Impact of Biomass Burning, Wildfires, and Wind Events on Aerosol Optical Depth: Implications for Climate Change
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Description of the Study Area and the Methods
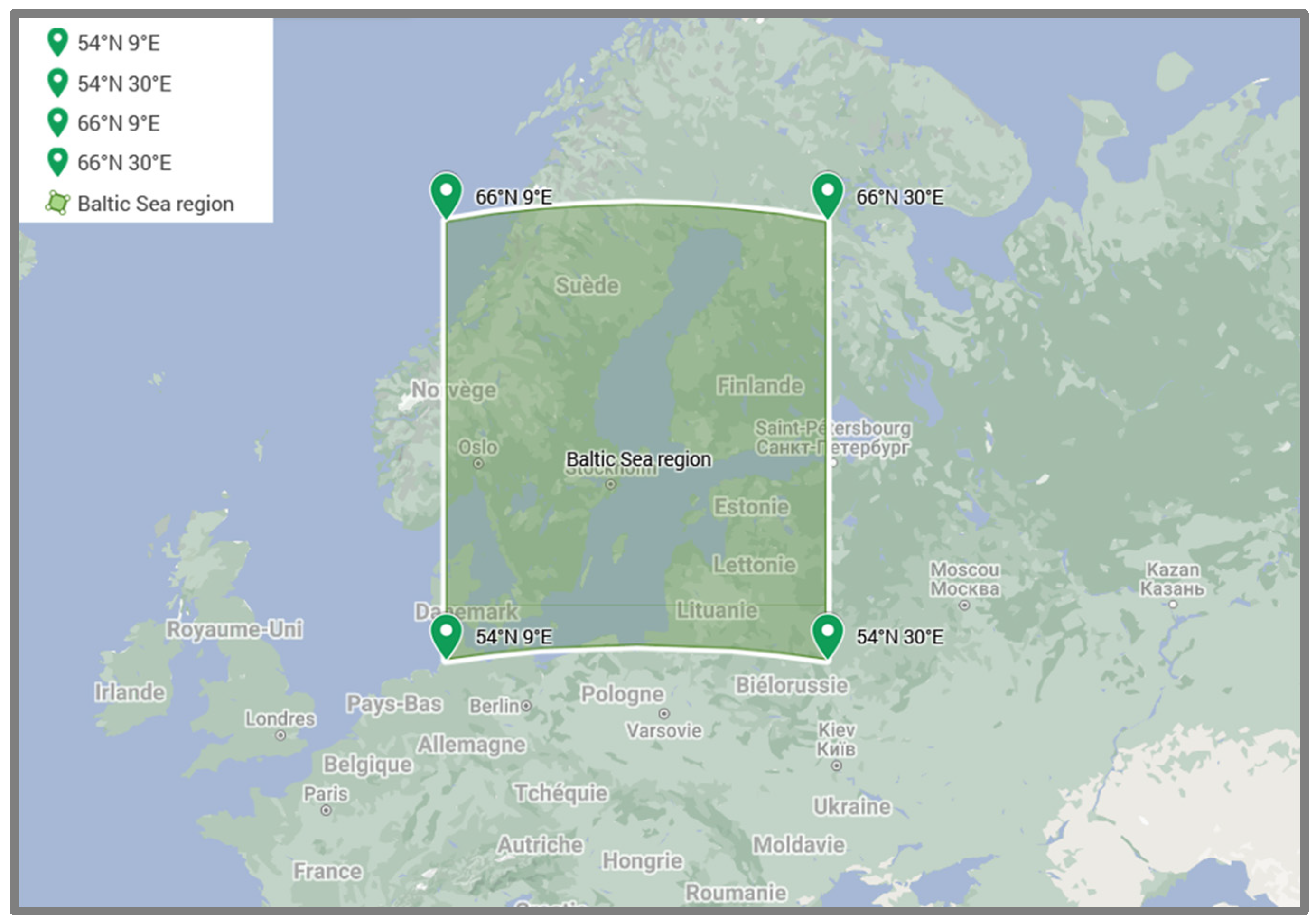
2.1. The Baltic Sea Region
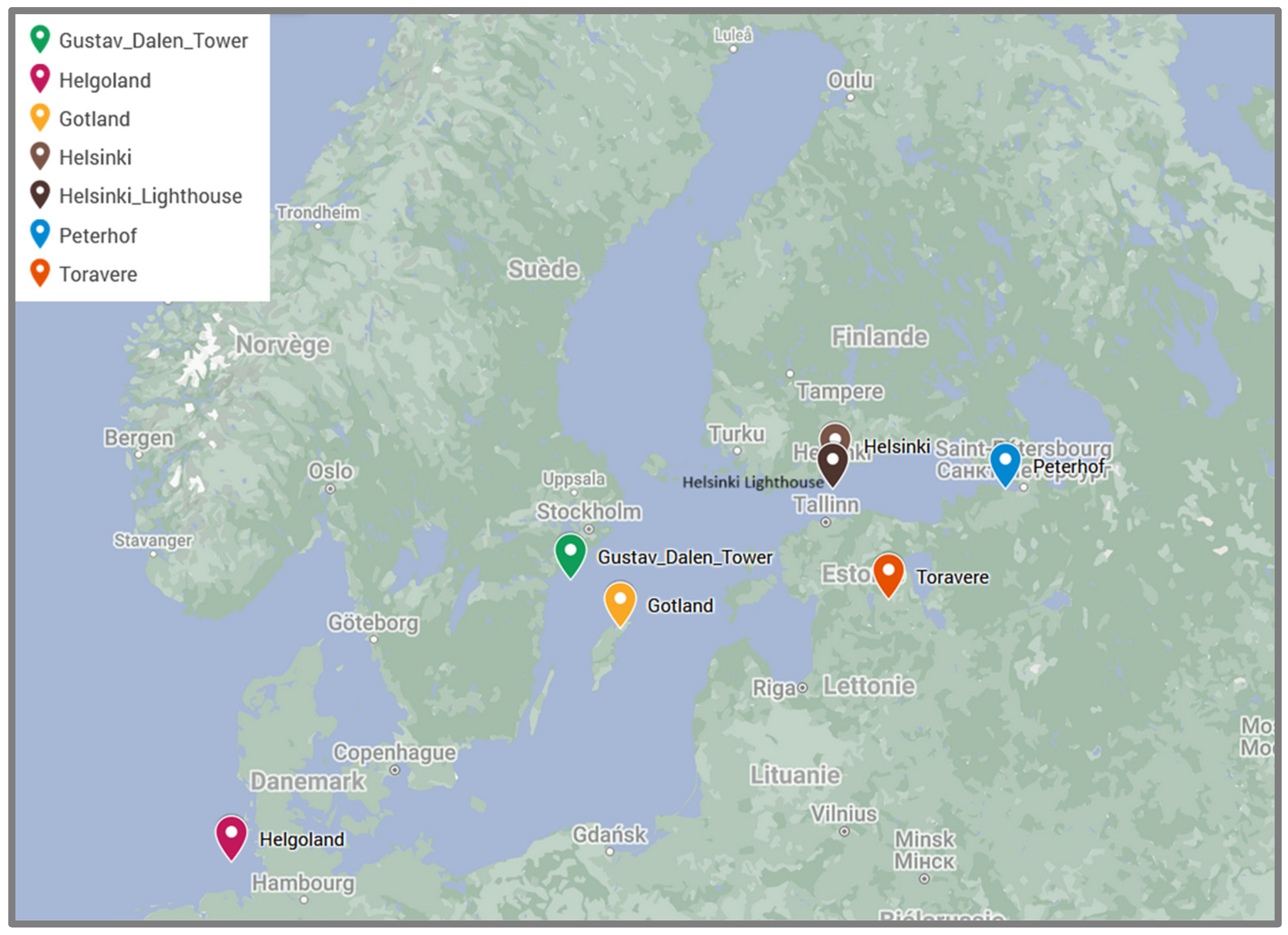
2.2. Data and Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Long-Term AOD Analyses
3.2. Focus on the Particle Size: Fine and Coarse Aerosols
3.3. Focus on 2019 and Link with Wildfires
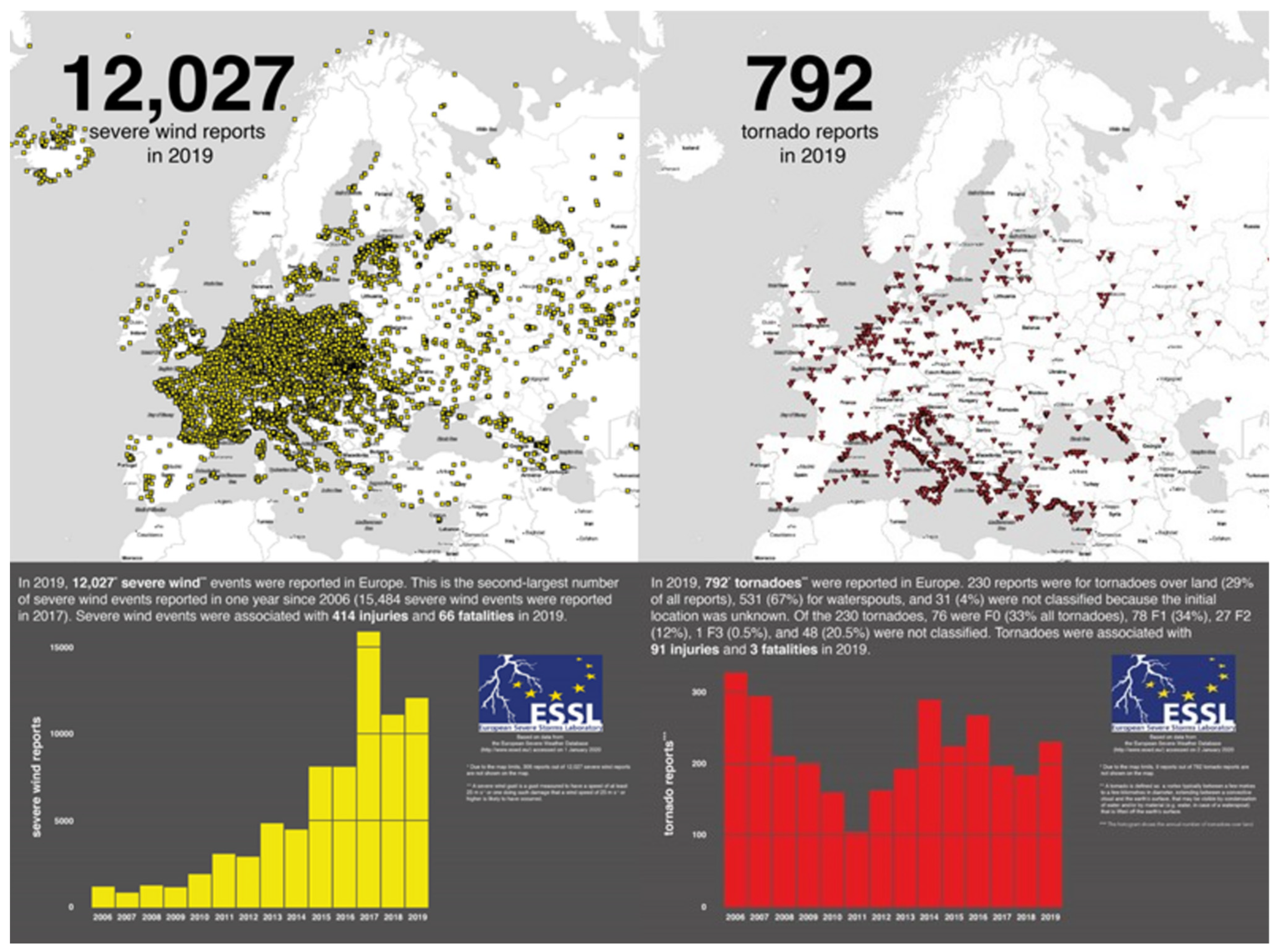
3.4. Transport of Aerosols by Wind and Link with Wildfires
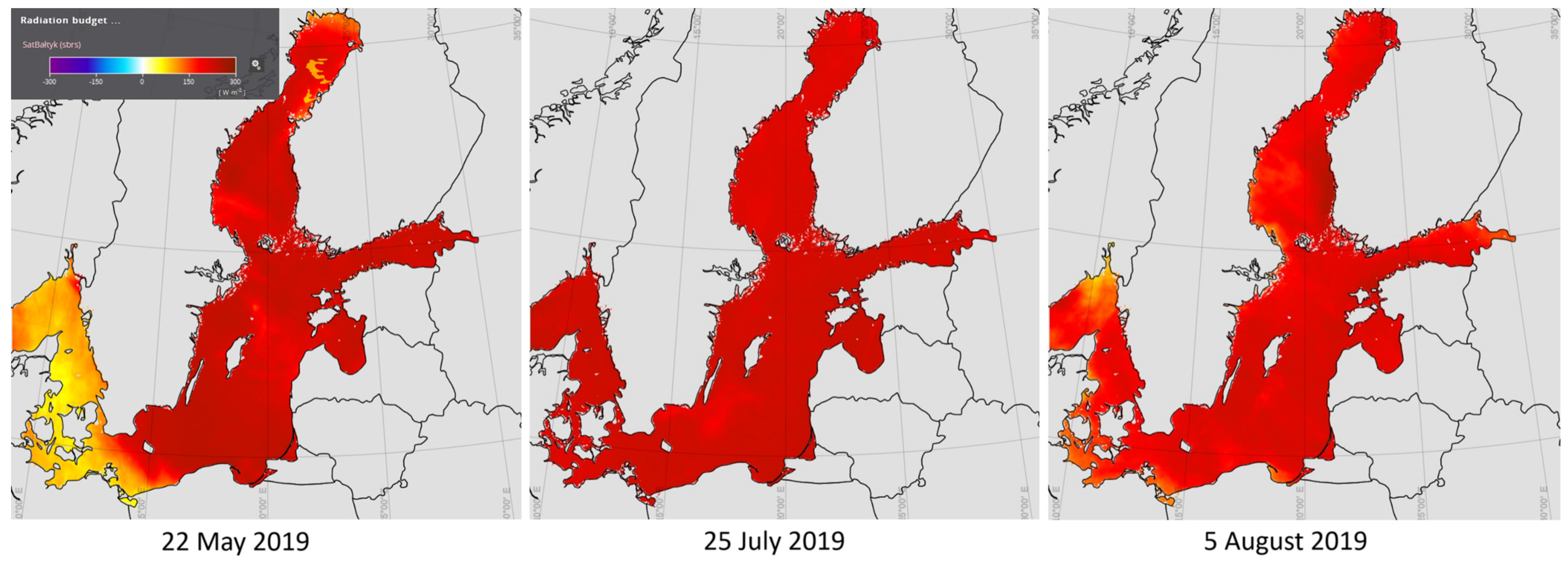
3.5. Aerosols and Climate Change
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bates, T.S.; Huebert, B.J.; Gras, J.L.; Griffiths, F.B.; Durkee, P.A. International Global Atmospheric Chemistry (IGAC) project’s first Aerosol Characterization Experiment (ACE 1): Overview. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 16297–16318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Almeida, G.; Koepke, P.; Shettle, E. Atmospheric aerosols. In Global Climatology and Radiative Characteristics; A. DEEPAK Publishing: Hampton, VA, USA, 1991; p. 561. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/syr/ (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Sano, I.; Lynch, M.; Ogasa, K.; Mukai, S. Photopolarimetric observations of atmospheric aerosols from space and/or sea surface. Adv. Space Rev. 2002, 29, 1867–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Slutsker, I.; Giles, D.M.; McClain, C.R.; Eck, T.F.; Sakerin, S.M.; Macke, A.; Croot, P.; Zibordi, G.; et al. Maritime Aerosol Network as a component of Aerosol Robotic Network. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voiland, A. Aerosols: Tiny Size, Big Impact. Earth Observatory; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2010.
