Abstract
The continuous deepening of coal-seam extraction has sharply increased both gas pressure and content. The use of viscoelastic surfactant fracturing fluids (VESFFs) has been demonstrated to effectively improve coal-seam permeability and mitigate the occurrence of gas disasters. After injection into coal, VESFFs interact with the coal and affect its surface characteristics. In this study, to characterize changes in zeta potential, oxygen-containing functional groups, and the microcrystalline structure of hard and soft coal surfaces under the influence of VESFFs with different formulations, zeta potential measurements and Fourier-transform infrared and Raman spectroscopies were performed. The VESFFs enhanced the electrostatic repulsion between the pore wall and coal particles, which is favorable for the removal of coal particles from hard and soft coal surfaces. The combination of cationic with zwitterionic viscoelastic surfactants (VESs) in the VESFFs exposed more hydrophilic functional groups on the surfaces of hard and soft coal, increasing wettability and affecting nanometer pores. A VESFF based on anionic and zwitterionic VESs as the primary agents could enhance the extension of the aromatic layer (La) of the aromatic crystal nuclei and reduce the interlayer spacing (d002) of hard and soft coal, thereby increasing the volume of micropores. This research offers theoretical guidance for optimizing the primary components of VESFFs and elucidates the mechanism through which VESFFs act on nanopores in coal from a microscopic perspective.
1. Introduction
Coalbed methane (CBM) is a high-quality, efficient, and clean energy source; however, it also presents considerable risks to coal mines [1]. It is therefore important to ensure the efficient extraction of CBM in order to address energy shortages and reduce the incidence of accidents in coal mines [2]. The permeability of coal seams is a critical factor in determining the efficiency of CBM extraction [3]. Hydraulic fracturing is an effective measure to improve coal-seam permeability, for which fracturing fluids (FFs) play a pivotal role [4]. Compared with conventional polymer-based FFs, viscoelastic surfactant FFs (VESFFs) have the characteristics of being economical and environmentally friendly. Thus, VESFFs have become the main substitute for traditional-polymer based fluids in the exploitation of unconventional reservoirs and are used industrially [5,6,7,8]. Zuo et al. [9], Wang et al. [10], Lu et al. [11,12], Yang et al. [13], and Ge et al. [14] have pointed out that VESFFs are also suitable for enhancing coal-seam permeability. However, as the depth of CBM extraction increases, the majority of CBM reservoirs exhibit traits associated with elevated gas content, low permeability, and high ground temperature [15,16]. This situation has prompted the pursuit of novel VESFFs with augmented performance.
The addition of VESs to the solution can lead to the formation of self-assembling aggregates. This causes the solution to thicken and gives the FFs sufficient viscoelasticity and sand-carrying capacity. VESs have amphiphilic structures, which are reflected in their molecular head chains (hydrophilic groups, HLGs) and tail chains (hydrophobic groups, HBGs). There are many types of HLGs that can promote contact between water and coal seams. HBGs are composed of hydrocarbon chains and their molecular formula contains mainly -CH2- subunits. Recently, many researchers have directed their attention toward enhancing the performance of VES-based fluids [17]. It has been highlighted that the optimization of the hydrophobic chain length of VESs and the combination of different ionic VESs represent opportunities for the enhancement of VESFF performance. Wang et al. [18] have demonstrated that an increase in the hydrophobic chain length of VESs is conducive to micellization. Yang et al. [13] investigated the impact of the length of the hydrocarbon chain in surfactants on the viscoelasticity, temperature resistance, and wettability of VESFFs on coal surfaces. Sehgal et al. [19] found that the mixing of cationic and zwitterionic VESs had a weakly synergistic effect, which could make the micelles more stable. Therefore, VESFFs with varying hydrocarbon chain lengths of VESs and a combination of different VES types as the main agent are studied in this paper.
The physicochemical properties, counter ion type, and solution environment of VESs determine different physical and chemical effects that VESFFs can produce on coal. Lu et al. [20], Yang et al. [21], and Xue et al. [22] noted that VESFFs can affect the pore structure of coal. Yang et al. [23] explained the reasons why VESFFs change the pore structure of coal in terms of clay mineral expansion, mineral dissolution, and coal particle movement. The current work focuses on revealing the mechanism by which VESFFs act on coal nanopores from the perspective of zeta potential, surface functional groups, and macromolecular structure.
Coal is a structurally complex medium composed of molecules, atoms, and electrons, exhibiting certain surface electrical characteristics. The zeta potential on the coal surface can be altered by the action of ionic VESs. Lin et al. [24] explored the effects of zeta potential on coal particle agglomeration and concluded that the control of zeta potential can optimize the agglomeration of coal particles. Liu et al. [25] proposed that neutralizing the charge on coal particles can eliminate the electrostatic force between coal particles that have the same charges, which is beneficial for the agglomeration of coal fine particles. It has been demonstrated that VESFFs can influence the pore structure of coal by modifying the zeta potential on its surface. In this paper, the zeta potential of coal treated with VESFFs was measured.
The surface of coal is composed of many HBGs, such as aromatic hydrocarbons and fatty hydrocarbons, making coal highly hydrophobic [26]. Oxygen-containing functional groups, such as hydroxyl (-OH), carbonyl (C=O), carboxyl (-COOH), and Si-O-, on the surface of coal contribute to its hydrophilicity [27]. Yue et al. [28] pointed out that VESs can alter the proportion of oxygen-containing functional groups on the coal surface. Liu et al. [29] discovered that the COO/COOH group of coal exhibits a high adsorption capacity for hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide. Additionally, VESs have been observed to cover the oxygenated functional groups on the surfaces of coal pores, thereby markedly reducing their hydrophilicity. Li et al. [30] found that the content of oxygenated functional groups (CO, C=O, O=C-O) on the coal surface decreased after VES adsorption, enhancing the hydrophobicity of the coal surface. Hence, it can be seen that VESFFs can change oxygen-containing functional groups on the coal surface, affecting the wettability of the FFs on the coal surface and in turn changing the effects of the FFs on the pore structure of coal. Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy is a widely used and effective method for investigating functional groups on the surface of coal. This paper uses FTIR analysis to investigate the effect of VESFFs on oxygenated functional groups on coal surfaces.
The degree of order and compactness of the macromolecular arrangement of coal can affect pores with diameters less than 500 nm [31]. The water molecules and VES molecules in the VESFFs adsorb on the coal surface, changing the aromatic size and orderliness of the microcrystalline structure (MS) of the coal, in turn leading to alterations in the nanoporous structure of the coal. The HLGs and HBGs of VESs have different influences on the MS of coal. For this reason, VESFFs with varying hydrocarbon chain lengths and those with a combination of different VES types have different effects on the nanopores of coal; however, there have been few studies in this area. Some carbon skeletons exhibit strong Raman spectral responses owing to their symmetrical vibrations and non-polar groups. Raman spectroscopy is a suitable way to identify the molecular skeleton of coal. Raman spectroscopy can identify the hybridization of carbon atoms forming the coal skeleton, and can non-destructively, simply, and quickly analyze the disorder and graphitization of carbon atoms qualitatively and quantitatively [32]. Since the 1970s, Raman spectroscopy has been used extensively in coal studies [33,34]. Jiang et al. [27] used Raman spectroscopy to study the impact of the molecular structure of medium-to-high-rank coal on coalification. Lupoi et al. [35] used Raman spectroscopy to quantitatively evaluate the reflectivity of vitrinite and O/C atoms in coal. This paper examines the impact of VESFFs on the MS of coal.
In this study, VESs with different hydrocarbon chain lengths and VESs with different ionic types (such as cationic VESs, anionic VESs, and zwitterionic VESs) were selected as the main agents for fracturing fluids, and four different formulations of fracturing fluids were prepared. Two coal samples with different hardness coefficients were treated with deionized water and four VESFFs under the same experimental conditions. The treated coal samples were tested for zeta potential, functional groups, and MS using a zeta potential analyzer, FTIR spectrometer, and Raman spectrometer. The mechanism by which VESFFs act on coal nanopores is revealed from a molecular perspective. The results of this study can serve as a theoretical basis for the development of high-performance VESFFs for coal-seam applications.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. VESFF Preparation
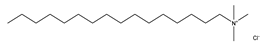
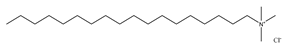
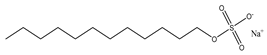
In this work, hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (CTAC, C19H42CIN, cationic VES), stearyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (STAC, C21H46CIN, cationic VES), STAC and cocoamidopropyl betaine (CAB, C19H38N2O3, zwitterionic VES) blends, and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS, C12H25SO4Na, anionic VES) and CAB blends were selected as the main reagents for the VESFFs (Table 1). Sodium salicylate (C7H5NaO3, NaSal) is used as a micelle promoter for fracturing fluids containing cationic surfactants. Potassium chloride (KCl) is used as a counter ion and anti-swelling agent in VESFFs. The fluid components are designated as B, B2, C, and D, respectively, while deionized water is identified as A (Table 2) [23]. The information on the test reagent, the preparation process of the FFs, and the viscosity test are detailed in reference [23].

Table 1.
The molecular structure diagrams of VESs.

Table 2.
The ratios of reagents utilized in the VESFFs [23].
2.2. Description of Coal Samples
Coal samples from the Tashan coal mine (Shanxi, China) and the Dongsheng coal mine (Nanchuan, Chongqing, China) were subjected to a crushing and grinding process. The coal samples from the two regions were named TS (Tashan) and NC (Nanchuan) coal samples, respectively. A comprehensive account of the industrial analysis parameters (moisture, volatile, fixed carbon content, ash) and coefficient of hardness of the coal samples is provided in reference [21]. Test samples with a particle size less than 0.074 mm were sieved and dried at 353.15 K for 48 h [36].
Adsorbed gas in the coal samples was removed using a vacuum extraction device, and the coal samples were then added to the VESFFs outlined in Table 2. Following the mixing process, the coal samples were subjected to a 48 h soaking period in a constant temperature water bath maintained at 313.15 K. The aforementioned soaking temperature is indicative of the temperature of the coal seam at an approximate burial depth of 1000 m. Following the soaking process, the coal particles were subjected to a washing and drying procedure. The coal particles were washed and then placed in an oven at 353.15 K for drying [37,38].
