Abstract
The competition and the volatility of today’s production context require that enterprises are able to rapidly adapt to changes, reducing total costs in production. The main relationship between producer and consumer can be conducted through Make-To-Order (MTO) or Make-To-Stock (MTS) systems. This study proposes a hybrid MTS and MTO production system with a dynamic decoupling point. The proposed model concerns the monitoring of earliness and tardiness of customer orders to move the decoupling point towards MTS or MTO. Simulation models are proposed to test the proposed model following periodic or continuous review. The numerical results highlight that the best dynamic approach is the periodic review, which is more effective when the customer demand rate is higher.
1. Introduction
Production is the process aimed at meeting customer demand for a product. It can be categorized into two main types, Make-To-Stock (MTS) and Make-To-Order (MTO), based on the relationship between the producer and the customer [1]. Make-To-Stock (MTS) involves manufacturing products in advance and maintaining an inventory to fulfill customer demand promptly. This approach is commonly used for products with predictable demand, allowing companies to achieve economies of scale through mass production and reduce lead times for customer orders. However, it also requires accurate demand forecasting to avoid overproduction and excess inventory costs. Make-To-Order (MTO), on the other hand, involves producing products directly for customers upon receiving a specific order. This approach is typically employed for customized products or those with less predictable demand. MTO allows companies to offer greater customization and flexibility, as production is initiated only after an order is received, minimizing inventory holding costs. However, it may result in longer lead times for customers due to the production process starting only after order placement. Understanding the distinctions between MTS and MTO is crucial for businesses to align their production strategies with market demand, manage inventory effectively, and optimize operational efficiency. Companies often adopt a hybrid approach, combining elements of both MTS and MTO, to better respond to varying customer needs and market conditions [2,3]. Make-To-Stock (MTS) production operates by continuously manufacturing products independently of the arrival of job orders. This approach enhances production efficiency by decoupling the production rate from order arrival, allowing for streamlined and consistent production processes. However, it requires accurate demand forecasting and inventory management to avoid overproduction and excess inventory costs. In contrast, Make-To-Order (MTO) production does not maintain inventory and starts manufacturing products only after receiving a job order. While this approach is highly responsive to customer needs and allows for greater customization, it is less efficient in terms of production due to the need to start the manufacturing process only after an order is received. This can lead to longer lead times and potential delays in fulfilling fluctuating demand without relying on stocked inventory. The distinction between MTS and MTO production strategies highlights the importance of manufacturers strategically aligning their production methods with the nature of their products and the demands of their customer base. Utilizing MTS and MTO approaches can significantly impact production efficiency, with each method presenting distinct advantages and drawbacks. In the context of MTS, products are manufactured continuously, independent of incoming job orders. This method enhances efficiency by streamlining production processes; however, to maintain efficiency, the production rate must meet or exceed the order rate. Provisions must also be made to accommodate demand fluctuations within production capacity, which can reduce the overall efficiency of MTS in the face of variable demand patterns. Conversely, in MTO systems, products are manufactured only upon receipt of a specific job order. This method addresses the inefficiencies associated with maintaining high inventory levels to meet periods of peak demand. However, variations in the timing of order arrivals can result in periods of idle production capacity, leading to decreased overall efficiency. Eivazy et al. [4] introduced a third type of production control alongside pure MTO and MTS: the hybrid MTS–MTO approach. In this system, products are produced and stocked in the initial production stages and serve as components for MTO in the final stages. Recognizing the limitations of each approach, hybrid MTS–MTO production systems have emerged as a solution. These systems aim to optimize machine utilization efficiency while effectively meeting customer demand. By combining elements of both MTS and MTO strategies, hybrid systems seek to strike a balance between efficiency and responsiveness to demand fluctuations, thereby improving overall production efficiency.
Peeters and van Ooijen [5] identified three primary types of hybrid production systems: sequential, float, and parallel systems. In sequential systems, MTS and MTO operations are integrated in a linear fashion. This means that part of the production process operates under MTS principles to minimize lead time and efficiently meet customer demands, while the remaining part of the process switches to MTO to accommodate variations in customer order volume [6]. The transition point from MTS to MTO, known as the customer order decoupling point (CODP), marks the shift in production strategy. In floating systems, the CODP is allowed to move dynamically. This means that the transition between MTS and MTO is not fixed at a specific point in the production process but can adjust based on various factors such as demand patterns, production capacity, or inventory levels. This flexibility enables the system to adapt more effectively to changing market conditions and customer requirements, enhancing overall production efficiency.
This study proposes an approach to dynamically adjust the decoupling point based on the observation of order tardiness and earliness in deliveries to customers. When earliness increases, the decoupling point shifts towards the initial production stages; conversely, when tardiness increases, the decoupling point moves towards the final production stages. The proposed approach is tested using two control methods: the first based on periodic review and the second on continuous review. The performance of the proposed model is compared to traditional MTO and MTS systems using various performance measures.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents a literature review summarizing the contributions regarding hybrid control methods of MTS–MTO systems. Section 3 describes the reference context studied, while Section 4 explains the proposed dynamic decoupling model proposed. Section 5 describes the simulation models developed to test the proposed model, and Section 6 discusses the numerical results. Finally, Section 7 presents the conclusions of this study and recommends future research directions.
2. Literature Review
In [5], a comprehensive review of Make-To-Stock (MTS) and Make-To-Order (MTO) production systems is provided, offering valuable insights into the foundational concepts and strategies that have shaped these models. Building on this foundation, this section delves into the latest advancements and research focused specifically on hybrid MTS–MTO systems. Recent studies have explored the dynamic interplay between MTS and MTO strategies, seeking to optimize production efficiency while balancing inventory costs and responsiveness to customer demand. These works highlight the growing importance of flexible, hybrid approaches in today’s complex manufacturing environments, where adaptability and efficiency are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
Jia et al. [7] introduced two models designed to enhance the efficiency of hybrid Make-To-Stock (MTS) and Make-To-Order (MTO) production systems. The first model operates on a static basis, maintaining a fixed decoupling point, while the second model features a dynamic approach, allowing for real-time adjustments to the decoupling point based on fluctuating customer demand. The numerical results from their study clearly demonstrated the superior performance of the dynamic model, particularly in its ability to respond to changing market conditions and order patterns. The dynamic model proposed by Jia et al. [7] functions by collecting incoming customer orders and subsequently adjusting the decoupling point to optimize the balance between MTS and MTO operations. However, the model adapts the decoupling point primarily when new orders are released, which may limit its responsiveness to other critical events within the manufacturing system. In contrast, the model proposed in this research takes the concept of dynamic adjustment a step further by continuously monitoring and adapting the decoupling point in real time. Unlike the model in [7], this approach is not solely triggered by the release of new orders but also responds to a broader range of dynamic events within the manufacturing process. This continuous adjustment capability allows the model to better capture and react to fluctuations in production flow, machine availability, and other operational variables, thereby providing a more nuanced and efficient means of managing the hybrid MTS–MTO system. The proposed model, therefore, offers a more robust solution for environments characterized by high variability and complexity, ensuring that the production system remains agile and responsive to both customer needs and internal operational dynamics
Another approach proposed in the literature to support dynamic hybrid MTS–MTO systems concerns the allocation of a set of machines that can be assigned to the MTS or MTO system. The switching of the machines changes the production capacity of one system, reducing the capacity of the other system. Zhang et al. [8] considered only the inventory level of the MTS system, while Yano et al. [9] considered a threshold based on inventory levels of MTS production and the waiting orders of MTO products. The solution for the proposed policy is obtained using a Markov process model and a heuristic algorithm with the limited performance measures that these systems can study.
