Peptides and Their Mechanisms of Action in the Skin †
1. Introduction
2. An Overview of Publications and Intellectual Property Literature
2.1. Signal Peptides
2.2. Enzyme Inhibitors
2.3. Neurotransmitter Peptides
2.4. Carrier Peptides
- ActiMatrix: Peptide based mushroom Extract;
- Actimp 1.9.3: Hydrolyzed Lupine Protein
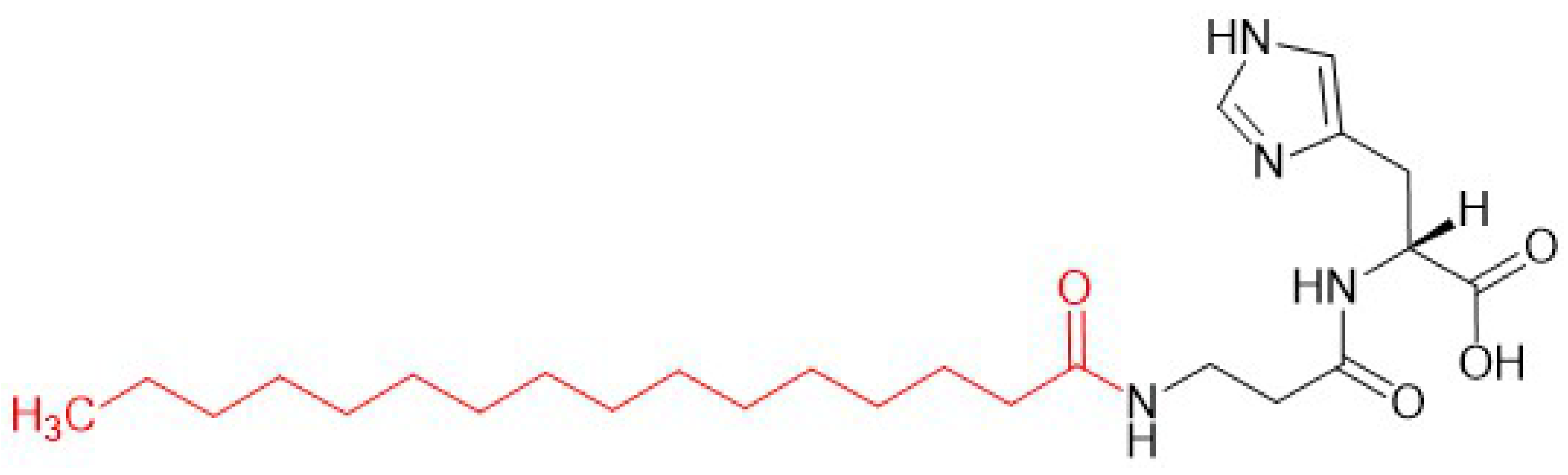
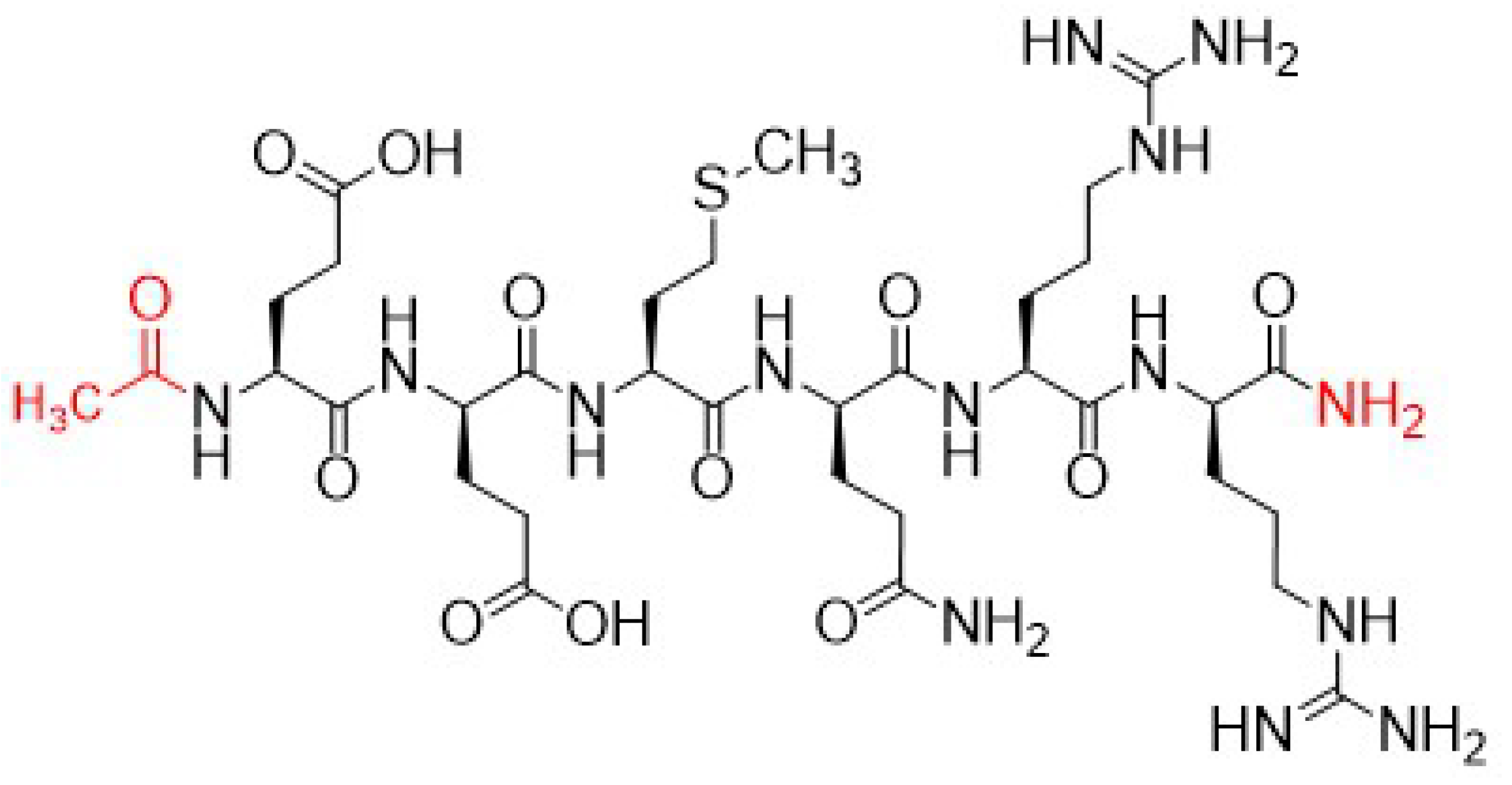
- Adifyline: Acetyl Hexapeptide-38
- Aldenine: Hydrolized Wheat Protein, Hydrolized Soy Protein, Tripeptide- 1
- Ascotide: Ascorbyl Phosphate Succinoyl Pentapeptide-12
- BeauActive MTP: Hydrolyzed milk protein
- Bio-Bustyl: Rahnella Soy Protein Ferment, Palmitoyl Oligopeptide
- Biopeptide CL: Palmitoyl Oligopeptide
- Biopeptide EL: Palmitoyl Oligopeptide
- BONT-L-Peptide: Palmitoyl Hexapeptide-19
- Caspaline 14: Hexapeptide-42
- ChroNOgen: Tetrapeptide-26
- ChroNOline: Caproyl Tetrapeptide-3
- Colhibin: Hydrolyzed Rice Protein
- Collaxyl: Hexapeptide-9
- Cytokino: Hydrolyzed Casein, Hydrolyzed Yeast Protein
- Decorinol: Tripeptide-9 Citrulline
- Decorinyl: Tripeptide-10 Citrulline
- Deepaline: Palmitoyl hydrolyzed Wheat Protein
- Delisens: Acetyl Hexapeptide-46
- DermaPep A350: Myristol Tripeptide-31
- DermaPep A420: Myristoyl Tetrapeptide-6
- Dermican: Acetyl Tetrapeptide-9
- dGlyage: Lysine HCl, Lecithin, Tripeptide-9 Citrulline
- Diffuporine: Acetyl Hexapeptide-37
- Drieline: Yeast Betaglucan
- Dynachondrine ISR: Hydrolized Soy Protein
- ECM Moduline: Palmitoyl Tripeptide-28
- ECM Protect: Tripeptide-2
- Effipulp: Hydrolyzed Avocado Protein
- Elhibin: Glycine Soja Protein
- Extracellium: Hydrolyzed Potato Protein
- Eyeseryl: Acetyl Tetrapeptide-5
- Granactive AGE: Palmitoyl Hexapeptide-14
- Inyline: Acetyl Hexapeptide-30
- IP 2000: Trifluoroacetyl Tripeptide-2
- Juvefoxo: Acetyl Hexapeptide-50
- Kollaren: Tripeptide-1
- Laminixyl IS: Heptapeptide
- Leuphasyl: Pentapeptide-18
- Liftline: Hydrolyzed Wheat Protein
- Lipacide PVB: Palmitoyl hydrolyzed Wheat Protein
- Lipeptide: Hydrolized Vegetable Protein
- Marine Filling Spheres: Atelocollagen
- Pentacare-NA: Hydrolyzed Wheat Gluten
- Pep 4-17: Tetrapeptide-17
- Pepha-Timp: Human oligopeptide-20
- Peptamide 6: Hexapeptide-11
- Peptide AC29: Acetyl Tripeptide-30 Citrulline
- Peptide Q10: Pentapeptide-34 Trifluoroacetate
- Peptide Vinci 01: Penta-decapeptide-1
- Peptide Vinci 02: Hexapeptide-3
- Peptiskin: Arginine/Lysine polypeptide
- Preregen: Glycine soja (Soybean) Protein, Oxido Reductases
- Preventhelia: Diaminopropionoyl Tripeptide-33
- Prodejine: Yeast Extract
- Prolixir S20: Dimer Tripeptide-43
- Quintescine: Dipeptide-4
- Raffermine: Hydrolyzed Soy Flour
- Relistase: Acetylarginyltriptophyl Diphenylglycine
- Renaissance: Hydrolyzed Wheat Protein, Palmitoyl Decapeptide-21, Decapeptide-22, Oligopeptide-78, Zinc Palmitoyl Nonapeptide-14
- Regu-Age: Hydrolyzed Rice Bran Protein, Glycine Soja Protein
