Composite Copolymer Beads Incorporating Red Mud for Water Amendment by Adsorption—Oxidation Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
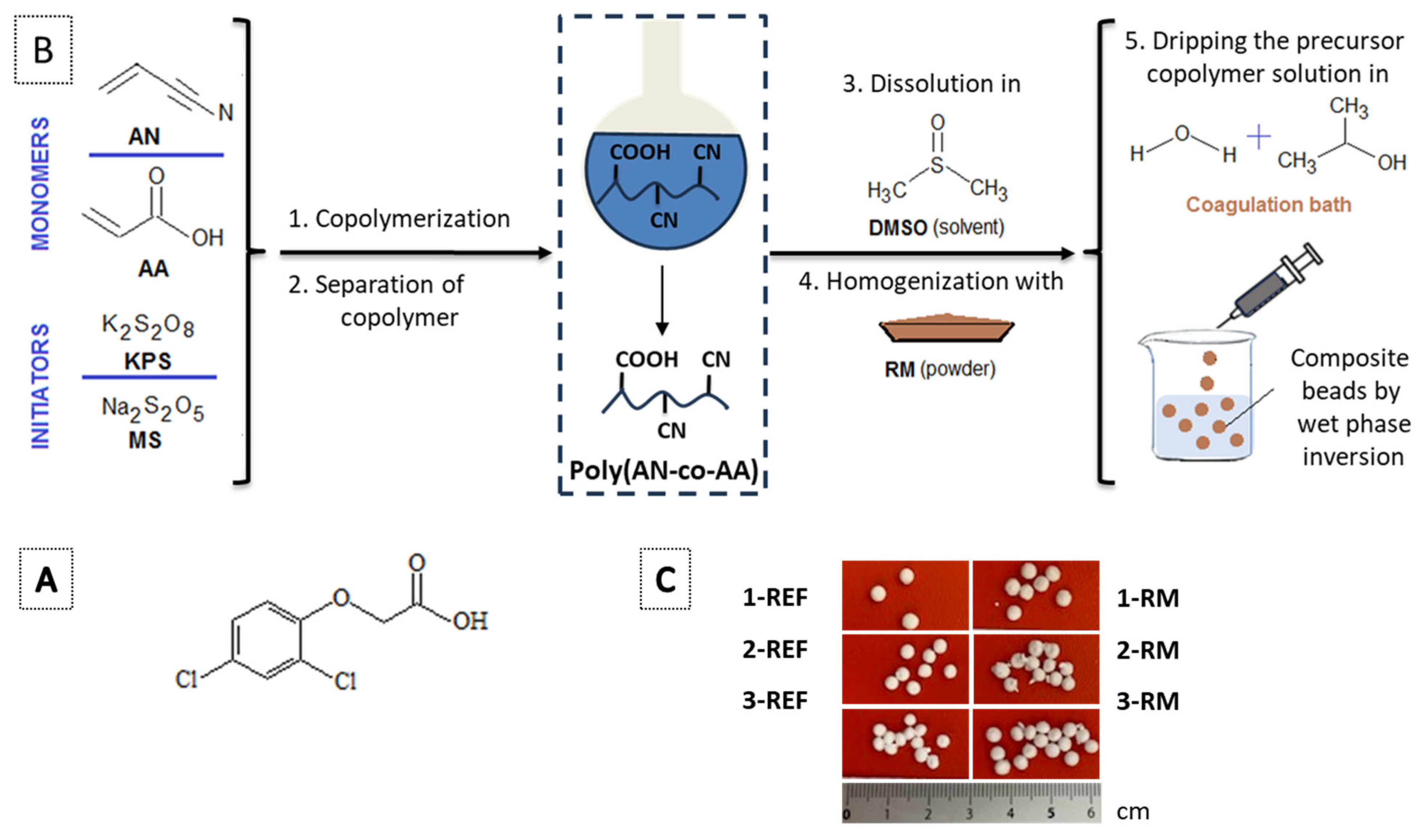
2.2. Synthesis of Composite Copolymer Beads
2.2.1. Preparation of PAN-co-PAA
2.2.2. Preparation of Copolymer Composite Beads
2.3. Characterization Techniques for Composite Beads and Instruments
2.3.1. Characterization of Composite Beads
2.3.2. Evaluation of Removal Efficiency for 2.4- DCFA Pesticide
3. Results and Discussion
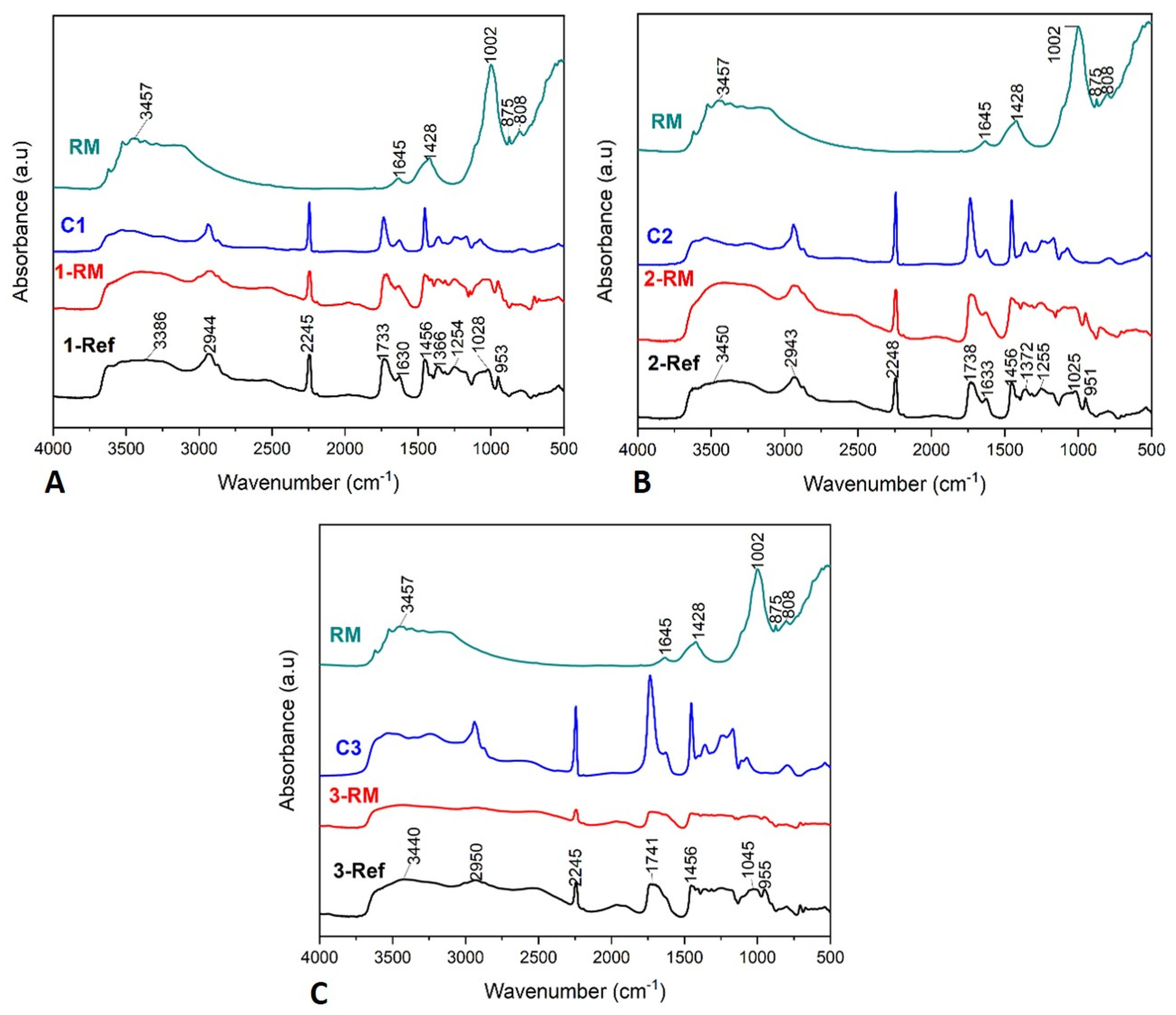
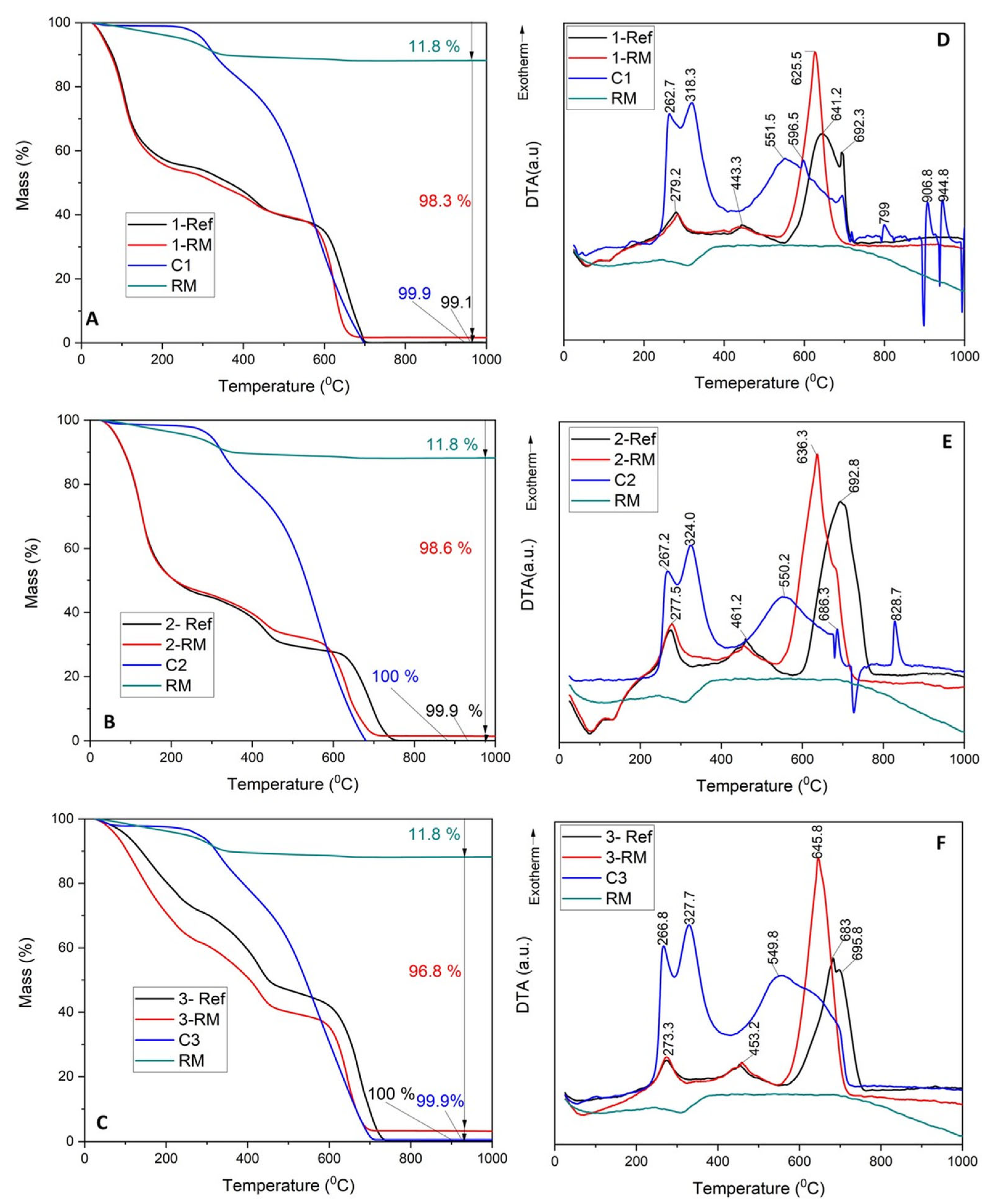
3.1. Investigation of Structure and Composition for Composite Beads
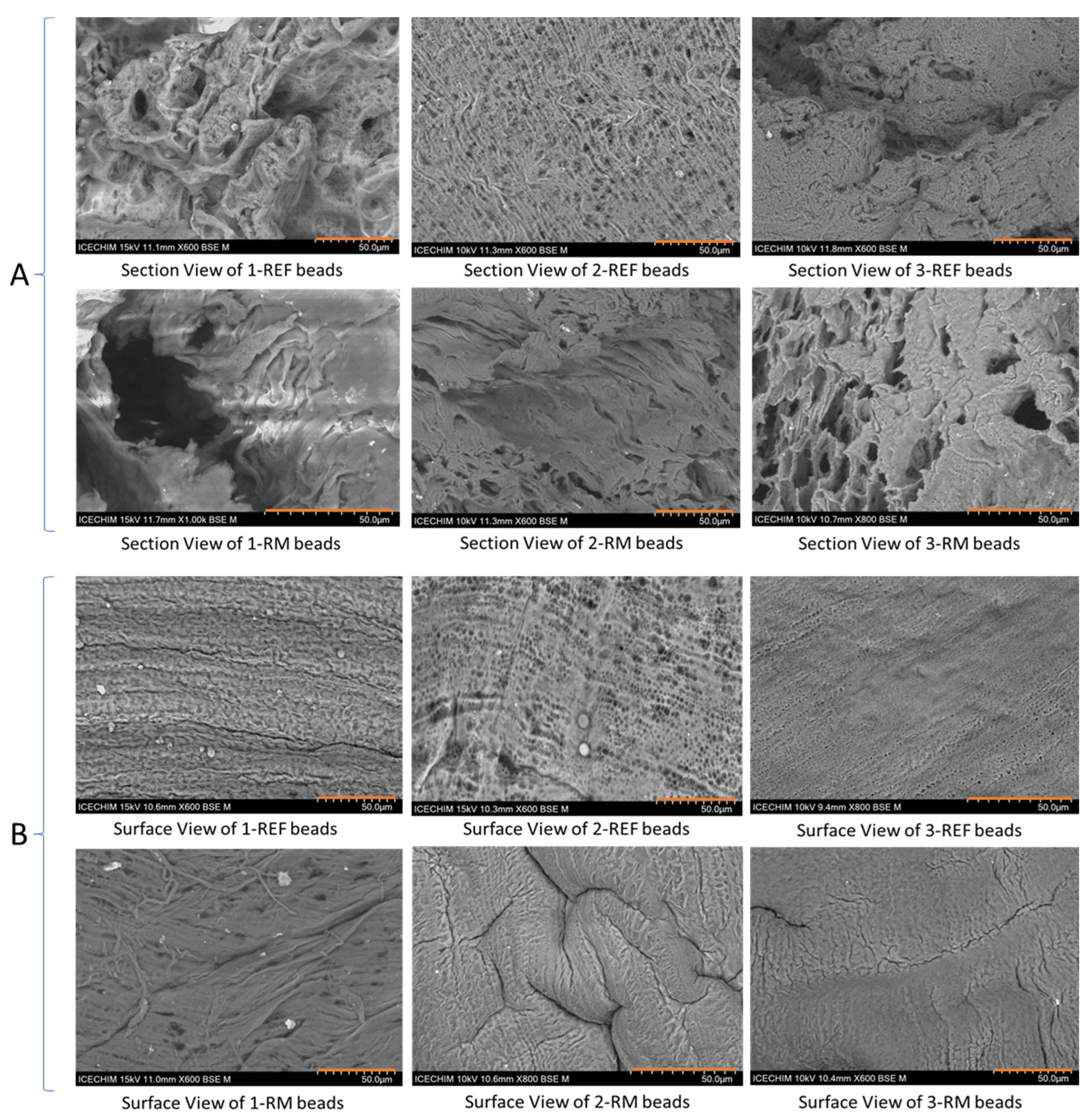
3.2. Porosity and Morphology Investigation of Composite Copolymer Beads
3.3. Retention of 2,4-DCFA by Composite Beads in Adsorption/Oxidation Processes
3.4. Investigation of Structure Modification after Composite Beads’ Recovery
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kvande, H. Cap 3 Production of primary aluminium in Fundamentals of Aluminium Metallurgy. Production, Processing and Applications. Woodhead Publ. Ser. Met. Surf. Eng. 2011, 49–69. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, A.H.; Khalil, H.P.S.A.; Bhat, I.H.; Banthia, A.K. Dielectric and material properties of poly (vinyl alcohol): Based modified red mud polymer nanocomposites. J. Polym Environ. 2012, 20, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Li, L.; Yao, X.; Rudolph, V.; Hagheresht, F. Phosphate removal from wastewater using red mud. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunori, C.; Cremisini, C.; Massanisso, P.; Pinto, V.; Torricelli, L. Reuse of a treated red mud bauxite waste: Studies on environmental compatibility. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 117, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Xiao, B. Review on treatment and utilization of bauxite residues in China. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2009, 93, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, H. Metallurgical process for valuable metals recovery from red mud—A review. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 155, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, J.M.; Cabeza, M.; Tenza-Abril, A.J.; Real-Herraiz, T.; Climent, M.A.; Sanchez, I. Effects of red mud addition in the microstructure, durability and mechanical performance of cement mortars. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, A.; Fakhariyan, A. Recovery of Al2O3, Fe2O3 and TiO2 from Bauxite Processing Waste (Red Mud) by Using Combination of Different Acids. J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res. 2013, 3, 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, M.S.S.; Thives, L.P.; Haritonovs, V.; Bajars, K. Red mud application in construction industry: Review of benefits and possibilities. IOP Conf. Ser. Mat. Sci. Eng. 2017, 251, 012033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deelwal, K.; Dharavath, K.; Kulshreshtha, M. Evaluation of characteristic properties of red mud for possible use as a geotechnical material in civil construction. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. 