2.3. Zeta Potential Test
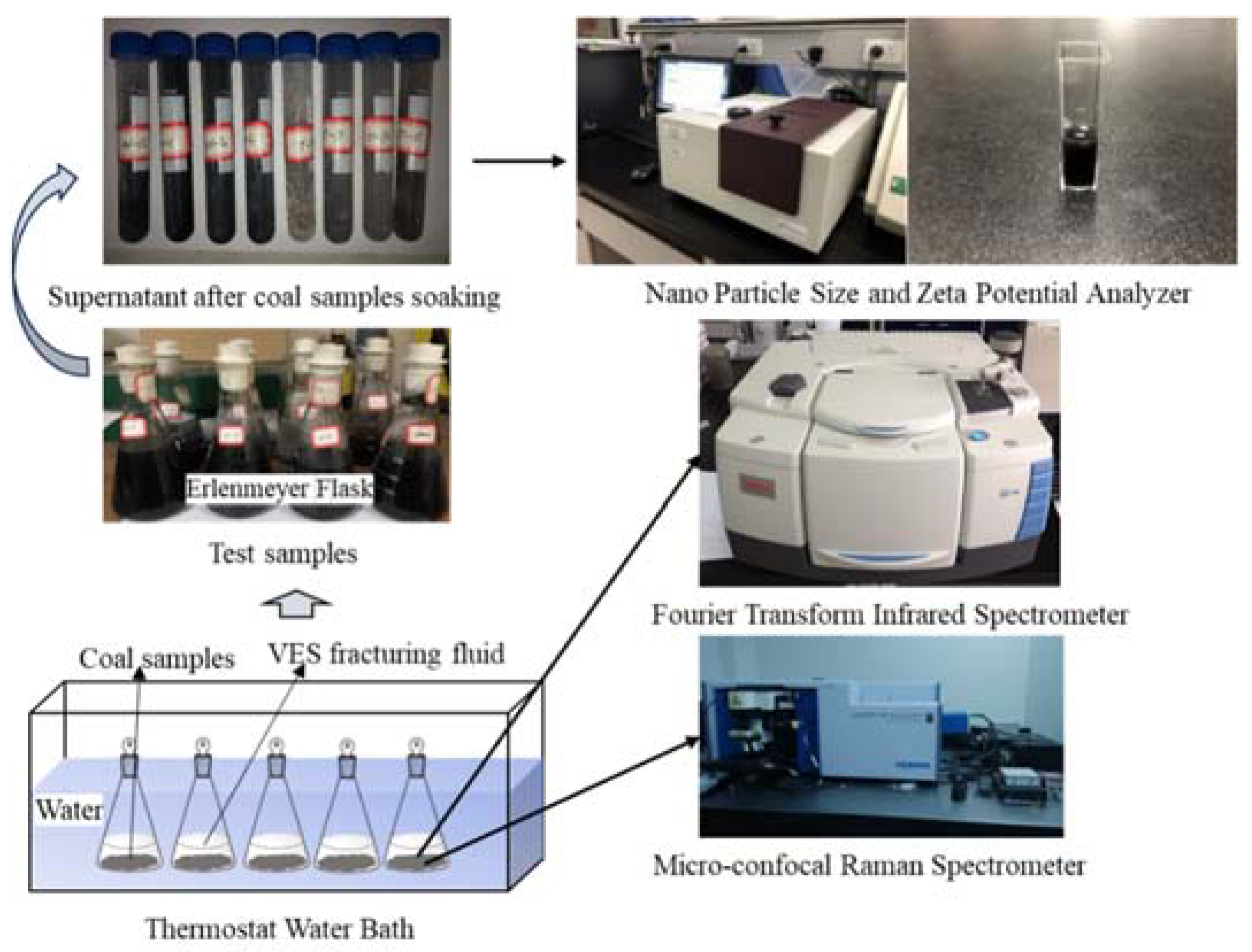
The instrument utilized for zeta potential testing was the Nano Particle Size and Zeta Potential Analyzer (NanoBrook Omni, New York, NY, USA) (Figure 1). The instrument was operated by hardware PALS technology, which is suitable for measurements of electrophoresis with a particle size range of 1 nm–100 μm, a conductivity range of 0–30 S/m, an electrophoretic mobility range of 10−11–10−7 m2/V.s, and a pH measurement range of 2–14. A 5 mL portion of the supernatant was taken (Figure 1) for use in the Nano Particle Size and Zeta Potential Analyzer to measure the zeta potential, with 5 repeat measurements, reporting the average value after the removal of outlying data points.
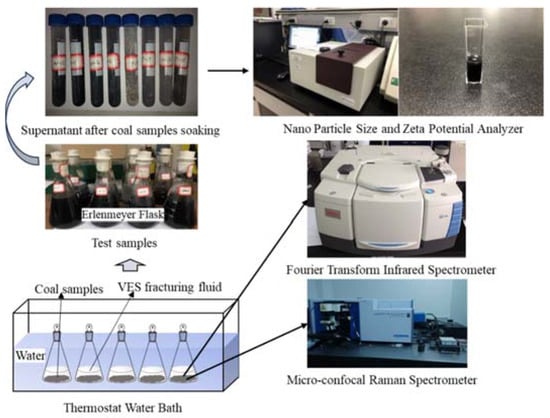

Figure 1.
Coal sample preparation and testing flowchart.
2.4. FTIR Analysis
FTIR spectra were obtained using a Nicolet iS50 spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) with a resolution of 2.25 px−1, a scanning range of 4000–400 cm−1, and 16 scans. A 1–2 mg sample was obtained following the FF treatment and ground into a fine powder in an agate mortar. This powder was then mixed evenly with dry potassium bromide (AR grade) powder (~100 mg, particle size < 0.074 mm) and placed in a mold. The resulting mixture was pressed into a tablet using a tablet press for subsequent testing.
The FTIR spectrum of coal is influenced by the presence of multiple functional groups, which can result in spectral peaks overlapping at specific locations. This phenomenon makes it challenging to accurately determine the position and intensity of the infrared absorption peaks associated with each functional group. Accordingly, peak separation and curve fitting of the FTIR spectrum were conducted using Peakfit software 4.12 (SeaSolve Software Inc., Framingham, MA, USA). PeakFit software is a signal processing software commonly used for baseline removal, smoothing, peak finding, and the fitting of spectral and chromatographic signal peaks. The software is capable of accurately and efficiently acquiring data such as peak position, intensity, integrated area, and full width at half maximum [39]. In this instance, the AutoFit Peaks II Second Derivative function was employed to ascertain the approximate location and number of spectral peaks within the overlapping region. The Addl Adjust function was employed to conduct iterative calculations for data fitting, with the objective of minimizing the sum of the squared residuals between the curves obtained through PeakFit software peak fitting and the original spectral line [40]. The results obtained after peak fitting were normalized. Following the completion of peak separation and fitting, the quantity of the corresponding functional groups was represented by the peak area. On the basis of the shape of the band, the selected spectral region was subjected to curve-fitting analysis using Lorentz and Gaussian functions. The curve-fitting spectrum was employed to ascertain the FTIR spectral parameters, including the position, width, area, and intensity of the spectral band [41].
2.5. Raman Analysis
Raman spectroscopy was conducted using a LabRAM HR Evolution micro-confocal Raman spectrometer (HORIBA, Jobin Yvon S.A.S, Longjumeau, Essonne, France) with an excitation wavelength of 532 nm and a scanning spectral range of 100–9000 cm−1. The spectral resolution of the visible spectrum was superior, exceeding 1 cm−1, with a maximum resolution of 0.5 cm−1. A 50× objective lens was used to focus the laser beam on the surface of the coal sample, with a beam diameter of approximately 2 μm and a laser power of approximately 5 mW. The acquisition time for the Raman signal in each test was 10 s. Furthermore, 10 to 15 particles were randomly selected from each coal sample for testing, which improved the accuracy of the results.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Zeta Potential of Coal Processed with VESFFs
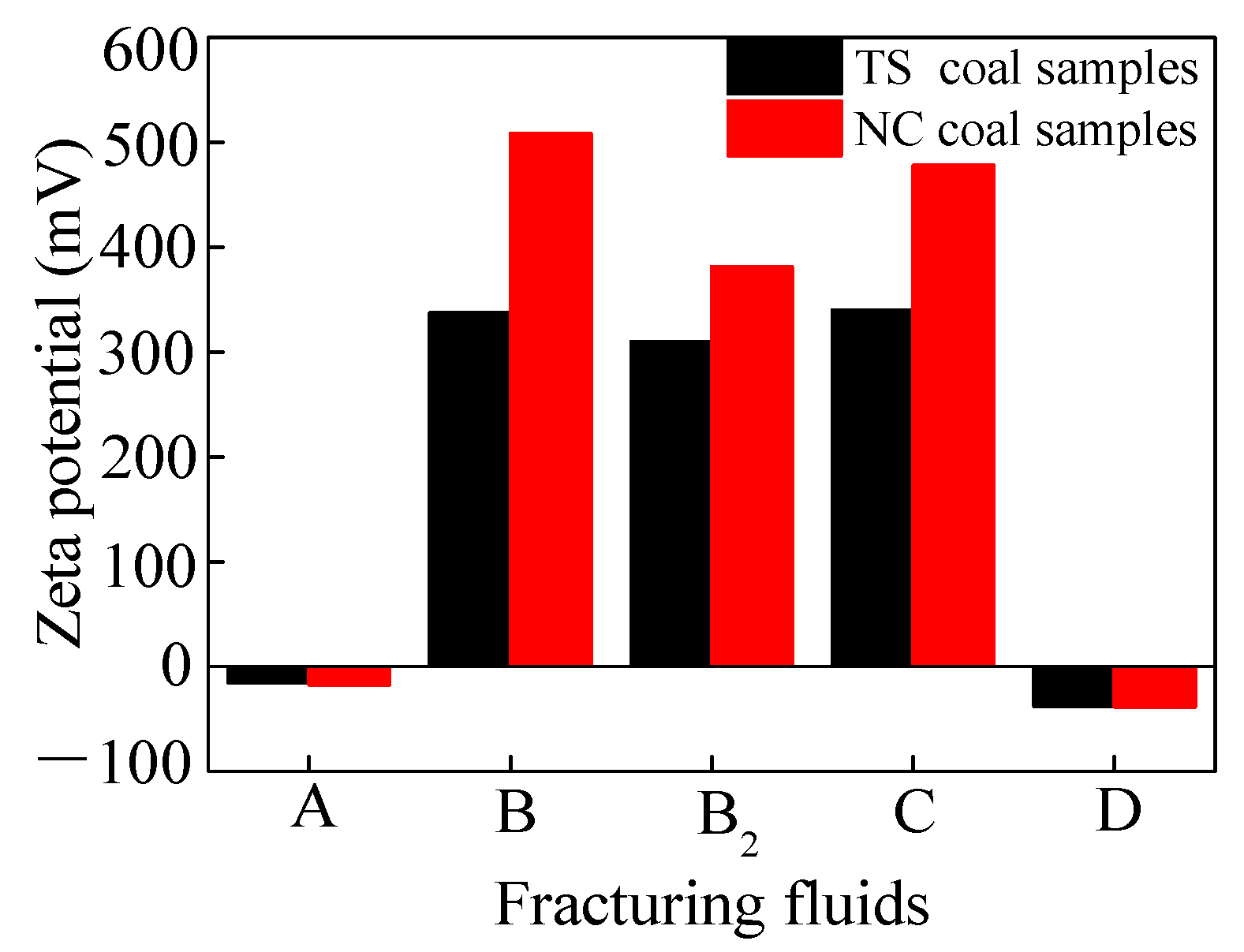
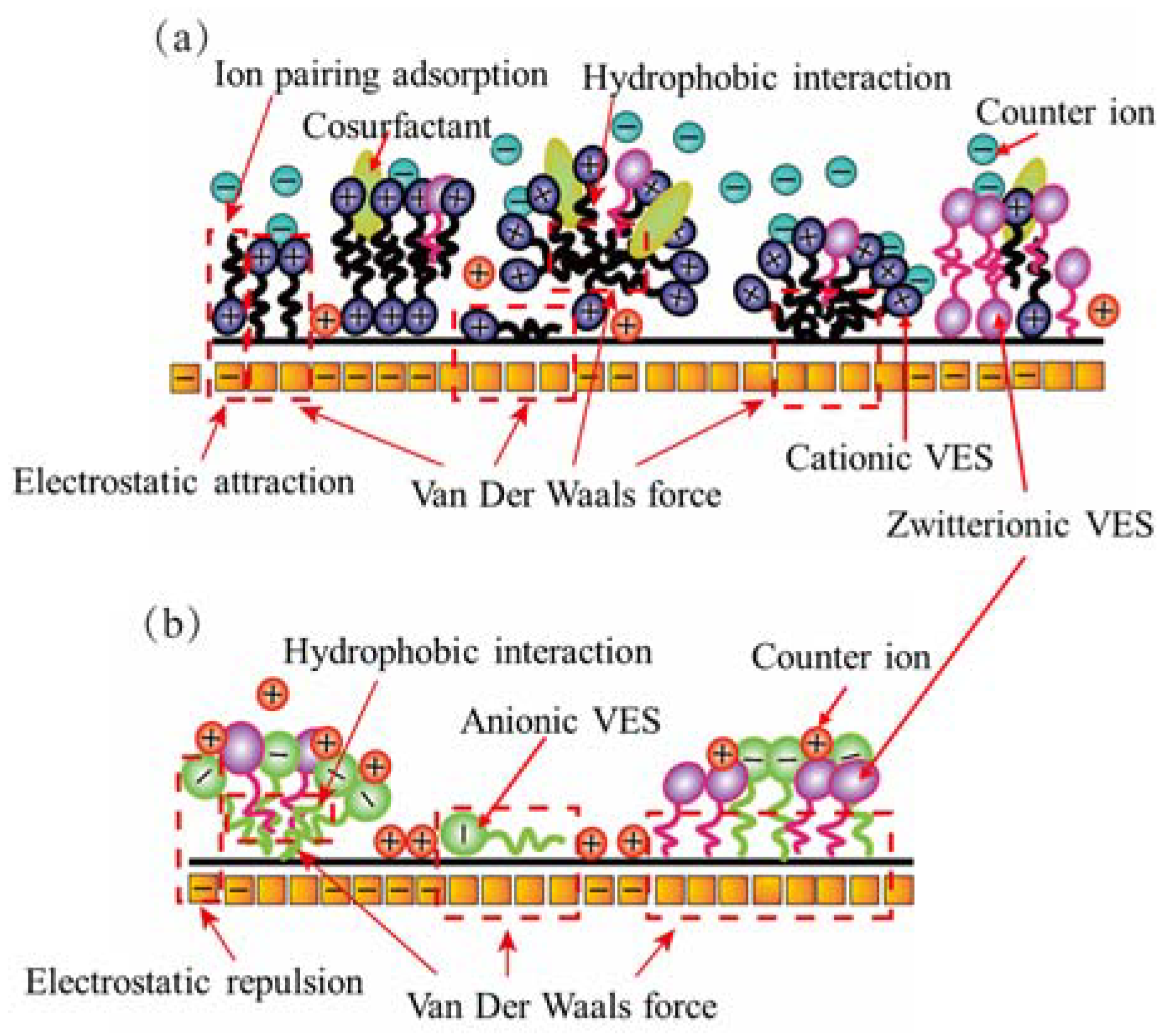
