AI-Enhanced Prediction of Peak Rate of Torque Development from Accelerometer Signals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Protocol
2.3. Explosive Isometric Contractions (Strength and Acceleration Signals)
2.4. Signal Processing and Dataset Organization
2.5. Deep Learning
2.6. Rate of Torque Development
2.7. Statistical Analysis
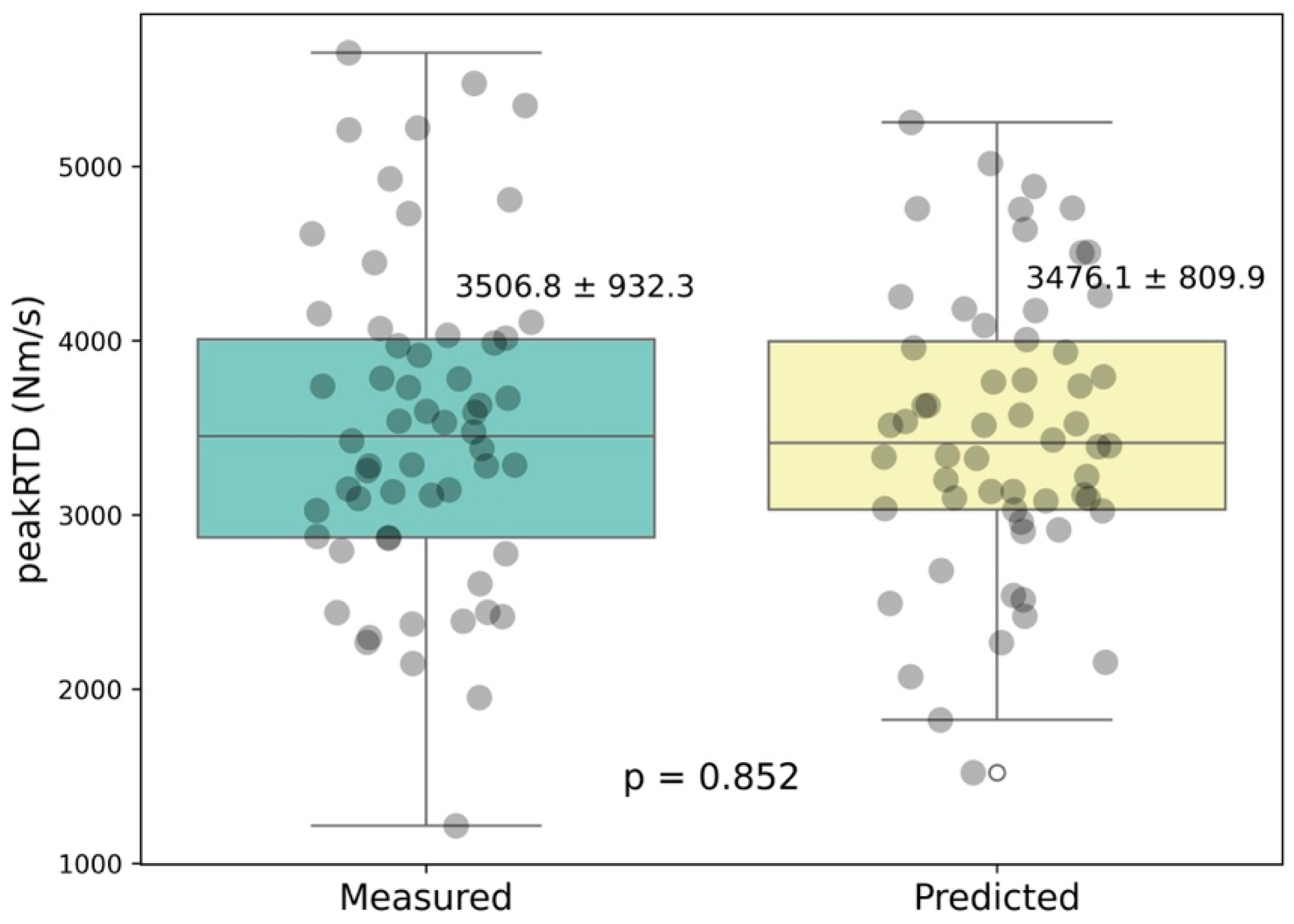
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cossich, V.; Maffiuletti, N.A. Early vs. Late Rate of Torque Development: Relation with Maximal Strength and Influencing Factors. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2020, 55, 102486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maffiuletti, N.A.; Aagaard, P.; Blazevich, A.J.; Folland, J.; Tillin, N.; Duchateau, J. Rate of Force Development: Physiological and Methodological Considerations. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 116, 1091–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozinc, Ž.; Smajla, D.; Šarabon, N. Relationship between Hip Abductor Strength, Rate of Torque Development Scaling Factor and Medio-Lateral Stability in Older Adults. Gait Posture 2020, 95, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, L.L.; Aagaard, P. Influence of Maximal Muscle Strength and Intrinsic Muscle Contractile Properties on Contractile Rate of Force Development. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 96, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folland, J.P.; Buckthorpe, M.W.; Hannah, R. Human Capacity for Explosive Force Production: Neural and Contractile Determinants. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2014, 24, 894–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Vecchio, A.; Negro, F.; Holobar, A.; Casolo, A.; Folland, J.P.; Felici, F.; Farina, D. You Are as Fast as Your Motor Neurons: Speed of Recruitment and Maximal Discharge of Motor Neurons Determine the Maximal Rate of Force Development in Humans. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 2445–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Vecchio, A.; Negro, F.; Falla, D.; Bazzucchi, I.; Farina, D.; Felici, F. Higher Muscle Fiber Conduction Velocity and Early Rate of Torque Development in Chronically Strength-Trained Individuals. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 125, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazevich, A.J.; Gill, N.D.; Zhou, S. Intra- and Intermuscular Variation in Human Quadriceps Femoris Architecture Assessed in Vivo. J. Anat. 2006, 209, 289–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maden-Wilkinson, T.M.; Balshaw, T.G.; Massey, G.J.; Folland, J.P. What Makes Long-Term Resistance-Trained Individuals so Strong? A Comparison of Skeletal Muscle Morphology, Architecture, and Joint Mechanics. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 128, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossich, V.R.A.; Laett, C.T.; Gavilão, U.F.; Blazevich, A.J.; Oliveira, C.G.d. Faster Intrinsic Rate of Torque Development in Elbow Flexors than Knee Extensors: Effect of Muscle Architecture? J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2021, 59, 102570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mornas, A.; Racinais, S.; Brocherie, F.; Alhammoud, M.; Hager, R.; Desmedt, Y.; Guilhem, G. Faster Early Rate of Force Development in Warmer Muscle: An in Vivo Exploration of Fascicle Dynamics and Muscle-Tendon Mechanical Properties. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2022, 323, R123–R132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aeles, J.; Bellett, M.; Lichtwark, G.A.; Cresswell, A.G. The Effect of Small Changes in Rate of Force Development on Muscle Fascicle Velocity and Motor Unit Discharge Behaviour. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2022, 122, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, L.P.; Suchomel, T.J.; Comfort, P.; Haff, G.G.; Connick, M.J. Rate of Force Development Adaptations After Weightlifting-Style Training: The Influence of Power Clean Ability. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2022, 36, 1560–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangine, G.T.; Huet, K.; Williamson, C.; Bechke, E.; Serafini, P.; Bender, D.; Hudy, J.; Townsend, J. A Resisted Sprint Improves Rate of Force Development During a 20-m Sprint in Athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, S.; Peeling, P.; Binnie, M.J.; Goods, P.S.R.; Latella, C.; Taylor, J.L.; Blazevich, A.J.; Timmerman, W.P.; Abbiss, C.R. Sprint Cycling Rate of Torque Development Associates with Strength Measurement in Trained Cyclists. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2023, 123, 1215–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laett, C.T.; Silva, R.; Cossich, C.F.S.; Monteiro, W.; Barcellos, L.C.; Cossich, V.R.A. Maximum and Explosive Strength in Brazilian Kickboxing Athletes: Asymmetries between Limbs and the Relationship with the Single Jump Distance. Sport Sci. Health 2023, 19, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgic, J.; Grgic, I. Resistance Training-Induced Gains in Rate of Force Development Are Maintained during Training Cessation: A Meta-Analysis. Strength Cond. J. 2023, 45, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpeinen, J.T.; Freitas, T.T.; Rubio-Arias, J.Á.; Jordan, M.J.; Aagaard, P. Contractile Rate of Force Development after Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction—A Comprehensive Review and Meta-Analysis. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2020, 30, 1572–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goes, R.A.; Cossich, V.R.A.; França, B.R.; Campos, A.S.; Souza, G.G.A.; Bastos, R.D.C.; Neto, J.A.G. Return to Play after Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Rev. Bras. Med. Esporte 2020, 26, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M.J.; Aagaard, P.; Herzog, W. Rapid Hamstrings/Quadriceps Strength in ACL-Reconstructed Elite Alpine Ski Racers. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckthorpe, M.; Roi, G.S. The Time Has Come to Incorporate a Greater Focus on Rate of Force Development Training in the Sports Injury Rehabilitation Process. Muscle Ligaments Tendons J. 2017, 7, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossich, V.R.A.; Gavilão, U.F.; Goes, R.A.; Perini, J.A.; Laett, C.T.; Maffiuletti, N.A. Maximal vs. Explosive Knee Extensor Strength in Professional Soccer Players: Inter-Limb Asymmetries and Relationship with Knee Function. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2023, 23, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Jiang, T.; Ong, M.T.Y.; He, X.; Choi, C.Y.; Fu, S.C.; Fong, D.T.P.; Yung, P.S.H. Bilateral Impairments of Quadriceps Neuromuscular Function Occur Early after Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury. Res. Sport. Med. 2024, 32, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Ong, M.T.Y.; Choi, C.Y.; He, X.; Lau, L.C.M.; Fu, S.C.; Fong, D.T.P.; Yung, P.S.H. Associations of Patient Characteristics, Rate of Torque Development, Voluntary Activation of Quadriceps with Quadriceps Strength, and Knee Function before Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Res. Sport. Med. 2024, 32, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botta, A.F.B.; Waiteman, M.C.; Ducatti, M.H.M.; Garcia, C.L.G.; Farinelli, L.A.L.B.; Bazett-Jones, D.M.; Briani, R.V.; de Azevedo, F.M. Patellofemoral Pain over Time: Protocol for a Prospective, Longitudinal Study Investigating Physical and Non-Physical Features. Front. Sport. Act. Living 2023, 4, 1081943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawes, J.; Orr, R.; Heinrich, K.M.; Ferguson, H.; Piquet, J.; Jemni, M.; Delextrat, A. Effects of a Football Simulated Exercise on Injury Risk Factors for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injury in Amateur Female Players. Biology 2023, 12, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symons, T.B.; Roberts, A.H.; Carter, K.A.; Caruso, J.F. The Addition of Sprint Interval Training to Field Lacrosse Training Increases Rate of Torque Development and Contractile Impulse in Female High School Field Lacrosse Players. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2023, 8, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelozzi, M.; Madama, M.; Corsica, C.; Calvisi, V.; Properzi, G.; McCaw, S.T.; Cacchio, A. Rate of Force Development as an Adjunctive Outcome Measure for Return-to-Sport Decisions after Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2012, 42, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenze, C.; Lisee, C.; Birchmeier, T.; Triplett, A.; Wilcox, L.; Schorfhaar, A.; Shingles, M. Sex Differences in Quadriceps Rate of Torque Development within 1 year of ACL Reconstruction. Phys. Ther. Sport 2019, 38, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rosell, D.; Pareja-Blanco, F.; Aagaard, P.; González-Badillo, J.J. Physiological and Methodological Aspects of Rate of Force Development Assessment in Human Skeletal Muscle. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2018, 38, 743–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, T.B.; Blinch, J.; Farrow, A.C.; Agu-Udemba, C.C.; Mitchell, E.A. Real-Time Measurement of Isometric Peak Torque and Rate of Torque Development Using a Novel Strength Testing Device: A Validity and Reliability Study. Physiol. Meas. 2020, 41, 115005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, L.C.; Clermont, C.A.; Bošnjak, E.; Ferber, R. The Use of Wearable Devices for Walking and Running Gait Analysis Outside of the Lab: A Systematic Review. Gait Posture 2018, 63, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristoffersson, A.; Lindén, M. A Systematic Review of Wearable Sensors for Monitoring Physical Activity. Sensors 2022, 22, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grouios, G.; Ziagkas, E.; Loukovitis, A.; Chatzinikolaou, K.; Koidou, E. Accelerometers in Our Pocket: Does Smartphone Accelerometer Technology Provide Accurate Data? Sensors 2023, 23, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroganam, G.; Manivannan, N.; Harrison, D. Review on Wearable Technology Sensors Used in Consumer Sport Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurchiek, R.D.; Cheney, N.; McGinnis, R.S. Estimating Biomechanical Time-Series with Wearable Sensors: A Systematic Review of Machine Learning Techniques. Sensors 2019, 19, 5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossich, V.R.A.; Carlgren, D.; Holash, R.J.; Katz, L. Technological Breakthroughs in Sport: Current Practice and Future Potential of Artificial Intelligence, Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, and Modern Data Visualization in Performance Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Emanuele, S.; Maffiuletti, N.A.; Tarperi, C.; Rainoldi, A.; Schena, F.; Boccia, G. Rate of Force Development as an Indicator of Neuromuscular Fatigue: A Scoping Review. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 701916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomborg, S.D.; Dalgas, U.; Hvid, L.G. The Importance of Neuromuscular Rate of Force Development for Physical Function in Aging and Common Neurodegenerative Disorders—A Systematic Review. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2022, 22, 562. [Google Scholar]
