Use of Silybum marianum Extract and Bio-Ferment for Biodegradable Cosmetic Formulations to Enhance Antioxidant Potential and Effect of the Type of Vehicle on the Percutaneous Absorption and Skin Retention of Silybin and Taxifolin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Plant Materials
2.3. The Milk Thistle Bio-Ferment and Extract Preparation
2.4. Hydrogel (H-B, H-E) and Organogel (O-B, O-E) Preparation
2.5. The Stability of Hydrogels and Organogels
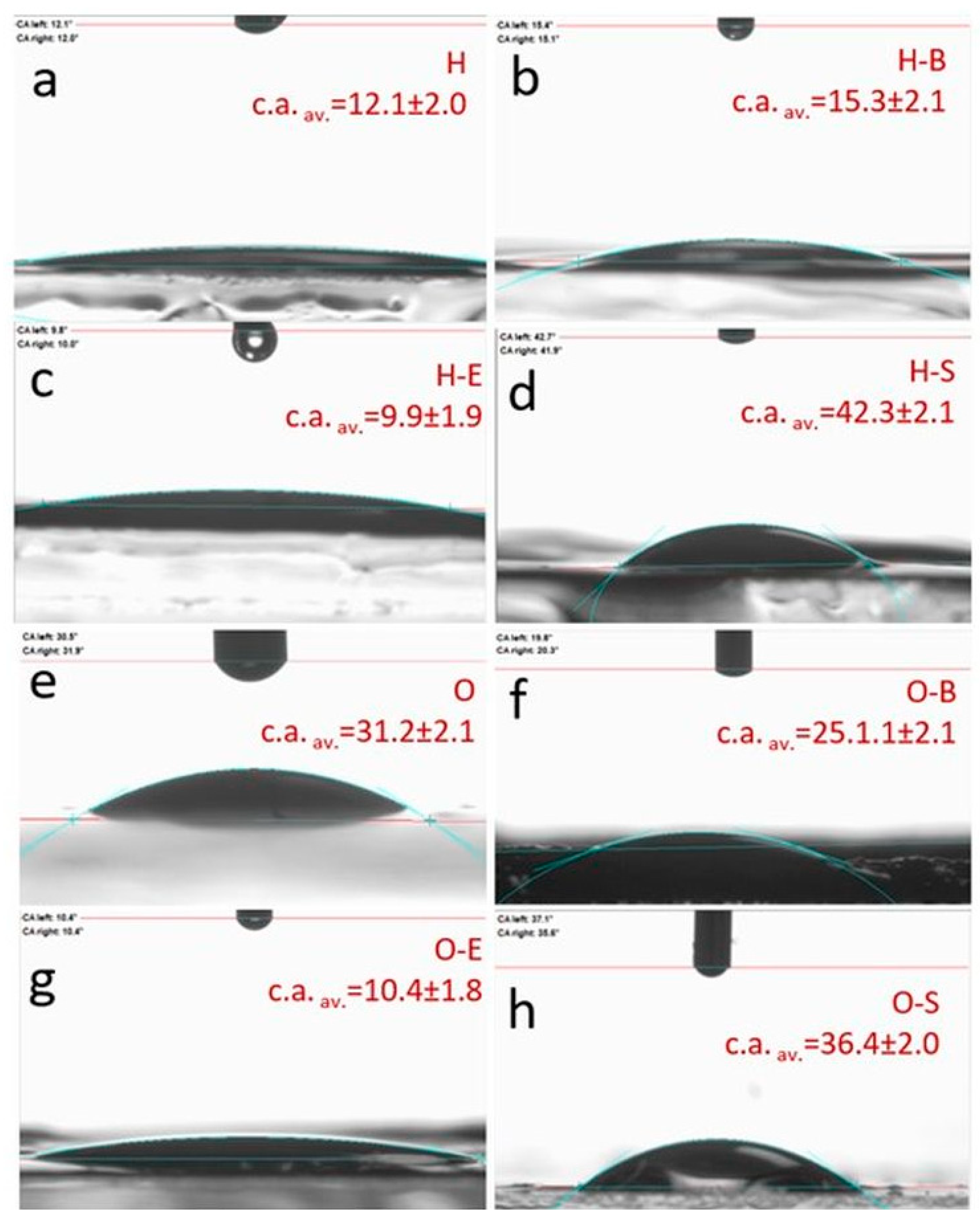
2.6. Wettability of Hydrogel and Organogel
2.7. Antioxidant Activity and Total Polyphenos Content of Silymarin, Bio-Ferment, and Extract
2.7.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
2.7.2. ABST Method
2.7.3. FRAP Method
2.7.4. Total Polyphenol Content (TPC)
2.7.5. Chelating Activity of Fe2+
2.7.6. Acidity
2.8. The Skin Permeability of Hydrogels and Organogels and the Cumulative Mass of Active Compounds
2.9. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.10. Elemental Analysis
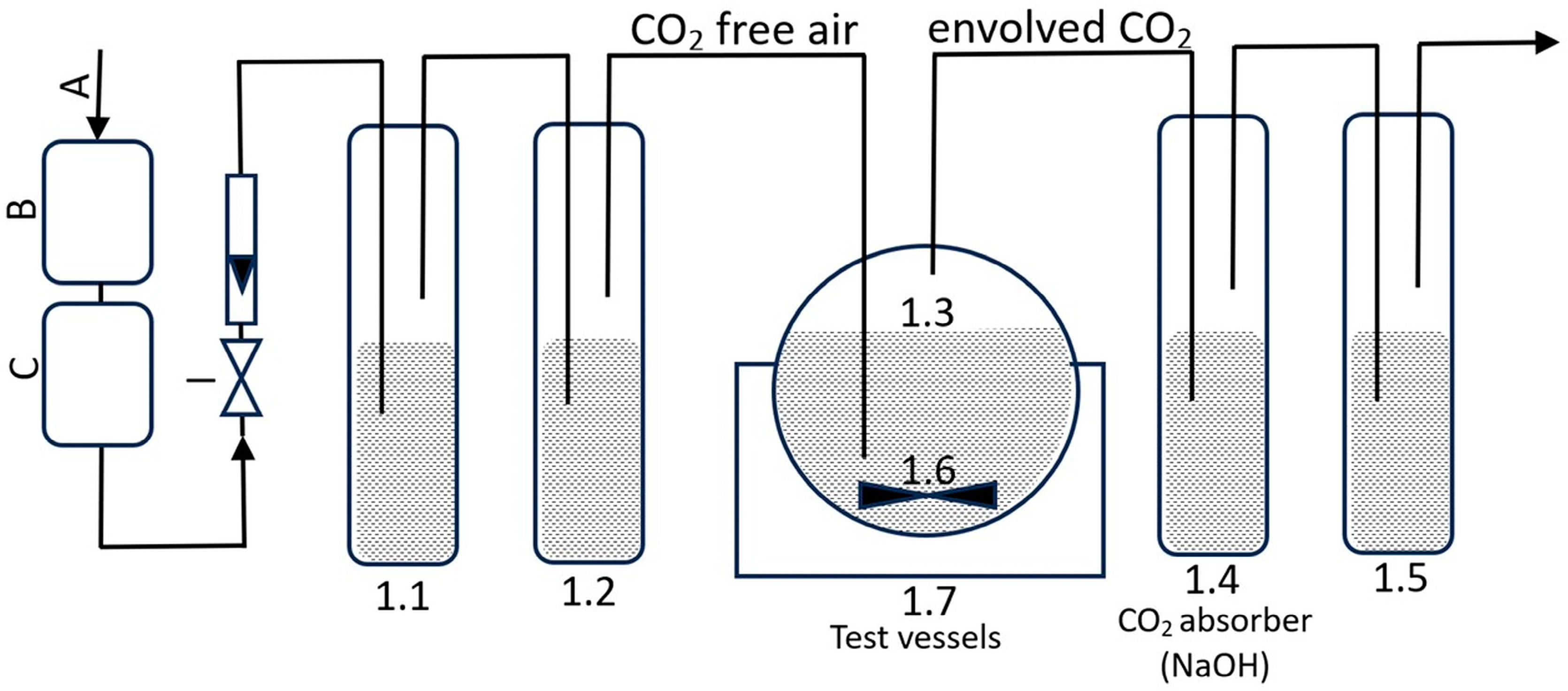
2.11. Biodegradation of Formulations by Bacterial Cultures
2.11.1. The Test Medium and Origin of Samples of Active Sludge
2.11.2. Method for Determining the Potential for Aerobic Biodegradation of Formulations
3 NaHCO3 + H3PO4 = CO2 + Na3PO4 + 3 H2O
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Contact Angle
3.2. Activity, Fe2+ Chelating Activity, Antioxidant Activity, and Total Polyphenol Content
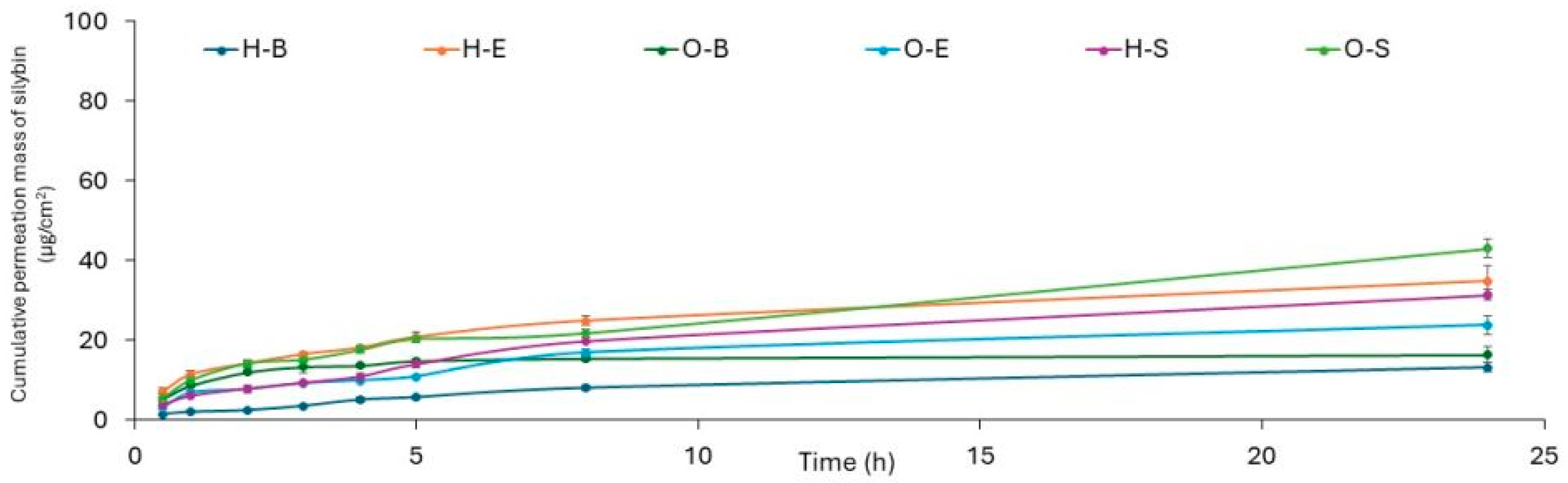
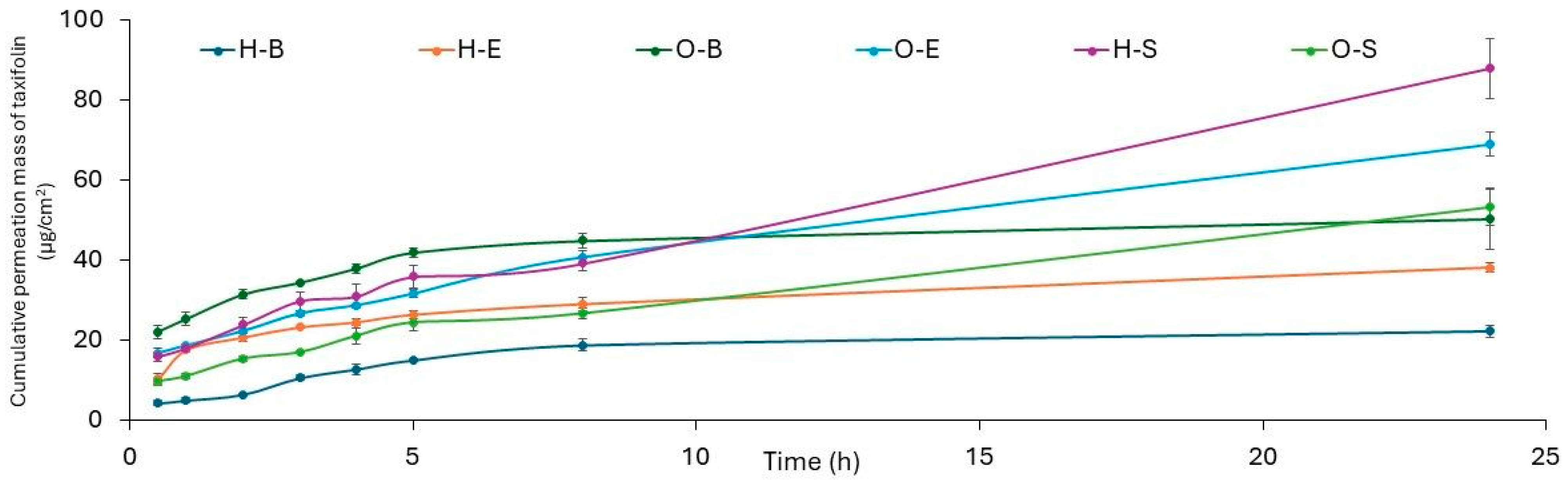
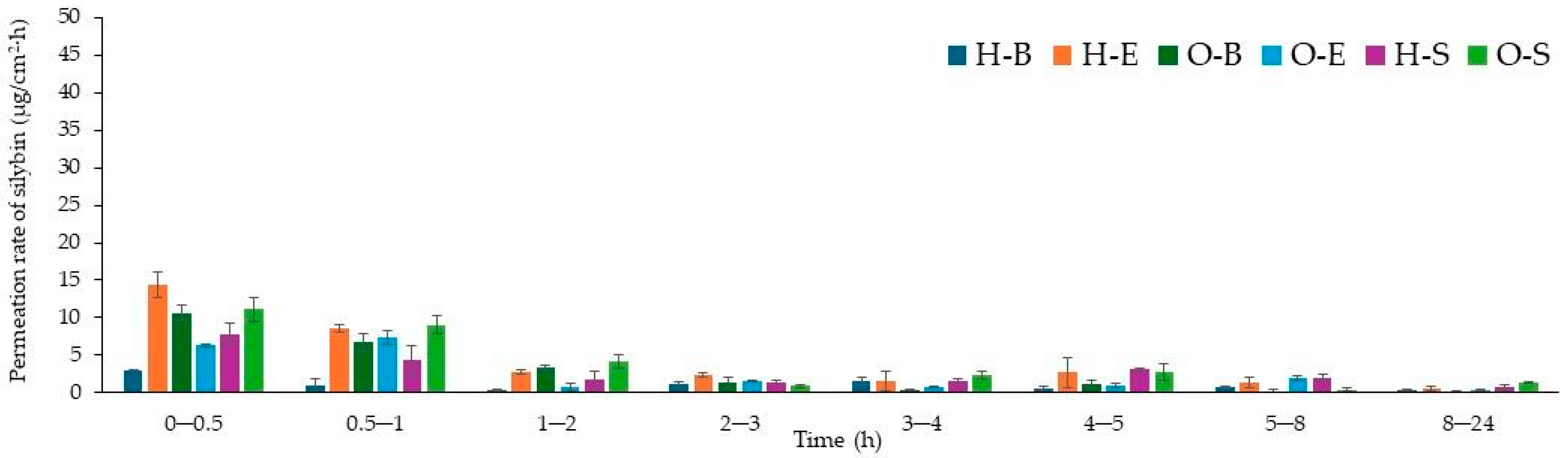
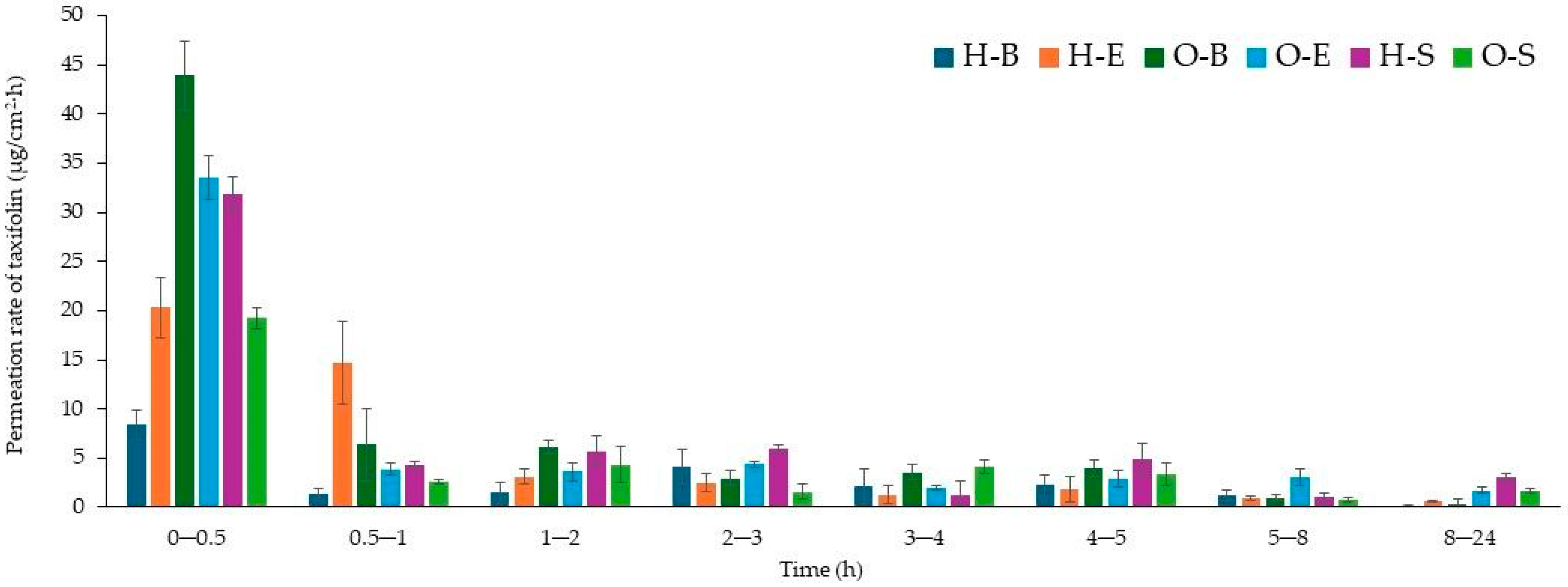
3.3. Penetration Studies
3.4. Elemental Analysis of Formulations
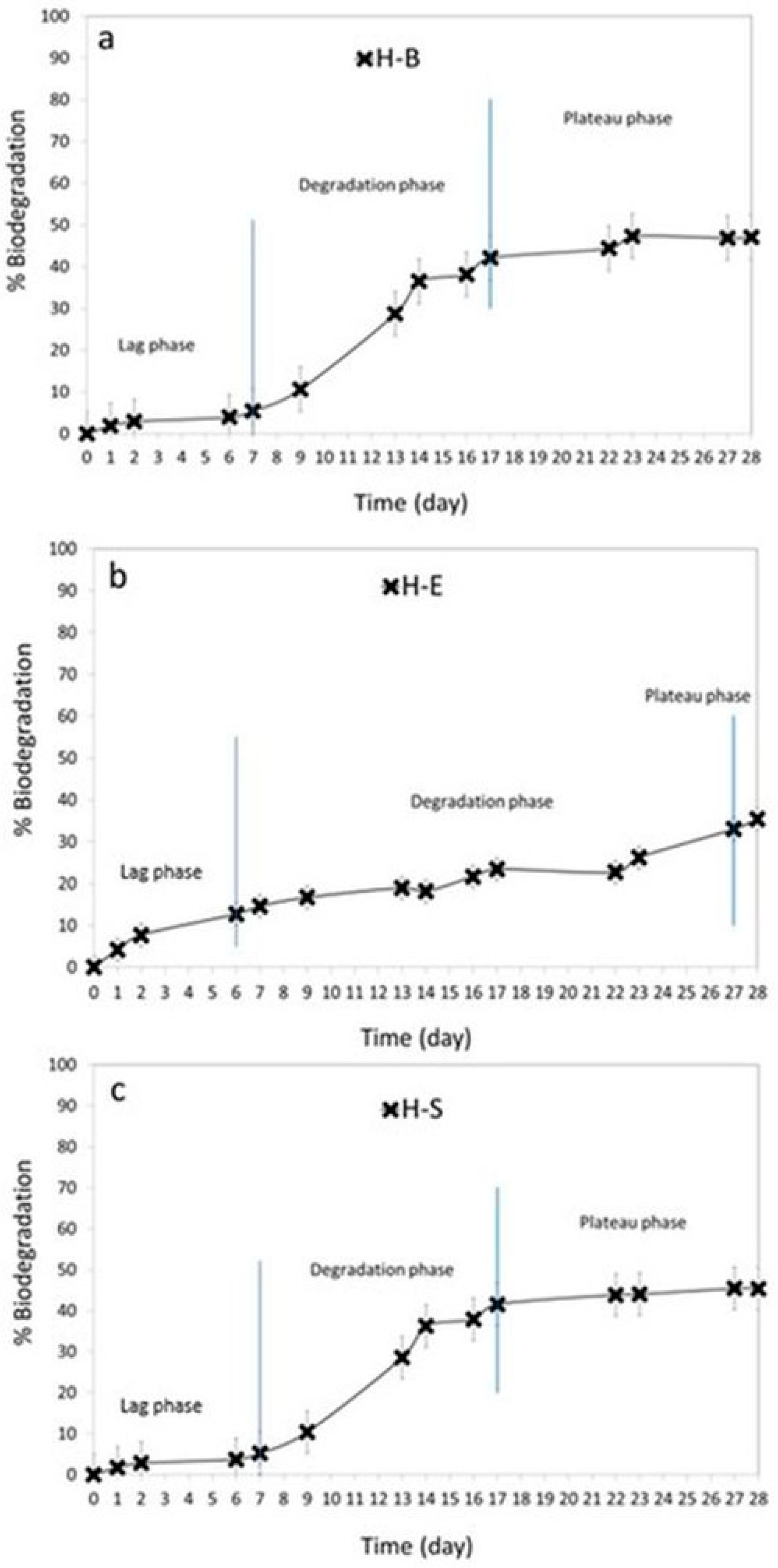
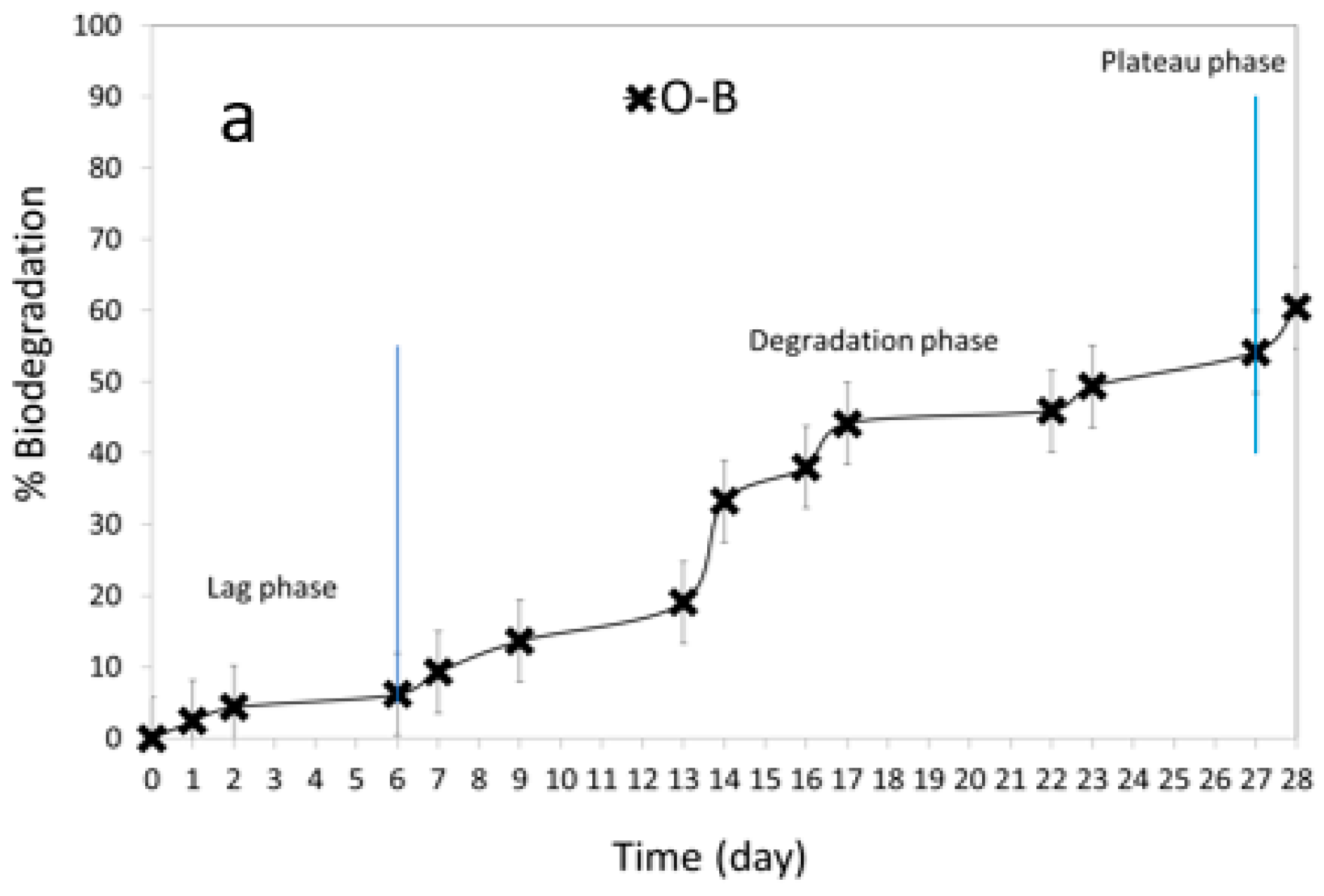
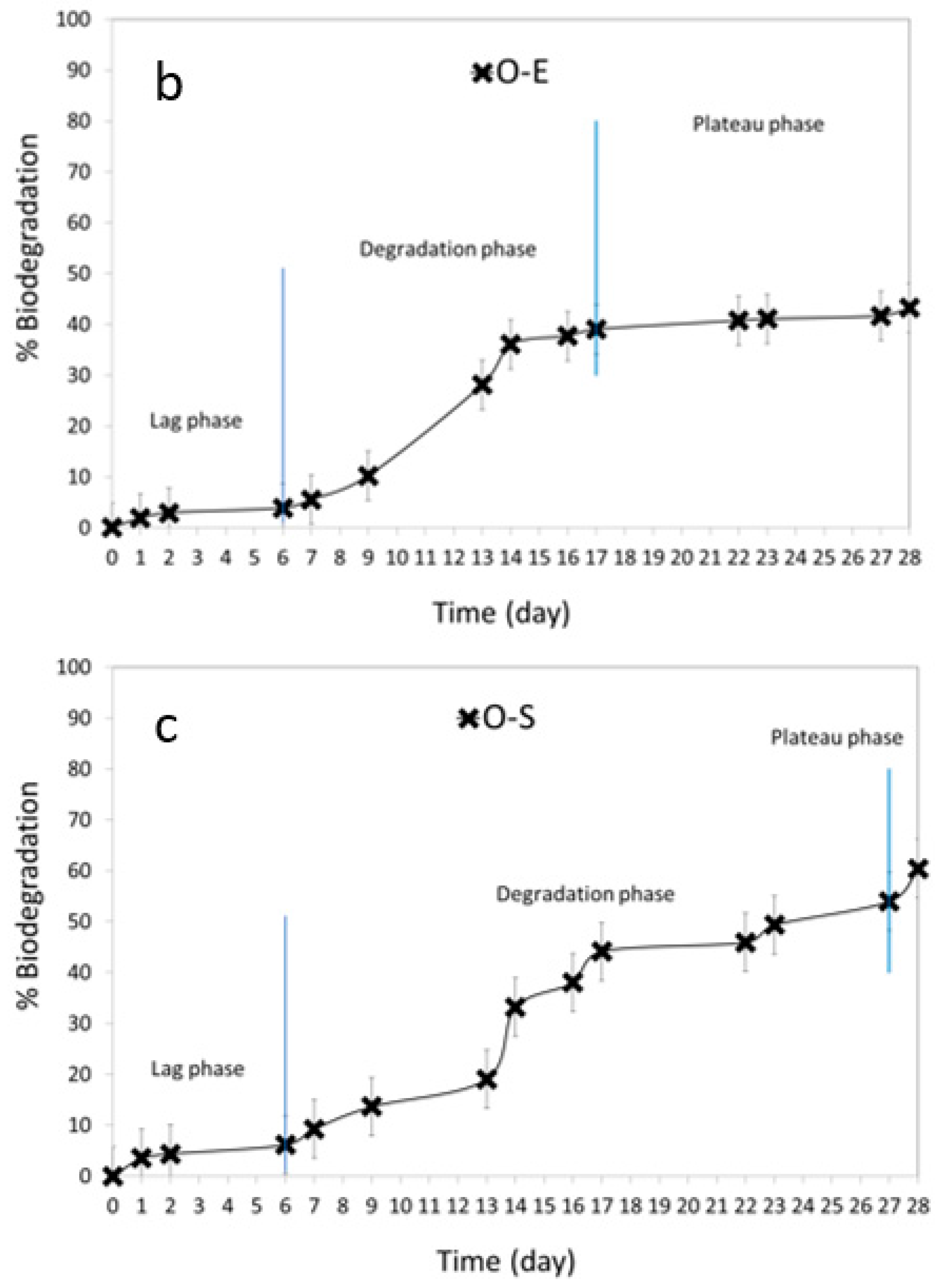
3.5. Biodegradation Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reihani, S.F.S.; Khosravi-Darani, K. Influencing Factors on Single-Cell Protein Production by Submerged Fermentation: A Review. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, H.T.; Moon, J.-Y.; Lee, Y.-C. Natural Antioxidants from Plant Extracts in Skincare Cosmetics: Recent Applications, Challenges and Perspectives. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yang, K.; Zhan, L.; Lu, T.; Chen, X.; Cai, X.; Zhou, C.; Li, H.; Qian, L.; Lv, G.; et al. Optimization of Flavonoid Extraction in Dendrobium Officinale Leaves and Their Inhibitory Effects on Tyrosinase Activity. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2019, 2019, 7849198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziemlewska, A.; Nizioł-Łukaszewska, Z.; Bujak, T.; Zagórska-Dziok, M.; Wójciak, M.; Sowa, I. Effect of Fermentation Time on the Content of Bioactive Compounds with Cosmetic and Dermatological Properties in Kombucha Yerba Mate Extracts. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Toalá, J.E.; Garcia-Varela, R.; Garcia, H.S.; Mata-Haro, V.; González-Córdova, A.F.