Experimental and Parametric Analysis of Pull-Out Resistance of Notched T-Perfobond Connectors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Pull-Out Test
2.1. Test Program
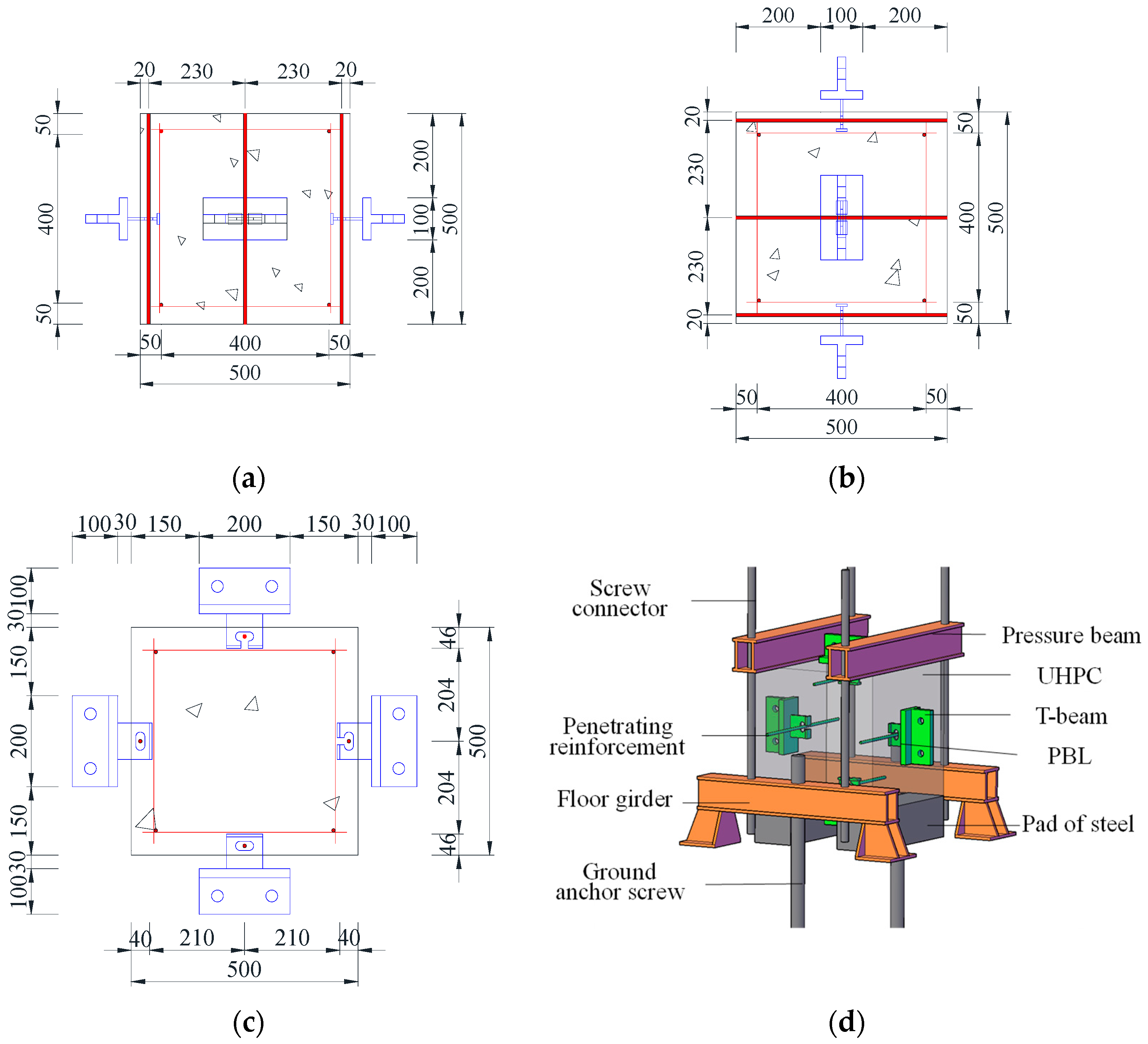
2.2. Specimen Layout
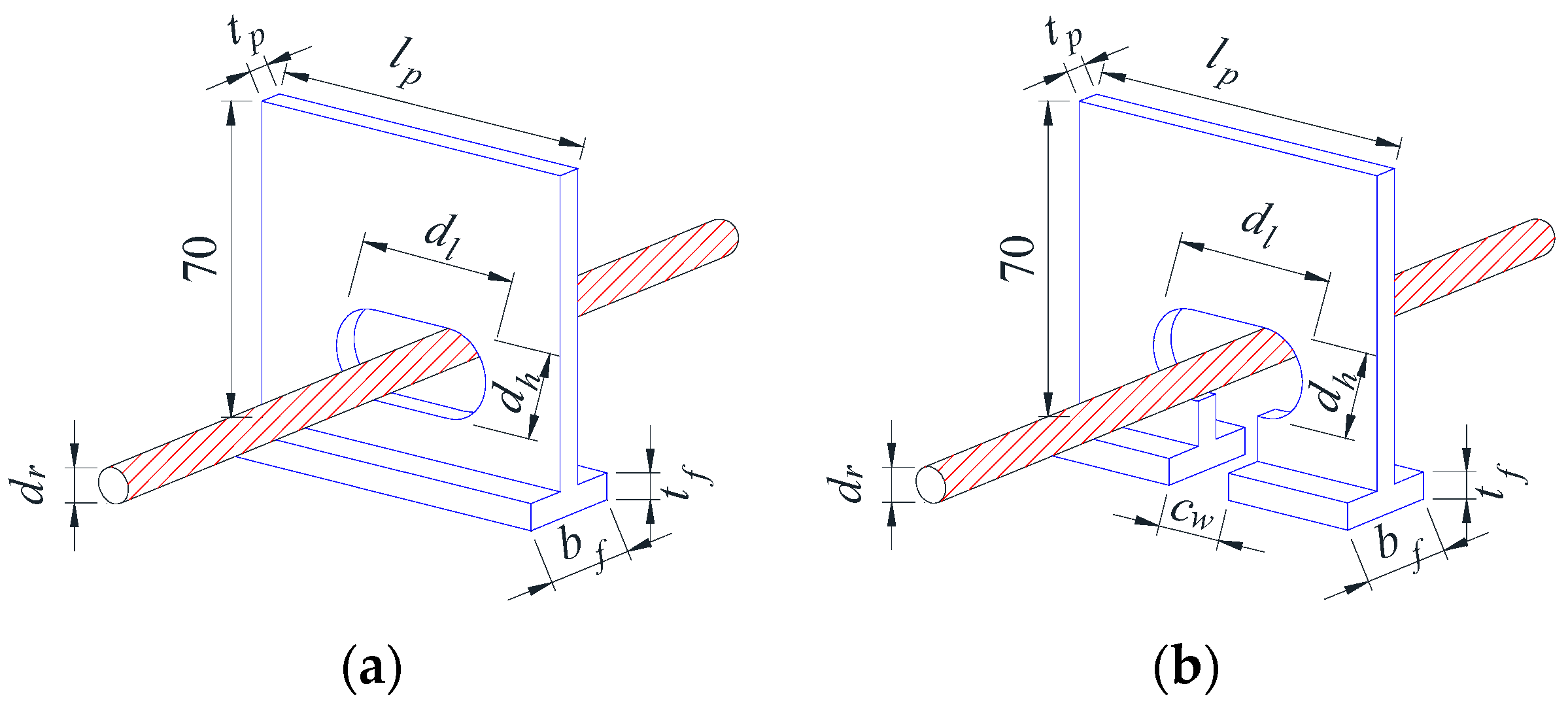
2.3. Details of Perfobond Ribs
2.4. Material Properties
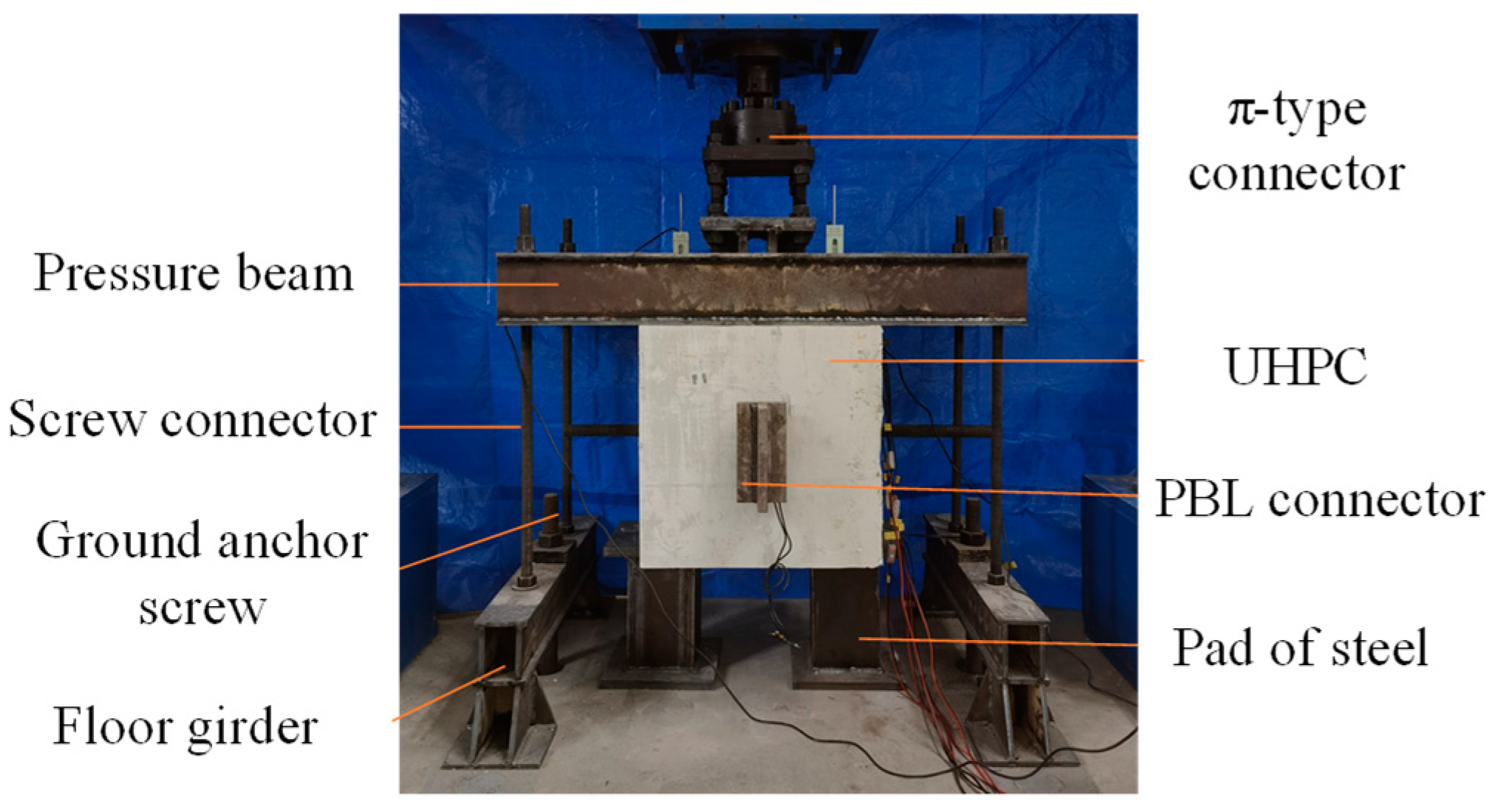
2.5. Test Setup and Instrumentation
3. Test Results and Analysis
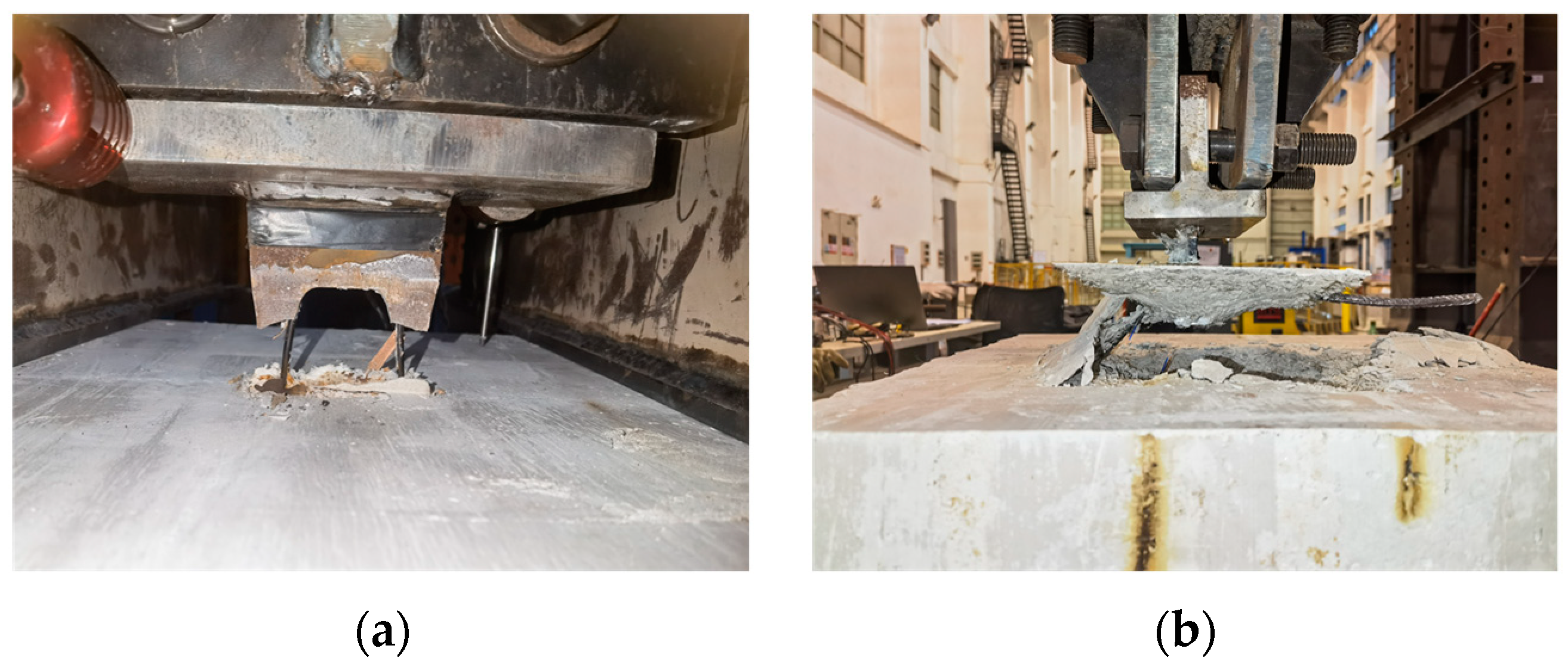
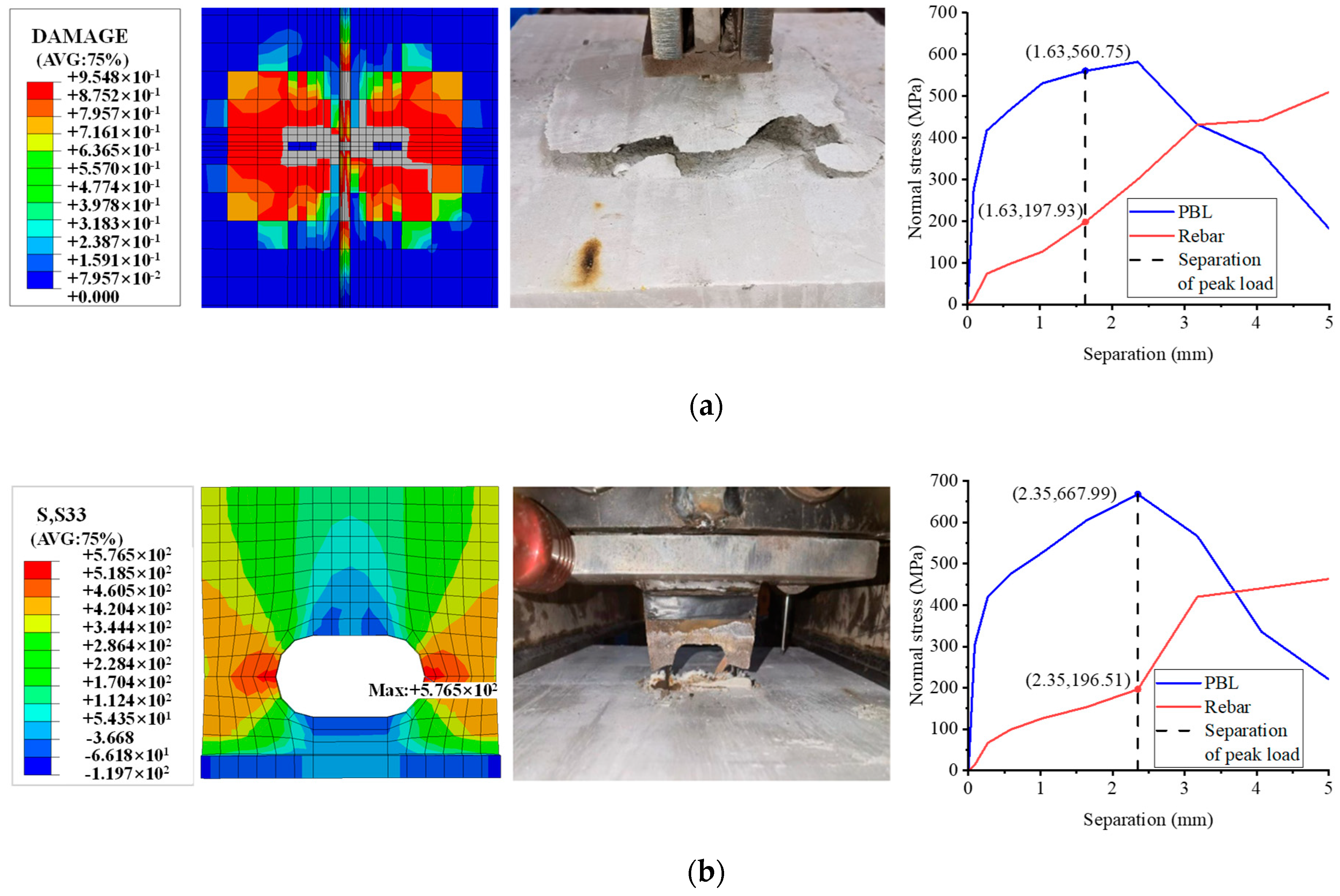
3.1. Failure Mode
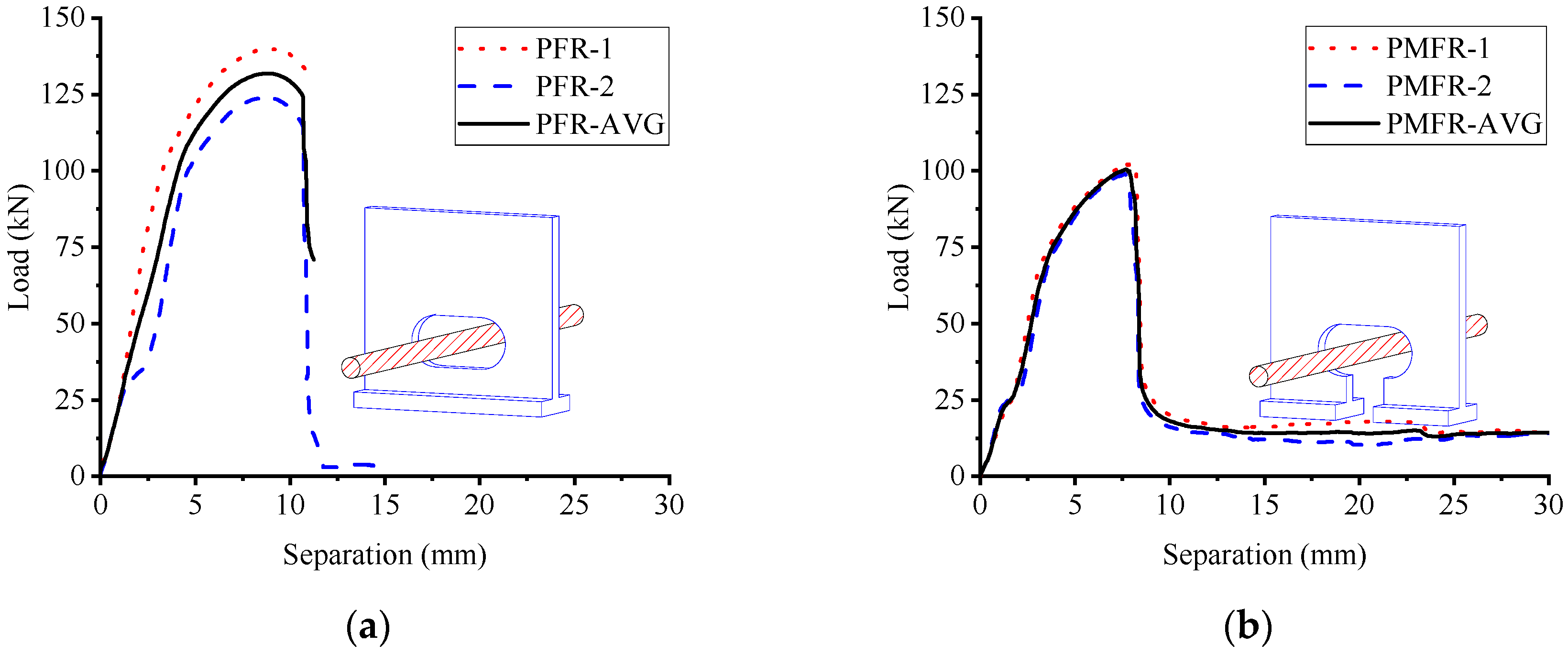
