Abstract
In this study, by using the texts describing the hazards and precautions taken during text mining, the necessary processes were carried out to first estimate the probability value and severity value of the risk and then calculate the risk values by Natural Language Processing analysis. In order to be used within the scope of the study, two data sets were generated from the data in the risk assessment report prepared by applying the L-type matrix risk assessment in marble quarries between 2015 and 2021. Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) was used for classification and prediction by analyzing text data. One data set was used to analyze the probability value of the risk and the other was used to analyze the severity value of the risk. In light of the results, when a text containing hazard and precaution information was entered, a system was developed that analyzed this text, estimated the probability and severity values, and calculated the risk assessment score. The application of the SGD algorithm to learning models developed on text data yielded an accuracy rate of 91.2% in the risk probability data set and 97.5% in the risk severity data set. The results indicated that the models were capable of conducting automatic risk assessment on text data and of effectively predicting the requisite probability and severity values. Due to the high accuracy rates obtained during the study, this risk assessment software was recommended for use in marble quarries.
1. Introduction
Marble mining, a substantial sub-branch of the mining sector, has an important place in Türkiye. There are more than 2000 mines in Türkiye, and more than 600 kinds of marble have been found. In 2018, Türkiye had 40 unique kinds of marble and the largest variety of marble in the world [1]. Furthermore, marble mining has made significant contributions to Türkiye’s economy in terms of both employment and foreign exchange earnings [2]. Nevertheless, along with these positive effects, marble quarrying involves various dangers and risks: collapse, falls, accidents caused by machinery and equipment, explosions, respiratory problems caused by dust, and exposure to loud noise [3,4]. Risk is defined as the possibility of loss, injury or other harmful consequences arising from a hazard [5]. The types of occupational accidents in marble quarries generally vary depending on the working conditions of the quarries, the equipment utilized, and the occupational safety standards [6,7,8]. The aforementioned dangers and risks need to be identified and assessed, and precautions need to be proactively taken before an occupational accident occurred [9,10]. For this purpose, a risk assessment method needs to be used [11]. In studies performed in the mining sector, decision matrix risk assessment was used to assess hazard risks in underground mining by Janjuhah et al. [12]. In one of the recent studies, the method proposed by Spanidis et al. [13] was a combination of the analytical hierarchy process (AHP), the quantification of risk factors, and the preference ranking technique based on the similarity to the ideal solution (TOPSIS) method for ranking restoration alternatives based on the low-risk approach. In another recent study, Spanidis et al. [14] proposed a methodology for risk assessment of natural hazards in surface mining projects, using the triangular Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process (FAHP) to determine the probability of risk occurrence, the Expected Value (EV) function, the Monte Carlo simulation, and the Program Evaluation Review Technique (PERT) method to make cost and time overrun estimates. Korshunow et al. [15] improved an occupational risk management approach and basically tried to put forward a matrix method for occupational risk assessment based on a new mining enterprise. Tripathy [16] intended to identify and evaluate mining hazards and risks using different risk assessment techniques, such as Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) and Workplace Risk Assessment and Control (WRAC), to improve mining safety. Kemajl et al. [17] outlined a methodology for accident prediction and risk assessment as a case study at Stanterg Mine. Matloob and Khan [18] emphasized the unidentified hazards during mining and found solutions to these hazards using Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. Esmaeilzadeh et al. [19] investigated and performed hazard risk assessment utilizing the Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) method for incidents and risks emerging in quarries in West Azerbaijan. Stojance et al. [20] used the fuzzy TOPSIS method for workplace risk assessment in an underground lead and zinc mine and compared the results with the numbers of injuries and accidents occurring at individual workplaces to assess its accuracy.
In studies carried out on risk assessment in the literature, it was noted that subjects such as Probability [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36], Severity [25,30,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44], Detectability [29,44,45,46,47], Exposure [21,22,31,46,48], Consequence [21,22,31,49,50], Undetectability [33,49,51,52,53], Cost [29,30,45,54] and Impact [55,56,57] were considered to be risk criteria. The methods utilized to determine the risk criteria in these studies were the Fuzzy AHP, AHP, BWM, SWARA, SWARA, Expert judgment, Fuzzy cognitive map, Direct given, ITARA, Set-valued statistics, Combination weighting, QFD, Multi-criteria Weighting, and BRAW methods (1) [5]. In addition, the methods used in risk assessment methods were Fuzzy sets (TFNs) [24,29,33,37,39,40,46,48,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66], Pythagorean fuzzy sets [52,67,68,69], Interval-valued Pythagorean fuzzy sets [23,26,70], Fuzzy sets (Trapezoidal fuzzy numbers [71,72,73] Interval type-2 fuzzy sets [38,74], Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets [34,75], Grey linguistic term sets [76], Hesitant fuzzy sets [75], Bipolar fuzzy sets [77], Q-rung orthopair uncertain linguistic sets [75], Fermatean fuzzy sets in 2019 [78], Spherical fuzzy sets [46], Linguistic spherical fuzzy sets [53], Picture fuzzy sets [53], D numbers [79], Neutrosophic sets [47], Intuitionistic fuzzy sets [80], Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets [36], Interval 2-Tuple linguistic variables [31], 3,4-quasirung fuzzy sets [39], Fermatean fuzzy linguistic sets [43], and Rough sets (1) [81]. In these studies, risk assessment, Fine Kinney [21,22,33,36,62,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90], Failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA) [26,44,91,92,93,94,95,96], L type matrix [97,98], Hazard and Operability Methodology (HAZOP) [32,35,99,100,101,102], Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) [100,103,104], Bayesian network [29,88,105,106,107], Event tree [105,108,109], and Bow-tie [110] methods were used. Studies in which risk score was estimated were Adem et al. in 2018 [111], Gnoni and Bragatto in 2013 [112], Janjuhah et al. [12], Moatari-Kazerouni et al., Zhou et al. [113,114], Oliveira et al., Ozbakır [115,116], Halabi et al. [117], Ridwan et al. [118], Tadic et al., Jafari et al. [66,119], Oturakci, Yang [64,120], Mohandes and Zhang, Mohandes et al. [48,121], Golinko et al. [122], Mo [29,79], and Gul and Ak [27]. Reviewing the studies, it became clear that there were not many studies on risk assessment methods in marble quarries.
In this study, taking into consideration the risk assessment report made by using the L-type risk assessment method in a marble quarry, the required processes were conducted to estimate the probability and severity values that constituted the risk with Natural Language Processing analysis and to calculate the risk scores, utilizing the texts identifying the hazards and the precautions taken.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Risk Assessment Process
In the marble quarry risk assessment process used within the scope of the study area, primarily workplace-specific hazards and risks were established. Afterward, field inspections and interviews with employees were performed and the outcomes obtained were evaluated.
The L-type matrix (5 × 5) method was used as the risk assessment method. In this method, the risk value was found by multiplying the probability and severity values (Equilibrium (1)):
Risk (R) = Likelihood (P) × Severity (S)
Using the L-type matrix method, scoring was performed in accordance with the information presented in Table 1 and Table 2.

Table 1.
Likelihood ratings (S) [122].

Table 2.
Severity (degree of damage) ratings (P) [122].
As seen in Table 1, in the L-type matrix method, the probability of the damage occurring was ranked with scores from 1 to 5. The probabilities were described as daily, weekly, monthly, every three to six months, and very low. The explanations made against these probabilities were stated as very high, high, medium, low, and almost never. In Table 2, in the L-type matrix method, the effects of the hazard are listed from Severity 1 to 5. The severity was grouped as multiple deaths, death or permanent disability, very large material and environmental pollution, severe injury, occupational disease, major material damage, injuries requiring at least three days of rest, material damage, minor injuries requiring first aid, material damage beyond repair, accidents that did not lead to damage or injury, and no loss of working hours. The severity of the hazard was determined to be very serious, serious, medium, slight, or very slight. Afterward, in the L-type matrix method, the probability value for each hazard in the study area was determined with the assistance of Table 1, the severity value with Table 2, and the risk scores were presented with the assistance of Equilibrium (1), as seen in Table 3. Hence, the damage effect degree was found by multiplying the probability and severity levels. In addition, the approval of sector experts was obtained in the creation of the matrix and the risk assessment.