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B.; Hernández-Mendoza, A. Postbiotics: An Evolving Term within the Functional Foods Field. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 75, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majchrzak, W.; Motyl, I.; Śmigielski, K. Biological and Cosmetical Importance of Fermented Raw Materials: An Overview. Molecules 2022, 27, 4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Rivero, C.; López-Gómez, J.P. Unlocking the Potential of Fermentation in Cosmetics: A Review. Fermentation 2023, 9, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.M.; Marto, J.M. A Sustainable Life Cycle for Cosmetics: From Design and Development to Post-Use Phase. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2023, 35, 101178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.-Y.; Yang, H.-J.; Moon, H.-I.; Cho, Y.-S. Inhibitory Effect and Mechanism on Melanogenesis from Fermented Herbal Composition for Medical or Food Uses. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijak, M. Silybin, a Major Bioactive Component of Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum L. Gaernt.)—Chemistry, Bioavailability, and Metabolism. Molecules 2017, 22, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailović, V.; Srećković, N.; Popović-Djordjević, J.B. Silybin and Silymarin: Phytochemistry, Bioactivity, and Pharmacology. In Handbook of Dietary Flavonoids; Xiao, J., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1–45. ISBN 978-3-030-94753-8. [Google Scholar]
- Raclariu-Manolică, A.C.; Socaciu, C. Detecting and Profiling of Milk Thistle Metabolites in Food Supplements: A Safety-Oriented Approach by Advanced Analytics. Metabolites 2023, 13, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, C.S.; Holečková, V.; Petrásková, L.; Biedermann, D.; Valentová, K.; Buchta, M.; Křen, V. The Silymarin Composition… and Why Does It Matter??? Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, N.; Balwierz, R.; Biernat, P.; Ochędzan-Siodłak, W.; Lipok, J. Natural Ingredients of Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems as Permeation Enhancers of Active Substances through the Stratum Corneum. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 3278–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevinç-Özakar, R.; Seyret, E.; Özakar, E.; Adıgüzel, M.C. Nanoemulsion-Based Hydrogels and Organogels Containing Propolis and Dexpanthenol: Preparation, Characterization, and Comparative Evaluation of Stability, Antimicrobial, and Cytotoxic Properties. Gels 2022, 8, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sannino, A.; Demitri, C.; Madaghiele, M. Biodegradable Cellulose-Based Hydrogels: Design and Applications. Materials 2009, 2, 353–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceddu, R.; Dinolfo, L.; Carrubba, A.; Sarno, M.; Di Miceli, G. Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum L.) as a Novel Multipurpose Crop for Agriculture in Marginal Environments: A Review. Agronomy 2022, 12, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillessen, A.; Schmidt, H.H.