- Zbizika, R.; Pakszys, P.; Zielinski, T. Deep Neural Networks for Aerosol Optical Depth Retrieval. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julia Cole 19 March 2001. Available online: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/features/BiomassBurning (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Plauskaite, K.; Ulevicius, V.; Spirkauskaite, N.; Bycenkiene, S.; Zielinski, T.; Petelski, T.; Ponczkowska, A. Observations of new particle formation events in the south-eastern Baltic Sea. Oceanologia 2010, 52, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutgens, N.; Sayer, A.M.; Heckel, A.; Hsu, C.; Jethva, H.; de Leeuw, G.; Leonard, P.J.T.; Levy, R.C.; Lipponen, A.; Lyapustin, A.; et al. An AeroCom/AeroSat Study: Intercomparison of Satellite AOD Datasets for Aerosol Model Evaluation; Copernicus GmbH: Göttingen, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twomey, S. Atmospheric Aerosols; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1977; p. 289. [Google Scholar]
- Cappelletti, D.; Petroselli, C.; Mateos, D.; Herreras, M.; Ferrero, L.; Losi, N.; Gregorič, A.; Frangipani, C.; La Porta, G.; Lonardi, M.; et al. Vertical profiles of black carbon and nanoparticles pollutants measured by a tethered balloon in Longyearbyen (Svalbard islands). Atmos. Environ. 2022, 290, 119373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Carlson, B.E.; Yung, Y.L.; Lv, D.; Hansen, J.; Penner, J.E.; Liao, H.; Ramaswamy, V.; Kahn, R.A.; Zhang, P.; et al. Scattering and absorbing aerosols in the climate system. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, H.; Liu, X.; Pokhrel, R.; Murphy, S.; Lu, Z.; Saleh, R.; Mielonen, T.; Kokkola, H.; Bergman, T.; Myhre, G.; et al. Biomass burning aerosols in most climate models are too absorbing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China, S.; Scarnato, B.; Owen, R.C.; Zhang, B.; Ampadu, M.T.; Kumar, S.; Dzepina, K.; Dziobak, M.P.; Fialho, P.; Perlinger, J.A.; et al. Morphology and mixing state of aged soot particles at a remote marine free troposphere site: Implications for optical properties. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Zhang, N.; Li, J.; Fan, X.; Guan, X.; Lu, Y.; Shi, J.