Abstract
This work presents a review and evaluation of studies measuring exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields (RF-EMF). The review meets the basic quality criteria and the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines after the eligibility criteria of the PECO (Population, Exposure, Comparator, and Outcome) methodology and the instrument Critical Appraisal Skills Programme Español (CASPe). A total of 86 papers published between 1 January 1998 and 31 December 2023 are included: 61 studies with spot measurements and 25 studies with mixed methodologies (spot measurements, personal measurements with volunteers or with a trained researcher and prediction models) are highlighted. Forty-three percent of the studies use Spectrum Analyzers in the spot measurements, mainly the Narda SRM–3006, followed by the Narda SRM-3000, highlighting the introduction and use of Sensors for this kind of study. The minimum mean value was measured in Palestine at 0.0600 µW/m2, and the maximum mean value was measured in Norway at 200,000 µW/m2. The RF-EMF exposure levels measured in the different microenvironments are minimal and far from the maximum levels established by the ICNIRP guidelines.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the proliferation of connected applications has caused changes in our electromagnetic environment. The accelerated development and increase in telecommunication technologies are an important factor influencing Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields (RF-EMF) exposure patterns in the different microenvironments in which we live, and they are everywhere: in schools [1,2,3,4,5], residences [6], malls [7,8], industries and transport [9,10,11], and urban, suburban, and rural areas [2,12,13,14,15,16,17,18].
International institutions such as the International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) have established guidelines for limiting and monitoring human exposure to these fields [19,20]. Nevertheless, some countries, for instance, Canada, Italy, Poland, Switzerland, China, Russia, France, and Belgian regions, have adopted even stricter limits based on RF-EMF guidelines [21] that could postpone or even hinder the implementation of new technologies, such as 5G networks and future generations [22].
In 1998, the ICNIRP made the first publication on maximum reference levels, and RF-EMF exposure measurement studies began to monitor the RF-EMF exposure levels to which we are exposed (100 kHz to 300 GHz) [19,23,24,25]. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses allow us to know and analyze published scientific studies based on the declaration Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) [26,27,28,29]. In addition, the comparison of studies allows us to know the different methodologies that these studies have used, such as RF-EMF studies (Figure 1).
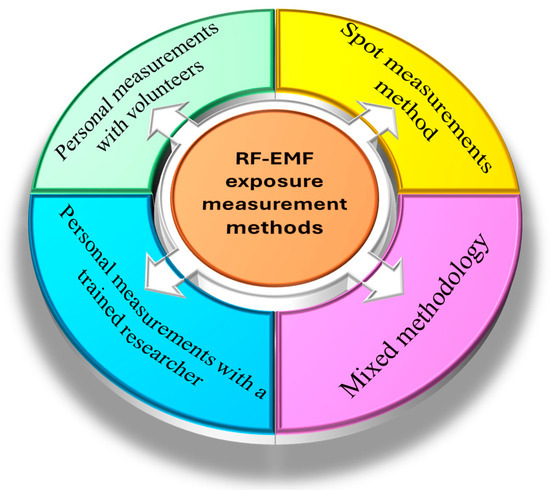
Figure 1.
Methods used in RF-EMF exposure measurement studies. This review includes spot measurements and mixed methodology.
This review presents scientific works published between 1 January 1998 and 31 December 2023, in which the RF-EMF exposure has been measured by means of the spot measurements method and studies using a mixed methodology, combining spot measurements, personal measurements with volunteers or with trained researcher, spatiotemporal exposure measurements and using model predictions (Figure 1).
In a recent publication [30], studies were presented and carried out through personal measurements with volunteers and with a trained researcher. The present review has been motivated by this review [30] to answer the following questions: What studies have been carried out applying spot measurements and mixed methodology? Also, what were the results? Do these results comply with the reference limits established by the ICNIRP?
2. Materials and Methods
This article is based on the PRISMA statement [28,31] on the Population, Exposure, Comparator, and Outcome (PECO) methodology [32] of the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme Español (CASPe) [33].
We searched and analyzed studies published between 1 January 1998 and 31 December 2023. The search was conducted on the Web of Science (WOS) and PubMed databases, resulting in 2372 articles in WOS and 489 in PubMed. The publications recorded on the PubMed database were the same as those found in the WOS database. Therefore, to avoid duplication of papers, these were eliminated, and those in the WOS were considered.
The suitability criteria are:
Topics: Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields or RF-EMF, personal exposure and environment, and measurements Mobile phone or base stations, wireless or Wi-Fi, Exposure assessment or exposure measurement, personal experiment and children, and school and spot measurements.
Document Types: Article.
Database: Web of Science Core Collection.
Research Areas: Physics or Research Experimental Medicine or Public Environmental Occupational Health or Life Sciences Biomedicine Other Topics.
Languages: English.
Publication Years: 1998 to 2023.
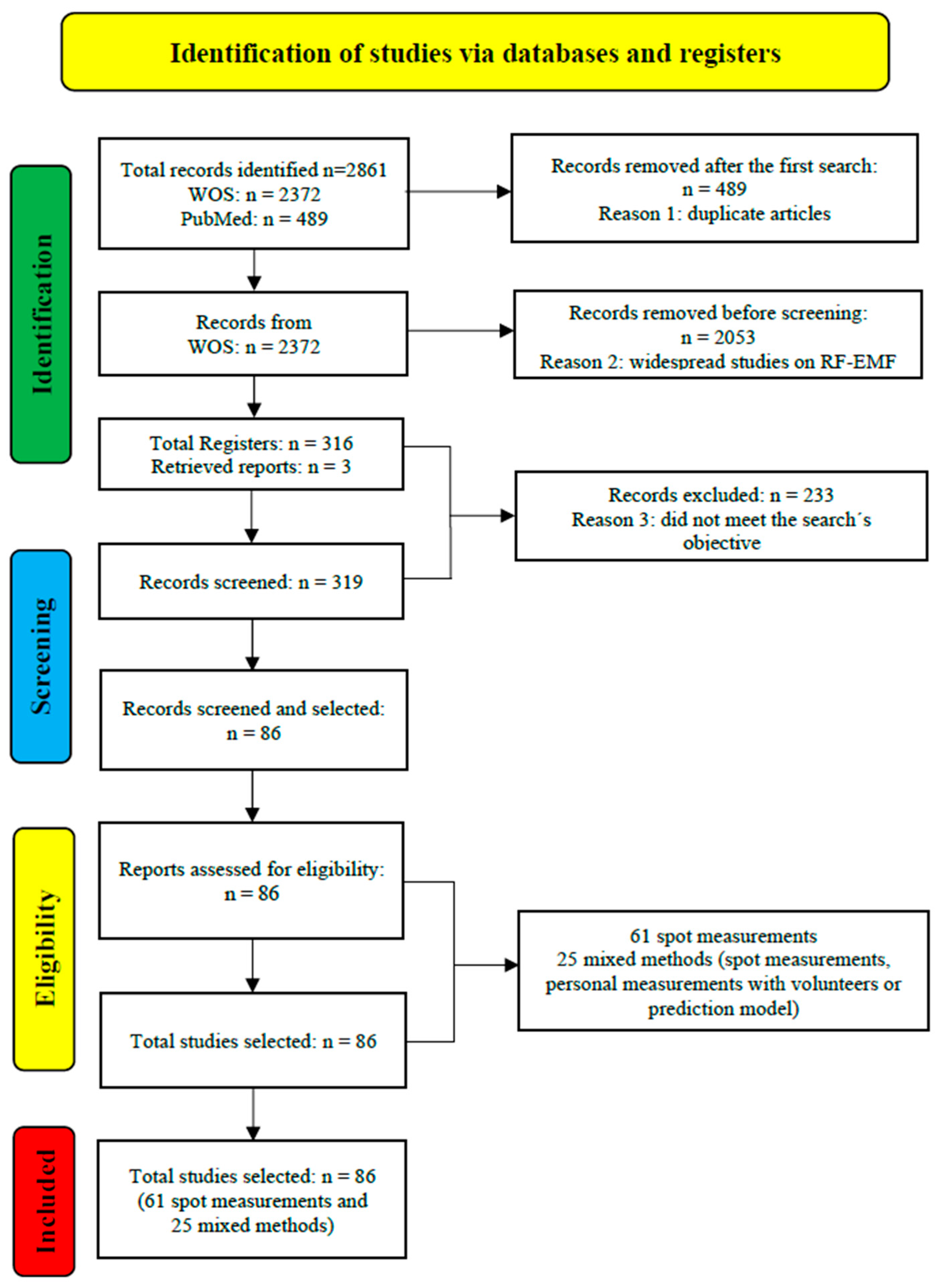
Of the 2372 records, 2053 were excluded because they did not meet the objective of the review. Thus, only 319 abstracts of the publications were reviewed and examined. Of these 319 documents, 316 full papers were found in PDF format, and 3 works were requested and retrieved from the corresponding authors of the study. A general review of the 319 complete papers was conducted, of which 233 publications were excluded because they did not meet the objective of the search. They did not report on exposure measurements using the spot measurements method or using a mixed methodology, including spot measurements, personal measurements with volunteers or with a trained researcher, spatiotemporal exposure measurements, and model predictions. Finally, 86 complete papers were selected and analyzed and, finally, were included in this review (Figure 2 and Table 1).
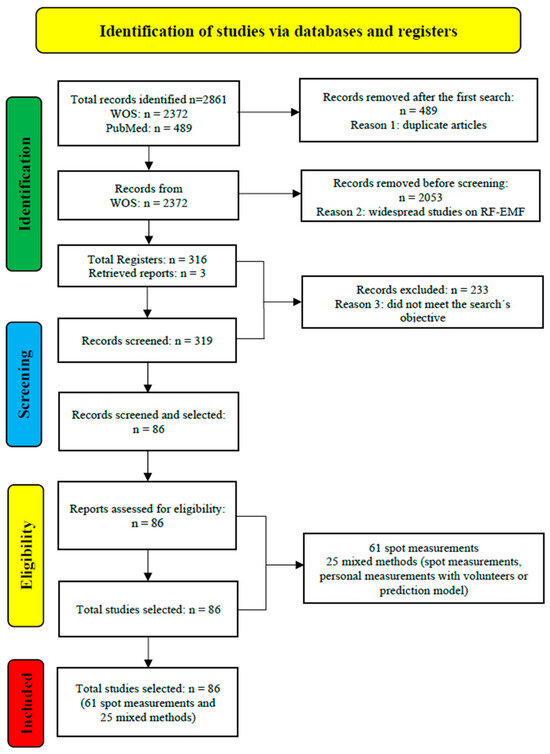
Figure 2.
