The Vibro-Acoustic Characteristics Analysis of the Coupled System between Composite Laminated Rotationally Stiffened Plate and Acoustic Cavities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Modeling of the Unified Analysis Model of Vibro-acoustic Characteristics
2.1. Model Description
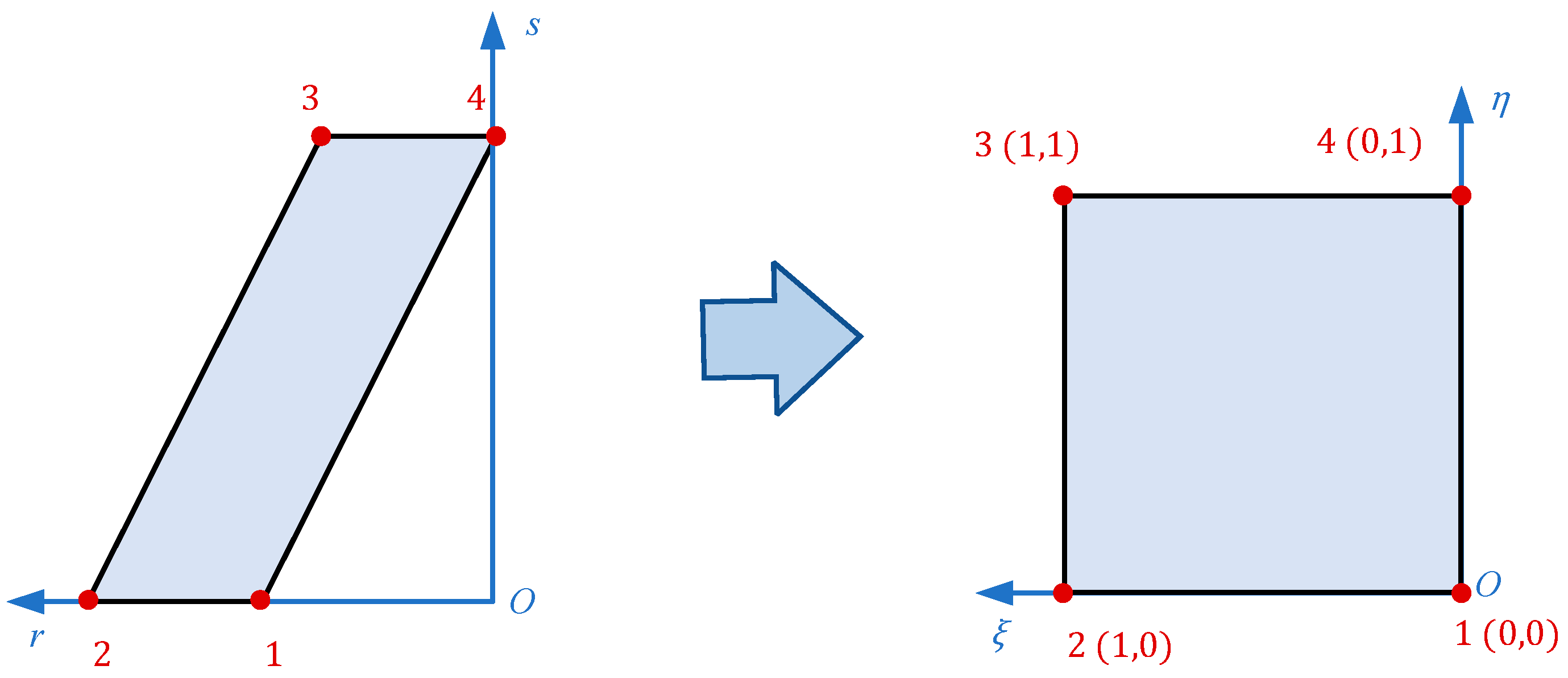
2.2. Construction of Allowable Displacement and Sound Pressure Functions
2.3. Stress-Strain and Displacement Relations
2.4. Energy Functional
3. Numerical Results and Discussion
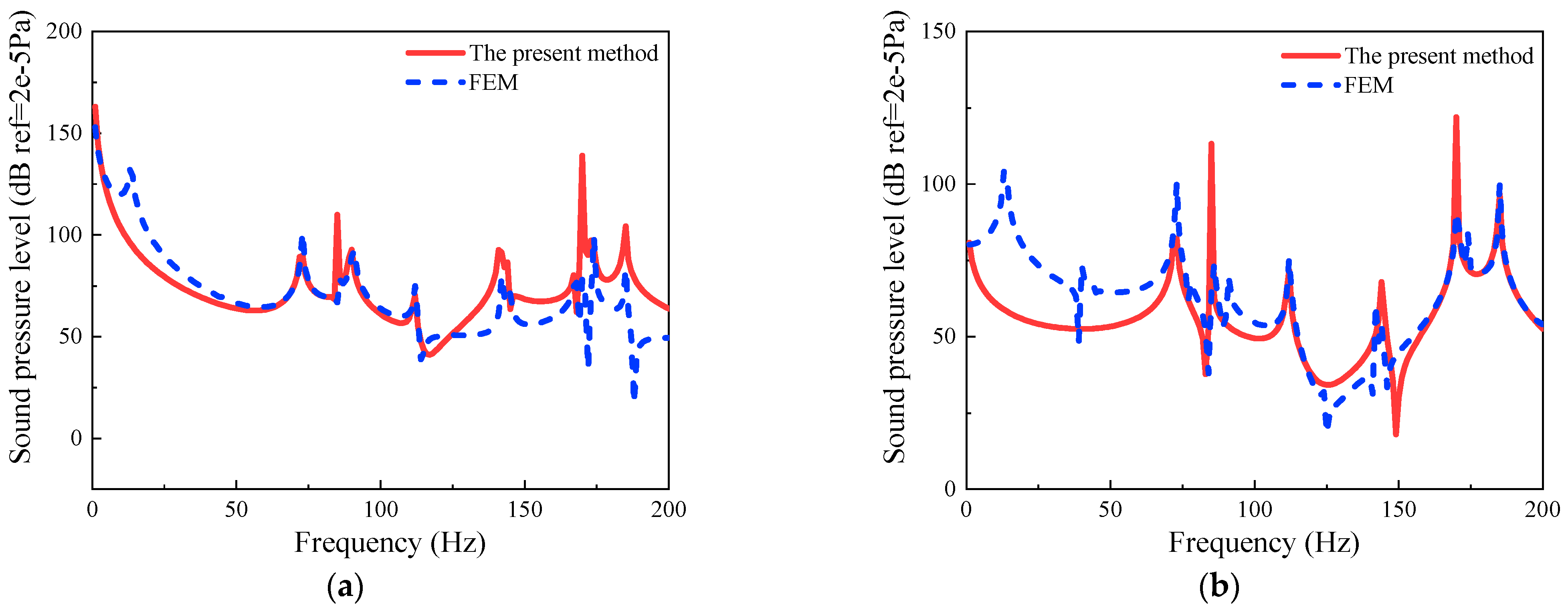
3.1. Verification of Convergence and Correctness
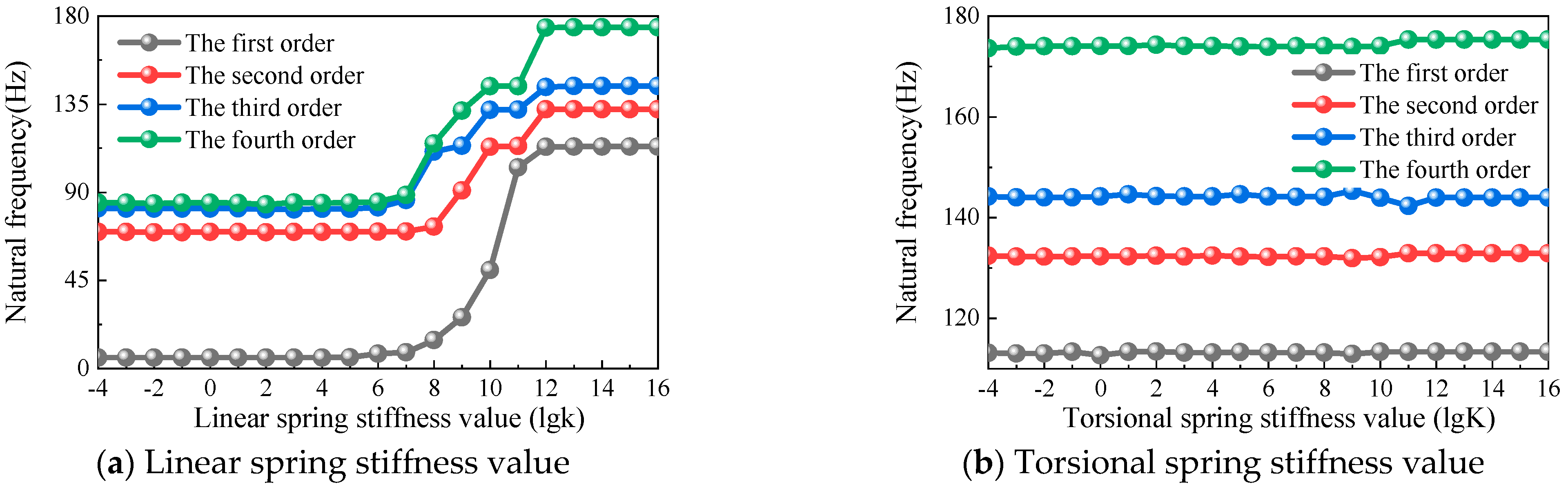
3.2. Free Vibration Analysis
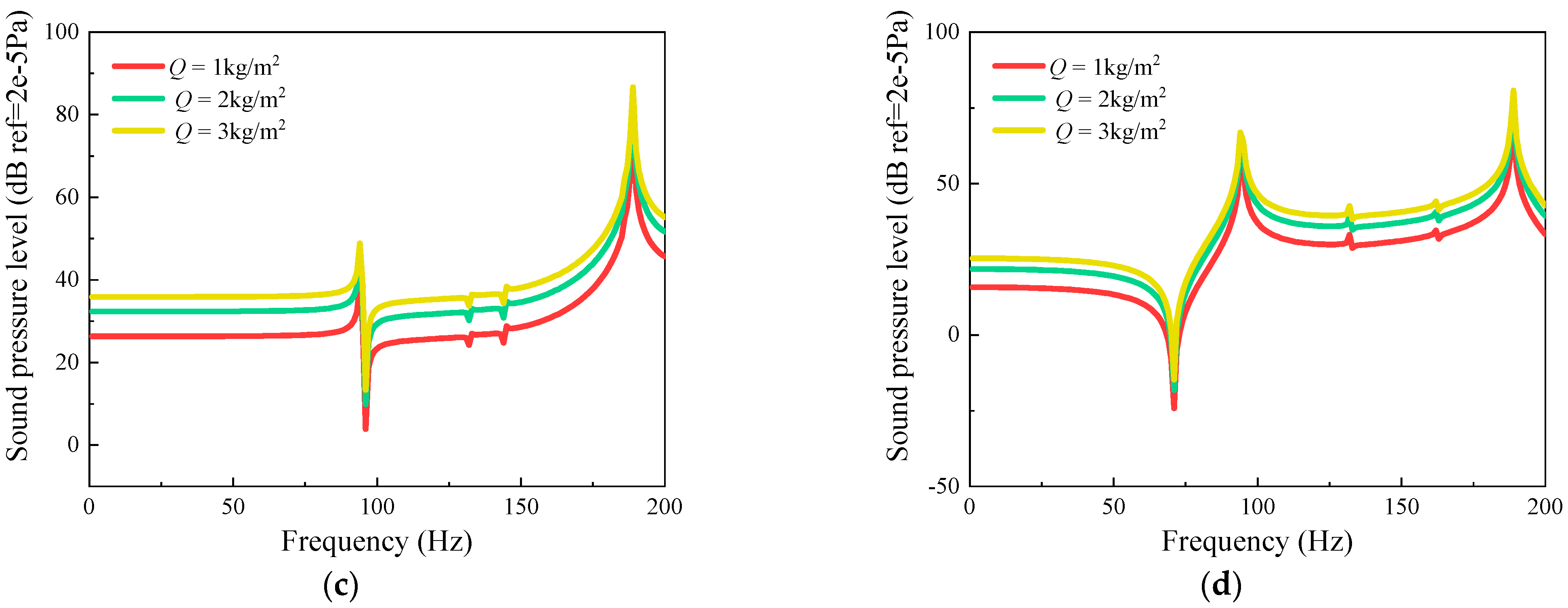
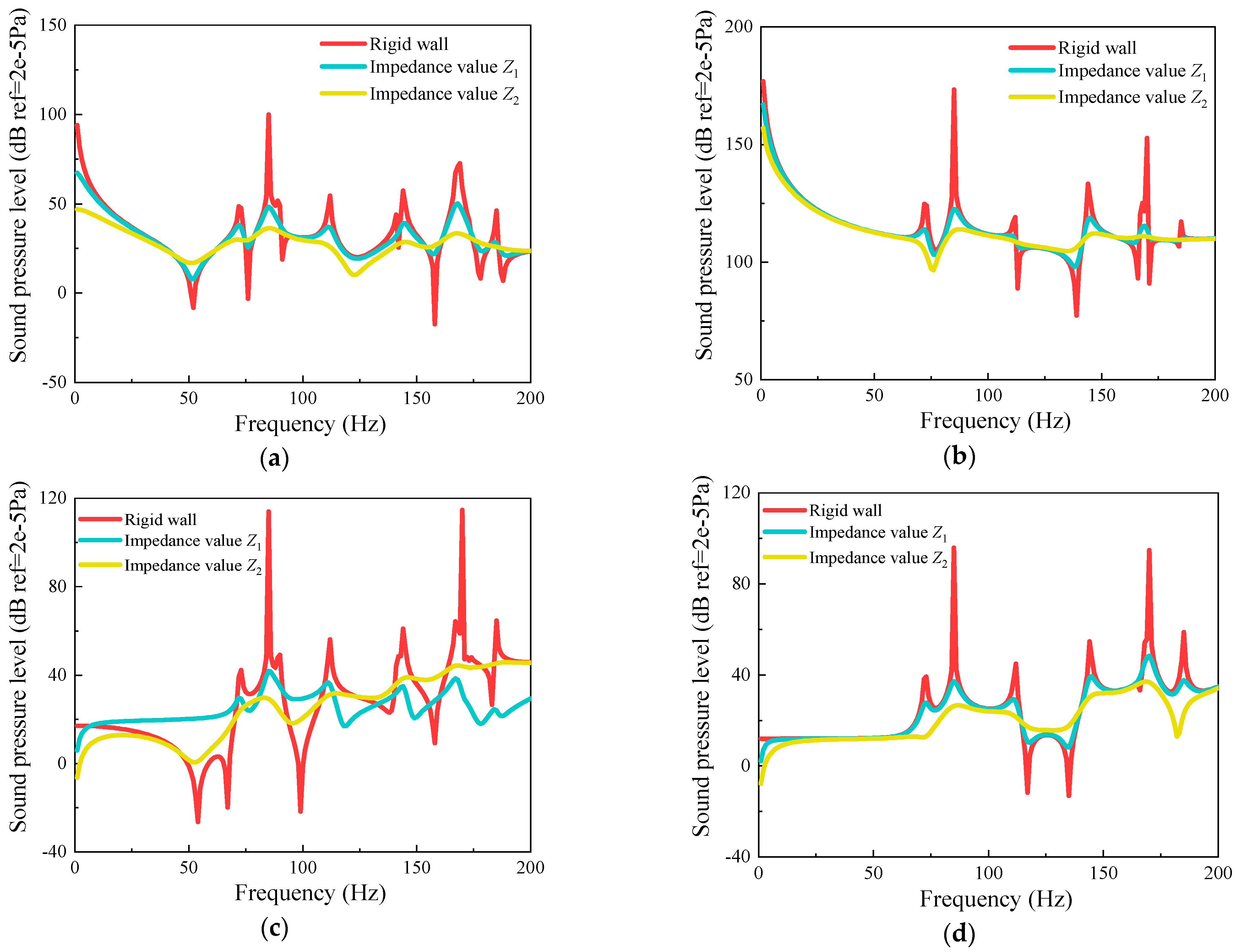
3.3. Steady-State Response Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Rp | Radius of laminated plate | hp | Thickness of laminated plate |
| Rbn | Radius of the NTH laminated curved beam | bn | Width of the NTH laminated curved beam |
| hn | Thickness of the NTH laminated curved beam | ϑ | Rotation angle |
| ku, kv, kw | Boundary linear spring stiffness value coupled in the beam | Kr, Kθ | Boundary torsional spring stiffness value |
| , , | The stiffness value of linear spring coupled in the beam | , | The stiffness value of torsional spring coupled in the beam |
| , , | The stiffness value of the linear spring coupled with plate and beam | , | The stiffness value of the torsional spring coupled with plate and beam |
| Up, Vp, Wp | Displacement component of laminated plate | Ubn, Vbn, Wbn | Displacement component of laminated curved beam |
| Correlation stiffness coefficient | T | Transformation matrix | |
| θk | The Angle between the principal direction and the r direction | Material coefficient of the k layer | |
| E1, E2 | Young’s modulus | G12, G13, G23 | Shear modulus |
| μ12, μ21 | Poisson’s ratio | Shear correction factor | |
| Number of floors | Zk | The base thickness of the k layer | |
| Zk+1 | Upper surface thickness coordinates | Total kinetic energy of the laminated plate | |
| Total kinetic energy of the NTH laminated curved beam | Total potential energy of the laminated plate | ||
| Total potential energy of the NTH laminated curved beam | Coupling potential energy of laminated plate | ||
| Coupling potential energy of the NTH laminated curved beam | Potential energy of boundary spring | ||
| Potential energy coupling between the plate and the NTH beam | Work done by the harmonic point force F | ||
| Material density of the k layer of laminates | Material density of the k layer of laminated curved beams | ||
| Tensile potential energy | Bending potential energy | ||
| Bending coupled potential energy | fi | Function of external load distribution | |
| Pmn | Two-dimensional unknown Fourier coefficient matrix | Ql | One-dimensional unknown Fourier coefficient matrix |
