Enhancement of Phenylpropanoid Accumulation and Antioxidant Activities of Agastache rugosa Transgenic Hairy Root Cultures by Overexpressing the Maize Lc Transcription Factor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Hairy Root Induction
2.3. Total RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.4. Gene Expression Analysis
2.5. Analysis of Phenylpropanoid Content by HPLC
2.6. Analysis of TPC and TFC
2.7. Determination of RPA from Extracts of A. rugosa
2.8. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
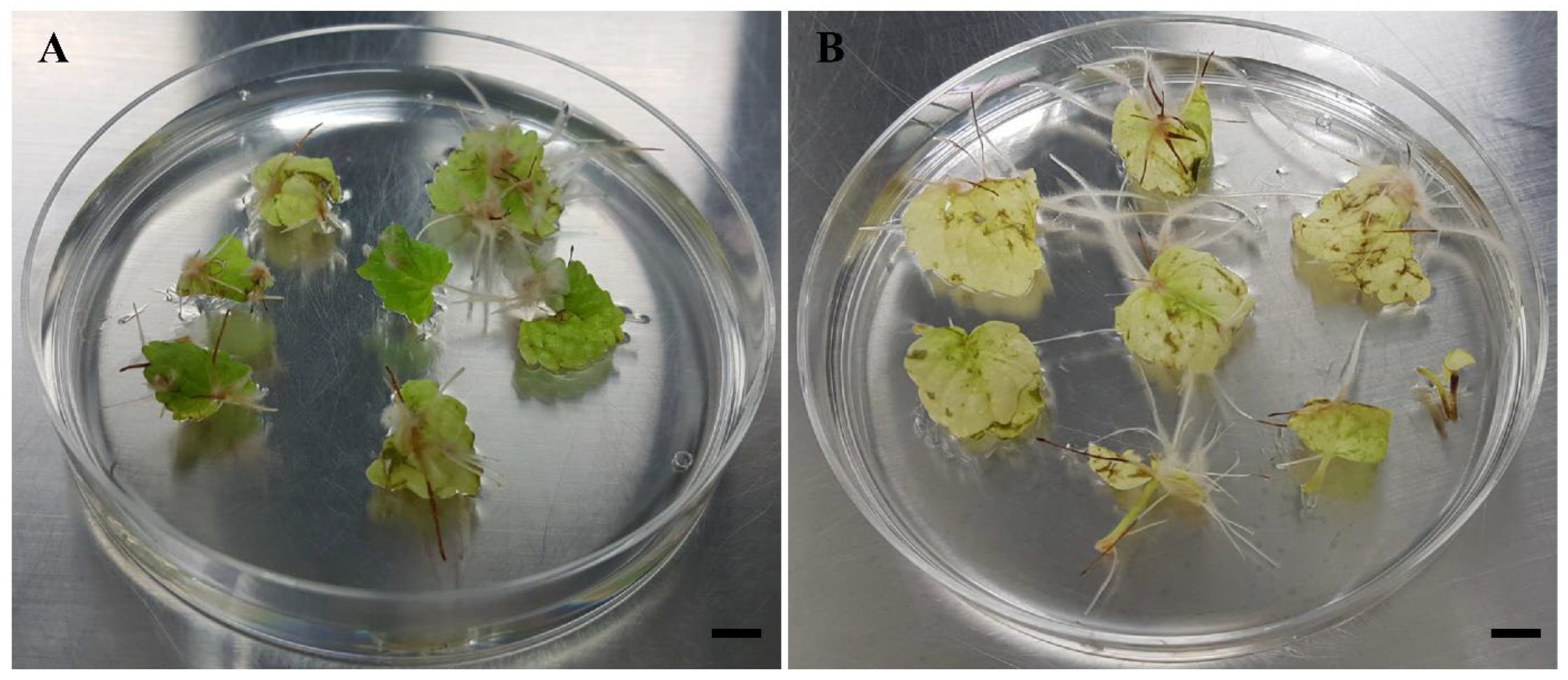
3.1. Hairy Root Induction
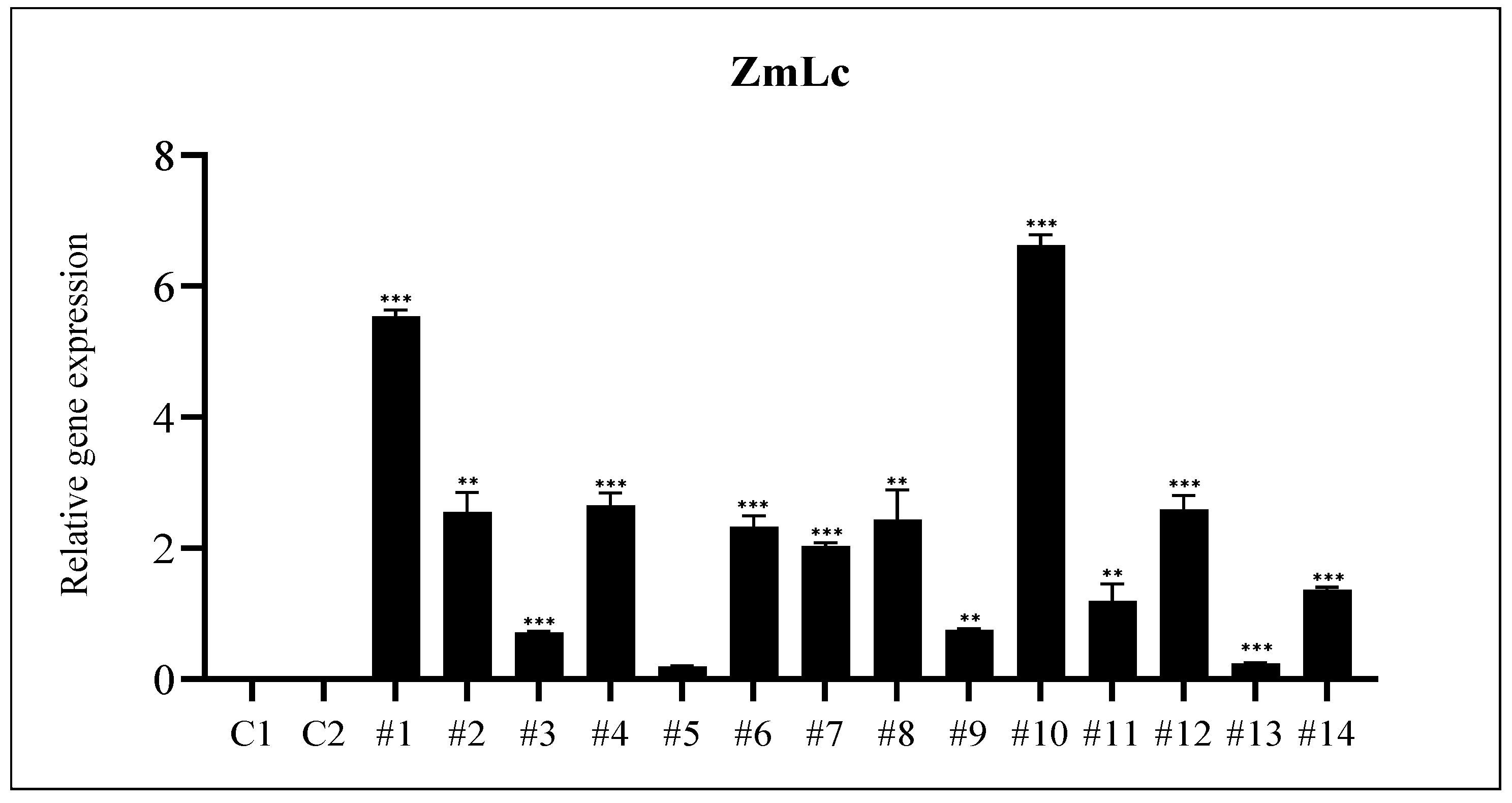
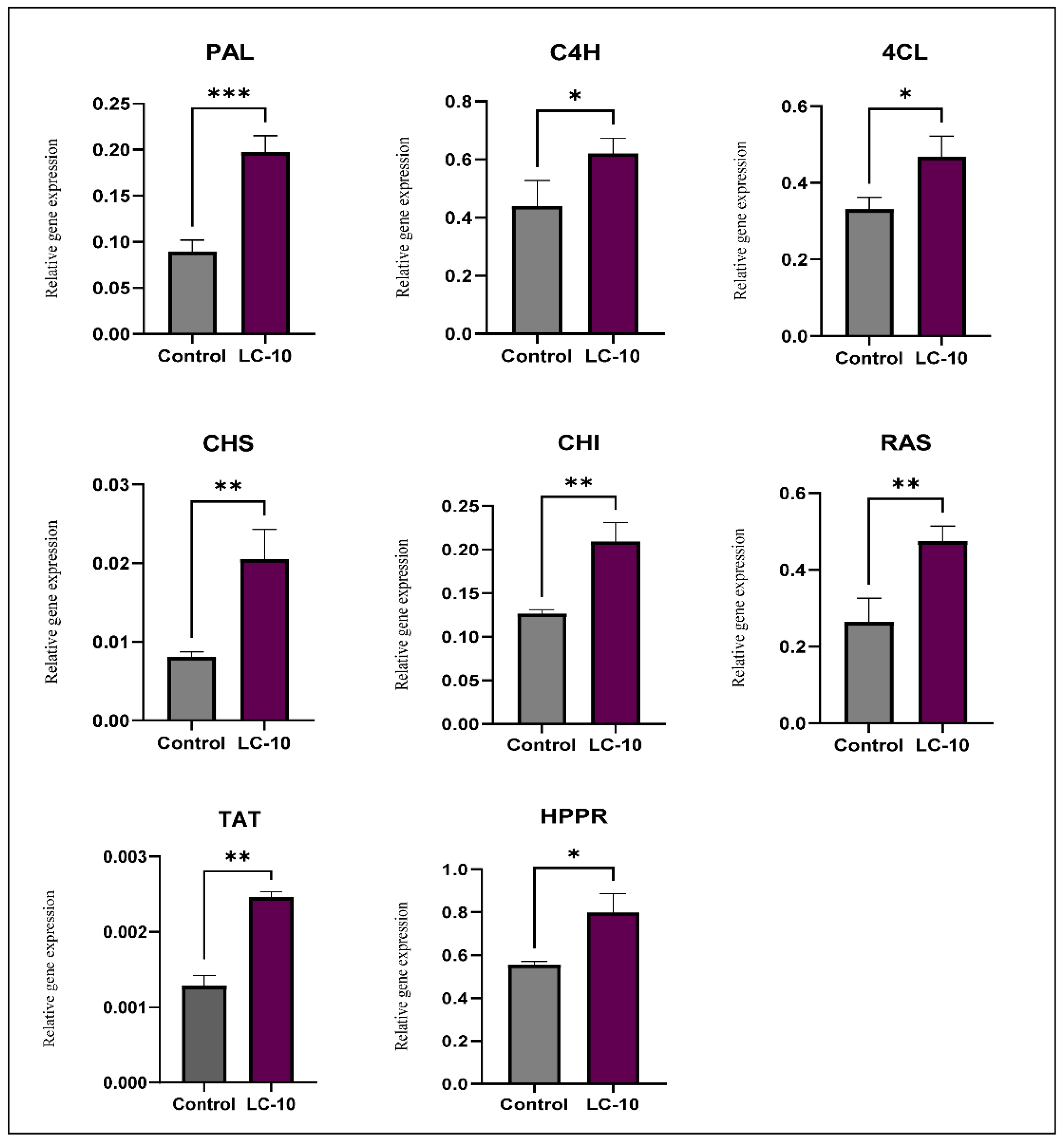
3.2. Analysis of Phenylpropanoid Biosynthesis Pathway Genes Expression in A. rugosa Grown under Light Condition
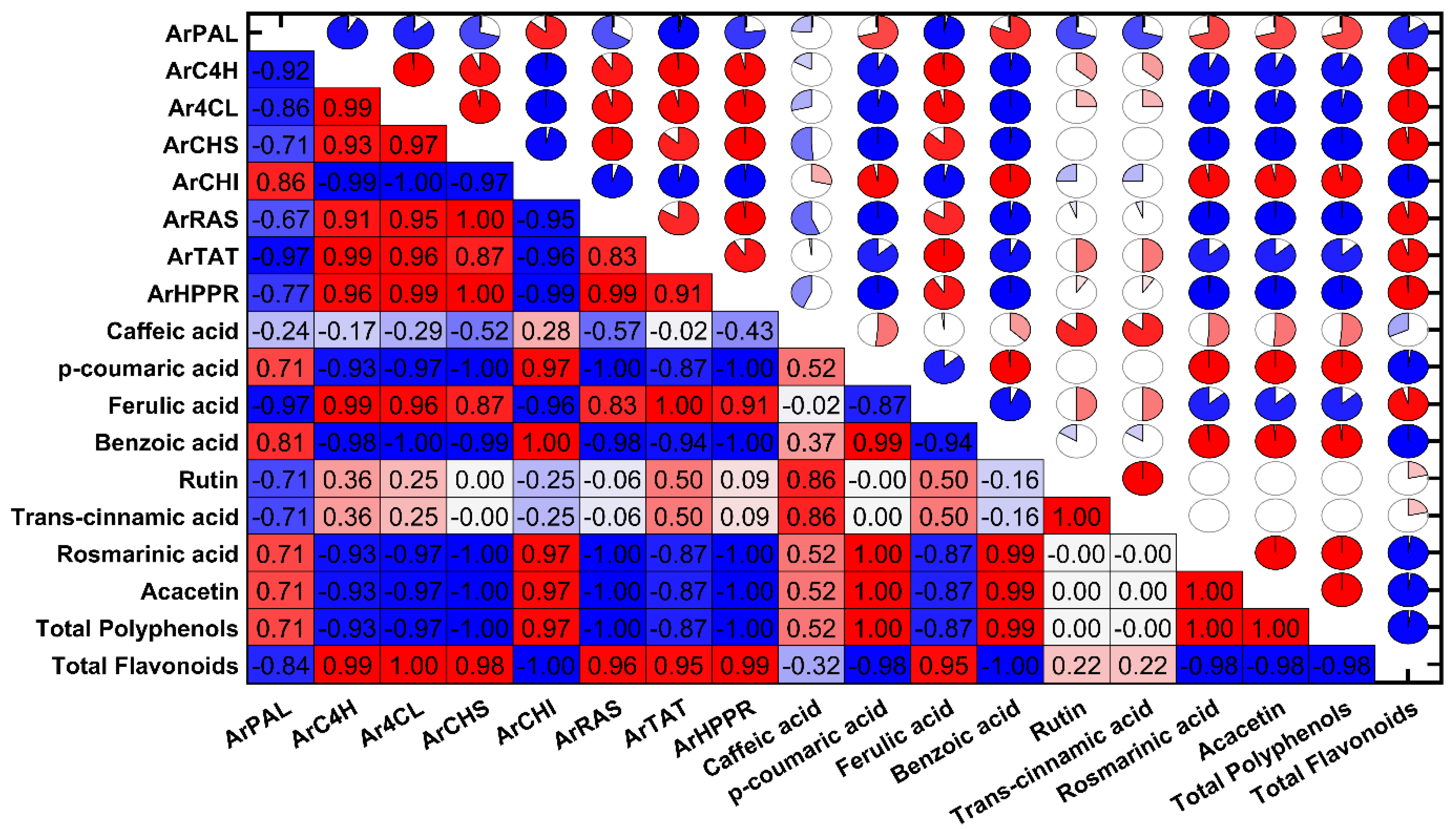
3.3. Analysis of Phenylpropanoid from A. rugosa Extracts
3.4. Quantification of TPC and TFC
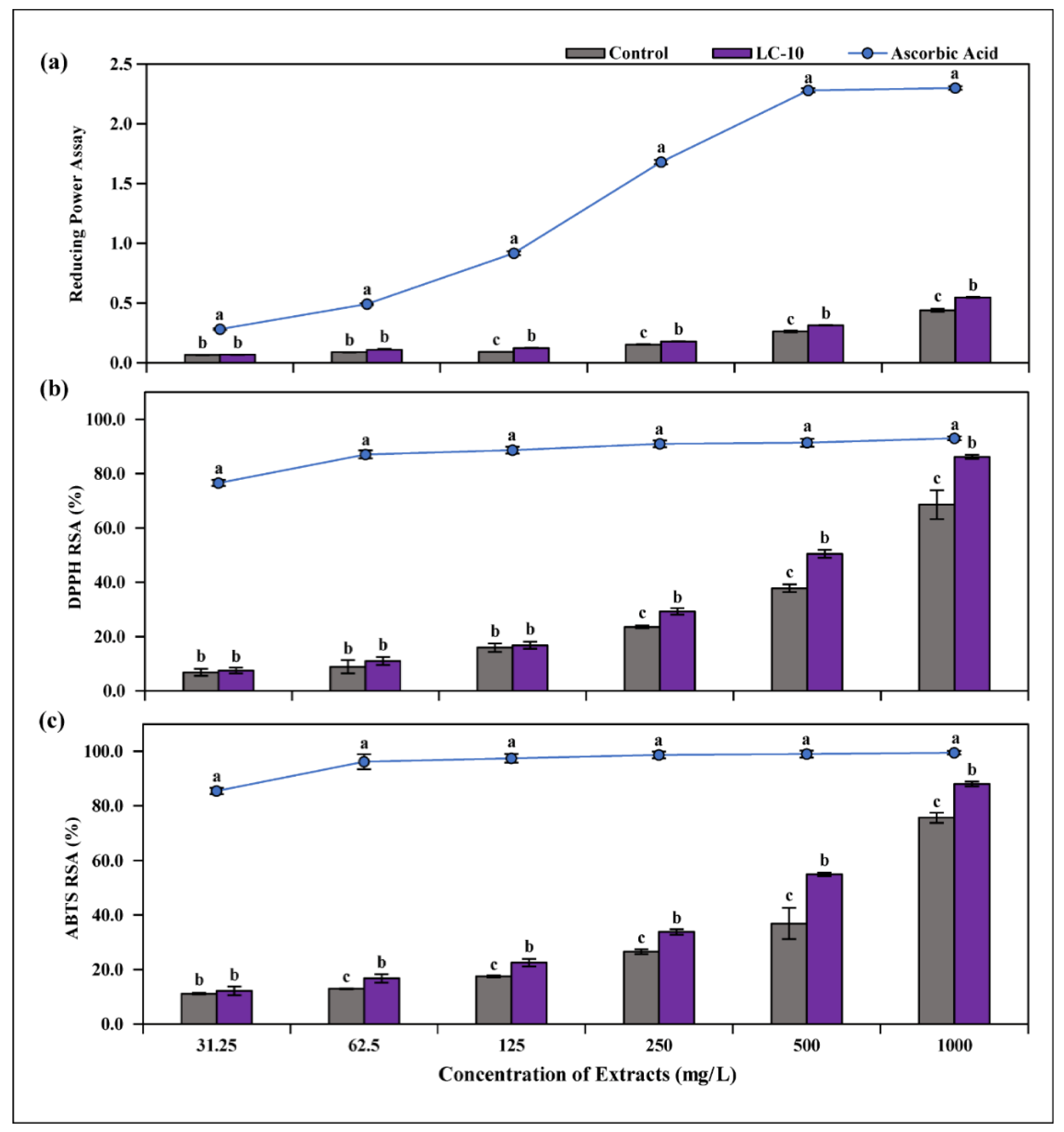
3.5. Determination of RPA and Antioxidant Activities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, W.T.; Yeo, S.K.; Sathasivam, R.; Park, J.S.; Kim, J.K.; Park, S.U. Influence of light-emitting diodes on phenylpropanoid biosynthetic gene expression and phenylpropanoid accumulation in Agastache rugosa. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2020, 63, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, K.T.; Kim, G.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, W.S.; Lee, S.J.; Jin, J.S.; Abd El-Aty, A.; Shin, H.C.; Shim, J.H.; Shin, S.C. The polyphenolic profiles and antioxidant effects of Agastache rugosa Kuntze (Banga) flower, leaf, stem and root. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2016, 30, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Xie, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Wei, J.; Kang, W.-Y. Chemical constituents and coagulation activity of Agastache rugosa. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Li, S.; He, L.; Kasimu, R. Microscopic identification and in vitro activity of Agastache rugosa (Fisch. et Mey) from Xinjiang, China. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 95. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, B.; Marasini, B.P.; Rayamajhee, B.; Bhattarai, B.R.; Lamichhane, G.; Khadayat, K.; Adhikari, A.; Khanal, S.; Parajuli, N. Potential roles of medicinal plants for the treatment of viral diseases focusing on COVID-19: A review. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 1298–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez Gutierrez, R.M.; Flores Cotera, L.B.; Gonzalez, A.M.N. Evaluation of the antioxidant and anti-glication effects of the hexane extract from Piper auritum leaves in vitro and beneficial activity on oxidative stress and advanced glycation end-product-mediated renal injury in streptozotocin-treated diabetic rats. Molecules 2012, 17, 11897–11919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Chen, R.; Zhang, L. Simple phenylpropanoids: Recent advances in biological activities, biosynthetic pathways, and microbial production. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2023, 41, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Lu, S. Biosynthesis and regulation of phenylpropanoids in plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2017, 36, 257–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaroson, M.-L.; Koutouan, C.; Helesbeux, J.-J.; Le Clerc, V.; Hamama, L.; Geoffriau, E.; Briard, M. Role of phenylpropanoids and flavonoids in plant resistance to pests and diseases. Molecules 2022, 27, 8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Wang, Z.; Wei, C.; Amo, A.; Ahmed, B.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X. Phenylpropanoid pathway engineering: An emerging approach towards plant defense. Pathogens 2020, 9, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S.L.; Upadhyaya, H.D.; Chung, I.-M.; De Vita, P.; Garcia-Lara, S.; Guajardo-Flores, D.; Gutierrez-Uribe, J.A.; Serna-Saldivar, S.O.; Rajakumar, G.; Sahrawat, K.L.; et al. Exploiting phenylpropanoid derivatives to enhance the nutraceutical values of cereals and legumes. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 763. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura, Y.; Kitabatake, M.; Kayano, S.-I.; Ito, T. Dietary phenolic compounds: Their health benefits and association with the gut microbiota. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutha, R.E.; Tatiya, A.U.; Surana, S.J. Flavonoids as natural phenolic compounds and their role in therapeutics: An overview. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelam; Khatkar, A.; Sharma, K.K. Phenylpropanoids and its derivatives: Biological activities and its role in food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2655–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.M.H.; Choi, M.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, C.; Park, C.H.; Park, N.I.; Kim, C.; Sathasivam, R.; Park, S.U. Impact of light and dark treatment on phenylpropanoid pathway genes, primary and secondary metabolites in Agastache rugosa transgenic hairy root cultures by overexpressing Arabidopsis transcription factor AtMYB12. Life 2023, 13, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Singh, S.K.; Pattanaik, S.; Wang, H.; Yuan, L. Light regulation of the biosynthesis of phenolics, terpenoids, and alkaloids in plants. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 1055. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Zou, H.; Qiu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y. Effects of light on secondary metabolite biosynthesis in medicinal plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 781236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Yang, M.; Li, S.; Zhang, G.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, L.; Shi, G.; Li, Y. Mechanisms and biotechnological applications of transcription factors. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2023, 8, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Kong, W.; Wong, G.; Fu, L.; Peng, R.; Li, Z.; Yao, Q. AtMYB12 regulates flavonoids accumulation and abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2016, 291, 1545–1559. [Google Scholar]
- Park, N.I.; Li, X.; Thwe, A.A.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, S.G.; Wu, Q.; Park, S.U. Enhancement of rutin in Fagopyrum esculentum hairy root cultures by the Arabidopsis transcription factor AtMYB12. Biotechnol. Lett. 2012, 34, 577–583. [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramanian, M.; Girija, S. Overexpression of AtMYB12 transcription factor simultaneously enhances quercetin-dependent metabolites in radish callus. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Sathasivam, R.; Park, N.I.; Wu, Q.; Park, S.U. Enhancement of phenylpropanoid accumulation in tartary buckwheat hairy roots by overexpression of MYB transcription factors. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 156, 112887. [Google Scholar]
- Zvi, M.M.B.; Shklarman, E.; Masci, T.; Kalev, H.; Debener, T.; Shafir, S.; Ovadis, M.; Vainstein, A. PAP1 transcription factor enhances production of phenylpropanoid and terpenoid scent compounds in rose flowers. New Phytol. 2012, 195, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsunami, T.; Nishihara, M.; Galis, I.; Alamgir, K.M.; Hojo, Y.; Fujita, K.; Sasaki, N.; Nemoto, K.; Sawasaki, T.; Arimura, G.-i. Overexpression of the PAP1 transcription factor reveals a complex regulation of flavonoid and phenylpropanoid metabolism in Nicotiana tabacum plants attacked by Spodoptera litura. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108849. [Google Scholar]
- Zuluaga, D.L.; Gonzali, S.; Loreti, E.; Pucciariello, C.; Degl’Innocenti, E.; Guidi, L.; Alpi, A.; Perata, P. Arabidopsis thaliana MYB75/PAP1 transcription factor induces anthocyanin production in transgenic tomato plants. Funct. Plant Biol. 2008, 35, 606–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Gao, F.; Shen, G.; Li, C.; Han, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, D.; Hua, X.; Pang, Y. Metabolic engineering of the phenylpropanoid pathway enhances the antioxidant capacity of Saussurea involucrata. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Flachowsky, H.; Fischer, T.C.; Hanke, M.-V.; Forkmann, G.; Treutter, D.; Schwab, W.; Hoffmann, T.; Szankowski, I. Maize Lc transcription factor enhances biosynthesis of anthocyanins, distinct proanthocyanidins and phenylpropanoids in apple (Malus domestica Borkh.). Planta 2007, 226, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-A.; Zhao, T.; Wang, N.; Zheng, S.-S. Ectopic expression of Lc differentially regulated anthocyanin biosynthesis in the floral parts of tobacco (Nicotiana tobacum L.) plants. Bot. Stud. 2016, 57, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Xu, H.; Yeo, H.J.; Park, Y.E.; Hwang, G.