PRISMA flowchart for selection and exclusion of articles. Methods used in RF-EMF exposure measurement studies: spot measurements and mixed methodology.

Table 1.
Studies on exposure to RF-EMF: Spot measurements and Mixed method.
The eligibility criteria considered in the PECO methodology were: (1) Title + Abstract + Results relevant; Original research + Peer reviewer + RF-EMF exposure measurements Results report; (2) Population; (3) Exposure; (4) Comparator; (5) Outcome. The CASPe questions [33] are as follows: Were the research objectives clearly defined? Is the research method adequate to achieve the objectives? Is the case selection strategy consistent with the research question and the method used? Are the data collection techniques used consistently with the research question and the method applied? Was data analysis sufficiently rigorous? Is the presentation of the results clear? Finally, the chosen studies were classified in Table 1.
3. Results
We are providing RF-EMF exposure measurement studies through spot measurement and mixed methodology (combining spot measurements, personal measurements with volunteers or with a trained researcher, and a prediction model).
3.1. Selected Studies
By analyzing the studies that have measured RF-EMF exposure using exposimeters, Spectrum Analyzers or other devices, in addition to the studies presented in the last review [30], we can identify and classify other studies into two types: (1) Spot measurements in specific places or points during a fixed period of time (without moving), points previously selected by the researcher, carrying the personal exposimeters hanging on his body or placing them on a fixed base (such as a cardboard or plastic tube), or exposimeters or equipment placed on a fixed base, such as a tripod for a continuous period of time, including equipment temporarily placed at one or more points in a city [1,3,4,67,112,113], involving measurements carried out by the researcher himself or by a trained person. The second type is (2) Mixed method (combining spot measurements, personal measurements with volunteers or including a prediction model) in which measurements with volunteers, spot measurement, mobile measurements with a trained researcher, and a prediction model are combined.
3.2. Study Description
Table 1 shows all the studies in the Review, highlighting the two kinds of studies: (1) spot measurements and (2) mixed method. After Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3 show the studies ordered according to the measurement method applied and the descriptive statistical results.

Table 2.
Results of the spot measurements studies (µW/m2 and V/m).

Table 3.
Results of the studies with mixed methods (µW/m2 and V/m).
3.3. Spot Measurements
Studies on exposure to RF-EMF using spot measurements in different microenvironments, measure at a previously selected fixed point and without moving for a specific period of time [7,18,35,36,51,53,54,55,57,60,61,62,63,64,65,70,78,79,81,82,87,93,96]; near MBPSs [34,46,58,94,98]; around buildings [2,52,114]; in university areas (inside and outside buildings) [1,3,84,92]; in a library [91]; at home [40,68,69,86,95,115]; in schools [4,44,80,83,85]; and in residences [116]. Most of these studies were performed in European countries.
In this study, the terms power density and intensity of electromagnetic waves will be considered fully equivalent. The intensity of an electromagnetic wave is measured in Watts per square meter (W/m2) in the International System of Units (SI). Additionally, some people refer to it as power density [117].
3.4. Mixed Method Measurements
Some studies have used a mixed method, personal measurements with volunteers and spot measurements [37,88,101,118,119], sometimes including a prediction model [120]. Other investigations have measured exposure with the participation of volunteers, with specific measurements in a university setting [45] and in a home setting [48,49,100].
Other studies made spot measurements in different microenvironments and developed simulation models to predict exposure in zones or microenvironments that were not measured [38,42,54,56,75,76,97,99,121]. In other studies, measurement prediction models were applied [14,41,122]. Table 3 shows the studies that used the mixed method and the published descriptive results, with the units needing to be changed in the majority of the studies.
3.5. Analysis of RF-EMF Studies
In the 86 publications included in this work, 27 countries are involved: Spain, Belgium, Switzerland, France, Greece, Turkey, Poland, Sweden, Austria, Netherlands, Serbia, Asia, China, Germany, Italy, Romania, United Kingdom, USA, Amsterdam, Australia, India, Korea, Malaysia, Mexico, Norway, Palestine, and Slovenia (Table 4).

Table 4.
Total studies by nations involved.
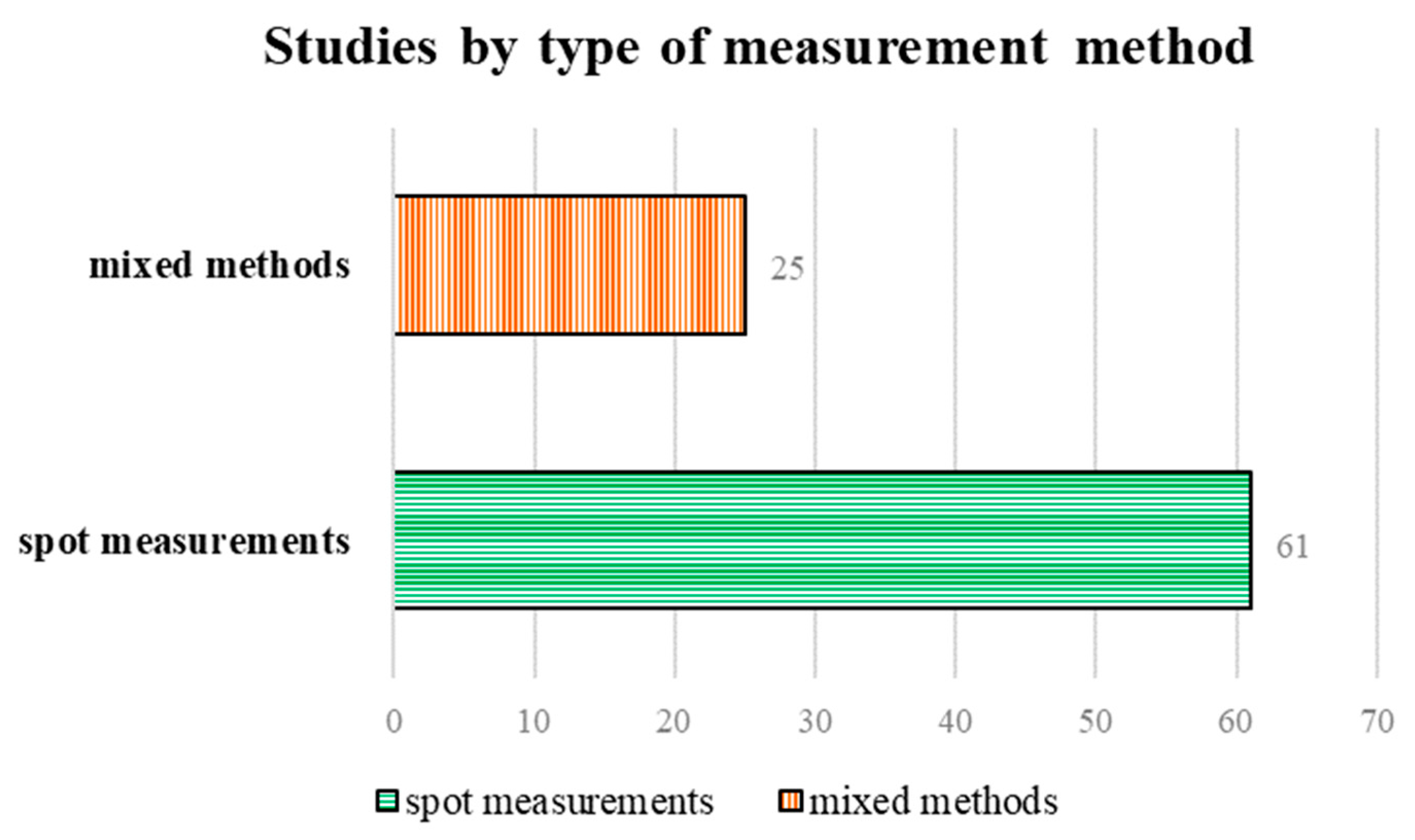
Of the 86 studies included in this review, 61 conducted spot measurements, and 25 used a mixed method (Figure 3).
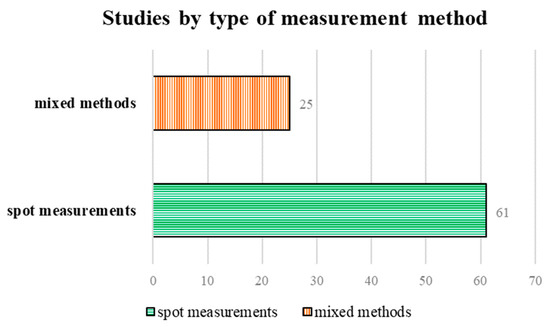
Figure 3.
Type and number of studies included in the review.