Table 3.
5 × 5 L-type risk decision matrix [97,98].
In the L-type matrix method, the risk value action and timetable are presented in Table 4. The risk values were numbered from 1 to 25. Explanatory information was given for each value in the action and time planning.

Table 4.
Risk value, action, and time planning [123].
Unacceptable Risk: The activity cannot be continued without improvement in the subjects that scored 15, 16, 20, 25 points as a result of the evaluation. Strict measures shall be taken, and intensive training shall be implemented. In case of a violation, a fine will be applied.
Considerable Risk: Improvement is absolutely required in the subjects that scored 8, 9, 10, or 12 points as a result of the evaluation. The activity may be continued with temporary measures where the improvement is performed. Precautionary measures and policies shall be determined.
Acceptable Risk: Improvements in subjects that scored 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 points as a result of the evaluation are evaluated within the framework of financial and technological means. Improvements are made in subjects that are deemed appropriate. They are among the acceptable risks. Regular training shall be procured on the subject.
Insignificant risks: 1. There is no need to plan control processes to eliminate the identified risks and to keep echoes of the activities to be carried out.
2.2. Data Science Process
The aim of this study was to estimate the risk probability value and the risk severity value by analyzing the texts defining the hazards and the precautions taken utilizing natural language processing techniques. Therefore, the processes needed for the calculation of risk values were conducted meticulously.
Within the extent of the study, data collected from risk assessment reports prepared by a marble quarry were brought together, and two different data sets were created. The first of these data sets was used for the analysis of the risk probability value, and the other was reserved for the analysis of the risk severity value.
The risk probability value specified the probability of a risk occurring, whereas the risk severity value measured the level of damage that could occur.
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Study
In order to be utilized within the scope of the study, two data sets were produced by combining the data in the risk assessment reports made by occupational safety experts in a marble quarry between 2015 and 2021. One of the data sets was employed for the analysis of the risk probability value, and the other for the analysis of the risk severity value. Summary representations of the data sets are demonstrated in Table 5 and Table 6.

Table 5.
Summary of the data set produced for risk probability value analysis.

Table 6.
Summary of the data set produced for the analysis of risk severity values.
As seen from Table 5 and Table 6, both data sets consist of 306 rows of data. To ensure consistency in the analysis outcomes, the same hazard and precaution expressions were utilized as independent attributes in the data sets. The dependent attribute was marked with the Class label in the data sets. As the probability and severity values would be estimated separately according to the specified hazard and precaution expressions, these values were planned to form class attributes in two separate data sets.
To establish the risk score of a hazard before and after the precaution, the probability and severity values had to be identified. The multiplication operation was implemented to the acquired probability and severity values and the risk score, and the risk level was increased to Moderate. For this reason, the objective of the study was to predict the risk probability and risk severity values as accurately as possible. To estimate the probability and severity values, the preprocessing and creation of data, the testing of the learning algorithm, and the estimation of the results were performed in the data analysis phase.
3.2. Data Preprocessing
Data preprocessing, also named data preparation, is the process of processing raw data and cleaning, manipulating, and reorganizing it prior to analysis. This step typically includes formatting, adjusting, and integrating to improve the information contained in data sets. Data preprocessing is an essential step to prepare data for processing and to mitigate the probability of bias; however, it might be a laborious task [124].
To make our data ready for natural language processing analysis, the data were subjected to various preprocessing processes:
- Our data were gathered in a way that creates data sets with certain orders.
- Data were augmented to enable enrichment and inter-class balance adjustment in the collected data.
