A Comprehensive Review of Theories, Methods, and Techniques for Bottleneck Identification and Management in Manufacturing Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Categories of Manufacturing Bottlenecks
2.1. Definition of Bottlenecks in Manufacturing Systems
2.1.1. Bottleneck Machines
2.1.2. Logistics Bottlenecks
2.1.3. Bottleneck Processes
2.1.4. Bottleneck Workpieces
2.1.5. Human Resource Bottlenecks
2.1.6. Bottlenecks Caused by Maintenance and Upkeep
2.2. Extensional Concept of Manufacturing Bottlenecks
3. Manufacturing System Bottleneck Research
3.1. Bottleneck Identifications
3.1.1. Bottleneck Identification Based on Static Models
3.1.2. Bottleneck Identification Based on Simulations
3.1.3. Bottleneck Identification Based on Data-Driven Approaches
3.2. Shifting Bottlenecks
3.2.1. Causes of Bottleneck Shifting
3.2.2. Consequence of System Bottlenecks
3.3. Bottleneck Management
3.3.1. Proactive Bottleneck Prediction
3.3.2. Reactive Mitigation Strategies
4. Bottleneck Research Trends in Manufacturing System
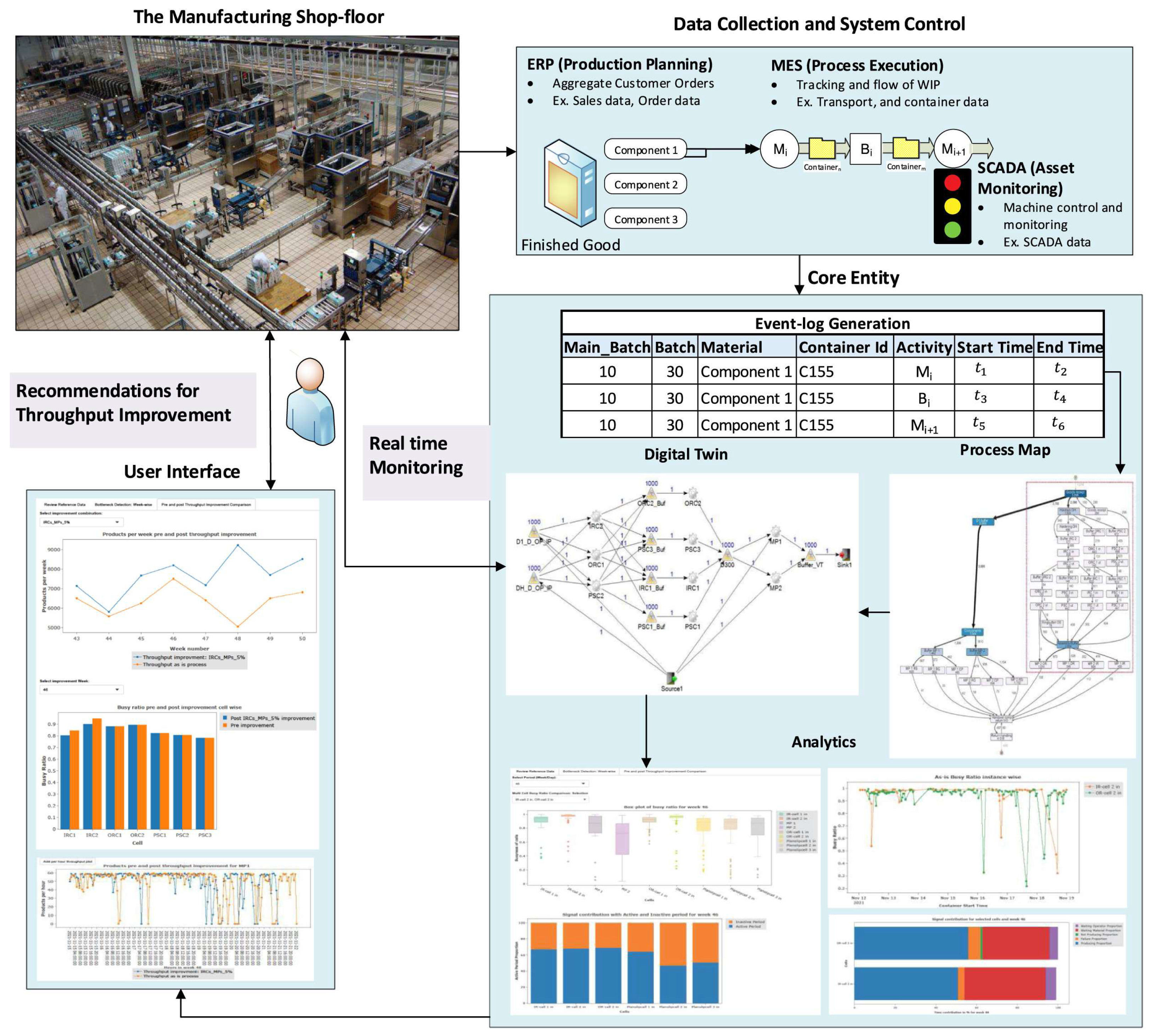
4.1. Digital Twin Technology Promotes the Development of Data-Driven Bottleneck Analysis
4.2. Use Neural Networks to Identify and Analyze Manufacturing System Bottlenecks
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldratt, E.; Cox, J. The Goal: A Process of Ongoing Improvement: A Process of Ongoing Improvement; North River Press: Great Barrington, MA, USA, 1984; ISBN 9780884271956. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.-T.; Meerkov, S.M.; Top, F. Homogeneous, Asymptotically Reliable Serial Production Lines: Theory and a Case Study. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1990, 35, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biller, S.; Li, J.; Marin, S.P.; Meerkov, S.M.; Zhang, L. Bottlenecks in Bernoulli Serial Lines with Rework. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2010, 7, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guide, D.R.; Srivastava, R. Buffering from Material Recovery Uncertainty in a Recoverable Manufacturing Environment. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1997, 48, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Laan, E.; Salomon, M.; Dekker, R.; Wassenhove, L.V. Inventory Control in Hybrid Systems with Remanufacturing. Manag. Sci. 1999, 45, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundogar, E.; Sari, M.; Kokcam, A.H. Dynamic Bottleneck Elimination in Mattress Manufacturing Line Using Theory of Constraints. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inderfurth, K.; van der Laan, E. Leadtime Effects and Policy Improvement for Stochastic Inventory Control with Remanufacturing. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2001, 71, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferencikova, D. Bottleneck Management in Discrete Batch Production. J. Compet. 2012, 4, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunter, R.H.; Flapper, S.D.P. Optimal Core Acquisition and Remanufacturing Policies under Uncertain Core Quality Fractions. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2011, 210, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inderfurth, K. Impact of Uncertainties on Recovery Behavior in a Remanufacturing Environment. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2005, 35, 318–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upreti, N.; Sunder, R.G.; Dalei, N.N.; Garg, S. Application of Theory of Constraints to Foster the Services of Indian Power Transmission System. Int. J. Energy Sect. Manag. 2019, 14, 547–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juiña, L.; Cabrera, V.H.; Reina, S. Aplicación de La Teoría de Restricciones En La Implementación de Un Sistema de Manufactura CAD-CAM En La Industria Metalmecánica-Plástica. Enfoque UTE 2017, 8, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Arabzad, S.M.; Shirouyehzad, H.; Shahin, A. Developing a Logical Model for Cellular Manufacturing Systems by Theory of Constraints Thinking Process Approach. Int. J. Logist. Syst. Manag. 2014, 18, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.K.; Panda, J.P. Applying Theory of Constraints on Ongoing Improvement in Manufacturing System Dealing with Animal Feed. Int. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2007, 10, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Guo, Y.; Huang, S.; Wang, S.; Wu, T. Dynamic Production Bottleneck Prediction Using a Data-Driven Method in Discrete Manufacturing System. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2023, 58, 102162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.; Burri, C.; Kila, J.S.N.; Bambwelo, N.; Bakukulu, J.T.; de Savigny, D. Systems Thinking for Supply Chains: Identifying Bottlenecks Using Process Mapping of a Child Health Intervention in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Systems 2024, 12, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, D.; Cheng, L.; Wang, P.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L. Identifying Service Bottlenecks in Public Bikesharing Flow Networks. J. Transp. Geogr. 2024, 116, 103830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Singh, D.; Singh, K.; Verma, L.P. An Adaptive Congestion Control Algorithm. J. Discret. Math. Sci. Cryptogr. 2021, 24, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, E.; Fathi, M.; Ghobakhloo, M.; Amos, H.C. Ng A Framework for Throughput Bottleneck Analysis Using Cloud-Based Cyber-Physical Systems in Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 232, 3121–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragazzini, L.; Negri, E.; Fumagalli, L.; Macchi, M. Digital Twin-Based Bottleneck Prediction for Improved Production Control. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 192, 110231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, S.R.; Buss, A.H. Economic Analysis of Production Bottlenecks. Math. Probl. Eng. 1995, 1, 341–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollett, P.K. Modelling Congestion in Closed Queueing Networks. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2000, 7, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-T.; Lim, J.-T.; Meerkov, S.M. Bottlenecks in Serial Production Lines: A System-Theoretic Approach. Math. Probl. Eng. 1996, 2, 233–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Gu, H.; Xi, Y. Modified Bottleneck-Based Heuristic for Large-Scale Job-Shop Scheduling Problems with a Single Bottleneck. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2007, 18, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roser, C.; Nakano, M.; Tanaka, M. A Practical Bottleneck Detection Method. