of a 6-DOF Robotic Stereo Flexible Endoscope. IEEE Trans. Med. Robot. Bionics 2022, 4, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkaman, T.; Roshanfar, M.; Dargahi, J.; Hooshiar, A. Embedded Six-DoF Force-Torque Sensor for Soft Robots with Learning-based Calibration. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 4204–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermelho, R.; Alexandre, L.A. Grasping and Sorting Cutlery in an Unconstrained Environment with a 6 DoF Robotic Arm and an RGB+D Camera. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Autonomous Robot Systems and Competitions (ICARSC), Santa Maria da Feira, Portugal, 29–30 April 2022; pp. 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rambach, J.; Pagani, A.; Schneider, M.; Artemenko, O.; Stricker, D. 6DoF Object Tracking based on 3D Scans for Augmented Reality Remote Live Support. Computers 2018, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhu, L.; Liu, J.; Song, A. A SLAM-based 6DoF controller with smooth auto-calibration for virtual reality. Vis. Comput. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribo, M.; Pinz, A.; Fuhrmann, A.L. A new optical tracking system for virtual and augmented reality applications. In Proceedings of the IMTC 2001, 18th IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Rediscovering Measurement in the Age of Informatics (Cat. No. 01CH 37188), Budapest, Hungary, 21–23 May 2001; Volume 3, pp. 1932–1936. [Google Scholar]
- Rabbi, I.; Ullah, S. A survey on augmented reality challenges and tracking. Acta Graph. Znan. Časopis Tisk. Graf. Komun. 2013, 24, 29–46. [Google Scholar]
- Falk, V.; Mourgues, F.; Adhami, L.; Jacobs, S.; Thiele, H.; Nitzsche, S.; Mohr, F.W.; Coste-Manière, È. Cardio Navigation: Planning, Simulation, and Augmented Reality in Robotic Assisted Endoscopic Bypass Grafting. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2005, 79, 2040–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, R.; Tscholl, M.; Wang, S.; Johnson, E. Enhancing learning and engagement through embodied interaction within a mixed reality simulation. Comput. Educ. 2016, 95, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabinia, M.; Caprio, A.; Fenster, T.B.; Mosadegh, B. Single Evaluation of Use of a Mixed Reality Headset for Intra-Procedural Image-Guidance during a Mock Laparoscopic Myomectomy on an Ex-Vivo Fibroid Model. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.J.; Torabinia, M.; Dhrif, H.; Caprio, A.; Liu, J.; Wong, S.C.; Mosadegh, B. Development of a Hybrid Training Simulator for Structural Heart Disease Interventions. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 2000109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Al’Aref, S.J.; Singh, G.; Caprio, A.; Moghadam, A.A.; Jang, S.J.; Wong, S.C.; Min, J.K.; Dunham, S.; Mosadegh, B. An augmented reality system for image guidance of transcatheter procedures for structural heart disease. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currie, M.E.; McLeod, A.J.; Moore, J.T.; Chu, M.W.; Patel, R.; Kiaii, B.; Peters, T.M. Augmented Reality System for Ultrasound Guidance of Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Innovations (Phila) 2016, 11, 31–39; discussion 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.A.; Dworakowski, R.; Bhan, A.; Delithanasis, I.; Hancock, J.; MacCarthy, P.A.; Wendler, O.; Thomas, M.R.; Monaghan, M.J. Real-time three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography adds value to transcatheter aortic valve implantation. J Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2013, 26, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanchahal, S.; Arjomandi Rad, A.; Naruka, V.; Chacko, J.; Liu, G.; Afoke, J.; Miller, G.; Malawana, J.; Punjabi, P. Mitral valve surgery assisted by virtual and augmented reality: Cardiac surgery at the front of innovation. Perfusion 2022, 2676591221137480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ender, J.; Končar-Zeh, J.; Mukherjee, C.; Jacobs, S.; Borger, M.A.; Viola, C.; Gessat, M.; Fassl, J.; Mohr, F.W.; Falk, V. Value of augmented reality-enhanced transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) for determining optimal annuloplasty ring size during mitral valve repair. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2008, 86, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torabinia, M.; Caprio, A.; Jang, S.J.; Ma, T.; Tran, H.; Mekki, L.; Chen, I.; Sabuncu, M.; Wong, S.C.; Mosadegh, B. Deep learning-driven catheter tracking from bi-plane X-ray fluoroscopy of 3D printed heart phantoms. Mini-Invasive Surg. 2021, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enriquez, A.; Saenz, L.C.; Rosso, R.; Silvestry, F.E.; Callans, D.; Marchlinski, F.E.; Garcia, F. Use of Intracardiac Echocardiography in Interventional Cardiology. Circulation 2018, 137, 2278–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Clark, J.W., Jr.; Khoury, D.S. Speckle tracking in intracardiac echocardiography for the assessment of myocardial deformation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 56, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanzadeh, F.; Annabestani, M.; Moghimi, S. Continuous emotion recognition during music listening using EEG signals: A fuzzy parallel cascades model. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 101, 107028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, H.K.; Dash, P.K.; Rath, N.P. NARX model based nonlinear dynamic system identification using low complexity neural networks and robust H∞ filter. Appl. Soft Comput. 2013, 13, 3324–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annabestani, M.; Naghavi, N.; Nejad, M.M. Nonautoregressive Nonlinear Identification of IPMC in Large Deformation Situations Using Generalized Volterra-Based Approach. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2016, 65, 2866–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babsuka, R.; Verbruggen, H. Neuro-Fuzzy methods for nonlinear system identification. Annu. Rev. Control 2003, 27, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annabestani, M.; Naghavi, N. Nonuniform deformation and curvature identification of ionic polymer metal composite actuators. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljung, L. System Identification Theory for Users; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).