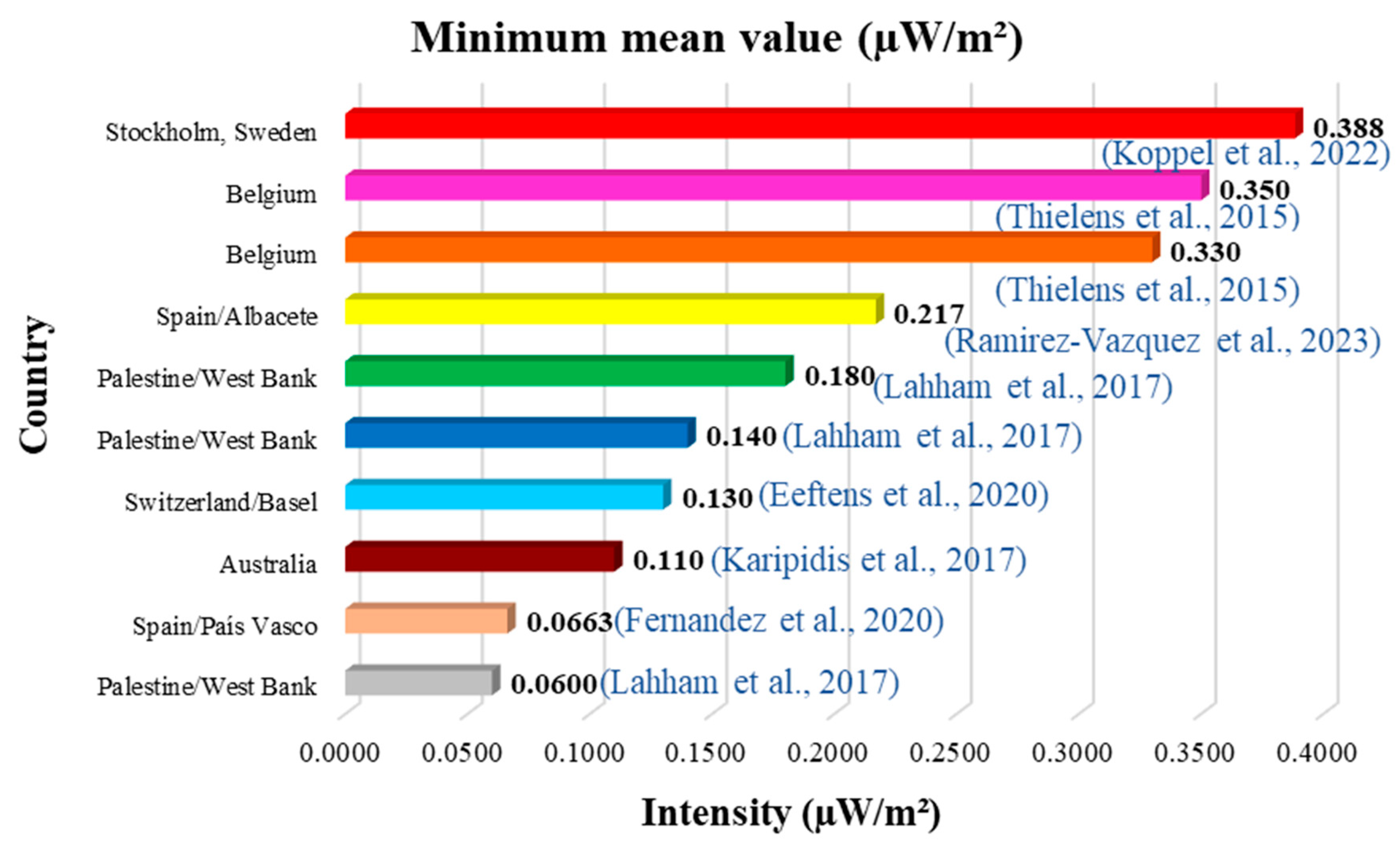
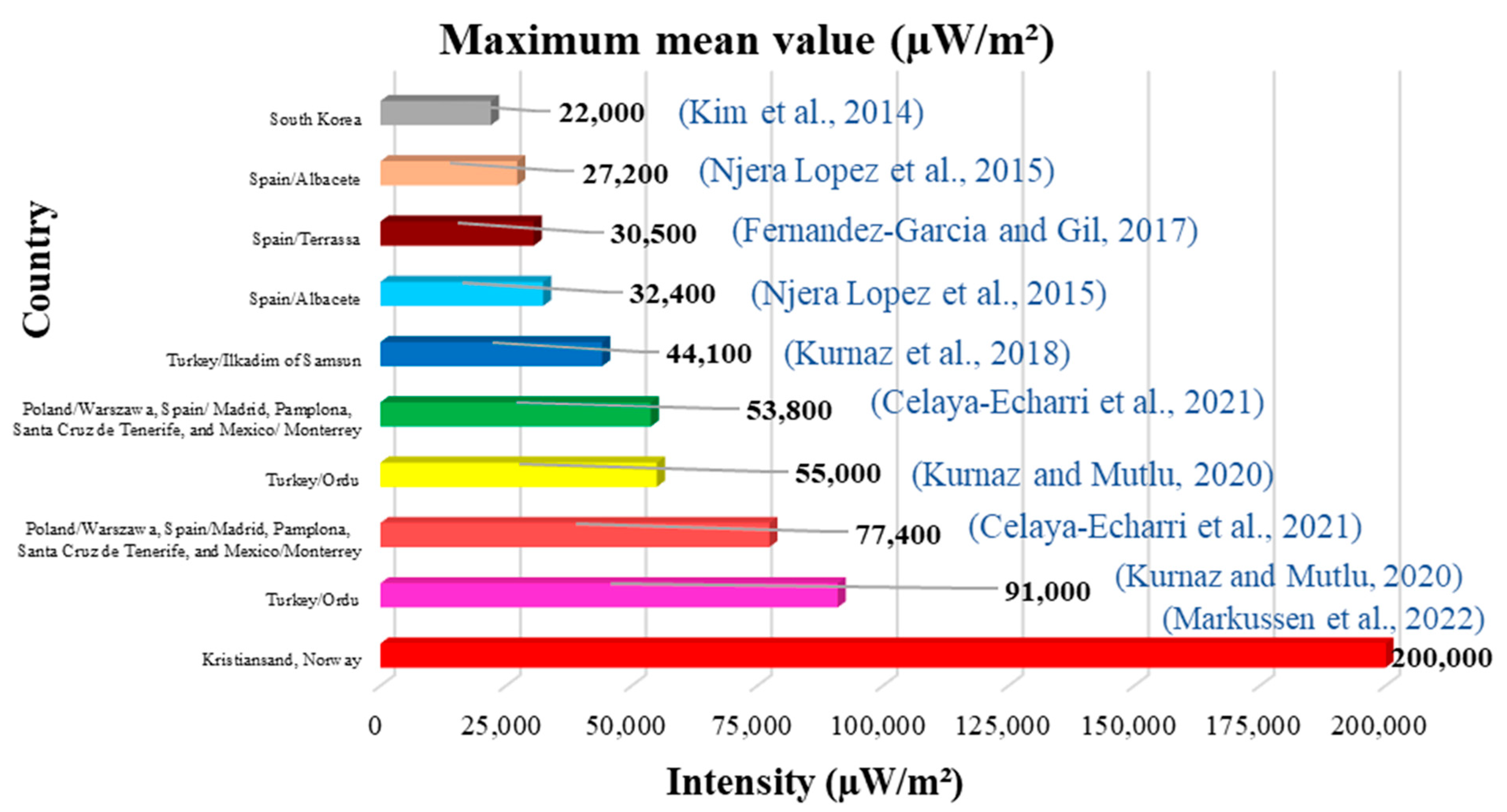
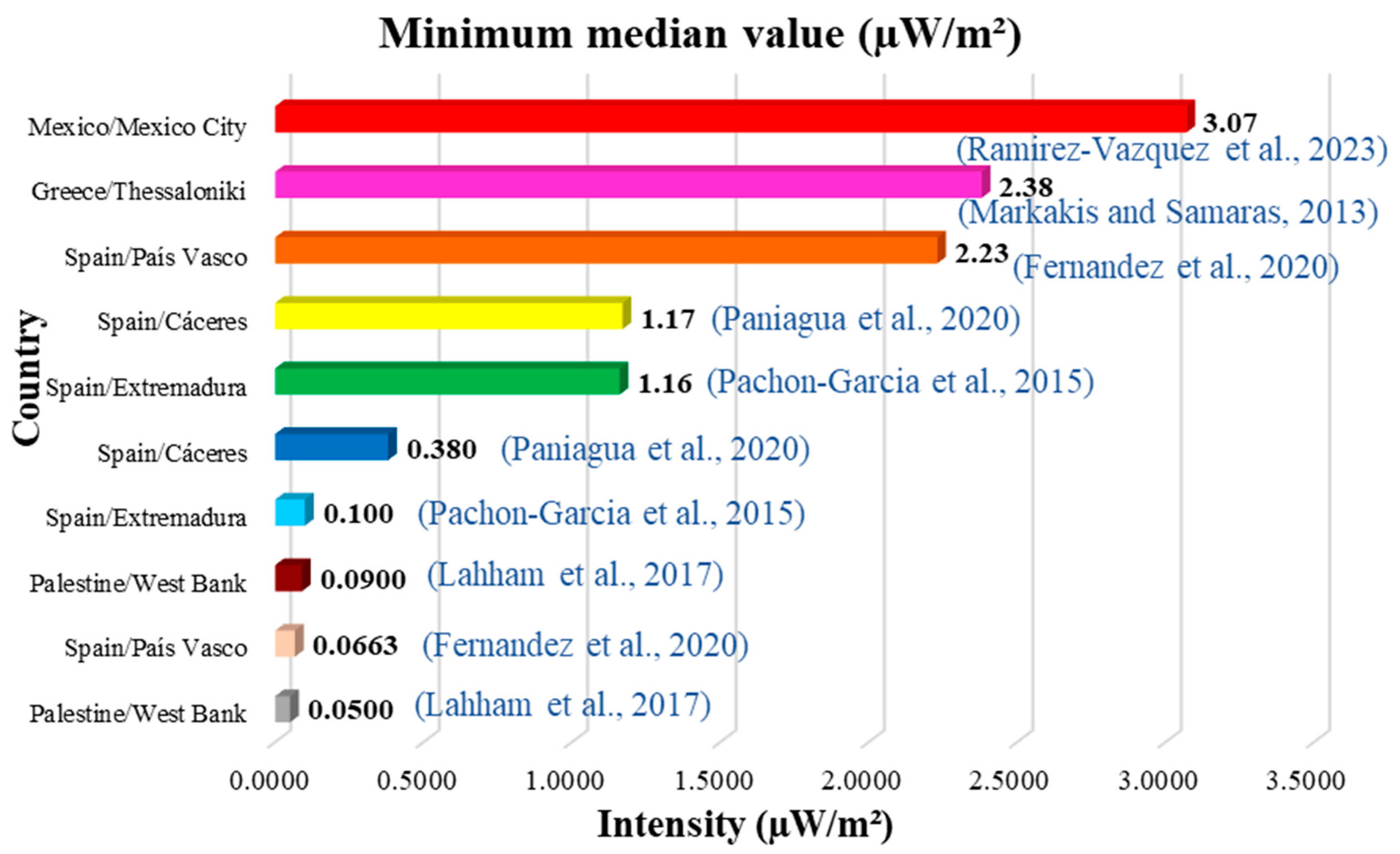
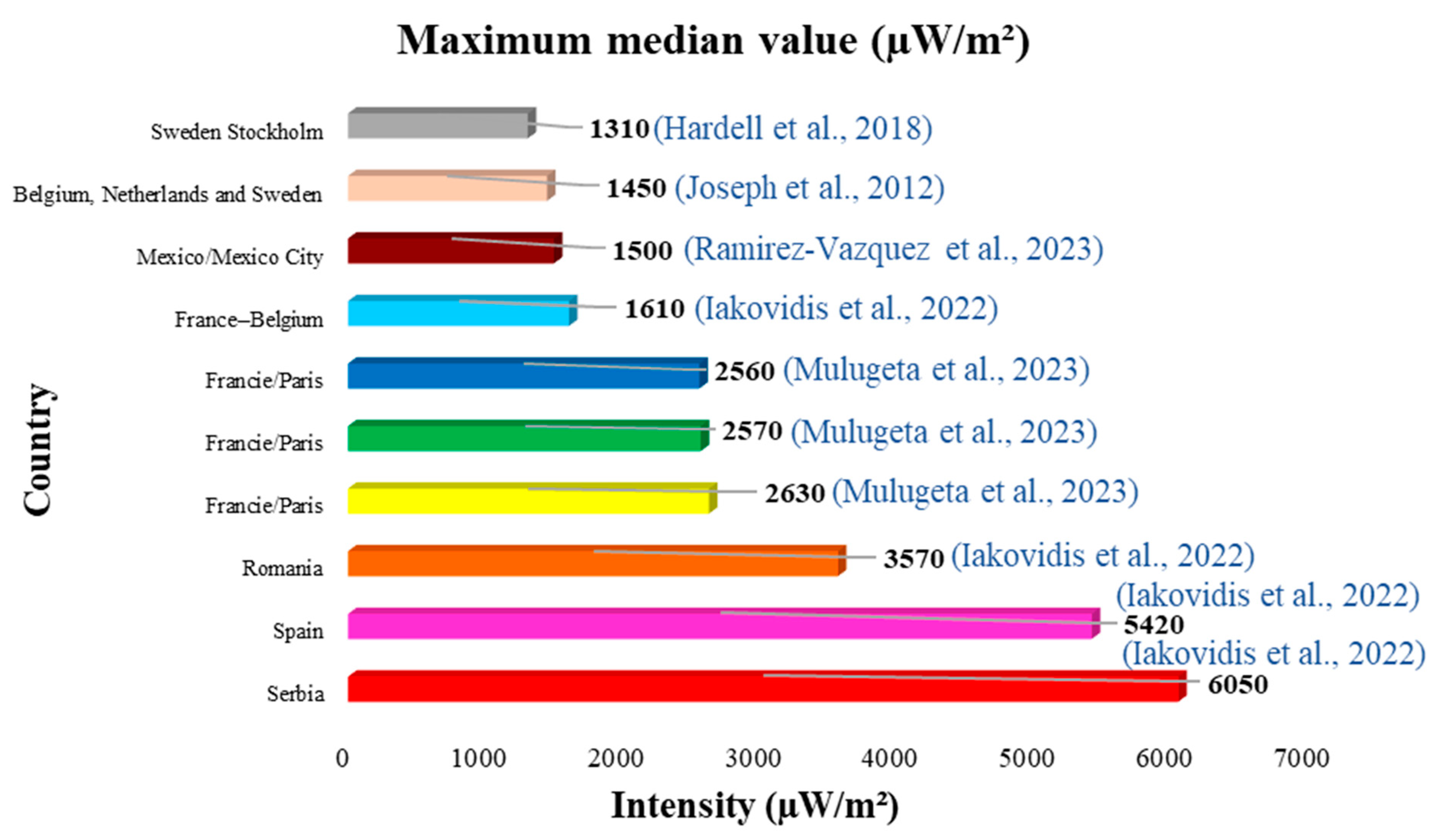
Of all the studies reviewed, the ten lowest values and the ten highest values of the mean and median have been identified (Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7). Figure 4 and Figure 5 show the ten lowest and highest mean values of the different studies.
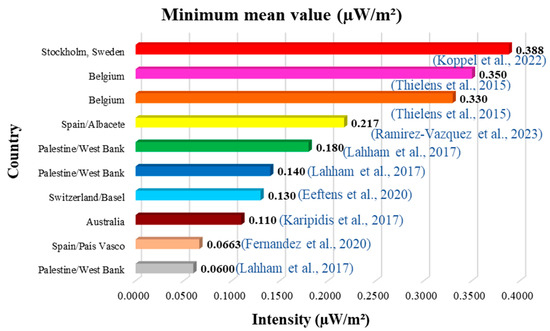
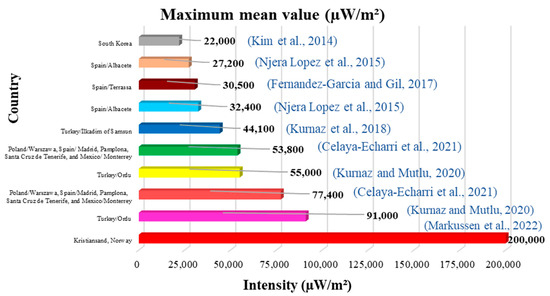
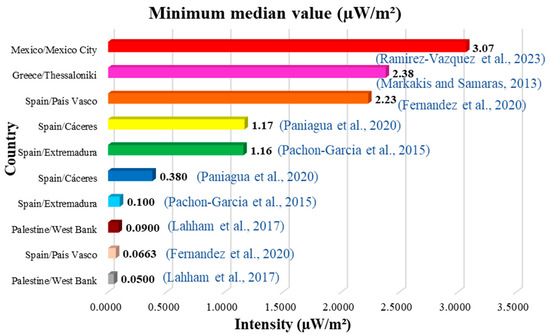
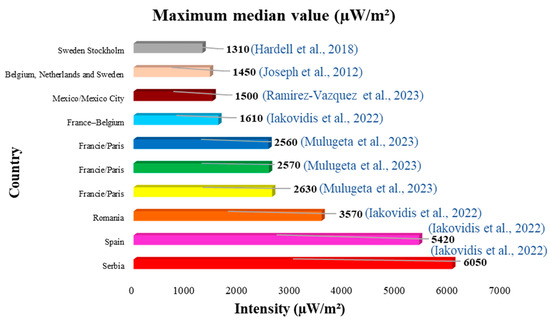
The highest average was 200,000 µW/m2 (0.20 W/m2) measured in Kristiansand, Norway (Figure 5), and the lowest was 0.0600 µW/m2 