Band-Pass and Band-Stop Filter Frequency Selective Surface with Harmonic Suppression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design of Proposed Frequency Selective Surface with Harmonic Suppression
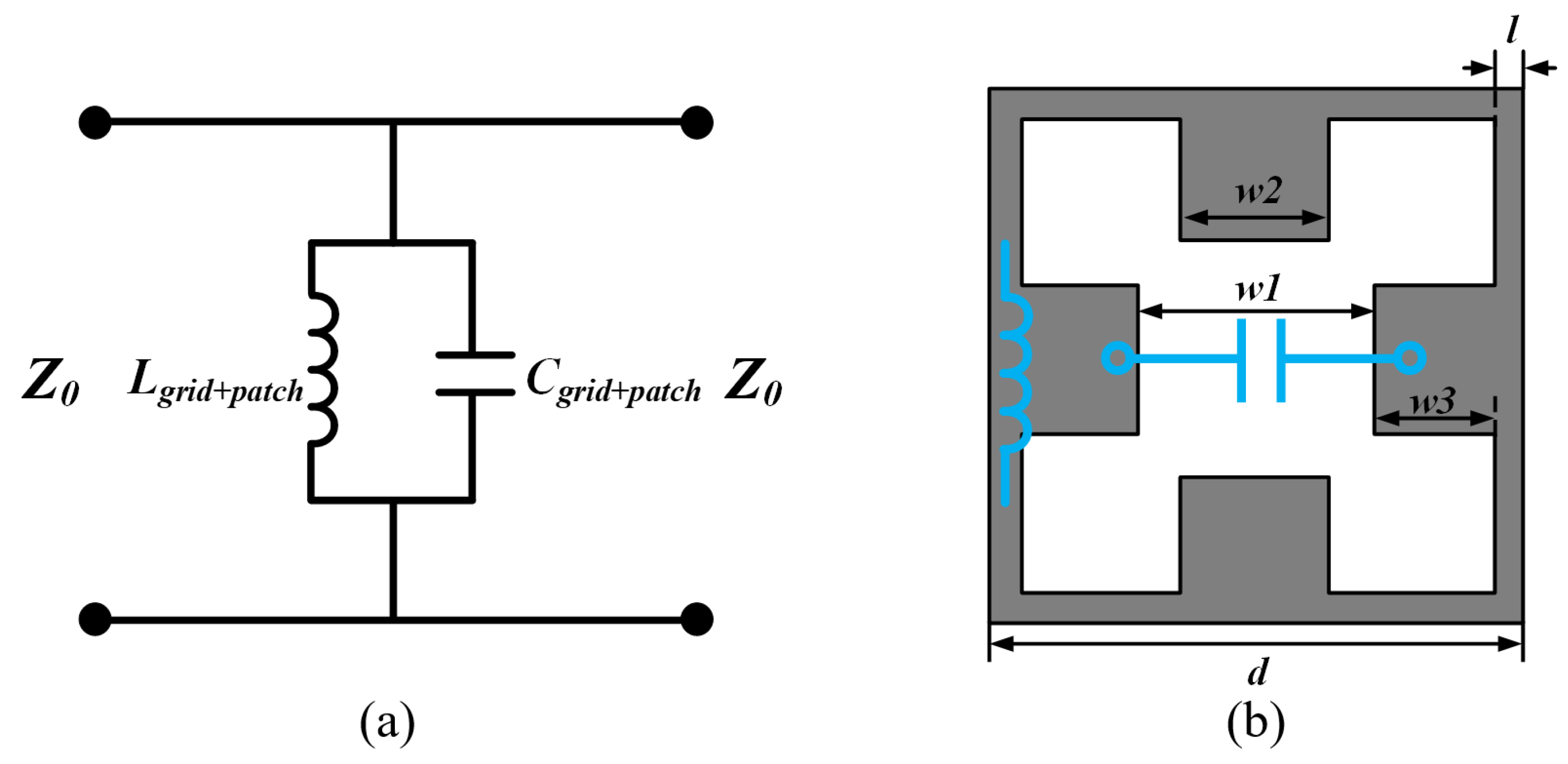
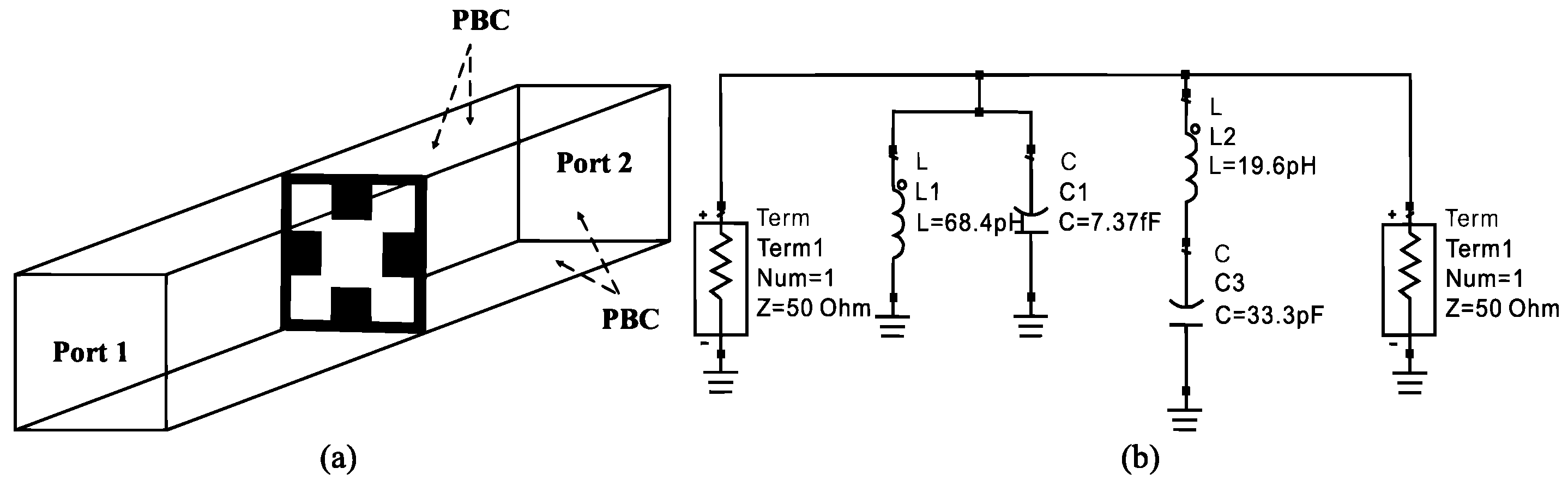
2.1. Design of Proposed Grid Structure with Band-Pass Filter Characteristics
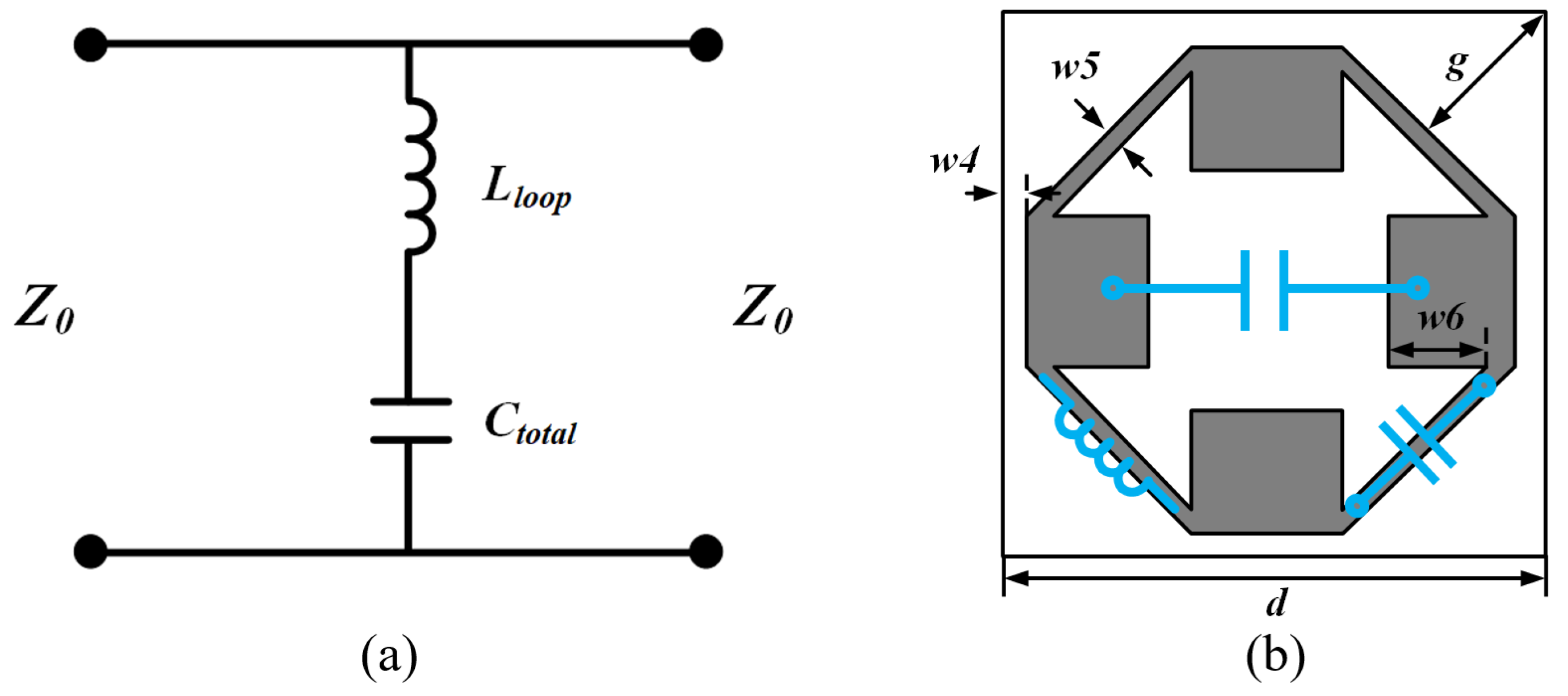
2.2. Design of Proposed Loop Structure with Band-Stop Filter Characteristics
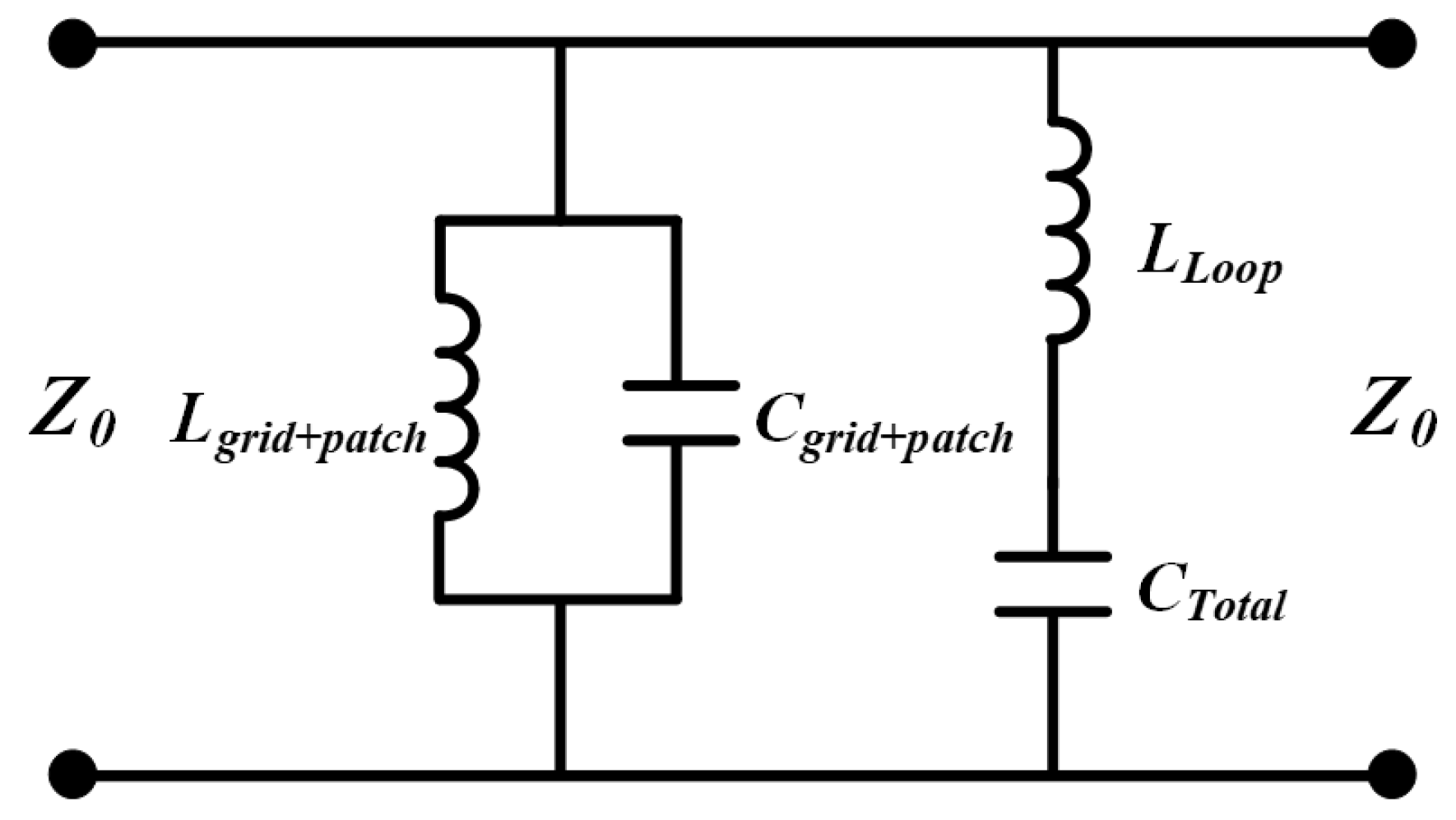
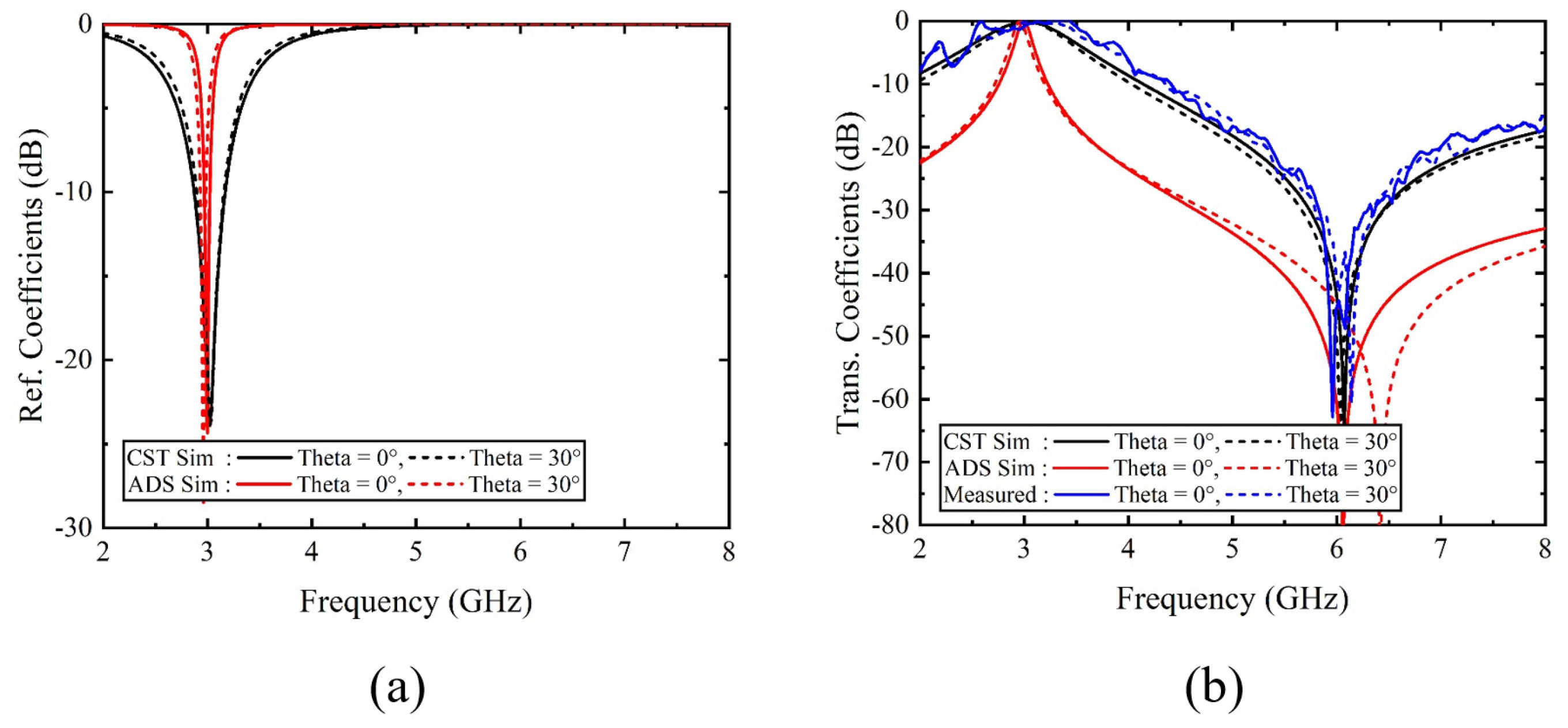
2.3. The Reflection Coefficient and Transmission Coefficient Results of the Proposed FSS
3. Method for Beam Steering
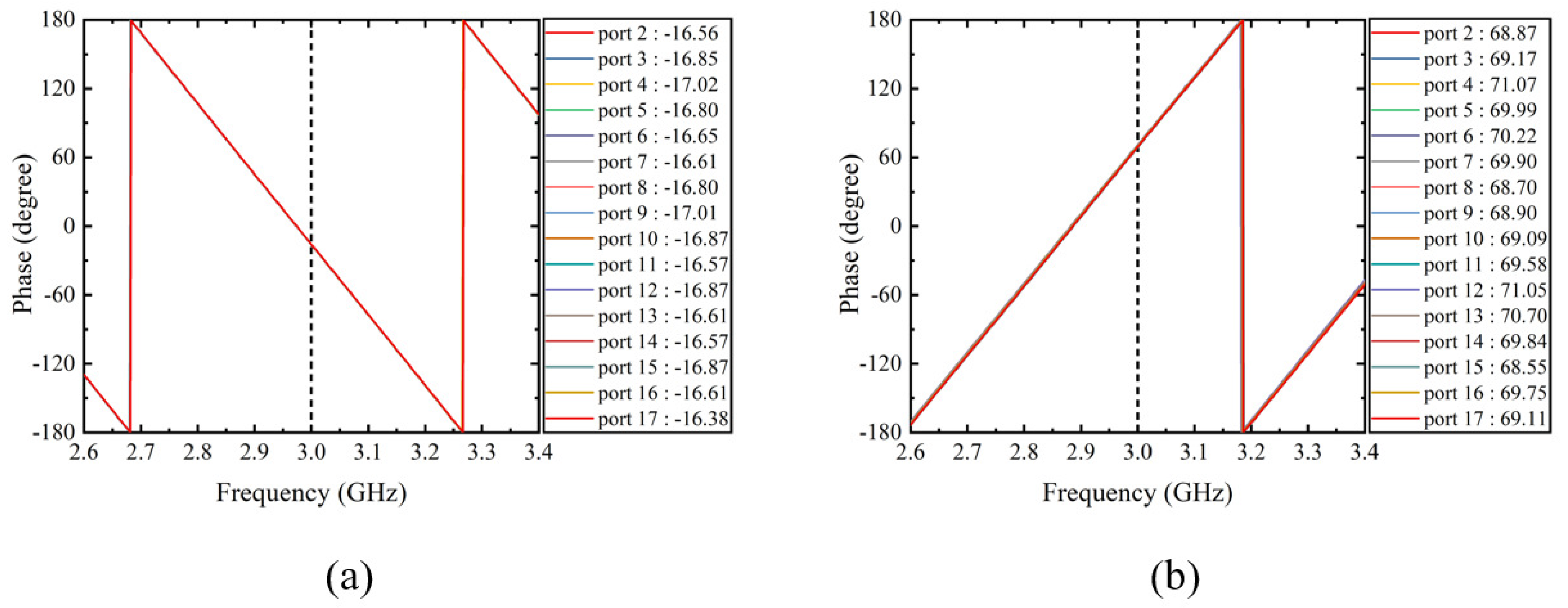
3.1. Phase Calculation for Electronic Beam Steering
3.2. Phase Calculation for Electronic Beam Steering
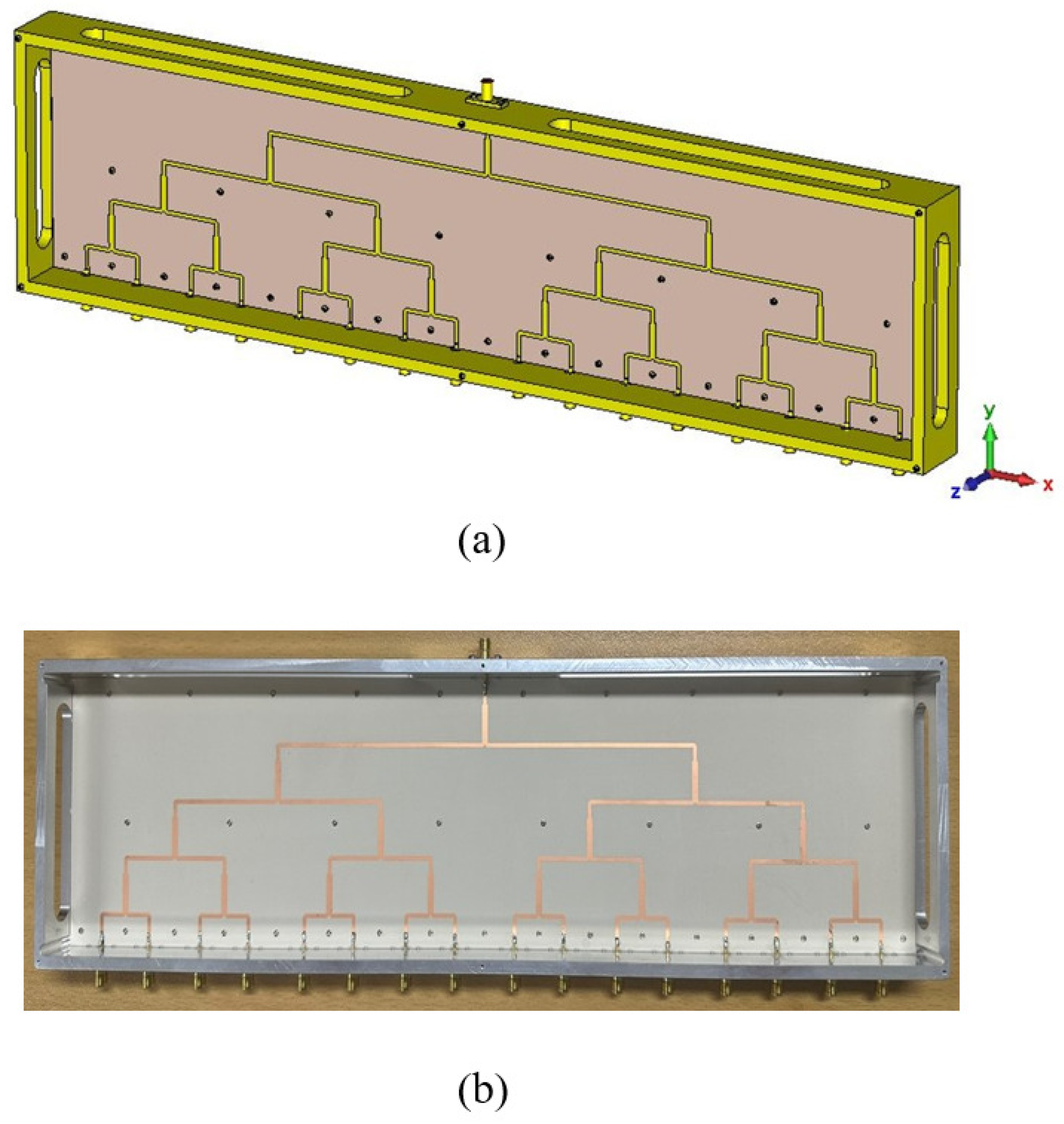
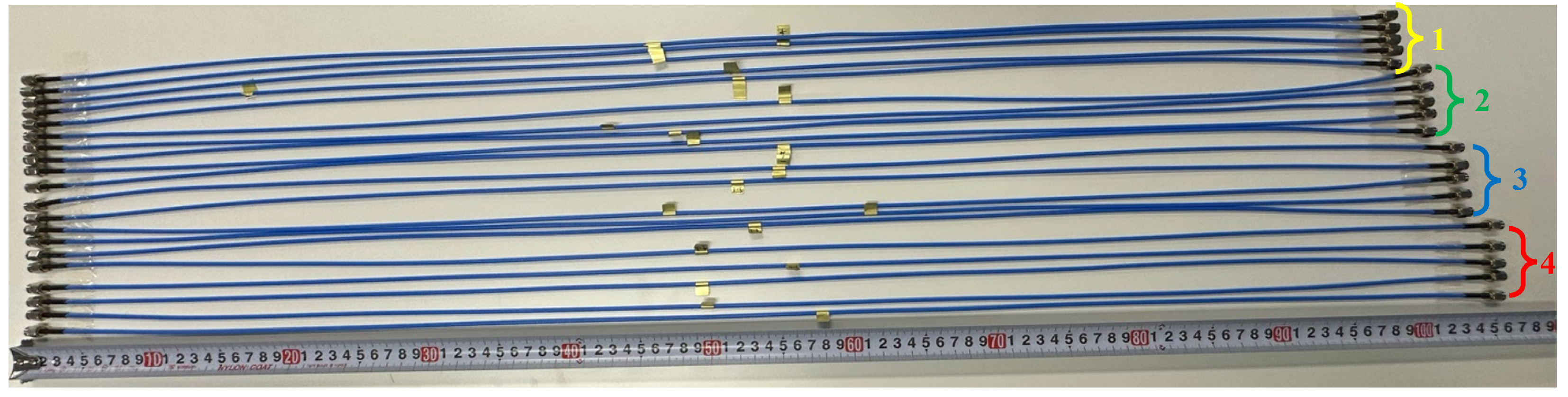