| Stiffness matrix of laminated plate | Stiffness matrix of the NTH laminated curved beam | ||
| Mass matrix of laminated plate | Mass matrix of the NTH laminated curved beam | ||
| The coupling matrix between the NTH beam and the plate | ω | Natural frequency | |
| Ω | Frequency parameter | Mp, Np | Truncation value of the laminated plate |
| Mb | Truncation value of laminated curved beam | Rα | Mean radius of curvature in the α direction of the middle surface |
| Rβ | Mean radius of curvature in the β direction of the middle surface | Lα | Medium surface α direction length dimension |
| Lβ | Medium surface β direction length dimension | Lz | Middle surface z direction length dimension |
| ζ | Damping value | H | Thickness of cavity |
| ϕ | Apex angle of Spherical cavity | L | Length of cavity |
| α | Cone apex Angle of cone sound cavity | Total potential energy of cavity n | |
| Total kinetic energy of cavity n | The energy consumed by the cavity n impedance wall | ||
| The coupled potential energy of cavity n | The work done by a point source in cavity n | ||
| Potential energy coupling between cavities 1 and 2 | The density of acoustic media in cavity n | ||
| The speed at which sound waves travel in cavity n | j | Pure imaginary number | |
| Sr | Area of the r-th acoustic wall | Zr | Impedance value of the r-th acoustic wall |
| Distribution function of point sound source in cavity n | A | The amplitude of the point sound source | |
| k | The wave number of sound | δc | Three-dimensional Dirac function |
| Kn | Stiffness matrix of sound cavity n | Mn | Mass matrix of cavity n |
| Cn | Coupling matrix of sound cavity n | Qn | Sound field source vector of cavity n |
| Zn | Impedance matrix of the acoustic wall of cavity n | C12, C21 | Coupling matrix between cavities 1 and 2 |
| Mc, Nc, Lc | The truncation value of the cavity |
Appendix A
References
- Shahraeeni, M.; Shakeri, R.; Hasheminejad, S.M. An analytical solution for free and forced vibration of a piezoelectric laminated plate coupled with an acoustic enclosure. Comput. Math. Appl. 2015, 69, 1329–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zou, M.-S.; Jiang, L.-W. Study on the integrated calculation method of fluid–structure interaction vibration, acoustic radiation, and propagation from an elastic spherical shell in ocean acoustic environments. Ocean. Eng. 2019, 177, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Meng, G. Nonlinear Vibro-Acoustic Analysis of Composite Sandwich Plates with Skin–Core Debondings. AIAA J. 2017, 55, 1723–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seçgin, A.; Kara, M.; Ozankan, A. A modal impedance-based statistical energy analysis for vibro-acoustic analysis of complex systems having structural uncertainty. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2019, 233, 1972–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarıgül, A.S.; Karagözlü, E. Vibro-acoustic coupling in composite plate-cavity systems. J. Vib. Control 2018, 24, 2274–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozio, L.; Alimonti, L. Variable kinematic finite element models of multilayered composite plates coupled with acoustic fluid. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2016, 23, 981–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Mahapatra, T.R.; Panda, S.K. Vibro-acoustic analysis of un-baffled curved composite panels with experimental validation. Struct. Eng. Mech. Int. J. 2017, 64, 93–107. [Google Scholar]
- Balakrishnan, B.; Raja, S.; Dwarakanathan, D.; Rajagopal, A. Vibroacoustic performance of fiber metal laminates with delamination. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2016, 23, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, F.X.; Lu, T.J. Analytical modeling of fluid loaded orthogonally rib-stiffened sandwich structures: Sound transmission. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2010, 58, 1374–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Chen, Z.; Yu, H.; Li, C.; Liu, X. An analytical study of the vibroacoustic response of a ribbed plate. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2018, 73, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Squicciarini, G.; Ferguson, N.S. The acoustic response of stiffened plates. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1264, 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedini Baghbadorani, A.; Kiani, Y. Free vibration analysis of functionally graded cylindrical shells reinforced with graphene platelets. Compos. Struct. 2021, 276, 114546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Zha, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q. Free Vibration Analysis of the Unified Functionally Graded Shallow Shell with General Boundary Conditions. Shock Vib. 2017, 2017, 7025190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Zha, S. Free and Forced Vibration of the Moderately Thick Laminated Composite Rectangular Plate on Various Elastic Winkler and Pasternak Foundations. Shock Vib. 2017, 2017, 7820130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petyt, M. Vibration of curved plates. J. Sound Vib. 1971, 15, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Choe, K.; Shi, D.; Sin, K. Vibration analysis of the coupled doubly-curved revolution shell structures by using Jacobi-Ritz method. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 135, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Cui, X.; Qin, B.; Liang, Q. Vibration analysis of the functionally graded carbon nanotube reinforced composite shallow shells with arbitrary boundary conditions. Compos. Struct. 