- A data cleaning process was implemented on text data by eliminating non-word and non-space punctuation marks and special characters, converting all letters to lowercase, identifying unnecessary words, and removing them.
At the end of these processes, the data were made ready for analysis.
Figure 1 and Figure 2 were reviewed as examples of how text data looked before and after preprocessing.

Figure 1.
Text data before data preprocessing.

Figure 2.
Text data after data preprocessing.
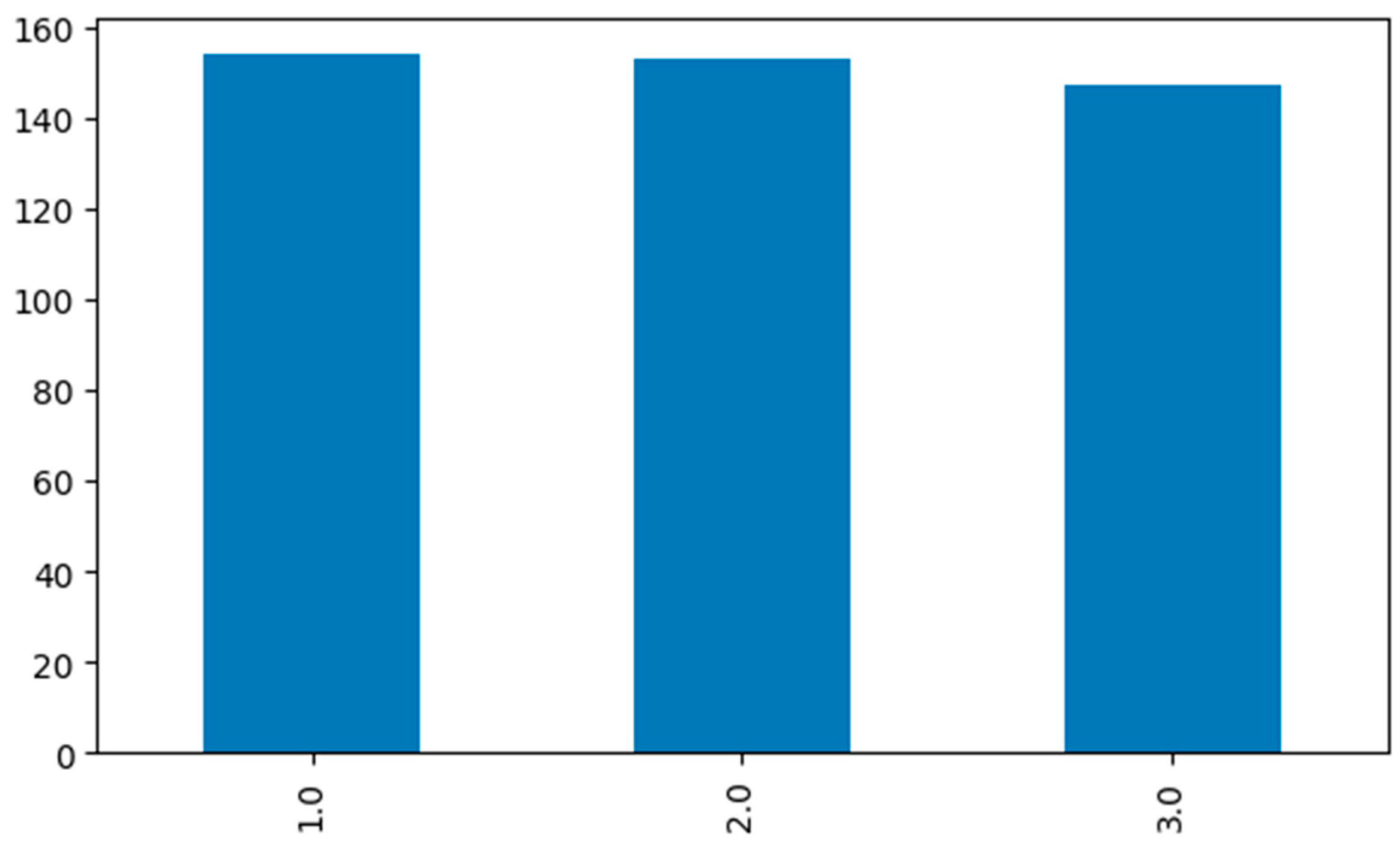
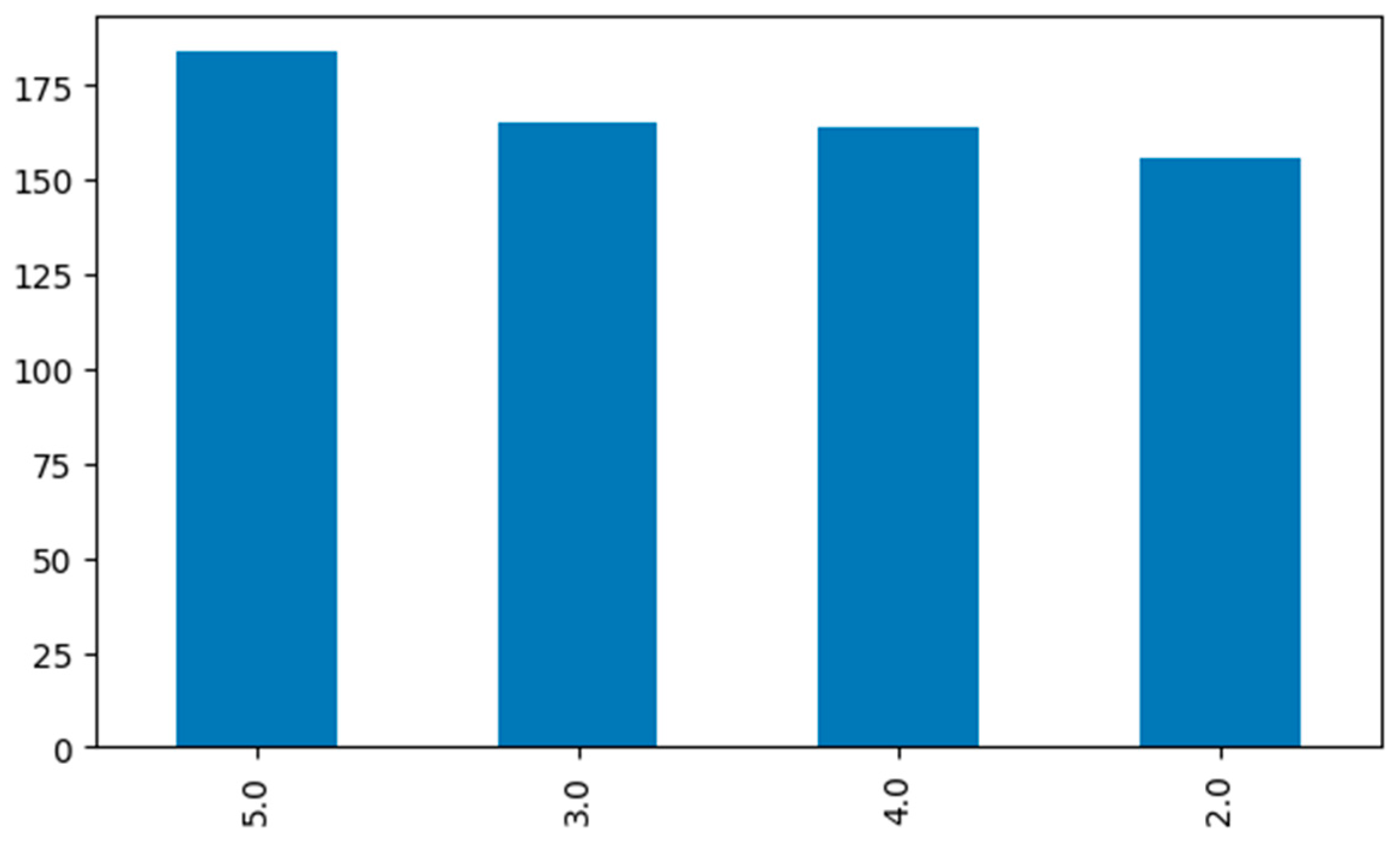
To create a near-normal order in the distribution of class labels in the data sets, following the data augmentation processes applied to both data sets, the numbers of rows in the data sets were updated to 454 for the risk probability data set and 669 for the risk severity data set. The distributions of class labels in the current data sets are given in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
Figure 3.
Risk probability data set class label distribution.
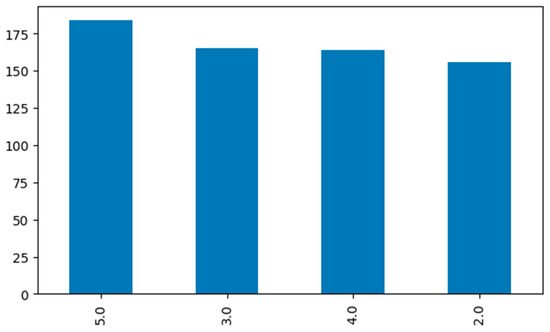
Figure 4.
Risk severity data set class label distribution.
With the other preprocessing steps applied to the text data, the number of words in the text data to be analyzed in the current version of the Risk Probability data set was reduced from 9968 words to 5786 words. The number of words to be analyzed in the current version of the Risk Severity data set was reduced from 16,692 words to 9388 words. This data reduction process was conducted by eliminating stop words, which were considered ineffective elements in the text data.
3.3. Data Analysis
By analyzing the independent variable text data available in the data sets, the Natural Language Processing (NLP) technique was utilized for the process of estimating class labels. Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a field focusing on the interactions between computers and human language, allowing computers to understand, interpret, and produce natural language [125]. Recently, NLP is one of the most substantial technologies. Comprehending complex structures in language and extracting insights and actions from them is of vital importance for artificial intelligence. The significance of natural language processing in various areas is enormous and constantly increasing because digital information in the form of language is widespread [126].
In the data sets, the Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) algorithm was used to carry out classifications and predictions by analyzing text data. The SGD algorithm performed a great simplification process in gradient descent processes and worked depending on randomly selected examples in each iteration. SGD algorithm did not require remembering the examples observed in previous iteration stages. Therefore, the algorithm could analyze all the examples in the deployed system instantly. In this case, SGD could optimize the expected error rate, as the examples to be analyzed were randomly selected from the basic distribution [127,128]. SGD has become quite popular in machine learning applications recently. It has a serious role in performing convex and non-convex optimizations. The SGD algorithm could be utilized in machine learning applications; it has a lower cost than the stochastic approach due to the extreme costs of full gradient calculations in objective functions [129]. In this study, the learning models for NLP were created on the generated data sets using the SGD algorithm. The purpose of utilizing these models was to predict the risk probability and risk severity values by inserting the hazard or precaution information into the system. After these values were estimated, the risk score could be calculated, and the risk could be graded.
Table 7 and Table 8 demonstrate the complexity matrices of the learning models created as an outcome of the analysis processes performed on the data sets, whereas Table 9 and Table 10 demonstrate the analysis outcomes of the data sets.

Table 7.
Complexity matrix of the risk probability data set analysis results.

Table 8.
Complexity matrix of the risk severity data set analysis results.

Table 9.
Risk probability data set analysis results.

Table 10.
Risk severity data set analysis results.
Based on an examination of the outcomes in the tables showing the complexity matrices and analysis outcomes, the learning models created on text data with the SGD algorithm ensured an accuracy rate of 91.2% in the risk probability data set and 97.5% in the risk severity data set. These results indicated that the created learning models successfully estimated the probability and severity values required for automatic risk assessment on text data.