-J. Silymarin as Supportive Treatment in Liver Diseases: A Narrative Review. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 1279–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Ghosh, T.; Jain, S. Silymarin—A Review on the Pharmacodynamics and Bioavailability Enhancement Approaches. J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2010, 2, 348–355. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, S.; Kohli, K.; Ahsan, W. Bioavailability Augmentation of Silymarin Using Natural Bioenhancers: An in Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 58, e20160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, R.; Seidavi, A.; Bouyeh, M. A Review on the Mechanisms of the Effect of Silymarin in Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) on Some Laboratory Animals. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 8, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Kim, J.; Lee, M.Y.; Sudhanva, M.S.; Devakumar, S.; Jeon, Y.J. Silymarin Inhibits Cytokine-Stimulated Pancreatic Beta Cells by Blocking the ERK1/2 Pathway. Biomol. Ther. 2014, 22, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, T.M.; Mijaljica, D.; Townley, J.P.; Spada, F.; Harrison, I.P. Vehicles for Drug Delivery and Cosmetic Moisturizers: Review and Comparison. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, S.; Fitaihi, R.; Abdelhakim, H.E. Advances in Formulation and Manufacturing Strategies for the Delivery of Therapeutic Proteins and Peptides in Orally Disintegrating Dosage Forms. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 182, 106374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adepu, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Controlled Drug Delivery Systems: Current Status and Future Directions. Molecules 2021, 26, 5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, J.L.; Wyant, W.A.; Abdo Abujamra, B.; Kirsner, R.S.; Jozic, I. Diabetic Wound-Healing Science. Medicina 2021, 57, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkani-Esfahani, S.; Emami, Y.; Esmaeilzadeh, E.; Bagheri, F.; Namazi, M.R.; Keshtkar, M.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Noorafshan, A. Silymarin Enhanced Fibroblast Proliferation and Tissue Regeneration in Full Thickness Skin Wounds in Rat Models: A Stereological Study. J. Saudi Soc. Dermatol. Dermatol. Surg. 2013, 17, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuch, E.; Ossowicz-Rupniewska, P.; Klebeko, J.; Janus, E. Biodegradation of L-Valine Alkyl Ester Ibuprofenates by Bacterial Cultures. Materials 2021, 14, 3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, P. Single Cell Protein Production from Lignocellulosic Biomass; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; ISBN 978-981-10-5872-1. [Google Scholar]