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/977398 (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Chang, Q.; Ni, J.; Bandyopadhyay, P.; Biller, S.; Xiao, G. Supervisory Factory Control Based on Real-Time Production Feedback. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2006, 129, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.R.; Chen, A.N. Production Logistics Simulation and Optimization of Industrial Enterprise Based on Flexsim. Int. J. Simul. Model. 2016, 15, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straka, M.; Spirkova, D.; Filla, M. Improved Efficiency of Manufacturing Logistics by Using Computer Simulation. Int. J. Simul. Model. 2021, 20, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-Q.; Long, S.-S.; Meng, X.-R. Simulation and Optimization of Mining-Separating-Backfilling Integrated Coal Mine Production Logistics System. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2022, 40, 908–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero-Lanzac, T.; Ramirez Galilea, A.; Navajas, A. A Techno-Economic and Life Cycle Assessment for the Production of Green Methanol from CO2: Catalyst and Process Bottlenecks. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 68, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Qiu, S.; Song, Y.; Xu, X. Research on Multiple Resources Constrained & Multi-Objective Machining job Shop Scheduling Based on Bottleneck Operations. Mod. Manuf. Eng. 2013, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Song, Y.; Lei, Q.; Lv, X.; Liu, R.; Chen, J. Integrated Scheduling of Multiple AGVs and Machines in Flexible Job Shops. China Mech. Eng. 2018, 30, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M. A Survey of Data-Based Production Scheduling Methods. Acta Autom. Sin. 2009, 35, 785–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wu, C. A Hybrid Immune Simulated Annealing Algorithm for the Job Shop Scheduling Problem. Appl. Soft Comput. 2010, 10, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Li, C.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, D.; Hou, Y.; Li, R.; Cao, H.; Han, Z. Specific Energy and G Ratio of Grinding Cemented Carbide under Different Cooling and Lubrication Conditions. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 105, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, W.; Rogowska, P. Methodology for Bottleneck Identification in a Production System When Implementing TOC. Eng. Manag. Prod. Serv. 2020, 12, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovaskainen, H. Comparison of Harvester Work in Forest and Simulator Environments. Silva Fenn. 2005, 39, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J. Optimal Allocation of Resources in Production Line Based on Flexsim Simulation. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Management and Service Science, Wuhan, China, 24–26 August 2010; The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Langer, R.; Li, J.; Biller, S.; Chang, Q.; Huang, N.; Xiao, G. Simulation Study of a Bottleneck-Based Dispatching Policy for a Maintenance Workforce. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2010, 48, 1745–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, C.; Rémy, D.; Gilles, G. A Genetic Approach to the Scheduling of Preventive Maintenance Tasks on a Single Product Manufacturing Production Line. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2001, 74, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopka, J.M. Capacity Utilization Bottleneck Efficiency System-CUBES. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. Part A 1995, 18, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.-Y.; Kuo, C.-T.; Meerkov, S.M. DT-Bottlenecks in Serial Production Lines: Theory and Application. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 2000, 16, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.-Y.; Kuo, C.-T.; Meerkov, S.M. C-Bottlenecks in Serial Production Lines: Identification and Application. Math. Probl. Eng. 2001, 7, 543–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Meerkov, S.M. Bottlenecks with Respect to Due-Time Performance in Pull Serial Production Lines. Math. Probl. Eng. 2000, 5, 479–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.-Y.; Kuo, C.-T.; Meerkov, S.M. Bottlenecks in Markovian Production Lines: A Systems Approach. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1998, 14, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegels, C.C.; Watrous, C. Application of the Theory of Constraints to a Bottleneck Operation in a Manufacturing Plant. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2005, 16, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-L. A Heuristic Method for a Flexible Flow Line with Unrelated Parallel Machines Problem. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Conference on Robotics, Automation and Mechatronics, Bangkok, Thailand, 1–3 June 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, G.Q. Schedule-Based Execution Bottleneck Identification in a Job Shop. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2016, 98, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Lu, J.; Chen, C.; Yu, J.; Ji, W. Dynamic Bottleneck Identification of Manufacturing Resources in Complex Manufacturing System. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Meerkov, S.M. Production Variability in Manufacturing Systems: Bernoulli Reliability Case. Ann. Oper. Res. Ann. Oper. Res. 2000, 93, 299–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, S.; Meerkov, S.M.; Zhang, L. Assembly Systems with Non-Exponential Machines: Throughput Bottlenecks. Nonlinear Anal. Theory Methods Appl. 2008, 69, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, P.; Kun, G. Utilizing Higher Order Statistics of Packet Interarrival Times for Bottleneck Detection. In Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE/IFIP Workshop on End-to-End Monitoring Techniques and Services, Nice, France, 15–15 May 2005; pp. 152–163. [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniyan, M.; Skoogh, A.; Salomonsson, H.; Bangalore, P.; Bokrantz, J. A Data-Driven Algorithm to Predict Throughput Bottlenecks in a Production System Based on Active Periods of the Machines. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2018, 125, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qiao, F.; Wu, Q. A New Compound Priority Control Strategy in Semiconductor Wafer Fabrication. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Networking, Sensing and Control, Tucson, AZ, USA, 19–22 March 2005; pp. 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, F.; Wu, Q.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Shi, B. A Fuzzy Petri Net-Based Reasoning Method for Rescheduling. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2009, 33, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkowski, S.; Hedwig, M.; Parekh, J.; Pu, C.; Sahai, A. Bottleneck Detection Using Statistical Intervention Analysis. LNCS 2007, 4785, 122–134. [Google Scholar]