Ellabban and Abdelmaguid [10] studied the hybrid MTS–MTO from the point of view of production control assigning the orders in MTO or MTS. They used a simulation model to support the decision-making process for MTS or MTO control policies in a case study of a glass tube company. The production planning issue was investigated also by Xiong et al. [11], including the carbon emission costs. The allocation of the necessary resource for the production strategy in hybrid production system was studied by Abedi and Zhu [12]. They considered the order acceptance decisions that led to an increase in the number of totally satisfied orders and profits. A case study of sheet metal plate parts was studied by Bortolini et al. [13]. They developed a bi-objective mathematical model to assign the parts production to the MTS or MTO system to minimize both inventory space and set-up times.
The above works studied the production planning of hybrid systems with the release of the parts for the MTS or MTO system. Jalali et al. [14] studied three different production systems—MTS, MTO, and hybrid MTS–MTO—using a system dynamics simulation approach. The main performance metrics analyzed were holding costs and lead time. The simulation results highlighted the superior capacity of the hybrid MTS–MTO system to handle dynamic conditions such as demand uncertainty, variable operating expenses, and pricing fluctuations. However, the use of a system dynamics model limited the range of parameters that could be investigated. Danilczuk et al. [15] proposed a scheduling approach to select jobs for production in either a pure MTS or a hybrid MTS–MTO system. The proposed model was tested in a simplified manufacturing system with two machines and six jobs. Sato et al. [16] developed and analyzed a hybrid Make-To-Stock (MTS) and Make-To-Order (MTO) production system using a Markov decision process (MDP) model, extending previous single-machine models to multiple machines. The system allowed machines to switch between MTS and MTO production, incurring setup periods. The MDP model aimed to minimize average costs per period, including MTS inventory holding, MTO backlog, setup, and lost sales costs. Numerical investigations assessed optimal switching strategies and machine dedication. Results indicated that switching one machine per period was sufficient, and partial dedication to MTS or MTO did not affect average costs, demonstrating efficient control of hybrid systems.
Peeters and Van Oojen [5] in their review argued that hybrid production control has showcased substantial potential compared to other, more straightforward approaches. Nonetheless, these advancements frequently entail increased complexity, thereby posing implementation challenges in practical settings. To streamline the adoption of such intricate policies in real-world scenarios, sophisticated information technology becomes imperative. In this context, the Internet of Things (IoT) emerges as a pivotal concept, enabling pertinent product data to be transmitted and received autonomously, thereby facilitating network data exchange without the need for human intervention.
Harfeldt-Berg and Olhager [17] conducted a systematic literature review on empirical research regarding the customer order decoupling point (CODP) in operations and supply chain management. Analyzing 40 articles, they identified 32 factors influencing operations upstream and downstream of the CODP, categorized into market/product, operations, supply chain, and performance measures. They proposed a framework highlighting distinct configurations for MTS (upstream) and MTO (downstream) operations, and suggested areas for further research and practical implications. One of the future research paths suggested is the mix of MTO and MTS items in the same production system.
The review highlights various research efforts on hybrid MTS–MTO (Make-To-Stock/Make-to Order) production systems, but also identifies some limitations:
- -
- The complexity of the mathematical models proposed can be solved with heuristic approaches, and often the manufacturing systems are simplified. The complexity of real industrial cases can reduce the possibility of using these models.
- -
- The greater part of the models proposed are static and work with production planning models to assign to the MTO or MTS system. The dynamicity concerns the production planning of the systems, and not the changes of the decoupling point.
- -
- The dynamic decoupling point is studied in few works, with determination of the decoupling point when the customer orders are collected. Thus, a dynamic approach that changes the decoupling point during the manufacturing system activities has not been provided in the literature.
Overall, the reviewed research demonstrates the potential of hybrid MTS–MTO systems but highlights the need for further exploration to address limitations and facilitate practical implementation.
This research presents an innovative dynamic policy for adjusting the decoupling point between Make-To-Stock (MTS) and Make-To-Order (MTO) production strategies, specifically tailored to optimize the waiting time of customer orders. The policy continuously monitors waiting times and dynamically adjusts the decoupling point to maintain an optimal balance between earliness and tardiness. This adaptive approach is both computationally efficient and versatile, enabling its application across various manufacturing system configurations. By fine-tuning the decoupling point in real time, the policy enhances production efficiency and responsiveness, ultimately improving overall operational performance in complex and variable manufacturing environments.