2017, 182, 364–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Cui, X.; Qin, B.; Liang, Q.; Tang, J. A semi-analytical method for vibration analysis of functionally graded (FG) sandwich doubly-curved panels and shells of revolution. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2017, 134, 479–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Liu, T.; Wang, Q.; Qin, B.; Shao, W.; Wang, A. Spectral-Tchebychev technique for the free vibration analysis of composite laminated stepped and stiffened cylindrical shells with arbitrary boundary conditions. Compos. Struct. 2021, 272, 114193. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Shi, D.; Zha, S.; Wang, Q. Vibro-acoustic analysis of the thin laminated rectangular plate-cavity coupling system. Compos. Struct. 2018, 189, 570–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shi, D.; Zha, S.; Wang, Q. Parameterization study on the moderately thick laminated rectangular plate-cavity coupling system with uniform or non-uniform boundary conditions. Compos. Struct. 2018, 194, 537–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, H.; Ren, W.; Shi, D.; Huang, B. The modeling method of anisotropic U-shaped plate and U-shaped plate–cavity coupled system. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 172, 108880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, T. Vibro-acoustic characteristics analysis of the rotary composite plate and conical–cylindrical double cavities coupled system. J. Intell. Manuf. Spec. Equip. 2022, 3, 67–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, H.R.; Kiani, Y.; Beni, Y.T. Vibration characteristics of composite doubly curved shells reinforced with graphene platelets with arbitrary edge supports. Acta Mech. 2022, 233, 665–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Shi, D.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, Z. Exact solutions for the free in-plane vibrations of rectangular plates with arbitrary boundary conditions. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2017, 130, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Wang, Q.; Tang, J.; Shuai, C.; Qin, B. Vibration analysis of functionally graded carbon nanotube reinforced composites (FG-CNTRC) circular, annular and sector plates. Compos. Struct. 2018, 194, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.; Roy, T. Vibration analysis of functionally graded carbon nanotube-reinforced composite shell structures. Acta Mech. 2016, 227, 581–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurve, H.K.; Satankar, R.K. Free vibration analysis of curved shells using finite element method. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 50, 2336–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
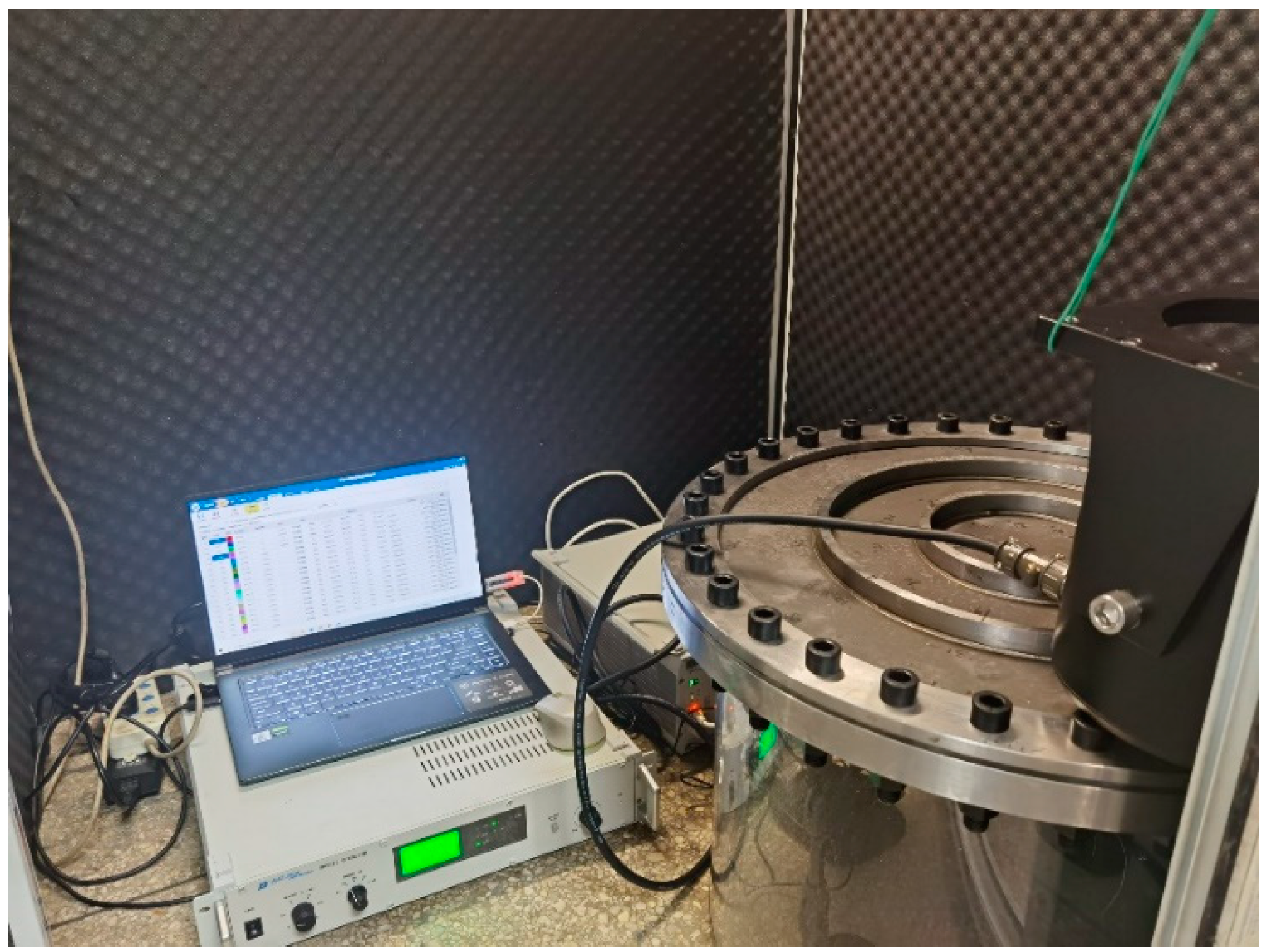

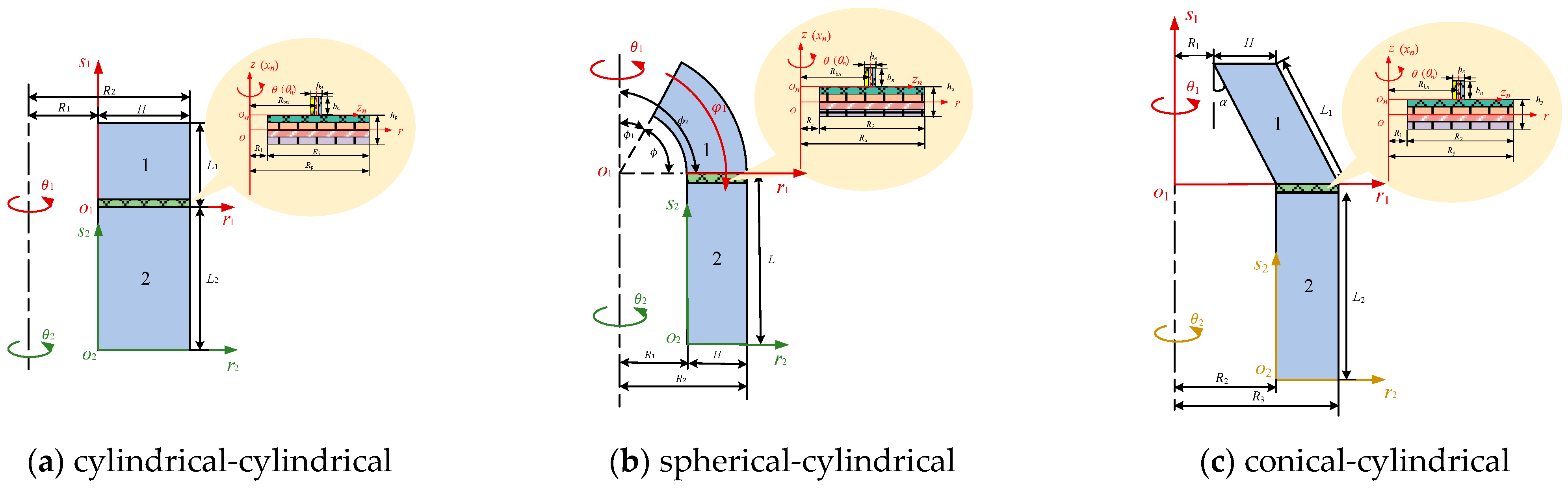
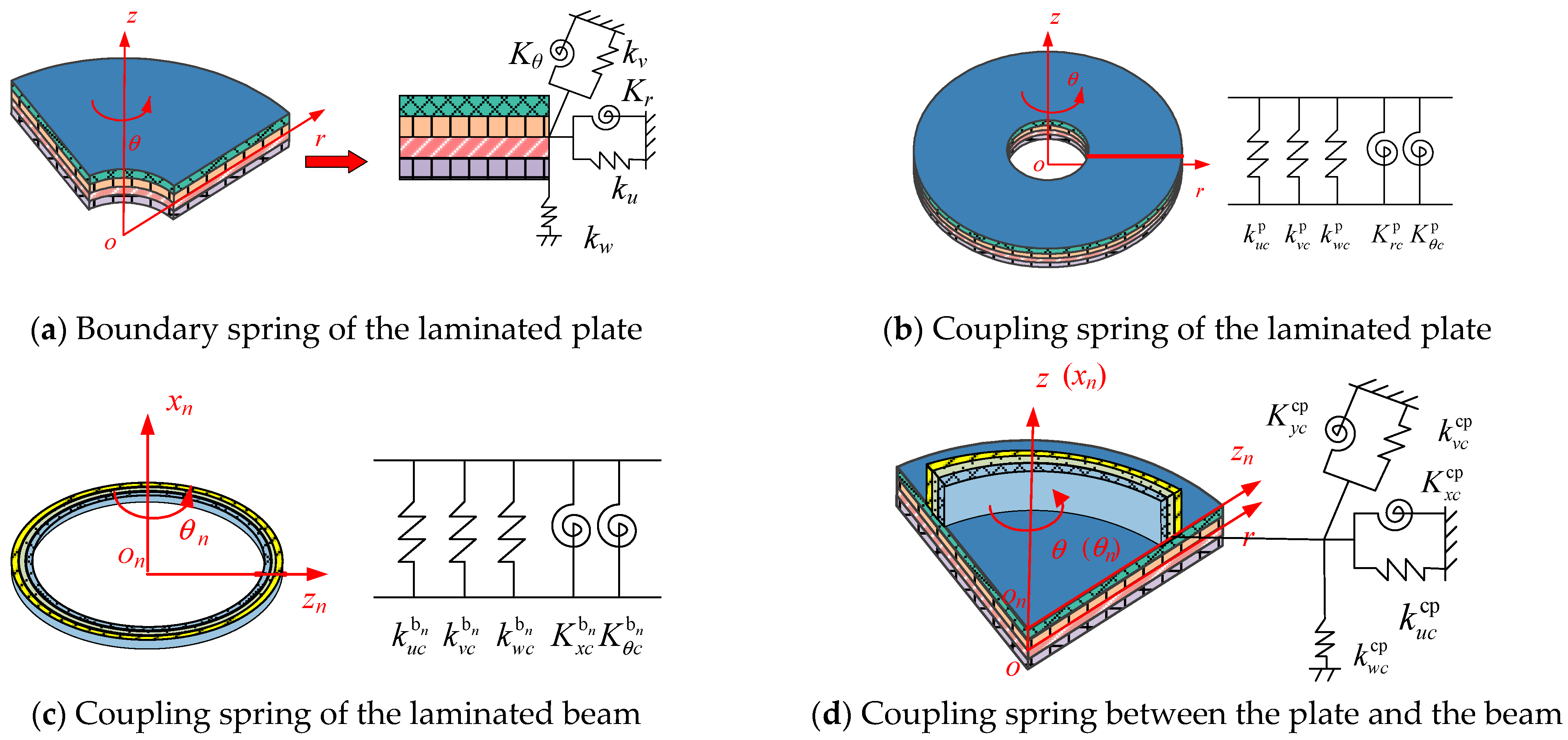

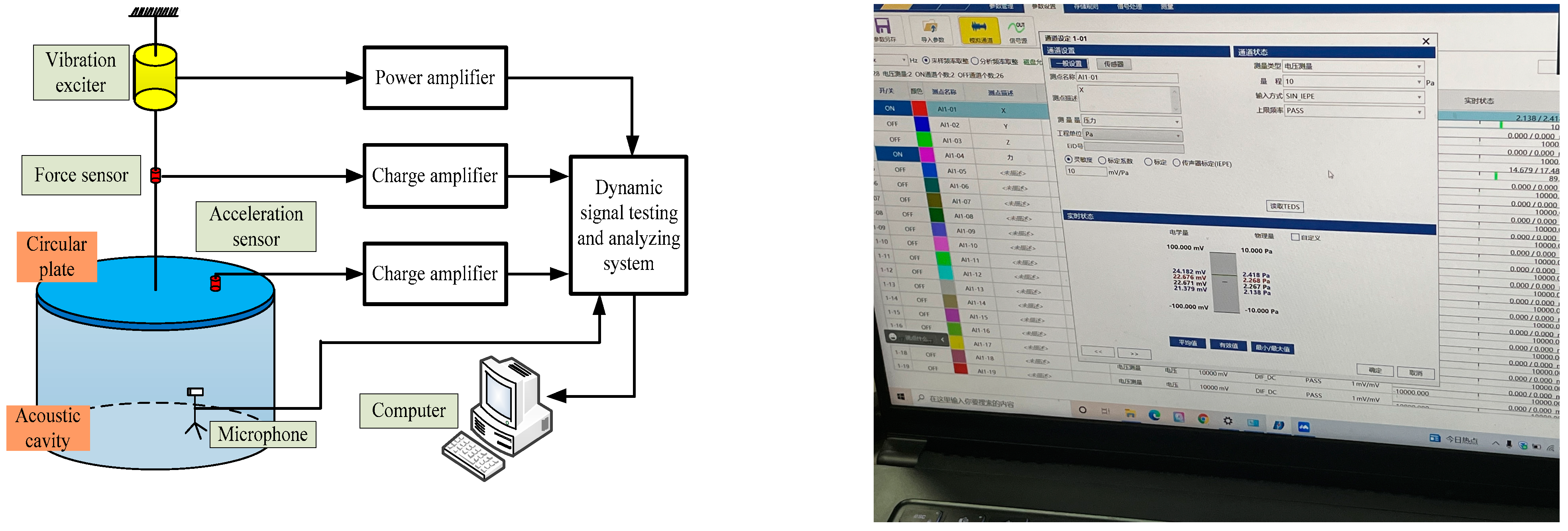