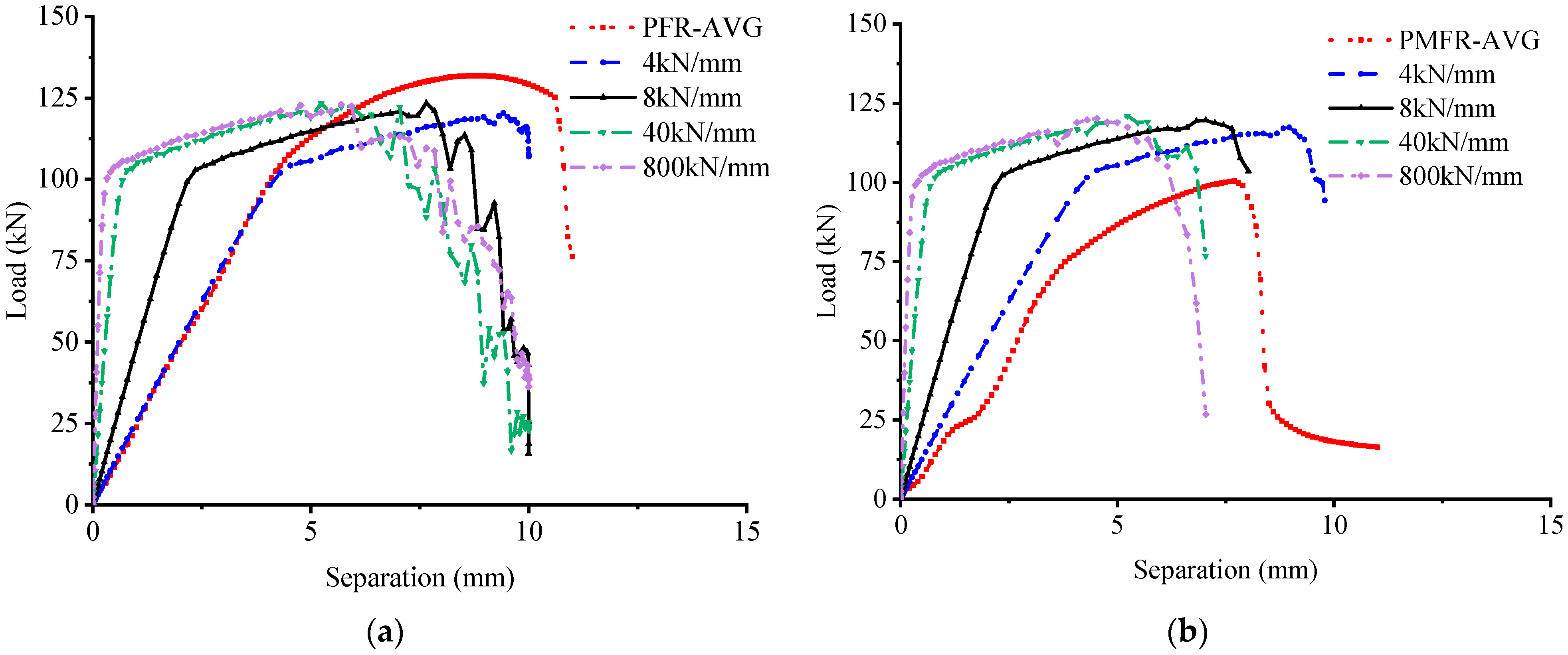
3.2. Load–Separation Behavior
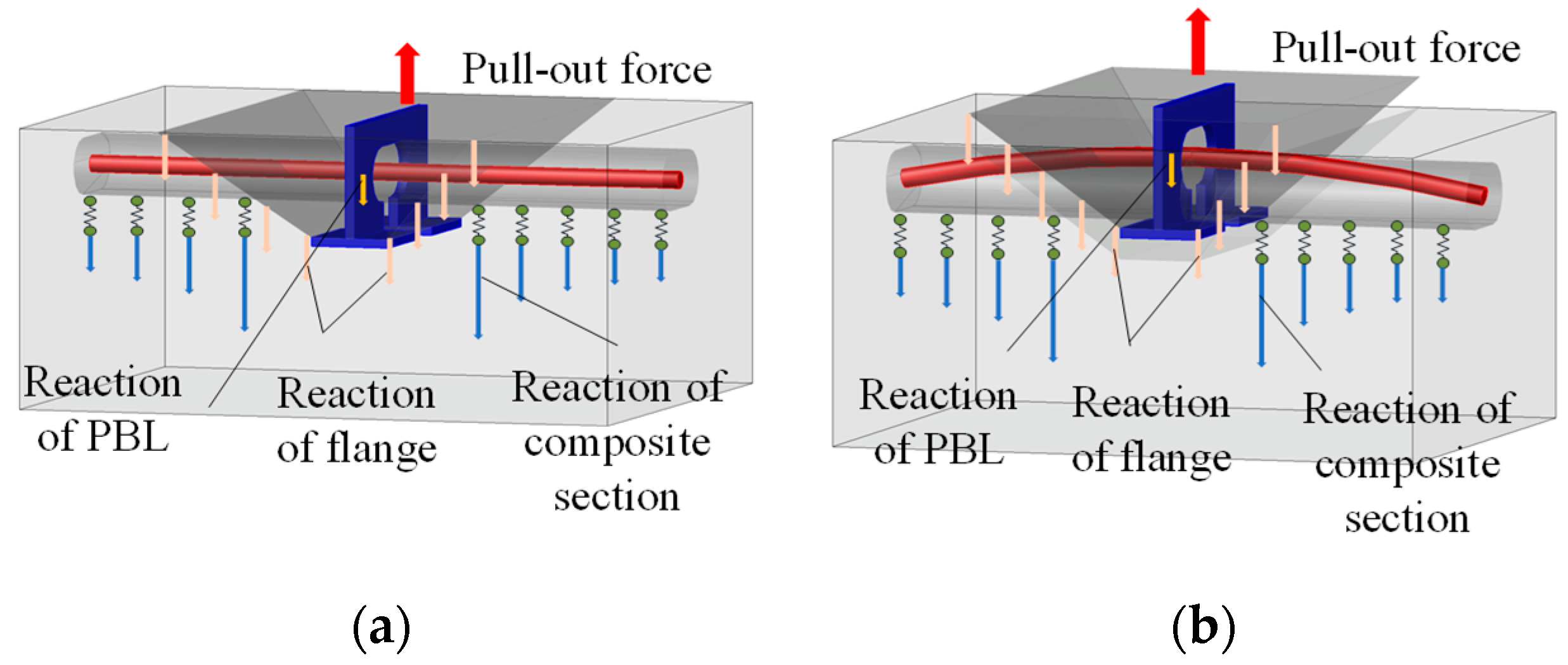
3.3. Pull-Out Mechanism
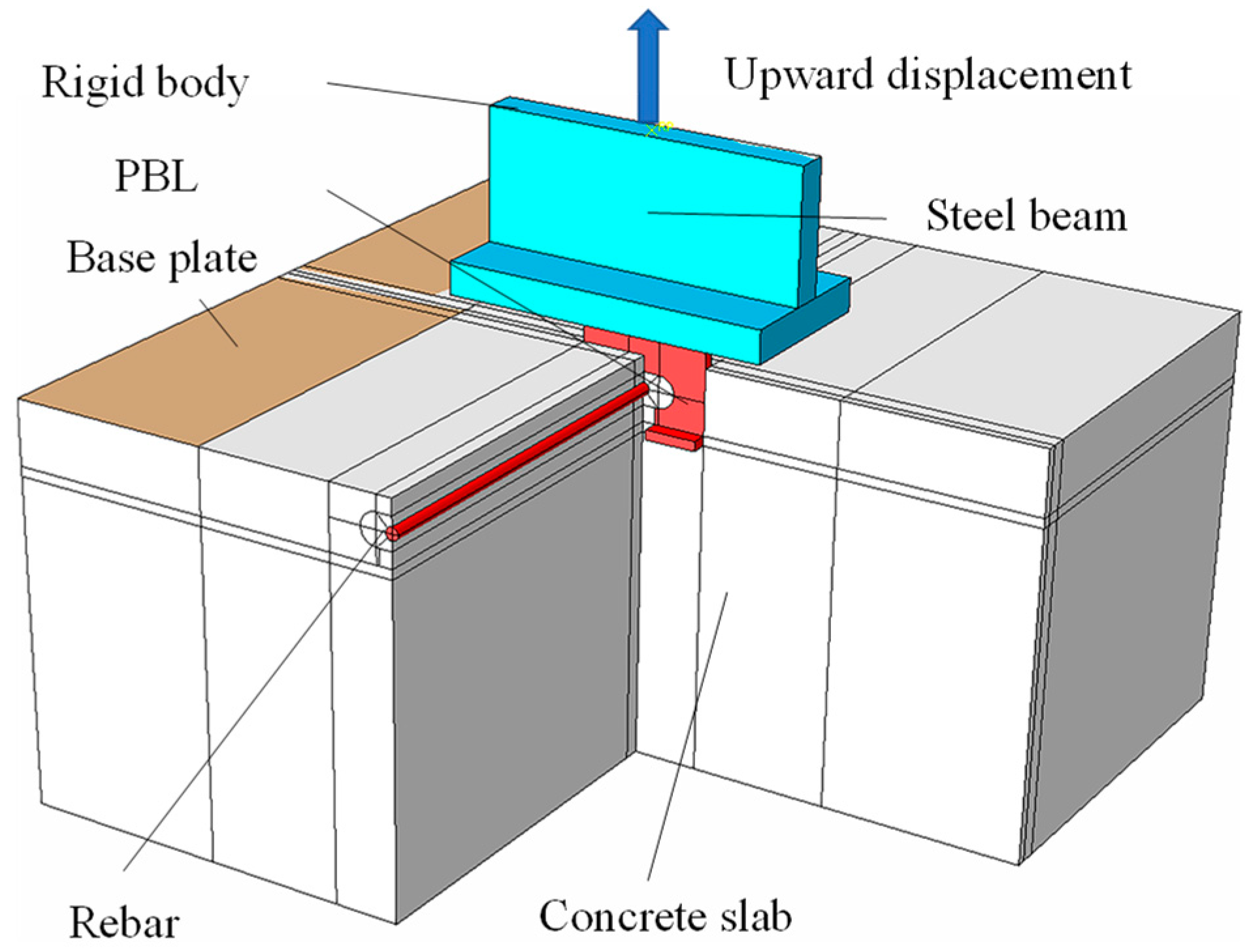
4. Numerical Simulation
4.1. General
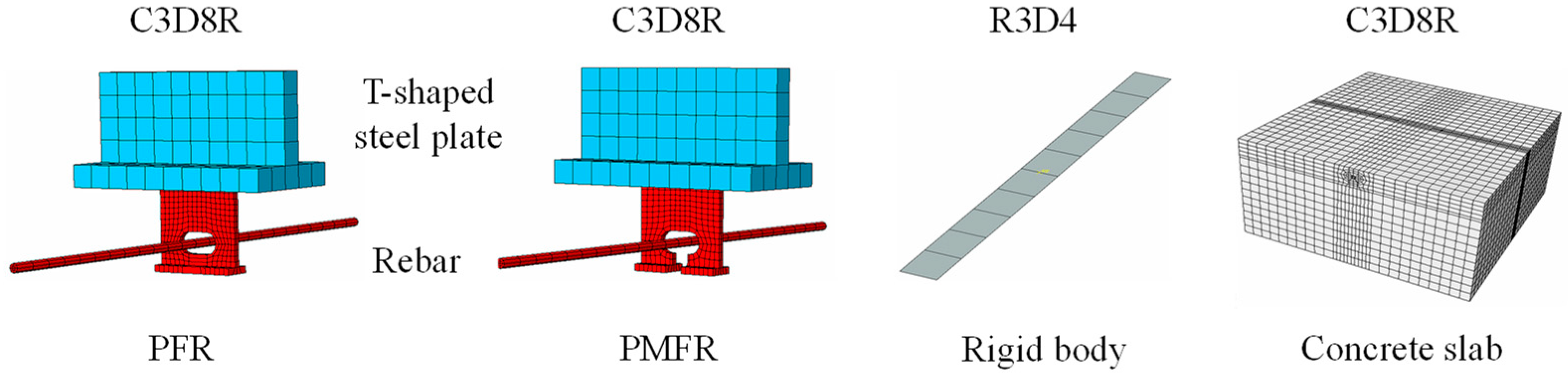
4.2. Finite-Element Type and Mesh
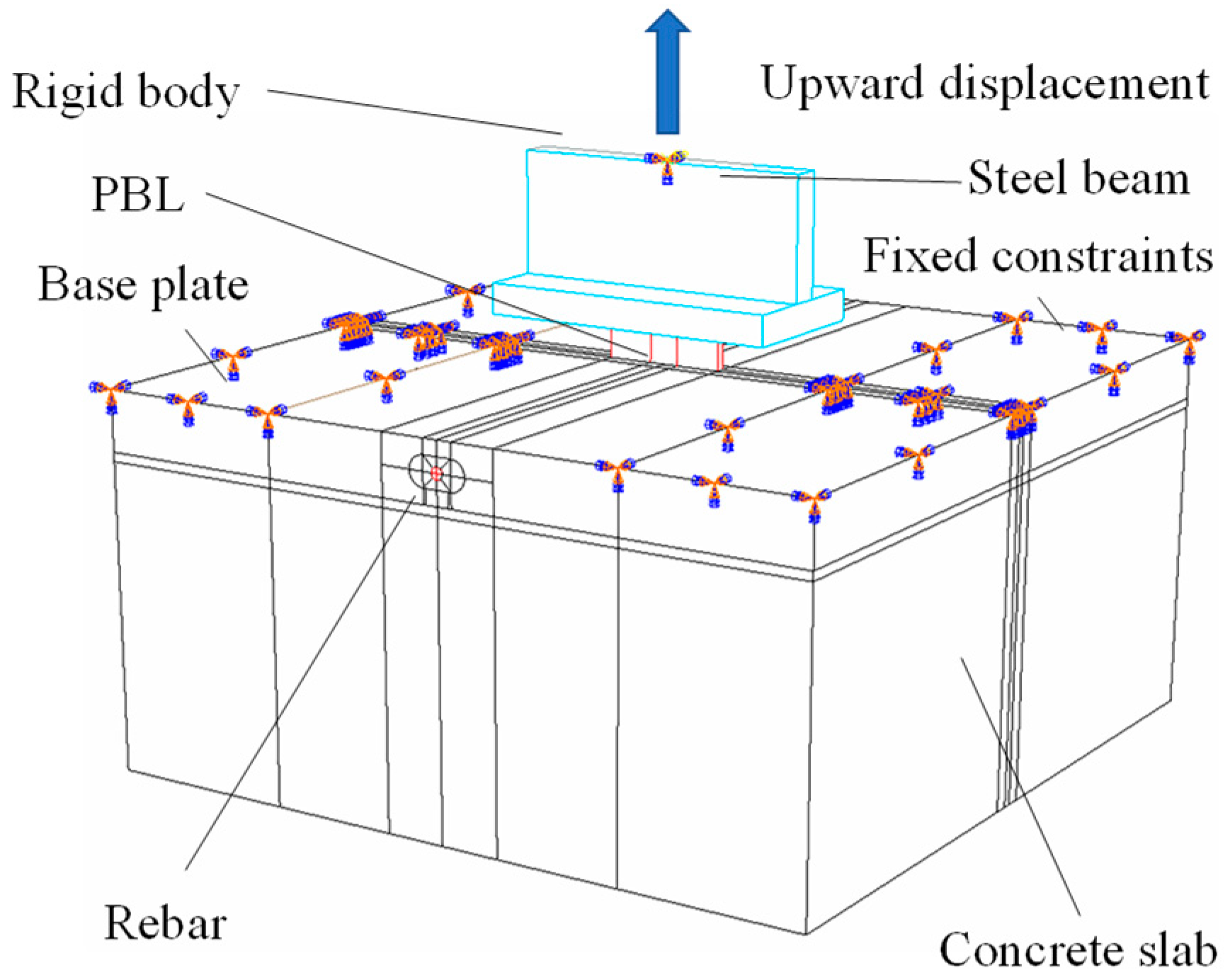
4.3. Interaction and Boundary Conditions
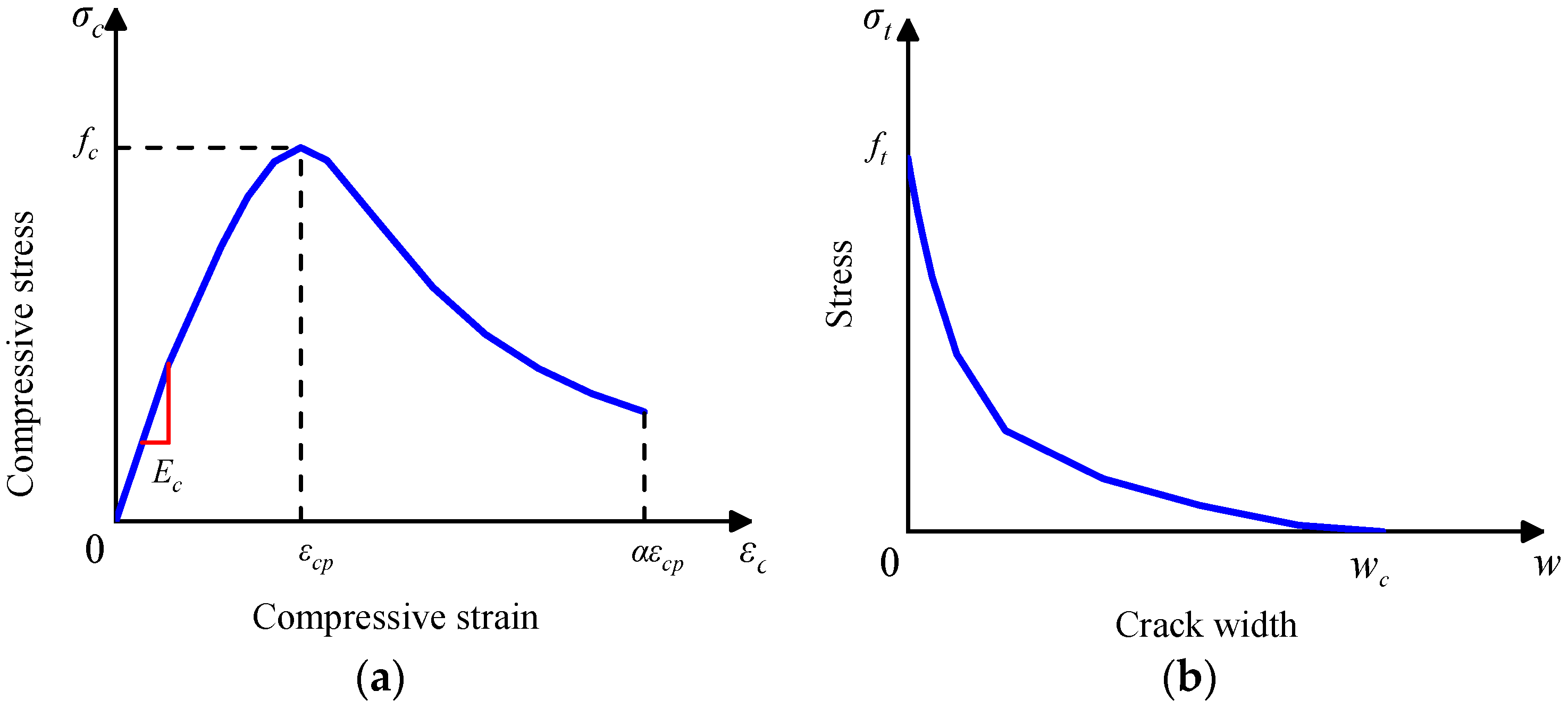
4.4. Material Constitution of Concrete
4.5. Material Constitution of Steel
4.6. Verification of Finite-Element Model
5. Parametric Study