3. Reference Context
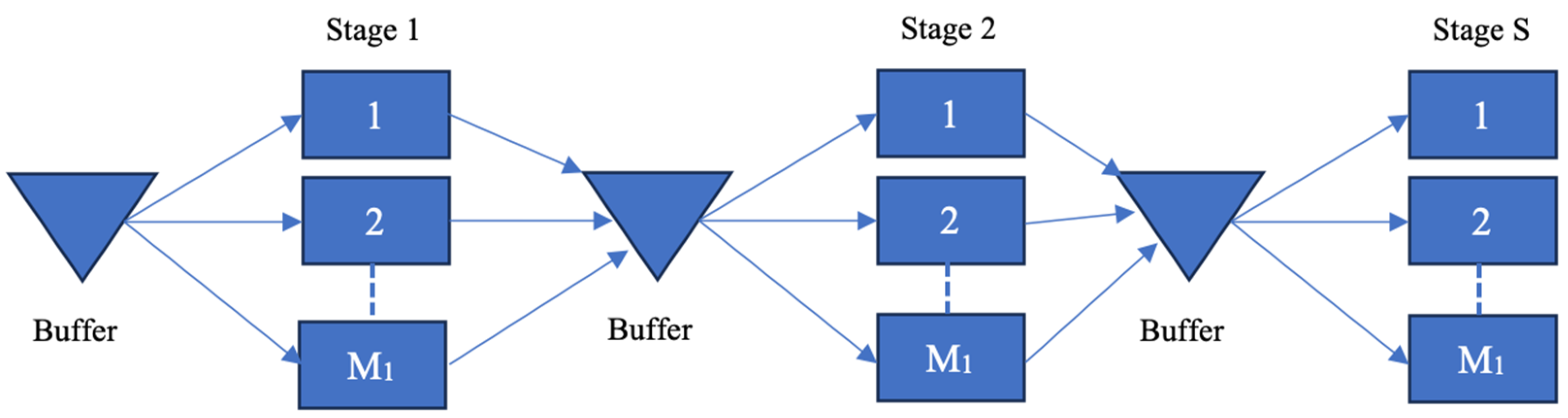
The manufacturing system considered is the Flexible Flow Shop (FFS), composed by multiple stages, and multiple machines for each stage, for processing multiple products. Each product flows through all stages in sequence to perform all the processes required to become a finished product. The production stages consist of identical parallel machines. This configuration allows an increase in capacity with better workload balance and reducing the impact of a bottleneck [18]. For the above reasons, several real industrial cases used FFS in printed circuit board and textile fabrication [19]. This system is denoted as the S stages (s = 1, 2… S), with Ms machines in each stage (m = 1, 2… Ms) and P (p = 1, 2… P) kinds of products that can be manufactured.
The manufacturing systems can be controlled following the Make-To-Order (MTO) or Make-To-Stock (MTS) policy. Both MTS and MTO have a final buffer to satisfy the customer demand, while the MTS is characterised by the introduction of buffers for each stage. The control of the buffer capacity can be used to support a hybrid MTS–MTO control approach, also called a hybrid flow shop (HFS).
Considering the management of the buffers, the following cases can be considered:
- -
- In the case of MTS, a maximum level of the buffer is designed for each stage and for the final buffer.
- -
- In the case of MTO, no buffers are introduced and the raw item starts production when the customer places an order.
- -
- The hybrid model is characterized by a decoupling point that divides the system into a first MTS part and a second MTO part.
As shown in Figure 1, in the general FFS model, the control of the buffer can switch its approach from a pure MTO (capacity buffers set to zero) to pure MTS (capacity buffers set to a level greater than 0). The hybrid model dynamically moves the decoupling point from the first to the last stage, assigning the capacity of the buffers as depicted below.
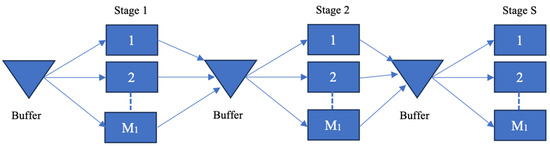
Figure 1.
MTS, MTO, and hybrid FFS.
4. Proposed Decoupling Dynamic Point
The proposed model involves dynamically assigning the decoupling point within the system. The primary objective of adjusting the decoupling point is to minimize total costs associated with tardiness and work in process within the manufacturing system. This dynamic adjustment is based on evaluating the earliness or tardiness of products delivered to customers.
When the generic customer places an order, it defines the maximum waiting time for the product, following Equation (1):
Equation (1) defines the waiting time of the customer considering the time when the customer places the order (Tnow), the processing time of the last production stage (processing time last), and an uncertain parameter by a uniform distribution. This approach follows the total work content (TWK) rule, with an allowance factor extracted by a uniform distribution [20]. If the order is delivered over this waiting time, the customer can request a penalty proportional to the tardiness.
The delivery time is the time when the order is given to the customer. Then, for each order delivered to the customer, two parameters are computed: tardiness and earliness.
If the delivery time is lower than the waiting time, the earliness parameter is updated following Equation (2):
If the delivery time is greater than the waiting time, the earliness parameter is updated following Equation (3):
The decision on the decoupling point change can follow two review approaches: periodic and continuous review.
The periodic policy, at fixed period Tp, evaluates the earliness and tardiness during the last period Tp.
If the earliness is greater than the tardiness, the decoupling point is moved one stage towards the end of the flow line. This means that the flow line is closer to an MTO because the orders are delivered early compared to the waiting time expected by the customers.
Otherwise, if the tardiness is greater than the earliness, then the decoupling point is moved one stage towards the start of the flow line. This means that the flow line tends to an MTS to reduce the tardiness of the orders. After that, the earliness and tardiness are set to zero.
The continuous policy starts the movement of the decoupling point when certain events occur. The model applies the following steps.
The continuous model monitors the number of products delivered consecutively in either an early or late state. If the number of consecutive orders exceeds a threshold, the model adjusts the decoupling point: moving it one stage towards the end of the production line for consecutive tardy orders, or one stage towards the beginning of the flow line for consecutive early orders.
The main assumptions of the system are as follows: each machine can process only one item at a time; customer orders are fulfilled according to the earliest due date (EDD) rule; and the transportation time of items between machines is negligible.
5. Simulation Models
Simulation models are developed to evaluate the proposed approaches compared to the cases of pure MTO and MTS, using discrete event models. The flow line tested consists of three production stages, and each stage includes two identical parallel machines. To test and highlight the only effect of the proposed method, the three production stages have the same processing time, which follows the normal distribution with mean 25 and standard deviation of 2.5, and one type of product is considered. The focus of the research is the comparison between the proposed model and the two benchmarks (MTO and MTS systems), and the data are then used to evaluate different conditions.
The models are tested for three inter-arrival orders with exponential parameters 12, 13, and 14 to evaluate different inter-arrival order levels. The simulations have been conducted for different buffer sizes from 1 to 5 with a step of one. In the case of periodic review, the three periodic time points considered are 100, 50, and 25. From the customer point of view, the waiting time is assigned as Tnow + 25 ∗ UNIFORM [3,5].
Considering the MTS (5 × 3 cases), MTO (3 cases), dynamic model under periodic review (5 × 3 × 3 cases), and dynamic model under continuous review (5 × 3 cases), the total cases simulated are 78 cases.
The performance measures considered to evaluate the proposed approaches are the following:
- ○
- Total customer orders satisfied over the simulation horizon (throughput).