- Ridulisse C: Hydrolyzed Soy Protein
- Serilesine: Hexapeptide-10
- Silusyne: Soybean (Glycine Soja) Oil, Lauryldimonium Hydroxypropyl Hydrolized Soy Protein, Acetyl Hexapeptide-39
- SNAP-7: Acetyl Heptapeptide-4
- Survixyl IS: Pentapeptide- 31
- Syn-Glycan: Tetradecyl Aminobutyroylvalyl-aminobutyric Urea Trifluoroacetate
- Syn-Tacks: Palmitoyl Dipeptide-5 Diaminobutyloyl Hydroxythreonine, Palmitoyl Dipeptide-6 Diaminohydroxybutyrate
- Syn-TC: Tetradecyl Aminobutyroylvalylaminobutyric Urea Trifluoroacetate, Palmitoyl Tripeptide-5, Palmitoyl Dipeptide-5 Diaminobutyroyl Hydroxythreonine
- Syniorage: Acetyl Tetrapeptide-11
- TEGO Pep 4-Even: Tetrapeptide-30
- Telangyn: Acetyl Tetrapeptide-33
- Telosense: Hydrolized Soy Protein, Hydrolized Yeast Protein
- Thermostressine: Acetyl Tetrapeptide-22
- Thymulen 4: Acetyl Tetrapeptide-2
- TIMP Peptide: Acetylhexapeptide-20
- Triactigen: Yeast Extract
- Trylagen: Hydrolyzed Wheat Protein, Hydrolyzed Soy Protein, Tripeptide-10 Citrulline, Tripeptide-1
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rawlings, A.V.; Harding, C.R. Moisturization and Skin Barrier Function. Dermatol. Ther. 2004, 17, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobin, D.J. Biochemistry of Human Skin—Our Brain on the Outside. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pai, V.; Bhandari, P.; Shukla, P. Topical Peptides as Cosmeceuticals. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2017, 83, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Wang, F.; Qu, L. Role of Peptide—Cell Surface Interactions in Cosmetic Peptide Application. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1267765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, R.; Bharadvaja, N. Nutricosmetics: Role in Health, Nutrition, and Cosmetics. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 2023, 89, 584–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc, L.T.N.; Moon, J.Y.; Lee, Y.C. Insights into Bioactive Peptides in Cosmetics. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, T.N.; Moraes, C.A.P. Bioactive Peptides: Applications and Relevance for Cosmeceuticals. Cosmetics 2018, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schagen, S.K. Topical Peptide Treatments with Effective Anti-Aging Results. Cosmetics 2017, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschard, O.; Doucet, A.; Leroux, R.; Mondon, P. Peptides, Compositions Comprising Them and Uses in Particular Cosmetic Uses 2014. EP 3 145 943 B1, 21 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tałałaj, U.; Uścinowicz, P.; Bruzgo, I.; Surażyński, A.; Zaręba, I.; Markowska, A. The Effects of a Novel Series of KTTKS Analogues on Cytotoxicity and Proteolytic Activity. Molecules 2019, 24, 3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szychowski, K.A.; Skóra, B. Elastin-Derived Peptides (EDPs) Affect Gene and Protein Expression in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells (HMSCs)—Preliminary Study. Cytokine 2024, 182, 156725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skóra, B.; Piechowiak, T.; Szychowski, K.A. Interaction Between Aging-Related Elastin-Derived Peptide (VGVAPG) and Sirtuin 2 and Its Impact on Functions of Human Neuron Cells in an In Vitro Model. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreno Serraima, C.; Garcia Sanz, N.; Cebrian Puche, J.; Alminana Domenech, N.; Ferrer Montiel, A.; Van Den Nest, W. Useful Peptides in the Treatmnet and/or Care of Skin, Mucouses and/or Leather and Its Use in Cosmetic or Pharmaceutical Compositions. EP 2 349 972, 23 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhmak, M.N.; Utkin, Y.N.; Andreeva, T.V.; Kudryavtsev, D.S.; Kryudova, E.V.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Shelukhina, I.V.E. Peptide Inhibitors of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. US 9550,808 B2, 20 January 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Waugh, J. Compositions for Topical Application of Compounds. US 2017/0290778 A1, 14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Wei, X. Improvement of Mild Photoaged Facial Skin in Middle-Aged Chinese Females by a Supramolecular Retinol plus Acetyl Hexapeptide-1 Containing Essence. Ski. Health Dis. 2023, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boo, Y.C. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factors Associated with Hair Graying (Canities) and Therapeutic Potential of Plant Extracts and Phytochemicals. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida Scalvino, S.; Chapelle, A.; Hajem, N.; Lati, E.; Gasser, P.; Choulot, J.C.; Michel, L.; Hocquaux, M.; Loing, E.; Attia, J.; et al. Efficacy of an Agonist of α-MSH, the Palmitoyl Tetrapeptide-20, in Hair Pigmentation. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2018, 40, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer Montiel, A.V.; Alminana Domenech, N.; Cebrian Puche, J.; Van Den Nest, W.; Carreno Serraima, C.; Delgado Gonzalez, R. Compounds Useful in the Treatment and/or Care of the Skin and Their Cosmetic or Pharmaceutical Compositions. EP 2 986 626 B1, 15 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Xiao, S.; Pan, P.; Li, P.; Huo, J. The Anti-Wrinkle Efficacy of Argireline, a Synthetic Hexapeptide, in Chinese Subjects: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2013, 14, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, G.S.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, J.H.; An, S.K.; Choe, T.B.; Kwon, T.J.; Pyo, H.B.; Lee, B.C. Black Rice (Oryza Sativa L. Var. Japonica) Hydrolyzed Peptides Induce Expression of Hyaluronan Synthase 2 Gene in HaCaT Keratinocytes. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 17, 271–279. [Google Scholar]