- Gershwin, S.B. An Efficient Decomposition Method for the Approximate Evaluation of Tandem Queues with Finite Storage Space and Blocking. Anal. Optim. Syst. 1987, 35, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Sun, S.; Yang, H. Multi-Bottleneck Scheduling Algorithm for Large-Scale Job Shop. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2011, 17, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Y.; Sun, S.; Wang, J. Scheduling Algorithm Based on Bottleneck Operations Decomposition for Large-Scale Job Shop Scheduling Problems. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2011, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, S.; Das, K.; Vantil, R. A New Method for Bottleneck Detection. In Proceedings of the 2008 Winter Simulation Conference, Miami, FL, USA, 7–10 December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Sawhney, R.; Zhang, C.; Chen, S.; Zhang, T.; Lisar, V.G.; Jiang, K.; Ji, W. Data Mining–Based Disturbances Prediction for Job Shop Scheduling. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 168781401983817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Bottleneck Detection of Complex Manufacturing Systems Using a Data-Driven Method. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2009, 47, 6929–6940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alden, J.M.; Burns, L.D.; Costy, T.; Hutton, R.D.; Jackson, C.A.; Kim, D.S.; Kohls, K.A.; Owen, J.H.; Turnquist, M.A.; Veen, D.J.V. General Motors Increases Its Production Throughput. Interfaces 2006, 36, 6–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedel, M.; Philipp, N.; Metternich, J. Development of Bottleneck Detection Methods Allowing for an Effective Fault Repair Prioritization in Machining Lines of the Automobile Industry. Prod. Eng. 2016, 10, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chang, Q.; Ni, J. Data Driven Bottleneck Detection of Manufacturing Systems. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2009, 47, 5019–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahmias, S.; Olsen, T.L. Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Edition; Waveland Press, Inc.: Long Grove, IL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Roser, C.; Lorentzen, K.; Deuse, J. Reliable Shop Floor Bottleneck Detection for Flow Lines through Process and Inventory Observations: The Bottleneck Walk. Logist. Res. 2015, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Tang, J.; Ge, M. Dynamic Prediction Method of Production Logistics Bottleneck Based on Bottleneck Index. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2009, 22, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deal, R.B.; Law, A.M.; Kelton, W.D. Simulation Modeling and Analysis. Technometrics 1994, 36, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chang, Q.; Ni, J.; Biller, S. Real Time Production Improvement through Bottleneck Control. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2009, 47, 6145–6158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, C.; Staehr, T.; Cohen, S.; Stricker, N.; Haefner, B.; Lanza, G. Augmented Go & See: An Approach for Improved Bottleneck Identification in Production Lines. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 31, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roser, C.; Nakano, M.; Tanaka, M. Shifting Bottleneck Detection. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/1166360 (accessed on 25 April 2022).