- Wijaya, H.; Sasaki, K.; Kahar, P.; Yopi, Y.; Kawaguchi, H.; Sazuka, T.; Ogino, C.; Prasetya, B.; Kondo, A. Repeated Ethanol Fermentation from Membrane-Concentrated Sweet Sorghum Juice Using the Flocculating Yeast Saccharomyces Cerevisiae F118 Strain. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yang, T.; Shen, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L. Study on the Properties of Dendrobiumofficinale Fermentation Broth as Functional Raw Material of Cosmetics. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuch, E.; Nowak, A.; Günther, A.; Pełech, R.; Kucharski, Ł.; Duchnik, W.; Klimowicz, A. The Effect of Cream and Gel Vehicles on the Percutaneous Absorption and Skin Retention of a New Eugenol Derivative With Antioxidant Activity. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 658381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Zagórska-Dziok, M.; Ossowicz-Rupniewska, P.; Makuch, E.; Duchnik, W.; Kucharski, Ł.; Adamiak-Giera, U.; Prowans, P.; Czapla, N.; Bargiel, P.; et al. Epilobium angustifolium L. Extracts as Valuable Ingredients in Cosmetic and Dermatological Products. Molecules 2021, 26, 3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makuch, E.; Nowak, A.; Günther, A.; Pełech, R.; Kucharski, Ł.; Duchnik, W.; Klimowicz, A. Enhancement of the Antioxidant and Skin Permeation Properties of Eugenol by the Esterification of Eugenol to New Derivatives. AMB Expr. 2020, 10, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucharski, Ł.; Cybulska, K.; Kucharska, E.; Nowak, A.; Pełech, R.; Klimowicz, A. Biologically Active Preparations from the Leaves of Wild Plant Species of the Genus Rubus. Molecules 2022, 27, 5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamać, M.; Pegg, R.B. Limitations of the Tetramethylmurexide Assay for Investigating the Fe(II) Chelation Activity of Phenolic Compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6425–6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.A.; Piyatida, P.; da Silva, J.A.T.; Fujita, M. Molecular Mechanism of Heavy Metal Toxicity and Tolerance in Plants: Central Role of Glutathione in Detoxification of Reactive Oxygen Species and Methylglyoxal and in Heavy Metal Chelation. J. Bot. 2012, 2012, e872875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellawell, J.M.; Abel, R. A Rapid Volumetric Method for the Analysis of the Food of Fishes. J. Fish Biol. 1971, 3, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, E.; Xiao, M.; Chen, C.; Xu, W. Enhanced Chemical and Biological Activities of a Newly Biosynthesized Eugenol Glycoconjugate, Eugenol α-d-Glucopyranoside. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Cybulska, K.; Makuch, E.; Kucharski, Ł.; Różewicka-Czabańska, M.; Prowans, P.; Czapla, N.; Bargiel, P.; Petriczko, J.; Klimowicz, A. In Vitro Human Skin Penetration, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity of Ethanol-Water Extract of Fireweed (Epilobium angustifolium L.). Molecules 2021, 26, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, J.M.; Putnik, P.; Bursać Kovačević, D.; Petrović, M.; Munekata, P.E.; Gómez, B.; Marszałek, K.; Roohinejad, S.; Barba, F.J. Chapter 4—Silymarin Compounds: Chemistry, Innovative Extraction Techniques and Synthesis. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Bioactive Natural Products; Atta-Ur-Rahman, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 64, pp. 111–130. [Google Scholar]
