Color Changes of a Heat-Polymerized Polymethyl-Methacrylate (PMMA) and Two 3D-Printed Denture Base Resin Materials Exposed to Staining Solutions: An In Vitro Spectrophotometric Study
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Resin Disc Specimen Production
2.2. Staining Solution Preparation
2.3. Immersion Protocol
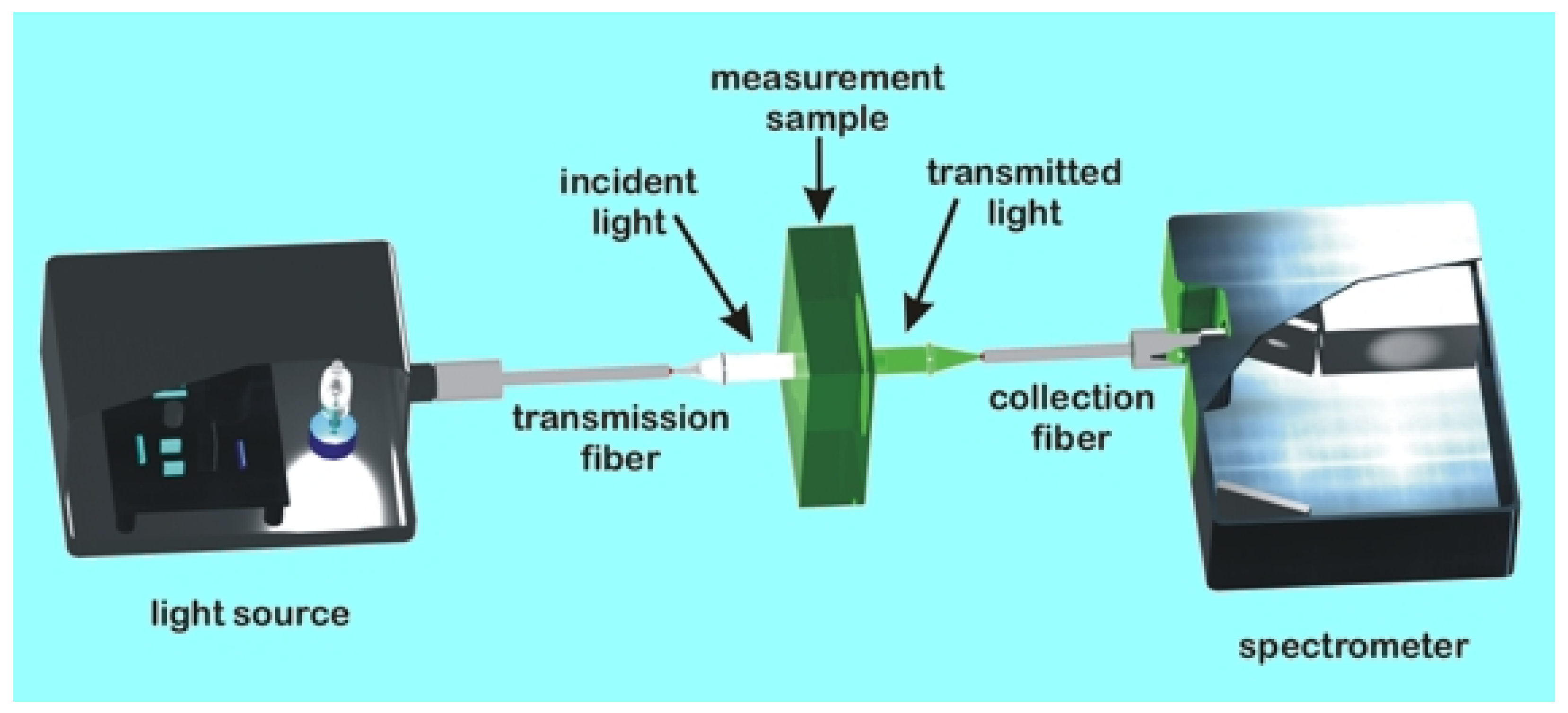
2.4. Color Measurement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
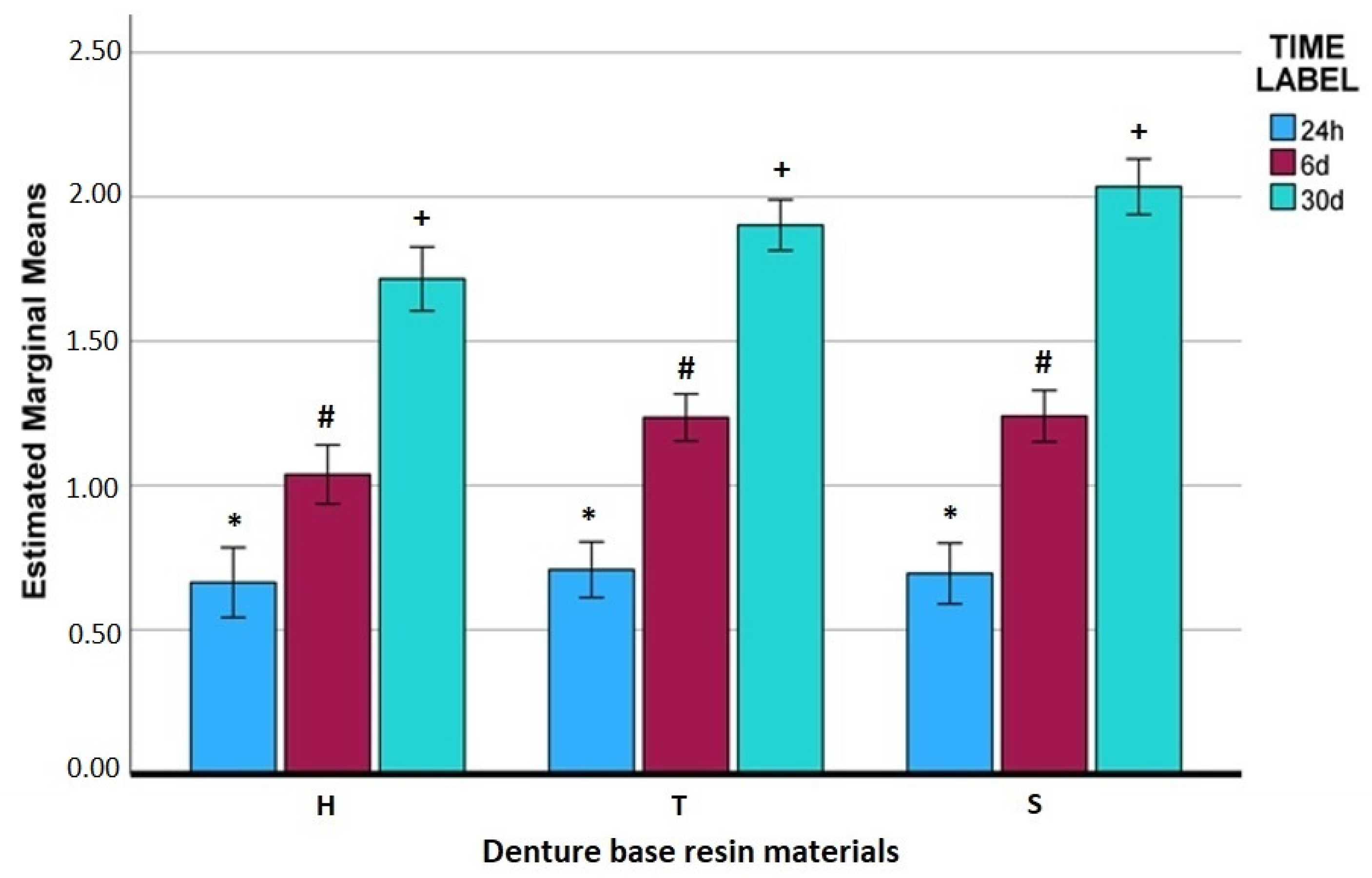
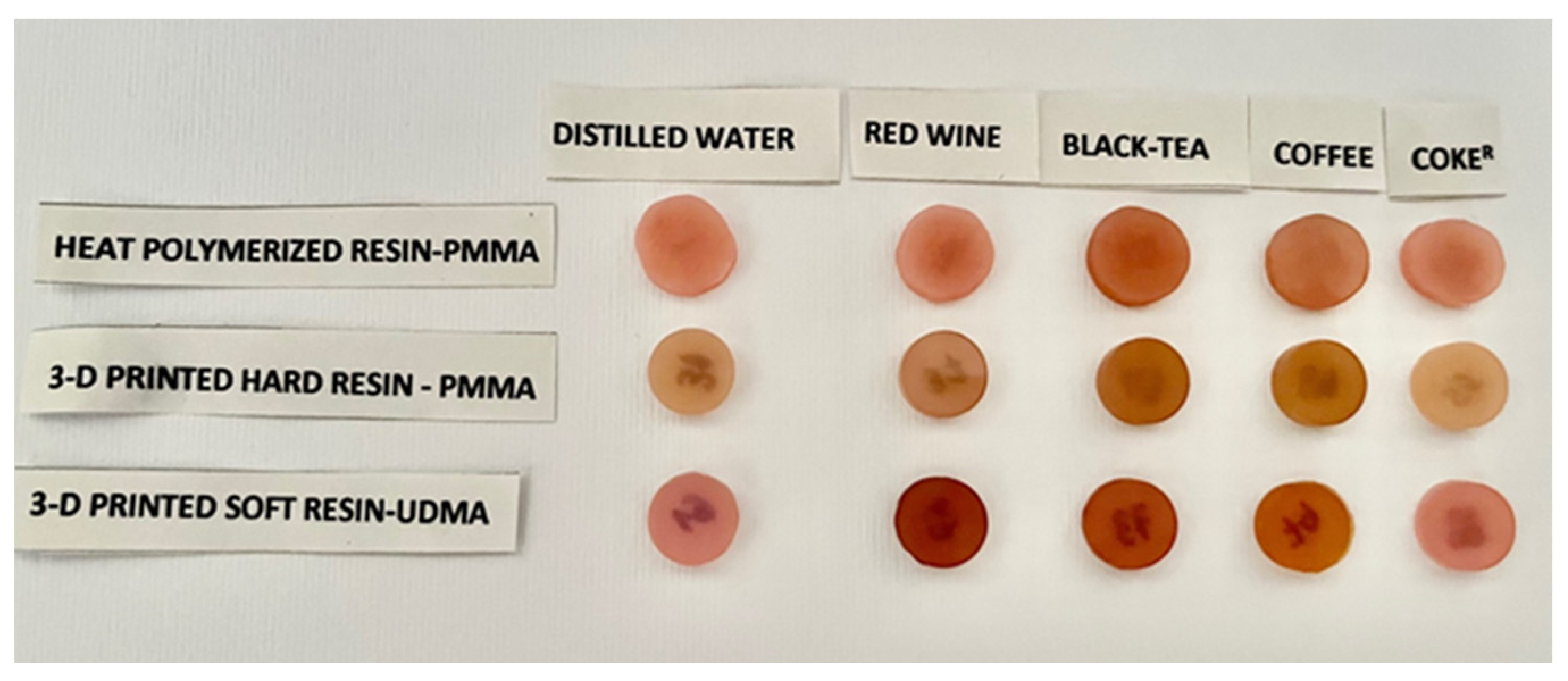
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anadioti, E.; Musharbash, L.; Blatz, M.B.; Papavasiliou, G.; Kamposiora, P. 3D printed complete removable dental prostheses: A narrative review. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantaros, A.; Soulis, E.; Alysandratou, E. Digitization of Ancient Artefacts and Fabrication of Sustainable 3D-Printed Replicas for Intended Use by Visitors with Disabilities: The Case of Piraeus Archaeological Museum. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantaros, A.; Ganetsos, T. From Static to Dynamic: Smart Materials Pioneering Additive Manufacturing in Regenerative Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantaros, A. Bio-Inspired Materials: Exhibited Characteristics and Integration Degree in Bio-Printing Operations. Am. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2022, 15, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantaros, A. 3D Printing in Regenerative Medicine: Technologies and Resources Utilized. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantaros, A.; Petrescu, F.I.T.; Abdoli, H.; Diegel, O.; Chan, S.; Iliescu, M.; Ganetsos, T.; Munteanu, I.S.; Ungureanu, L.M. Additive Manufacturing for Surgical Planning and Education: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantaros, A.; Ganetsos, T.; Petrescu, F.I.T. Transforming Object Design and Creation: Biomaterials and Contemporary Manufacturing Leading the Way. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Chen, C.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Hou, X.; Li, K.; Lu, X.; Shi, H.; Lee, E.-S.; Jiang, H.B. A Review of 3D Printing in Dentistry: Technologies, Affecting Factors, and Applications. Scanning 2021, 2021, 9950131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhallak, K.; Hagi-Pavli, E.; Nankali, A. A review on clinical use of CAD/CAM and 3D printed dentures. Br. Dent. J. 2023, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorsandi, D.; Fahimipour, A.; Abasian, P.; Saber, S.S.; Seyedi, M.; Ghanavati, S.; Ahmad, A.; De Stephanis, A.A.; Taghavinezhaddilami, F.; Leonova, A.; et al. 3D and 4D printing in dentistry and maxillofacial surgery: Printing techniques, materials, and applications. Acta Biomater. 