A Study of the Corrosion Resistance of 316L Stainless Steel Manufactured by Powder Bed Laser Additive Manufacturing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrochemical Analyses
2.3. Sample Characterisation
3. Results and Discussion
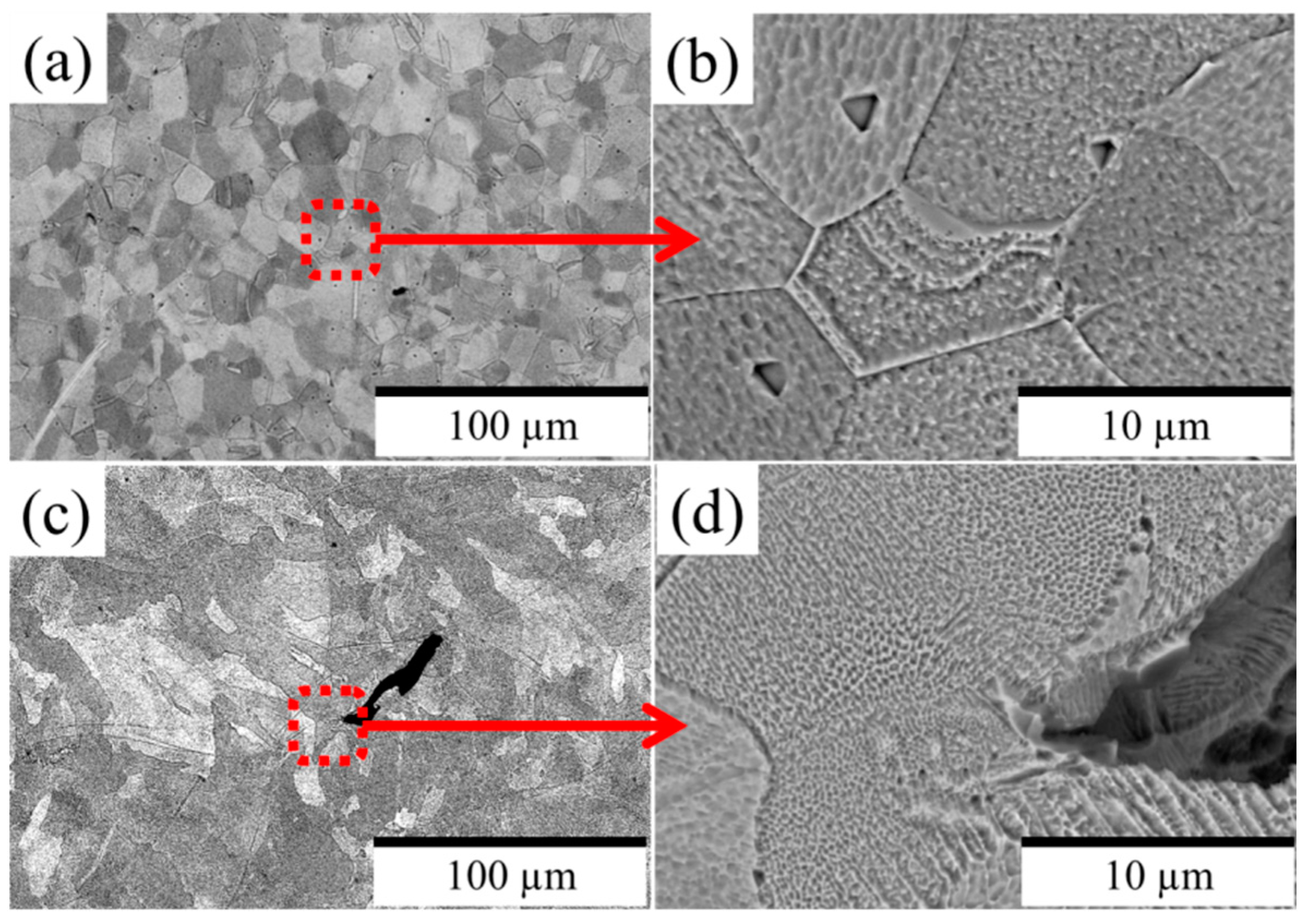
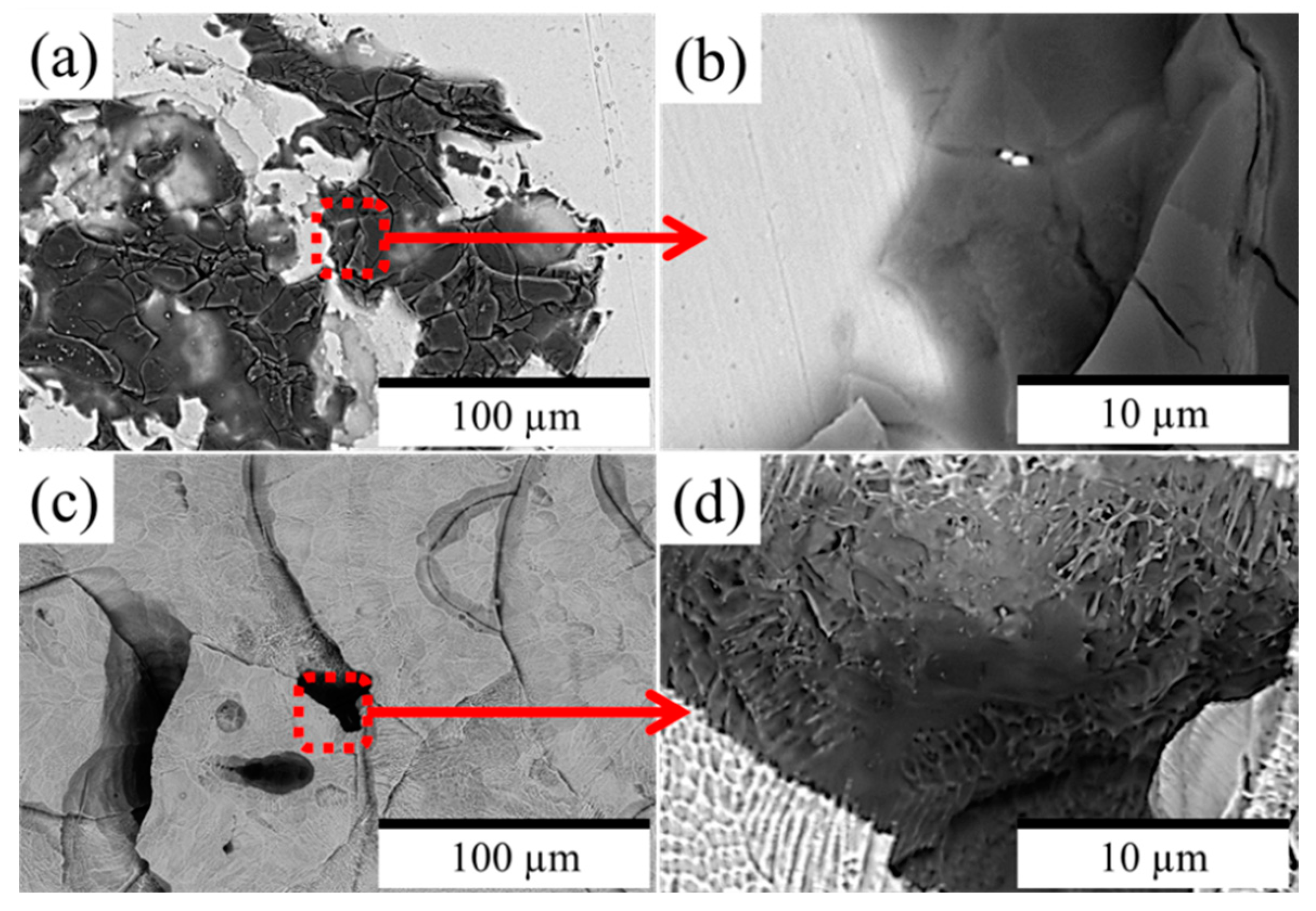
3.1. Microstructural and Chemical Composition Assessment
3.2. Electrochemical Assessment
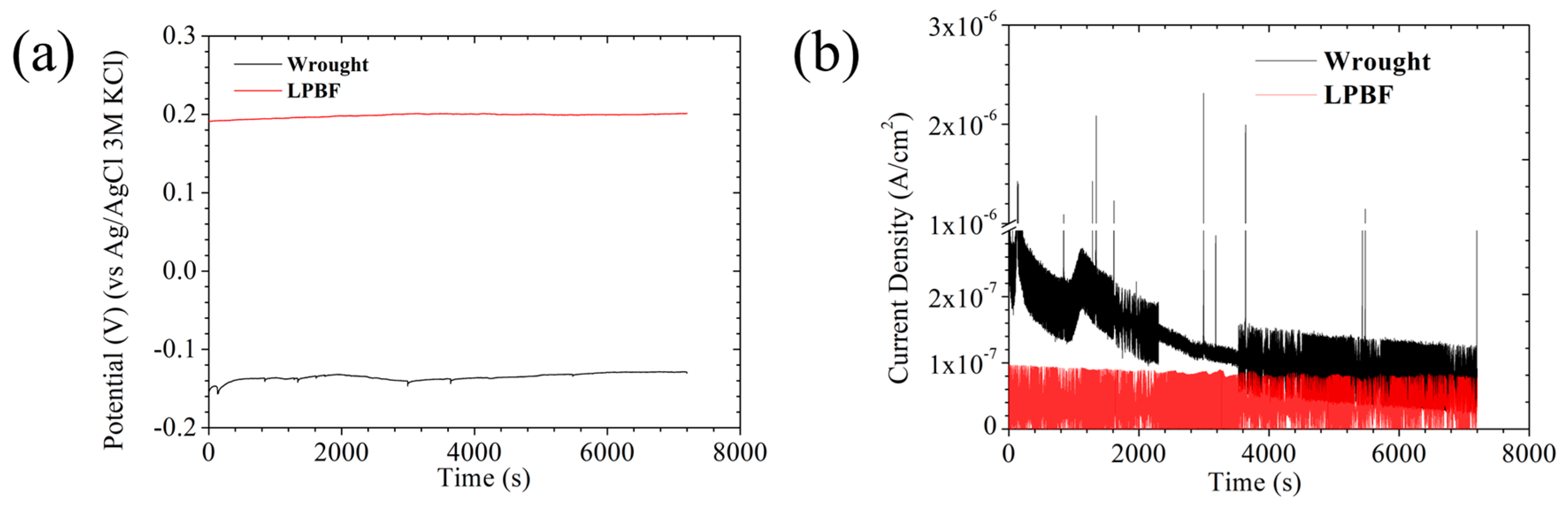
3.2.1. AEN Assessments
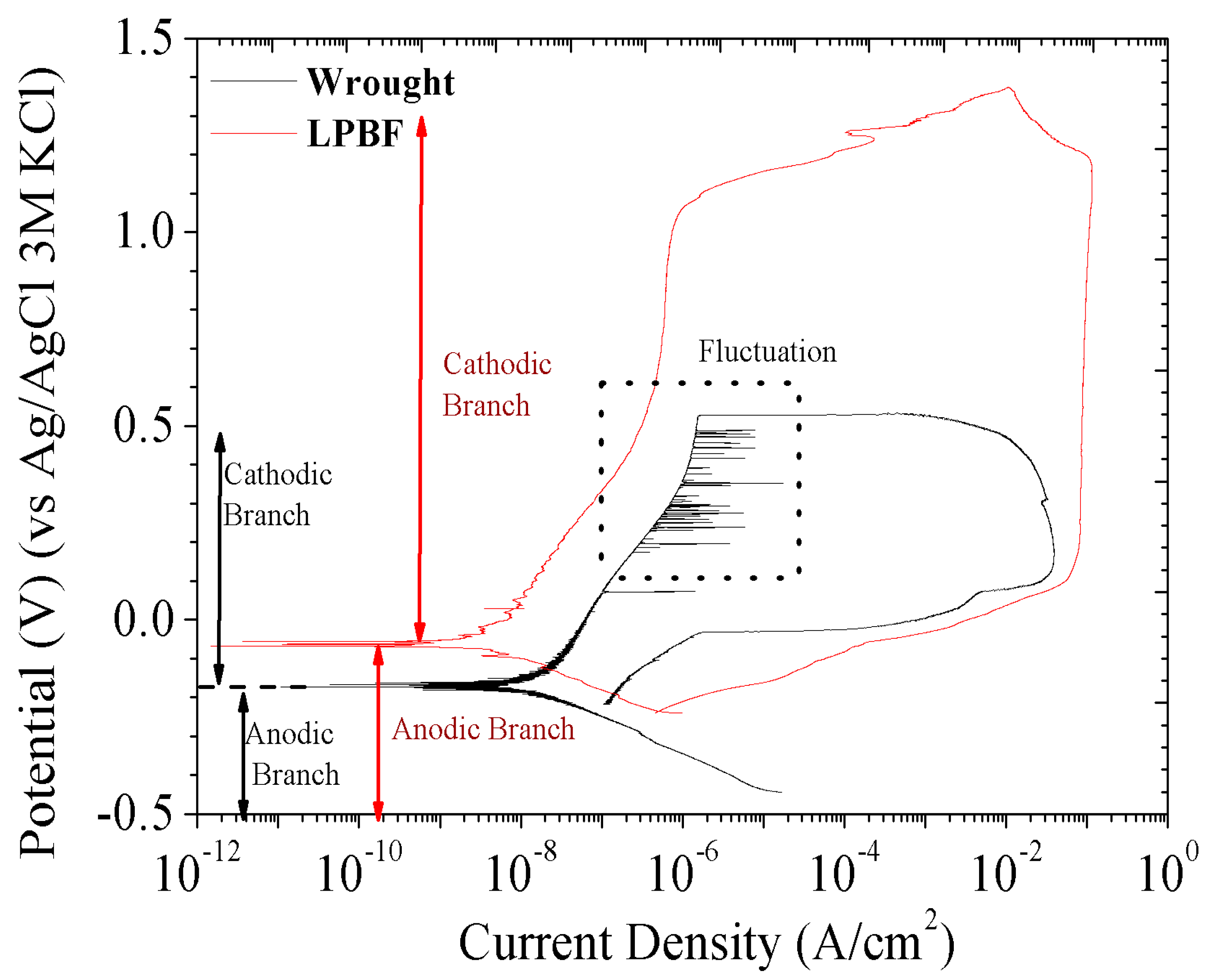
3.2.2. PPC Evaluation
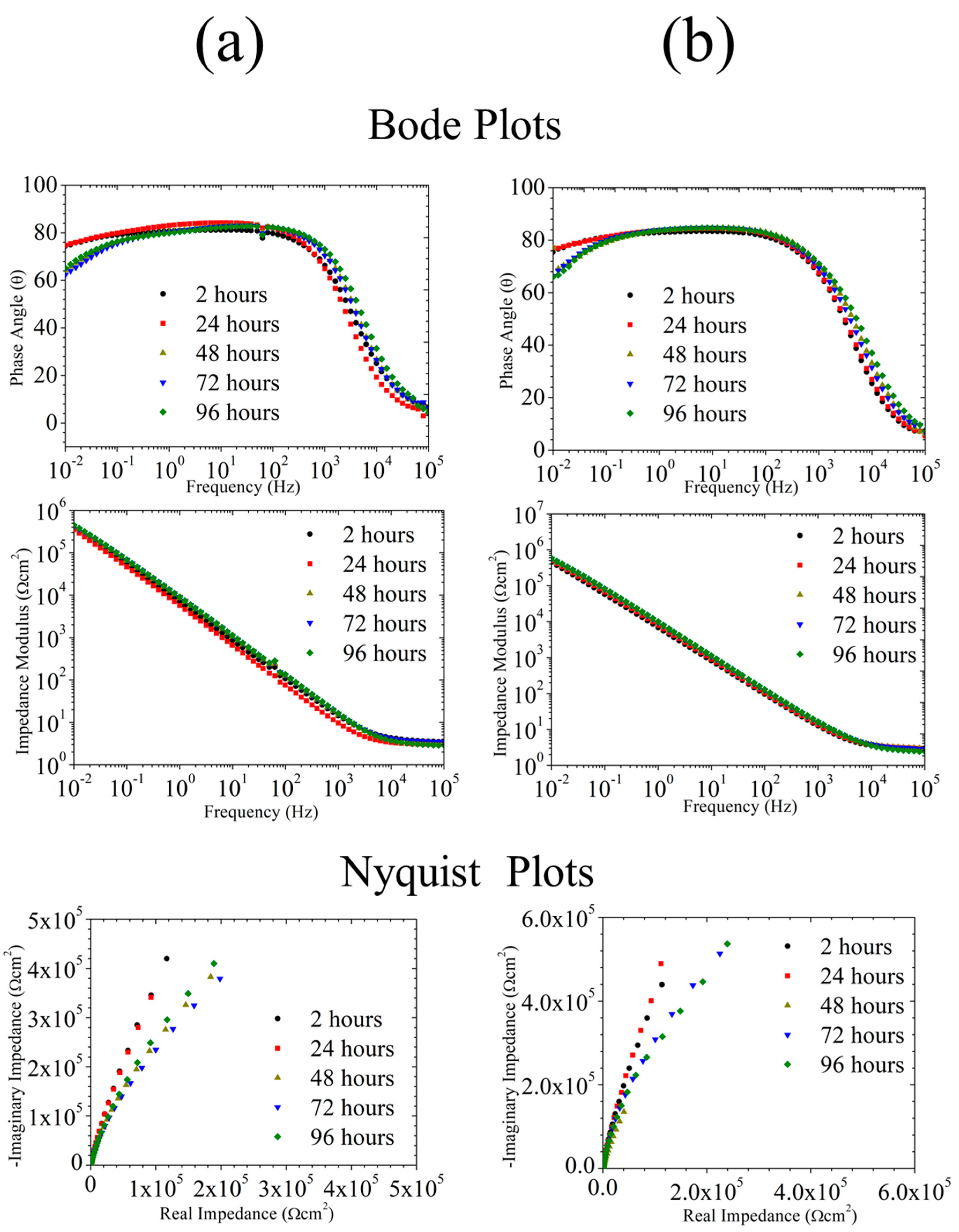
3.2.3. EIS Analyses
3.3. Evaluation of the Corroded Surface
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karimi, M.S.; Yeganeh, M.; Zaree, S.A.; Eskandari, M. Corrosion behavior of 316L stainless steel manufactured by laser powder bed fusion (L-PBF) in an alkaline solution. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 138, 106918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maicas-Esteve, H.; Taji, I.; Wilms, M.; Gonzalez-Garcia, Y.; Johnsen, R. Corrosion and microstructural investigation on additively manufactured 316L stainless steel: Experimental and statistical approach. Materials 2022, 15, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Tan, Q.; Bermingham, M.; Mo, N.