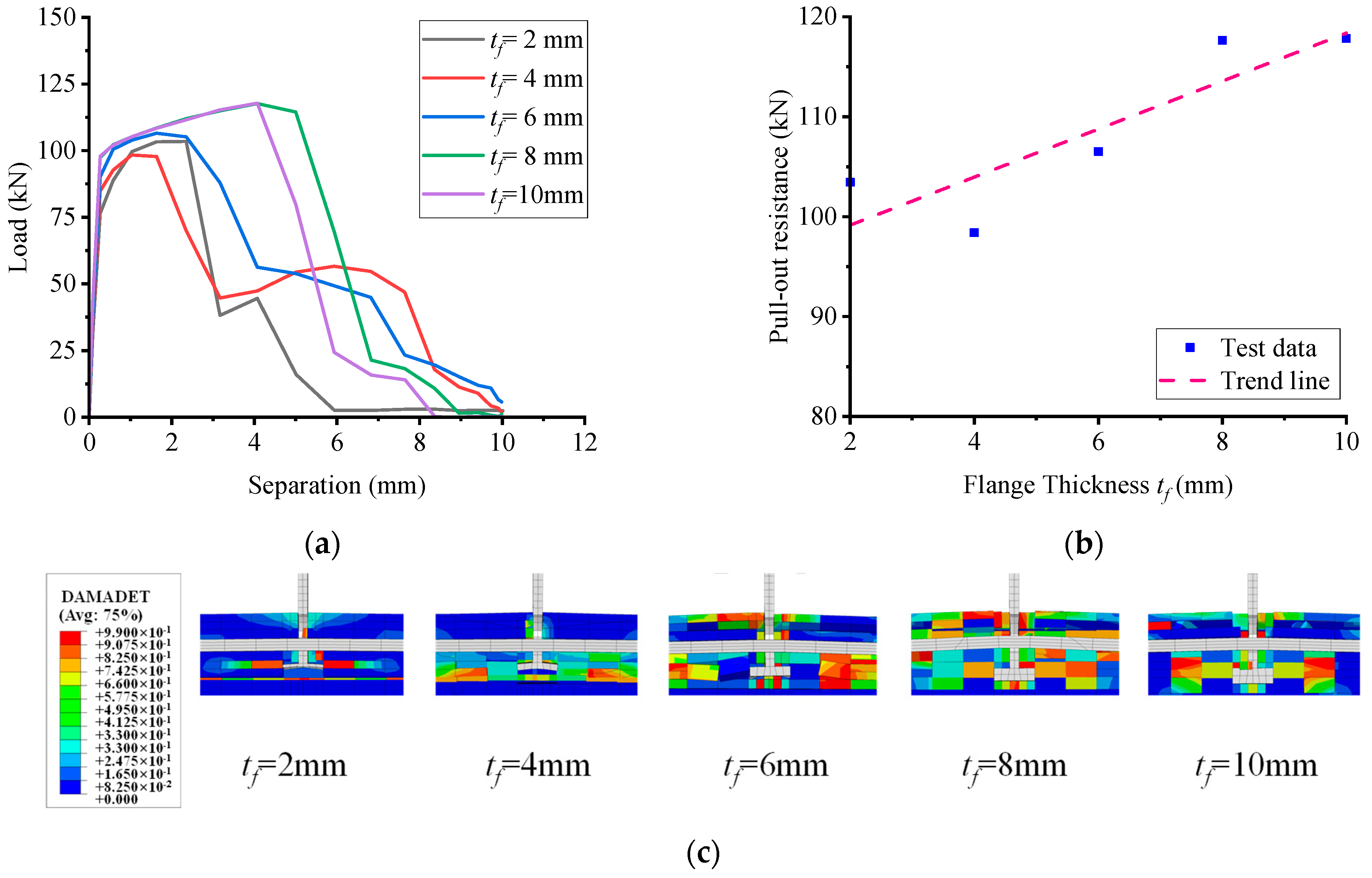
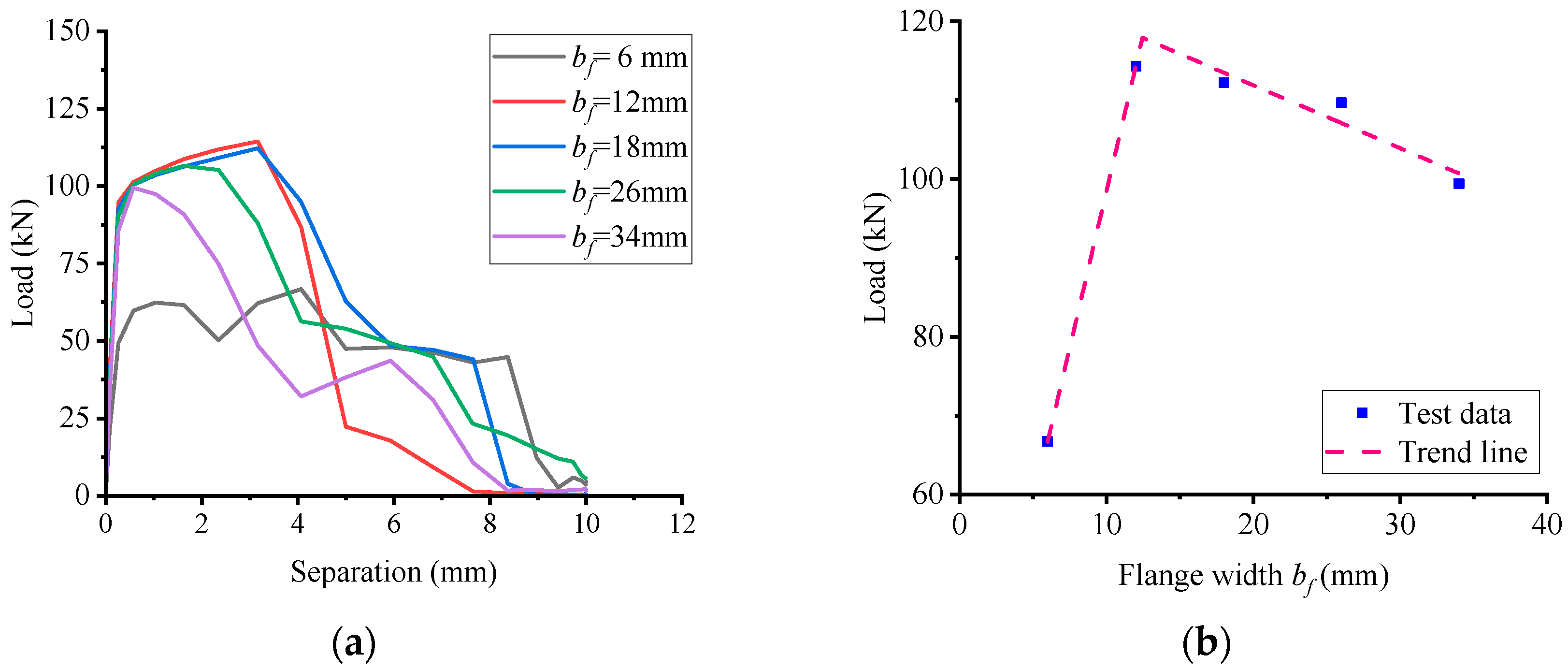
5.1. Influence of Flange Size
5.2. Influence of Cut Width
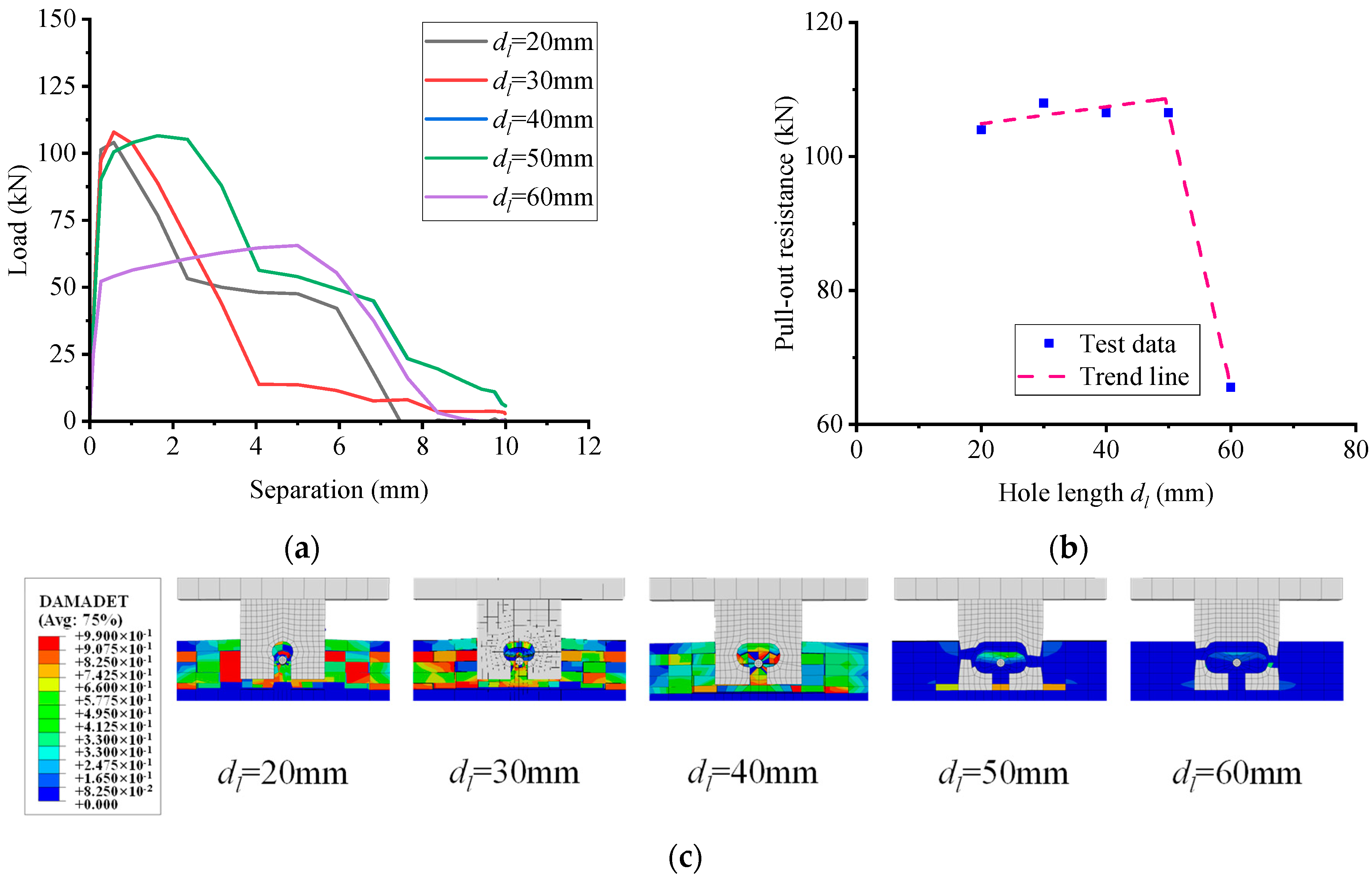
5.3. Influence of Hole Size
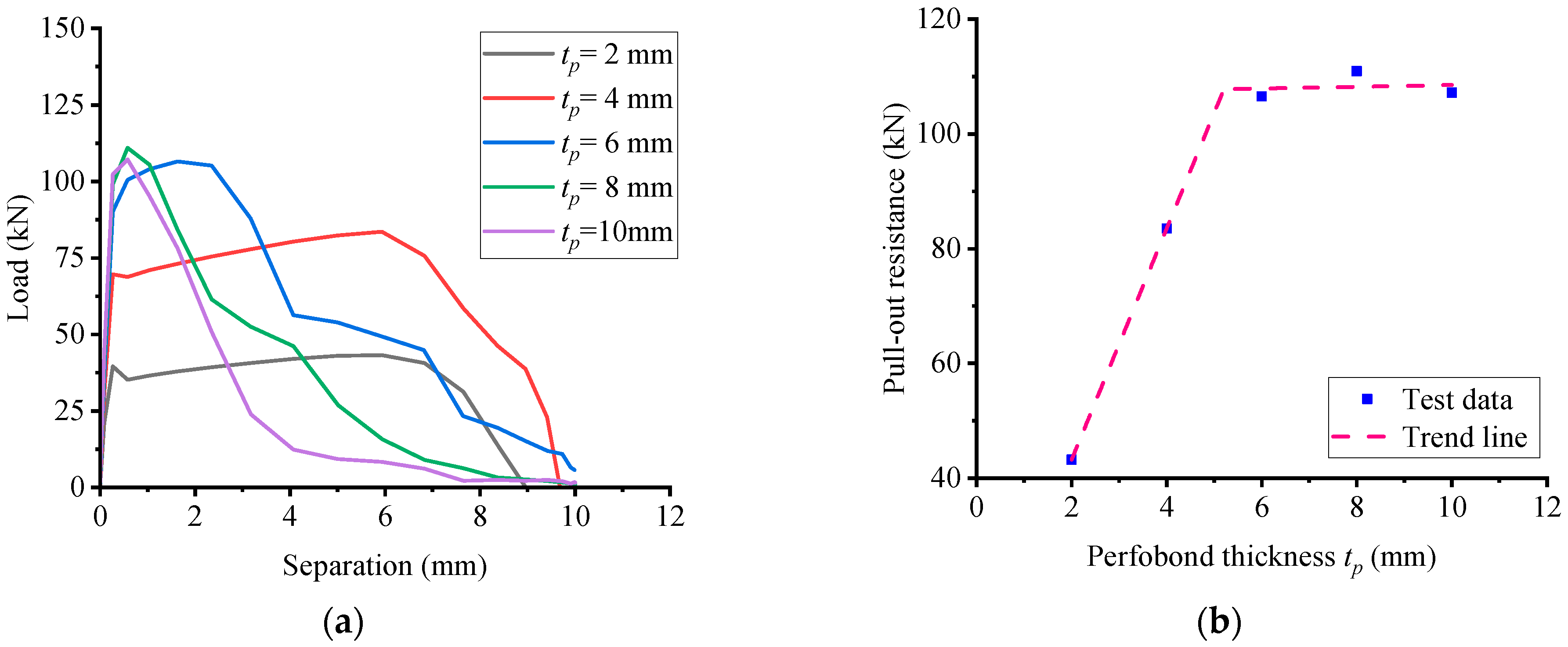
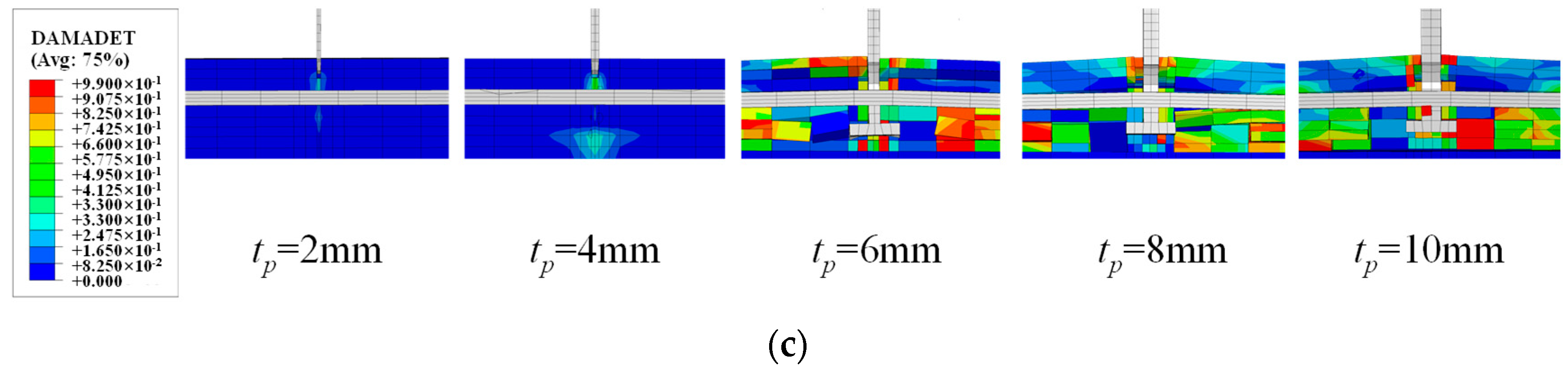
5.4. Influence of Perfobond Size
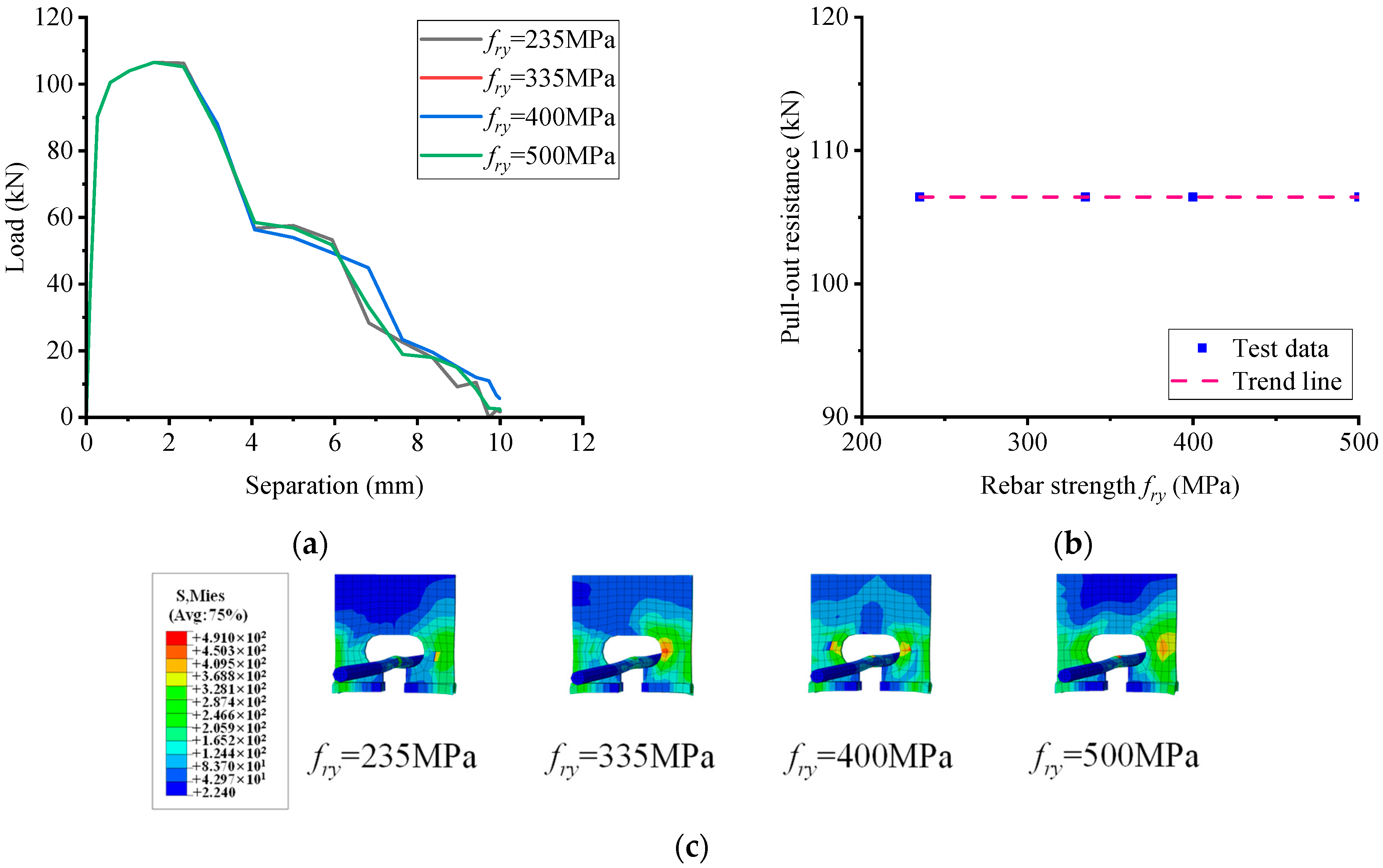
5.5. Influence of Rebar Diameter
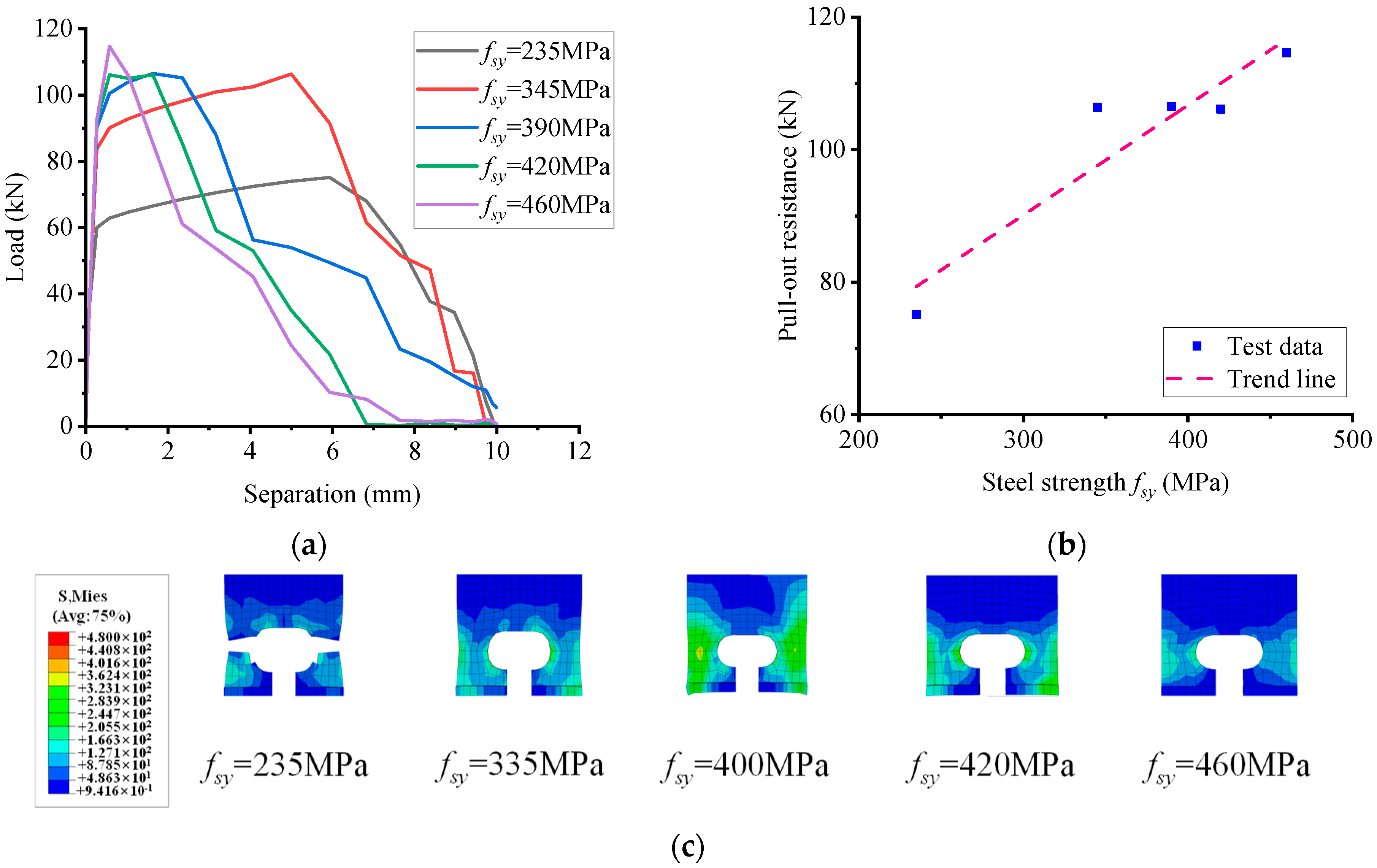
5.6. Influence of Material Strength
6. Analytical Work
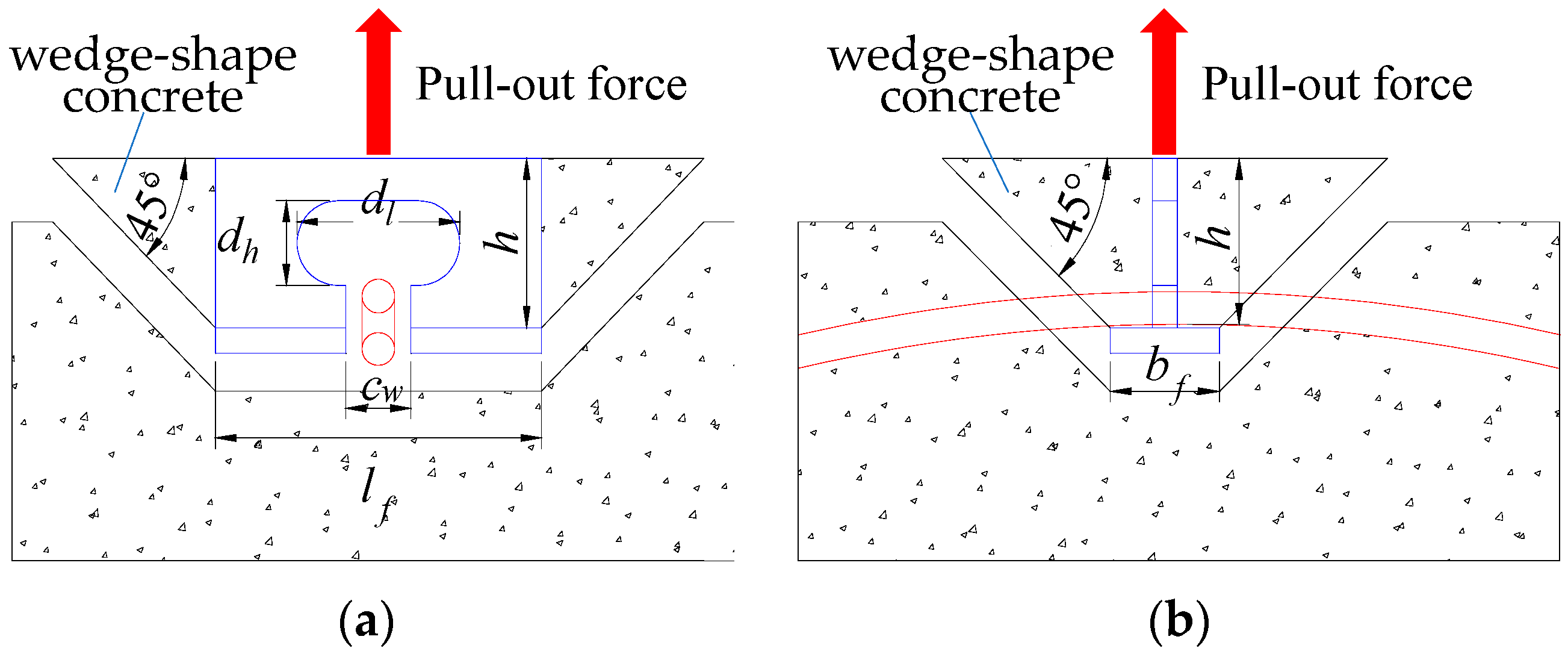
6.1. Fracture Damage of Perfobond Ribs