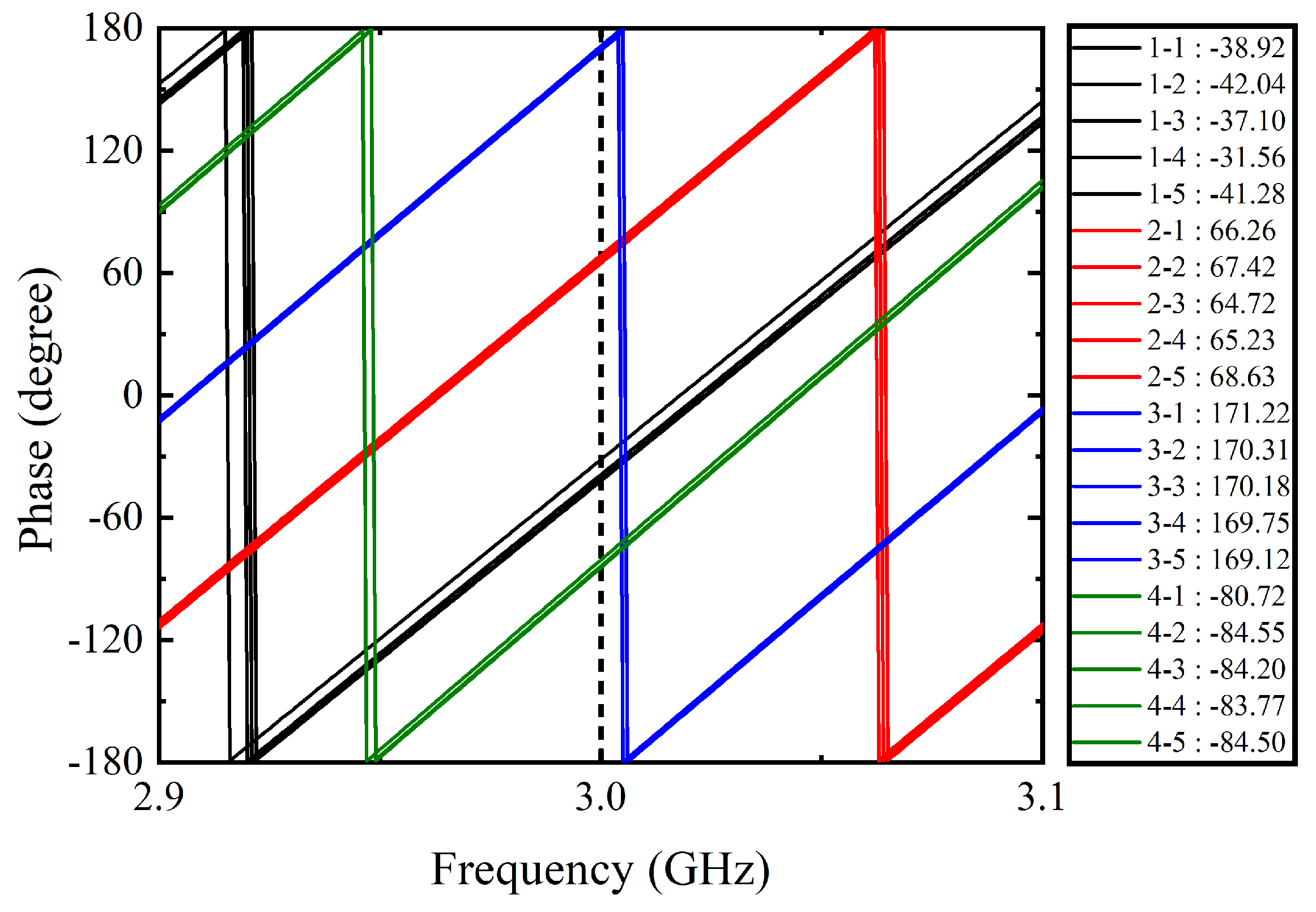
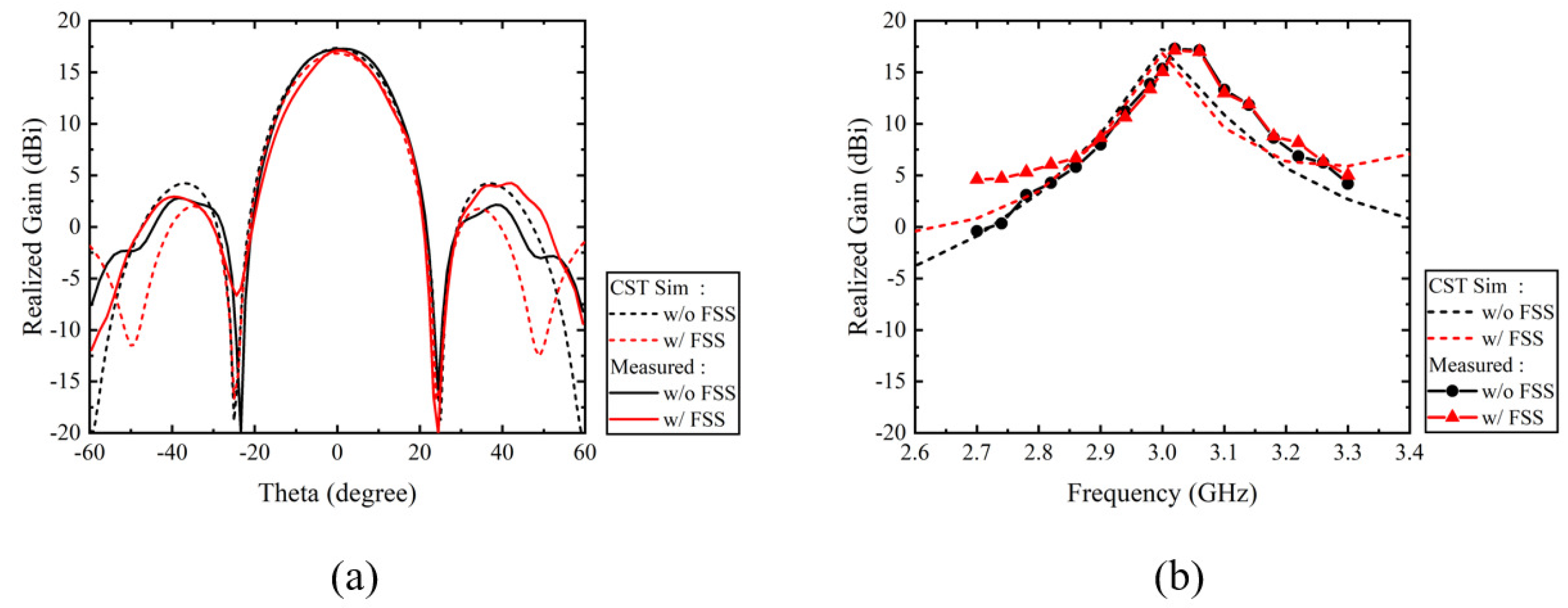
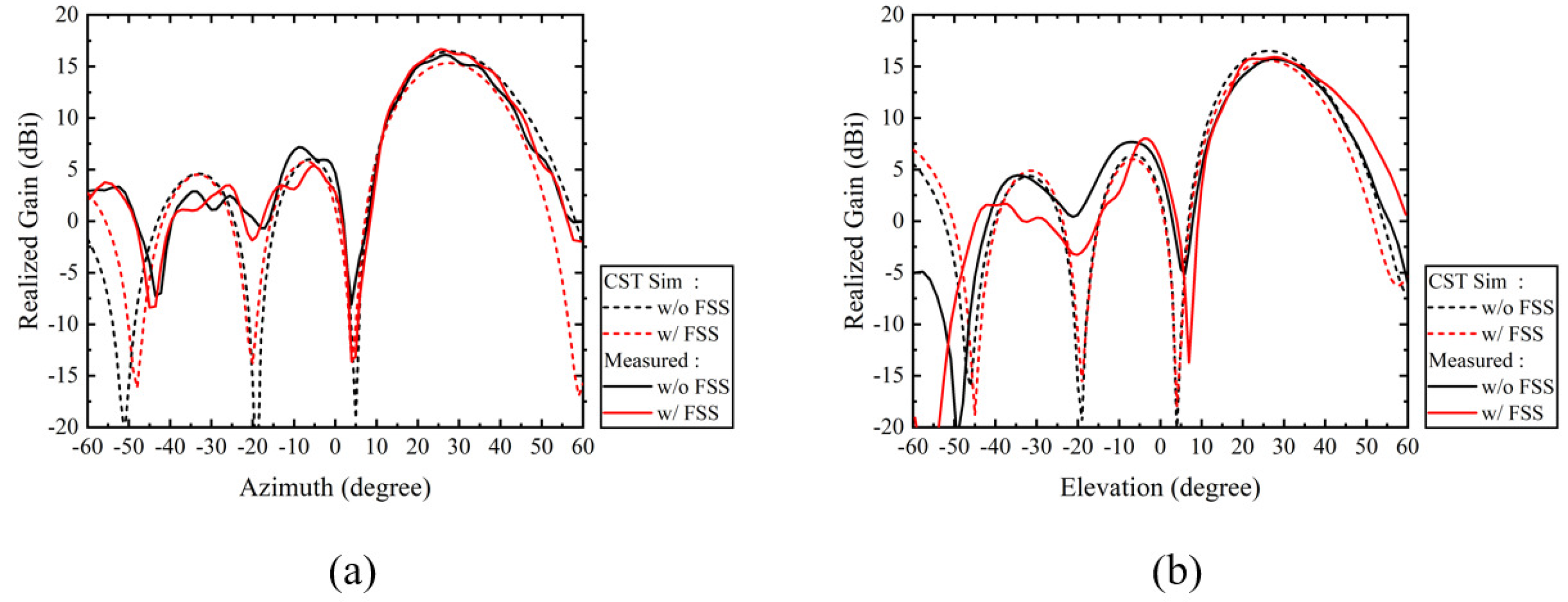
3.3. Measured Result Analysis of the Fabricated Coaxial Cable
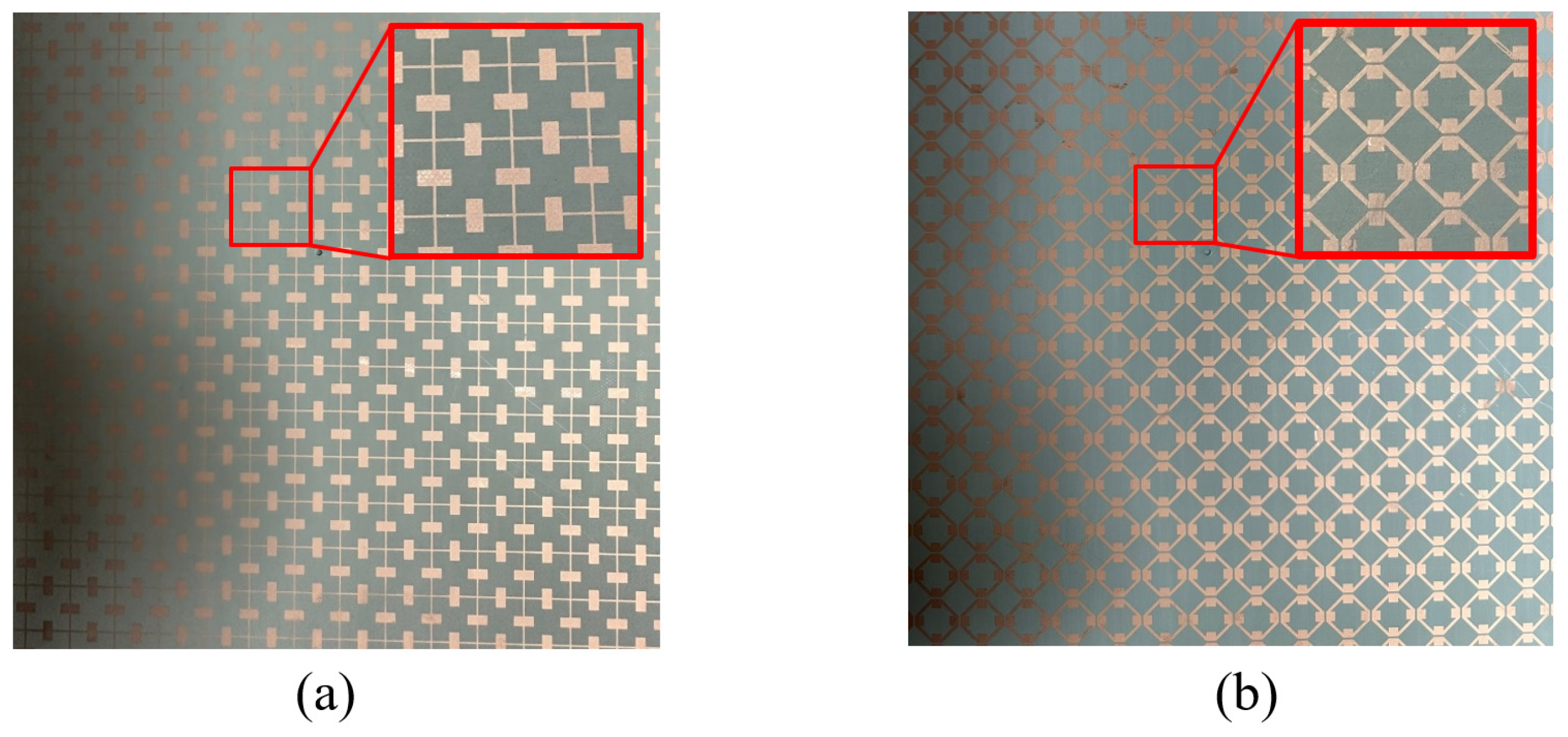
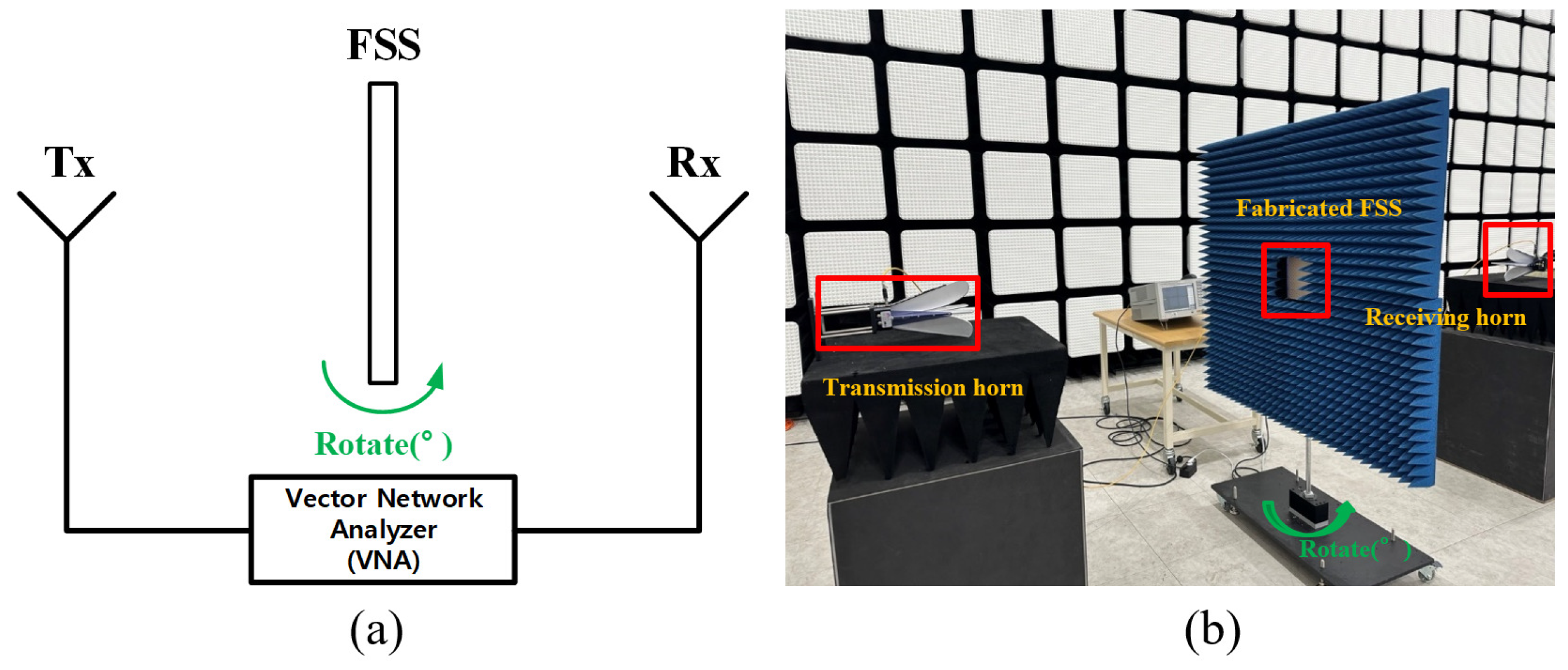
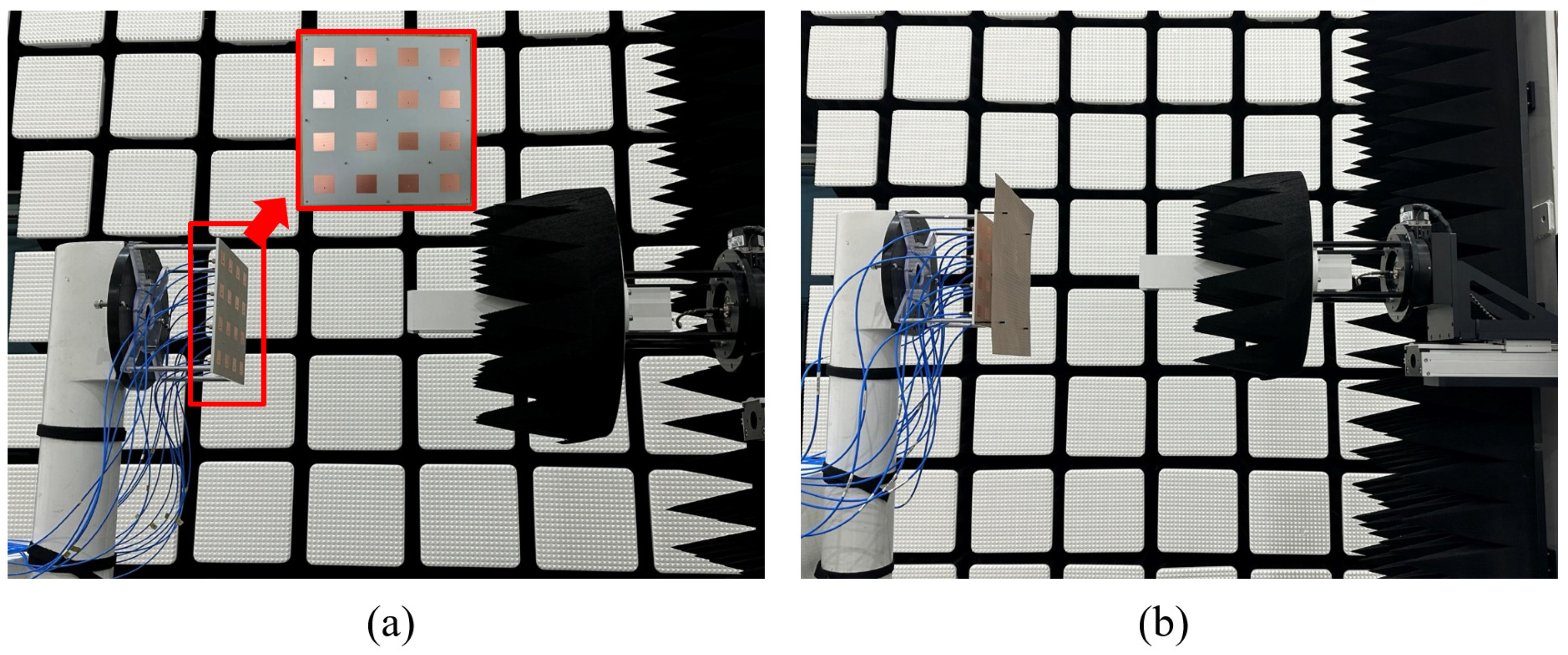
4. Measured Result Analysis of the Proposed FSS
5. Results
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Curlander, J.C.; McDonough, R.N. Synthetic Aperture Radar: Systems and Signal Processing, 1st ed.; John Wiley, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik, M. Introduction to Radar Systems; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Harger, R.O. Harmonic radar systems for near-ground in-foliage nonlinear scatterers. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1976, 12, 230–245. [Google Scholar]