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.X. Laser additive manufacturing of steels. Int. Mater. Rev. 2022, 67, 487–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, W.E. Metal additive manufacturing: A review. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 1917–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisin, T.; Shi, R.; Zhu, Y.; Qi, Z.; Wu, M.; Sen-Britain, S.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, S.R.; Wang, Y.M.; Thomas, S.; et al. Pitting corrosion in 316L stainless steel fabricated by laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing: A review and perspective. JOM 2022, 74, 1668–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trelewicz, J.R.; Halada, G.P.; Donaldson, O.K.; Manogharan, G. Microstructure and corrosion resistance of laser additively manufactured 316L stainless steel. JOM 2016, 68, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Wei, L.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Q.; Luo, H. Corrosion mechanism of additively manufactured 316 L stainless steel in 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 26, 101648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprouster, D.J.; Cunningham, W.S.; Halada, G.P.; Yan, H.; Pattammattel, A.; Huang, X.; Olds, D.; Tilton, M.; Chu, Y.S.; Dooryhee, E.; et al. Dislocation microstructure and its influence on corrosion behavior in laser additively manufactured 316L stainless steel. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 47, 102263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leicht, A.; Klement, U.; Hryha, E. Effect of build geometry on the microstructural development of 316L parts produced by additive manufacturing. Mater. Charact. 2018, 143, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzynowski, T.; Gruber, K.; Stopyra, W.; Kuźnicka, B.; Chlebus, E. Correlation between process parameters, microstructure and properties of 316 L stainless steel processed by selective laser melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 718, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.V.; Narra, S.P.; Cunningham, R.W.; Liu, H.; Chen, H.; Suter, R.M.; Beuth, J.L.; Rollett, A.D. Defect structure process maps for laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthomé, G.; Malki, B.; Baroux, B. Pitting transients analysis of stainless steels at the open circuit potential. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 2432–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghuy, A.A.; Zakeri, M.; Moayed, M.H.; Mazinani, M. Effect of grain size on pitting corrosion of 304L austenitic stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2015, 94, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, A.; Thierry, D. Thierry, Rate-determining reactions of atmospheric corrosion. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 2717–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfeld, F.; Sun, Z. Localization index obtained from electrochemical noise analysis. Corrosion 1999, 55, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmailzadeh, S.; Aliofkhazraei, M.; Sarlak, H. Interpretation of cyclic potentiodynamic polarization test results for study of corrosion behavior of metals: A review. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2018, 54, 976–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Area ratio of cathode/anode effect on the galvanic corrosion of high potential difference coupling in seawater. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 322, 022046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Nogales, R.; Estupiñán-López, F.; Gaona-Tiburcio, C.; Lopez-Botello, O.E.; Ramírez-Rodríguez, J.G.; Zambrano-Robledo, P.C. Corrosion Resistance Measurement of 316L Stainless Steel Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting. Materials 2021, 14, 4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, R.G.; Scully, J.R.; Shoesmith, D.; Buchheit, R.G. Electrochemical Techniques in Corrosion Science and Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuir-Torres, J.I.; Kotadia, H.R.; Öpoz, T.T.; Sharp, M.C. A study on the corrosion behaviour of laser textured pure aluminium in saltwater. Processes 2023, 11, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakaei, K.; Esrafili, M.D.; Ehsani, A. Graphene and Anticorrosive Properties. In Interface Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 303–337. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.L.; Jiang, Z.H.; Yao, Z.P.; Song, Y.; Wu, Z.D. Effects of scan rate on the potentiodynamic polarization curve obtained to determine the Tafel slopes and corrosion current density. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuir-Torres, J.I.; Gibbons, G.J.; West, G.; Das, A.; Kotadia, H.R. Understanding the corrosion behaviour of Al-Mg alloy fabricated using a Laser Powder Bed Fusion (L-PBF) Additive Manufacturing (AM) process. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 969, 172300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazanas, A.C.; Prodromidis, M.I. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy—A tutorial. ACS Meas. Sci. Au 2023, 3, 162–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, X.; Kong, D.; Wu, W.; Zhang, L.; Dong, C.; He, B.; Lu, L.; Wu, K.; Zhu, D. Corrosion behavior of 316L stainless steel fabricated by selective laser melting under different scanning speeds. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 3667–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cai, J.M.; Guan, L.; Wang, G. pH-dependent electrochemical behaviour of Al3Mg2 in NaCl solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 467, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Morales, A.; Galvan, J.C.; Rodriguez, R.; De Damborenea, J.J. Electrochemical study of the corrosion behaviour of copper surfaces modified by nitrogen ion implantation. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1997, 27, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Samples | (nA/cm2) | (mV) | (kΩ/cm2) | (nA/cm2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wrought | 66 | 4 | 62 | 130 | 0.55 |
| LPBF | 40 | 3 | 97 | 64 | 0.97 |
| Sample | (nA/cm2) | (µm/Year) | (µA/cm2) | (µm/Year) | (mV/A Decade) | (mV/A Decade) | (MΩ/cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wrought | 9.260 | 70.646 | 1.860 | 19.403 | −0.028 | 0.693 | 1.253 |
| LPBF | 10.900 | 90.230 | 0.743 | 5.671 | −0.029 | 0.065 | 2.325 |
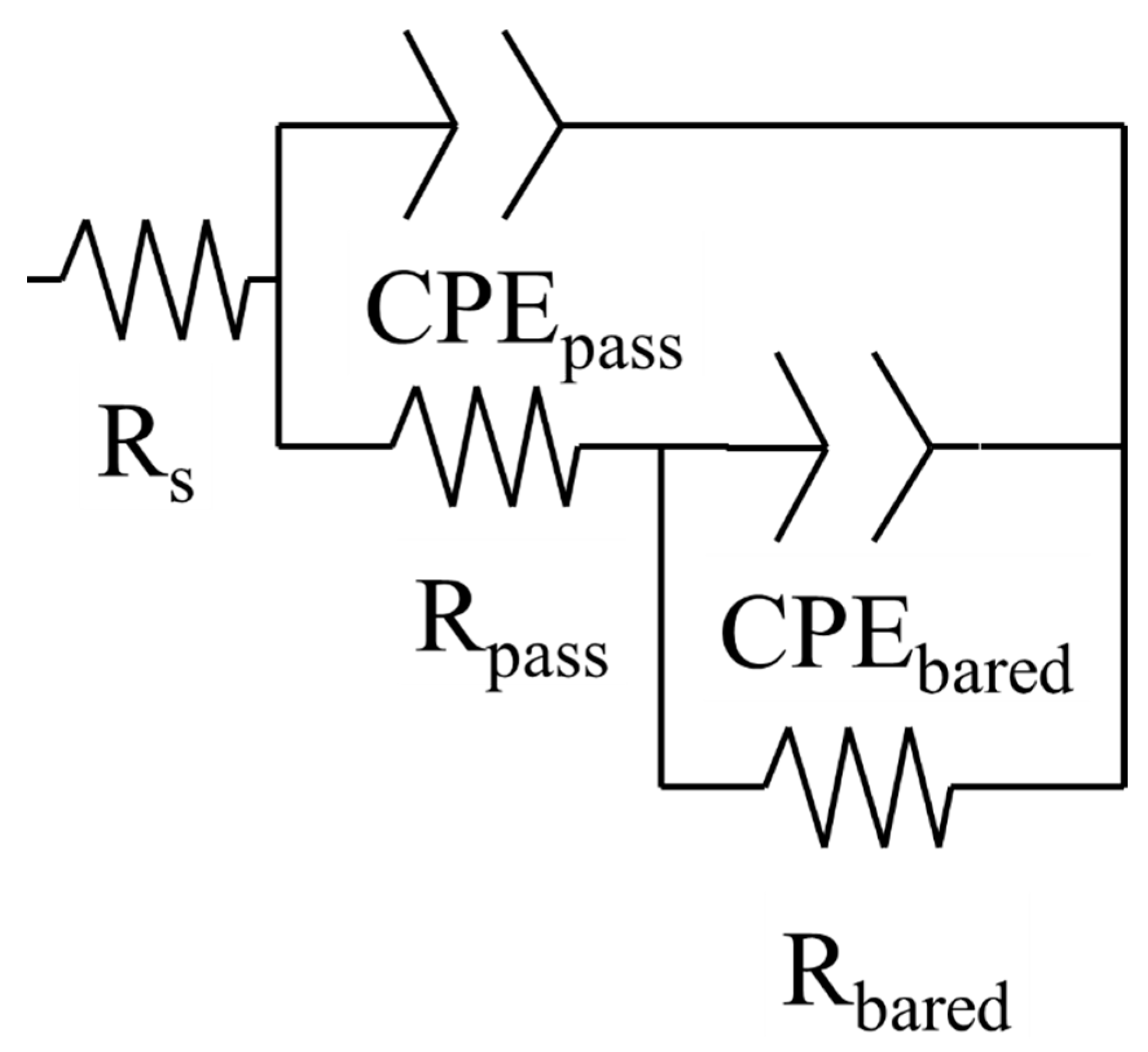