- ○
- Total tardiness of the customer orders over the simulation horizon (tardiness). This index is an indicator of the costs of penalty for the orders delivered in delay.
- ○
- Total earliness of the customer orders over the simulation horizon (earliness). This index is used to support the dynamic decupling policy.
- ○
- The average time that the customers wait for the orders (average time in system).
- ○
- The standard deviation of the average waiting time of the customers (st. dev.).
- ○
- The average work in process of the manufacturing systems (WIP). This is an index of the costs of the items in the buffers of the manufacturing system.
6. Numerical Results
The simulation results are presented in Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3. For each scenario, the buffer size corresponding to the optimal results is indicated. The results are expressed as the percentage difference relative to the baseline MTS case, which serves as the reference point. The term ‘Dynamic P’ refers to the periodic review intervals tested, ranging from 100 to 25. As observed in the tables, throughput remains relatively stable across all simulated scenarios, with no significant fluctuations. To provide a more comprehensive understanding of the models’ behavior, additional performance metrics are illustrated in the accompanying graphs.

Table 1.
Simulation results EXPO (14).

Table 2.
Simulation results EXPO (13).

Table 3.
Simulation results EXPO (12).
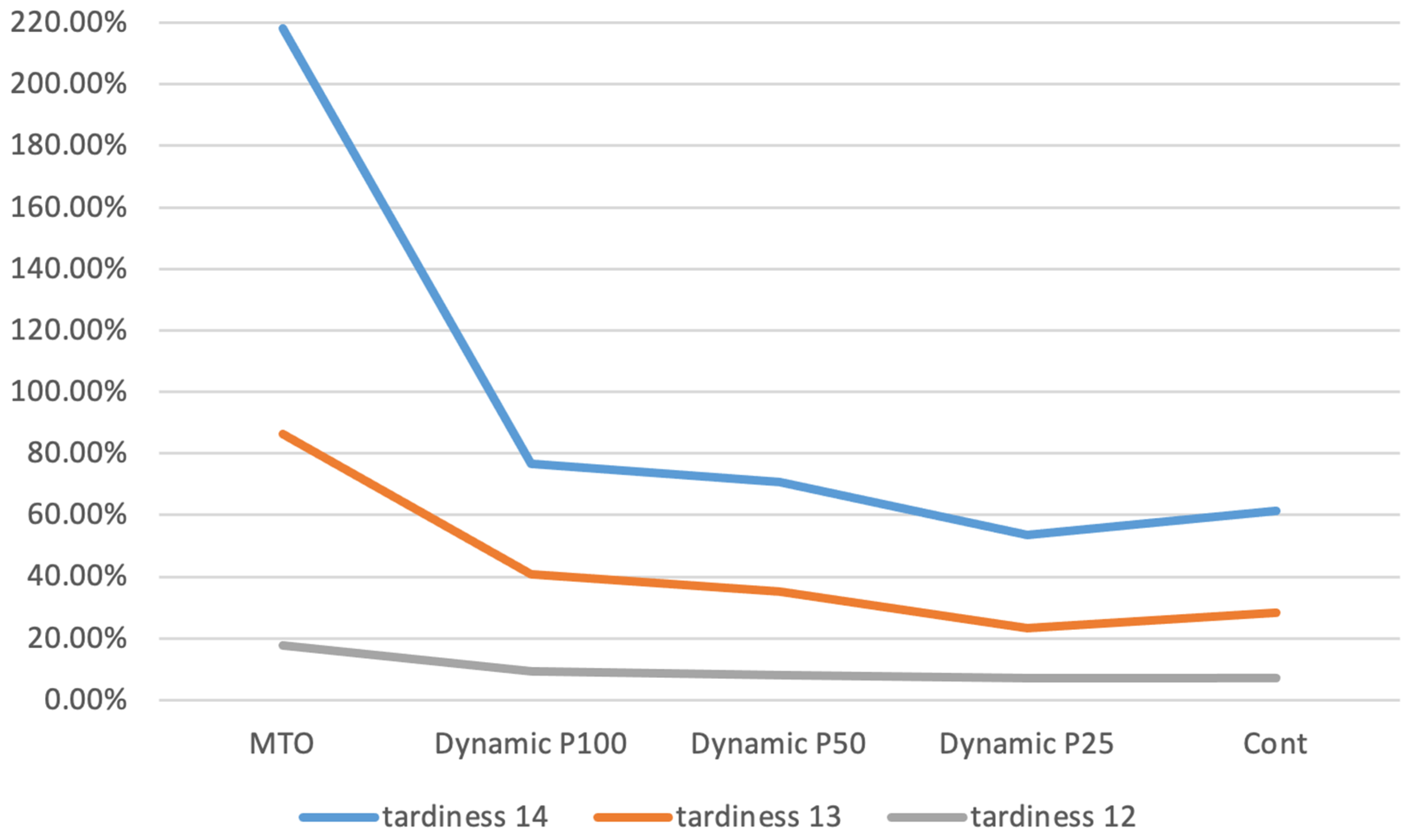
Figure 2 illustrates the tardiness values for exponential parameters 12, 13, and 14, expressed as a percentage difference compared to the MTS baseline. It is evident that the deviation from the MTS is smaller when the exponential parameter is set to 12. Additionally, the dynamic approach with a periodic review interval of 25 yields superior results for exponential parameters 13 and 14, demonstrating improved performance in these cases.
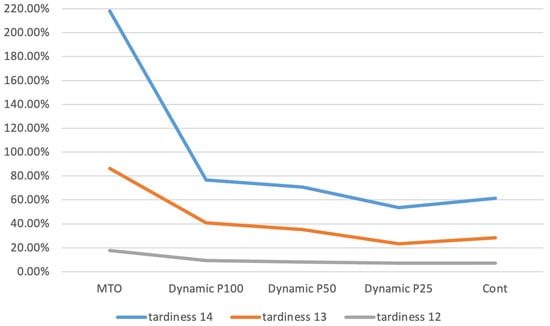
Figure 2.
Tardiness.