6.2. Punching Damage of Concrete
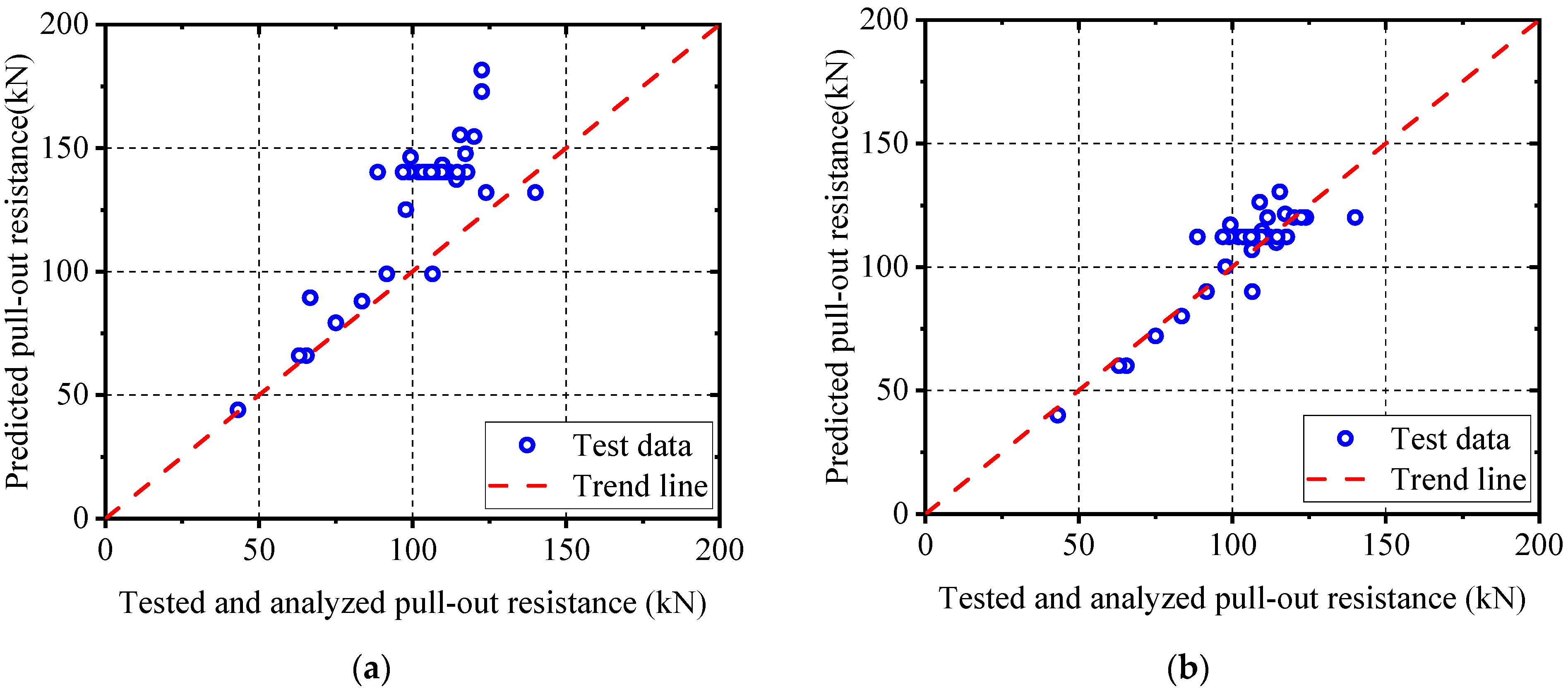
6.3. Comparison and Validation
7. Conclusions
- (1)
- The pull-out damage modes for notched T-perfobond connectors consist of perfobond rib fracture and concrete punching damage. As the pull-out force increases, the interaction between the perforating rebar and the notched T-perfobond rib diminishes, making the connectors more susceptible to concrete damage in a wedge-shaped inverted pyramid pattern. In contrast, for un-notched T-perfobond connectors, the strong interaction between the perforating rebar and the