- Aiken, A.C.; DeCarlo, P.F.; Jimenez, J.L. Elemental Analysis of Organic Species with Electron Ionization High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 8350–8358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmowafy, M.; Viitala, T.; Ibrahim, H.M.; Abu-Elyazid, S.K.; Samy, A.; Kassem, A.; Yliperttula, M. Silymarin Loaded Liposomes for Hepatic Targeting: In Vitro Evaluation and HepG2 Drug Uptake. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 50, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, J.M.; Hotchkiss, J.H. Polymer Surface Modification for the Attachment of Bioactive Compounds. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 698–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, K.C.; Coco, J.C.; dos Santos, É.M.; Ataide, J.A.; Martinez, R.M.; do Nascimento, M.H.M.; Prata, J.; da Fonte, P.R.M.L.; Severino, P.; Mazzola, P.G.; et al. Pluronic® Triblock Copolymer-Based Nanoformulations for Cancer Therapy: A 10-Year Overview. J. Control Release 2023, 353, 802–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyles, D.A.; Castro, L.D.; Silva, J.O.C.; Ribeiro-Costa, R.M. A Review of the Designs and Prominent Biomedical Advances of Natural and Synthetic Hydrogel Formulations. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 88, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemlewska, A.; Nizioł-Łukaszewska, Z.; Zagórska-Dziok, M.; Bujak, T.; Wójciak, M.; Sowa, I. Evaluation of Cosmetic and Dermatological Properties of Kombucha-Fermented Berry Leaf Extracts Considered to Be By-Products. Molecules 2022, 27, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogrodowczyk, A.M.; Kalicki, B.; Wróblewska, B. The Effect of Lactic Acid Fermentation with Different Bacterial Strains on the Chemical Composition, Immunoreactive Properties, and Sensory Quality of Sweet Buttermilk. Food Chem. 2021, 353, 129512. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33740512/ (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- Mojović, L.; Pejin, D.; Grujić, O.; Markov, S.; Pejin, J.; Rakin, M.; Vukašinović, M.; Nikolić, S.; Savić, D. Progress in the Production of Bioethanol on Starch-Based Feedstocks. Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q. CICEQ 2009, 15, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, H.; Ryu, A.; Hashimoto, A.; Oka, M.; Ichihashi, M. Linoleic Acid and Alpha-Linolenic Acid Lightens Ultraviolet-Induced Hyperpigmentation of the Skin. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1998, 290, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatatikun, M.; Tedasen, A.; Pattaranggoon, N.C.; Palachum, W.; Chuaijit, S.; Mudpan, A.; Pruksaphanrat, S.; Sohbenalee, S.; Yamasaki, K.; Klangbud, W.K. Antioxidant Activity, Anti-Tyrosinase Activity, Molecular Docking Studies, and Molecular Dynamic Simulation of Active Compounds Found in Nipa Palm Vinegar. PeerJ 2023, 11, e16494. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10680452/ (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Lisov, N.; Čakar, U.; Milenković, D.; Čebela, M.; Vuković, G.; Despotović, S.; Petrović, A. The Influence of Cabernet Sauvignon Ripeness, Healthy State and Maceration Time on Wine and Fermented Pomace Phenolic Profile. Fermentation 2023, 9, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertges, F.S.; da Penha Henriques do Amaral, M.; Rodarte, M.P.; Vieira Fonseca, M.J.; Sousa, O.V.; Pinto Vilela, F.M.; Alves, M.S. Assessment of Chemical Changes and Skin Penetration of Green Arabica Coffee Beans Biotransformed by Aspergillus oryzae. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 23, 101512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossowicz-Rupniewska, P.; Bednarczyk, P.; Nowak, M.; Nowak, A.; Duchnik, W.; Kucharski, Ł.; Klebeko, J.; Świątek, E.; Bilska, K.; Rokicka, J.; et al. Evaluation of the Structural Modification of Ibuprofen on the Penetration Release of Ibuprofen from a Drug-in-Adhesive Matrix Type Transdermal Patch. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamiak-Giera, U.; Nowak, A.; Duchnik, W.; Ossowicz-Rupniewska, P.; Czerkawska, A.; Machoy-Mokrzyńska, A.; Sulikowski, T.; Kucharski, Ł.; Białecka, M.; Klimowicz, A.; et al. Evaluation of the in Vitro Permeation Parameters of Topical Ketoprofen and Lidocaine Hydrochloride from Transdermal Pentravan® Products through Human Skin. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1157977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zillich, O.V.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Hasenkopf, K.; Eisner, P.; Kerscher, M. Release and in vitro Skin Permeation of Polyphenols from Cosmetic Emulsions. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013, 35, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, A.; Zagórska-Dziok, M.; Perużyńska, M.; Cybulska, K.; Kucharska, E.; Ossowicz-Rupniewska, P.; Piotrowska, K.; Duchnik, W.; Kucharski, Ł.; Sulikowski, T.; et al. Assessment of the Anti-Inflammatory, Antibacterial and Anti-Aging Properties and Possible Use on the Skin of Hydrogels Containing Epilobium Angustifolium L. Extracts. Front Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 896706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.P.; Agarwal, R. Cosmeceuticals and Silibinin. Clin. Dermatol. 2009, 27, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigon, C.; Marchiori, M.C.L.; da Silva Jardim, F.; Pegoraro, N.S.; dos Santos Chaves, P.; Velho, M.C.; Beck, R.C.R.; Ourique, A.F.; Sari, M.H.M.; de Oliveira, S.M.; et al. Hydrogel Containing Silibinin Nanocapsules Presents Effective Anti-Inflammatory Action in a Model of Irritant Contact Dermatitis in Mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 137, 104969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micek, I.; Nawrot, J.; Seraszek-Jaros, A.; Jenerowicz, D.; Schroeder, G.; Spiżewski, T.; Suchan, A.; Pawlaczyk, M.; Gornowicz-Porowska, J. Taxifolin as a Promising Ingredient of Cosmetics for Adult Skin. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajnochová Svobodová, A.; Ryšavá, A.; Psotová, M.; Kosina, P.; Zálešák, B.; Ulrichová, J.; Vostálová, J. The Phototoxic Potential of the Flavonoids, Taxifolin and Quercetin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2017, 93, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ingredient | H-B | H-E | H-S |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silymarin | - | - | 8.13 |
| Bio-ferment/Extract | 86.32 | 86.32 | - |
| HEC | 3.16 | 3.16 | 2.44 |
| Glycerin | 10.53 | 10.53 | 8.13 |
| Water | - | - | 81.30 |
| Ingredient | O-B | O-E | O-S |
| Silymarin | - | - | 1.69 |
| Bio-ferment/Extract | 68.67 | 68.67 | - |
| Soy lecithin | 3.43 | 3.43 | 3.38 |
| Pluronic F-127 | 10.73 | 10.73 | 10.55 |
| Isopropyl myristate | 17.17 | 17.17 | 16.88 |
| Water | - | - | 67.51 |
| Cosmetic Raw Material | Antioxidant Activity | Fe2+ Chelating Activity | Acidity/Lactic Acid Content | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPPH | ABTS | FRAP | TPC | ChA | A | |
| mmol Trolox/L c.r.m. | mmol FeSO4/L c.r.m. | mmol GA/L c.r.m. | mmol Fe/L c.r.m. | mmol COOH/L c.r.m./g | ||
| Extract | 0.91 ± 0.2 a | 0.10 ± 0.02 a | 0.52 ± 0.12 a | 0.61 ± 0.04 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a,b | not tested |
| Bio-ferment | 1.19 ± 0.2 a | 0.20 ± 0.01 b | 1.34 ± 0.19 b | 0.92 ± 0.05 a,b | 0.05 ± 0.01 b | 215.00 ± 1.00/5.60 |
| Silymarin | 1.14 ± 0.3 a | 0.11 ± 0.02 a | 0.99 ± 0.19 b | 0.76 ± 0.09 a | na | not tested |
| Formulation | Silybin | Taxifolin |
|---|---|---|
| Cumulative Penetration Mass (µg/cm2) | ||
| H-B | 13.283 ± 1.072 a | 22.136 ± 1.431 a |
| H-E | 34.851 ± 3965 d | 38.025 ± 1.218 b |
| H-S | 43.107 ± 2.401 e | 87.739 ± 7.457 e |
| O-B | 16.410 ± 2.070 ab | 50.213 ± 7.586 bc |
| O-E | 23.838 ± 2.213 bc | 68.852 ± 3.132 d |
| O-S | 31.385 ± 1.416 cd | 53.082 ± 4.51 c |
| Cosmetic Raw Material | Silybin | Taxifolin |
|---|---|---|
| mg/100 mL | ||
| Bio-ferment | 5.915 ± 0.238 b | 49.357 ± 1.942 b |
| Extract | 2.099 ± 0.079 a | 22.550 ± 0.232 a |
| Time (Days) | * Biodegradation after 28 Days | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-B | H-E | H-S | O-B | O-E | O-S | |
| (%) | ||||||
| 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 |
| 1 | 2 ± 1 | 4 ± 2 | 2 ± 3 | 2 ± 1 | 2 ± 2 | 2 ± 1 |
| 2 | 3 ± 2 | 8 ± 1 | 3 ± 4 | 4 ± 2 | 3 ± 2 | 4 ± 1 |
| 6 | 4 ± 4 | 13 ± 3 | 4 ± 2 | 6 ± 3 | 4 ± 1 | 6 ± 1 |
| 7 | 5 ± 3 | 15 ± 2 | 5 ± 3 | 9 ± 2 | 6 ± 5 | 9 ± 2 |
| 9 | 11 ± 4 | 17 ± 3 | 10 ± 1 | 14 ± 3 | 10 ± 3 | 14 ± 2 |
| 13 | 29 ± 2 | 19 ± 2 | 29 ± 1 | 19 ± 3 | 28 ± 2 | 19 ± 2 |
| 14 | 36 ± 1 | 18 ± 4 | 36 ± 1 | 33 ± 4 | 36 ± 4 | 33 ± 3 |
| 16 | 38 ± 2 | 22 ± 5 | 38 ± 3 | 38 ± 3 | 38 ± 4 | 38 ± 2 |