- Blanes-Mira, C.; Clemente, J.; Jodas, G.; Gil, A.; Fernández-Ballester, G.; Ponsati, B.; Gutierrez, L.; Pérez-Payá, E.; Ferrer-Montiel, A. A Synthetic Hexapeptide (Argireline) with Antiwrinkle Activity. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2002, 24, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truniger, S.; Wolfinger, T. Personal Care Composition. US 11,278,475 B2, 5 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Siméon, A.; Emonard, H.; Hornebeck, W.; Maquart, F. The Tripeptide-Copper Complex Glycyl-L-Histidyl-L-Lysine-Cu2+ Stimulates Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Expression by Fibroblast Cultures. Life Sci. 2000, 67, 2257–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maquart, F.X.; Pickart, L.; Laurent, M.; Gillery, P.; Monboisse, J.C.; Borel, J.P. Stimulation of Collagen Synthesis in Fibroblast Cultures by the Tripeptide-Copper Complex Glycyl-L-Histidyl-L-Lysine-Cu2+. FEBS Lett. 1988, 238, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickart, L.; Lovejoy, S. Biological Activity of Human Plasma Copper-Binding Growth Factor Glycyl-L-Histidyl-L-Lysine. Methods Enzymol. 1987, 147, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickart, L.; Vasquez-Soltero, J.M.; Margolina, A. GHK Peptide as a Natural Modulator of Multiple Cellular Pathways in Skin Regeneration. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 648108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.R.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.I.; Yang, S.R. The Tri-Peptide GHK-Cu Complex Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharideinduced Acute Lung Injury in Mice. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 58405–58417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosto, R.; Vecchio, G.; Bellia, F. New Biotinylated GHK and Related Copper(II) Complex: Antioxidant and Antiglycant Properties In Vitro against Neurodegenerative Disorders. Molecules 2023, 28, 6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Waszkielewicz, A.M.; Mirosław, K. Peptides and Their Mechanisms of Action in the Skin. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11495. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411495
Waszkielewicz AM, Mirosław K. Peptides and Their Mechanisms of Action in the Skin. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(24):11495. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411495
Chicago/Turabian StyleWaszkielewicz, Anna Maria, and Kaja Mirosław. 2024. "Peptides and Their Mechanisms of Action in the Skin" Applied Sciences 14, no. 24: 11495. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411495
APA StyleWaszkielewicz, A. M., & Mirosław, K. (2024). Peptides and Their Mechanisms of Action in the Skin. Applied Sciences, 14(24), 11495. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411495