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, L. Potential influence of fine aerosol chemistry on the optical properties in a semi-arid region. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 0013–9351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, T.; Ferrero, L.; Grassl, S.; Hansen, G.H.; Mateos, D.; Mazzola, M.; Neuber, R.; Pakszys, P.; Posyniak, M.; Ritter, C.; et al. Study of aerosol optical and chemical properties during a long-range transport of biomass burning particles towards Spitsbergen in summer. Atmosphere 2017, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokhanovsky, A.; Tomasi, C.; Smirnov, A.; Herber, A.; Neuber, R.; Ehrlich, A.; Lupi, A.; Petkov, B.H.; Mazzola, M.; Ritter, C.; et al. Remote Sensing of Arctic Atmospheric Aerosols. In Physics and Chemistry of the Arctic Atmosphere in Springer Polar Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakszys, P.; Zielinski, T.; Fererro, L.; Kotynska-Zielinska, I.; Wichorowski, M. Changing Arctic. Firm scientific evidence versus public interest in the issue. Where is the gap? Oceanologia 2020, 62, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, L.; Sangiorgi, G.; Perrone, M.; Rizzi, C.; Cataldi, M.; Markuszewski, P.; Pakszys, P.; Makuch, P.; Petelski, T.; Becagli, S.; et al. Chemical composition of aerosol over the Arctic Ocean from two years of summer AREX cruise: Ions, amines, EC/OM, PAHs, n-alkanes, and metalsresults from two years of summer AREX cruise. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabanov, D.; Sakerin, S.; Kruglinsky, I.; Ritter Ch Sobolewski, P.; Zielinski, T. Comparison of atmospheric aerosol optical depths measured with different sun photometers in three regions of Spitsbergen Archipelago. In Proceedings of the SPIE 24th International Symposium on Atmospheric and Ocean Optics: Atmospheric Physics, Tomsk, Russia, 2–5 July 2018; p. 10833. [Google Scholar]