measured in Palestine (Figure 4). Figure 6 and Figure 7 show the ten lowest and highest median values of the different studies reviewed.
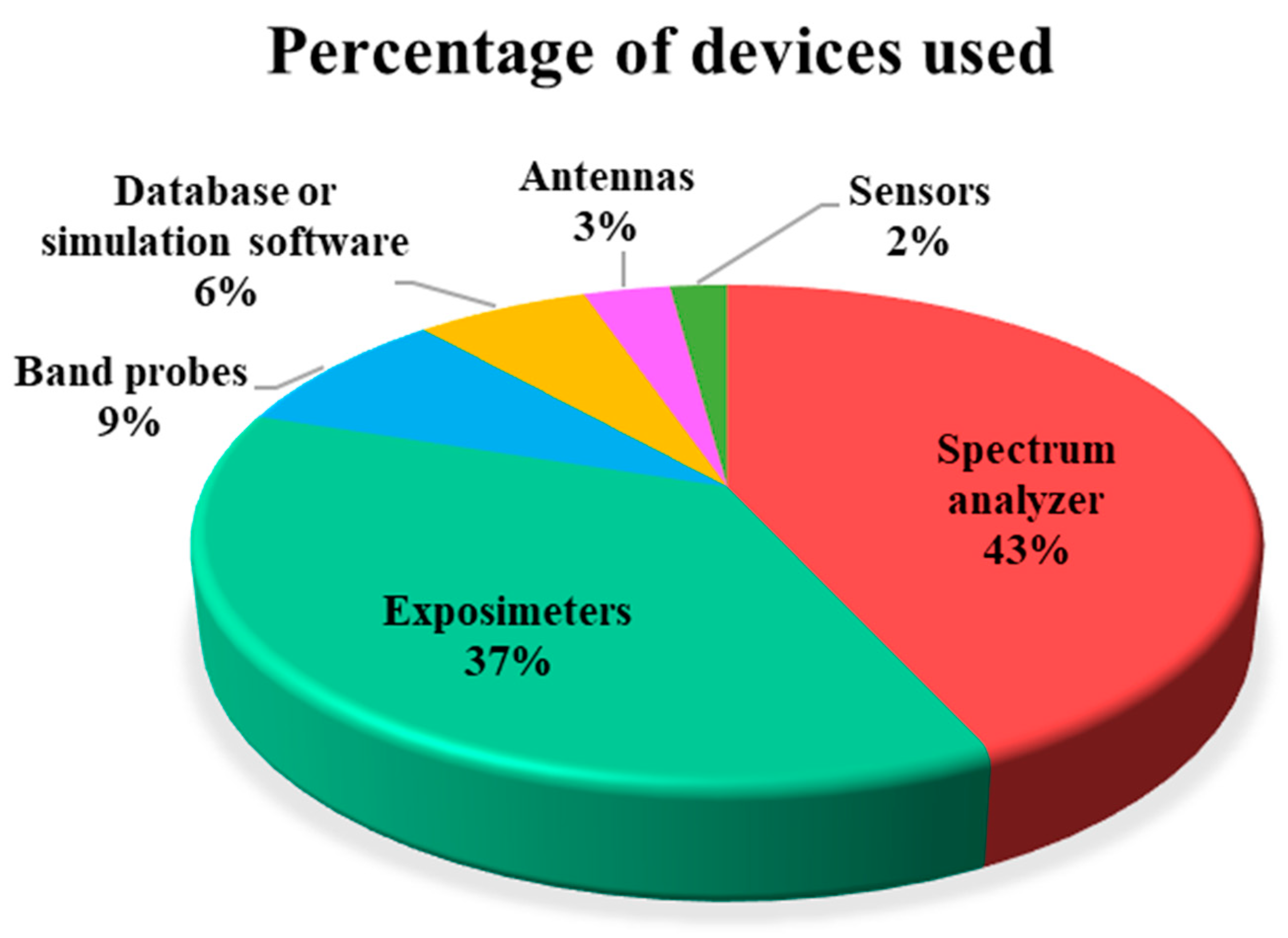
Out of the 86 studies included in this Review, 43% of them used a Spectrum Analyzer, a device that is mostly used for spot measurements. The most commonly used model was the Narda SRM-3006, followed by the Narda SRM-3000 (Figure 8). As we know, personal exposimeters are more appropriate for measurements involving moving volunteers. In addition to Spectrum Analyzer, Exposimeters, Band probes, Databases and Antennas, we want to highlight the introduction and use of Sensors, devices that allow us to monitor at different spatial points over time.