perfobond rib, along with the anchorage effect of the concrete, leads to the fracture of the perfobond connectors. Notably, these damage modes do not exhibit the extensive fine cracks on the concrete surface that are typical of conventional concrete.
- (2)
- The proposed finite-element method is verified by comparison with the pull-out test results, demonstrating a favorable similarity to the observed pull-out damage. The analytical pull-out resistance values are 106.0% and 84.5% of the average test results for notched and un-notched T-perfobond connectors, respectively. This suggests that the finite-element model can generate rational parametric results for the pull-out performance of these connectors.
- (3)
- A total of 54 parameter simulations indicate that pull-out performance is mainly affected by flange size, connector thickness, and perfobond rib strength. Rebar diameter and strength have little effect. Concrete strength has a notable impact up to a point. Specifically, the flange thickness increases resistance from 2 to 8 mm, then plateaus. The flange width increases resistance significantly from 6 to 12 mm, then declines. The notch width has a minor influence and stabilizes beyond 16 mm. The hole height leads to a slight increase at 15 mm, then a decline. The hole length leads to an increase up to 50 mm, then a significant decrease. The perfobond rib thickness results in a dramatic increase, then plateaus. The perfobond rib length results in a linear increase up to 90 mm. The concrete strength leads to a significant increase and plateaus beyond 110 MPa. The perfobond rib strength leads to a significant linear increase. Design should balance these parameters for the desired resistance.