Figure 2 illustrates the zeta potential values of the coal in deionized water and four VESFFs. The presence of negatively charged functional groups, including -OH, -NH2, -NH, -C=O, and -COOH, on the surface of the coal particles resulted in a negative zeta potential for coal samples from two regions subjected to treatment with deionized water (Figure 2). Following the application of VESFFs B, B2, and C to the coal, a positive zeta potential was observed on the coal surface. Following the application of VESFF D to the coal samples, a negative zeta potential was observed on the coal surface. However, the electronegativity exhibited an increase when compared to that of the coal subjected to treatment with deionized water. As shown in Figure 3a, the cationic VESs and zwitterionic VESs in the B, B2, and C VESFFs adsorbed on to the coal surface mainly through electrostatic attraction and Van der Waals forces. Ion pairing adsorption, which occurs through the action of electrostatic forces, involves the cationic VES molecule adsorbing onto the surface of the coal through the hydrophilic group, while the hydrophobic group extends into the solution. The hydrophobic group in the solution interacts through Van der Waals forces to form various structural forms of adsorbed micelles, resulting in a change from a negative to positive zeta potential, as shown in Figure 2. The anionic VES in VESFF D has an opposite electrical charge to the coal surface, so that the VES generates an electrostatic repulsion on the coal surface, as illustrated in Figure 3b. The anionic VES only adsorbs on the coal surface through Van der Waals forces. Anionic and zwitterionic VESs also adsorb on the coal surface through HBGs, while their hydrophilic groups extend into the solution. The HBGs interact through Van der Waals forces to form adsorbed micelles, leading to an increase in the electronegativity of the coal surface. The electrostatic force between the pore wall surface and coal particles is generally outweighed by the Van der Waals forces between the two, resulting in the adsorption of numerous coal particles onto the pore wall surface. Following treatment with VESFFs B, B2, C, and D, the electrical properties of the coal surfaces of coal samples from two regions exhibited an increase, accompanied by a notable enhancement in the electrostatic force between the pore wall and coal particles, which surpassed the Van der Waals force [42]. The mutual repulsion between the pore wall and coal particles was beneficial for the removal of particles from the coal surface. After the action of VESFFs, the coal particles blocked in the pores of coal are removed, which is beneficial to the migration of CBM.
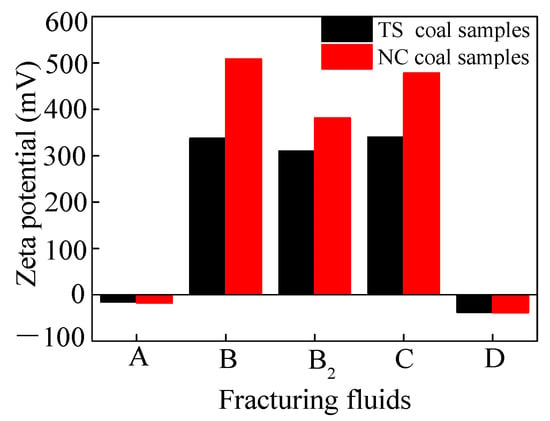
Figure 2.
Zeta potential of coal in VESFFs and deionized water.
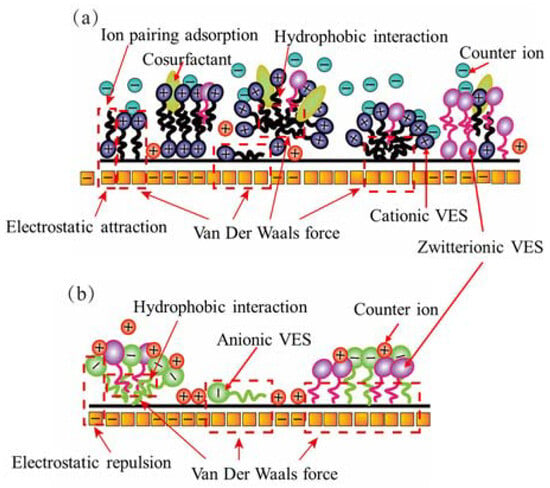
Figure 3.
Adsorption mode of VESs on coal surfaces: (a) mixing of cationic–zwitterionic VESs; (b) mixing of anionic–zwitterionic VESs.
3.2. Oxygenated Functional Groups on Coal Surfaces Processed with VESFFs
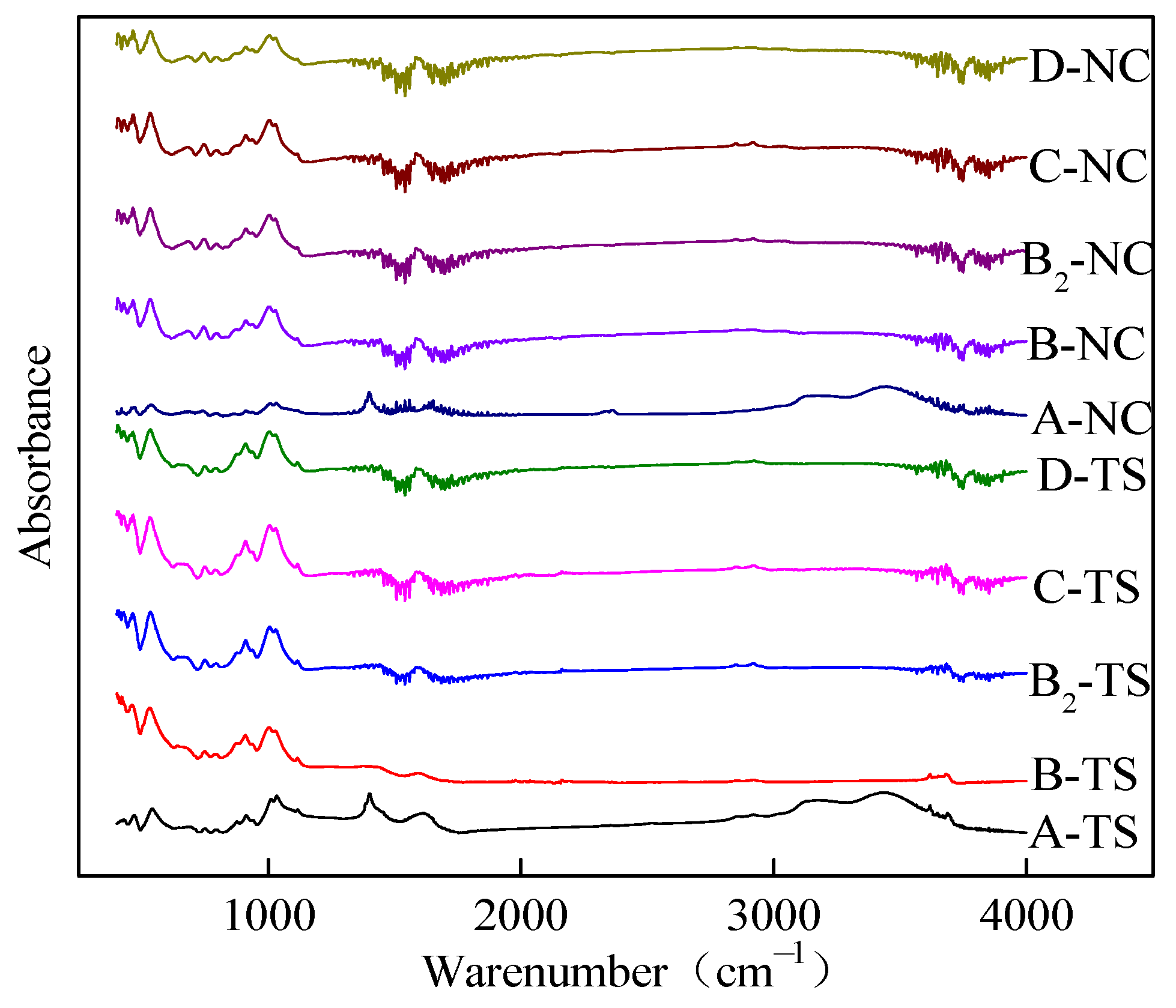
Figure 4 illustrates the FTIR spectra of coal samples from two regions following treatment with FFs. Although the peak intensities were different, it can be seen that the coal subjected to treatment with FFs had similar adsorption peaks. This finding is indicative of the fact that despite the disparate nature of the FFs utilized for the treatment of the coal samples, the types of surface functional groups present within the treated coal samples remain consistent, albeit with varying degrees of abundance. Because the coal samples examined by FTIR spectroscopy were not demineralized prior to the FF treatment, the absorption peaks at 1000–1100 cm−1 in the FTIR spectrum are attributed to the stretching and vibration of -Si-O- groups. The spectral band 1800–2300 cm−1 is the absorption peak of diamond, which is an interference peak and is not discussed.
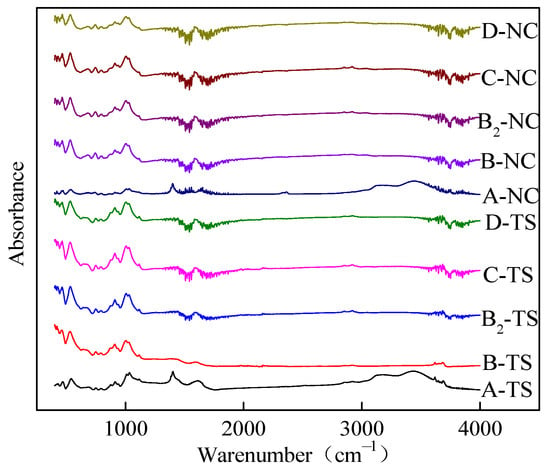
Figure 4.
FTIR spectra of test samples from two regions processed with VESFFs.