- Aniktar, H.; Baran, D.; Karav, E.; Akkaya, E.; Birecik, Y.S.; Sezgin, M. Getting the bugs out: A portable harmonic radar system for electronic countersurveillance applications. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2015, 16, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzaro, G.J.; Martone, A.F.; Ranney, K.I.; Narayanan, R.M. Nonlinear Radar for Finding RF Electronics: System Design and Recent Advancements. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2017, 65, 1716–1726. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, J.; Trinh-Van, S.; Park, J.Y.; Yang, Y.; Lee, K.Y.; Hwang, K.C. Cavity-Backed Patch Filtenna for Harmonic Suppression. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 221580–221589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, T.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, D.G.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.; Hwang, D.H.; Hwang, K.C. Quasi-Isotropic Hybrid Dielectric Resonator Antenna—Bow-Tie Patch with Harmonic Suppression. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Wu, Q.; Liu, N.; Wu, W. A Compact Microstrip-Fed Patch Antenna With Enhanced Bandwidth and Harmonic Suppression. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 5030–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.X.; Zhu, L.; Liu, N.W. A Compact Omnidirectional Patch Antenna With Ultrawideband Harmonic Suppression. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 7640–7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, B.A. Frequency Selective Surfaces: Theory and Design; John Wiley, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, X.-J.; Fan, J.-J.; Liu, N.; Zhang, C.-B. A miniaturized dual-band FSS with controllable frequency resonances. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Components Lett. 2017, 27, 915–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.J.; Mo, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, C.; Ni, C. Design of a FSS Radome with High Harmonic Emission Suppression. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), Xi’an, China, 27–30 October 2019; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Kou, N.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, Z. Harmonic-Absorption Frequency Selective Rasorber Based on Non-Resonant FSS and Resistive-Sheet. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2021, 69, 3737–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Luyen, H.; Xu, S.; Behdad, N. Design Method for Low-Profile, Harmonic-Suppressed Filter-Antennas Using Miniaturized-Element Frequency Selective Surfaces. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2019, 18, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuvitz, N. Waveguide Handbook; Peregrinus: Stevenage, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Luukkonen, O.; Simovski, C.; Granet, G.; Goussetis, G.; Lioubtchenko, D.; Raisanen, A.V.; Tretyakov, S.A. Simple and accurate analytical model of planar grids and high-impedance surfaces comprising metal strips or patches. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2008, 56, 1624–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Langley, R.J. Equivalent-circuit models for frequency selective surfaces at oblique angles of incidence. IEE Proc. H-Microwaves Opt. Antennas 1985, 132, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, R.J.; Parker, E.A. Equivalent circuit model for arrays of square loops. Electron. Lett. 1982, 18, 294–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| h | 0.25 | 2 | |
| d | 10.5 | 0.3 | |
| l | 0.3 | 0.91 | |
| 5.9 | 0.68 | ||