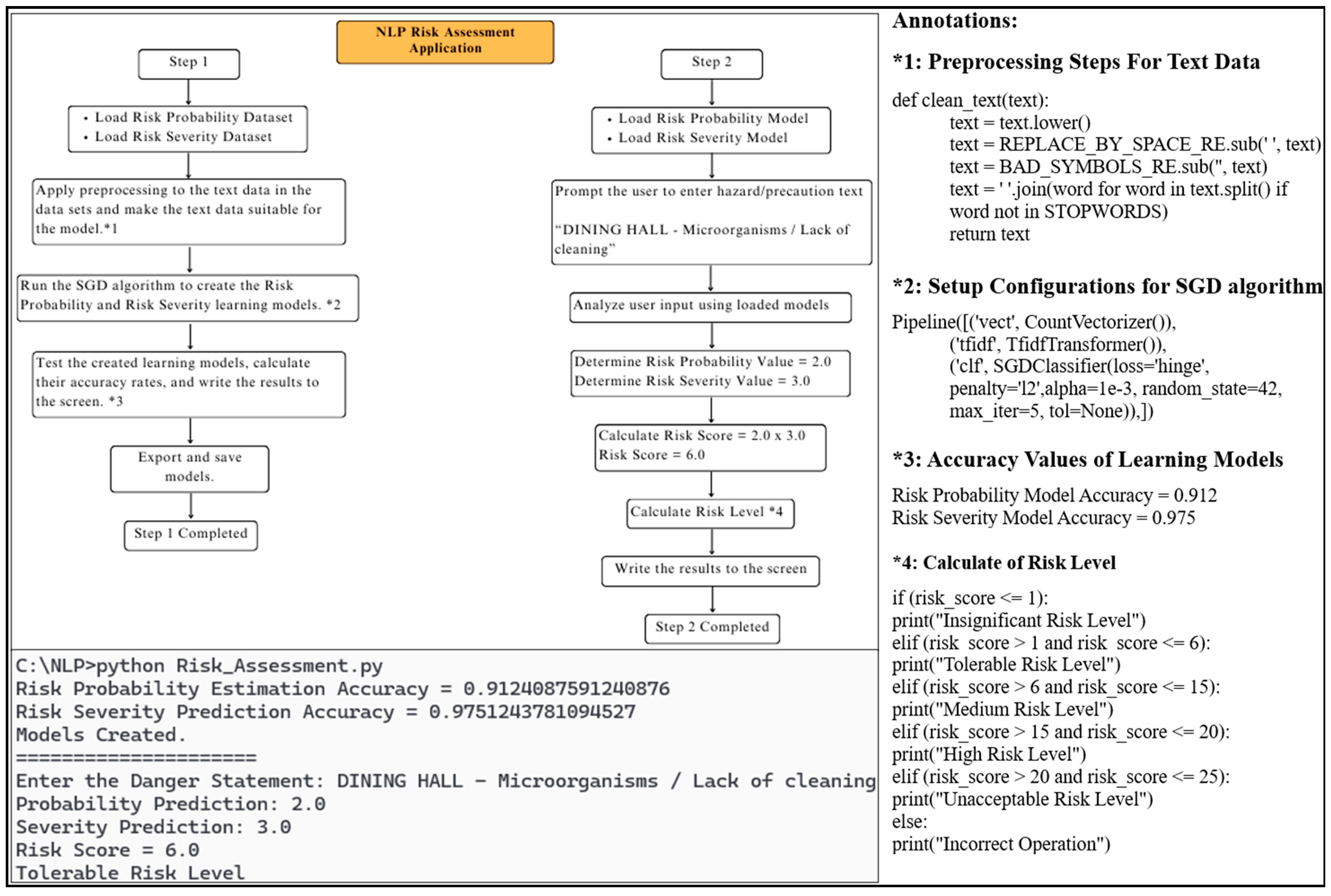
In line with the results obtained, a structure was created that predicted the likelihood and severity values by performing an analysis by inserting the text expression indicating the hazard and precaution statuses. Then, the risk assessment score was calculated, and the risk level of the entered text expression was changed to Moderate (Figure 5). Within the scope of the study, the attained risk assessment software was recommended for use in marble quarries due to the Extreme success in the accuracy rates of the outcomes.
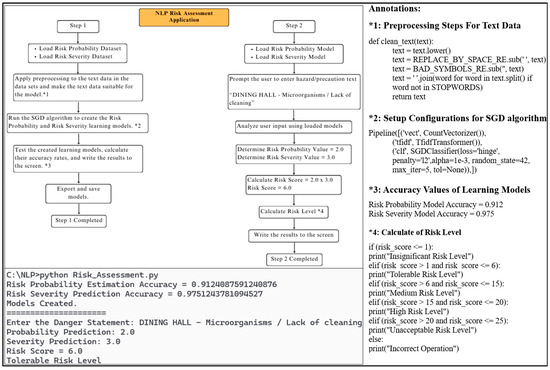
Figure 5.
NLP risk assessment application developed for marble quarries.
4. Discussion
The results of this study demonstrate the successful application of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Text Mining techniques for risk assessment in marble quarries. The study developed a machine learning-based system that predicts the probability and severity of risks based on hazard and precaution descriptions, achieving high accuracy rates of 91.2% for probability and 97.5% for severity. These results demonstrate the potential of NLP-driven risk assessment systems to improve occupational safety by automating the identification and assessment of hazards.
Compared to traditional risk assessment methods, such as manual inspections and expert judgements, the NLP-based system reduces the reliance on human expertise and the time required to perform the assessment. Previous studies in the mining industry have used various risk assessment approaches such as the Fine–Kinney [21,33,36,62,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90], Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) [26,44,91,92,93,94,95,96], and Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchy Process (FAHP) [13,14] methods. However, these methods often involve manual analysis or expert judgement, which can create subjectivity and inconsistency in risk assessment. The integration of NLP into risk assessment offers a more objective, consistent and scalable solution for analyzing data sets with large textual information.
The engineering applications of this system can be extended beyond marble quarries to other sub-areas of mining, including underground mining and coal mining. This wider applicability is supported by the system’s ability to process textual data from any risk assessment report, making it versatile in different sectors where occupational hazards need to be systematically assessed.
After evaluating the outcomes obtained, a marble quarry in Türkiye was analyzed, and risk assessment reports made with the L-type matrix method were employed within the scope of the study. In the studies where other risk values were addressed [12,39,48,64,65,79,85,111,113,115,122,123], no study was detected investigating a marble quarry, which is a mining sector. The studies mostly considered petrochemical plants [112,130], underground mines [12], the production sector in 2017 [113], hydroelectric power plants [123,131], the processing industry [65,66,132], textile enterprises [29,64], gas plants [88], tank production processes [26], hospitals [48], oil stations [86], construction sites [45,66], bus drivers [122], wind turbines [79], and marble factories [39].
Moreover, in this study, probability and severity values were estimated using NLP and Text Mining methods. In previous studies, a decision matrix risk assessment [12,48,115], which is a hybrid estimation tool for production systems, was developed by combining the characteristics and strengths of a systematic risk analysis method to control major accident hazards in an industrial environment [117]. Furthermore, a hazard identification risk assessment risk control (HIRARC) model [118,123] was made. A fuzzy model for risk assessment was designed [65,66,132]. In addition, a model was created to determine the ranking of hazards with the AHP method [64,120]. A comprehensive model using fuzzy ANP, grey relational analysis, and interval-valued Pythagorean fuzzy TOPSIS [70] was designed. Finally, a modified risk score method [122] and BWM method [39] were employed.
Studies in which the risk score was predicted include Adem et al. in 2018 [111], Gnoni and Bragatto in 2013 [113], Janjuhah et al. [12], Moatari-Kazerouni et al., Zhou et al. [113,114], Oliveira et al., Ozbakir [115,116], Halabi et al. [117], Saedi et al., Ridwan et al. [118,123], Tadic et al., Jafari et al. [66,121], Oturakci, Yang [64,120], Mohandes and Zhang, Mohandes et al. [70,121], Golinko et al. [122], Mo, [79], Gul and Ak [39], and Spanidis et al. [13,14].
Adem et al. in 2018 [111], Moatari-Kazerouni et al., and Zhou et al. [113,114] used the hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. Oturakcı, Yang [64,120], Mohandes and Zhang [70], Stefanovic et al. in 2017 [65], Gul and Ak [39], and Gul et al. in 2017 [51] used fuzzy sets (TFNs). Mo [79] used D numbers by utilizing the risk assessment reports made by the authorized engineers of the marble quarry in this study.