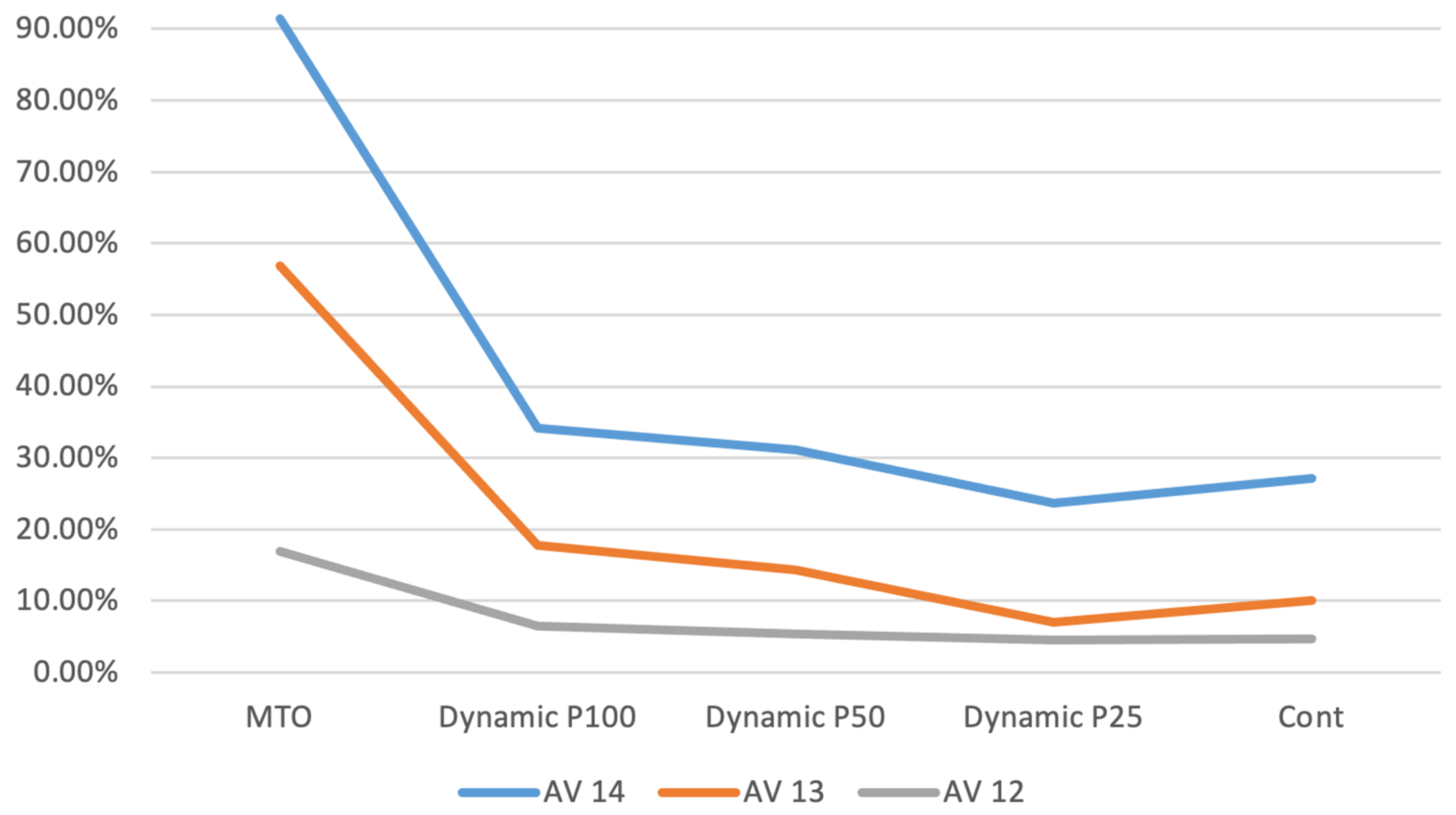
Figure 3 presents the average time in the system for customers (AV) corresponding to exponential parameters 12, 13, and 14, shown as a percentage difference relative to the MTS baseline. The trend observed in this performance measure mirrors that of the tardiness values. However, it is noteworthy that the percentage difference between the MTS and the proposed policies is less pronounced for the AV measures compared to the tardiness, indicating that the proposed policies have a smaller impact on average time in the system than on tardiness.
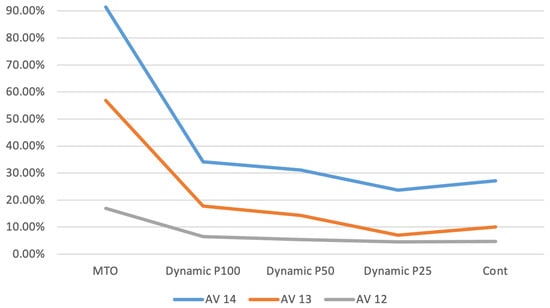
Figure 3.
Average time in system.
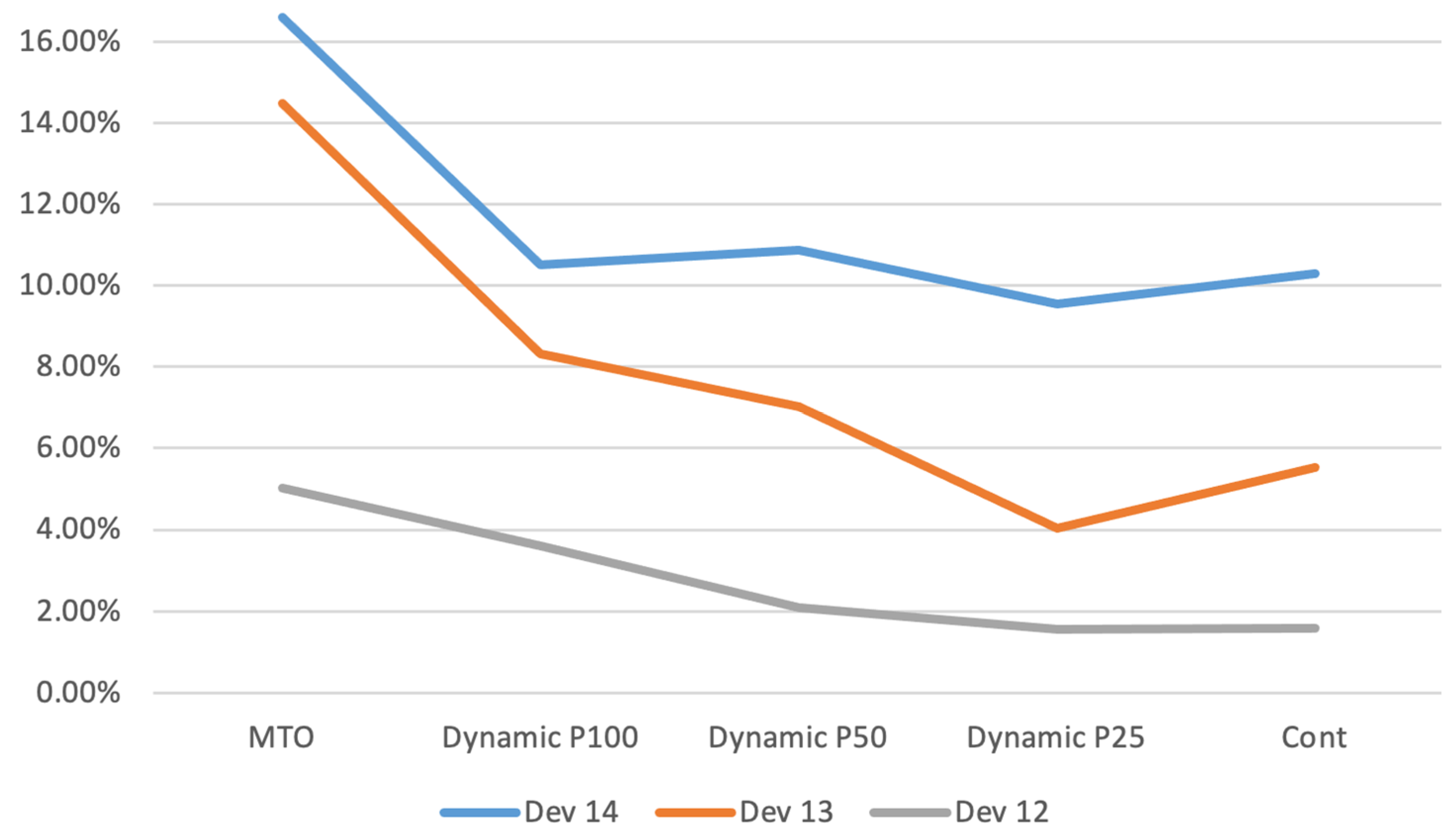
Figure 4 displays the standard deviation of the average time in the system for customers (Dev) for exponential parameters 12, 13, and 14, represented as a percentage difference relative to the MTS baseline. The analysis reveals that