- Markowicz, K.M.; Pakszys, P.; Ritter, C.; Zielinski, T.; Udisti, R.; Cappelletti, D.; Mazzola, M.; Shiobara, M.; Zawadzka, O.; Lisok, J.; et al. Impact of Canadian intense fires on aerosol optical properties measured over the European Arctic in July 2015. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 121, 14487–14512. [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi, C.; Kokhanovsky, A.; Lupi, A.; Ritter, C.; Smirnov, A.; O’Neill, N.T.; Stone, R.; Holben, B.N.; Nyeki, S.; Wehrli, C.; et al. Aerosol remote sensing in polar regions. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 140, 108–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, L.; Zhang, H.K.; Li, Z.; de Leeuw, G.; Huang, B. Himawari-8 Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Retrieval Using a Deep Neural Network Trained Using AERONET Observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Lee, H.; Park, J. A First Approach to Aerosol Classification Using Space-Borne Measurement Data: Machine Learning-Based Algorithm and Evaluation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Blanco, E.; Calvo, A.I.; Pont, V.; Mallet, M.; Fraile, R.; Castro, A. Impact of Biomass Burning on Aerosol Size Distribution, Aerosol Optical Properties and Associated Radiative Forcing. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 708–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, L.; Cappelletti, D.; Busetto, M.; Mazzola, M.; Lupi, A.; Lanconelli, C.; Becagli, S.; Traversi, R.; Caiazzo, L.; Giardi, F.; et al. Vertical profiles of aerosol and black carbon in the Arctic: A seasonal phenomenology along 2 years (2011–2012) of field campaigns. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 12601–12629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.; Smirnov, A.; Kaufman, Y.; King, M.; Tanre, D.; Slutsker, L. Variability of absorption and optical properties of key aerosol types observed in worldwide locations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 590–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuśmierczyk-Michulec, J.; Rozwadowska, A. Seasonal changes of the aerosol optical thickness for the atmosphere over the Baltic Sea-preliminary results. Oceanologia 1999, 41, 127–145. [Google Scholar]