- Zheng, N.; Lu, X. Comparative Study on Push and Pull Production System Based on Anylogic. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Electronic Commerce and Business Intelligence, Beijing, China, 6–7 June 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedri Liraviasl, K.; ElMaraghy, H.; Hanafy, M.; Samy, S.N. A Framework for Modelling Reconfigurable Manufacturing Systems Using Hybridized Discrete-Event and Agent-Based Simulation. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2015, 48, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, Z.; Gong, B. Key Techniques of Production Process Optimization in Manufacturing Shop Oriented to Bottleneck Shifting. China Mechinal Eng. 2014, 25, 2761. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, M.N.A.; Yusof, U.K. Incorporating Shifting Bottleneck Identification in Assembly Line Balancing Problem Using an Artificial Immune System Approach. Flex. Serv. Manuf. J. 2020, 33, 717–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wang, W.; Ren, S.; Zhong, R.Y.; Jiang, J. A Proactive Task Dispatching Method Based on Future Bottleneck Prediction for the Smart Factory. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2019, 32, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungern-Sternberg, R.; Teriete, T. Data-Driven Analysis of Dynamic Bottlenecks in Order-Based Value Streams. Procedia CIRP 2023, 120, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. A Systematic-Theoretic Analysis of Data-Driven Throughput Bottleneck Detection of Production Systems. J. Manuf. Syst. 2018, 47, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roser, C.; Nakano, M. A Quantitative Comparison of Bottleneck Detection Methods in Manufacturing Systems with Particular Consideration for Shifting Bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Production Management Systems: Innovative Production Management Towards Sustainable Growth, Tokyo, Japan, 7–9 September 2015; pp. 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roser, C.; Nakano, M.; Tanaka, M. Monitoring Bottlenecks in Dynamic Discrete Event Systems. In Proceedings of the European Simulation Multiconference, Magdeburg, Germany, 13–16 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Jin, X.; Ni, J. Prediction of Passive Maintenance Opportunity Windows on Bottleneck Machines in Complex Manufacturing Systems. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2015, 137, 031017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J.-Q.; Du, X.-Y. Shifting Bottleneck-Driven TOCh for Solving Product Mix Problems. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 59, 5558–5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thürer, M.; Qu, T.; Stevenson, M.; Li, C.D.; Huang, G.Q. Deconstructing Bottleneck Shiftiness: The Impact of Bottleneck Position on Order Release Control in Pure Flow Shops. Prod. Plan. Control 2017, 28, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thürer, M.; Stevenson, M. Bottleneck-Oriented Order Release with Shifting Bottlenecks: An Assessment by Simulation. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2018, 197, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Liu, M.; Tang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Ge, M. The Coupling Relationship among Bottleneck Shifting Factors in Job Shop. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2013, 227, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz-Reiter, B.; Windt, K.; Liu, H. Modelling Dynamic Bottlenecks in Production Networks. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2011, 24, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, S.R.; Buss, A.H. Shifting Production Bottlenecks: Causes, Cures, and Conundrums. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2009, 3, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhan, Y. Study on Due-Time Bottleneck Identification in Job Shop Based on Fuzzy Inferenc System. J. Zhe Jiang Univ. Technol. 2011, 39, 670–673. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. The New Machine Breaks the Process Bottleneck of “Removing the Attached Sand” of 3D Printing Sand Core. Foundry 2023, 9, 1217–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Tadesse, H.; Singh, B.; Deresso, H.; Lemma, S.; Singh, G.K.; Srivastava, A.K.; Dogra, N.; Kumar, A. Investigation of Production Bottlenecks and Productivity Analysis in Soft Drink Industry: A Case Study of East Africa Bottling Share Company. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
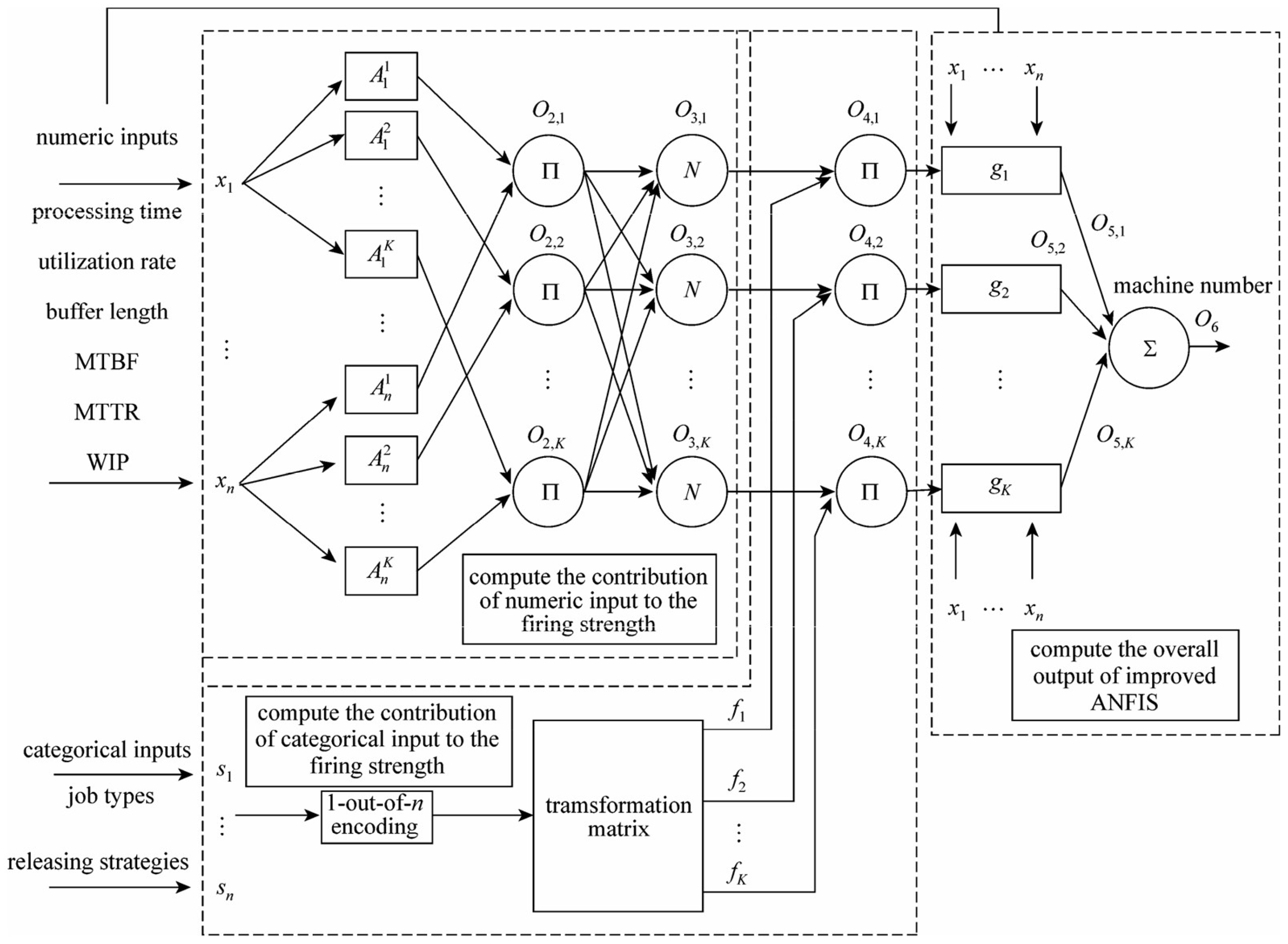
- Cao, Z.; Deng, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y. Bottleneck Prediction Method Based on Improved Adaptive Network-Based Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) in Semiconductor Manufacturing System. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 20, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roser, C.; Lorentzen, K.; Lenze, D.; Deuse, J.; Klenner, F.; Richter, R.; Schmitt, J.; Willats, P. Bottleneck Prediction Using the Active Period Method in Combination with Buffer Inventories. IFIP Adv. Inf. Commun. Technol. 2017, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Yin, M.; Sun, C. Bottleneck Identification and Prediction of Wafer Fabrication Systems in Transient States. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Bottleneck-Identification-and-Prediction-of-Wafer-%E5%91%A8%E7%82%B3%E6%B5%B7-%E6%AE%B7%E8%90%8C/3bac81bfbac79e78ca77a319f4dc7bbc77c2835a (accessed on 13 July 2024).
- Subramaniyan, M.; Skoogh, A.; Gopalakrishnan, M.; Hanna, A. Real-Time Data-Driven Average Active Period Method for Bottleneck Detection. Int. J. Des. Nat. Ecodynamics 2016, 11, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Li, T.; Peng, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H. A Data-Driven Method to Predict Future Bottlenecks in a Remanufacturing System with Multi-Variant Uncertainties. J. Cent. South Univ. 2022, 29, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhong, X.; Wei, H.; Liu, K.; Jiang, Z. Root Cause Locating Method of Performance Bottleneck in Host, Involves Performing Path State Analysis to Target Path Based on Path Performance, and Determining Root Cause of Bottleneck in To-Be-Tested Host 2023.