| 2.3 | g | 3.12 |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 68.4 pH | 7.37 fF | ||
| 19.6 pH | 33.3 pF |
| Ref | FSS Filter Type | Unit Cell Size (Length × Width) [] | Height | Insertion Loss [dB] | Harmonic Suppression | Beam Tilting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [11] | Dual Band-Pass Filter | 0.113 × 0.113 | 1 mm | 0.5 | N/A | Azi, Ele () |
| [12] | Band-Stop Filter | 0.15 | 0.16 mm | 0.5 | o | N/A |
| [13] | Dual Band-Pass Filter | 0.1 | 23 nm | 0.98 | o | Azi, Ele () |
| [14] | Dual Band-Pass Filter | 0.2 | 5.5 mm | 0.3 | o | Azi, Ele () |
| Proposed Work | Band-Pass, Band-Stop Filter | 0.105 | 0.25 mm | 0.12 | o | Azi, Ele () |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, D.H.; Jeong, T.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, K.C. Band-Pass and Band-Stop Filter Frequency Selective Surface with Harmonic Suppression. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6633. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156633
Hwang DH, Jeong T, Kim JH, Hwang KC. Band-Pass and Band-Stop Filter Frequency Selective Surface with Harmonic Suppression. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(15):6633. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156633
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Dong Hyee, Taeyong Jeong, Jun Hee Kim, and Keum Cheol Hwang. 2024. "Band-Pass and Band-Stop Filter Frequency Selective Surface with Harmonic Suppression" Applied Sciences 14, no. 15: 6633. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156633
APA StyleHwang, D. H., Jeong, T., Kim, J. H., & Hwang, K. C. (2024). Band-Pass and Band-Stop Filter Frequency Selective Surface with Harmonic Suppression. Applied Sciences, 14(15), 6633. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156633