the dynamic policies effectively mitigate the increase in deviation compared to the MTS. This indicates that the dynamic approaches are successful in reducing variability in customer time in the system, leading to a more consistent performance compared to the MTS.
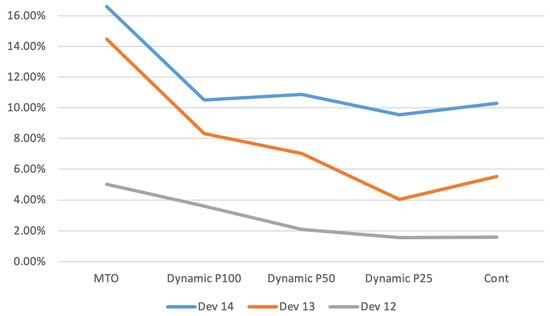
Figure 4.
Deviation of average time in system.
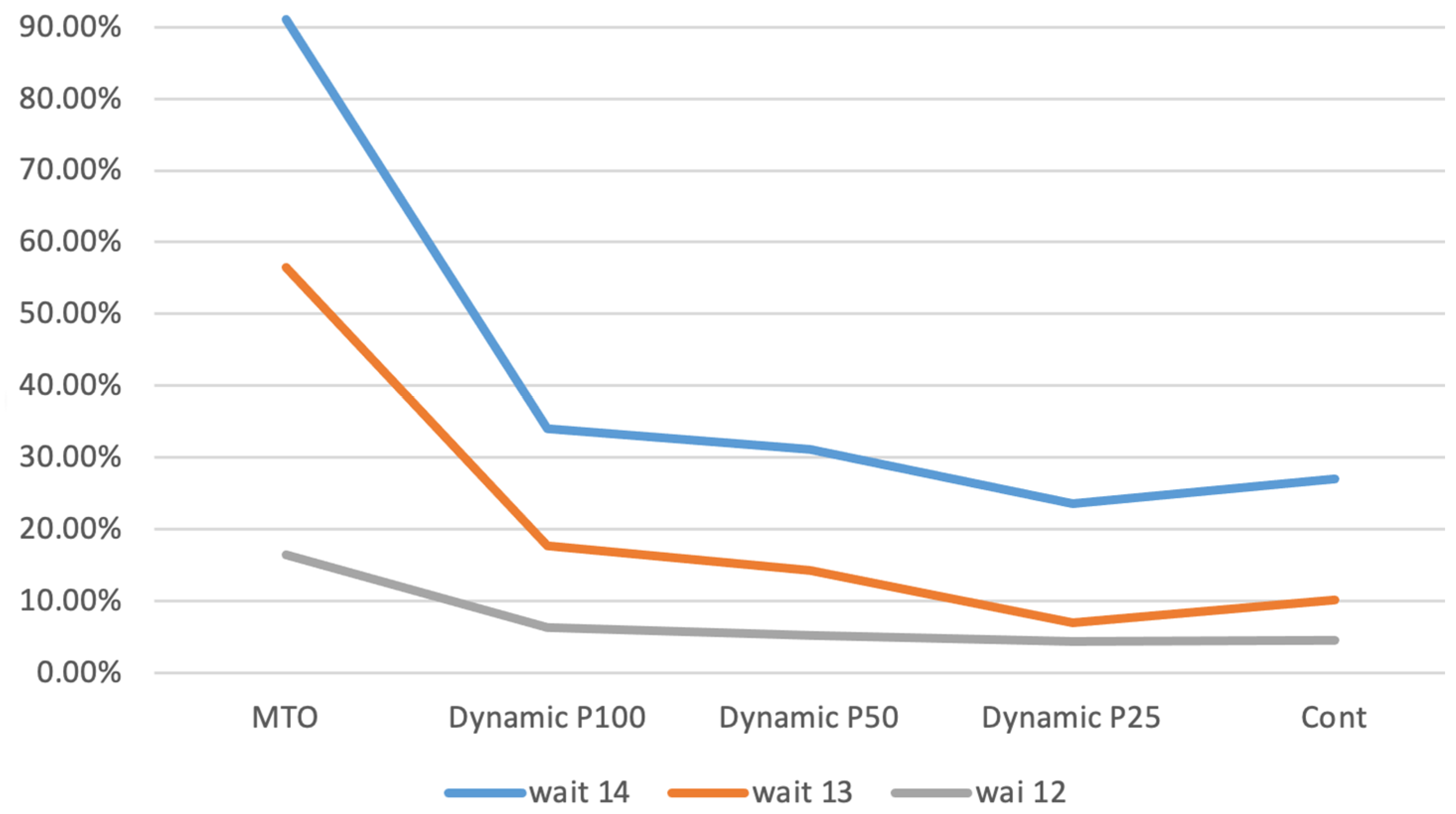
Figure 5 presents the average waiting time for customers (wait) for exponential parameters 12, 13, and 14, displayed as a percentage difference relative to the MTS baseline. For this performance measure, the increase in waiting time is notably limited when the exponential parameter is set to 12. This suggests that, similar to other performance metrics, the impact of the proposed policies on average waiting time is less pronounced in the case where the exponential parameter is 12, resulting in more favorable outcomes compared to the MTS.