- Qi, W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, W.; Yang, H. Data Mining Based Root-Cause Analysis of Performance Bottleneck for Big Data Workload. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 19th International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications; IEEE 15th International Conference on Smart City; IEEE 3rd International Conference on Data Science and Systems (HPCC/SmartCity/DSS), Bangkok, Thailand, 18–20 December 2017; pp. 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duclos, L.K.; Spencer, M.S. The Impact of a Constraint Buffer in a Flow Shop. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 1995, 42, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.H.; Zhao, K.L.; Zheng, Y.B.; Zhu, X.Y.; Pan, Y.C.; Huang, L.L. The Research of Bottleneck Procedures of Truck Frame Assembly Line in Manufacturing System. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 252, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, T.; Matsui, K.; Miyake, Y.; Nishioka, K. Dynamic Bottleneck Control in Wide Variety Production Factory. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 1999, 12, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangalore, P.; Tjernberg, L.B. An Artificial Neural Network Approach for Early Fault Detection of Gearbox Bearings. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbhar, M.; Ng, A.H.; Bandaru, S. A Digital Twin Based Framework for Detection, Diagnosis, and Improvement of Throughput Bottlenecks. J. Manuf. Syst. 2023, 66, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latsou, C.; Farsi, M.; Erkoyuncu, J.A. Digital Twin-Enabled Automated Anomaly Detection and Bottleneck Identification in Complex Manufacturing Systems Using a Multi-Agent Approach. J. Manuf. Syst. 2023, 67, 242–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Qiu, T.; Shui, H.; Ding, D.; Ni, J. Predicting Future Production System Bottlenecks with a Graph Neural Network Approach. J. Manuf. Syst. 2023, 67, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, H.; Zhou, H.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Gu, Z. Bottleneck Identification and Transfer Prediction for Automated Production Lines Based on FNN. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2787, 012046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| States | Definitions | Categories | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Producing | The machine is processing products. | Effective machine states |
| 2 | Set up | Preparing a machine for its next run after completing the previous one. | |
| 3 | Tool change | Replacing the required tooling for the equipment. | |
| 4 | Repair | Checking, testing, and replacing worn parts on a planned and ongoing basis. | |
| 5 | Breakdown | Period during which equipment or machine is not functional or cannot work. | Ineffective machine states |
| 6 | Waiting for repair | Waiting time between machine breakdown and maintenance. | |
| 7 | Stop | Waiting beyond starvation and blockages that cannot increase system output. | |
| 8 | Blockage | The machine is idle because it cannot transport WIP downstream. | |
| 9 | Starvation | The machine is idle due to a lack of WIP from upstream. |
| Identification Methods | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Based on static models | Easier to understand; it can be built and analyzed more quickly. Does not involve a time dimension, which means that less computing and resources are required. | Applies only to long-term stable systems and lacks flexibility. Fails to respond to dynamic changes promptly in random models. |
| Based on simulations | More flexible and has higher accuracy than the static model-based method. By simulating different scenarios and conditions, you can identify and take preventive measures in advance. | Accuracy relies on software performance and alignment with the actual system. Bottlenecks result from multifactor; simulations considering only a few factors may yield wrong results. |
| Based on data-driven approaches | Can identify real-time dynamic bottlenecks in the system. Helps dynamically adjust predictions and decisions in response to system changes. | Quantitative calculation of bottlenecks is not available. The impact of dynamic bottlenecks on system performance cannot be quantified. Requires lots of real-time data. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, J.; Dai, Z.; Jiang, W.; Wu, X.; Zhuravkov, M.A.; Xue, Z.; Wang, J. A Comprehensive Review of Theories, Methods, and Techniques for Bottleneck Identification and Management in Manufacturing Systems. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7712. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177712
Tang J, Dai Z, Jiang W, Wu X, Zhuravkov MA, Xue Z, Wang J. A Comprehensive Review of Theories, Methods, and Techniques for Bottleneck Identification and Management in Manufacturing Systems. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(17):7712. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177712
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Jiachao, Zongxu Dai, Wenrui Jiang, Xuemei Wu, Michael Anatolievich Zhuravkov, Zheng Xue, and Jiazhi Wang. 2024. "A Comprehensive Review of Theories, Methods, and Techniques for Bottleneck Identification and Management in Manufacturing Systems" Applied Sciences 14, no. 17: 7712. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177712
APA StyleTang, J., Dai, Z., Jiang, W., Wu, X., Zhuravkov, M. A., Xue, Z., & Wang, J. (2024). A Comprehensive Review of Theories, Methods, and Techniques for Bottleneck Identification and Management in Manufacturing Systems. Applied Sciences, 14(17), 7712. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177712