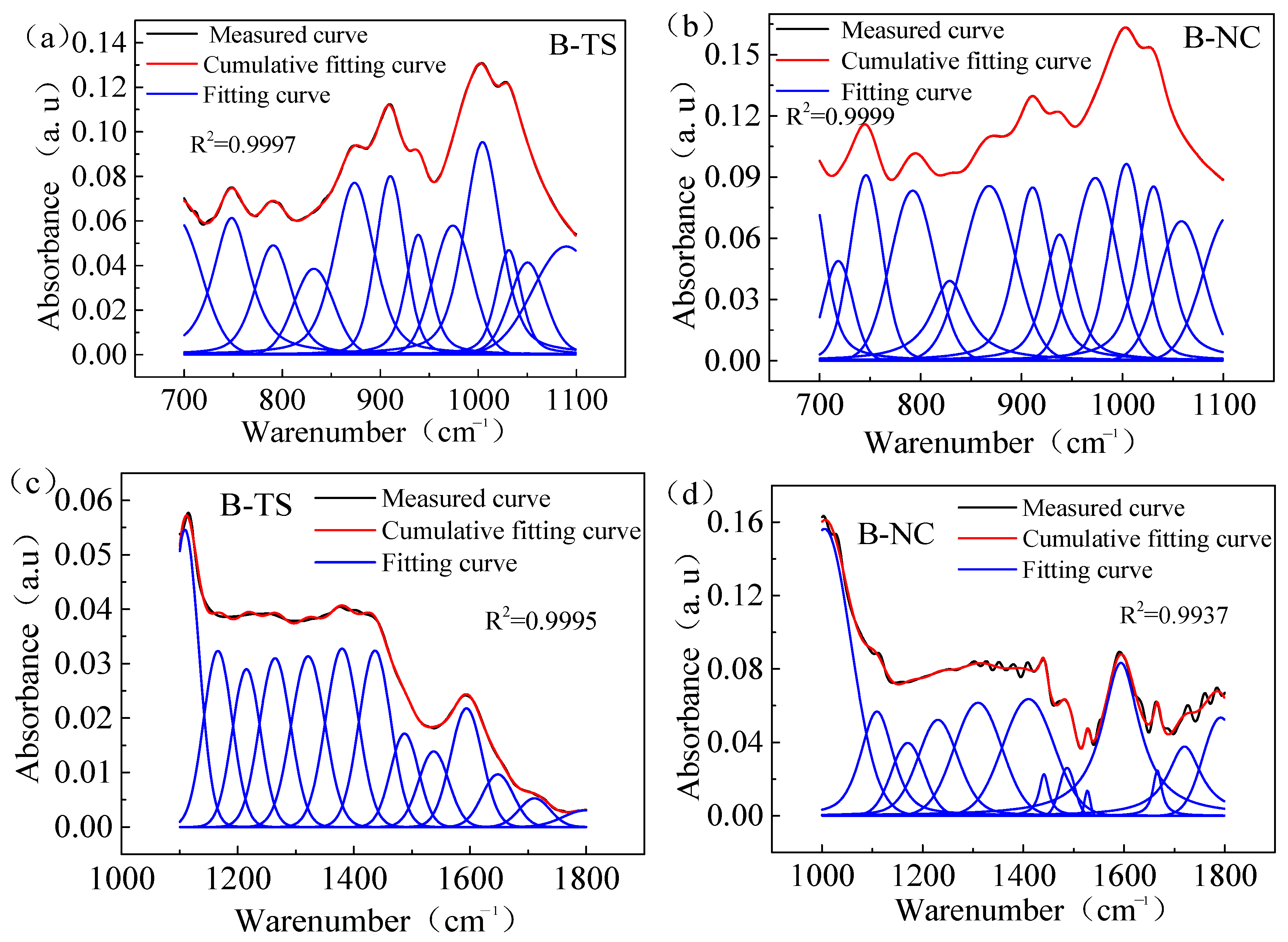
Figure 5 illustrates the peak separation and fitting of the FTIR spectral curves of coal samples sourced from two distinct regions processed with VESFF B. The study focuses on analyzing the vibrations of -COOH and -C=O on the coal surface, as well as the vibrations of -Si-O- in clay minerals, such as the kaolinite present in coal. As illustrated in Figure 6, the surfaces of the coal from two regions processed with VESFFs exhibited a higher content of -Si-O- in comparison to the coal processed with deionized water. This suggests that the action of the VESFFs resulted in the loss of soluble minerals, such as pyrite, that were present in the coal matrix, thereby increasing the exposure of -Si-O-. The impact of the VESFF C was the most significant. As illustrated in Figure 7, the carboxyl groups of the coal from two different locations exhibited an increase following treatment with FFs B, B2, C, and D, with the most pronounced effect observed for VESFF D. In conclusion, the coal that underwent treatment with VESFFs B, B2, C, and D displayed a markedly elevated degree of exposure of HLGs. The C and D FFs, which were formulated with cationic VESs plus zwitterionic VESs and anionic VESs plus zwitterionic VESs as the main agents, exhibited the most pronounced effect.
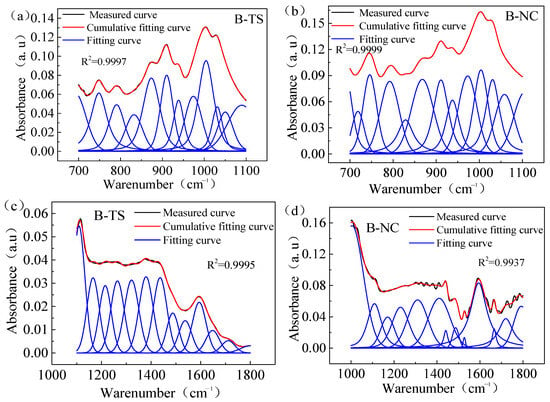
Figure 5.
Peak fitting of FTIR spectra of test samples from two regions processed with VESFF B: (a) the absorption peaks at 700–1100 cm−1 of TS coal samples; (b) the absorption peaks at 700–1100 cm−1 of NC coal samples; (c) the absorption peaks at 1100–1800 cm−1 of TS coal samples; (d) the absorption peaks at 1000–1800 cm−1 of NC coal samples.
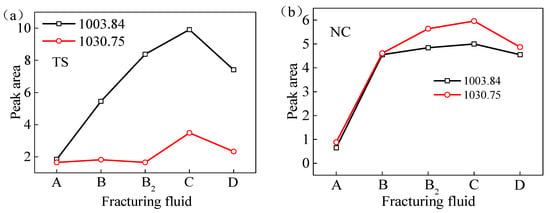
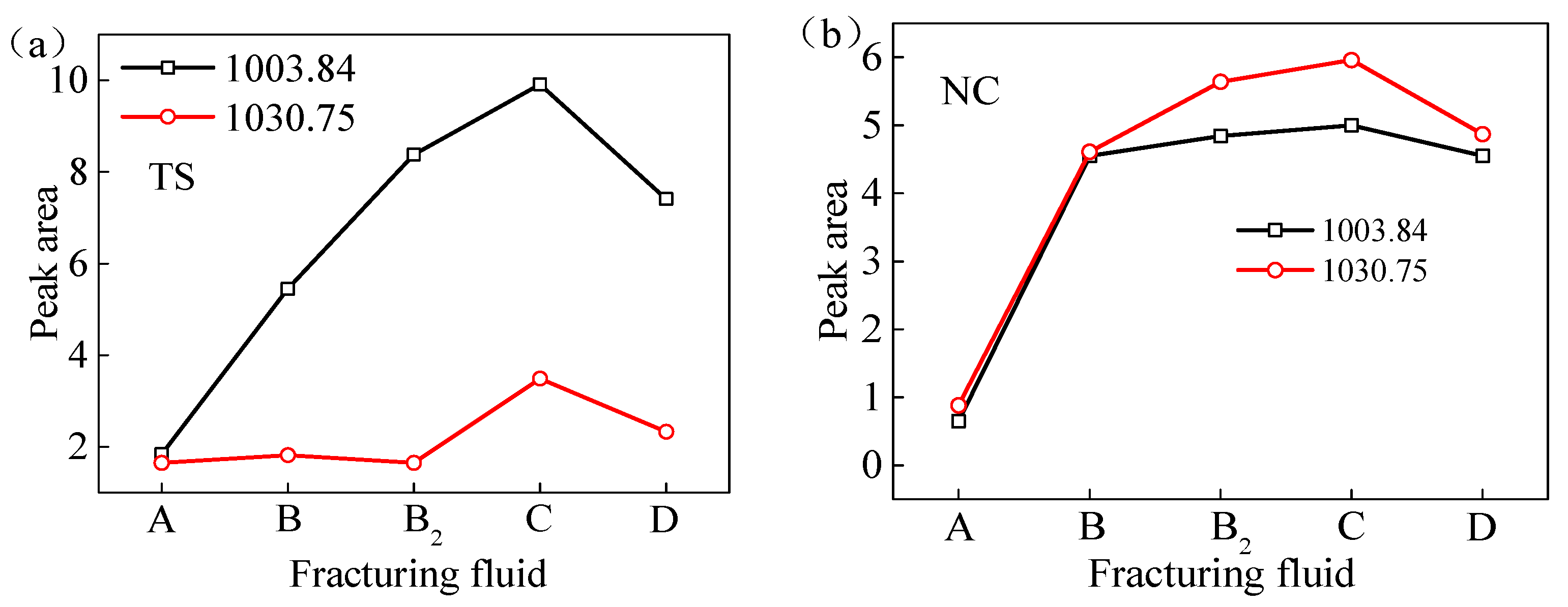
Figure 6.
Peak areas of clay minerals (-Si-O-) of test samples from two regions processed with VESFFs: (a) TS coal samples; (b) NC coal samples.
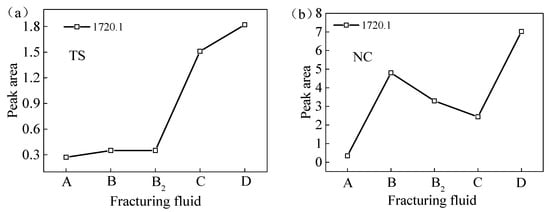
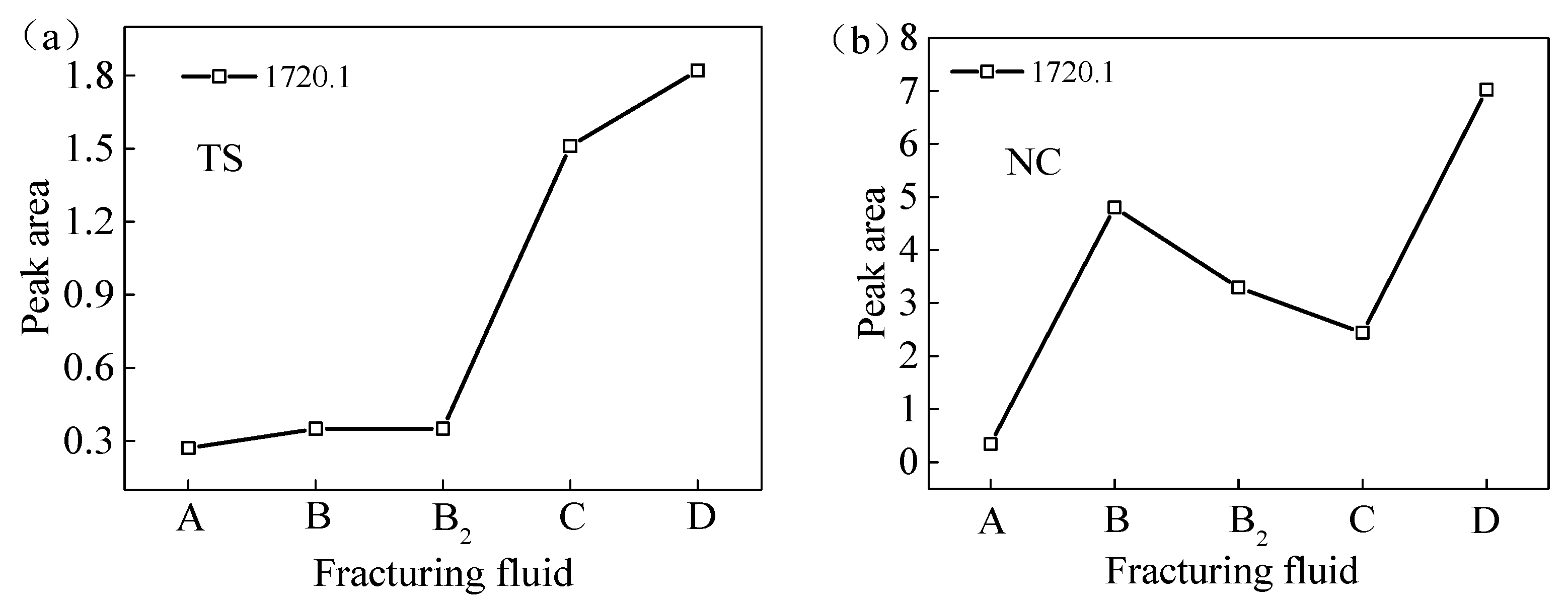
Figure 7.