Oturakçı, Yang [64,120], Golinko et al. [122], and Mo [79] estimated only hazard values, and Gul and Ak [37] utilized severity values in their studies. This study estimated both probability and severity values that created the risk score.
Kantas Yılmaz and Karakus [98] and Ates and Albayrak [97] implemented risk assessment in two different laboratories by using the L-type matrix method, whereas in this study, the data in a risk assessment method were considered and the probability and severity values were estimated by using NLP and Text Mining methods. Shekhar et al. [133] also analyzed the Directorate General of Mine Safety (DGMS) fatality reports for non-coal mines in India using NLP and Text mining. This method eliminated the large number of labor hours spent on reviewing each report and the technical expertise required to analyze mining accidents. Similarly, with the method used in this study, risk assessment values and probability and severity values were estimated with high accuracy to carry out the risk assessment study in the marble quarry without the need for much time or an expert.
Moatari-Kazerouni et al. [113] reached approximately 70% accuracy in the outcomes attained with the risk estimation tool, while this study reached 91% accuracy in risk probability and 97% accuracy in risk severity.
A notable advantage of this system is its capacity for continuous improvement with the addition of new data. As more hazard and precaution reports are processed, the model can be refined to potentially improve the prediction accuracy even further. Furthermore, as only Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) was used in the current study, future work could focus on comparing different machine learning algorithms to optimize performance.
Despite the high accuracy rates achieved, the study has limitations. The current application is specific to marble quarries, and the extent to which the system can generalize to other industries requires further investigation. Additionally, while the NLP-based model eliminates some of the manual efforts associated with traditional methods, it still requires high-quality textual data, which might not always be readily available or well-documented in every industrial setting. Addressing this limitation will require the development of a more robust data collection process or the integration of additional data sources to enrich the model’s learning capability.
As a result, compared to other traditional methods, the inaccurate or incomplete assessments made by the L-type matrix risk assessment method using NLP and Text Mining methods are eliminated; thus, it helps to perform accurate and detailed risk assessment, which is easier to apply in the sub-branches of any mining industry.
After the identification of risks in the risk assessment process in the engineering application, the risk scores of the risks identified using the proposed model can be calculated easily, with high accuracy and without wasting time. Accordingly, the planning phase of the measures to be taken by the relevant authorities can be started immediately. Once the actions to be taken have been determined, the proposed model can be re-run on the action expressions, and the potential impact on the risk score can be calculated quickly with high accuracy. As a result, with the use of the proposed model, the ratings of the risks that may occur in mines can be calculated automatically much faster and with a higher level of accuracy than manual calculations. In this process, it can significantly benefit the authorities in terms of time and accuracy.
Furthermore, future work is planned to establish a program to facilitate the application of this method.
5. Conclusions
By analyzing the texts identifying the hazards and precautions taken in risk assessment reports of a marble quarry utilizing natural language processing techniques, the probability and severity values creating the risk were predicted. Within this study, the data attained from the risk assessment reports prepared by occupational safety experts and employees in the marble quarry between 2015 and 2021 were brought together, and two different data sets were created. The first of these data sets was used for the analysis of the probability value, whereas the other was reserved for the analysis of the risk severity value. A model that could estimate risk scores was created due to the gathered data. Learning models developed on text data using the SGD algorithm achieved an accuracy rate of 91.2% in the risk probability data set and 97.5% in the risk severity data set. These outcomes suggested that the models had the ability to conduct automatic risk assessment on text data and could effectively predict the required probability and severity values. Hence, when a text expression indicating the hazard and precaution statuses was inserted, a system was developed that predicted the probability and severity values. The risk assessment score was calculated by performing model analysis. This system classified the risk level of the entered text expression as Moderate. Taking into consideration the outcomes obtained in the study, the developed risk assessment software was recommended for use in marble quarries due to the extreme success in accuracy rates. In future studies, this model will be applied to other risk assessment methods.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kekec, B.; Bilim, N.; Ghiloufi, D. A Review on the Evolution of the Turkey Mining Sector. Acad. Perspect. Procedia 2018, 1, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdoğan, M.; Örs, Ş.; Demirbağ, O.; Ayaydın, H. International Competitive Advantage of the Turkish Mining Sector: A Wprldwide and Brics Countries Comparison. Int. Anatol. J. Soc. Sci. 2024, 8, 520–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yari, M.; Jamali, S.; Abdullah, G.M.S.; Ahmad, M.; Badshah, M.U.; Najeh, T. Development a Risk Assessment Method for Dimensional Stone Quarries. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcelik, M. Environmental Effects of Marble Quarry Operations in Burdur Lake Basin (Burdur-Turkey). J. Degrad. Min. Lands Manag. 2023, 10, 4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Liu, H.-C.; Shi, H.; Gu, X. Occupational Health and Safety Risk Assessment: A Systematic Literature Review of Models, Methods, and Applications. Saf. Sci. 2023, 160, 106050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gümüş, R.; Ayhan, M.; Gümüş, B. Safety Climate in Marble Industry and Its Influence on Safety Performance and Occupational Accidents. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2023, 78, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Hanieh, A.; Hasan, A.A.; Abdelall, S.; Alhanjouri, M.A. Investigating Artificial Intelligence and Modern Technologies Enhancement in Stone and Marble Cutting in Palestine. Jordan J. Mech. Ind. Eng. 2024, 18, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel Elsayed, S.; Elahmady Mohamed, A.; Atta Mohammed, W. Occupational Health Hazards among Workers in Marble and Granite Workshops in Benha City. J. Nurs. Sci. Benha Univ. 2023, 4, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idayu Ahmad, M.; Ramli, N.K.; Ahmad, N.A.; Ahmad, H. Pesticides and Risk Assessment in Agriculture. In Bioremediation Technologies; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2023; pp. 89–110. [Google Scholar]
- Niv, Y.; Tal, Y. Patient Safety and Risk Management in Medicine; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; ISBN 978-3-031-49864-0. [Google Scholar]
- Khinvasara, T.; Ness, S.; Tzenios, N. Risk Management in Medical Device Industry. J. Eng. Res. Rep. 2023, 25, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjuhah, H.T.; Ishfaque, M.; Mehmood, M.I.; Kontakiotis, G.; Shahzad, S.M.; Zarkogiannis, S.D. Integrated Underground Mining Hazard Assessment, Management, Environmental Monitoring, and Policy Control in Pakistan. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanidis, P.-M.; Roumpos, C.; Pavloudakis, F. A Multi-Criteria Approach for the Evaluation of Low Risk Restoration Projects in Continuous Surface Lignite Mines. Energy 2020, 13, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanidis, P.-M.; Roumpos, C.; Pavloudakis, F. A Fuzzy-AHP Methodology for Planning the Risk Management of Natural Hazards in Surface Mining Projects. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshunov, G.I.; Kabanov, E.I. Michal CEHLÁR Occupational Risk Management In a Mining Enterprise With the Aid of an Improved Matrix Method for Risk Assessment. Acta Montan. Slovaca 2020, 25, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, D.P. Hazard Identification and Safety Risk Assessment in Mining Industry. J. Mines Met. Fuels 2022, 66, 733–741. [Google Scholar]