2014, 7, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Banjare, J.; Sahu, Y.K.; Agrawal, A.; Satapathy, A. Physical and thermal characterization of red mud reinforced epoxy composites: An experimental investigation. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 5, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deihimi, N.; Irannajad, M.; Rezai, B. Characterization studies of red mud modification processes as adsorbent for enhancing ferricyanide removal. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, M.K.; Mandal, S.; Dash, S.S.; Badhai, P.; Patel, R.K. Removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solution by acid activated red mud. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, A.; de Marco, I.; Caballero, B.M.; Laresgoiti, M.F.; Adrados, A.; Aranzabal, A. Catalytic pyrolysis of plastic wastes with two different types of catalysts: ZSM-5 zeolite and Red Mud. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 104, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandekar, S.; Korde, S.; Jugade, R.M. Red mud-chitosan microspheres for removal of coexistent anions of environmental significance from water bodies. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousif, A.M.; Rodgers, M.; Clifford, E. Studying the adsorption properties of modified red mud towards phosphate removal from its solutions. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2012, 3, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Vilar, V.J.P.; Botelho, C.M.S.; Boaventura, R.A.R. A review of the use of red mud as adsorbent for the removal of toxic pollutants from water and wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2011, 32, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra Sahu, R.; Patel, R.; Chandra Ray, B. Removal of hydrogen sulfide using red mud at ambient conditions. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldan, M. Hexavalent chromium adsorption using red mud as adsorbent. J. Multidiscip. Eng. Sci. Technol. (JMEST) 2015, 2, 2644–2647. [Google Scholar]
- Dursun, S.; Guclu, D.; Bas, M. Phosphate removal by using activated red mud from Seydisehir aluminum factory in Turkey. J. Int Environ. Appl. Sci. 2006, 1, 98–106. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Yue, Q.; Li, Q.; Xu, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Gao, B.; Yu, H. Characterization of red mud granular adsorbent (RMGA) and its performance on phosphate removal from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 193–194, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Li, Y.Z.; Luan, Z.K.; Chen, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.G.; Jia, Z.P. Adsorption removal of phosphate from aqueous solution by active red mud. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepper, R.A.; Couperthwaite, S.J.; Millar, G.J. Re-use of waste red mud: Production of a functional iron oxide adsorbent for removal of phosphorous. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 25, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Boyjoo, Y.; Choueib, A.; Zhu, Z.H. Removal of dyes from aqueous solution using fly ash and red mud. Water Res. 2005, 39, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Guo, W.; Tian, Y. Removal of malachite green and crystal violet cationic dyes from aqueous solution using activated sintering process red mud. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 93–94, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balarak, D.; Mahdavi, Y.; Sadeghi, S. Adsorptive removal of Acid Red 18 dye (AR 18) from aqueous solution by red mud: Characteristics, isotherm and kinetic studies. Sch. Acad. J. Biosci. (SAJB) 2015, 3, 644–649. [Google Scholar]
- Shirzad-Siboni, M.; Javari, S.J.; Giahi, O.; Kim, I.; Lee, S.M.; Yang, J.K. Removal of acid blue 113 and reactive black 5 dye from aqueous solutions by activated red mud. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, M.; Ioniță, A.D.; Filipescu, L. Chromium adsorption on neutralized red mud. Rev. Chim. 2010, 61, 200–205. [Google Scholar]
- Smiciklas, I.; Smiljanic, S.; Peric-Grujic, A.; Sljivic-Ivanovic, M.; Mitric, M.; Antonovic, D. Effect of acid treatment on red mud properties with implications on Ni (II) sorption and stability. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 242, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiciklas, I.; Smiljanic, S.; Peric-Grujic, A.; Sljivic-Ivanovic, M.; Mitric, M.; Antonovic, D. The influence of citrate anion on Ni (II) removal by raw red mud from aluminum industry. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 214, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiljanic, S.; Smiciklas, I.; Peric-Grujic, A.; Sljivic, M.; Dukic, B.; Loncar, B. Study of factors affecting Ni2+ immobilization efficiency by temperature activated red mud. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.; Wasewar, K.L.; Mukhopadhyay, J.; Yoo, C.K.; Uslu, H. Neutralization and utilization of red mud for its better waste management. Arch. Environ. Sci. 2012, 6, 13–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, R.J.; Sayadi, M.H.; Rezaei, M.R. Removal of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid from aqueous solutions by modified magnetic nanoparticles with amino functional groups. J. Water Env. Nanotechnol. 2020, 5, 147–156. [Google Scholar]
- Mokhter, M.A.; Magnenet, C.; Lakard, S.; Euvrard, M.; Aden, M.; Clément, S.; Mehdi, A.; Lakard, B. Use of Modified Colloids and Membranes to Remove Metal Ions from Contaminated Solutions. Colloids Interfaces 2018, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.H.; Banthia, A.K. Preparation and characterization of poly(vinyl alcohol)-modified red mud composite materials. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.H.; Banthia, A.K. Improvement of the red mud polymer-matrix composites by organophilization of red mud. Adv. Mat. Res. 2007, 29–30, 333–336. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, A.H.; Banthia, A.K. Mechanical and dynamic analysis of poly(vinyl alcohol)-modified inorganic filler composite. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2008, 47, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daw, S.; Basu, R.K.; Das, S.K. Red mud reinforced polyvinyl alcohol composite films: Synthesis, chemical modification and thermal properties. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naga Babu, A.; Krishna Mohan, G.V.; Kalpana, K.; Ravindhranath, K. Removal of lead from water using calcium alginate beads doped with hydrazine sulphate-activated red mud as adsorbent. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2017, 2017, 4650594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Zhen, Z.; Lv, F.; Chu, P.K.; Ji, J. Red mud/polypropylene composite with mechanical and thermal properties. J. Compos. Mater. 2011, 45, 2811–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gok, A.; Omastova, M.; Prokes, J. Synthesis and characterization of red mud/polyaniline composites: Electrical properties and thermal stability. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 2471–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gok, A.; Oguz, I. Structural and thermal characterization of poly(2-chloroaniline)/red mud nanocomposite materials. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 99, 2101–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Li, X.; Shuai, S. Research on the property improvement of PVC using red mud in industrial waste residue. IOP Conf Ser. Mat. Sci. Eng. 2015, 87, 012086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasdemir, M.; Kurt, M. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene/red mud polymer composites: Ultraviolet annealing. Adv. Sci. Eng. Med. 2016, 8, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Cao, X.; Huo, G.; Luo, S.; He, X. Non-isothermal crystallization behavior and kinetics of LLDPE/REDMUD blends. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2015, 23, 483–494. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, A.H.; Khalil, H.P.S.A.; Bhat, I.H.; Banthia, A.K. Development and characterization of novel modified red mud nanocomposites based poly(hydroxyl ether) of Bisphenol A. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 119, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Nam, K.N.; Jin, S.W.; Kim, D.M.; Song, I.H.; Park, H.J.; Chung, C.M. Preparation and properties of poly(imide-siloxane) copolymer composite films with micro-Al2O3 particles. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, S.; Kolinova, M.; Rahier, H.; DalPoggetto, G.; Blanco, I. Investigation of internal structure of fiber reinforced geopolymer composite under merchanical impact: A micro computed tomography (µ-CT) study. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.W.; Nie, F.Q.; Xu, Z.K. Acrylonitrile-based copolymer membranes containing reactive groups: Fabrication dual-layer biomimetic membranes by the immobilization of biomacromolecules. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 264, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kang, M.S.; Kim, C.K. Fabrication of membranes for the liquid separation Part 1. Ultrafiltration membranes prepared from novel miscible blends of polysulfone and poly(1-vinylpyrrolidone-co-acrylonitrile) copolymers. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 265, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohokare, H.R.; Kumbharkar, S.C.; Bhole, Y.S.; Kharul, U.K. Surface Modification of Polyacrylonitrile Based Ultrafiltration Membrane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 4378–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo Vieira, Y.; Gurgel, D.; Oliveira Henriques, R.; Machado, R.A.F.; de Oliveira, D.; Oechsler, B.F.; Furigo, A.J. A perspective review on the application of polyacrylonitrile-based supports for laccase immobilization. Chem. Rec. 2022, 22, e202100215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, D.S.; Bajpai, R.; Bajpai, A.K. Synthesis and characterization of polyvinyl alcohol based semi interpenetrating polymeric networks. J. Polym. Res. 2012, 19, 9938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Zhang, X.X.; Wang, X.C. Various comonomers in acrylonitrile based copolymers: Effects on thermal behavior. Iran. Polym. J. 2010, 19, 243–253. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, S.-H.; Deng, R.; Xu, J.; Wan, L.S.; Xu, Z.K. Composite membranes from polyacrylonitrile with poly(N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate)-grafted silica nanoparticles as additives. React. Funct. Polym. 2015, 86, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.S.; Xu, Z.K.; Huang, X.J. Asymmetric Membranes Fabricated from Poly(acrylonitrile-co-N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone)s with Excellent Biocompatibility. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 4577–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wu, L.G.; Zheng, X.C.; Mo, J.X.; Gao, C.J. Surface modification of phenolphthalein poly(ether sulfone) ultrafiltration membranes by blending with acrylonitrile-based copolymer containing ionic groups for imparting surface electrical properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 300, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, F.-Q.; Xu, Z.K.; Ming, Y.Q.; Kou, R.Q.; Liu, Z.M.; Wang, S.Y. Preparation and characterization of polyacrylonitrile-based membranes: Effects of internal coagulant on poly(acrylonitrile-co-maleic acid) ultrafiltration hollow fiber membranes. Desalination 2004, 160, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandu, T.; Sârbu, A.; Damian, C.M.; Marin, A.; Vulpe, S.; Budinova, T.; Tsyntsarski, B.; Yardim, M.F.; Sirkecioglu, A. Preparation and Characterization of Membranes Obtained from Blends of Acrylonitrile Copolymers with Poly(vinyl alcohol). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 41013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandu, T.; Sârbu, A.; Damian, C.M.; Pătroi, D.; Iordache, T.V.; Budinova, T.; Tsyntsarski, B.; Yardim, M.F.; Sirkecioglu, A. Functionalized bicomponent polymer membranes as supports for covalent immobilization of enzymes. React. Funct. Polym. 2015, 96, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.S.; Xu, Z.K.; Huang, X.J.; Che, A.F.; Wang, Z.G. A novel process for the post-treatment of polyacrylonitrile-based membranes: Performance improvement and possible mechanism. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 277, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandu, T.; Mitran, R.A.; Sârbu, A.; Stănică, N.; Gavrilă, A.M.; Pătroi, D.; Marinescu, V.; Petcu, C.; Ghiurea, M.; Dumitru, M.V.; et al. Two-component polymer beads with magnetic features as efficient means for active principles binding. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrzadeh, M.; Bhattacharjee, S. Rational design of phase inversion membranes by tailoring thermodynamics and kinetics of casting solution using polymer additives. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 441, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, Z.; Shamsaei, E.; Fang, X.Y.; Ladewig, B.; Wang, H. Simple fabrication of zeolitic imidazolate framework ZIF-8/polymer composite beads by phase inversion method for efficient oil sorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 493, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Wang, K.; Yao, J.; Wang, H. Hollow carbon beads fabricated by phase inversion method for efficient oil sorption. Carbon 2014, 69, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, M.; Hayeeye, F.; Chinpa, W.; Sirichote, O. Preparation and characterization of poly (lactic acid)/activated carbon composite bead via phase inversion method and its use as adsorbent for Rhodamine B in aqueous solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3780–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calisto, J.S.; Pacheco, I.S.; Freitas, L.L.; Santana, L.K.; Fagundes, W.S.; Amaral, F.A.; Conobre, S.C. Adsorption kinetic and thermodynamic studies of the 2,4-dichlophenoxyacetate (2,4-D) by [Co-Al-Cl]layered double hydroxide. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinayagam, R.; Ganga, S.; Murugesan, G.; Rangasamy, G.; Bhole, R.; Goveas, L.C.; Varadavenkatesan, T.; Dave, N.; Samanth, A.; Radhika Devi, V.; et al. 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) adsorptive removal by algal magnetic activated carbon nanocomposite. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zaben, M.I.; Mekhamer, W.K. Removal of 4-chloro-2-methyl phenoxy acetic acid pesticide using coffee wastes from aqueous solution. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S1523–S1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goscianska, J.; Olejnik, A. Removal of 2,4-D herbicide from aqueous solution by aminosilane-grafted mesoporous carbons. Adsorption 2019, 25, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Nasseri, S.; Karamimanesh, M. Removal of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid(2,4-D) herbicide in the aqueous phase using modified granular carbon. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandu, T.; Chiriac, A.L.; Tsyntsarski, B.; Stoycheva, I.; Căprărescu, S.; Damian, C.M.; Iordache, T.V.; Pătroi, D.; Marinescu, V.; Sârbu, A. Advanced hybrid membranes for efficient nickel retention from simulated wastewater. Polym. Int. 2021, 70, 866–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha, A.V.; Lander, L.; Rousse, G.; Tarascon, J.M.; Navrotsky, A. Thermodynamic stability and correlation with synthesis conditions, structure and phase transformations in orthorhombic and monoclinic Li2M(SO4)2 (M = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni) polymorphs. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 2601–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, J.; Hills, A.E.; Cerasoli, E.; Rakowska, P.D.; Ryadnov, M.G. FTIR markers of methionine oxidation for early detection of oxidized protein therapeutics. Eur. Biophys. J. 2011, 40, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatti, A.Z.; Qureshi, K.; Maitlo, G.; Ahmed, S. Study of PAN Fiber and Iron ore Adsorbents for Arsenic Removal. Civ. Eng. J. 2020, 6, 548–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, P.; Sreekumar, T.V.; Sen, K. Thermal behaviour of acrylonitrile copolymers having methacrylic and itaconic acid comonomers. Polymer 2001, 42, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassios, K.G. Poly (vinyl alcohol)-infiltrated carbon nanotube carpets. Mater. Sci. App. 2012, 3, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hamta, A.; Ashtiani, F.Z.; Karimi, M.; Moayedfard, S. Asymmetric block copolymer membrane fabrication mechanism through self-assembly and non-solvent induced phase separation (SNIPS) process. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harabi, S.; Guiza, S.; Álvarez-Montero, A.; Gómez-Avilés, A.; Bagané, M.; Belver, C.; Bedia, J. Adsorption of Pesticides on Activated Carbons from Peach Stones. Processes 2024, 12, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dima, S.-O.; Meouche, W.; Dobre, T.; Nicolescu, T.-V.; Sarbu, A. Diosgenin-selective molecularly imprinted pearls prepared by wet phase inversion. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florea, A.-M.; Iordache, T.-V.; Branger, C.; Ghiurea, M.; Avramescu, S.; Hubca, G.; Sarbu, A. An innovative approach to prepare hypericin molecularly imprinted pearls using a “phyto-template”. Talanta 2016, 148, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cates, E.L. Photocatalytic Water Treatment: So Where Are We Going with This? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 757–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrunik, M.; Skalny, M.; Gajewska, M.; Marzec, M.; Bajda, T. Comparison of pesticide adsorption efficiencies of zeolites and zeolite-carbon composites and their regeneration possibilities. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, B.H.; Salman, J.M.; Ahmad, A.L. Adsorption Isotherm and Kinetic Modeling of 2,4-D Pesticide on Activated Carbon Derived from Date Stones. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarotto, J.S.; da Boit Martinello, K.; Georgin, J.; Franco, D.S.P.; Netto, M.S.; Piccilli, D.G.A.; Silva, L.F.O.; Lima, E.C.; Dotto, G.L. Preparation of Activated Carbon from the Residues of the Mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) Production Chain for the Adsorption of the 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Herbicide. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample Code | TOC (mg/L) 1st Step | TOC (mg/L) 2nd Step |
|---|---|---|
| 1-REF | 8.99 | 1.76 |
| 1-RM | 14.55 | 1.28 |
| 2-REF | 1.21 | - |
| 2-RM | 1.84 | - |
| 3-REF | 0.71 | - |
| 3-RM | 1.78 | - |
| Sample Code | Residue at 250 °C | Residue at 500 °C | Residue at 1000 °C | Residue at 1000 °C of Dried Sample, RD (% wt) * | RMCalc (% wt) ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 REF | 55.49 | 39.58 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.00 |