Peak areas of -COOH and -C=O of test samples from two regions processed with VESFFs: (a) TS coal samples; (b) NC coal samples.
The B, B2, and C VESFF formulations contained NaSal. The chemical composition of NaSal includes carboxyl and hydroxyl groups, and its solution has greater acid hydrolysis activity than alkaline hydrolysis activity. Therefore, VESFFs B, B2, and C are weakly acidic and can dissolve minerals, such as calcite and pyrite, in coal, resulting in more exposure of -Si-O- functional groups. According to previous studies [23], VESFF C has a lower removal ability for kaolinite and montmorillonite than VESFF B2, and a lower removal and dissolution ability for illite than VESFFs D and B. Thus, the coal subjected to treatment with VESFF C retained the greatest amount of clay minerals, such as kaolinite. Consequently, the coal processed with VESFF C exhibited a greater number of Si-O functional groups, which resulted in excellent wettability of the FFs on the coal surface. VESFF C is more likely to invade pores with smaller pore sizes and thus has a more pronounced effect on micropores and transition pores.
The anion VES in VESFF D has oxidizing properties on the coal surface, which can break aromatic hydrocarbons and bridge bonds in the basic structural units of coal, oxidizing the aromatic hydrocarbons (-CH) and cycloalkanes on the coal surface into carbonyl groups (C=O) and hydroxyl groups (-OH), further generating stable carboxyl groups (-COOH) and anhydride groups [43]. Consequently, the coal samples processed with VESFF D exhibited the highest concentration of -COOH groups, as determined by the area under the vibration peak.
3.3. MS of Coal Processed with VESFFs
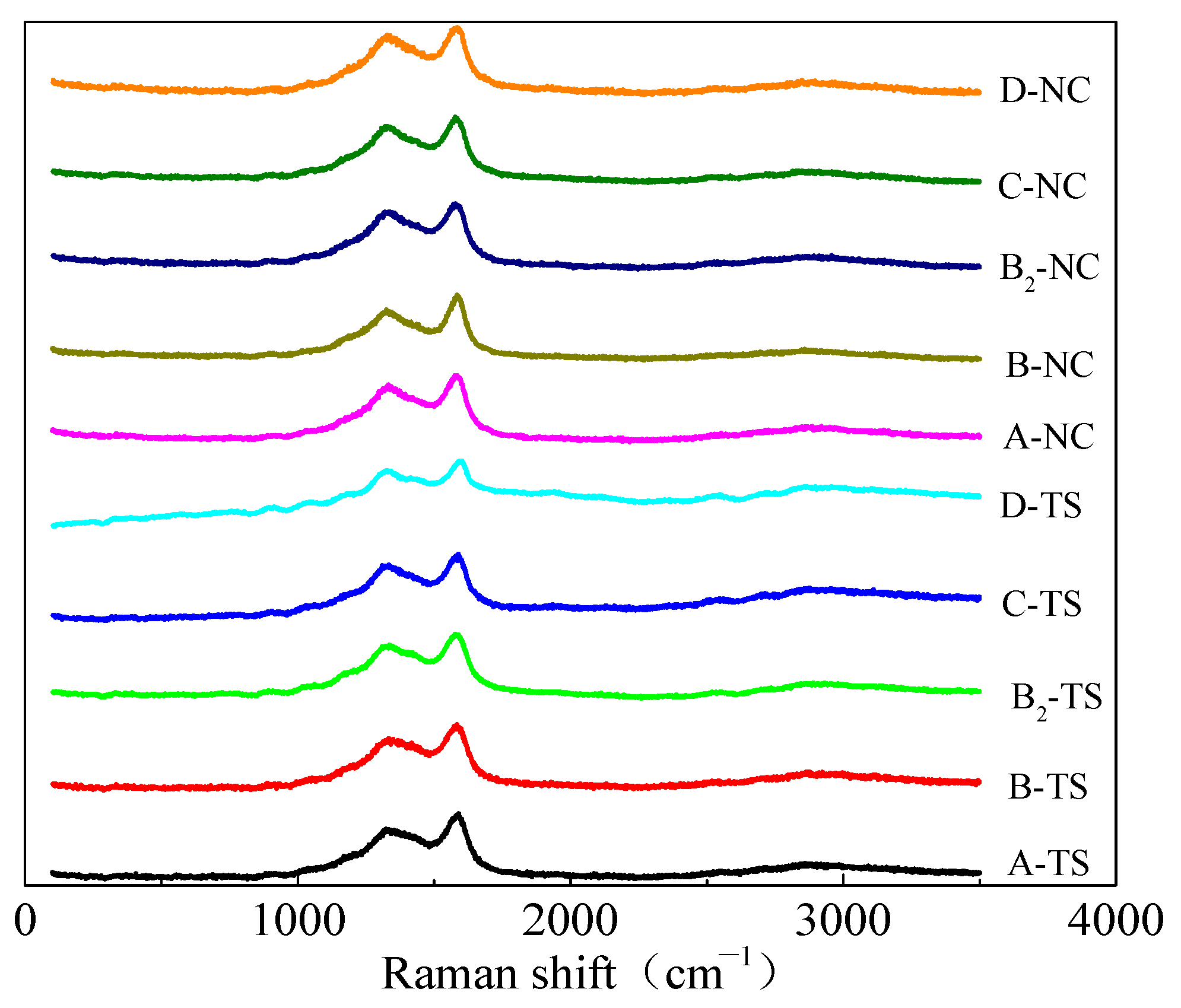
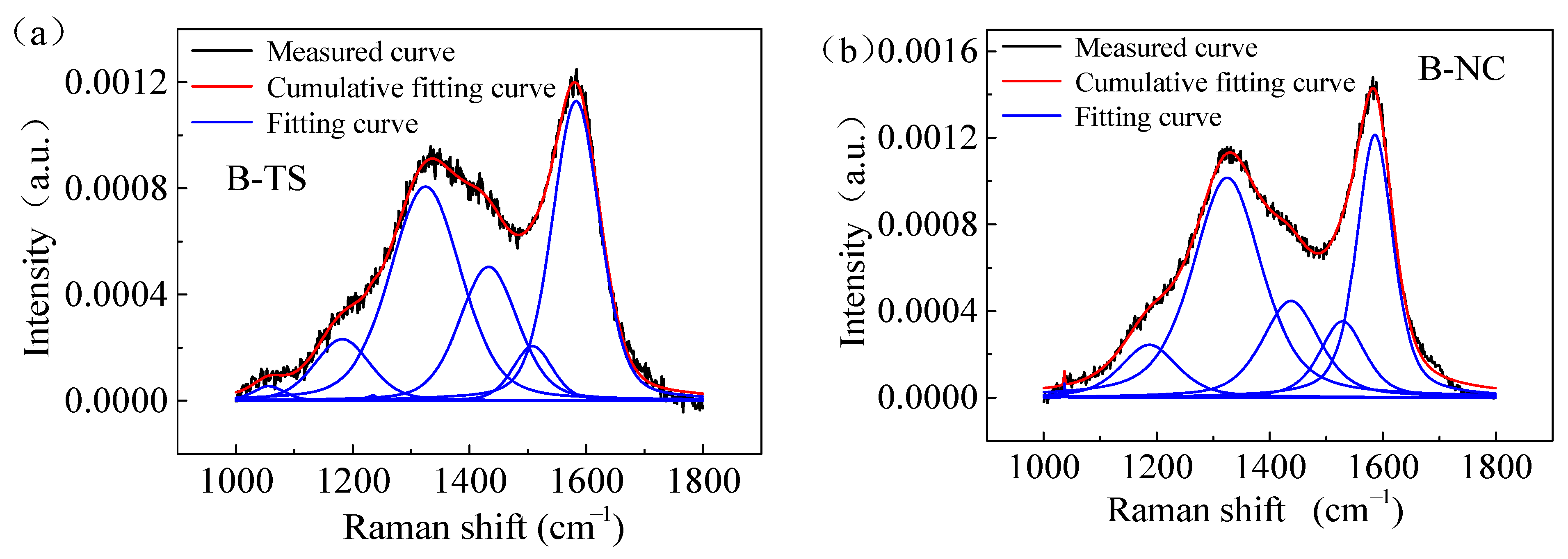
Figure 8 shows the Raman spectra of coal samples from two regions. The Raman spectra of the coal processed with VESFFs formulated with VESs of different ionic types as the main agent at 313.15 K had two peaks: a D peak (1335–1347 cm−1) and a G peak (1590–1600 cm−1). Due to the superposition of the G and D peaks, the Raman spectrum was analyzed using Peakfit software. For the determination of the approximate location and number of spectral peaks in the overlapping region, the Gauss + Lor Area and AutoFit Peaks I Second Derivative functions were selected. The first-order Raman spectrum band (1000–1800 cm−1) of the coal was analyzed to identify the presence of five distinct peaks. The peaks identified were D1, D2, D3, D4, and G. Of these, D1 and G were the most prominent (Figure 9).
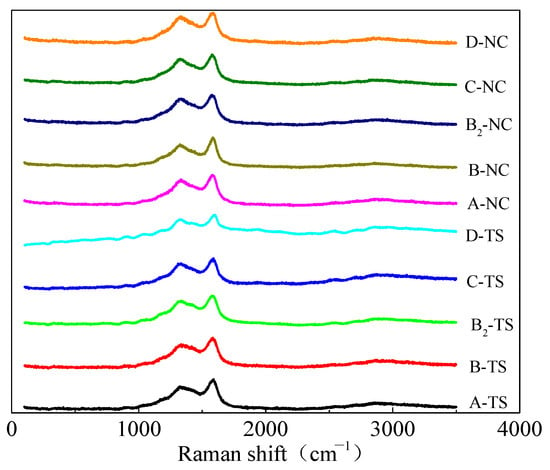
Figure 8.
Raman spectrum of coal samples.
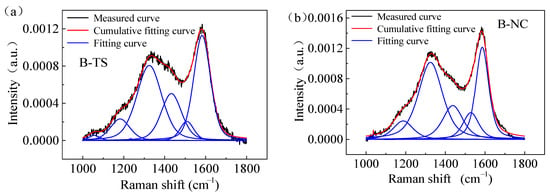
Figure 9.
Raman spectra showing peak fitting of coal samples processed with VESFF B: (a) TS coal samples; (b) NC coal samples.
The optimal first-order coal spectrum G band was identified at approximately 1590 cm−1, which corresponds to the E2g symmetric stretching vibration mode in the aromatic layer of graphite crystals [44]. The D1 band, which is associated with defects, typically occurs within the range of 1330–1370 cm−1. This range corresponds to the A1g symmetry mode of the graphite lattice and is caused by defects within the aromatic layer or disordered structures, such as heteroatoms [27,36,45]. The D2 band is approximately located at 1620 cm−1, and its intensity diminishes as the tissue degree rises. The D3 band is typically observed within the range of 1500–1550 cm−1 and is postulated to originate from amorphous sp2 carbon bonds, including those present in functional groups, organic molecules, and fragments in materials exhibiting disordered structures. The D4 band was observed at approximately 1150 cm−1 and is indicative of highly disordered materials, such as soot [44].