- Kemajl, Z.; Stojance, M.; Gzim, I.; Ledi, M.L. Comprehensive Analysis of the Mining Accident Forecasting and Risk Assessment Methodologies: Case Study—Stanterg Mine. Min. Miner. Depos. 2024, 18, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matloob, S.; Li, Y.; Khan, K.Z. Safety Measurements and Risk Assessment of Coal Mining Industry Using Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. Open J. Bus. Manag. 2021, 09, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilzadeh, A.; Shaffiee Haghshenas, S.; Mikaeil, R.; Guido, G.; Shirani Faradonbeh, R.; Abbasi Azghan, R.; Jafarpour, A.; Taghizadeh, S. Risk Assessment in Quarries Using Failure Modes and Effects Analysis Method (Case Study: West-Azerbaijan Mines). J. Min. Environ. 2022, 13, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijalkovski, S.; Peltechki, D.; Zeqiri, K.; Kortnik, J.; Mirakovski, D. Risk Assessment at Workplace in Underground Lead and Zinc Mine with Application of Fuzzy Topsis Method. J. Inst. Electron. Comput. 2020, 2, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokangül, A.; Polat, U.; Dağsuyu, C. A New Approximation for Risk Assessment Using the AHP and Fine Kinney Methodologies. Saf. Sci. 2017, 91, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, M.; Celik, E. Fuzzy Rule-Based Fine–Kinney Risk Assessment Approach for Rail Transportation Systems. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2018, 24, 1786–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilbahar, E.; Karaşan, A.; Cebi, S.; Kahraman, C. A Novel Approach to Risk Assessment for Occupational Health and Safety Using Pythagorean Fuzzy AHP & Fuzzy Inference System. Saf. Sci. 2018, 103, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulinas, G.K.; Marhavilas, P.K.; Demesouka, O.E.; Vavatsikos, A.P.; Koulouriotis, D.E. Risk Analysis and Assessment in the Worksites Using the Fuzzy-Analytical Hierarchy Process and a Quantitative Technique—A Case Study for the Greek Construction Sector. Saf. Sci. 2019, 112, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oz, N.E.; Mete, S.; Serin, F.; Gul, M. Risk Assessment for Clearing and Grading Process of a Natural Gas Pipeline Project: An Extended TOPSIS Model with Pythagorean Fuzzy Sets for Prioritizing Hazards. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 25, 1615–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mete, S. Assessing Occupational Risks in Pipeline Construction Using FMEA-Based AHP-MOORA Integrated Approach under Pythagorean Fuzzy Environment. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 25, 1645–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fargnoli, M.; Lombardi, M.; Haber, N.; Guadagno, F. Hazard Function Deployment: A QFD-Based Tool for the Assessment of Working Tasks—A Practical Study in the Construction Industry. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2020, 26, 348–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, M.; Lo, H.-W.; Yucesan, M. Fermatean Fuzzy TOPSIS-Based Approach for Occupational Risk Assessment in Manufacturing. Complex Intell. Syst. 2021, 7, 2635–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ak, M.F.; Yucesan, M.; Gul, M. Occupational Health, Safety and Environmental Risk Assessment in Textile Production Industry through a Bayesian BWM-VIKOR Approach. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 36, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, M.; Ak, M.F. Occupational Risk Assessment for Flight Schools: A 3,4-Quasirung Fuzzy Multi-Criteria Decision Making-Based Approach. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ding, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, S. An Interval 2-Tuple Linguistic Fine-Kinney Model for Risk Analysis Based on Extended ORESTE Method with Cumulative Prospect Theory. Inf. Fusion 2022, 78, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marhavilas, P.K.; Filippidis, M.; Koulinas, G.K.; Koulouriotis, D.E. The Integration of HAZOP Study with Risk-Matrix and the Analytical-Hierarchy Process for Identifying Critical Control-Points and Prioritizing Risks in Industry—A Case Study. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2019, 62, 103981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badida, P.; Janakiraman, S.; Jayaprakash, J. Occupational Health and Safety Risk Assessment Using a Fuzzy Multi-Criteria Approach in a Hospital in Chennai, India. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2023, 29, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çalış Boyacı, A.; Selim, A. Assessment of Occupational Health and Safety Risks in a Turkish Public Hospital Using a Two-Stage Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 36313–36325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marhavilas, P.K.; Filippidis, M.; Koulinas, G.K.; Koulouriotis, D.E. Safety-Assessment by Hybridizing the MCDM/AHP & HAZOP-DMRA Techniques through Safety’s Level Colored Maps: Implementation in a Petrochemical Industry. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 6959–6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seker, S. A Novel Risk Assessment Approach Using a Hybrid Method Based On Fine–Kinney and Extended MCDM Methods Under Interval-Valued Intuitionistic Fuzzy Environment. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Decis. Mak. 2022, 21, 1591–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, M.; Guneri, A.F. A Fuzzy Multi Criteria Risk Assessment Based on Decision Matrix Technique: A Case Study for Aluminum Industry. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2016, 40, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, Y.; Gul, M.; Celik, E. Assessment of Occupational Hazards and Associated Risks in Fuzzy Environment: A Case Study of a University Chemical Laboratory. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2017, 23, 895–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, M.; Ak, M.F. Assessment of Occupational Risks from Human Health and Environmental Perspectives: A New Integrated Approach and Its Application Using Fuzzy BWM and Fuzzy MAIRCA. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2020, 34, 1231–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandes, S.R.; Sadeghi, H.; Mahdiyar, A.; Durdyev, S.; Banaitis, A.; Yahya, K.; Ismail, S. Assessing construction labours’ safety level: A fuzzy MCDM approach. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2020, 26, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Fata, C.M.; Giallanza, A.; Micale, R.; La Scalia, G. Ranking of Occupational Health and Safety Risks by a Multi-Criteria Perspective: Inclusion of Human Factors and Application of VIKOR. Saf. Sci. 2021, 138, 105234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H. Occupational Health and Safety Risk Assessment Using an Integrated TODIM-PROMETHEE Model under Linguistic Spherical Fuzzy Environment. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2021, 36, 6814–6836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.-Y.; Liu, H.-C.; Wang, J.-H.; Shi, H. New Model for Occupational Health and Safety Risk Assessment Based on Fermatean Fuzzy Linguistic Sets and CoCoSo Approach. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 126, 109262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Johansson, J.; Zhang, J. An Occupational Disease Assessment of the Mining Industry’s Occupational Health and Safety Management System Based on FMEA and an Improved AHP Model. Sustainability 2017, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbagh, R.; Yousefi, S. A Hybrid Decision-Making Approach Based on FCM and MOORA for Occupational Health and Safety Risk Analysis. J. Saf. Res. 2019, 71, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, H.; Mohandes, S.R.; Hosseini, M.R.; Banihashemi, S.; Mahdiyar, A.; Abdullah, A. Developing an Ensemble Predictive Safety Risk Assessment Model: Case of Malaysian Construction Projects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamustafa, M.; Cebi, S. Extension of Safety and Critical Effect Analysis to Neutrosophic Sets for the Evaluation of Occupational Risks. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 110, 107719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandes, S.R.; Zhang, X. Towards the Development of a Comprehensive Hybrid Fuzzy-Based Occupational Risk Assessment Model for Construction Workers. Saf. Sci. 2019, 115, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutlu Gündoğdu, F.; Seyfi-Shishavan, S.A. Occupational Risk Assessment Using Spherical Fuzzy Safety and Critical Effect Analysis for Shipyards. J. ETA Marit. Sci. 2021, 9, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zermane, A.; Mohd Tohir, M.Z.; Baharudin, M.R.; Mohamed Yusoff, H. Risk Assessment of Fatal Accidents Due to Work at Heights Activities Using Fault Tree Analysis: Case Study in Malaysia. Saf. Sci. 2022, 151, 105724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, M.; Ak, M.F.; Guneri, A.F. Occupational Health and Safety Risk Assessment in Hospitals: A Case Study Using Two-Stage Fuzzy Multi-Criteria Approach. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2017, 23, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, M. Application of Pythagorean Fuzzy AHP and VIKOR Methods in Occupational Health and Safety Risk Assessment: The Case of a Gun and Rifle Barrel External Surface Oxidation and Colouring Unit. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2020, 26, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Mou, X.; Liu, H.-C. Occupational Health and Safety Risk Assessment Based on Combination Weighting and Uncertain Linguistic Information: Method Development and Application to a Construction Project. IISE Trans. Occup. Ergon. Hum. Factors 2020, 8, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debnath, J.; Biswas, A.; Sivan, P.; Sen, K.N.; Sahu, S. Fuzzy Inference Model for Assessing Occupational Risks in Construction Sites. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2016, 55, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badri, A.; Nadeau, S.; Gbodossou, A. Proposal of a Risk-Factor-Based Analytical Approach for Integrating Occupational Health and Safety into Project Risk Evaluation. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2012, 48, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersoy, M. A Proposal on Occupational Accident Risk Analysis: A Case Study of a Marble Factory. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2015, 21, 2099–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, I.; Prieto, M. The Impact of Skills Mismatches on Occupational Accidents: An Analysis of the Effectiveness of Organizational Responses. Saf. Sci. 2024, 170, 106349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinar, U.; Cebi, S. A Novel Approach to Assess Occupational Risks and Prevention of Hazards: The House of Safety & Prevention. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 42, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durdyev, S.; Mohandes, S.R.; Tokbolat, S.; Sadeghi, H.; Zayed, T. Examining the OHS of Green Building Construction Projects: A Hybrid Fuzzy-Based Approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragiadakis, N.G.; Tsoukalas, V.D.; Papazoglou, V.J. An Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (Anfis) Model for Assessing Occupational Risk in the Shipbuilding Industry. Saf. Sci. 2014, 63, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, M. A Fuzzy-Based Occupational Health and Safety Risk Assessment Framework and a Case Study in an International Port Authority. J. Mar. Eng. Technol. 2020, 19, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacibektasoglu, S.E.; Mertoglu, B.; Tozan, H. Application of a Novel Hybrid F-SC Risk Analysis Method in the Paint Industry. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.W.; Ali, Y.; De Felice, F.; Petrillo, A. Occupational Health and Safety in Construction Industry in Pakistan Using Modified-SIRA Method. Saf. Sci. 2019, 118, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oturakci, M. A New Fuzzy-Based Approach for Environmental Risk Assessment. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 25, 1718–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanovic, M.; Tadic, D.; Djapan, M.; Macuzic, I. Software for Occupational Health and Safety Risk Analysis Based on a Fuzzy Model. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2012, 18, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tadic, D.; Djapan, M.; Misita, M.; Stefanovic, M.; Milanovic, D.D. A Fuzzy Model for Assessing Risk of Occupational Safety in the Processing Industry. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2012, 18, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, M.; Ak, M.F. A Comparative Outline for Quantifying Risk Ratings in Occupational Health and Safety Risk Assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 196, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasan, A.; Ilbahar, E.; Cebi, S.; Kahraman, C. A New Risk Assessment Approach: Safety and Critical Effect Analysis (SCEA) and Its Extension with Pythagorean Fuzzy Sets. Saf. Sci. 2018, 108, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepe, S.; Kaya, İ. A Fuzzy-Based Risk Assessment Model for Evaluations of Hazards with a Real-Case Study. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2020, 26, 512–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandes, S.R.; Zhang, X. Developing a Holistic Occupational Health and Safety Risk Assessment Model: An Application to a Case of Sustainable Construction Project. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 291, 125934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beriha, G.S.; Patnaik, B.; Mahapatra, S.S.; Padhee, S. Assessment of Safety Performance in Indian Industries Using Fuzzy Approach. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 3311–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.; Ardeshir, A.; Fazel Zarandi, M.H. Fuzzy Probabilistic Expert System for Occupational Hazard Assessment in Construction. Saf. Sci. 2017, 93, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Ding, R.; Wang, H. A Novel Approach for Occupational Health and Safety and Environment Risk Assessment for Nuclear Power Plant Construction Project. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, E.; Gul, M. Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Control for Dam Construction Safety Using an Integrated BWM and MARCOS Approach under Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Sets Environment. Autom. Constr. 2021, 127, 103699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adem, A.; Çakit, E.; Dağdeviren, M. Occupational Health and Safety Risk Assessment in the Domain of Industry 4.0. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foli, S.; Durst, S.; Romero, E.D. Evaluation of Operational Knowledge Risks in SMEs—Using a Grey-Dematel Technique. J. Inf. Knowl. Manag. 2023, 22, 2350071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Hou, L.-X.; Liu, H.-C.; Lin, W. Occupational Health and Safety Risk Assessment Using an Integrated SWARA-MABAC Model under Bipolar Fuzzy Environment. Comput. Appl. Math. 2020, 39, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, M.; Ak, M.F.; Guneri, A.F. Pythagorean Fuzzy VIKOR-Based Approach for Safety Risk Assessment in Mine Industry. J. Saf. Res. 2019, 69, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, H. A SWOT Method to Evaluate Safety Risks in Life Cycle of Wind Turbine Extended by D Number Theory. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 40, 4439–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziquan, X.; Jiaqi, Y.; Naseem, M.H.; Zuquan, X. Occupational Health and Safety Risk Assessment of Cruise Ship Construction Based on Improved Intuitionistic Fuzzy TOPSIS Decision Model. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5966711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Ejaz, N.; Maiti, J.; Pramanik, A. An Integrated Approach Using Growing Self-Organizing Map-Based Genetic K-Means Clustering and Tolerance Rough Set in Occupational Risk Analysis. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 9661–9687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, M.; Guven, B.; Guneri, A.F. A New Fine-Kinney-Based Risk Assessment Framework Using FAHP-FVIKOR Incorporation. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2018, 53, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, M.; Mete, S.; Serin, F.; Celik, E. Fine–Kinney-Based Fuzzy Multi-Criteria Occupational Risk Assessment; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 398, ISBN 978-3-030-52147-9. [Google Scholar]
- Gul, M.; Mete, S.; Serin, F.; Celik, E. Fine–Kinney Occupational Risk Assessment Method and Its Extensions by Fuzzy Sets: A State-of-the-Art Review. In Fine–Kinney-Based Fuzzy Multi-Criteria Occupational Risk Assessment; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Can, G.F.; Toktaş, P. An Advanced Stochastic Risk Assessment Approach Proposal Based on KEMIRA-M, QFD and Fine–Kinney Hybridization. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Decis. Mak. 2021, 20, 431–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, B.; Oturakci, M.; Dagsuyu, C. Action Selection in Risk Assessment with Fuzzy Fine–Kinney-Based AHP-TOPSIS Approach: A Case Study in Gas Plant. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 66222–66234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökler, S.H.; Yılmaz, D.; Ürük, Z.F.; Boran, S. A New Hybrid Risk Assessment Method Based on Fine-Kinney and ANFIS Methods for Evaluation Spatial Risks in Nursing Homes. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, M.; Yucesan, M.; Ak, M.F. Control Measure Prioritization in Fine − Kinney-Based Risk Assessment: A Bayesian BWM-Fuzzy VIKOR Combined Approach in an Oil Station. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 59385–59402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayvaz, B.; Tatar, V.; Sağır, Z.; Pamucar, D. An Integrated Fine-Kinney Risk Assessment Model Utilizing Fermatean Fuzzy AHP-WASPAS for Occupational Hazards in the Aquaculture Sector. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 186, 232–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, W. A Hybrid Risk Prioritization Method Based on Generalized TODIM and BWM for Fine-Kinney under Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Environment. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2021, 27, 954–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Aguirre, P.A.; Pérez-Domínguez, L.; Luviano-Cruz, D.; Solano Noriega, J.J.; Martínez Gómez, E.; Callejas-Cuervo, M. PFDA-FMEA, an Integrated Method Improving FMEA Assessment in Product Design. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Geng, Y. An FMEA Risk Assessment Method Based on Social Networks Considering Expert Clustering and Risk Attitudes. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2024, 71, 10783–10796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çeliker, S.; Saraç Eşsiz, E.; Oturakci, M. Integrated AHP-FMEA Risk Assessment Method to Stainless Tank Production Process. Turk. J. Eng. 2021, 5, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, T. Risk Assessment Based on a STPA–FMEA Method: A Case Study of a Sweeping Robot. Risk Anal. 2023, 43, 590–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Xia, Q.; Ji, L. Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) with Extended MULTIMOORA Method Based on Interval-Valued Intuitionistic Fuzzy Set: Application in Operational Risk Evaluation for Infrastructure. Information 2019, 10, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Chu, J. Internal Risk Assessment of Whole Process Engineering Consulting Consortium Based on GRA-TOPSIS-FMEA. J. Mechatron. Artif. Intell. Eng. 2023, 4, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateş, F.M.; Albayrak, M. Ataturk University Vocational School of Health Services Laboratories Risk Analysis Application. Int. J. Innov. Res. Rev. 2022, 6, 132–157. [Google Scholar]