- (4)
- An analytical model is proposed to estimate the pull-out resistance of notched T-perfobond connectors. This model’s formula for calculating pull-out resistance correlates well with test and numerical simulation results, demonstrating its utility for evaluating the pull-out resistance of these connectors.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| dl | hole length |
| dr | diameter of the rebar |
| tf | flange thickness |
| lf | flange length |
| cw | cut width |
| Tu | pull-out resistance |
| fcu | concrete cube strength |
| fry | yield strength of the reinforcing bar |
| fsy | yield strength of the perfobond rib |
| σc | compressive stress of concrete |
| εcp | peak strain of concrete |
| Ec | Young’s modulus of concrete |
| n | ratio of peak point cut-line modulus to initial modulus of elasticity |
| ft | tensile strength of concrete |
| wc | crack width upon the complete release of stress |
| ci | constants (i = 1, 2) |
| dt | uniaxial damage variables of concrete due to tensile cracking |
| εcin | inelastic strain of concrete |
| wpl | “plastic” crack width of concrete |
| l0 | unit length |
| Tu | pulling resistance |
| Ts | tensile resistance calculated based on the strength of the perfobond connectors |
| Sh | projected area of concrete punching damage surface |
| dh | hole height |
| tp | perfobond rib thickness |
| bf | flange breadth |
| lp | perfobond rib length |
| h | perfobond rib burial depth |
| Tu,avg | averaged pull-out resistance |
| fc | uniaxial compressive strength |
| fru | tensile strength of the reinforcing bar |
| fsu | tensile strength of the perfobond rib |
| εc | compressive strain of concrete |
| ξ | ratio of strain to peak strain |
| Ecp | peak point cut-line modulus |
| σt | tensile stress of concrete |
| w | crack width of concrete |
| GF | fracture energy required to create a unit area of stress-free crack |
| dc | uniaxial damage variables of concrete due to compressive crushing |
| εcpl | plastic strain of concrete |
| bc | constant factor for concrete damage in compression |
| bt | constant factor for concrete damage in tension |
| Es | Young’s modulus of steel |
| Tc | tensile bearing capacity calculated based on concrete strength |
| As | fractured cross-sectional area of perfobond connectors |
| β | influence factor of the notch |
References
- He, S.; Yang, G.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Dong, Y. Effective width evaluation for HSS-UHPC composite beams with perfobond strip connectors. Eng. Struct. 2023, 295, 116828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, B.; Peng, A.; Wang, L. Experimental and analytical investigation on shear mechanism of steel-UHPC composite T-perfobond connectors. Eng. Struct. 2023, 286, 116061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Shi, F.; Liu, J.; Jiang, L. Tensile stiffness of perfobond rib connectors in steel–concrete composite pylon of bridges. Eng. Struct. 2023, 284, 115931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Huang, W.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Shao, J.; Tian, B. Experimental investigation on mechanical behavior of T-type perfobond rib shear connectors under combined shear and tension. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 73, 106840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cândido-Martins, J.P.S.; Costa-Neves, L.F.; Vellasco, P.C.G.S. Experimental evaluation of the structural response of perfobond connectors. Eng. Struct. 2010, 32, 1976–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vianna, J.D.C.; De Andrade, S.A.L.; Vellasco, P.D.S.; Costa-Neves, L.F. Experimental study of perfobond connectors in composite construction. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2013, 81, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kang, J.Y.; Koo, H.B.; Kim, D.J. Pull-Out Resistance Capacity of a New perfobond connector for Steel Pile Cap Strengthening. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1374689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Fang, Z.; Mosallam, A.S. Push-out tests for perfobond strip connectors with UHPC grout in the joints of steel-concrete hybrid bridge girders. Eng. Struct. 2017, 135, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, J.; Zou, Y.; Zhou, X.; Qin, F.; Peng, X. Push-out test of large perfobond connectors in steel–concrete joints of hybrid bridges. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2018, 150, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, C. Experimental and parametric study on the pull-out resistance of a notched perfobond connector. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguejiofor, E.C.; Hosain, M.U. Numerical analysis of push-out specimens with perfobond rib connectors. Comput. Struct. 1997, 62, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Darzi, S.Y.K.; Chen, A.R.; Liu, Y.Q. Finite element simulation and parametric studies of perfobond rib connector. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2007, 4, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Liu, Y.; Yoda, T.; Lin, W. Parametric study on shear capacity of circular-hole and long-hole perfobond connector. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2016, 117, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Han, O.; Gombosuren, M.; Kim, S.H. Numerical simulation of Y-type perfobond rib shear connectors using finite element analysis. Steel Compos. Struct. 2019, 31, 53–67. [Google Scholar]
- Karam, M.S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Miura, T. Numerical evaluation of the perfobond (PBL) shear connector subjected to lateral pressure using coupled rigid body spring model (RBSM) and nonlinear solid finite element method (FEM). Crystals 2020, 10, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Suzuki, K.; Kimura, Y. Ultimate shear strength of perfobond connectors subjected to fully reversed cyclic loading. Eng. Struct. 2021, 248, 113240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vianna, J.D.C.; Costa-Neves, L.F.; Vellasco, P.D.S.; De Andrade, S.A.L. Experimental assessment of Perfobond and T-perfobond connectors’ structural response. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2009, 65, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munemoto, S.; Sonoda, Y. An analytical study on dynamic strength evaluation of perfobond strip shear connectors. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 566, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Liu, Y.; Yoda, T.; Lin, W. Shear behavior and analytical model of perfobond connectors. Steel Compos. Struct. 2016, 20, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Zhao, C.; Liu, Y. Analytical model for load–slip relationship of perfobond connector based on push-out test. Materials 2018, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.Y.; Nie, X.; Fan, J.S.; Cui, B.; Huang, L.J. Experimental and analytical investigation on pull-out performance of multihole thin-rib perfobond connectors. J. Bridge Eng. 2019, 24, 04019037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Guan, P.; Wang, Q.; Fang, Z.; Mosallam, A. Investigation on structural performance of perfobond strip connector group in steel-concrete joints. Eng. Struct. 2021, 242, 112571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, G.; Liao, S.; Wu, N.; Fang, Z.; Fang, S.; Liu, F.; Li, L.; Zhu, H.; Xiong, Z. Static behavior of small-rib-height perfobond connectors embedded in UHPC: Experimental and analytical studies. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 85, 108750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Luan, L.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Du, X. Three failure modes of high-strength steel (HSS) perfobond connector embedded in UHPC. Eng. Struct. 2023, 286, 116147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Li, Q.; Yang, G.; Zhou, X.; Mosallam, A.S. Experimental study on flexural performance of HSS-UHPC composite beams with perfobond strip connectors. J. Struct. Eng. 2022, 148, 04022064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassault System. ABAQUS Documentation, Version 6.10; Dassault System: Waltham, WA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hordijk, D.A. Tensile and tensile fatigue behaviour of concrete; experiments, modelling and analyses. Heron 1992, 37, 1. [Google Scholar]









| Specimen | dl (mm) | dh (mm) | dr (mm) | tp (mm) | tf (mm) | bf (mm) | lp (mm) | cw (mm) | Tu (kN) | Tu,avg (kN) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFR–1 | 40 | 20 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 26 | 80 | 0 | 140 | 132.0 |
| PFR–2 | 40 | 20 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 26 | 80 | 0 | 124 | |
| PMFR–1 | 40 | 20 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 26 | 80 | 16 | 102 | 100.5 |
| PMFR–2 | 40 | 20 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 26 | 80 | 16 | 99 |
| Model | tf (mm) | bf (mm) | cw (mm) | dh (mm) | dl (mm) | tp (mm) | lp (mm) | dr (mm) | fc (MPa) | fry (MPa) | fsy (MPa) | Tu (kN) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TF-02 | 2 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 103.44 |
| TF-04 | 4 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 98.39 |
| TF-06 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 106.51 |
| TF-08 | 8 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 117.64 |
| TF-10 | 10 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 117.82 |
| BF-06 | 6 | 6 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 66.71 |
| BF-12 | 6 | 12 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 114.31 |
| BF-18 | 6 | 18 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 112.2 |
| BF-26 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 106.51 |
| BF-34 | 6 | 34 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 99.43 |
| CW-00 | 6 | 26 | 0 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 111.52 |
| CW-08 | 6 | 26 | 8 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 109.01 |
| CW-16 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 106.51 |
| CW-24 | 6 | 26 | 24 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 108.45 |
| CW-40 | 6 | 26 | 40 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 107.27 |
| DH-10 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 10 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 108.3 |
| DH-15 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 15 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 110.02 |
| DH-20 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 106.51 |
| DH-25 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 25 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 105.19 |
| DH-30 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 30 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 88.66 |
| DL-20 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 20 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 103.98 |
| DL-30 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 30 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 107.93 |
| DL-40 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 106.51 |
| DL-50 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 50 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 106.51 |
| DL-60 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 65.55 |
| TP-02 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 2 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 43.22 |
| TP-04 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 4 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 83.51 |
| TP-06 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 106.51 |
| TP-08 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 8 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 110.95 |
| TP-10 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 10 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 107.13 |
| LP-60 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 60 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 63.1 |
| LP-70 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 70 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 91.62 |
| LP-80 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 106.51 |
| LP-90 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 90 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 117.26 |
| LP-100 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 100 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 115.54 |
| DR-04 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 4 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 109.9 |
| DR-06 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 6 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 109.77 |
| DR-08 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 106.51 |
| DR-10 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 10 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 108.29 |
| DR-12 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 12 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 109.53 |
| FC-80 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 80 | 400 | 390 | 97.83 |
| FC-95 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 106.51 |
| FC-110 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 110 | 400 | 390 | 120.13 |
| FC-130 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 130 | 400 | 390 | 122.59 |
| FC-140 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 140 | 400 | 390 | 122.57 |
| RY-235 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 235 | 390 | 106.51 |
| RY-335 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 335 | 390 | 106.51 |
| RY-400 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 106.51 |
| RY-500 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 500 | 390 | 106.51 |
| SY-235 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 235 | 75.1 |
| SY-345 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 345 | 106.38 |
| SY-390 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 390 | 106.51 |
| SY-420 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 420 | 106.11 |
| SY-460 | 6 | 26 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 6 | 80 | 8 | 95 | 400 | 460 | 114.61 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Z.; Zheng, S.; Jiao, L.; Xu, X.; Yao, Y.; Gao, Z.; Li, H. Experimental and Parametric Analysis of Pull-Out Resistance of Notched T-Perfobond Connectors. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7089. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14167089
Dong Z, Zheng S, Jiao L, Xu X, Yao Y, Gao Z, Li H. Experimental and Parametric Analysis of Pull-Out Resistance of Notched T-Perfobond Connectors. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(16):7089. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14167089
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Zifa, Shuangjie Zheng, Lizhe Jiao, Xiaoqing Xu, Yao Yao, Zhuoru Gao, and Haifeng Li. 2024. "Experimental and Parametric Analysis of Pull-Out Resistance of Notched T-Perfobond Connectors" Applied Sciences 14, no. 16: 7089. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14167089
APA StyleDong, Z., Zheng, S., Jiao, L., Xu, X., Yao, Y., Gao, Z., & Li, H. (2024). Experimental and Parametric Analysis of Pull-Out Resistance of Notched T-Perfobond Connectors. Applied Sciences, 14(16), 7089. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14167089