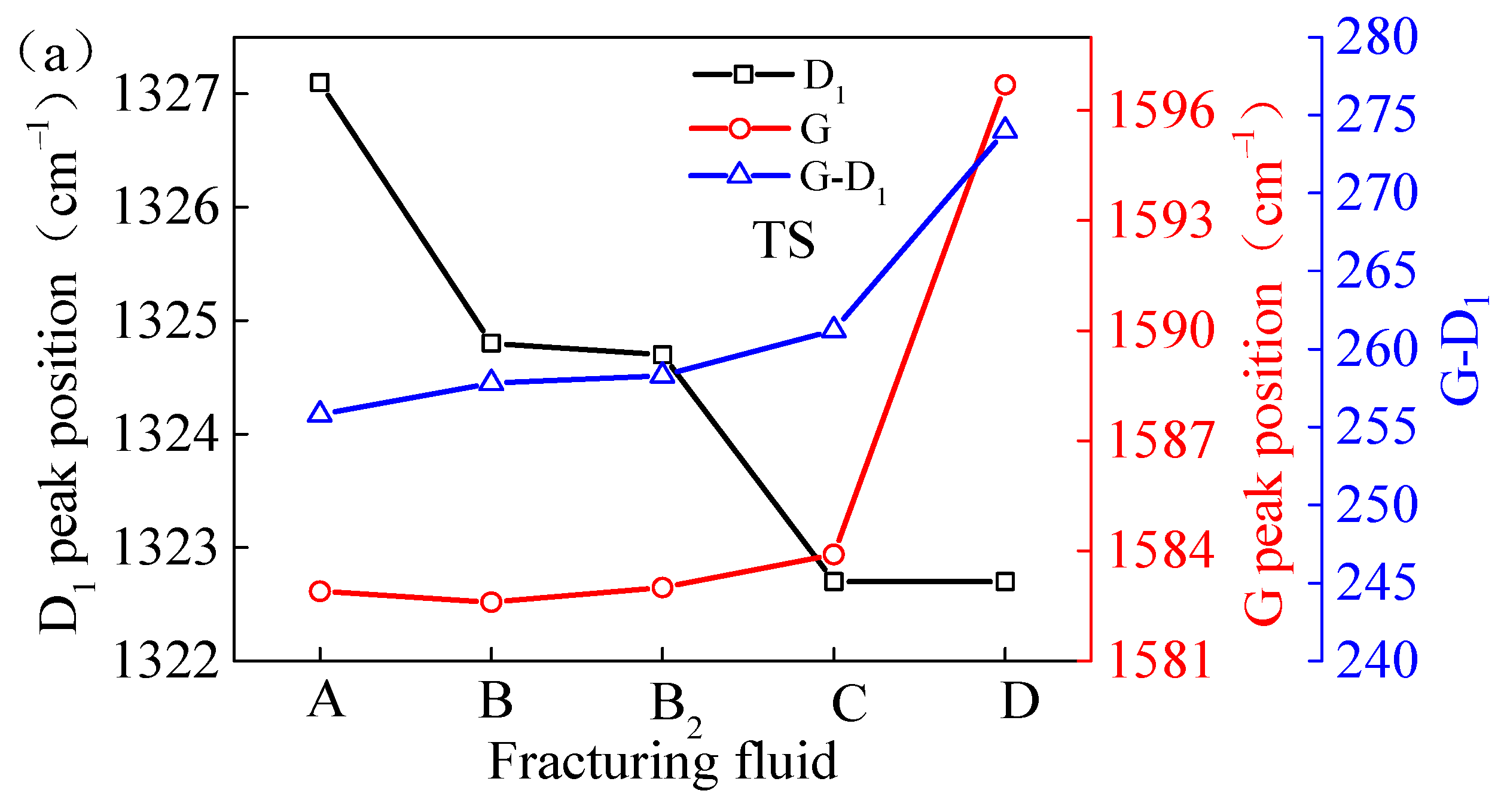
As illustrated in Table 3, the Raman spectrum D1 peak shift of the TS coal exhibited a range of 1322.7 to 1327.1 cm−1, with a maximum difference of 4.4 cm−1. The peak G shift exhibited a range of 1582.6 to 1596.7 cm−1, with a maximum difference of 14.1 cm−1. The maximum peak position difference (G-D1) was observed to be 274.0 cm−1, while the minimum was 255.8 cm−1. The Raman spectrum D1 peak shift of the NC coal varied in the range of 1323.6–1326.5 cm−1, with a maximum difference of 2.9 cm−1. The peak G shift varied in the range of 1572.9–1588.2 cm−1, with a maximum difference of 15.3 cm−1. The maximum peak position difference (G-D1) was 264.6 cm−1 and the minimum was 246.4 cm−1. The peak D1 shifts of the coal samples from two areas processed with VESFFs B, B2, C, and D showed few differences. The peak position difference (G-D1) of coal undergoing treatment with VESFFs B, B2, and C changed slightly (maximum 5.4 cm−1). The G peak of the VESFF D treatment on the TS coal shifted to a higher wavenumber domain, resulting in an increase in peak position difference (approximately 18.2 cm−1) in Figure 10a. This indicates a reduction in the bandwidth of the amorphous structure and an increase in the sp2 content, which suggests that the carbon atoms were undergoing a transition towards a more ordered structure. The mean value of the dry ash-free volatile matter (Vdaf) of the TS coal samples was 30.07%, while the mean value of the dry ash-free volatile matter (Vdaf) of the NC coal samples was 10.6%. The TS coal samples were a type of highly volatile bituminous coal, having more side chains and functional groups on their surface molecules and larger defects in molecular structure than the NC coal samples. When exposed to anionic VESs, the -CH-, -CH2-, and -CH3 groups of the TS coal were oxidized to carboxyl, alcohol hydroxyl, ketone, and aldehyde groups, and even further oxidized to generate CO, CO2, and H2O, reducing the side chain length, leading to a relative increase in the proportion of aromatic carbon atoms, aromatic rings, and aromatic C=C bond content, and an increase in the peak position difference (G-D1) in the coal.

Table 3.
Raman structure parameters of coal samples treated with FFs.
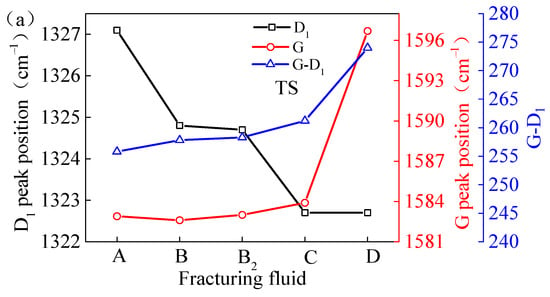
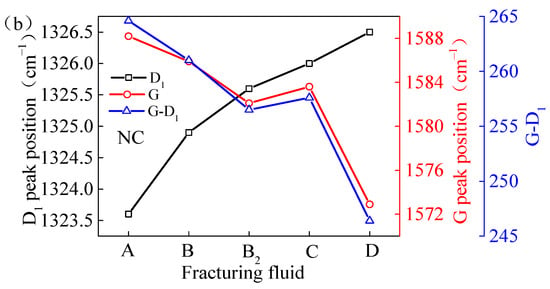
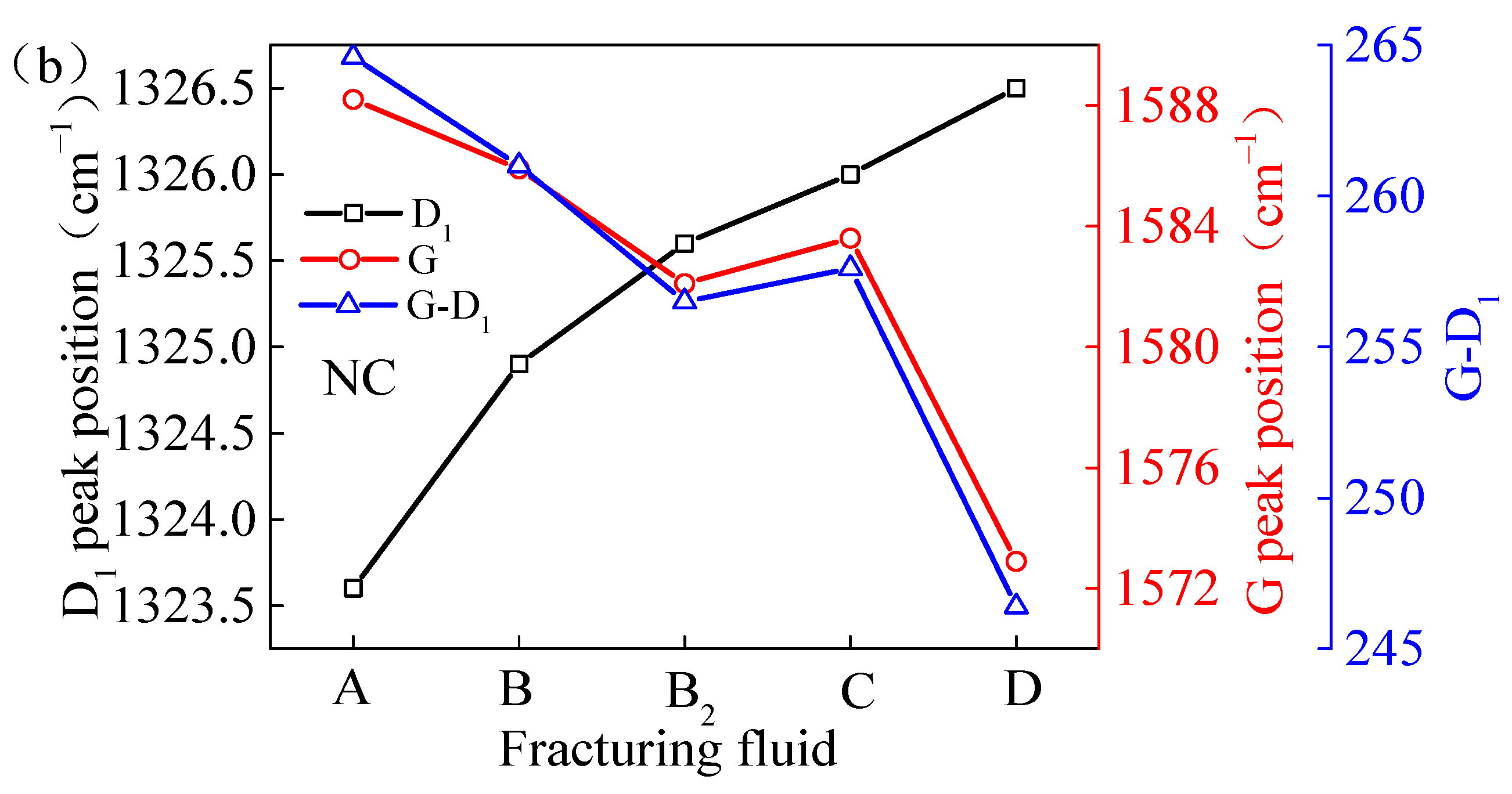
Figure 10.
Peak position difference of coal samples treated by FFs: (a) TS coal samples; (b) NC coal samples.
The G peak position of the NC samples that had been processed with VESFFs B, B2, C, and D exhibited a shift to a lower wavenumber range, which is indicative of a decline in the orderliness of the macromolecular structure within the coal. The effect of VESFF D was the most pronounced. This phenomenon can be attributed to the adsorption of water and VES molecules onto the coal surface. The adsorption capacity of VES molecules on the coal surface is superior to that of methane molecules, leading to alterations in the aromatic size and order of the original microscale crystalline structure of the coal. The NC coal samples were a lean coal that had undergone significant metamorphism and exhibited a reduced number of side chains and oxygen-containing functional groups. Consequently, the oxidation of the VESs in VESFF D by anions was not readily apparent. The MS of coal is primarily affected by the adsorption of VESs, which impairs the ordered arrangement of the macromolecular structure of coal.