| 17 | 42 ± 3 | 23 ± 4 | 42 ± 4 | 44 ± 3 | 39 ± 6 | 44 ± 3 |
| 22 | 44 ± 1 | 23 ± 2 | 44 ± 2 | 46 ± 2 | 41 ± 3 | 46 ± 3 |
| 23 | 47 ± 5 | 26 ± 3 | 44 ± 4 | 49 ± 4 | 41 ± 6 | 49 ± 5 |
| 27 | 47 ± 4 | 33 ± 3 | 45 ± 5 | 54 ± 2 | 42 ± 5 | 54 ± 4 |
| 28 | 47 ± 3 | 35 ± 3 | 45 ± 4 | 60 ± 4 | 43 ± 4 | 60 ± 2 |
| ** Qualitative assessment of aerobic biodegradability | ◐ | ◐ | ◐ | ● | ◐ | ● |
| The Half-Life of the Analyzed Formulations | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-B | H-E | H-S | O-B | O-E | O-S |
| (h/Days) | |||||
| 733/31 | 949/40 | 742/31 | 556/23 | 777/32 | 556/23 |
| Compound Name | Phase of Degradation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lag Phase | Degradation Phase | Plateau Phase | ||||
| % | Day | % | Day | % | Day | |
| H-B | 0–5 | 0–7 | 5–41 | 7–17 | 41–46 | 17–28 |
| H-E | 0–4 | 0–6 | 4–32 | 6–27 | 32–35 | 27–28 |
| H-S | 0–5 | 0–7 | 5–41 | 7–17 | 41–45 | 17–28 |
| O-B | 0–6 | 0–6 | 6–54 | 6–27 | 54–60 | 27–28 |
| O-E | 0–4 | 0–6 | 4–39 | 6–17 | 39–43 | 17–28 |
| O-S | 0–6 | 0–6 | 6–54 | 6–27 | 54–60 | 27–28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kucharska, E.; Sarpong, R.; Bobkowska, A.; Ryglewicz, J.; Nowak, A.; Kucharski, Ł.; Muzykiewicz-Szymańska, A.; Duchnik, W.; Pełech, R. Use of Silybum marianum Extract and Bio-Ferment for Biodegradable Cosmetic Formulations to Enhance Antioxidant Potential and Effect of the Type of Vehicle on the Percutaneous Absorption and Skin Retention of Silybin and Taxifolin. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010169
Kucharska E, Sarpong R, Bobkowska A, Ryglewicz J, Nowak A, Kucharski Ł, Muzykiewicz-Szymańska A, Duchnik W, Pełech R. Use of Silybum marianum Extract and Bio-Ferment for Biodegradable Cosmetic Formulations to Enhance Antioxidant Potential and Effect of the Type of Vehicle on the Percutaneous Absorption and Skin Retention of Silybin and Taxifolin. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(1):169. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010169
Chicago/Turabian StyleKucharska, Edyta, Richard Sarpong, Anna Bobkowska, Joanna Ryglewicz, Anna Nowak, Łukasz Kucharski, Anna Muzykiewicz-Szymańska, Wiktoria Duchnik, and Robert Pełech. 2024. "Use of Silybum marianum Extract and Bio-Ferment for Biodegradable Cosmetic Formulations to Enhance Antioxidant Potential and Effect of the Type of Vehicle on the Percutaneous Absorption and Skin Retention of Silybin and Taxifolin" Applied Sciences 14, no. 1: 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010169
APA StyleKucharska, E., Sarpong, R., Bobkowska, A., Ryglewicz, J., Nowak, A., Kucharski, Ł., Muzykiewicz-Szymańska, A., Duchnik, W., & Pełech, R. (2024). Use of Silybum marianum Extract and Bio-Ferment for Biodegradable Cosmetic Formulations to Enhance Antioxidant Potential and Effect of the Type of Vehicle on the Percutaneous Absorption and Skin Retention of Silybin and Taxifolin. Applied Sciences, 14(1), 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010169