- Kuśmierczyk-Michulec, J.; Schulz, M.; Ruellan, S.; Kruger, O.; Marks, R.; de Leeuw, G.; Cachier, H. Aerosol composition and related optical properties in the marine boundary layer over the Baltic Sea. J. Aerosol Sci. 2001, 32, 933–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://aeronet.gsfc.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Available online: https://aeronet.gsfc.nasa.gov/new_web/data_description.html (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Goloub, P.; Li, Z.; Dubovik, O.; Blarel, L.; Podvin, T.; Jankowiak, I.; Lecoq, R.; Deroo, C.; Chatenet, B.; Morel, J.P.; et al. PHOTONS/AERONET Sunphotometer Network Overview. Description—Activities—Results. Available online: https://repositorio.aemet.es/bitstream/20.500.11765/5980/1/PHOTONSAERONET_sunphotometer.pdf (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Zielinski, T.; Petelski, T.; Strzalkowska, A.; Pakszys, P.; Makuch, P. Impact of wild forest fires in Eastern Europe on aerosol composition and particle optical properties. Oceanologia 2016, 58, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://euneighbourseast.eu/news/publications/forest-fires-in-europe-middle-east-and-north-africa-2019/ (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Available online: https://www.euronews.com/my-europe/2019/06/25/eu-hit-by-1-381-wildfires-so-far-in-2019-risk-higher-in-areas-with-heatwave (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- NOAA, National Weather Service—National Centers for Environmental Prediction—Climate Prediction Center. Available online: https://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/analysis_monitoring/regional_monitoring/europe.shtml (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Crumeyrolle, S.; Augustin, P.; Rivellini, L.-H.; Choël, M.; Riffault, V.; Deboudt, K.; Fourmentin, M.; Dieudonné, E.; Delbarre, H.; Derimian, Y.; et al. Aerosol Variability Induced by Atmospheric Dynamics in a Coastal Area of Senegal, North-Western Africa. Available online: https://hal.science/hal-02080486/document (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Data from CAMS/Copernicus and European Commission. Available online: http://earth.nullschool.net/ (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Available online: https://www.essl.org/cms/severe-weather-season-2019-summary/ (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Markowicz, K.M.; Chilinski, M.T.; Lisok, J.; Zawadzka, O.; Janicka, L.; Stachlewska, I.S.; Makuch, P.; Pakszys, P.; Rozwadowska, A.; Petelski, T.; et al. Study of aerosol optical properties during long-range transport of biomass burning from Canada to Central Europe in July 2013. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 101, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.satbaltyk.en/ (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Available online: https://www.fondriest.com/environmental-measurements/ (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Liu, L.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Wei, C.; Pöhlker, M.L.; Pöhlker, C.; Artaxo, P.; Shrivastava, M.; Andreae, M.O.; Pöschl, U.; et al. Impact of biomass burning aerosols on radiation, clouds, and precipitation over the Amazon: Relative importance of aerosol–cloud and aerosol–radiation interactions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 13283–13301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotynska-Zielinska, I.; Olenin, S.; Fornalewicz, K.; Pradzinska, A.; Weslawski, J.M. Perception of Arctic issues among young learners in Poland and Lithuania. Oceanologia 2020, 62, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
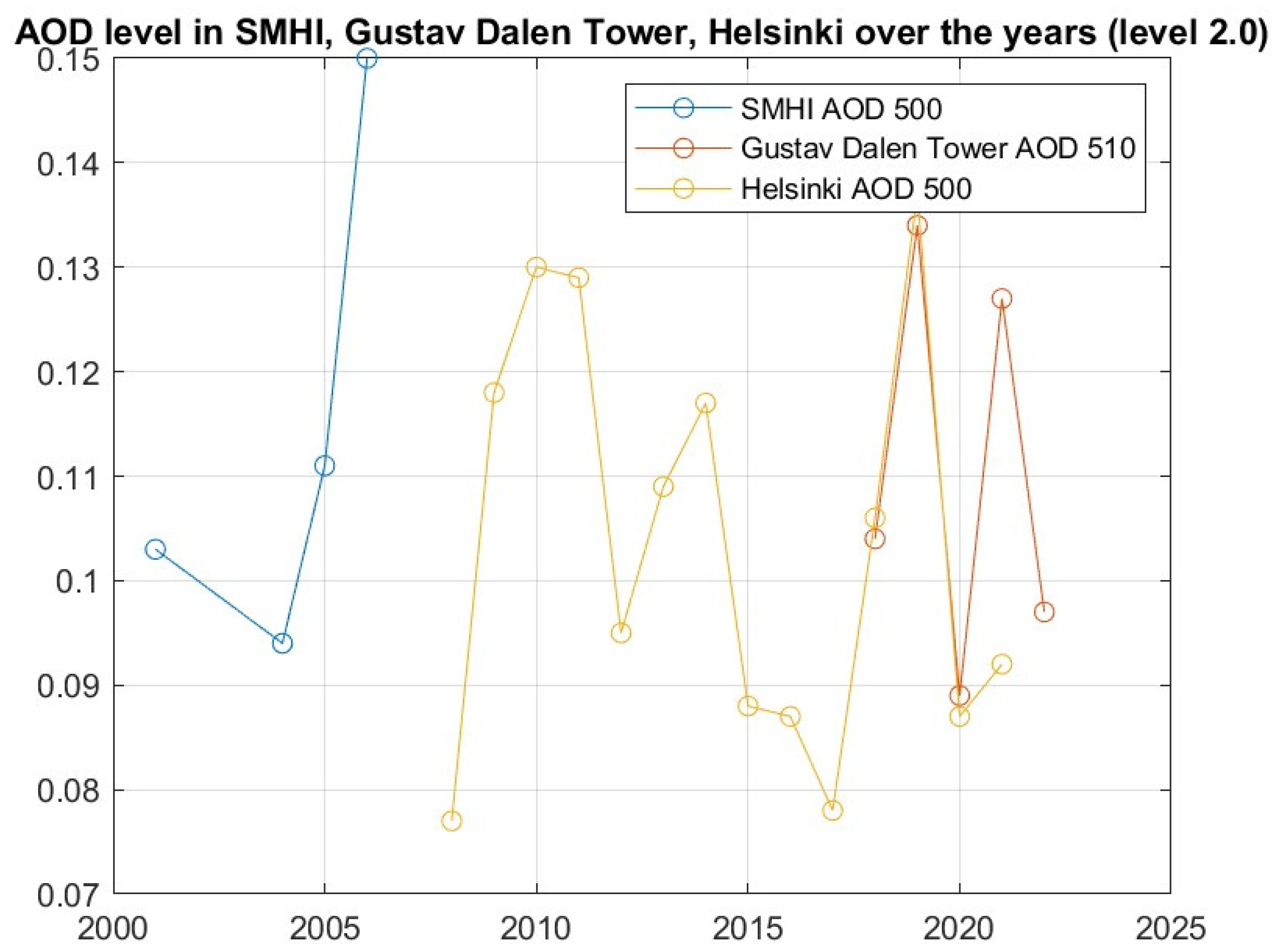
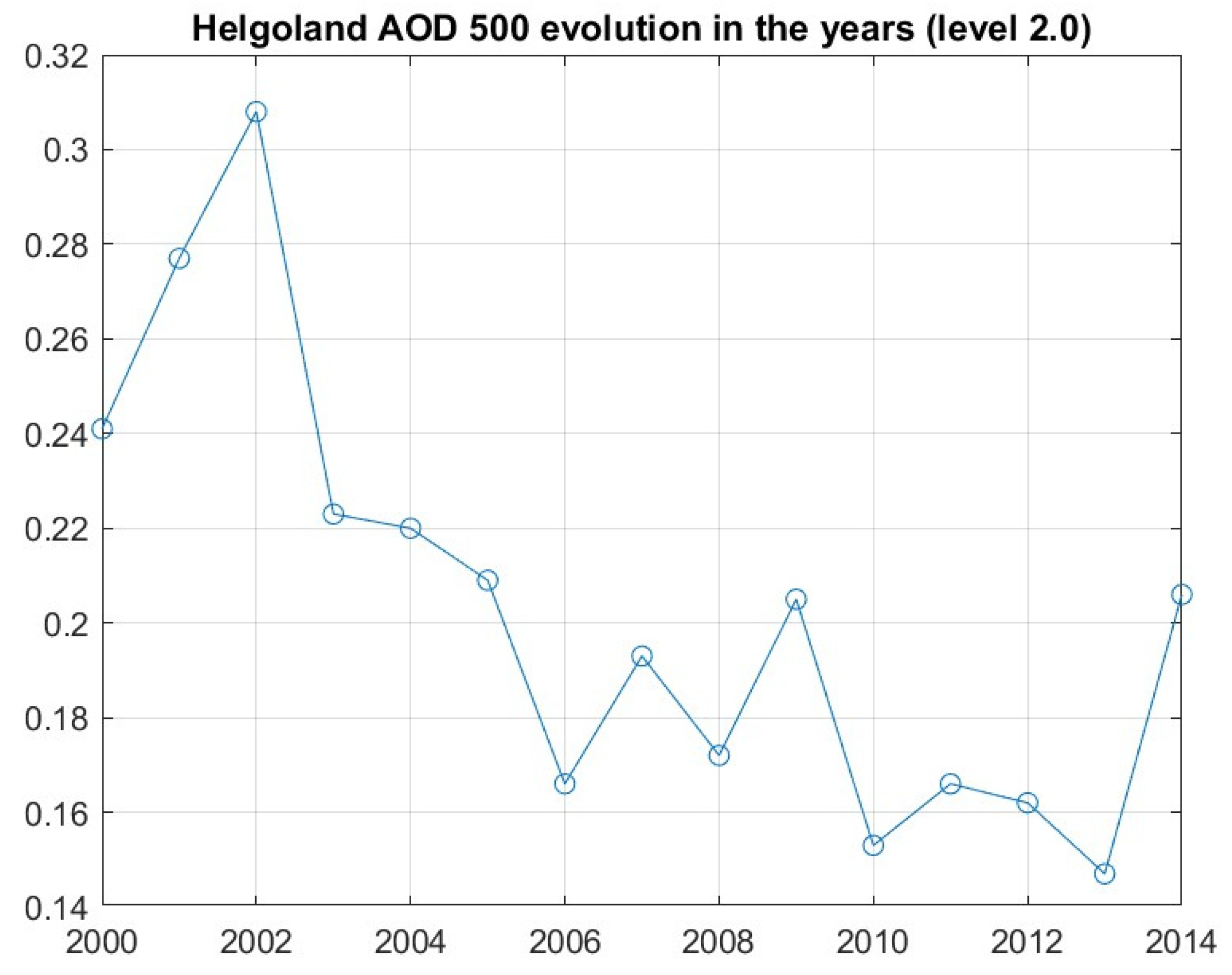
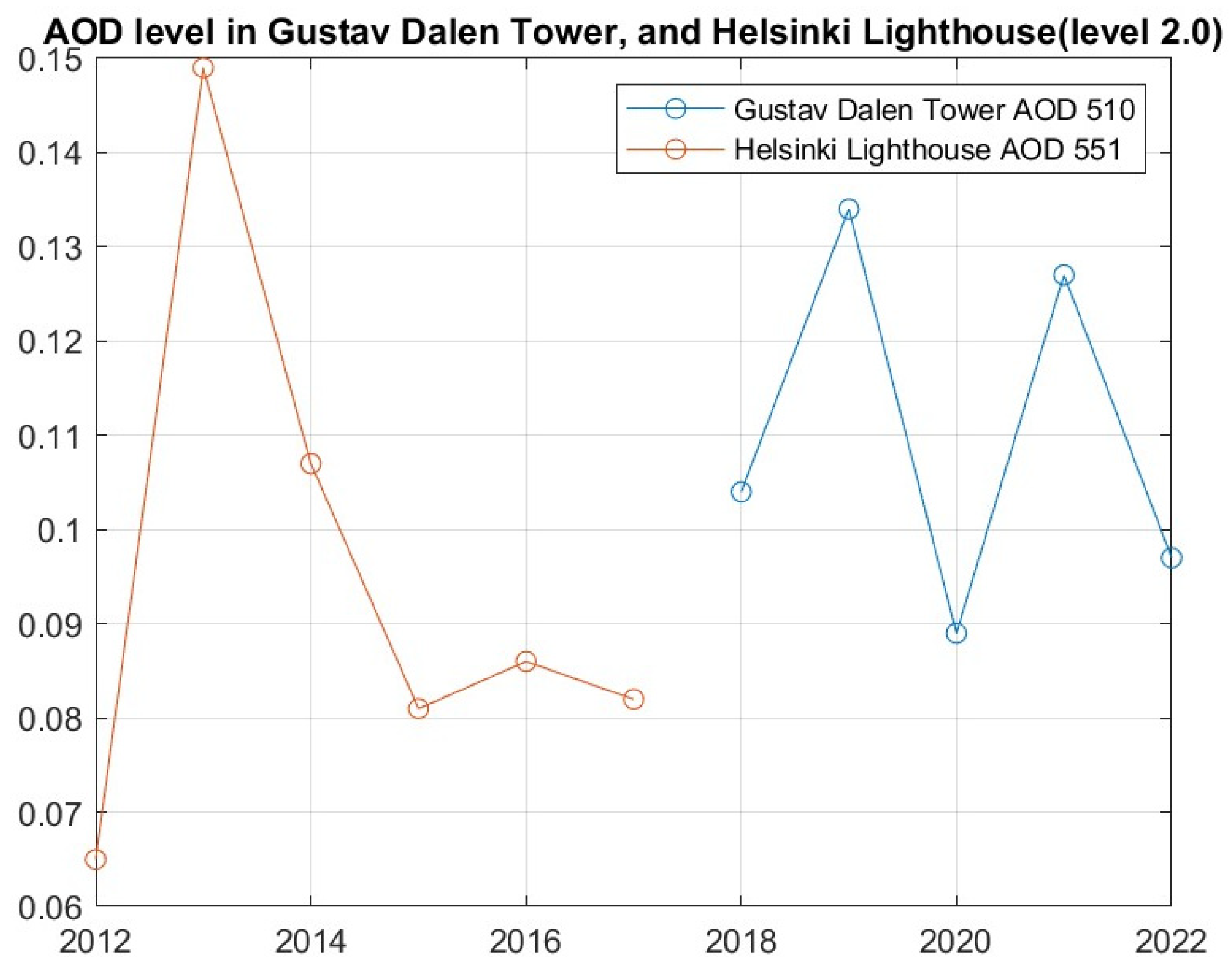
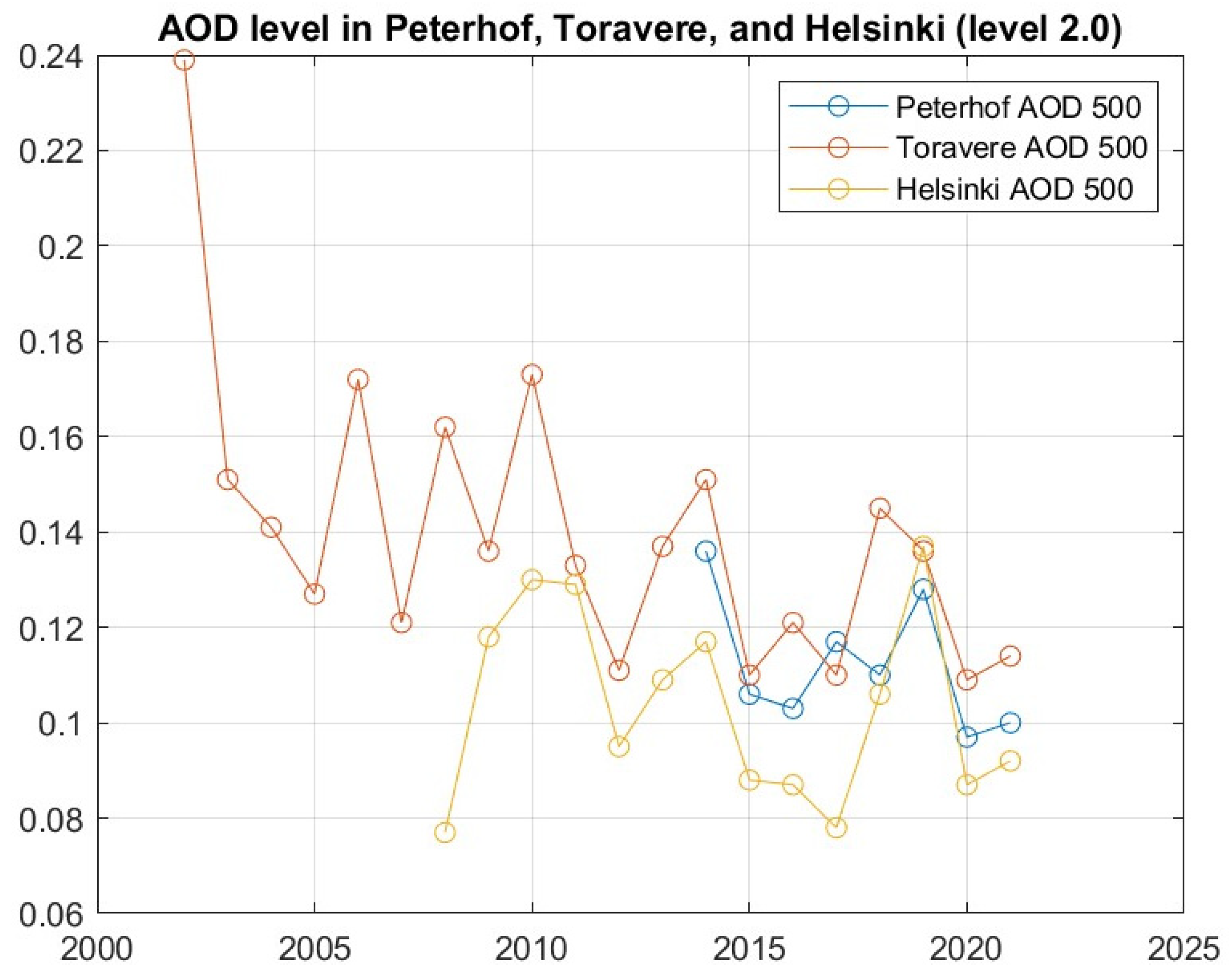
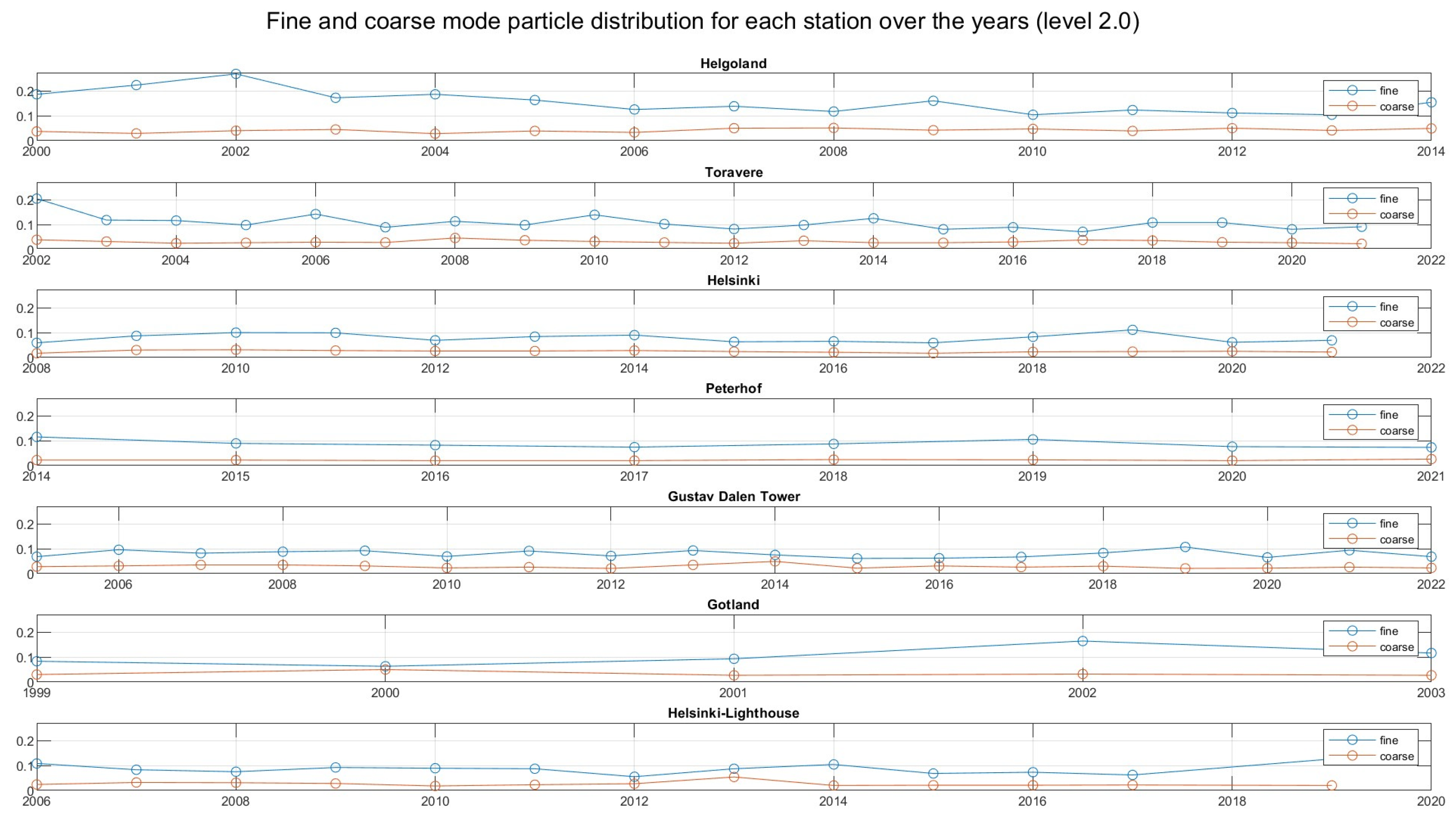


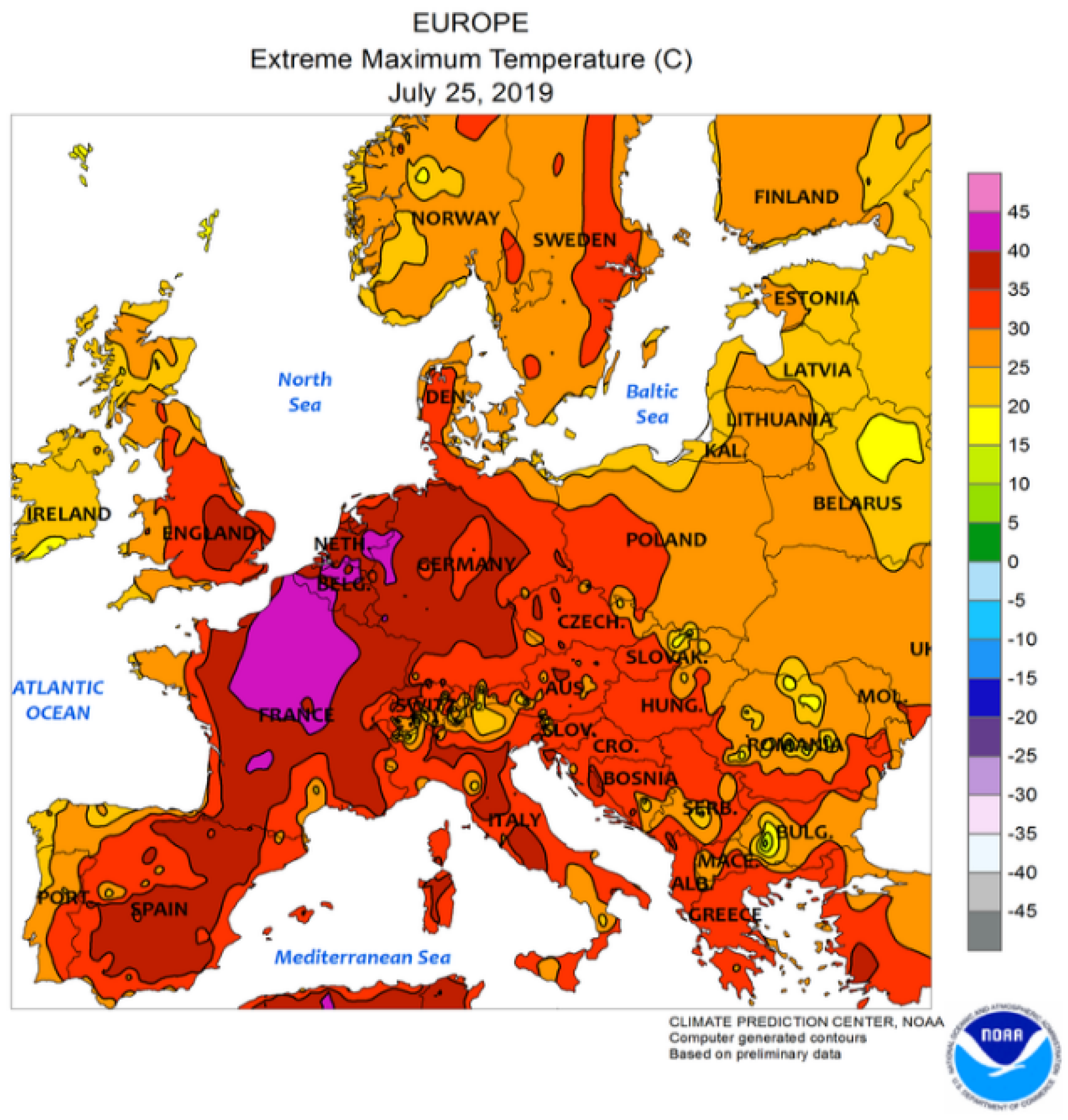
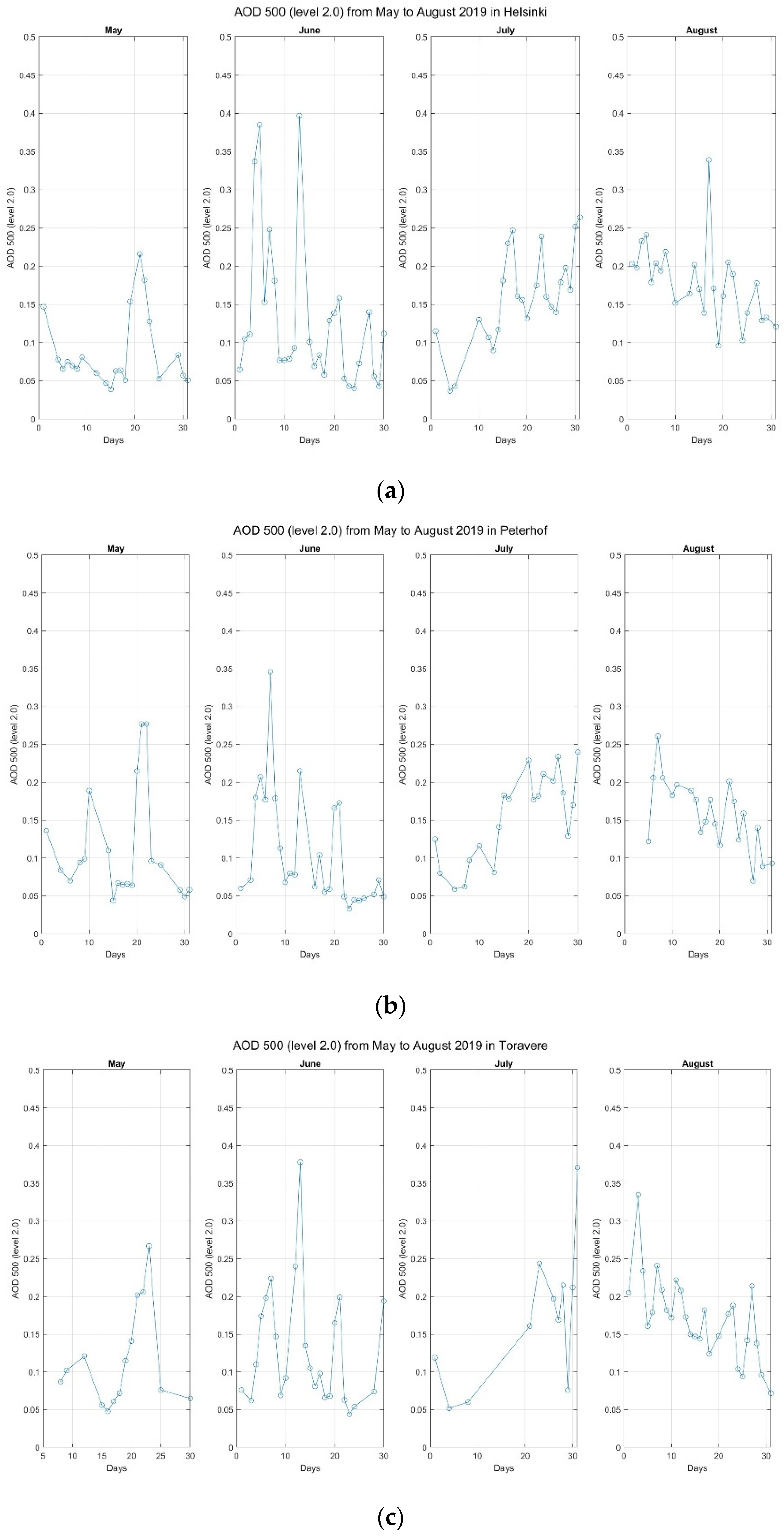

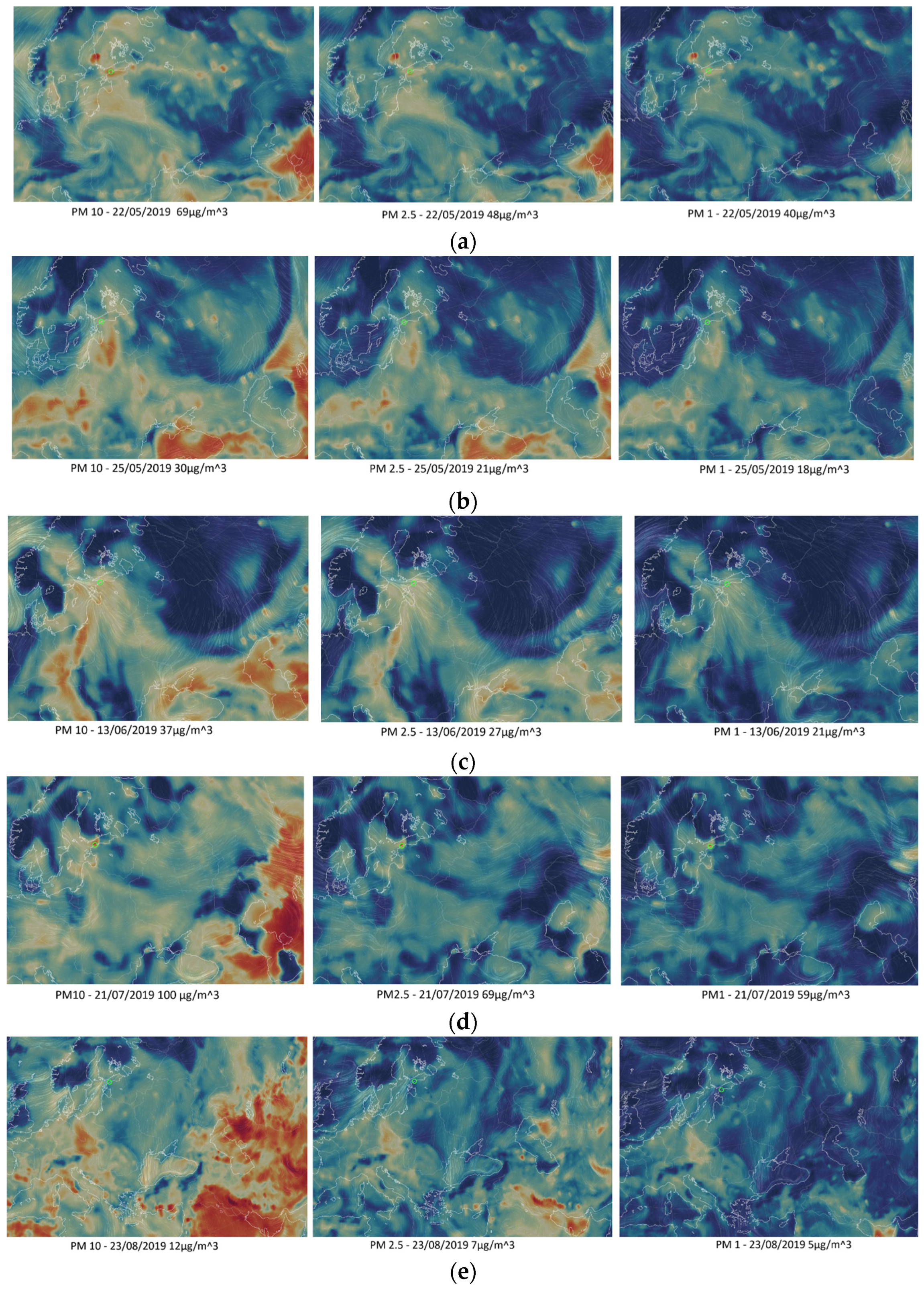

| Station | Years | AOD Difference | Increase/Decrease | Standard Deviation | Curve Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gotland | 2001–2006 | 0.046 | 145.63% (I) | 0.0246 | 7.29 × 10−4 |
| Gustav Dalen | 2005–2022 | 0.025 | 131.25% (I) | 0.0135 | 5.36 × 10−4 |
| Helgoland | 2000–2014 | −0.035 | 85.48% (D) | 0.0461 | −7.81 × 10−4 |
| Helsinki | 2008–2021 | 0.001 | 101.29% (I) | 0.0201 | 7.29 × 10−4 |
| Helsinki Lighthouse | 2006–2011 | 0.017 | 86.18% (I) | 0.01309 | 3.71 × 10−4 |
| Peterhof | 2014–2021 | −0.036 | 73.53% (D) | 0.01387 | −2.73 × 10−3 |
| Toravere | 2002−2021 | −0.106 | 55.65% (D) | 0.03398 | −3.03 × 10−3 |