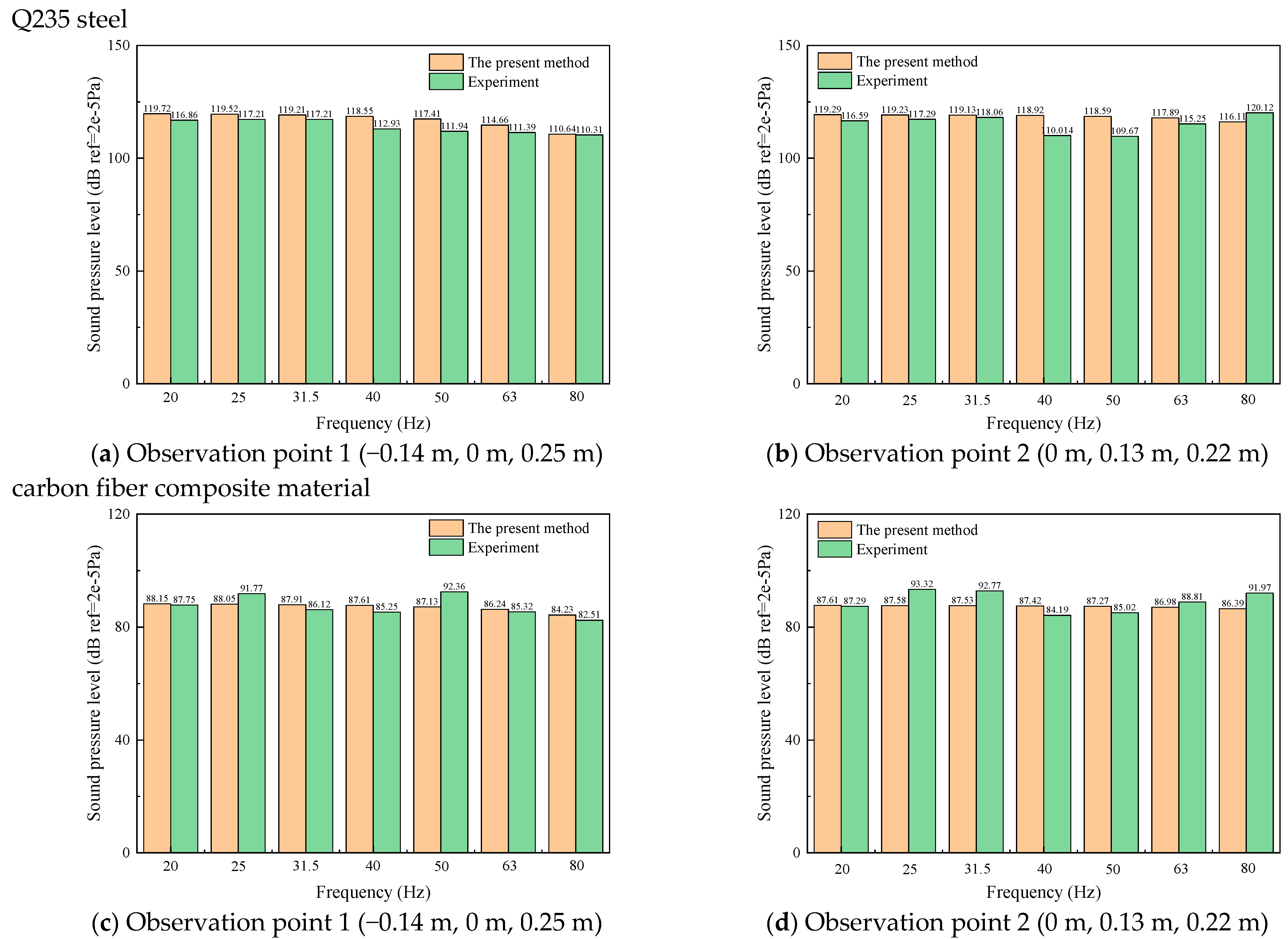
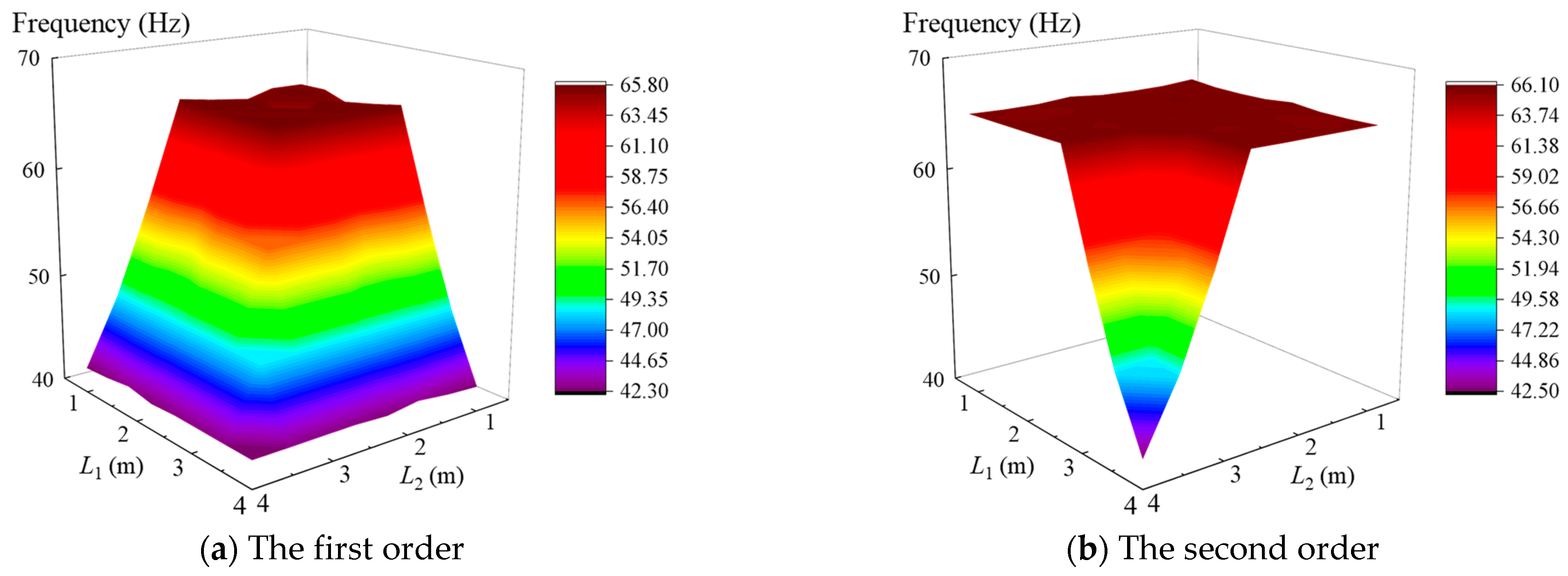

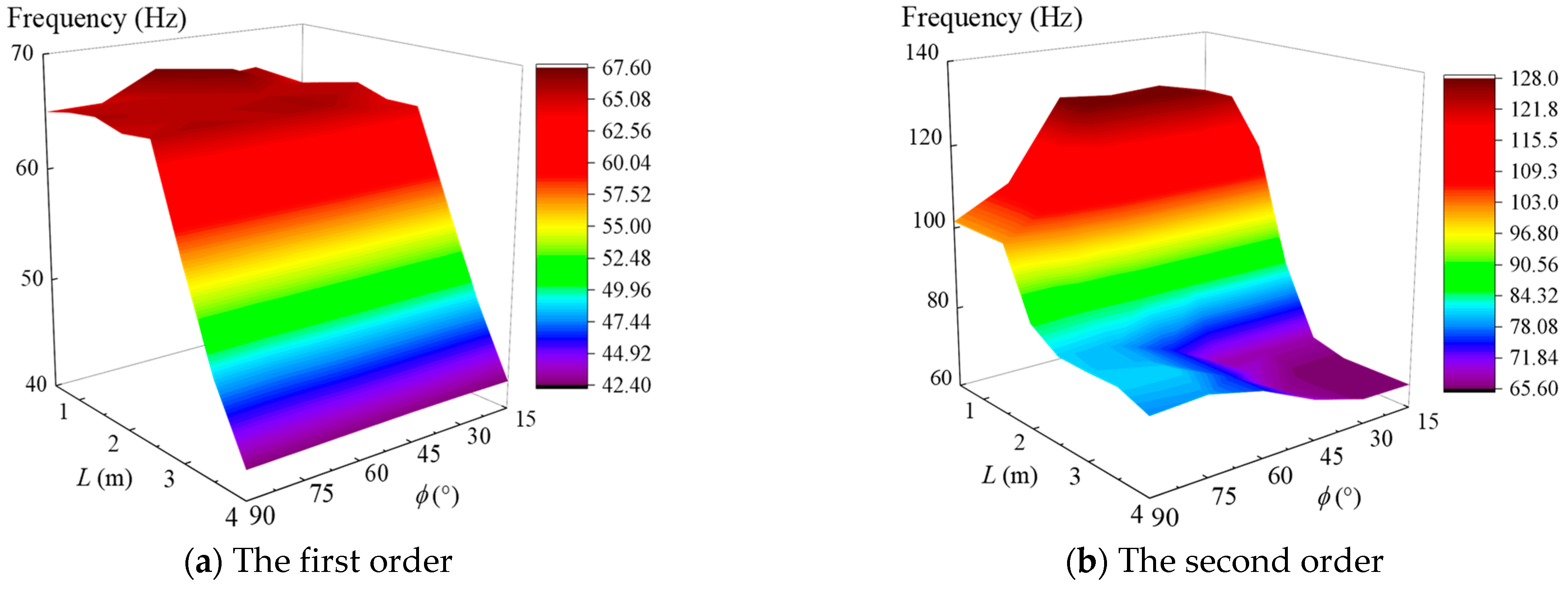
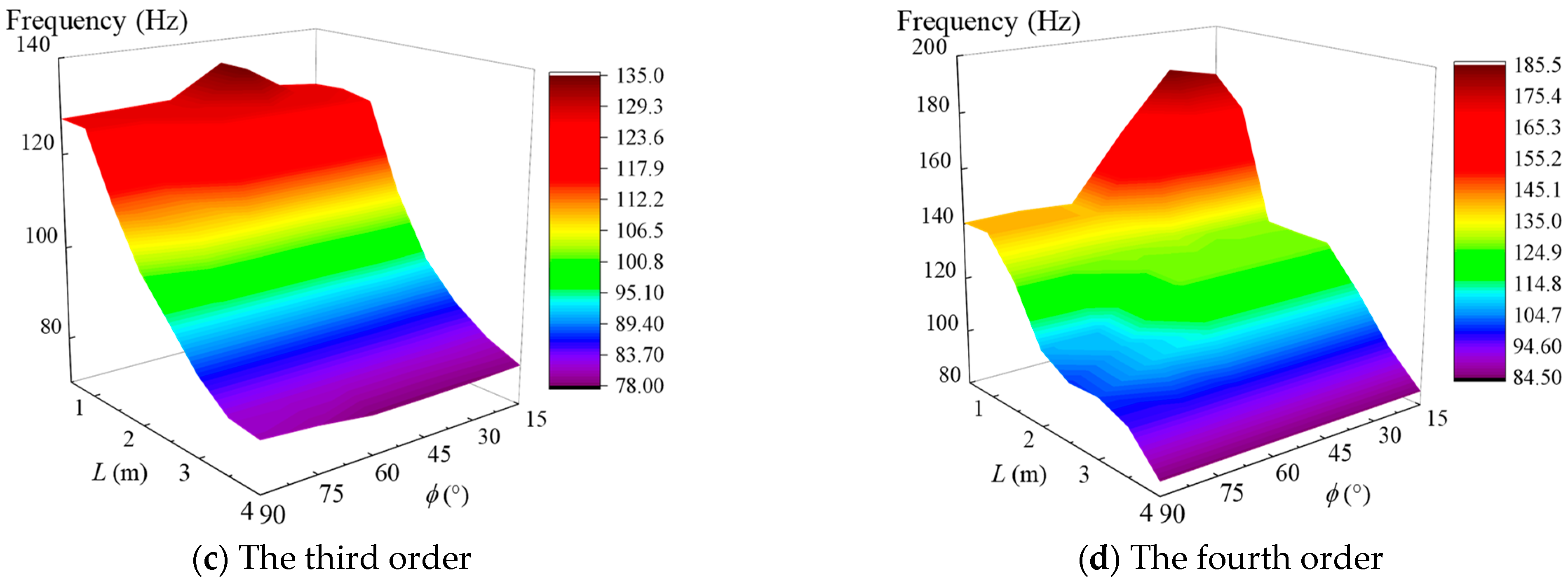
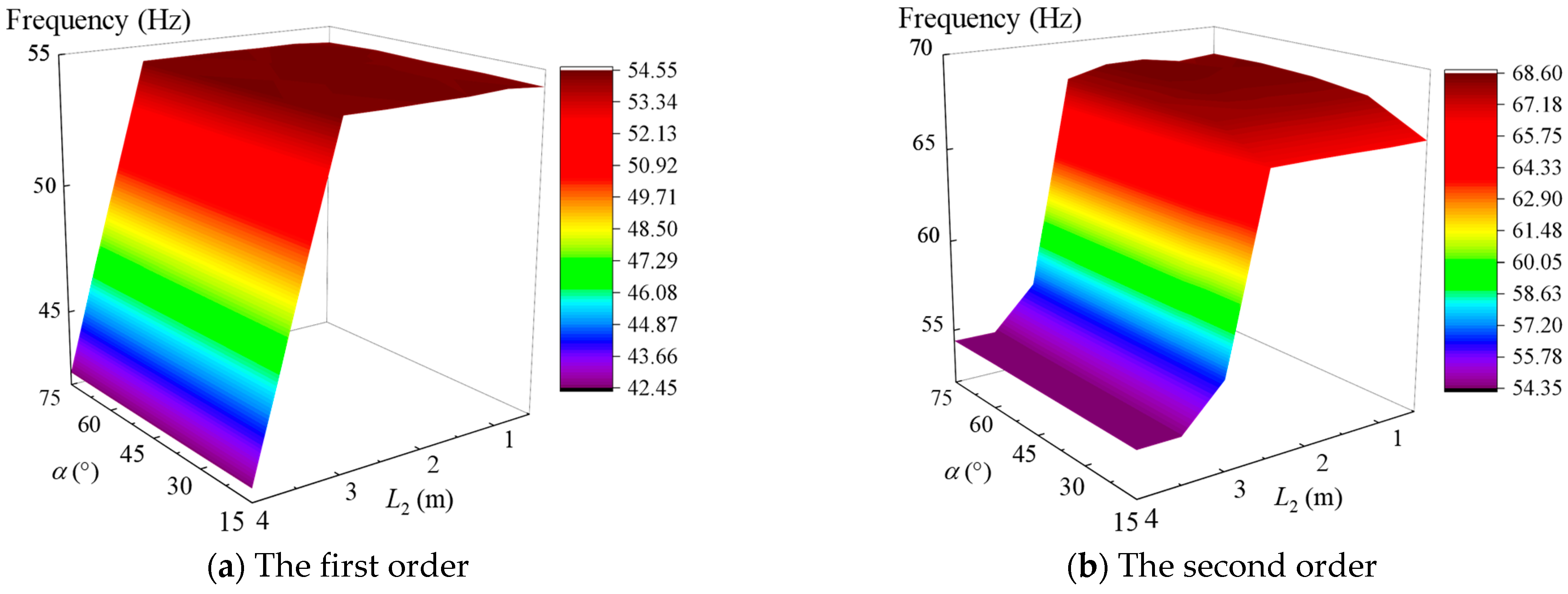
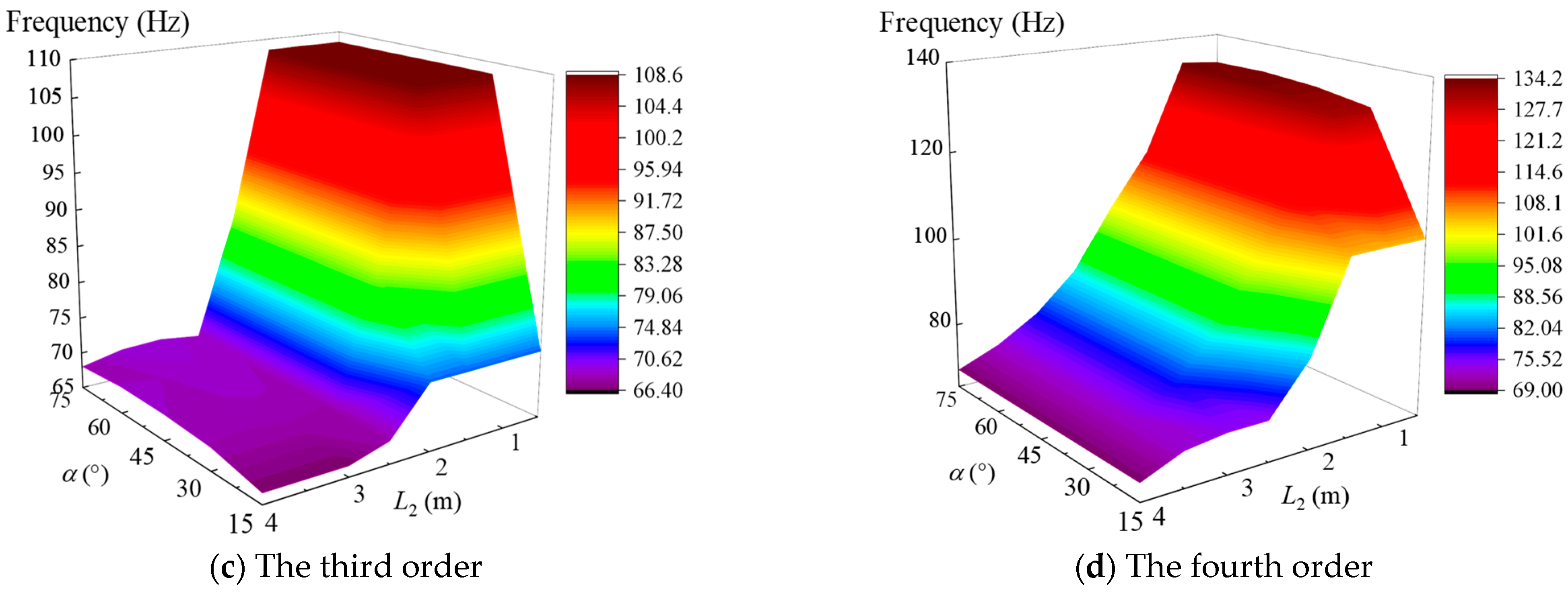
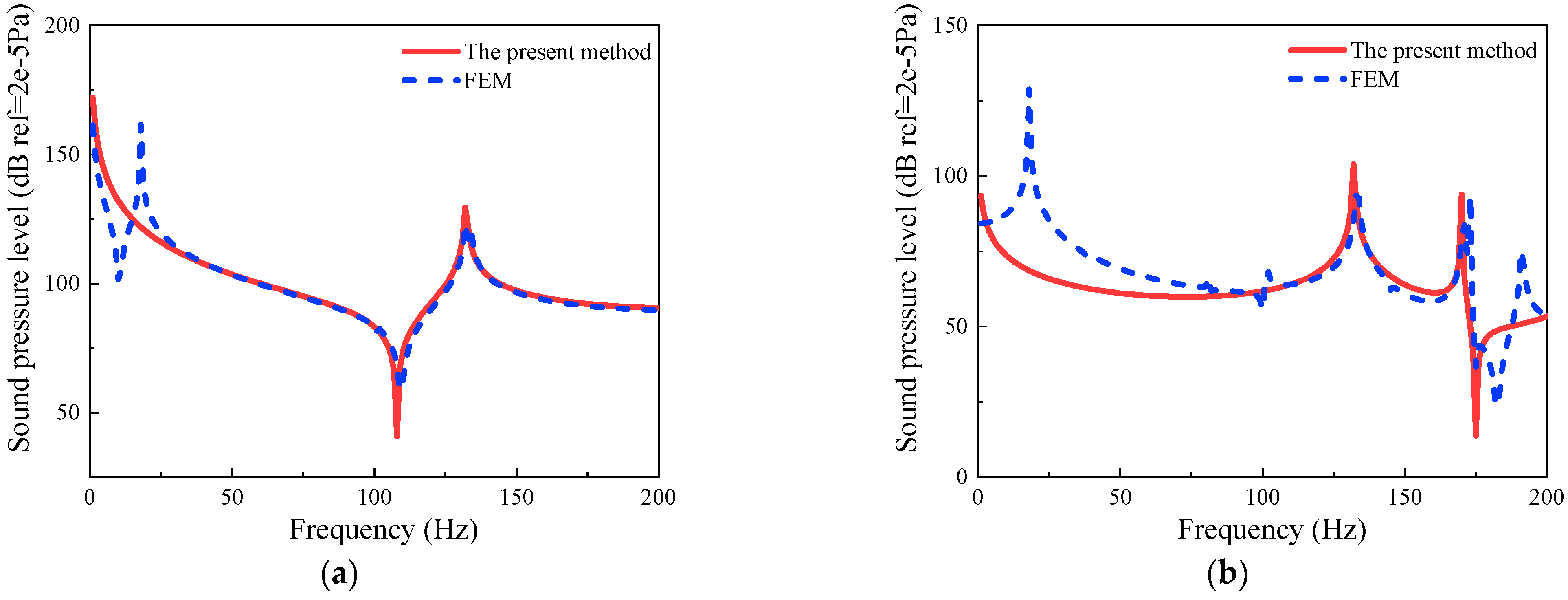
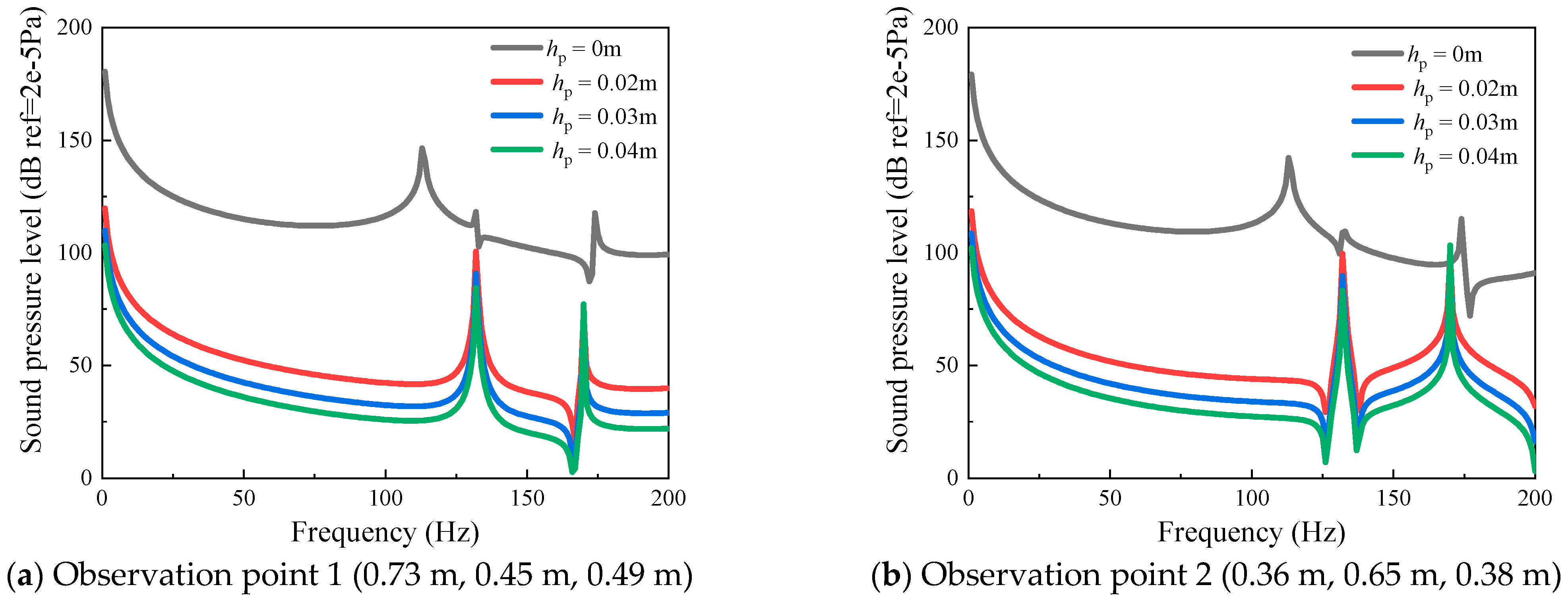
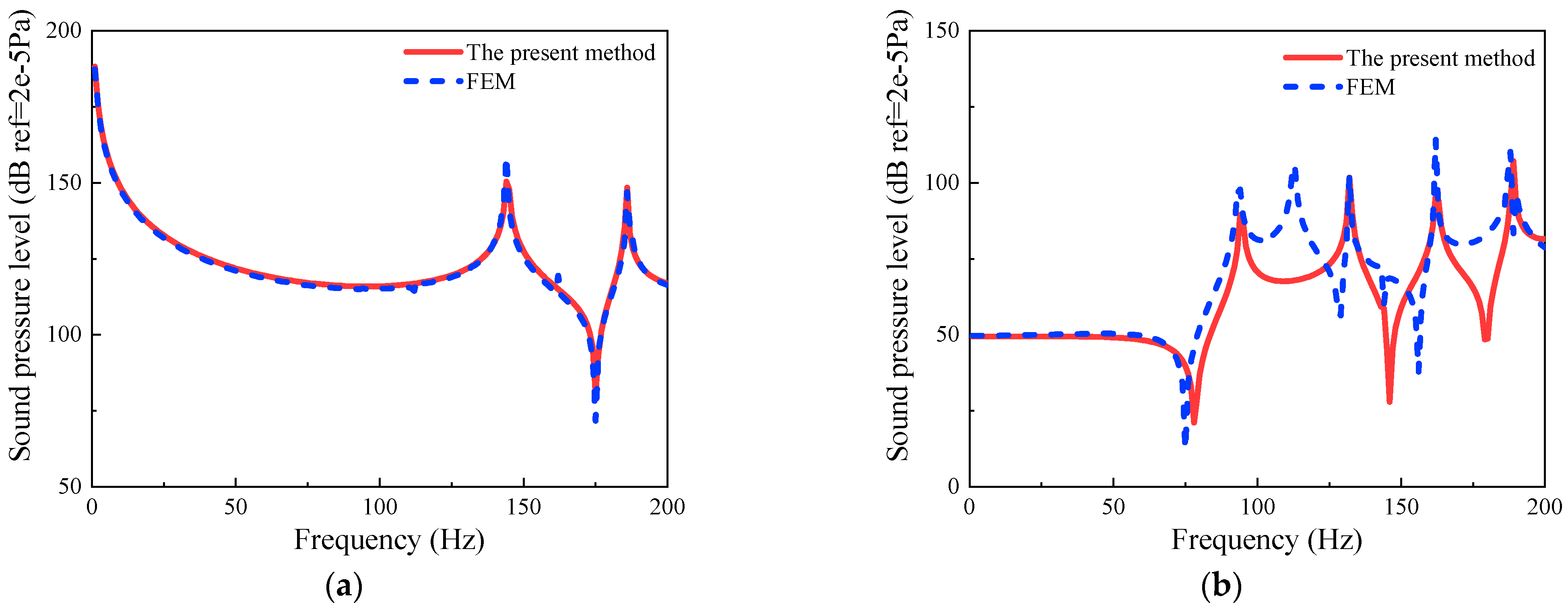
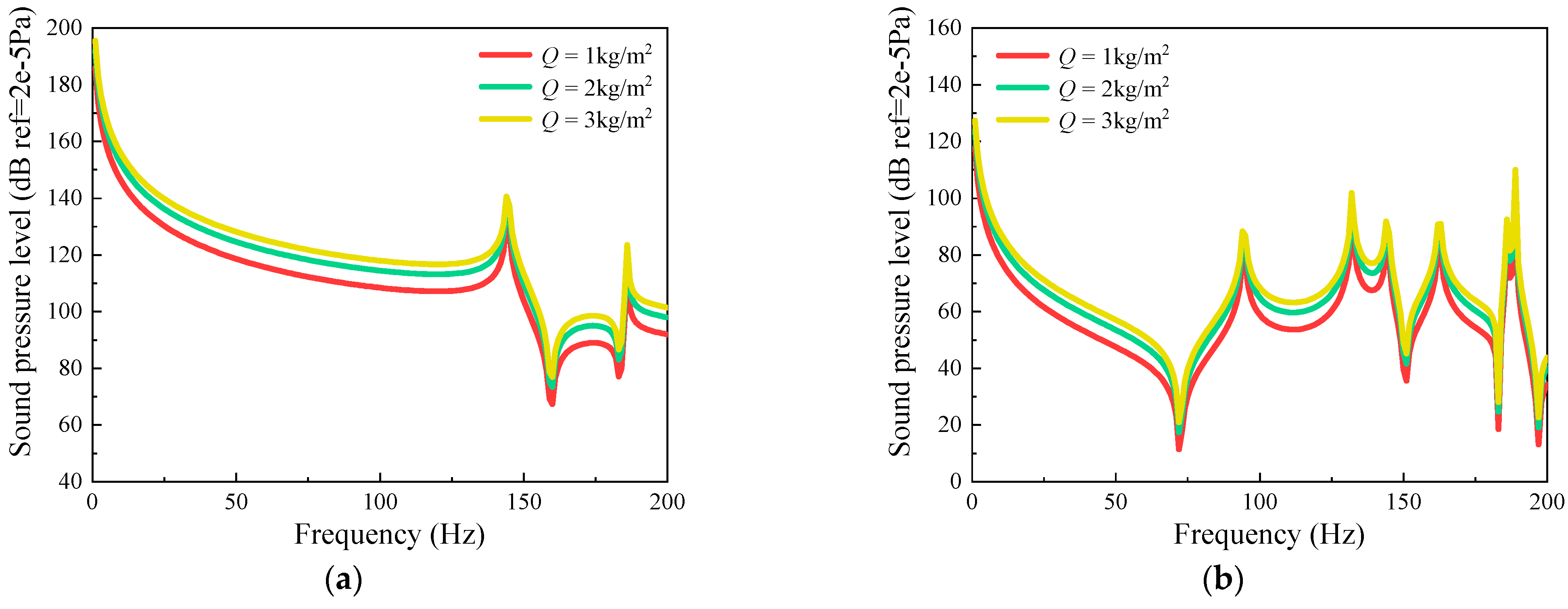
| System Type | Parameter |
|---|---|
| cylinder-cylinder cavity coupling system | (1) , , ; , , (2) , , ; , , (3) , , ; , , (4) , , ; , , |
| spherical-cylinder cavity coupling system | (1) , , ; , , (2) , , ; , , (3) , , ; , , (4) , , ; , , |
| cone-cylinder cavity coupling system | (1) , , ; , , (2) , , ; , , (3) , , ; , , (4) , , , , ; , , |
| Material | ρ (kg/m3) | Material Property Parameter | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 (Pa) | E2 (Pa) | G23 (Pa) | G12(Pa) | G13 (Pa) | μ12 | ||
| Graphite fiber resin | 1600 | 1.85 × 1011 | 1.09 × 1010 | 7.3 × 109 | 7.3 × 109 | 7.3 × 109 | 0.28 |
| Glass epoxy resin | 1810 | 3.9 × 1010 | 8.4 × 109 | 4.2 × 1010 | 4.2 × 1010 | 4.2 × 1010 | 0.26 |
| Q235 steel | 7800 | 2.16 × 1011 | 2.16 × 1011 | 8.31 × 1010 | 8.31 × 1010 | 8.31 × 1010 | 0.3 |
| Mc × Nc × Qc | Mp × Np | Modal Order | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | ||
| 3 × 3 × 3 | 10 × 10 | 82.33 | 132.23 | 132.24 | 169.89 | 210.59 | 215.29 | 221.15 | 221.27 |
| 12 × 12 | 81.78 | 132.23 | 132.24 | 169.89 | 210.30 | 215.28 | 221.15 | 221.27 | |
| 14 × 14 | 81.32 | 132.23 | 132.29 | 169.86 | 210.01 | 215.28 | 221.14 | 221.27 | |
| 16 × 16 | 80.95 | 132.21 | 132.24 | 169.89 | 209.78 | 215.27 | 221.14 | 221.27 | |
| 18 × 18 | 80.64 | 132.18 | 132.23 | 169.89 | 209.54 | 215.27 | 221.14 | 221.27 | |
| 4 × 4 × 4 | 10 × 10 | 82.33 | 132.24 | 132.25 | 169.89 | 210.59 | 215.28 | 221.17 | 221.27 |
| 12 × 12 | 81.78 | 132.23 | 132.24 | 169.90 | 210.30 | 215.28 | 221.14 | 221.27 | |
| 14 × 14 | 81.32 | 132.22 | 132.24 | 169.89 | 210.01 | 215.28 | 221.17 | 221.27 | |
| 16 × 16 | 80.95 | 132.17 | 132.36 | 169.88 | 209.77 | 215.27 | 221.14 | 221.27 | |
| 18 × 18 | 80.64 | 132.29 | 132.33 | 169.88 | 209.54 | 215.27 | 221.24 | 221.27 | |
| 5 × 5 × 5 | 10 × 10 | 82.33 | 132.24 | 132.26 | 169.89 | 210.59 | 215.28 | 221.15 | 221.27 |
| 12 × 12 | 81.78 | 132.23 | 132.24 | 169.89 | 210.30 | 215.28 | 221.15 | 221.27 | |
| 14 × 14 | 81.32 | 132.22 | 132.24 | 169.89 | 210.01 | 215.28 | 221.14 | 221.27 | |
| 16 × 16 | 80.95 | 132.21 | 132.24 | 169.89 | 209.77 | 215.27 | 221.14 | 221.27 | |
| 18 × 18 | 80.64 | 132.15 | 132.23 | 169.88 | 209.54 | 215.27 | 221.14 | 221.27 | |
| FEM | 82.33 | 132.24 | 132.26 | 169.89 | 210.59 | 215.28 | 221.15 | 221.27 | |
| Mc × Nc × Qc | Mp × Np | Modal Order | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | ||
| 3 × 3 × 3 | 10 × 10 | 83.63 | 113.18 | 132.05 | 144.43 | 174.01 | 185.80 | 212.10 | 221.18 |