- Winters, J.D.; Christiansen, C.L.; Stevens-Lapsley, J.E. Preliminary Investigation of Rate of Torque Development Deficits Following Total Knee Arthroplasty. Knee 2014, 21, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alba-Jiménez, C.; Moreno-Doutres, D.; Peña, J. Trends Assessing Neuromuscular Fatigue in Team Sports: A Narrative Review. Sports 2022, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, J.; Kim, J.; Yeo, W.H. Advances in Biosignal Sensing and Signal Processing Methods with Wearable Devices. Anal. Sens. 2023, 3, e202200062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunavath, V.; Johansen, S.; Johannessen, T.S.; Jiao, L.; Hansen, B.H.; Berntsen, S.; Goodwin, M. Deep Learning for Classifying Physical Activities from Accelerometer Data. Sensors 2021, 21, 5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breasail, M.; Biswas, B.; Smith, M.D.; Mazhar, M.K.A.; Tenison, E.; Cullen, A.; Lithander, F.E.; Roudaut, A.; Henderson, E.J. Wearable GPS and Accelerometer Technologies for Monitoring Mobility and Physical Activity in Neurodegenerative Disorders: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 8261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantashloo, Z.; Abbasi, A.; Tazji, M.K.; Pedram, M.M. Lower Body Kinematics Estimation during Walking Using an Accelerometer. J. Biomech. 2023, 151, 111548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawan, N.; Eltweri, A.; De Lucia, C.; Cavaliere, L.P.L.; Faccia, A.; Moşteanu, N.R. Mixed and Augmented Reality Applications in the Sport Industry. In ACM International Conference Proceedings Series, Proceedings of the EBEE 2020: 2020 2nd International Conference on E-Business and E-Commerce Engineering, Bangkok, Thailand, 29–31 December 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whang, S.E.; Roh, Y.; Song, H.; Lee, J.G. Data Collection and Quality Challenges in Deep Learning: A Data-Centric AI Perspective. VLDB J. 2023, 32, 791–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Layer | Output Shape | |
|---|---|---|
| Input | [3, 1000] | ACC (x, y, and z) |
| Dense (ReLU) | [3, 9000] | |
| Flatter | [27,0] | |
| Dense (ReLU) | [9000] | |
| Dense (ReLU) | [6000] | |
| Output | [1000] | Predicted RTD |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cossich, V.R.A.; Katz, L.; Laett, C.T. AI-Enhanced Prediction of Peak Rate of Torque Development from Accelerometer Signals. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5137. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125137
Cossich VRA, Katz L, Laett CT. AI-Enhanced Prediction of Peak Rate of Torque Development from Accelerometer Signals. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(12):5137. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125137
Chicago/Turabian StyleCossich, Victor R. A., Larry Katz, and Conrado T. Laett. 2024. "AI-Enhanced Prediction of Peak Rate of Torque Development from Accelerometer Signals" Applied Sciences 14, no. 12: 5137. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125137
APA StyleCossich, V. R. A., Katz, L., & Laett, C. T. (2024). AI-Enhanced Prediction of Peak Rate of Torque Development from Accelerometer Signals. Applied Sciences, 14(12), 5137. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125137