- Kantaş Yılmaz, F.; Karakuş, S. Laboratory Risk Analysis in a Branch Hospital: The L-Type Matrix. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Health 2024, 14, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, F.; Steyn, E.; Pretorius, L. Using the HAZOP Method to Conduct a Risk Assessment on the Dismantling of Large Industrial Machines and Associated Structures: Case Study. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2021, 147, 05020021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasempour, M.; Gholamnia, R.; Jabbari, M.; Saeedi, R. Reliability Assessment and Verification of Safety Instrumented Systems with the Application of LOPA and FTA in the Isomerisation Unit of the Isfahan Oil Refinery. Int. J. Qual. Eng. Technol. 2021, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, S.; Gur, B.; Cakir, A.D.; Kose, D.A. Investigation of The Posture Positions of The Apparel Workshop Employees with The REBA and RULA Method. Hittite J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 8, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zendel, O.; Murschitz, M.; Humenberger, M.; Herzner, W. How Good Is My Test Data? Introducing Safety Analysis for Computer Vision. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2017, 125, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, M.; Roozbahani, A.; Shahdany, S.M.H. Risk Assessment of Agricultural Water Conveyance and Delivery Systems by Fuzzy Fault Tree Analysis Method. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 4079–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani, A.; Mokhtari, H. An Integrated Relief Network Design Model under Uncertainty: A Case of Iran. Saf. Sci. 2019, 111, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazoglou, I.A.; Aneziris, O.N.; Bellamy, L.J.; Ale, B.J.M.; Oh, J. Quantitative Occupational Risk Model: Single Hazard. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2017, 160, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.R.A.; Nogueira, D.J.; Nassar, S.M.; Vaz, V.P.; da Silva, M.L.N.; Vicentini, D.S.; Matias, W.G. Probabilistic Model for Assessing Occupational Risk during the Handling of Nanomaterials. Nanotoxicology 2020, 14, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efe, B.; Kurt, M.; Efe, Ö.F. Hazard Analysis Using a Bayesian Network and Linear Programming. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2020, 26, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazoglou, I.A.; Aneziris, O.N.; Bellamy, L.J.; Ale, B.J.M.; Oh, J. Multi-Hazard Multi-Person Quantitative Occupational Risk Model and Risk Management. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2017, 167, 310–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, F. Reliability Assessment of Space Station Based on Multi-Layer and Multi-Type Risks. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimecka-Tatar, D.; Ulewicz, R.; Ingaldi, M. Minimizing Occupational Risk by Automation of the Special Processes—Based on Occupational Risk Assessment. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 217, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adem, A.; Çolak, A.; Dağdeviren, M. An Integrated Model Using SWOT Analysis and Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Term Set for Evaluation Occupational Safety Risks in Life Cycle of Wind Turbine. Saf. Sci. 2018, 106, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnoni, M.G.; Bragatto, P.A. Integrating Major Accidents Hazard into Occupational Risk Assessment: An Index Approach. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2013, 26, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moatari-Kazerouni, A.; Chinniah, Y.; Agard, B. A Proposed Occupational Health and Safety Risk Estimation Tool for Manufacturing Systems. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2015, 53, 4459–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Liang, D.; Tang, M. A New Risk Analysis Approach to Seek Best Production Action during New Product Introduction. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2023, 262, 108911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.D.; Lopes, D.F.; Bana e Costa, C.A. Improving Occupational Health and Safety Risk Evaluation through Decision Analysis. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2018, 25, 375–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbakır, O. Occupational Health and Safety in Flour Mills: A Research and Risk Assessment. Int. J. Agric. Environ. Food Sci. 2024, 8, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halabi, Y.; Xu, H.; Long, D.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Alhaek, F.; Alhaddad, W. Causal Factors and Risk Assessment of Fall Accidents in the U.S. Construction Industry: A Comprehensive Data Analysis (2000–2020). Saf. Sci. 2022, 146, 105537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridwan, A.; Nuroni, A.; Adelia, A.; Sonda, A. Analysis of Occupational Health and Safety at a Maritime Warehouse Using Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Risk Control (HIRARC). J. Ind. Serv. 2022, 8, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, H.; Ehsanifar, M. Approach to Implementing Health and Environmental Safety System in Construction Projects Using Fuzzy Logic. Int. J. Innov. Eng. 2022, 2, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M. Risk Management of Prefabricated Building Construction Based on Fuzzy Neural Network. Sci. Program. 2022, 2022, 2420936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandes, S.R.; Sadeghi, H.; Fazeli, A.; Mahdiyar, A.; Hosseini, M.R.; Arashpour, M.; Zayed, T. Causal Analysis of Accidents on Construction Sites: A Hybrid Fuzzy Delphi and DEMATEL Approach. Saf. Sci. 2022, 151, 105730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golinko, V.; Cheberyachko, S.; Deryugin, O.; Tretyak, O.; Dusmatova, O. Assessment of the Risks of Occupational Diseases of the Passenger Bus Drivers. Saf. Health Work. 2020, 11, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saedi, A.M.; Thambirajah, J.J.; Pariatamby, A. A HIRARC Model for Safety and Risk Evaluation at a Hydroelectric Power Generation Plant. Saf. Sci. 2014, 70, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Morr, C.; Jammal, M.; Ali-Hassan, H.; El-Hallak, W. Data Preprocessing. In Machine Learning for Practical Decision Making: A Multidisciplinary Perspective with Applications from Healthcare, Engineering and Business Analytics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 117–163. [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh, N. Machine Learning for Natural Language Processing: Techniques and Applications. In Cutting-Edge Technologies in Innovations in Computer Science and Engineering; San International Scientific Publications: Kanyakumari, India, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pattanayak, S. Natural Language Processing. In Pro Deep Learning with TensorFlow 2.0; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2023; pp. 293–405. [Google Scholar]
- Bottou, L. Large-Scale Machine Learning with Stochastic Gradient Descent. In Proceedings of COMPSTAT’2010; Physica-Verlag HD: Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- Gerbelot, C.; Troiani, E.; Mignacco, F.; Krzakala, F.; Zdeborová, L. Rigorous Dynamical Mean-Field Theory for Stochastic Gradient Descent Methods. SIAM J. Math. Data Sci. 2024, 6, 400–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtowytsch, S. Stochastic Gradient Descent with Noise of Machine Learning Type Part I: Discrete Time Analysis. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2023, 33, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Yang, Z. Research and Application of Risk-Based Safety Insurance Technology for Petrochemical Plants. ASCE ASME J. Risk Uncertain. Eng. Syst. A Civ. Eng. 2024, 10, 04024054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksel, S.; Eti, S.; Dinçer, H.; Gökalp, Y. Comprehensive Risk Analysis and Decision-Making Model for Hydroelectricity Energy Investments. J. Soft Comput. Decis. Anal. 2024, 2, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavorska, T.; Kostyuk, O.; Kostiuk, M.; Tsviliy, S.; Ogloblina, V. The Determinants of Neutralizing the Influence of the Production Risks of Agricultural Enterprises on the Competitiveness of the Processing Industry. Zywnosc Nauka Technol. Jakosc/Food Sci. Technol. Qual. 2024, 31, 211–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, H.; Agarwal, S. Automated Analysis through Natural Language Processing of DGMS Fatality Reports on Indian Non-Coal Mines. In Proceedings of the 2021 5th International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Networks (ISCON), Mathura, India, 22–23 October 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).