| 12 × 12 | 82.77 | 113.18 | 132.05 | 144.39 | 173.99 | 185.80 | 211.90 | 221.18 | |
| 14 × 14 | 82.04 | 113.19 | 132.03 | 144.36 | 174.01 | 185.80 | 211.65 | 221.18 | |
| 16 × 16 | 81.45 | 113.18 | 132.01 | 144.33 | 173.96 | 185.79 | 211.48 | 221.17 | |
| 18 × 18 | 80.93 | 113.16 | 131.99 | 144.22 | 173.95 | 185.80 | 211.27 | 221.18 | |
| 4 × 4 × 4 | 10 × 10 | 83.59 | 113.18 | 132.03 | 144.42 | 174.00 | 185.80 | 209.37 | 221.17 |
| 12 × 12 | 82.74 | 113.17 | 132.01 | 144.38 | 173.98 | 185.81 | 209.24 | 221.16 | |
| 14 × 14 | 82.02 | 113.23 | 131.99 | 144.39 | 173.96 | 185.80 | 209.07 | 221.16 | |
| 16 × 16 | 81.42 | 113.13 | 131.97 | 144.31 | 173.98 | 185.80 | 208.97 | 221.15 | |
| 18 × 18 | 80.91 | 113.21 | 131.93 | 144.33 | 173.96 | 185.80 | 208.83 | 221.15 | |
| 5 × 5 × 5 | 10 × 10 | 83.59 | 113.18 | 132.03 | 144.40 | 174.00 | 185.79 | 209.29 | 221.17 |
| 12 × 12 | 82.73 | 113.18 | 132.01 | 144.38 | 173.98 | 185.79 | 209.16 | 221.17 | |
| 14 × 14 | 82.01 | 113.17 | 131.99 | 144.39 | 173.96 | 185.79 | 208.99 | 221.16 | |
| 16 × 16 | 81.42 | 113.18 | 131.96 | 144.34 | 173.95 | 185.80 | 208.89 | 221.16 | |
| 18 × 18 | 80.91 | 113.18 | 131.93 | 144.32 | 173.94 | 185.80 | 208.75 | 221.15 | |
| FEM | 82.42 | 113.65 | 132.18 | 144.20 | 173.89 | 185.89 | 206.74 | 221.19 | |
| Mc × Nc × Qc | Mp × Np | Modal Order | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | ||
| 3 × 3 × 3 | 10 × 10 | 72.86 | 84.98 | 89.62 | 95.60 | 111.71 | 131.07 | 141.42 | 144.26 |
| 12 × 12 | 72.56 | 85.03 | 89.62 | 95.09 | 111.71 | 130.72 | 141.42 | 144.27 | |
| 14 × 14 | 72.53 | 84.98 | 89.66 | 94.58 | 111.70 | 130.35 | 141.42 | 144.26 | |
| 16 × 16 | 72.52 | 84.96 | 89.62 | 94.18 | 111.70 | 130.08 | 141.42 | 144.26 | |
| 18 × 18 | 72.51 | 84.98 | 89.65 | 93.78 | 111.70 | 129.79 | 141.42 | 144.29 | |
| 4 × 4×4 | 10 × 10 | 72.86 | 84.95 | 89.63 | 95.60 | 111.71 | 131.07 | 141.42 | 144.27 |
| 12 × 12 | 72.56 | 84.98 | 89.62 | 95.09 | 111.70 | 130.72 | 141.42 | 144.27 | |
| 14 × 14 | 72.53 | 85.02 | 89.62 | 94.58 | 111.70 | 130.35 | 141.42 | 144.26 | |
| 16 × 16 | 72.52 | 85.01 | 89.62 | 94.18 | 111.70 | 130.08 | 141.42 | 144.26 | |
| 18 × 18 | 72.51 | 84.98 | 89.61 | 93.78 | 111.70 | 129.79 | 141.42 | 144.26 | |
| 5 × 5×5 | 10 × 10 | 72.85 | 85.02 | 89.62 | 95.60 | 111.71 | 131.07 | 141.40 | 144.27 |
| 12 × 12 | 72.56 | 84.98 | 89.62 | 95.09 | 111.71 | 130.72 | 141.40 | 144.26 | |
| 14 × 14 | 72.53 | 84.95 | 89.62 | 94.58 | 111.70 | 130.35 | 141.40 | 144.26 | |
| 16 × 16 | 72.53 | 84.93 | 89.62 | 94.17 | 111.70 | 130.08 | 141.40 | 144.27 | |
| 18 × 18 | 72.52 | 84.98 | 89.62 | 93.78 | 111.70 | 129.79 | 141.40 | 144.26 | |
| FEM | 72.48 | 84.04 | 89.46 | 90.60 | 111.49 | 130.89 | 141.63 | 144.27 | |
| Boundary Condition | The Stiffness Value of the Boundary Spring | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ku | kv | kw | Kr | Kθ | |