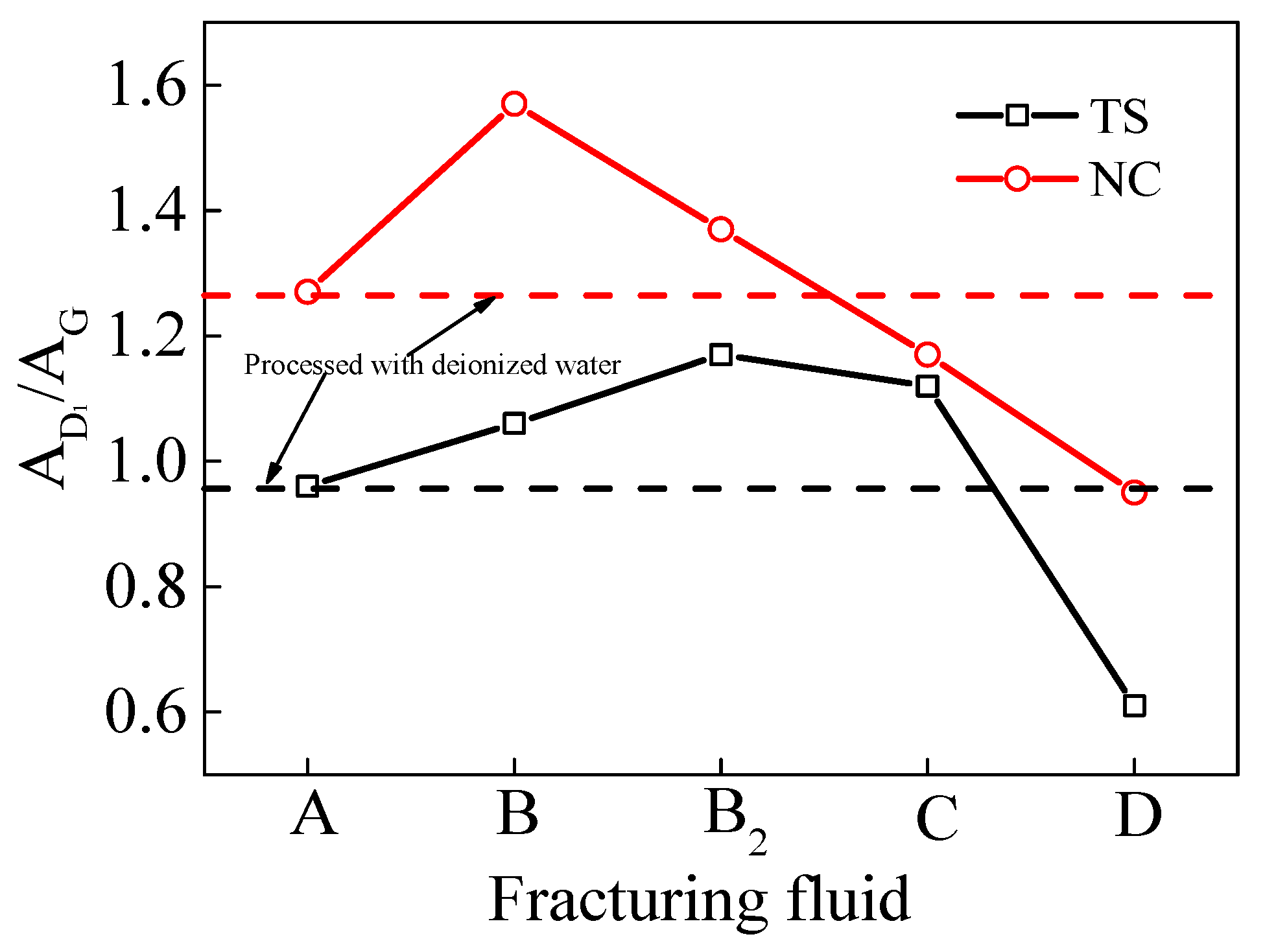
The area of the G peak (AG) in the Raman spectrum of coal can be considered to be an indicator of the number of aromatic rings present in the macro-molecular structure. The area of peak D1 (AD1) is indicative of the degree of molecular order and the number of structural unit defects present in the macro-molecules of coal. The ratio of the peak areas between the D1 and G peaks (AD1/AG) demonstrated an inverse proportional relationship with the size of the macromolecular planar MS of the coal samples [46,47]. As illustrated in Figure 11, the peak area ratio of the D1 and G peaks (AD1/AG) in the TS coal processed with VESFF D was lower (approximately 0.35) than that of the TS coal processed with deionized water, indicating that the aromatic layer extension in the aromatic crystal nucleus of the TS coal processed with VESFF D and the micropore volume both increased. The ratios of the peak areas of the D1 and G peaks (AD1/AG) for the TS coal processed with VESFFs B, B2, and C were all greater than those for the coal processed with deionized water, decreasing in the following order: B2 > C > B. This result indicates that these three VESFFs destroyed the MS of coal, and the VESFFs composed of VESs with a longer hydrocarbon chain length and cationic–zwitterionic VESs more severely damaged the MS of the coal. As illustrated in Figure 11, the peak area ratios of the D1 and G peaks (AD1/AG) in the NC coal processed with VESFFs C and D were notably lower than those of the coal processed with deionized water, with VESFF D demonstrating the most pronounced impact. This result suggests that VESFFs C and D enhance the aromatic layer extension (La) within the aromatic crystal nuclei of NC coal, thereby enlarging the micropore volume of the coal. Conversely, VESFFs B and B2 were detrimental to the increase in aromatic layer extension (La) within the aromatic crystal nuclei of the NC coal.
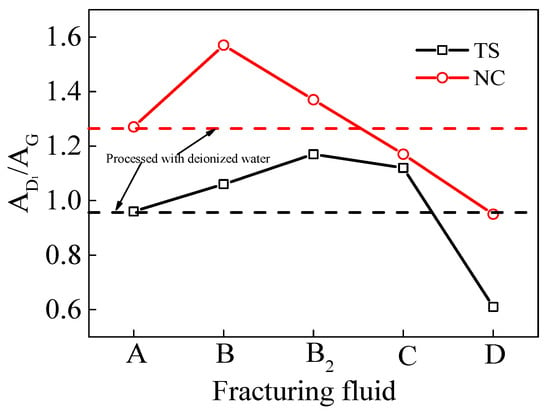
Figure 11.
Peak surface ratio of coal samples processed with FFs.
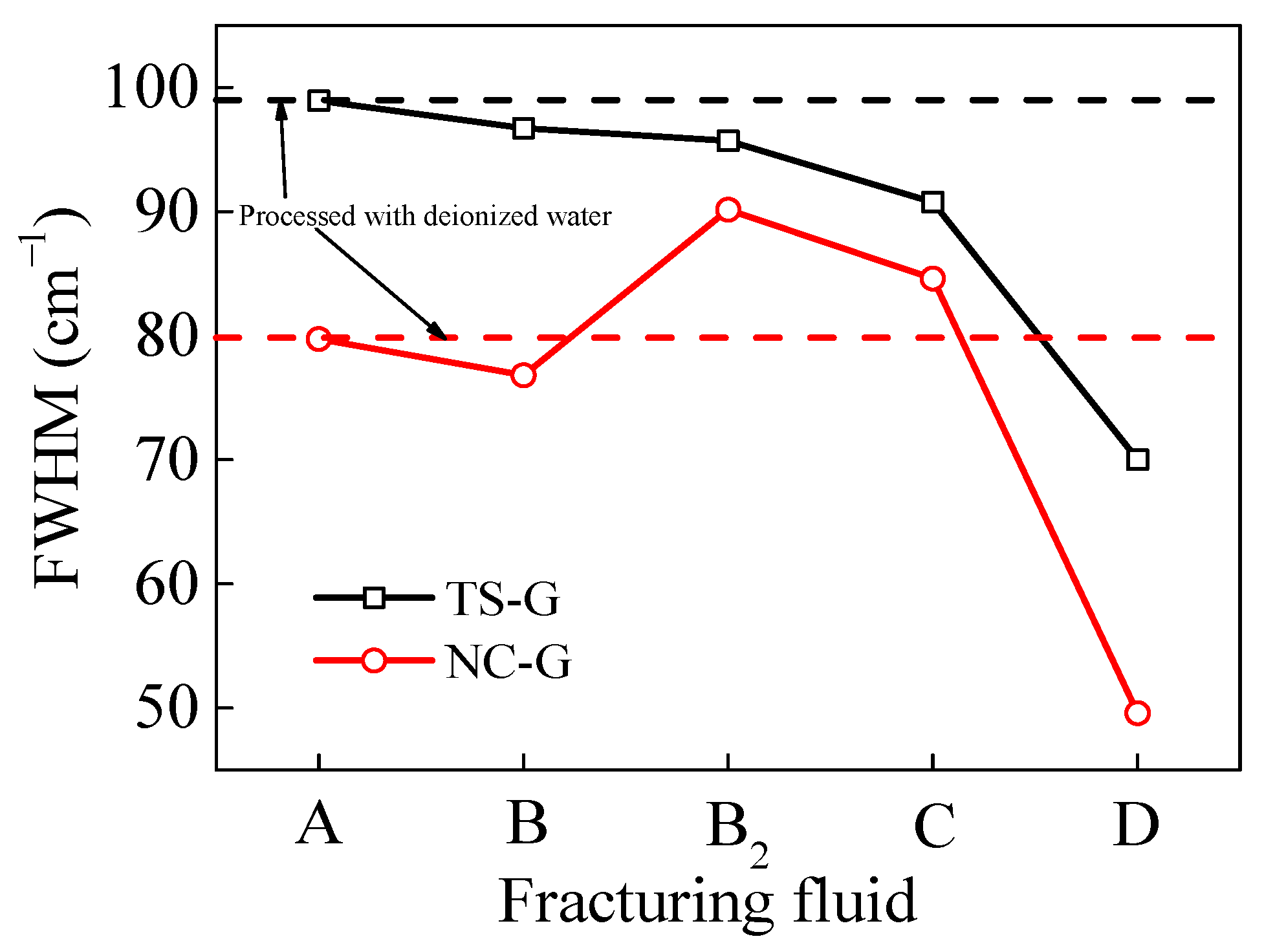
In Raman spectroscopy, the full width at half maximum of the D peak (FWHM-D) and the full width at half maximum of the G peak (FWHM-G) are defined as the spectral line widths at half the maximum peak heights of the D1 and G peaks, respectively [48,49]. Greater sharpness of the D and G peaks, particularly the G peak, indicates an increase in the size and order of the graphite microcrystals in the coal [50]. As illustrated in Figure 12, the FWHM-G of VESFF D acting on the coal from two regions exhibited a reduction, indicating that the spacing (d002) between the aromatic ring layers of the macromolecules in the coal processed with VESFF D diminished, and the micropore volume increased. With regard to the TS coal, the sensitivity of the VESFF to the FWHM-G was found to decrease in the following order: D > C > B2 > B. Furthermore, in comparison with the coal processed with deionized water, the interlayer spacing (d002) of the macro-molecular aromatic rings exhibited a reduction. This result indicates that VESFFs B, B2, C, and D increased the micropore volume of the TS coal. A comparison of the interlayer spacing (d002) of the macromolecular aromatic rings in the NC coal processed with VESFF B with that of the coal processed with deionized water revealed a slight reduction in the former. The interlayer spacing (d002) of the macromolecular aromatic rings in the coal processed with VESFFs B2 and C was increased, indicating that the VESs containing longer hydrocarbon chains were not conducive to increasing the micropores in the NC coal.
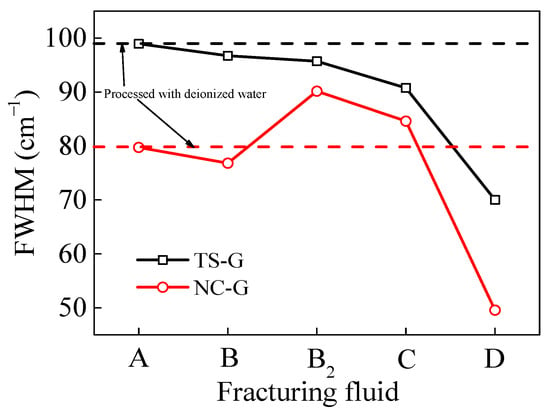
Figure 12.
FWHM of D peak and G peak of coal samples processed with FFs.
4. Conclusions
Four VESFFs were formulated using VESs with different hydrocarbon chain lengths and different ionic types as the main reagents. The effects of deionized water and four VESFFs on the zeta potential, functional groups with oxygen content, and MS of soft coal and hard coal surfaces were compared. The research results are helpful to reveal the mechanism of VESFFs on the micropores of coal, and can provide theoretical guidance for the optimization of VESFF formulations. The following conclusions were reached.
- (1)
- VESFFs B, B2, C, and D increased the electrical properties of the surface of the coal, and the electrostatic force between the pore wall and coal particles became greater than the Van der Waals force, leading to a repulsive effect beneficial for removing particles from the coal surface.