-S.; Park, N.I.; Park, S.U. Enhancement of the flavone contents of Scutellaria baicalensis hairy roots via metabolic engineering using maize Lc and Arabidopsis PAP1 transcription factors. Metab. Eng. 2021, 64, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boase, M.; Bradley, J.; Borst, N. Genetic transformation mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens of florists’ chrysanthemum (Dendranthema xgrandiflorum) cultivar “Peach Margaret”. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 1998, 34, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.M.; Davies, K.M.; Deroles, S.C.; Bloor, S.J.; Lewis, D.H. The maize Lc regulatory gene up-regulates the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway of Petunia. Plant J. 1998, 13, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-J.; Kim, Y.-M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, S.J.; Cho, K.-C.; Chandrasekhar, T.; Song, P.-S.; Woo, Y.-M.; Kim, J.-I. Production of purple-colored creeping bentgrass using maize transcription factor genes Pl. and Lc through Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Plant Cell Rep. 2009, 28, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, H.; Yu, M.; Auser, P.; Blahut-Beatty, L.; McKersie, B.; Bowley, S.; Westcott, N.; Coulman, B.; Lloyd, A.; Gruber, M.Y. Expression of anthocyanins and proanthocyanidins after transformation of alfalfa with maize Lc. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 1448–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, N.W.; Lewis, D.H.; Zhang, H.; Irving, L.J.; Jameson, P.E.; Davies, K.M. Light-induced vegetative anthocyanin pigmentation in Petunia. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 2191–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Fan, B.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W. Anthocyanin accumulation enhanced in Lc-transgenic cotton under light and increased resistance to bollworm. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2016, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procissi, A.; Dolfini, S.; Ronchi, A.; Tonelli, C. Light-dependent spatial and temporal expression of pigment regulatory genes in developing maize seeds. Plant Cell 1997, 9, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Park, Y.E.; Yeo, H.J.; Park, N.I.; Park, S.U. Effect of light and dark on the phenolic compound accumulation in Tartary buckwheat hairy roots overexpressing ZmLC. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, P.A.; Park, W.T.; Xu, H.; Park, N.I.; Park, S.U. Accumulation of tilianin and rosmarinic acid and expression of phenylpropanoid biosynthetic genes in Agastache rugosa. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 5945–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathasivam, R.; Kim, M.C.; Yeo, H.J.; Nguyen, B.V.; Sohn, S.I.; Park, S.U.; Kim, J. Accumulation of phenolic compounds and glucosinolates in sprouts of pale green and purple kohlrabi (Brassica oleracea var. gongylodes) under light and dark conditions. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Kim, K.; Kwon, D.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Sathasivam, R.; Park, S.U. Effects of different solvents on the extraction of phenolic and flavonoid compounds, and antioxidant activities, in Scutellaria baicalensis Hairy Roots. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, A.M.; Walbot, V.; Davis, R.W. Arabidopsis and Nicotiana anthocyanin production activated by maize regulators R and C1. Science 1992, 258, 1773–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooney, M.; Desnos, T.; Harrison, K.; Jones, J.; Carpenter, R.; Coen, E. Altered regulation of tomato and tobacco pigmentation genes caused by the delila gene of Antirrhinum. Plant J. 1995, 7, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong-Sheng, H.; Zhang, L.; Peng, D.; Wan-Sheng, C. Cloning and induction of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene from Salvia miltiorrhiza and its effect on hydrophilic phenolic acids levels. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2009, 7, 449–457. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Wang, Z. RNAi-mediated suppression of the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene in Salvia miltiorrhiza causes abnormal phenotypes and a reduction in rosmarinic acid biosynthesis. J. Plant Res. 2011, 124, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzel, C.; Petersen, M. Enzymes of phenylpropanoid metabolism in the important medicinal plant Melissa officinalis L. Planta 2010, 232, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemm, M.R.; Rider, S.D.; Ogas, J.; Murry, D.J.; Chapple, C. Light induces phenylpropanoid metabolism in Arabidopsis roots. Plant J. 2004, 38, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.; Donnelly, C.; Crozier, A.; Wheeler, C. Effects of the exposure of roots of Alnus glutinosa to light on flavonoids and nodulation. Can. J. Bot. 1999, 77, 1311–1315. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, Z.; Yang, T.; Nopo-Olazabal, L.; Wu, S.; Ingle, T.; Joshee, N.; Medina-Bolivar, F. Effect of light, methyl jasmonate and cyclodextrin on production of phenolic compounds in hairy root cultures of Scutellaria lateriflora. Phytochemistry 2014, 107, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, B.H.; Tian, C.-L.; Murch, S.J.; Saxena, P.K.; Liu, C.-Z. Light-enhanced caffeic acid derivatives biosynthesis in hairy root cultures of Echinacea purpurea. Plant Cell Rep. 2007, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Lee, H.-D.; Chung, J.M.; Lee, S. Antioxidant Activity of vitex rotundifolia seeds and phytochemical analysis using HPLC-PDA. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2023, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.T.; Ferraro, T. Phenolic compounds in food and cancer prevention. In Phenolic Compounds in Food and Their Effects on Health; Huang, H.T., Ho, C.T., Lee, C.Y., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; pp. 8–34. [Google Scholar]
- Atasoy, N.; Yücel, U.M. Antioxidants from plant sources and free radicals. In Reactive Oxygen Species; Ahmad, R., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]

| No. | Compound | Control | LC-10 | Fold Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Caffeic acid | 0.687 ± 0.015 | 0.951 ± 0.026 | 1.38 |
| 2 | p-coumaric acid | 0.005 ± 0.001 | 0.022 ± 0.001 | 4.40 |
| 3 | Ferulic acid | 0.01 ± 0.001 | 0.011 ± 0.004 | 1.10 |