2021, 122, 26–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla-León, M.; Özcan, M. Additive Manufacturing Technologies Used for Processing Polymers: Current Status and Potential Application in Prosthetic Dentistry. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrova, M.; Corsalini, M.; Kazakova, R.; Vlahova, A.; Chuchulska, B.; Barile, G.; Capodiferro, S.; Kazakov, S. Comparison between Conventional PMMA and 3D Printed Resins for Denture Bases: A Narrative Review. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-M.; Lai, Y.-L.; Lee, S.-Y. Mechanical properties, accuracy, and cytotoxicity of UV-polymerized 3D printing resins composed of BisEMA, UDMA, and TEGDMA. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 123, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumcu, E.; Cilingir, A.; Gencel, B.; Sülün, T. Flexural properties of a light-cure and a self-cure denture base materials compared to conventional alternatives. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2011, 3, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binaljadm, T.M. Flexible Denture: A Literature Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e55425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla-León, M.; Meyers, M.J.; Zandinejad, A.; Özcan, M. A review on chemical composition, mechanical properties, and manufacturing work flow of additively manufactured current polymers for interim dental restorations. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2019, 31, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-C.; Byeon, D.-J.; Jeong, E.-J.; Go, H.-B.; Yang, S.-Y. Color stability, surface, and physicochemical properties of three-dimensional printed denture base resin reinforced with different nanofillers. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kentrou, C.; Papadopoulos, T.; Lagouvardos, P. Color changes in staining solutions of four light-cured indirect resin composites. Odontology 2014, 102, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfouzan, A.F.; Alotiabi, H.M.; Labban, N.; Al-Otaibi, H.N.; Al Taweel, S.M.; AlShehri, H.A. Color stability of 3D-printed denture resins: Effect of aging, mechanical brushing and immersion in staining medium. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2021, 13, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, E.-S.; Cha, H.-S.; Kim, T.-H.; Ahn, J.-S.; Lee, J.-H. Color stability of three dimensional-printed denture teeth exposed to various colorants. J. Korean Acad. Prosthodont. 2020, 58, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakmak, G.; Weber, F.A.; Donmez, M.B.; Kahveci, Ç.; Schimmel, M.; Yilmaz, B. Effect of coffee thermocycling on the surface roughness and stainability of denture base materials with different chemical compositions manufactured with additive and subtractive technologies. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2024, 36, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.-W.; Kim, J.-E.; Choi, Y.-J.; Shin, S.-H.; Nam, N.-E.; Shim, J.-S.; Lee, K.-W. Evaluation of the color stability of 3D-printed crown and bridge materials against various sources of discoloration: An in vitro study. Materials 2020, 13, 5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niakoula, D.; Raptis, I.; Goustouridis, D.; Argitis, P. Glass transition temperature monitoring in bilayer and patterned photoresist films. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 1 Regul. Pap. Short Notes Rev. Pap. 2004, 43, 5247–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceau, S.; Tortai, J.-H.; Tillier, J.; Vourdas, N.; Gogolides, E.; Raptis, I.; Beltsios, K.; van Werden, K. Thickness-dependent glass transition temperature of thin resist films for high resolution lithography. Microelectron. Eng. 2006, 83, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoli, K.; Goustouridis, D.; Chatzandroulis, S.; Raptis, I.; Valamontes, E.S.; Sanopoulou, M. Vapor sorption in thin supported polymer films studied by white light interferometry. Polymer 2006, 47, 6117–6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vourdas, N.; Karadimos, G.; Goustouridis, D.; Gogolides, E.; Boudouvis, A.G.; Tortai, J.; Beltsios, K.; Raptis, I. Multiwavelength interferometry and competing optical methods for the thermal probing of thin polymeric films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 4764–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drygiannakis, D.; Raptis, I.; Patsis, G.; Boudouvis, A.; Vanwerden, K. Processing effects on the dissolution properties of thin chemically amplified photoresist films. Microelectron. Eng. 2008, 85, 955–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarantopoulou, E.; Kollia, Z.; Cefalas, A.; Manoli, K.; Sanopoulou, M.; Goustouridis, D.; Chatzandroulis, S.; Raptis, I. Surface