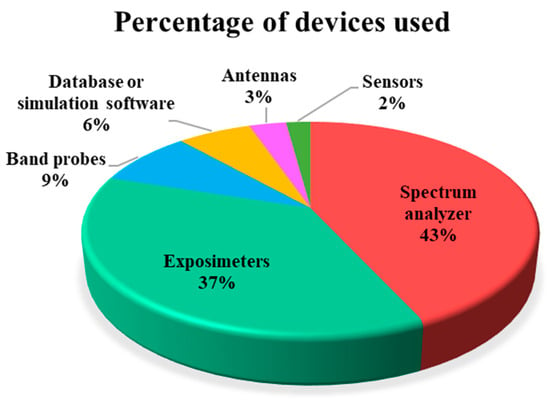
Figure 8.
Equipment used in the studies included in the review.
4. Discussion
Two main approaches were identified in RF-EMF exposure studies: spot measurements and mixed methodologies. Spot measurements involve taking measurements at specific locations during a fixed period of time, while mixed methodologies combine different approaches, such as personal measurements with volunteers, mobile measurements with trained researchers, and prediction models.
Spot measurements allow for the intensity of the electromagnetic wave and, therefore, the exposure in specific locations chosen by the researcher. In studies that aim to characterize the signals from RF-EMF, they are widely used because they allow the knowledge of the exposure in a room, a classroom, a work area, or a laboratory environment. Spot measurements are key in research on electromagnetic waves because they help analyze propagation patterns and signal losses within buildings, and they are particularly useful for the study and design of wireless networks.
We know that spot measurements have specific limitations, such as fluctuations in the intensity of the RF signal that can vary due to changes in the environment or the influence of other electronic devices. It is known that a spot measurement is not able to capture these temporal variations. There are also limitations with the frequency bands that can lead to obtaining values far from the real ones. A single measurement does not provide us with information on how an RF wave interacts with other variables (people, obstacles, etc.). But these types of measurements help us understand the sophisticated way in which waves interact with the medium in which they travel.
If we want to compare the different studies in which RF-EMF exposure measures have been carried out, we realize that it is difficult to make a direct comparison of the results since both the methodologies and the equipment used are different. For this reason, it is necessary to define the objectives of the different studies and, accordingly, determine the type of study and select the measurement and analysis method, measurement devices, even the microenvironments and the subjects that will participate in the study.
As Jalilian [123] has highlighted in his review, different study protocols could affect the results; for instance, in measurements with volunteers, the body effect could be one of the main factors of underestimation of the exposure, including the use of their electronic devices during the measurement process. In the spot measurements, one of the aspects that could affect the results is, for instance, the inadequate selection of the chosen spatio-temporal points or the measurements recorded below the equipment’s detection limit. These types of difficulties can be solved by following the strategies used by other researchers, as specified in each study. Just to highlight some, on the one hand, to avoid the effect on the body, two exposimeters have been used (one on each side of the waist of the study subject) or carrying the exposimeter above the head; and on the other hand, to know the intensity levels at unmeasured points, interpolation methods have been used.
We want to highlight the 23 systematic reviews published in this field of study that have also helped us find publications on the RF-EMF [30,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142], reviews cited in the latest review by Ramirez-Vazquez [30] that is based on the PRISMA guidelines, combining the PECO methodology and the CASPe instrument.
We would like to highlight some of the works cited in this review, which were conducted by Joseph, Chiaramello, Roosli, Markussen, Jalilian, and Ramirez-Vazquez. Joseph [50] evaluates the in-situ exposure to RF-EMF from base stations of emerging wireless technologies in 311 locations, 68 indoors and 243 outdoors, distributed in three European countries (Belgium, the Netherlands and Sweden) using spectrum analyzers. It has been extensive study, and the results are valued well below the limits allowed by ICNIRP. We see that the maximal total field value was measured in a residential environment and was equal to 3.9 V/m (0.0255 W/m2) from GSM900 signals, 11 times below the ICNIRP reference levels for electric field strength.
Chiaramello [127] also reports that from the last ten years of studies reviewed on RF-EMF exposure in indoor environments, the highest average maximum exposure levels considering all RF-EMF frequency bands were 1.14 V/m (0.0034 W/m2) in offices, which are also very far from the maximum permitted values.
The contributions of Roosli [142] are also very interesting, reporting that the exposure cut-off points for the most exposed groups were lower than 0.5 V/m (663.13 µW/m2) in all studies, a value that is much lower than the reference levels established by the ICNIRP. On the other hand, Markussen [105], who obtained an overview of the changes in exposure when new technologies were introduced during the period 2013 to 2019, reported that the population exposure is well below the limits established by the ICNIRP and relatively constant over time despite the introduction of new technologies. In this same study, Markussen shows a graph with the total values of all frequency bands measured in relation to the limit values for the different measurement points. We could even see that there is a value of 200,000 µW/m2 in the 800 MHz band in 2017 (Figure 5 of this review) that seems to be high, but it really is not; this value is equivalent to 0.20 W/m. Markussen highlights that levels increased in 2017 and then decreased again at the end of the year and beyond 2018 due to reconfigurations at mobile operators and the installation of new base stations. Some UMTS base stations were removed during the same period, and with the implementation of 4G technology, these totals also decreased.
In another of the most recent works, Jalilian [123], who has reviewed 144 investigations, shows that in homes, schools and offices, the average exposure to RF-EMF was between 0.04 and 0.76 V/m (4.24 µW/m2 and 1532.10 µW/m2, respectively); and the mean values for outdoor exposure ranged between 0.07 and 1.27 V/m (13.00 µW/m2 and 4278.25 µW/m2, respectively), with the downlink signals from mobile phone base stations being the most significant contributors. Finally, the highest levels ranged between 1.97 V/m (0.0103 W/m2) measured at public transport stations, with the downlink being the most significant. We also observed that the values are very small compared to the limits established by ICNIRP. The review that precedes the present article is Ramirez-Vazquez [30], which includes measurement studies with volunteers and/or with a trained researcher (touring a specific area, one or several microenvironments, an entire city, walking or in some means of transport), which covers the period from 1 January 1998 to 31 December 2021, in which other important and preceding reviews were also mentioned. In this last review, it is highlighted that after comparing 56 investigations, the minimum value was measured in Egypt with a value of 0.00100 μW/m2 (1.00 nW/m2) in 2007, and the highest average was measured in Belgium with a value of 285,000 μW/m2 (0.285 W/m2) in 2019, also very far from the reference limits established by the ICNIRP.
5. Conclusions
This study reviewed 86 scientific works on personal exposure to RF-EMF that conducted measurements through spot measurements and/or using different methods (mixed method) combining spot measurements, personal measurements with volunteers or with trained researchers, spatiotemporal exposure measurements and in some cases using model predictions.
In addition to the exposure measurement studies, we want to refer to a study recently published by McKenzie [143] in which electromagnetic fields produced by “smart” devices used daily in a modern “smart” home are measured. It is interesting to see the activity of these EMFs in different periods of time while they are used. This study has not been included in this review because although specific measures have been taken, exposure to these fields has not been measured.
As far as we know, today, despite the different methodologies used, the results are comparable with international reference levels and comparable between microenvironments and countries; although it is true that some values are higher than others, they are still lower than these reference levels. The minimum average was measured in Palestine at 0.0600 µW/m2 in 2017, and the maximum average was measured in Norway at 200,000 µW/m2 in 2022, equivalent to 0.200 W/m2, far below the permitted international reference levels. During the development of this work, we have seen that the statistical data confirm that the exposure levels to RF-EMF are much lower than the maximum levels allowed in the ICNIRP guidelines, both for the general public scenario (10 W/m2) and for the occupational scenario (50 W/m2). However, these values can change over time, considering the new 5G technologies introduced everywhere right at this moment, so it is recommended to stay vigilant and continue expanding research in this field.
As previously indicated, with this work, we want to help researchers scrutinize this field with a review that classifies, orders, and synthesizes, thus making a reference for future research and comparisons. We believe that in the future, some research areas may be prioritized in the field of radiofrequency electromagnetic exposure fields: exploring new measurement devices, such as the use of sensors that have already begun to be used to monitor RF-EMF [111], as well as carrying out longitudinal studies to evaluate possible long-term effects.
We want to highlight that in this society in which we currently live, in which we are always immersed in a sea of electromagnetic waves, the importance of clear and effective communication of the possible risks associated with RF-EMF exposure, as well as the need to educate the public on how to minimize exposure in everyday environments.
Author Contributions
All the authors, R.R.-V., I.E., E.A., and G.A.E.V., made a substantial contribution to this manuscript. R.R.-V., I.E., E.A., and G.A.E.V. collaborated in the drafting of the manuscript and discussed the results and the implications of the manuscript at all stages. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
R.R.-V. gratefully acknowledges financial support from the University of Castilla-La Mancha through the postdoctoral contract Margarita Salas MS2022, Junta de Comunidades de Castilla-La Mancha, through the predoctoral contract PREJCCM2019/13. E.A., I.E. and R.R.-V. gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Junta de Comunidades de Castilla-La Mancha of Spain, Project SBPLY/23/180225/00089, and from the University of Castilla-La Mancha grant number 2022-GRIN-34356.