| C | 1016 | 1016 | 1016 | 1016 | 1016 |
| S | 1016 | 1016 | 1016 | 0 | 0 |
| F | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| E1 | 108 | 108 | 108 | 108 | 108 |
| E2 | 106 | 106 | 106 | 0 | 0 |
| Rotation Angle ϑ | Modal Order | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
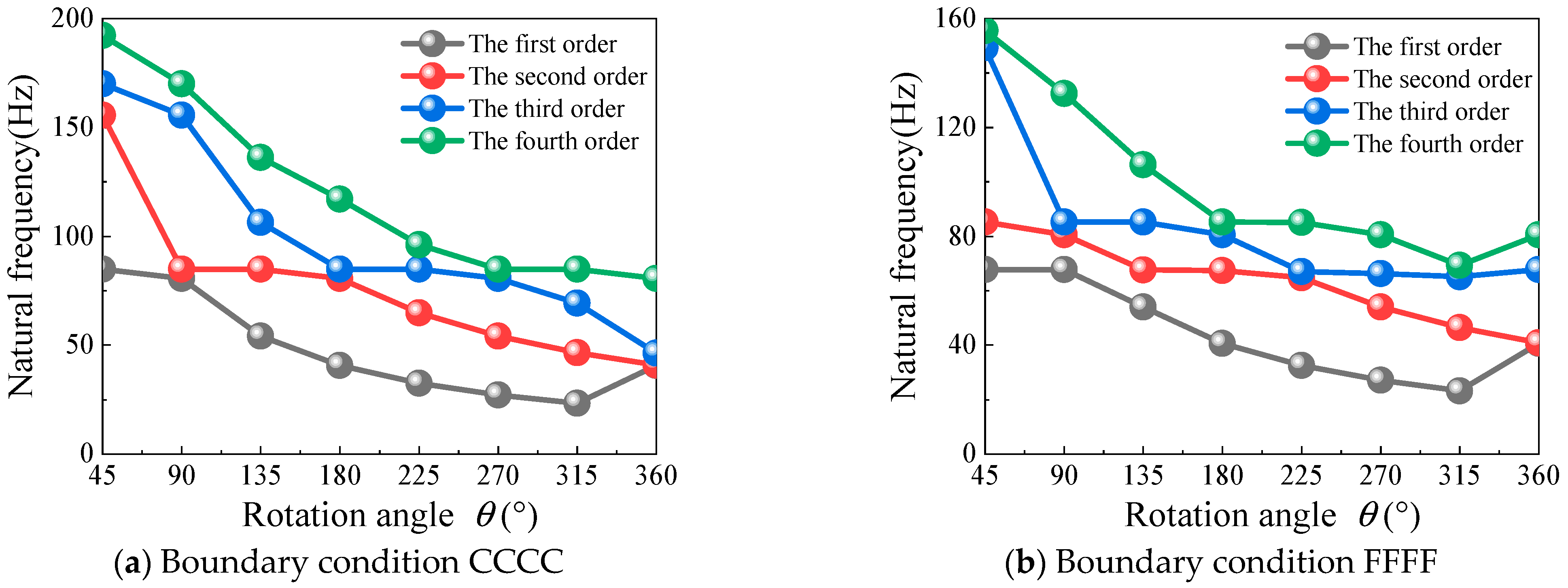
| 45° | 85.00 | 155.58 | 155.58 | 169.99 | 170.00 | 177.30 | 192.19 | 192.20 |
| 90° | 80.60 | 80.62 | 85.00 | 117.13 | 155.58 | 155.58 | 169.99 | 169.99 |
| 135° | 54.13 | 54.15 | 84.99 | 100.78 | 106.37 | 106.38 | 136.16 | 155.57 |
| 180° | 40.72 | 40.73 | 80.60 | 80.60 | 84.99 | 94.25 | 117.13 | 118.98 |
| 225° | 32.60 | 32.62 | 64.80 | 64.81 | 84.99 | 91.04 | 96.15 | 96.16 |
| 270° | 27.21 | 27.22 | 54.16 | 54.16 | 80.60 | 80.61 | 84.98 | 89.24 |
| 315° | 23.32 | 23.33 | 46.49 | 46.50 | 69.34 | 69.35 | 84.94 | 88.14 |
| 360° | 40.71 | 40.73 | 40.88 | 40.94 | 46.37 | 79.98 | 80.60 | 80.60 |
| Rotation Angle ϑ | Modal Order | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
| 45° | 85.21 | 120.15 | 155.55 | 167.37 | 169.99 | 177.25 | 192.20 | 197.54 |
| 90° | 80.57 | 84.94 | 91.78 | 117.15 | 120.09 | 155.64 | 157.96 | 167.33 |
| 135° | 54.51 | 62.77 | 84.67 | 101.03 | 106.46 | 118.36 | 120.05 | 136.82 |
| 180° | 40.55 | 47.83 | 81.04 | 85.00 | 91.51 | 94.32 | 117.22 | 118.78 |
| 225° | 33.78 | 36.13 | 64.85 | 74.81 | 85.06 | 91.10 | 96.26 | 106.92 |
| 270° | 27.07 | 32.53 | 54.30 | 62.82 | 80.64 | 85.06 | 89.60 | 90.75 |
| 315° | 22.97 | 26.34 | 46.46 | 54.80 | 69.30 | 79.89 | 84.99 | 87.91 |
| 360° | 39.78 | 40.84 | 47.76 | 47.91 | 47.97 | 80.52 | 83.49 | 85.04 |
| Rotation Angle ϑ | Modal Order | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
| 45° | 85.15 | 141.85 | 144.06 | 167.83 | 168.87 | 169.93 | 222.99 | 243.87 |
| 90° | 72.43 | 85.03 | 89.84 | 111.83 | 142.29 | 143.89 | 167.78 | 169.52 |
| 135° | 48.20 | 60.57 | 85.21 | 96.57 | 98.19 | 118.24 | 128.03 | 142.61 |
| 180° | 36.48 | 44.39 | 72.36 | 85.39 | 87.11 | 92.59 | 108.35 | 111.85 |
| 225° | 28.48 | 37.10 | 58.33 | 73.33 | 84.86 | 87.26 | 89.65 | 102.84 |
| 270° | 24.76 | 28.97 | 48.03 | 61.36 | 72.35 | 85.09 | 88.39 | 90.03 |
| 315° | 23.33 | 23.61 | 41.37 | 49.49 | 62.27 | 76.84 | 83.38 | 85.25 |
| 360° | 36.37 | 38.22 | 42.77 | 44.80 | 60.53 | 72.71 | 83.96 | 84.22 |
| Boundary Condition | Type | Modal Order | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | ||
| SFSF | Cylindrical-Cylindrical | 40.72 | 40.72 | 80.60 | 80.61 | 84.44 | 85.79 | 94.26 | 117.14 |
| Spherical-Cylindrical | 40.22 | 45.54 | 80.32 | 84.99 | 91.37 | 94.36 | 117.49 | 118.88 | |
| Conical-Cylindrical | 36.96 | 41.79 | 72.51 | 85.06 | 89.66 | 92.25 | 108.49 | 112.10 | |
| FFFS | Cylindrical-Cylindrical | 40.63 | 40.67 | 61.31 | 80.56 | 80.60 | 84.99 | 94.25 | 117.14 |