nano/micro functionalization of PMMA thin films by 157nm irradiation for sensing applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 1710–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieh, M.T.; Waddell, J.N.; Choi, J.J.E. Optical Properties and Color Stability of Denture Teeth-A Systematic Review. J. Prosthodont. 2022, 31, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrova, M.; Vlahova, A.; Hristov, I.; Kazakova, R.; Chuchulska, B.; Gladysheva, A. Color Changes of 3D Printed and Conventional Dental Resins for Removable Prosthodontics After Immersion in Different Staining Agents. J. Imab Annu. Proceeding (Sci. Pap.) 2023, 29, 4861–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Feng, D.; Song, A.; Gong, H.; Zhu, S. Effects of organic-inorganic hybrid coating on the color stability of denture base resins. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2015, 115, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, S.; Kamnoedboon, P.; Özcan, M.; Srinivasan, M. CAD/CAM Complete Denture Resins: An In Vitro Evaluation of Color Stability. J. Prosthodont. 2021, 30, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, C.; Guven, M.C.; Gencel, B.; Bural, C. A color stability comparison of conventional and cad/cam polymethyl methacrylate denture base materials. Acta Stomatol. Croat. 2019, 53, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregorius, W.C.; Kattadiyil, M.T.; Goodacre, C.J.; Roggenkamp, C.L.; Powers, J.M.; Paravina, R.D. Effects of ageing and staining on color of acrylic resin denture teeth. J. Dent. 2012, 40 (Suppl. S2), e47–e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hipólito, A.C.; Barão, V.A.; Faverani, L.P.; Ferreira, M.B.; Assunção, W.G. Color degradation of acrylic resin denture teeth as a function of liquid diet: Ultraviolet-visible reflection analysis. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 105005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polychronakis, N.; Lagouvardos, P.; Polyzois, G.; Sykaras, N.; Zoidis, P. Color changes of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) and polyoxymethelene (POM) denture resins on single and combined staining/cleansing action by CIELab and CIEDE2000 formulas. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2020, 64, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berli, C.; Thieringer, F.M.; Sharma, N.; Müller, J.A.; Dedem, P.; Fischer, J.; Rohr, N. Comparing the mechanical properties of pressed, milled, and 3D-printed resins for occlusal devices. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 124, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietschi, D.; Campanile, G.; Holz, J.; Meyer, J.-M. Comparison of the color stability of ten new-generation composites: An in vitro study. Dent. Mater. 1994, 10, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imirzalioglu, P.; Karacaer, O.; Yilmaz, B.; Ozmen Msc, I. color stability of denture acrylic resins and a soft lining material against tea, coffee, and nicotine. J. Prosthodont. 2010, 19, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanasiou, I.; Papavasiliou, G.; Kamposiora, P.; Zoidis, P. Effect of Staining Solutions on Color Stability, Gloss and Surface Roughness of Removable Partial Dental Prosthetic Polymers. J. Prosthodont. 2022, 31, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerby, R.E.; Knobloch, L.A.; Schricker, S.; Gregg, B. Synthesis and evaluation of modified urethane dimethacrylate resins with reduced water sorption and solubility. Dent. Mater. 2009, 25, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gad, M.M.; Fouda, S.M.; Abualsaud, R.; Alshahrani, F.A.; Al-Thobity, A.M.; Khan, S.Q.; Akhtar, S.; Ateeq, I.S.; Helal, M.A.; Al-Harbi, F.A. Strength and Surface Properties of a 3D-Printed Denture Base Polymer. J. Prosthodont. 2022, 31, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.R.; Cui, G.; Rigg, B. The development of the CIE 2000 colour-difference formula: CIEDE2000. Color Res. Appl. 2001, 26, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qarni, F.D.; Gad, M.M. Printing Accuracy and Flexural Properties of Different 3D-Printed Denture Base Resins. Materials 2022, 15, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantaros, A.; Ganetsos, T.; Petrescu, F.I.T.; Ungureanu, L.M.; Munteanu, I.S. Post-Production Finishing Processes Utilized in 3D Printing Technologies. Processes 2024, 12, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Commercial Name | Composition | Lot No. | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meliodent pink (Heat-polymerized Denture Resin) |
Powder (polymethylmethacrylate) Liquid (methylmethacrylate, dimetha crylate) PMMA | KO10062 | Kulzer Gmbh, Hanau, Germany |
| Denta Base pink (Hard 3D-printed resin for denture base) | PMMA resin 7,7,9(or 7,9,9)-trimethyl-4,13-dioxo-3,14-dioxa-5,12-diazahexadecane-1,16-diyl bismethacrylate; Diphenyl(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl) phosphine oxide; Tetrahydrofurfuryl methacrylate | Not available | ASIGA Pty Ltd., Alexandria, Australia |