Data Availability Statement
Not Applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fernández, M.; Guerra, D.; Gil, U.; Trigo, I.; Peña, I.; Arrinda, A. Measurements and Analysis of Temporal and Spatial Variability of WiFi Exposure Levels in the 2.4 GHz Frequency Band. Measurement 2020, 149, 106970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Vazquez, R.; Escobar, I.; Martinez-Plaza, A.; Arribas, E. Comparison of Personal Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields from Wi-Fi in a Spanish University over Three Years. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 160008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Vazquez, R.; Arabasi, S.; Al-Taani, H.; Sbeih, S.; Gonzalez-Rubio, J.; Escobar, I.; Arribas, E. Georeferencing of Personal Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields from Wi-Fi in a University Area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Vazquez, R.; Escobar, I.; Thielens, A.; Arribas, E. Measurements and Analysis of Personal Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields at Outdoor and Indoor School Buildings: A Case Study at a Spanish School. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 195692–195702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wel, L.; Vermeulen, R.; van Eijsden, M.; Vrijkotte, T.; Kromhout, H.; Huss, A. Radiofrequency Exposure Levels in Amsterdam Schools. Bioelectromagnetics 2017, 38, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thielens, A.; Vanveerdeghem, P.; Van Torre, P.; Gaengler, S.; Roeoesli, M.; Rogier, H.; Martens, L.; Joseph, W. A Personal, Distributed Exposimeter: Procedure for Design, Calibration, Validation, and Application. Sensors 2016, 16, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminzadeh, R.; Thielens, A.; Bamba, A.; Kone, L.; Gaillot, D.P.; Lienard, M.; Martens, L.; Joseph, W. On-Body Calibration and Measurements Using Personal Radiofrequency Exposimeters in Indoor Diffuse and Specular Environments. Bioelectromagnetics 2016, 37, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celaya-Echarri, M.; Azpilicueta, L.; Ramos, V.; Lopez-Iturri, P.; Falcone, F. Empirical and Modeling Approach for Environmental Indoor RF-EMF Assessment in Complex High-Node Density Scenarios: Public Shopping Malls Case Study. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 46755–46775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, C.R.; Thielens, A.; Redmayne, M.; Abramson, M.J.; Billah, B.; Sim, M.R.; Vermeulen, R.; Martens, L.; Joseph, W.; Benke, G. Measuring Personal Exposure from 900 MHz Mobile Phone Base Stations in Australia and Belgium Using a Novel Personal Distributed Exposimeter. Environ. Int. 2016, 92–93, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celaya-Echarri, M.; Azpilicueta, L.; Karpowicz, J.; Ramos, V.; Lopez-Iturri, P.; Falcone, F. From 2G to 5G Spatial Modeling of Personal RF-EMF Exposure Within Urban Public Trams. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 100930–100947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardell, L.; Koppel, T.; Carlberg, M.; Ahonen, M.; Hedendahl, L. Radiofrequency Radiation at Stockholm Central Railway Station in Sweden and Some Medical Aspects on Public Exposure to RF Fields. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frei, P.; Mohler, E.; Neubauer, G.; Theis, G.; Bürgi, A.; Fröhlich, J.; Braun-Fahrländer, C.; Bolte, J.; Egger, M.; Röösli, M. Temporal and Spatial Variability of Personal Exposure to Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Fields. Environ. Res. 2009, 109, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyare, R.N.; Volskiy, V.; Vandenbosch, G.A.E. Comparison of Peak Electromagnetic Exposures from Mobile Phones Operational in Either Data Mode or Voice Mode. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 110902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Vazquez, R.; Gonzalez-Rubio, J.; Escobar, I.; Suarez Rodriguez, C.D.P.; Arribas, E. Personal Exposure Assessment to Wi-Fi Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields in Mexican Microenvironments. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Vazquez, R.; Gonzalez-Rubio, J.; Arribas, E.; Najera, A. Characterisation of Personal Exposure to Environmental Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields in Albacete (Spain) and Assessment of Risk Perception. Environ. Res. 2019, 172, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Vazquez, R.; Gonzalez-Rubio, J.; Arribas, E.; Najera, A. Personal RF-EMF Exposure from Mobile Phone Base Stations during Temporary Events. Environ. Res. 2019, 175, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röösli, M.; Frei, P.; Bolte, J.; Neubauer, G.; Cardis, E.; Feychting, M.; Gajsek, P.; Heinrich, S.; Joseph, W.; Mann, S.; et al. Conduct of a Personal Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field Measurement Study: Proposed Study Protocol. Environ. Health 2010, 9, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagar, S.; Struchen, B.; Finta, V.; Eeftens, M.; Roosli, M. Use of Portable Exposimeters to Monitor Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field Exposure in the Everyday Environment. Environ. Res. 2016, 150, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICNIRP. Guidelines for Limiting Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields (100 kHz to 300 GHz). Health Phys. 2020, 118, 483–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IEEE. IEEE Standard for Safety Levels with Respect to Human Exposure to Electric, Magnetic, and Electromagnetic Fields, 0 Hz to 300 GHz. In IEEE Std C95.1-2019 (Revision of IEEE Std C95.1-2005/Incorporates IEEE Std C95.1-2019/Cor 1-2019); IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Vazquez, R.; Escobar, I.; Vandenbosch, G.A.E.; Arribas, E. Personal Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields: A Comparative Analysis of International, National, and Regional Guidelines. Environ. Res. 2024, 246, 118124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ITU International Telecommunication Union. ITU-T—Recommendations on Human Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields. Available online: https://www.itu.int/net/ITU-T/lists/standards.aspx?Group=5&Domain=40 (accessed on 13 September 2023).
- ICNIRP International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection. Guidelines for Limiting Exposure to Time-Varying Electric, Magnetic, and Electromagnetic Fields (up to 300 GHz). Health Phys. 1998, 74, 494–522. [Google Scholar]
- ICNIRP International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection. Review of Concepts, Quantities, Units, and Terminology for Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection. Health Phys. 1985, 49, 1329–1362. [Google Scholar]
- ICNIRP International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection. Statement on the “Guidelines for Limiting Exposure to Time-Varying Electric, Magnetic, and Electromagnetic Fields (up to 300 GHz)”. Health Phys. 2009, 97, 257–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA Statement for Reporting Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses of Studies That Evaluate Health Care Interventions: Explanation and Elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 134, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetzlaff, J.; Page, M.; Moher, D. The Prisma 2020 Statement: Development of and Key Changes in an Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. Value Health 2020, 23, S312–S313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Vazquez, R.; Escobar, I.; Vandenbosch, G.A.E.; Vargas, F.; Caceres-Monllor, D.A.; Arribas, E. Measurement Studies of Personal Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields: A Systematic Review. Environ. Res. 2023, 218, 114979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 Explanation and Elaboration: Updated Guidance and Exemplars for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, R.L.; Whaley, P.; Thayer, K.A.; Schünemann, H.J. Identifying the PECO: A Framework for Formulating Good Questions to Explore the Association of Environmental and Other Exposures with Health Outcomes. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CASPe Instrumentos Para La Lectura Crítica|CASPe. Programa de Habilidades En Lectura Crítica Español (Critical Appraisal Skills Programme Español). Available online: https://redcaspe.org/materiales/ (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Keow, M.A.; Radiman, S. Assessment of Radiofrequency/Microwave Radiation Emitted by the Antennas of Rooftop-Mounted Mobile Phone Base Stations. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2006, 121, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, K.R. Radiofrequency Exposure from Wireless LANS Utilizing Wi-Fi Technology. Health Phys. 2007, 92, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trcek, T.; Valic, B.; Gajsek, P. Measurements of Background Electromagnetic Fields in Human Environment. In 11th Mediterranean Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing 2007; Jarm, T., Kramar, P., Zupanic, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 16, pp. 222–225. ISBN 978-3-540-73043-9. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, W.; Vermeeren, G.; Verloock, L.; Heredia, M.M.; Martens, L. Characterization of Personal RF Electromagnetic Field Exposure and Actual Absorption for the General Public. Health Phys. 2008, 95, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bürgi, A.; Theis, G.; Siegenthaler, A.; Röösli, M. Exposure Modeling of High-Frequency Electromagnetic Fields. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2008, 18, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotsis, A.; Papanikolaou, N.; Komnakos, D.; Yalofas, A.; Constantinou, P. Non-Ionizing Electromagnetic Radiation Monitoring in Greece. Ann. Telecommun. 2008, 63, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomitsch, J.; Dechant, E.; Frank, W. Survey of Electromagnetic Field Exposure in Bedrooms of Residences in Lower Austria. Bioelectromagnetics 2010, 31, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, P.; Mohler, E.; Buergi, A.; Froehlich, J.; Neubauer, G.; Braun-Fahrlaender, C.; Roosli, M. Classification of Personal Exposure to Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Fields (RF-EMF) for Epidemiological Research: Evaluation of Different Exposure Assessment Methods. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buergi, A.; Frei, P.; Theis, G.; Mohler, E.; Braun-Fahrlaender, C.; Froehlich, J.; Neubauer, G.; Egger, M.; Roeoesli, M. A Model for Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field Predictions at Outdoor and Indoor Locations in the Context of Epidemiological Research. Bioelectromagnetics 2010, 31, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verloock, L.; Joseph, W.; Vermeeren, G.; Martens, L. Procedure for Assessment of General Public Exposure from Wlan in Offices and in Wireless Sensor Network Testbed. Health Phys. 2010, 98, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyman, A.; Khalid, M.; Calderon, C.; Addison, D.; Mee, T.; Maslanyj, M.; Mann, S. Assessment of Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields from Wireless Computer Networks (Wi-Fi) in Schools; Results of Laboratory Measurements. Health Phys. 2011, 100, 594–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, B.; Blas, J.; Lorenzo, R.M.; Fernandez, P.; Abril, E.J. Statistical Perturbations in Personal Exposure Meters Caused by the Human Body in Dynamic Outdoor Environments. Bioelectromagnetics 2011, 32, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolte, J.F.B.; van der Zande, G.; Kamer, J. Calibration and Uncertainties in Personal Exposure Measurements of Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields. Bioelectromagnetics 2011, 32, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montana Rufo, M.; Paniagua, J.M.; Jimenez, A.; Antolin, A. Exposure to High-Frequency Electromagnetic Fields (100 Khz-2 Ghz) in Extremadura (Spain). Health Phys. 2011, 101, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomitsch, J.; Dechant, E. Trends in Residential Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields from 2006 to 2009. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2012, 149, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breckenkamp, J.; Blettner, M.; Schuez, J.; Bornkessel, C.; Schmiedel, S.; Schlehofer, B.; Berg-Beckhoff, G. Residential Characteristics and Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field Exposures from Bedroom Measurements in Germany. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2012, 51, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, W.; Verloock, L.; Goeminne, F.; Vermeeren, G.; Martens, L. Assessment of RF Exposures from Emerging Wireless Communication Technologies in Different Environments. Health Phys. 2012, 102, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhami, A.K. Study of Electromagnetic Radiation Pollution in an Indian City. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 6507–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua, J.M.; Rufo, M.; Jimenez, A.; Antolin, A. The Spatial Statistics Formalism Applied to Mapping Electromagnetic Radiation in Urban Areas. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markakis, I.; Samaras, T. Radiofrequency Exposure in Greek Indoor Environments. Health Phys. 2013, 104, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beekhuizen, J.; Vermeulen, R.; Kromhout, H.; Buergi, A.; Huss, A. Geospatial Modelling of Electromagnetic Fields from Mobile Phone Base Stations. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 445, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, S.; Deschrijver, D.; Verloock, L.; Dhaene, T.; Martens, L.; Joseph, W. Assessment of Outdoor Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field Exposure through Hotspot Localization Using Kriging-Based Sequential Sampling. Environ. Res. 2013, 126, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, S.; Deschrijver, D.; Joseph, W.; Verloock, L.; Goeminne, F.; Martens, L.; Dhaene, T. Exposure Assessment of Mobile Phone Base Station Radiation in an Outdoor Environment Using Sequential Surrogate Modeling. Bioelectromagnetics 2013, 34, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeeren, G.; Markakis, I.; Goeminne, F.; Samaras, T.; Martens, L.; Joseph, W. Spatial and Temporal RF Electromagnetic Field Exposure of Children and Adults in Indoor Micro Environments in Belgium and Greece. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2013, 113, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Shao, Q.; Yang, L.; Qi, D.; Lin, J.; Lin, X.; Yu, Z. A Large-Scale Measurement of Electromagnetic Fields near GSM Base Stations in Guangxi, China for Risk Communication. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2013, 155, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beekhuizen, J.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Huss, A.; Bürgi, A.; Kromhout, H.; Vermeulen, R. Impact of Input Data Uncertainty on Environmental Exposure Assessment Models: A Case Study for Electromagnetic Field Modelling from Mobile Phone Base Stations. Environ. Res. 2014, 135, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbinello, D.; Joseph, W.; Huss, A.; Verloock, L.; Beekhuizen, J.; Vermeulen, R.; Martens, L.; Röösli, M. Radio-Frequency Electromagnetic Field (RF-EMF) Exposure Levels in Different European Outdoor Urban Environments in Comparison with Regulatory Limits. Environ. Int. 2014, 68, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbinello, D.; Joseph, W.; Verloock, L.; Martens, L.; Röösli, M. Temporal Trends of Radio-Frequency Electromagnetic Field (RF-EMF) Exposure in Everyday Environments across European Cities. Environ. Res. 2014, 134, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryz, K.; Karpowicz, J.; Leszko, W.; Zradzinski, P. Evaluation of Exposure to Electromagnetic Radiofrequency Radiation in the Indoor Workplace Accessible to the Public by the Use of Frequency-Selective Exposimeters. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2014, 27, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verloock, L.; Joseph, W.; Goeminne, F.; Martens, L.; Verlaek, M.; Constandt, K. Assessment of Radio Frequency Exposures in Schools, Homes, and Public Places in Belgium. Health Phys. 2014, 107, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.C.; Kim, W.-K.; Lee, G.-T.; Choi, H.-D.; Kim, N.; Pack, J.-K. Evaluation of Radiofrequency Exposure Levels From Multiple Wireless Installations in Population Dense Areas in Korea. Bioelectromagnetics 2014, 35, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahham, A.; Sharabati, A.; ALMasri, H. Public Exposure from Indoor Radiofrequency Radiation in the City of Hebron, West Bank-Palestine. Health Phys. 2015, 109, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryz, K.; Karpowicz, J. Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Radiation Exposure inside the Metro Tube Infrastructure in Warszawa. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2015, 34, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Miguel-Bilbao, S.; Garcia, J.; Ramos, V.; Blas, J. Assessment of Human Body Influence on Exposure Measurements of Electric Field in Indoor Enclosures. Bioelectromagnetics 2015, 36, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomitsch, J.; Dechant, E. Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields in Households-Trends From 2006 to 2012. Bioelectromagnetics 2015, 36, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachon-Garcia, F.T.; Fernandez-Ortiz, K.; Paniagua-Sanchez, J.M. Assessment of Wi-Fi Radiation in Indoor Environments Characterizing the Time & Space-Varying Electromagnetic Fields. Measurement 2015, 63, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielens, A.; Agneessens, S.; De Clercq, H.; Lecoutere, J.; Verloock, L.; Tanghe, E.; Aerts, S.; Puers, R.; Rogier, H.; Martens, L.; et al. On-Body Calibration and Measurements Using a Personal, Distributed Exposimeter for Wireless Fidelity. Health Phys. 2015, 108, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njera Lopez, A.; Gonzalez-Rubio, J.; Villalba Montoya, J.M.; Arribas, E. Using Multiple Exposimeters to Evaluate the Influence of the Body When Measuring Personal Exposition to Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Fields. COMPEL—Int. J. Comp. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2015, 34, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottou, S.; Nikolopoulos, D.; Yannakopoulos, P.H.; Vogiannis, E.; Petraki, E.; Panagiotaras, D.; Koulougliotis, D. Preliminary Background Indoor EMF Measurements in Greece. Phys. Med. 2015, 31, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvente, I.; Fernandez, M.F.; Perez-Lobato, R.; Davila-Arias, C.; Ocon, O.; Ramos, R.; Rios-Arrabal, S.; Villalba-Moreno, J.; Olea, N.; Nunez, M.I. Outdoor Characterization of Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Fields in a Spanish Birth Cohort. Environ. Res. 2015, 138, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuric, N.; Kljajic, D.; Kasas-Lazetic, K.; Bajovic, V. The SEMONT Continuous Monitoring of Daily EMF Exposure in an Open Area Environment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, S.; Joseph, W.; Maslanyj, M.; Addison, D.; Mee, T.; Colussi, L.; Kamer, J.; Bolte, J. Prediction of RF-EMF Exposure Levels in Large Outdoor Areas through Car-Mounted Measurements on the Enveloping Roads. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolte, J.F.B.; Maslanyj, M.; Addison, D.; Mee, T.; Kamer, J.; Colussi, L. Do Car-Mounted Mobile Measurements Used for Radio-Frequency Spectrum Regulation Have an Application for Exposure Assessments in Epidemiological Studies? Environ. Int. 2016, 86, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, J.T.; Joyner, K.H. Observations from National Italian Fixed Radiofrequency Monitoring Network. Bioelectromagnetics 2016, 37, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engiz, B.K.; Kurnaz, C. Long-Term Electromagnetic Field Measurement and Assessment for a Shopping Mall. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2017, 175, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Garcia, R.; Gil, I. Measurement of the Environmental Broadband Electromagnetic Waves in a Mid-Size European City. Environ. Res. 2017, 158, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedendahl, L.K.; Carlberg, M.; Koppel, T.; Hardell, L. Measurements of Radiofrequency Radiation with a Body-Borne Exposimeter in Swedish Schools with Wi-Fi. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Montero, R.; Alén-Cordero, C.; López-Espí, P.L.; Rigelsford, J.M.; Aguilera-Benavente, F.; Alpuente-Hermosilla, J. Long Term Variations Measurement of Electromagnetic Field Exposures in Alcalá de Henares (Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahham, A.; Sharabati, A.; ALMasri, H. Assessment of Public Exposure Form Wlans in the West Bank-Palestine. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2017, 176, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karipidis, K.; Henderson, S.; Wijayasinghe, D.; Tjong, L.; Tinker, R. Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields from Wi-Fi in Australian Schools. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2017, 175, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnaz, C.; Engiz, B.K.; Kose, U. An Empirical Study: The Impact of the Number of Users on Electric Field Strength of Wireless Communications. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2018, 182, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurnaz, C.; Engiz, B.K.; Bozkurt, M.C. Measurement and Evaluation of Electric Field Strength Levels in Primary and Secondary Schools in a Pilot Region. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2018, 179, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardell, L.; Carlberg, M.; Hedendahl, L.K. Radiofrequency Radiation from Nearby Base Stations Gives High Levels in an Apartment in Stockholm, Sweden: A Case Report. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 7871–7883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cansiz, M.; Abbasov, T.; Kurt, M.B.; Celik, A.R. Mapping of Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Field Exposure Levels in Outdoor Environment and Comparing with Reference Levels for General Public Health. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2018, 28, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallastegi, M.; Huss, A.; Santa-Marina, L.; Aurrekoetxea, J.J.; Guxens, M.; Ellen Birks, L.; Ibarluzea, J.; Guerra, D.; Roeoesli, M.; Jimenez-Zabala, A. Children’s Exposure Assessment of Radiofrequency Fields: Comparison between Spot and Personal Measurements. Environ. Int. 2018, 118, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, S.; Wiart, J.; Martens, L.; Joseph, W. Assessment of Long-Term Spatio-Temporal Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field Exposure. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyare, R.N.; Volskiy, V.; Vandenbosch, G.A.E. Study of the Correlation between Outdoor and Indoor Electromagnetic Exposure near Cellular Base Stations in Leuven, Belgium. Environ. Res. 2019, 168, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Yang, C.; Cai, R.S.; Ye, H.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Lin, K.; Song, J.; Huang, X.; et al. Analysis of the Relationship between Electromagnetic Radiation Characteristics and Urban Functions in Highly Populated Urban Areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kljajic, D.; Djuric, N. Comparative Analysis of EMF Monitoring Campaigns in the Campus Area of the University of Novi Sad. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 14735–14750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, S.; Van den Bossche, M.; Vergara, X.; Odie, S.; Verloock, L.; Martens, L.; Joseph, W. Spatial and Temporal Assessment of Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields Emitted by Smart Meters and Smart Meter Banks in Urban Environments. Environ. Res. 2020, 183, 109196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiaraviglio, L.; Di Paolo, C.; Bianchi, G.; Blefari-Melazzi, N. Is It Safe Living in the Vicinity of Cellular Towers? Analysis of Long-Term Human EMF Exposure at Population Scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.00910. [Google Scholar]