| AERONET Station | April | June | July | August | Annual Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peterhof (500 nm) | 0.266 | 0.112 | 0.159 | 0.150 | 0.128 |
| Gustav Dalen (510 nm) | 0.200 | 0.137 | 0.125 | 0.172 | 0.137 |
| Helsinki (500 nm) | 0.170 | 0.131 | 0.161 | 0.168 | 0.137 |
| Helsinki Lighthouse (510 nm) | No data | 0.077 | 0.143 | 0.173 | 0.146 |
| Toravere (500 nm) | 0.144 | 0.119 | 0.148 | 0.154 | 0.134 |
| Number of Fires | Burnt Area (ha) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 2019 | 2009–2018 Average | 2019 as % of Average | 2019 | 2009–2018 Average | 2019 as % of Average | |
| Country | |||||||
| Finland | 1458 | 1238 | 118 | 565 | 525 | 108 | |
| Germany | 1523 | 789 | 193 | 2711 | 514 | 528 | |
| Latvia | 1107 | 552 | 201 | 805 | 596 | 135 | |
| Lithuania | 279 | 171 | 163 | 200 | 107 | 187 | |
| Poland | 9635 | 7141 | 135 | 3572 | 3110 | 115 | |
| Romania | 425 | 274 | 155 | 2496 | 1678 | 149 | |
| Sweden | 5483 | 4391 | 125 | 1233 | 4730 | 26 | |
| Ukraine | 1261 | 1992 | 63 | 1065 | 3720 | 29 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zielinski, T.; Willems, A.; Lartigaud, M. Impact of Biomass Burning, Wildfires, and Wind Events on Aerosol Optical Depth: Implications for Climate Change. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5633. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135633
Zielinski T, Willems A, Lartigaud M. Impact of Biomass Burning, Wildfires, and Wind Events on Aerosol Optical Depth: Implications for Climate Change. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(13):5633. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135633
Chicago/Turabian StyleZielinski, Tymon, Amandine Willems, and Mathilde Lartigaud. 2024. "Impact of Biomass Burning, Wildfires, and Wind Events on Aerosol Optical Depth: Implications for Climate Change" Applied Sciences 14, no. 13: 5633. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135633
APA StyleZielinski, T., Willems, A., & Lartigaud, M. (2024). Impact of Biomass Burning, Wildfires, and Wind Events on Aerosol Optical Depth: Implications for Climate Change. Applied Sciences, 14(13), 5633. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135633