| Flexo Denture Base V2 pink (Soft 3D-printed resin) | Urethane dimethacrylate UDMA (methacrylyloxy–2-ethoxy–carbonyl amino)-2,4, 4 trimethythexane. This is a reaction product of 2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate and 2, 4, 4-trimethyl-hexamethylenediisocyanate–UDMA (according to the manufacturer’s information, sent by mail) | SNR202300021 | Senertec 3D Yazici, Izmir, Turkey |
| Lipton Black Tea; Origin, Kenya | Black tea 100% | L4 076 1 J3 01 L4 076 2 J3 01 L4 076 3 J3 01 | Ekaterra global Operations BV, Rotterdam, The Netherlands |
| Jacobs Kronung (filtered coffee) | Ground coffee grains | LK00942063 01 | Jacobs Douwe Egberts, DK Amsterdam, The Netherlands |
| Akres 2023 (dry red wine) | Alcohol 14% vol. | L 240221 | Produced and bottled by Skouras Winery, Argos, Greece |
| Coke® Original Taste (Coca-Cola) | Water, Sugar, Carbon dioxide, Caffeine, phosphoric acid, Other Aromatic substances | 20B43E29B | Coca-Cola HBC Cyprus, Nicosia, Cyprus |
| Mallinckrodt Silica gel | Silica gel | 4000834 | Mallinckrodt Chemical Works, St. Louis, MO, USA |
| KMG POLISH LIQUID | Alcohols, C-16-18, ethoxylated Aquatic Acute 1, H400; Aquatic Chronic 3, H412 2.5 | Z02SNB | CANDULOR AG, Clattpark (Opfikon), Switzerland |
| Groups | |
|---|---|
| Heat-polymerized resin | H (Heat) |
| Distilled water (control) | |
| Wine | |
| Black Tea | |
| Coffee | |
| Coke® | |
| 3D-printed Hard Resin | T (Tough) |
| Distilled water (control) | |
| Wine | |
| Black Tea | |
| Coffee | |
| Coke® | |
| 3D-printed Soft Resin | S (Soft) |
| Distilled water (control) | |
| Wine | |
| Black Tea | |
| Coffee | |
| Coke® | |
| 95% Confidence Interval | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time Label | Solution Type | Material | Mean | Std. Error | Lower Bound | Upper Bound |
| 24 h | Water | H | 0.103 | 0.136 | −0.168 | 0.374 |
| T | 0.084 | 0.108 | −0.131 | 0.299 | ||
| S | 0.116 | 0.118 | −0.119 | 0.351 | ||
| Red_Wine | H | 0.667 | 0.136 | 0.396 | 0.937 | |
| T | 0.955 | 0.108 | 0.740 | 1.170 | ||
| S | 1.101 | 0.118 | 0.866 | 1.336 | ||
| Black_Tea | H | 2.164 | 0.136 | 1.894 | 2.435 | |
| T | 2.096 | 0.108 | 1.881 | 2.311 | ||
| S | 1.953 | 0.118 | 1.717 | 2.188 | ||
| Coffee | H | 0.241 | 0.136 | −0.030 | 0.512 | |
| T | 0.179 | 0.108 | −0.037 | 0.394 | ||
| S | 0.209 | 0.118 | −0.026 | 0.445 | ||
| Coke® | H | 0.144 | 0.136 | −0.127 | 0.415 | |