| 4 | Benzoic acid | 0.141 ± 0.007 | 0.148 ± 0.003 | 1.05 |
| 5 | Rutin | 0.29 ± 0.001 | 0.292 ± 0.003 | 1.01 |
| 6 | Trans-cinnamic acid | 0.004 ± 0.001 | 0.012 ± 0.001 | 3.00 |
| 7 | Rosmarinic acid | 24.4 ± 0.394 | 26.803 ± 0.635 *** | 1.10 |
| 8 | Acacetin | 0.007 ± 0.001 | 0.03 ± 0.003 | 4.29 |
| Control | LC-10 | |
|---|---|---|
| Total Polyphenol (GAE mg/g DW) | 19.92 ± 1.66 | 28.07 ± 0.22 *** |
| Total Flavonoid (QE mg/g DW) | 30.55 ± 0.15 | 42.35 ± 0.67 *** |
| IC50 of DPPH | IC50 of ABTS | |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.7 ± 0.03 | 0.63 ± 0.03 |
| LC-10 | 0.53 ± 0.00 | 0.48 ± 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, B.V.; Kim, J.K.; Lim, J.; Kim, K.; Sathasivam, R.; Cho, D.H.; Park, S.U. Enhancement of Phenylpropanoid Accumulation and Antioxidant Activities of Agastache rugosa Transgenic Hairy Root Cultures by Overexpressing the Maize Lc Transcription Factor. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9617. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14209617
Nguyen BV, Kim JK, Lim J, Kim K, Sathasivam R, Cho DH, Park SU. Enhancement of Phenylpropanoid Accumulation and Antioxidant Activities of Agastache rugosa Transgenic Hairy Root Cultures by Overexpressing the Maize Lc Transcription Factor. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(20):9617. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14209617
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Bao Van, Jae Kwang Kim, Jinsu Lim, Kihyun Kim, Ramaraj Sathasivam, Dong Ha Cho, and Sang Un Park. 2024. "Enhancement of Phenylpropanoid Accumulation and Antioxidant Activities of Agastache rugosa Transgenic Hairy Root Cultures by Overexpressing the Maize Lc Transcription Factor" Applied Sciences 14, no. 20: 9617. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14209617
APA StyleNguyen, B. V., Kim, J. K., Lim, J., Kim, K., Sathasivam, R., Cho, D. H., & Park, S. U. (2024). Enhancement of Phenylpropanoid Accumulation and Antioxidant Activities of Agastache rugosa Transgenic Hairy Root Cultures by Overexpressing the Maize Lc Transcription Factor. Applied Sciences, 14(20), 9617. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14209617