| 1 RM | 53.69 | 39.79 | 1.73 | 3.23 | 3.42 |
| 2 REF | 46.71 | 29.71 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.00 |
| 2 RM | 47.44 | 32.82 | 1.54 | 3.24 | 3.44 |
| 3 REF | 73.94 | 46.92 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.00 |
| 3 RM | 64.13 | 40.06 | 3.33 | 5.19 | 5.63 |
| RM | 96.27 | 89.04 | 88.11 | 91.53 | - |
| Sample | BET Surface Area (m2g−1) | Pore Surface Area (BJH) (m2g−1) | Mean Pore Diameter (BJH) (nm) | Mean Pore Volume (BJH) (cm3g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Ref | 56.72 | 65.51 | 3.47 | 0.0277 |
| 1-RM | 7.07 | 5.99 | 3.17 | 0.0113 |
| 2-Ref | 41.79 | 66.59 | 4.54 | 0.0545 |
| 2-RM | 2.74 | 18.60 | 4.54 | 0.0150 |
| 3-Ref | 1.15 | 3.09 | 4.54 | 0.0037 |
| 3-RM | 2.18 | 3.47 | 4.54 | 0.0070 |
| Sample Code | Adsorbent Amount (mg) | pH | TOCfinal (mg C/L) | Adsorption Capacity * (mg C/g Adsorbent) | Adsorbed Amount ** (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Ref | 40.5 | 3.70 | 48.54 | / | / |
| 1-RM | 40.7 | 3.67 | 47.23 | / | / |
| 2-Ref | 39.6 | 3.64 | 47.99 | / | / |
| 2-RM | 40.4 | 3.70 | 49.07 | / | / |
| 3-Ref | 40.1 | 3.80 | 47.83 | / | / |
| 3-RM | 41.0 | 3.75 | 41.85 | 1.65 | 9.71 |
| Sample | Adsorbent Amount (mg) | TOCinitial (mg C/L) | Adsorption/ Oxidation Capacity * (mg C/g Adsorbent) | Adsorbed/ Oxidized Amount vs. TOCinitial (%) ** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2,4 DCFA | +H2O2 | - | 46.64 | - | - |
| RM | +H2O2 | 40.4 | 1.34 | - | - |
| 3-Ref + 2,4 DCFA | +H2O2 | 40.2 | 42.03 | 5.73 | 9.88 |
| 3-RM + 2,4 DCFA | +H2O2 | 39.8 | 40.67 | 7.50 | 12.80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sandu, T.; Olaru, E.A.; Mitran, R.-A.; Miron, A.; Dolana, S.-V.; Zaharia, A.; Gavrilă, A.-M.; Dumitru, M.-V.; Chiriac, A.-L.; Sârbu, A.; et al. Composite Copolymer Beads Incorporating Red Mud for Water Amendment by Adsorption—Oxidation Processes. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6386. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146386
Sandu T, Olaru EA, Mitran R-A, Miron A, Dolana S-V, Zaharia A, Gavrilă A-M, Dumitru M-V, Chiriac A-L, Sârbu A, et al. Composite Copolymer Beads Incorporating Red Mud for Water Amendment by Adsorption—Oxidation Processes. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(14):6386. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146386
Chicago/Turabian StyleSandu, Teodor, Elena Alina Olaru, Raul-Augustin Mitran, Andreea Miron, Sorin-Viorel Dolana, Anamaria Zaharia, Ana-Mihaela Gavrilă, Marinela-Victoria Dumitru, Anita-Laura Chiriac, Andrei Sârbu, and et al. 2024. "Composite Copolymer Beads Incorporating Red Mud for Water Amendment by Adsorption—Oxidation Processes" Applied Sciences 14, no. 14: 6386. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146386
APA StyleSandu, T., Olaru, E. A., Mitran, R.-A., Miron, A., Dolana, S.-V., Zaharia, A., Gavrilă, A.-M., Dumitru, M.-V., Chiriac, A.-L., Sârbu, A., & Iordache, T.-V. (2024). Composite Copolymer Beads Incorporating Red Mud for Water Amendment by Adsorption—Oxidation Processes. Applied Sciences, 14(14), 6386. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146386