| T | 0.228 | 0.108 | 0.012 | 0.443 | ||
| S | 0.097 | 0.118 | −0.138 | 0.332 | ||
| 6 days | Water | H | 0.184 | 0.115 | −0.045 | 0.413 |
| T | 0.252 | 0.091 | 0.070 | 0.434 | ||
| S | 0.093 | 0.100 | −0.106 | 0.292 | ||
| Red_Wine | H | 1.270 | 0.115 | 1.041 | 1.499 | |
| T | 1.895 | 0.091 | 1.713 | 2.077 | ||
| S | 2.348 | 0.100 | 2.149 | 2.547 | ||
| Black_Tea | H | 2.855 | 0.115 | 2.626 | 3.083 | |
| T | 3.119 | 0.091 | 2.937 | 3.301 | ||
| S | 2.744 | 0.100 | 2.546 | 2.943 | ||
| Coffee | H | 0.429 | 0.115 | 0.201 | 0.658 | |
| T | 0.393 | 0.091 | 0.211 | 0.575 | ||
| S | 0.539 | 0.100 | 0.340 | 0.737 | ||
| Coke® | H | 0.452 | 0.115 | 0.223 | 0.681 | |
| T | 0.519 | 0.091 | 0.337 | 0.701 | ||
| S | 0.478 | 0.100 | 0.280 | 0.677 | ||
| 30 days | Water | H | 0.602 | 0.124 | 0.355 | 0.849 |
| T | 1.075 | 0.099 | 0.879 | 1.272 | ||
| S | 0.992 | 0.108 | 0.778 | 1.207 | ||
| Red_Wine | H | 1.966 | 0.124 | 1.718 | 2.213 | |
| T | 2.746 | 0.099 | 2.550 | 2.943 | ||
| S | 2.992 | 0.108 | 2.777 | 3.207 | ||
| Black_Tea | H | 4.021 | 0.124 | 3.774 | 4.268 | |
| T | 3.882 | 0.099 | 3.686 | 4.079 | ||
| S | 4.175 | 0.108 | 3.960 | 4.390 | ||
| Coffee | H | 1.065 | 0.124 | 0.818 | 1.312 | |
| T | 0.833 | 0.099 | 0.637 | 1.030 | ||
| S | 1.011 | 0.108 | 0.796 | 1.226 | ||
| Coke® | H | 0.925 | 0.124 | 0.678 | 1.172 | |
| T | 0.973 | 0.099 | 0.776 | 1.169 | ||
| S | 1.005 | 0.108 | 0.790 | 1.220 | ||
| Mean Difference (I) Time Label (J) Time Label (I–J) | Std. Error | Sig. | 95% Confidence Interval | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||||
| 24 h | 6 days | −0.4823 * | 0.05012 | <0.001 | −0.6050 | −0.3595 |
| 30 days | −1.1952 * | 0.05183 | <0.001 | −1.3221 | −1.0683 | |
| 6 days | 24 h | 0.4823 * | 0.05012 | <0.001 | 0.3595 | 0.6050 |
| 30 days | −0.7129 * | 0.04762 | <0.001 | −0.8296 | −0.5963 | |
| 30 days | 24 h | 1.1952 * | 0.05183 | <0.001 | 1.0683 | 1.3221 |
| 6 days | 0.7129 * | 0.04762 | <0.001 | 0.5963 | 0.8296 | |
| (I) Solution Type | (J) Solution Type | (I–J) | Std. Error | Sig. | 95% Lower Bound | 95% Upper Bound |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Red_Wine | −1.4294 * | 0.06379 | <0.001 | −1.6139 | −1.2449 |
| Black_Tea | −2.6541 * | 0.06379 | <0.001 | −2.8387 | −2.4696 | |
| Coffee | −0.1647 | 0.06379 | 0.118 | −0.3492 | 0.0198 | |
| Coke® | −0.1606 | 0.06379 | 0.140 | −0.3451 | 0.0239 | |
| Red_Wine | Water | 1.4294 * | 0.06379 | <0.001 | 1.2449 | 1.6139 |
| Black_Tea | −1.2247 * | 0.06379 | <0.001 | −1.4093 | −1.0402 | |