- Paniagua, J.M.; Rufo, M.; Jimenez, A.; Antolin, A. Dimensionless Coefficients for Assessing Human Exposure to Radio-Frequency Electromagnetic Fields Indoors and Outdoors in Urban Areas. Environ. Res. 2020, 183, 109188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurnaz, C.; Mutlu, M. Comprehensive Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field Measurements and Assessments: A City Center Example. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regrain, C.; Caudeville, J.; de Seze, R.; Guedda, M.; Chobineh, A.; de Doncker, P.; Petrillo, L.; Chiaramello, E.; Parazzini, M.; Joseph, W.; et al. Design of an Integrated Platform for Mapping Residential Exposure to Rf-Emf Sources. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarbu, A.; Miclaus, S.; Digulescu, A.; Bechet, P. Comparative Analysis of User Exposure to the Electromagnetic Radiation Emitted by the Fourth and Fifth Generations of Wi-Fi Communication Devices. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eeftens, M.; Dongus, S.; Burgler, A.; Roosli, M. A Real-World Quality Assessment Study in Six ExpoM-RF Measurement Devices. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.; De Giudici, P.; Genier, J.-C.; Cassagne, E.; Dore, J.-F.; Ducimetiere, P.; Evrard, A.-S.; Letertre, T.; Segala, C. Health Disturbances and Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields from Mobile-Phone Base Stations in French Urban Areas. Environ. Res. 2021, 193, 110583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giudici, P.; Genier, J.-C.; Martin, S.; Dore, J.-F.; Ducimetiere, P.; Evrard, A.-S.; Letertre, T.; Segala, C. Radiofrequency Exposure of People Living near Mobile-Phone Base Stations in France. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, I.; Félix, N.; Rivera, M.; Alonso, A.; Maestú, C. What Is the Radiation before 5G? A Correlation Study between Measurements in Situ and in Real Time and Epidemiological Indicators in Vallecas, Madrid. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryz, K.; Karpowicz, J.; Zradzinski, P. Complex Electromagnetic Issues Associated with the Use of Electric Vehicles in Urban Transportation. Sensors 2022, 22, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakovidis, S.; Apostolidis, C.; Manassas, A.; Samaras, T. Electromagnetic Fields Exposure Assessment in Europe Utilizing Publicly Available Data. Sensors 2022, 22, 8481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markussen, A.C.; Sjoemoen, T.-M.; Unander, E.H.; Klaeboe, L. Regular Measurements of EMF in a Representative Norwegian City-Constant Exposure over Time despite Introduction of New Technologies. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppel, T.; Ahonen, M.; Carlberg, M.; Hardell, L. Very High Radiofrequency Radiation at Skeppsbron in Stockholm, Sweden from Mobile Phone Base Station Antennas Positioned Close to Pedestrians’ Heads. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizeau, N.; Zahner, M.; Schindler, J.; Stephan, C.; Frohlich, J.; Gugler, M.; Ziegler, T.; Roosli, M. Comparison of Ambient Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field (RF-EMF) Levels in Outdoor Areas and Public Transport in Switzerland in 2014 and 2021. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 116921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Vazquez, R.; Escobar, I.; Moreno, J.J.H.; Martínez-Plaza, A.; Maffey, S.; Arribas, E. Personal Exposure from Free Wi-Fi Hotspots in Downtown Mexico City. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 91216–91225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrakis, C.; Theodorou, K.; Kiouvrekis, Y.; Alexias, A.; Kappas, C. Radiofrequency Exposure Levels in Greece. Bioelectromagnetics 2023, 44, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulugeta, B.A.; Wang, S.; Ben Chikha, W.; Liu, J.; Roblin, C.; Wiart, J. Statistical Characterization and Modeling of Indoor RF-EMF Down-Link Exposure. Sensors 2023, 23, 3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manassas, A.; Apostolidis, C.; Iakovidis, S.; Babas, D.; Samaras, T. A Study of the Long Term Changes in the Electromagnetic Environment Using Data from Continuous Monitoring Sensors in Greece. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Miguel-Bilbao, S.; Blas, J.; Ramos, V. Effective Analysis of Human Exposure Conditions with Body-Worn Dosimeters in the 2.4 GHz Band. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 135, e56525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miguel-Bilbao, S.; Ramos, V.; Blas, J. Assessment of Polarization Dependence of Body Shadow Effect on Dosimetry Measurements in 2.4 GHz Band. Bioelectromagnetics 2017, 38, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Cobos, F.J.; Paniagua-Sánchez, J.M.; Gordillo-Guerrero, A.; Marabel-Calderón, C.; Rufo-Pérez, M.; Jiménez-Barco, A. Personal Exposimeter Coupled to a Drone as a System for Measuring Environmental Electromagnetic Fields. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaramello, E.; Plets, D.; Fiocchi, S.; Bonato, M.; Tognola, G.; Parazzini, M.; Le Brusquet, L.; Martens, L.; Joseph, W.; Ravazzani, P. Innovative Stochastic Modeling of Residential Exposure to Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Field Sources. IEEE J. Electromagn. RF Microw. Med. Biol. 2021, 5, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, S.; Verloock, L.; Van den Bossche, M.; Martens, L.; Vergara, X.; Joseph, W. Emissions from Smart Meters and Other Residential Radiofrequency Sources. Health Phys. 2019, 116, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Vazquez, R.; Escobar, I.; Franco, T.; Arribas, E. Physical Units to Report Intensity of Electromagnetic Wave. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryz, K.; Zradzinski, P.; Karpowicz, J. The Role of the Location of Personal Exposimeters on the Human Body in Their Use for Assessing Exposure to the Electromagnetic Field in the Radiofrequency Range 98-2450MHz and Compliance Analysis: Evaluation by Virtual Measurements. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 272460–272472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, W.; Vermeeren, G.; Verloock, L.; Goeminne, F. In Situ Magnetic Field Exposure and ICNIRP-Based Safety Distances for Electronic Article Surveillance Systems. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2012, 148, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miguel-Bilbao, S.; Aguirre, E.; Lopez Iturri, P.; Azpilicueta, L.; Roldan, J.; Falcone, F.; Ramos, V. Evaluation of Electromagnetic Interference and Exposure Assessment from S-Health Solutions Based on Wi-Fi Devices. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 784362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Varsier, N.; Niksic, S.; Kocan, E.; Pejanovic-Djurisic, M.; Popovic, M.; Koprivica, M.; Neskovic, A.; Milinkovic, J.; Gati, A.; et al. Comparison of Average Global Exposure of Population Induced by a Macro 3G Network in Different Geographical Areas in France and Serbia. Bioelectromagnetics 2016, 37, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frei, P.; Mohler, E.; Buergi, A.; Froehlich, J.; Neubauer, G.; Braun-Fahrlaender, C.; Roosli, M. A Prediction Model for Personal Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Field Exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 408, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilian, H.; Eeftens, M.; Ziaei, M.; Röösli, M. Public Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields in Everyday Microenvironments: An Updated Systematic Review for Europe. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adair, E.R.; Bansal, R.; Bassen, H.; Black, D.; Bodemann, R.; Brecher, A.; Bushberg, J.T.; Chadwick, P.; Cohen, J.; D’Andrea, J.; et al. Comar Technical Information Statement: Expert Reviews on Potential Health Effects of Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields and Comments on the Bioinitiative Report. Health Phys. 2009, 97, 348–356. [Google Scholar]
- Baliatsas, C.; Van Kamp, I.; Bolte, J.; Schipper, M.; Yzermans, J.; Lebret, E. Non-Specific Physical Symptoms and Electromagnetic Field Exposure in the General Population: Can We Get More Specific? A Systematic Review. Environ. Int. 2012, 41, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolte, J.F.B. Lessons Learnt on Biases and Uncertainties in Personal Exposure Measurement Surveys of Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields with Exposimeters. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 724–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiaramello, E.; Bonato, M.; Fiocchi, S.; Tognola, G.; Parazzini, M.; Ravazzani, P.; Wiart, J. Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Fields Exposure Assessment in Indoor Environments: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopoulou, M.; Karabetsos, E. In Situ Measurements of Radiofrequency Exposure Levels in Greece from 2008 to 2013: A Multi-Parametric Annual Analysis. Bioelectromagnetics 2015, 36, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucurachi, S.; Tamis, W.L.M.; Vijver, M.G.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Bolte, J.F.B.; de Snoo, G.R. A Review of the Ecological Effects of Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields (RF-EMF). Environ. Int. 2013, 51, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duerrenberger, G.; Froehlich, J.; Roeoesli, M.; Mattsson, M.-O. EMF Monitoring-Concepts, Activities, Gaps and Options. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 9460–9479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, K.R.; Moulder, J.E. Wi-Fi and Health: Review of Current Status of Research. Health Phys. 2013, 105, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajsek, P.; Ravazzani, P.; Grellier, J.; Samaras, T.; Bakos, J.; Thuroczy, G. Review of Studies Concerning Electromagnetic Field (EMF) Exposure Assessment in Europe: Low Frequency Fields (50 Hz–100 kHz). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajsek, P.; Ravazzani, P.; Wiart, J.; Grellier, J.; Samaras, T.; Thuroczy, G. Electromagnetic Field Exposure Assessment in Europe Radiofrequency Fields (10 MHz–6 GHz). J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, C.; Pedrazzi, G.; Guizzardi, S. The Cellular Effects of Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields on Osteoblasts: A Review. Bioelectromagnetics 2019, 40, 211–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inyang, I.; Benke, G.; Mckenzie, R.; Abramson, M. Comparison of Measuring Instruments for Radiofrequency Radiation from Mobile Telephones in Epidemiological Studies: Implications for Exposure Assessment. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2008, 18, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, V.G.; Hardell, L.; Everaert, J.; Bortkiewicz, A.; Carlberg, M.; Ahonen, M. Epidemiological Evidence for a Health Risk from Mobile Phone Base Stations. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2010, 16, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, S. Assessing Personal Exposures to Environmental Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields. C. R. Phys. 2010, 11, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, J.E.; Foster, K.R.; Erdreich, L.S.; McNamee, J.P. Mobile Phones, Mobile Phone Base Stations and Cancer: A Review. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2005, 81, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pophof, B.; Burns, J.; Danker-Hopfe, H.; Dorn, H.; Egblomassé-Roidl, C.; Eggert, T.; Fuks, K.; Henschenmacher, B.; Kuhne, J.; Sauter, C.; et al. The Effect of Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields on Cognitive Performance in Human Experimental Studies: A Protocol for a Systematic Review. Environ. Int. 2021, 157, 106783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repacholi, M.H.; Lerchl, A.; Roosli, M.; Sienkiewicz, Z.; Auvinen, A.; Breckenkamp, J.; d’Inzeo, G.; Elliott, P.; Frei, P.; Heinrich, S.; et al. Systematic Review of Wireless Phone Use and Brain Cancer and Other Head Tumors. Bioelectromagnetics 2012, 33, 187–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röösli, M. Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field Exposure and Non-Specific Symptoms of Ill Health: A Systematic Review. Environ. Res. 2008, 107, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röösli, M.; Frei, P.; Mohler, E.; Hug, K. Systematic Review on the Health Effects of Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields from Mobile Phone Base Stations. Bull. World Health Organ. 2010, 88, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, R.J.; Iskra, S.; Knipe, P. Assessment of Radio Frequency Fields in the 2.45 GHz Band Produced by Smart Home Devices. Bioelectromagnetics 2024, 45, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).