| Spherical-Cylindrical | 40.46 | 47.00 | 80.59 | 85.02 | 91.73 | 94.41 | 117.23 | 119.00 | |
| Conical-Cylindrical | 35.55 | 45.95 | 72.03 | 85.57 | 89.88 | 92.68 | 108.50 | 112.31 | |
| SCSF | Cylindrical-Cylindrical | 40.72 | 40.73 | 80.60 | 80.60 | 84.99 | 94.24 | 108.33 | 117.13 |
| Spherical-Cylindrical | 40.22 | 45.54 | 80.32 | 84.99 | 91.37 | 94.36 | 117.49 | 118.88 | |
| Conical-Cylindrical | 38.03 | 41.31 | 72.61 | 84.63 | 89.80 | 92.30 | 108.39 | 111.61 | |
| SCSC | Cylindrical-Cylindrical | 40.73 | 40.73 | 80.60 | 80.63 | 85.00 | 94.24 | 117.13 | 118.97 |
| Spherical-Cylindrical | 40.26 | 46.28 | 80.29 | 84.91 | 91.50 | 94.17 | 117.48 | 118.83 | |
| Conical-Cylindrical | 38.51 | 40.80 | 74.63 | 83.79 | 90.86 | 95.28 | 106.32 | 112.51 | |
| CCCC | Cylindrical-Cylindrical | 40.73 | 40.74 | 80.55 | 80.60 | 85.00 | 94.25 | 117.14 | 118.98 |
| Spherical-Cylindrical | 41.07 | 46.98 | 80.78 | 85.11 | 91.16 | 94.19 | 117.98 | 118.55 | |
| Conical-Cylindrical | 38.57 | 45.26 | 67.83 | 80.51 | 87.18 | 92.83 | 108.57 | 112.34 | |
| E1E1E1E1 | Cylindrical-Cylindrical | 40.71 | 40.72 | 69.96 | 80.60 | 80.62 | 85.06 | 94.24 | 117.13 |
| Spherical-Cylindrical | 41.36 | 46.99 | 80.51 | 85.05 | 91.90 | 94.21 | 117.13 | 119.08 | |
| Conical-Cylindrical | 38.96 | 44.47 | 72.59 | 86.07 | 89.47 | 90.95 | 104.14 | 111.78 | |
| E2E2E2E2 | Cylindrical-Cylindrical | 40.71 | 40.90 | 68.34 | 80.60 | 80.63 | 85.13 | 94.22 | 117.13 |
| Spherical-Cylindrical | 41.30 | 47.06 | 80.44 | 84.95 | 91.58 | 94.04 | 117.13 | 119.00 | |
| Conical-Cylindrical | 37.39 | 44.33 | 72.77 | 85.70 | 87.06 | 92.05 | 108.37 | 111.80 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Ding, Y.; He, L.; Shuai, C.; Jiang, C. The Vibro-Acoustic Characteristics Analysis of the Coupled System between Composite Laminated Rotationally Stiffened Plate and Acoustic Cavities. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031002
Zhang H, Ding Y, He L, Shuai C, Jiang C. The Vibro-Acoustic Characteristics Analysis of the Coupled System between Composite Laminated Rotationally Stiffened Plate and Acoustic Cavities. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(3):1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031002
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hong, Yiqun Ding, Lin He, Changgeng Shuai, and Chao Jiang. 2024. "The Vibro-Acoustic Characteristics Analysis of the Coupled System between Composite Laminated Rotationally Stiffened Plate and Acoustic Cavities" Applied Sciences 14, no. 3: 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031002
APA StyleZhang, H., Ding, Y., He, L., Shuai, C., & Jiang, C. (2024). The Vibro-Acoustic Characteristics Analysis of the Coupled System between Composite Laminated Rotationally Stiffened Plate and Acoustic Cavities. Applied Sciences, 14(3), 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031002