| Sample | Time (h) | Rs (Ωcm−2) | CPEpass (µSsncm−2) | ηpass | Rpass (Ωcm−2) | CPEbared (µSsncm−2) | ηbared | Rbared (Ωcm−2) | d (nm) | χ2 (10−4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wrought | 2 | 2.010 | 46.680 | 0.92 | 0.225 × 106 | 9.510 | 0.90 | 3531 × 103 | 0.339 | 6.080 |
| 24 | 3.220 | 22.000 | 0.92 | 0.147 × 106 | 4.420 | 0.66 | 1750 × 103 | 0.718 | 4.310 | |
| 48 | 3.070 | 20.500 | 0.93 | 0.065 × 106 | 3.874 | 0.58 | 2370 × 103 | 0.771 | 2.740 | |
| 72 | 3.490 | 19.700 | 0.93 | 0.077 × 106 | 3.690 | 0.51 | 3030 × 103 | 0.802 | 4.190 | |
| 96 | 2.880 | 19.200 | 0.92 | 0.064 × 106 | 2.500 | 0.61 | 2500 × 103 | 0.823 | 2.760 | |
| LPBF | 2 | 3.890 | 21.453 | 0.92 | 0.052 × 106 | 2.778 | 0.93 | 32 × 103 | 0.737 | 3.528 |
| 24 | 2.652 | 314.250 | 0.57 | 0.867 × 106 | 18.250 | 0.95 | 879 × 103 | 0.050 | 2.879 | |
| 48 | 3.554 | 15.508 | 0.96 | 4.483 × 106 | 87.697 | 0.87 | 37 × 103 | 1.020 | 5.829 | |
| 72 | 3.616 | 17.185 | 0.97 | 4.980 × 106 | 464.900 | 0.70 | 8 × 103 | 0.920 | 8.608 | |
| 96 | 3.098 | 18.050 | 0.94 | 4.997 × 106 | 300.793 | 0.76 | 235 × 103 | 0.876 | 4.829 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahuir-Torres, J.I.; Burgess, A.; Sharp, M.C.; Öpöz, T.T.; Malkeson, S.P.; Falkingham, P.L.; Darlington, R.I.; Tammas-Williams, S. A Study of the Corrosion Resistance of 316L Stainless Steel Manufactured by Powder Bed Laser Additive Manufacturing. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7471. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177471
Ahuir-Torres JI, Burgess A, Sharp MC, Öpöz TT, Malkeson SP, Falkingham PL, Darlington RI, Tammas-Williams S. A Study of the Corrosion Resistance of 316L Stainless Steel Manufactured by Powder Bed Laser Additive Manufacturing. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(17):7471. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177471
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhuir-Torres, Juan Ignacio, Andrew Burgess, Martin Charles Sharp, Tahsin Tecelli Öpöz, Sean P. Malkeson, Peter L. Falkingham, Robert I. Darlington, and Samuel Tammas-Williams. 2024. "A Study of the Corrosion Resistance of 316L Stainless Steel Manufactured by Powder Bed Laser Additive Manufacturing" Applied Sciences 14, no. 17: 7471. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177471
APA StyleAhuir-Torres, J. I., Burgess, A., Sharp, M. C., Öpöz, T. T., Malkeson, S. P., Falkingham, P. L., Darlington, R. I., & Tammas-Williams, S. (2024). A Study of the Corrosion Resistance of 316L Stainless Steel Manufactured by Powder Bed Laser Additive Manufacturing. Applied Sciences, 14(17), 7471. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177471