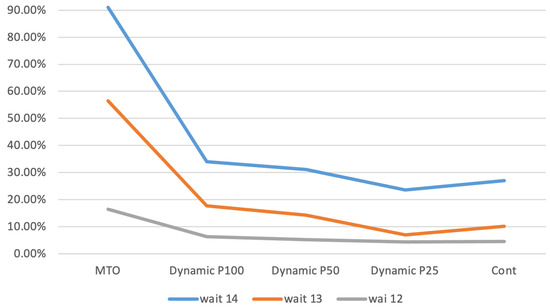
Figure 5.
Average customer waiting time.
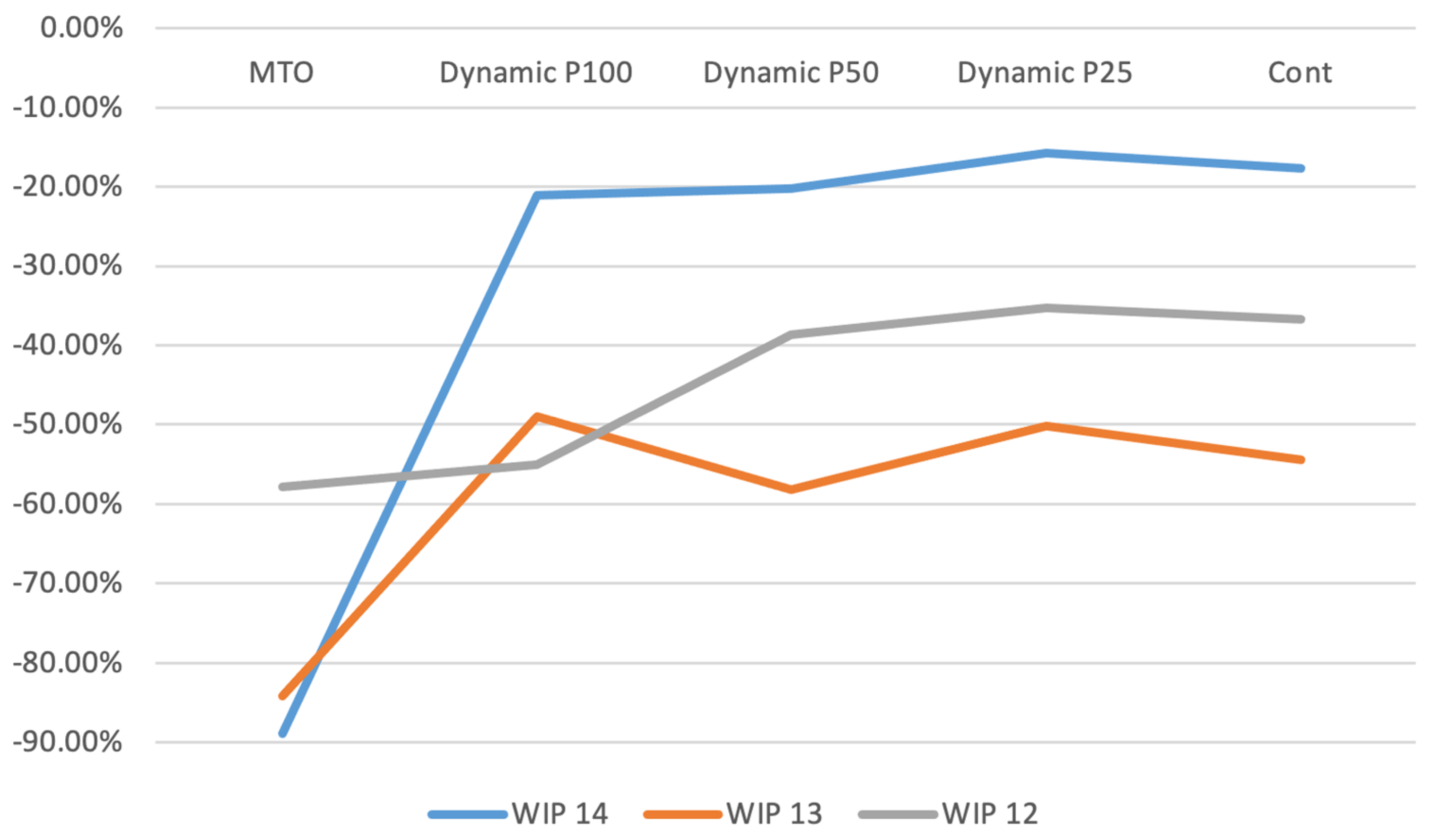
Figure 6 illustrates the work in process (WIP) for exponential parameters 12, 13, and 14, shown as a percentage difference relative to the MTS baseline. The proposed policies significantly reduce WIP compared to the MTS production system. Notably, for the exponential parameter set to 12, the dynamic policy with a periodic review interval of 25 achieves a reduction in WIP exceeding 30%, while its performance remains relatively close to that of the MTS. This substantial decrease in WIP highlights the effectiveness of the proposed policies in optimizing production efficiency.
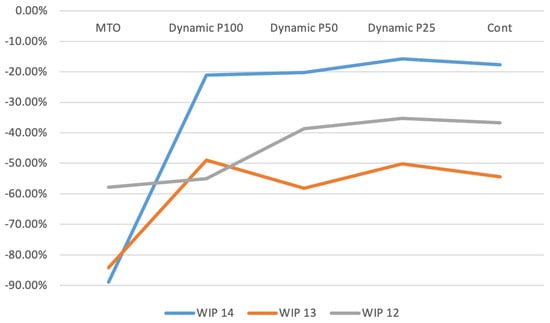
Figure 6.
Work in process.