| Coffee | 1.2647 * | 0.06379 | <0.001 | 1.0801 | 1.4492 | |
| Coke® | 1.2688 * | 0.06379 | <0.001 | 1.0843 | 1.4533 | |
| Black_Tea | Water | 2.6541 * | 0.06379 | <0.001 | 2.4696 | 2.8387 |
| Red_Wine | 1.2247 * | 0.06379 | <0.001 | 1.0402 | 1.4093 | |
| Coffee | 2.4894 * | 0.06379 | <0.001 | 2.3049 | 2.6739 | |
| Coke® | 2.4935 * | 0.06379 | <0.001 | 2.3090 | 2.6781 | |
| Coffee | Water | 0.1647 | 0.06379 | 0.118 | −0.0198 | 0.3492 |
| Red_Wine | −1.2647 * | 0.06379 | <0.001 | −1.4492 | −1.0801 | |
| Black_Tea | −2.4894 * | 0.06379 | <0.001 | −2.6739 | −2.3049 | |
| Coke® | 0.0041 | 0.06379 | 1.000 | −0.1804 | 0.1887 | |
| Coke® | Water | 0.1606 | 0.06379 | 0.140 | −0.0239 | 0.3451 |
| Red_Wine | −1.2688 * | 0.06379 | <0.001 | −1.4533 | −1.0843 | |
| Black_Tea | −2.4935 * | 0.06379 | <0.001 | −2.6781 | −2.3090 | |
| Coffee | −0.0041 | 0.06379 | 1.000 | −0.1887 | 0.1804 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vergos, V.; Ganetsos, T.; Kantaros, A.; Theocharopoulos, A.; Yannikakis, S. Color Changes of a Heat-Polymerized Polymethyl-Methacrylate (PMMA) and Two 3D-Printed Denture Base Resin Materials Exposed to Staining Solutions: An In Vitro Spectrophotometric Study. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11548. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411548
Vergos V, Ganetsos T, Kantaros A, Theocharopoulos A, Yannikakis S. Color Changes of a Heat-Polymerized Polymethyl-Methacrylate (PMMA) and Two 3D-Printed Denture Base Resin Materials Exposed to Staining Solutions: An In Vitro Spectrophotometric Study. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(24):11548. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411548
Chicago/Turabian StyleVergos, Vasileios, Theodore Ganetsos, Antreas Kantaros, Antonios Theocharopoulos, and Stavros Yannikakis. 2024. "Color Changes of a Heat-Polymerized Polymethyl-Methacrylate (PMMA) and Two 3D-Printed Denture Base Resin Materials Exposed to Staining Solutions: An In Vitro Spectrophotometric Study" Applied Sciences 14, no. 24: 11548. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411548
APA StyleVergos, V., Ganetsos, T., Kantaros, A., Theocharopoulos, A., & Yannikakis, S. (2024). Color Changes of a Heat-Polymerized Polymethyl-Methacrylate (PMMA) and Two 3D-Printed Denture Base Resin Materials Exposed to Staining Solutions: An In Vitro Spectrophotometric Study. Applied Sciences, 14(24), 11548. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411548