- (2)
- The coal samples subjected to treatment with VESFF C had more -Si-O- functional groups. VESFF C was more likely to penetrate into nanopores and thereby had a more pronounced effect on micropores and transition pores. The anionic VESs in VESFF D have oxidizing properties that destroy aromatic hydrocarbons and bridge bonds in the basic structural units on the surface of coal, generating stable carboxyl (-COOH) and anhydride groups.
- (3)
- The aromatic lamellae extension (La) in the aromatic crystal nuclei of the TS coal processed with VESFF D increased, resulting in an increase in micropore volume. VESFFs C and D were beneficial for increasing the aromatic layer extension (La) in the aromatic crystal nuclei of NC coal, resulting in an increase in micropore volume.
- (4)
- The treatment with VESFFs resulted in the aromatic ring spacing (d002) of the TS coal becoming smaller than that of the deionized-water-treated coal, decreasing in the following order: D > C > B2 > B. This indicates that VESFFs B, B2, C, and D all increased the micropore volume of the TS coal. The interlayer spacing (d002) of the aromatic rings in the macromolecules of the NC coal subjected to treatment with VESFFs B2 and C increased. This suggests that VESs with longer hydrocarbon chain lengths are not conducive to increasing micropores in NC coal.
Author Contributions
M.Y.: Methodology, Validation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing, Resources, Funding acquisition; S.G.: Investigation, Data curation, Methodology; Y.C.: Data curation, Writing—review and editing, Validation, Funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) [No. 52204230]; The Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province [No. 202203021212212]; The China Postdoctoral Science Foundation [2023M731834]; Scientific and Technological Innovation Programs of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi (STIP) [2021L056]; and the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing [CSTB2023NSCQ-MSX0854].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on demand.
Conflicts of Interest
Mengmeng Yang was employed by the company Pingdingshan Tianan Coal Mining Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Gao, H.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Z.T.; Li, C.; Li, Y.H. Experimental study on the effect of freeze-thaw cycles on the mechanical and permeability characteristics of coal. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Wu, S.W.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, L. Investigation of desorption and diffusion of gas within low-rank bituminous coal under moisture-stress constraints. Fuel 2024, 373, 132320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, E.R.; Zhu, X.Y.; Chen, X.J.; Zou, Q.L.; Yang, K.; Chen, H.D.; Wei, J.Q. Analysis of methane diffusion on permeability rebound and recovery in coal reservoirs: Implications for deep coalbed methane-enhanced extraction. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 076622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.J.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.C.; Gao, Y.B.; Li, Z.G.; Liu, H.W. A feasibility study of coal seam water injection processes: The effects of coal porosity and mass flow rates of injected water on wetting radii. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 16956–16967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, N.; Sheng, J.J. Mitigating near-fracture blockage and enhancing oil recovery in tight reservoirs by adding surfactants in hydraulic fracturing fluid. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 185, 106611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibaev, A.V.; Osiptsov, A.A.; Philippova, O.E. Novel Trends in the Development of Surfactant-Based Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids: A Review. Gels 2021, 7, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, S.C.; Hidayat, B.M.; Mohshim, D.F.; Zain, Z.M.; Chai, I.C.H.; Borhan, N.; Ismail, H.H.; Adam, M. Evaluation of anionic and non-ionic surfactant performance for Montney shale gas hydraulic fracturing fluids. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. 2021, 11, 1973–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.C.; Liu, T.Y.; Luo, P.Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.X.; Cheng, J.M.; Yu, Y. Performance and field implementation of a new fracturing fluid consisting of hydrophobically associating polyacrylamide and anionic surfactant. J. Polym. Eng. 2016, 36, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.Q.; Zhang, W.M.; Liu, Y.W.; Han, H.K.; Huang, C.; Jiang, W.J.; Mitri, H. Pore structure characteristics and adsorption and desorption capacity of coal rock after exposure to clean fracturing fluid. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 21407–21417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.M.; Zhou, G.; Jiang, W.J.; Niu, C.X.; Xue, Y.F. Preparation and performance analysis of bisamido-based cationic surfactant fracturing fluid for coal seam water injection. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 332, 115806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Y.; Yang, F.; Ge, Z.L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S.Q. Influence of viscoelastic surfactant fracturing fluid on permeability of coal seams. Fuel 2017, 194, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Y.; Yang, F.; Ge, Z.L.; Wang, S.Q.; Wang, Q. The influence of viscoelastic surfactant fracturing fluids on gas desorption in soft seams. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 27, 1649–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.M.; Lu, Y.Y.; Ge, Z.L.; Zhou, Z.; Chai, C.J.; Wang, H.M.; Zhang, L.; Bo, T. Viscoelastic surfactant fracturing fluids for use in coal seams: Effects of surfactant composition and formulation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 215, 115370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.L.; Gong, S.H.; Zhou, Z.; Ye, M.L.; Wang, Z.P.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.T.; Zhang, H.W. Influence of viscoelastic surfactant fracturing fluids on modified coal fracture flow characteristics. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 1495–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.B.; Wang, D.H.; Yang, X.L.; Yu, M.F.; Sun, B.; Yan, S.Y.; Zhang, G.R.; Xu, J. Mechanism of nozzle position affecting coalbed methane mining in high-pressure air blasting. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.Z.; Liu, Q.; Qiu, L.M.; Zhang, J.G.; Majid, K.; Peng, Y.J.; Zhao, Y.J.; Wang, M.; Guo, M.G.; Hong, T.T. Experimental study on resistivity evolution law and precursory signals in the damage process of gas-bearing coal. Fuel 2024, 362, 130798. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H.; Kang, Y. Inclusions in stainless steels—A review. Steel Res. Int. 2017, 88, 1700130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Han, Y.C.; Huang, X.; Cao, M.W.; Wang, Y.L. Aggregation behavior of a series of anionic sulfonate gemini surfactants and their corresponding monomeric surfactant. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 319, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehgal, P.; Doe, H.; Wimmer, R.; Tanaka, R.; Kosaka, O. Mixed monolayer and micelle formation of cationic and zwitterionic surfactant of identical hydrocarbon tail in an aqueous medium: Interfacial tension, fluorescence probe, dynamic light scattering, and viscosity studies. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2008, 29, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Y.; Chai, C.J.; Zhou, Z.; Ge, Z.L.; Yang, M.M. Influence of bioconversion on pore structure of bituminous coal. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 15, e2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.M.; Lu, Y.Y.; Ge, Z.L.; Zhou, Z.; Chai, C.J.; Zhang, L. Optimal selection of viscoelastic surfactant fracturing fluids based on influence on coal seam pores. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 2179–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Huang, Q.M.; Wang, G.; Bing, W.; Li, J. Experimental study of the influence of water-based fracturing fluids on the pore structure of coal. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 88, 103863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.M.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, L.; Gong, S.H. Physicochemical effect on coal pores of hydrocarbon chain length and mixing of viscoelastic surfactants in clean fracturing fluids. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 19418–19427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, H. Zeta potential of a subbituminous coal and its effect on particle agglomeration. Miner. Metall. Proc. 1996, 13, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lin, Y.; Marrero, T.R. Effect of ζ potential on the strength of compacted coal logs. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1996, 35, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.L.; Huang, Q.M.; Liu, Z. Effect of a newly synthesized anionic Gemini surfactant composite fracturing system on the wettability of coking coal. Process Saf. Environ. 2023, 169, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.Y.; Yang, W.H.; Cheng, Y.P.; Liu, Z.D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, K. Molecular structure characterization of middle-high rank coal via XRD, Raman and FTIR spectroscopy: Implications for coalification. Fuel 2019, 239, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.W.; Ma, Y.K.; Wang, Z.F.; Liang, Y.H.; Wang, L. Infiltration characteristics of surfactant solution in non gas-bearing coal and its influence mechanism. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 397, 124116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Liu, S.Y.; Fan, M.Q.; Zhang, L. Decrease of hydrophilicity of lignite using CTAB: Effects of adsorption differences of surfactant onto mineral composition and functional groups. Fuel 2017, 197, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Niu, J.D.; Wang, J.W.; Song, L.X.; Wang, Q.B.; Sun, L.Q.; He, M.; You, X.F. Effect of Gemini surfactant on wettability of Lignite: An experimental and molecular dynamics simulation study. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 399, 124394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.M.; Cao, D.Y.; Wei, Y.C.; Nie, J.; Qin, R.F. Comparison of nanopore evolution in vitrinite and inertinite in coalbed methane reservoirs during coalification. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 78, 103289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, A.P.; Khabibulina, E.R.; Mikhaylova, E.S.; Zhuravleva, N.V.; Ismagilov, Z.R. Structural defects and the demineralization of Kuznetsk basin coal: Data from Raman spectroscopy. Coke Chem. 2019, 62, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.F.; You, J.L.; Lu, L.M.; Wang, M.; Wang, J. Raman spectroscopic study of coal samples during heating. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lünsdorf, N.K.; Lünsdorf, J.O. Evaluating Raman spectra of carbonaceous matter by automated, iterative curve-fitting. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 160–161, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupoi, J.S.; Fritz, L.P.; Hackley, P.C.; Solotky, L.; Weislogel, A.; Schlaegle, S. Quantitative evaluation of vitrinite reflectance and atomic O/C in coal using Raman spectroscopy and multivariate analysis. Fuel 2018, 230, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.Q.; Liu, X.F.; Nie, B.S.; Song, D.Z. FTIR and Raman spectroscopy characterization of functional groups in various rank coals. Fuel 2017, 206, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Yang, W.; Yang, W.M.; Luo, L.M.; Lyu, J.Y. Effect of AES anionic surfactant on the microstructure and wettability of coal. Energy 2023, 289, 130118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ge, Z.L.; Zheng, J.L.; Tian, Z.Y. Viscoelastic surfactant fracturing fluid for underground hydraulic fracturing in soft coal seams. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 169, 646–653. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, T.; Hao, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.F. Mechanistic insights into the chemical structural changes of lignite on potential formation of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Li, X.L.; Wang, D.K.; Zhang, D.M. Experimental study on temperature response of different ranks of coal to liquid nitrogen soaking. Nat. Resour. Res. 2020, 30, 1467–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Song, D.Z.; He, X.Q.; Nie, B.S.; Wang, L.K. Insight into the macromolecular structural differences between hard coal and deformed soft coal. Fuel 2019, 245, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, F.; Deng, L.J.; Li, G.S.; Cao, Y.J.; Zhao, B.X.; Fan, K. Effective purification of the low-rank coal by the collaboration of the microemulsion collector and the CO2 nanobubbles. Fuel 2023, 339, 127370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Pan, J.N.; Hou, Q.L.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.L. Stress degradation mechanism of coal macromolecular structure: Insights from molecular dynamics simulation and quantum chemistry calculations. Fuel 2021, 303, 121258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, C.D. Char structure characterised by Raman spectroscopy and its correlations with combustion reactivity. Fuel 2007, 10, 2316–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Rimmer, S.M.; Liu, Q.F.; Zhang, Y.M. Micro-Raman spectroscopy of microscopically distinguishable components of naturally graphitized coals from central Hunan province, China. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Hayashi, J.; Li, C. FT-Raman spectroscopic study of the evolution of char structure during the pyrolysis of a Victorian brown coal. Fuel 2006, 85, 1700–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, M.J.; Pimenta, M.A.; Dresselhaus, G.; Dresselhaus, M.S.; Endo, M. Origin of dispersive effects of the Raman D band in carbon materials. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 6585–6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.N.; Lv, M.M.; Hou, Q.L.; Han, Y.Z.; Wang, K. Coal microcrystalline structural changes related to methane adsorption/desorption. Fuel 2019, 239, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.P.; Ge, Z.L.; Li, R.H.; Zhou, Z.; Hou, Y.D.; Zhang, H. Coupling effect of temperature, gas, and viscoelastic surfactant fracturing fluid on the chemical structure of deep coal: An experimental study. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 3468–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.N.; Lv, M.M.; Bai, H.L.; Hou, Q.L.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.Z. Effects of metamorphism and deformation on the coal macromolecular structure by laser Raman spectroscopy. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).