Based on the analysis of the numerical results, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- ○
- Effectiveness of Proposed Dynamic Policies: The proposed dynamic policies show better alignment with MTS performance when the exponential parameter is set to 12 for inter-arrival times. This indicates that the dynamic policies are more effective when the rate of customer orders is higher. Conversely, when the inter-arrival time is longer, the performance of the proposed dynamic policies deteriorates.
- ○
- Optimal Dynamic Policy: Among the dynamic policies tested, the periodic review with a review interval of 25 periods proves to be the most effective. The continuous review approach yields results that are comparable to those of the periodic review with a 25-period interval. This means that the periodic approach needs a lower interval to work better.
- ○
- Reduction in Work in Process (WIP): The most significant improvement offered by the proposed dynamic policies is the reduction in WIP. The reduction is 20% for an inter-arrival time of 14, approximately 35% for an inter-arrival time of 12, and 50% for an inter-arrival time of 13. The greatest reduction in WIP occurs when the inter-arrival time is intermediate, suggesting that the proposed policies are most effective in this range.
- ○
- Buffer Capacity and Performance: From the perspective of buffer capacity, the proposed dynamic policies perform better with the same capacity as the MTS, except when dealing with higher inter-arrival parameters. The most favorable trade-off between performance measures is achieved with an inter-arrival parameter of 12. In this scenario, while the performance is slightly worse compared to the MTS—by about 10%—there is a notable reduction in WIP of 35%.
Overall, the proposed dynamic policies demonstrate considerable improvements, particularly in reducing WIP, though their effectiveness varies with the inter-arrival time. The periodic review with a 25-period interval emerges as the most advantageous approach, offering a good balance between performance and efficiency.
7. Conclusions and Future Development Paths
The hybrid MTS–MTO models can reduce the inventory costs of the MTS while maintaining similar levels of other performance measures, such as tardiness, average time in the system, and stability of the average time in the system. Most hybrid models proposed are characterized by the determination of a static decoupling point or rely on mathematical models that may limit their application in more complex real-world industrial settings. The research presented in this paper proposes a dynamic decoupling point that adapts to changing conditions. The proposed models are characterized by lower computational complexity, allowing their implementation in more complex manufacturing systems.
Simulation models were developed to test the proposed models under various conditions, comparing the results with pure MTO and MTS systems. The numerical results highlighted that the proposed models can effectively reduce inventory costs (WIP) with minimal performance reduction compared to the MTS system. Specifically, the periodic review approach performed better, while the continuous review, despite being more complex, did not offer significant additional benefits. The proposed models performed better in conditions of higher manufacturing system congestion (lower inter-arrival parameter).
The managerial implications of this research provide decision-makers with support in selecting the optimal dynamic policy that balances the reduction of work in process with the potential degradation of manufacturing performance. This balance depends on the cost evaluation of the specific industrial case.
Future research extensions could include considering multi-product customer demand and evaluating batch sizes of customer orders. Additionally, further studies could investigate the costs associated with the degradation of manufacturing performance and inventory level costs.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kuthambalayand, T.S.; Bera, S. Managing Product Variety with Mixed Make-to-Stock/Make-to-Order Production Strategy and Guaranteed Delivery Time under Stochastic Demand. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 147, 106603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beemsterboer, B.; Land, M.; Teunter, R. Hybrid MTO-MTS production planning: An explorative study. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2016, 248, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiems, D.; De Cuypere, E.; De Turck, K.; Claeys, D. Performance Analysis of Hybrid MTS/MTO Systems with Stochastic Demand and Production. Mathematics 2020, 8, 1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eivazy, H.; Rabbani, M. A novel production control model for manufacturing systems with pure MTS, pure MTO, and hybrid MTS-MTO products. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Computers and Industrial Engineering, CIE, Troyes, France, 6–9 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Peeters, K.; van Ooijen, H. Hybrid make-to-stock and make-to-order systems: A taxonomic review. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 4659–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, K.; Takahashi, K.; Hirotani, D. Make-to-stock policies for a multistage serial system under a make-to-order production environment. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014, 147, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Weng, W.; Fujimura, S. A hybrid MTS-MTO production model with a dynamic decoupling point for flexible flow shops. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/ACIS 16th International Conference on Computer and Information Science (ICIS), Wuhan, China, 24–26 May 2017; pp. 803–807. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.G.; Kim, I.; Springer, M.; Cai, G.; Yu, Y. Dynamic pooling of make-to-stock and make-to-order operations. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2013, 144, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, S.; Nagasawa, K.; Morikawa, K.; Takahashi, K. A Dynamic Switching Policy with Thresholds of Inventory Level and Waiting Orders for MTS/MTO Hybrid Production Systems. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 39, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellabban, A.; Abdelmaguid, T. Optimized Production Control Policy for Hybrid MTS-MTO Glass Tube Manufacturing Using Simulation-Based Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2019 8th International Conference on Industrial Technology and Management (ICITM), Cambridge, UK, 2–4 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, S.; Feng, Y.; Huang, K. Optimal MTS and MTO Hybrid Production System for a Single Product under the Cap-and-Trade Environment. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, A.; Zhu, W. An advanced order acceptance model for hybrid production strategy. J. Manuf. Syst. 2020, 55, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolini, M.; Faccio, M.; Gamberi, M.; Pilati, F. MTO/MTS policy optimization for sheet metal plate parts in an ATO environment. Procedia Cirp 2019, 81, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M.S.; Ghomi, S.F.; Rabbani, M. A System Dynamics Approach towards Analysis of Hybrid Make-to-Stock/Make-to-Order Production Systems. Ind. Eng. Manag. Syst. 2020, 19, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilczuk, W.; Gola, A.; Grznar, P. Job Scheduling Algorithm for a Hybrid MTO-MTS Production Process. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Maeda, H.; Toshima, R.; Nagasawa, K.; Morikawa, K.; Takahashi, K. Switching decisions in a hybrid MTS/MTO production system comprising multiple machines considering setup. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2023, 263, 108877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harfeldt-Berg, M.; Jan Olhager, J. The customer order decoupling point in empirical operations and supply chain management research: A systematic literature review and framework. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 62, 6380–6399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, B.; Zandieh, M.; Roshanaei, V. Scheduling hybrid flowshops with sequence dependent setup times to minimize makespan and maximum tardiness. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2009, 41, 1186–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, R.; Vázquez-Rodríguez, J.A. The hybrid flow shop scheduling problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 205, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojstersek, R.; Brezocnik, M.; Buchmeister, B. Multi-objective optimization of production scheduling with evolutionary computation: A review. Int. J. Ind. Eng. Comput. 2020, 11, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).