Abstract
This paper addresses the limitations of relying solely on facial expressions for emotion recognition by proposing an advanced approach that emphasizes continuous monitoring of electroencephalography (EEG) signals. Recognizing the potential for deception in facial expressions, our study leverages the growing interest in EEG signals, tapping into advancements in deep learning and machine learning. By optimizing the configuration of EEG electrodes, our approach enhances the accuracy of emotion classification systems, offering a streamlined solution. The proposed multi-input system refines EEG-based emotion recognition efficiency and integrates facial expression analysis to enhance overall system effectiveness. Through the application of brain heat map topographies and facial expression recognition, our system, employing just nine electrodes, outperforms basic emotion recognition setups. Experimental results validate that combining facial expression analysis with EEG signals provides a more comprehensive and accurate understanding of human emotions. This innovative approach holds significance across various sectors, including healthcare, psychology, and human–computer interaction. The paper introduces a novel multi-input system approach, collaboratively fusing two powerful deep learning algorithms: two Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). The proposed EEG-based CNN algorithm achieves an efficiency of 87.43%, rising to 91.21% when integrated with the DeepFace CNN. The seamless integration of facial expressions and brain topographies enables the system to efficiently harness abundant information from both modalities, ensuring a thorough comprehension of human emotions. By capitalizing on the combined advantages of analyzing facial expressions and EEG-derived brain topography, this avant-garde technique substantially improves both precision and efficiency in emotion recognition systems. This enhancement establishes a foundation for the introduction of innovative applications across a spectrum of fields.
1. Introduction
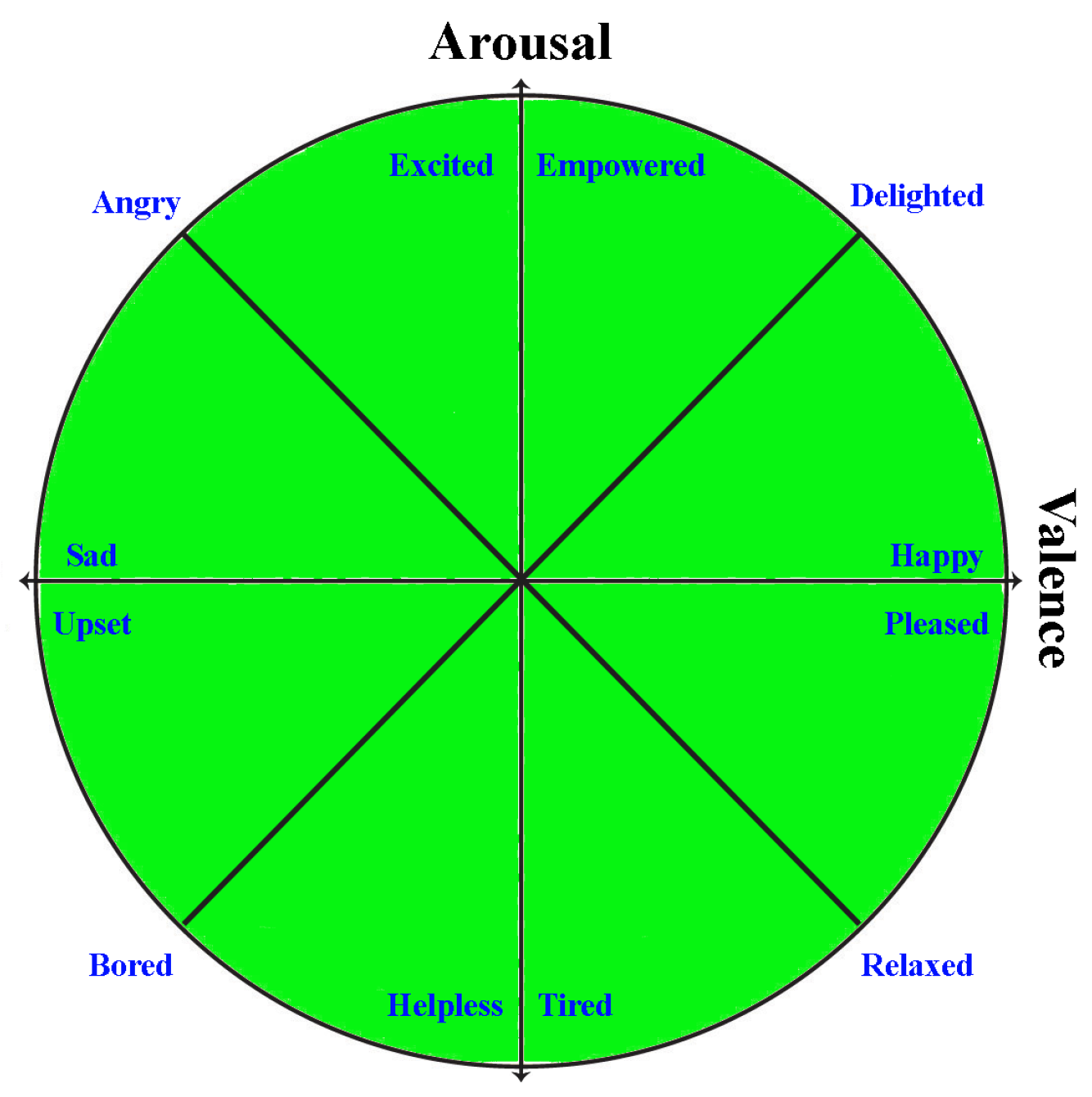
Emotion recognition involves the intricate task of identifying and categorizing human emotions, which are often nuanced and expressed in diverse ways. Several methods are employed for emotion recognition, including facial expression recognition, speech analysis, physiological signals, and EEG signals. Facial expression recognition relies on identifying and classifying facial expressions, known for their potent conveyance of emotions. Various methods exist for facial expression recognition, all grounded in the principle that different emotions correspond to distinct patterns of muscle activation in the face [1,2]. Speech analysis involves identifying emotional tones in speech utilizing factors such as pitch, volume, and rhythm as reliable indicators of emotion [3]. Different emotions are associated with unique patterns of acoustic features in speech. Physiological signals, including vital signs, offer another avenue for emotion recognition. Variations in emotional arousal can be reflected in physiological signals, including blood pressure, skin conductance, and heart rate [4]. Apart from the conventional techniques, electroencephalogram (EEG) signals offer a non-invasive approach to quantifying electrical activity in the brain. A wide spectrum of emotions can be accurately identified since different emotions have different EEG activity patterns. To define typical emotions, researchers frequently use a two-dimensional scale, namely the valence–arousal emotion axis. Arousal relates to the degree of an emotion, whereas valence specifies whether it is favorable or negative. These characteristics can be combined to map a broad spectrum of emotions and provide a more complex understanding of emotional experiences. The valence–arousal model is depicted in Figure 1, which offers a thorough framework for classifying emotions. The dimensional model provides valuable insights into emotional reactions and facilitates the development of successful regulation mechanisms for a range of persons and circumstances. It improves the analysis of emotions.
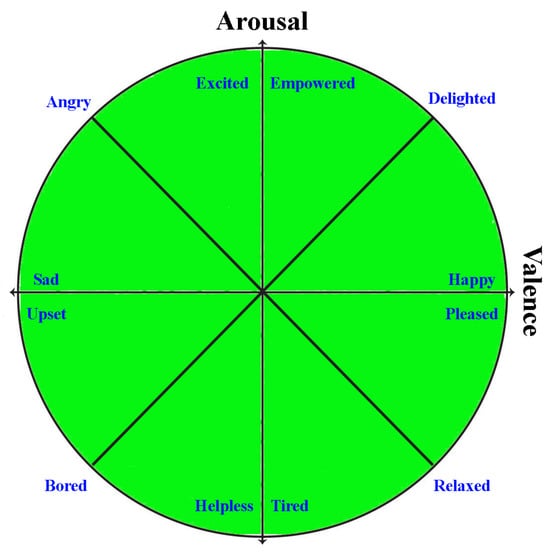
Figure 1.
Two-dimensional axes showing different human emotions.
Affective computing is a multidisciplinary field that focuses on enabling computers to recognize, interpret, process, and respond to human emotions. By combining principles from psychology, computer science, cognitive science, and other disciplines, affective computing aims to create systems that can perceive and understand human emotions through various modalities such as facial expressions, vocal intonations, gestures, and physiological signals like heart rate and skin conductivity. The ultimate goal of affective computing is to enhance human–computer interaction by enabling machines to adapt their behavior according to users’ emotional states, leading to more personalized and empathetic interactions in applications ranging from virtual assistants and healthcare to gaming and education [5]. In the context of EEG emotion recognition, psychological theories play a crucial role in understanding the underlying mechanisms of emotional processes. The James–Lange theory posits that physiological responses precede the conscious experience of emotion, suggesting that specific patterns of brain activity captured by EEG may correspond to distinct emotional states [6]. Similarly, the Cannon–Bard theory proposes that emotions arise simultaneously with physiological responses, implying that EEG signals could provide valuable insights into the neural correlates of emotional experiences [7]. Additionally, appraisal theories emphasize the role of cognitive evaluations in shaping emotional responses, suggesting that EEG-based emotion recognition systems should consider not only the physiological manifestations of emotion but also the cognitive appraisal processes that influence them. Integrating insights from these psychological theories into EEG emotion recognition models can lead to more nuanced and accurate assessments of individuals’ emotional states, enhancing the effectiveness of affective computing applications in real-world scenarios [8].
1.1. Emotion Recognition through Facial Expressions
The ability of facial expressions to effectively convey emotions across cultural and linguistic divides has attracted a great deal of study in the field of emotion recognition research. The human face is remarkably versatile in conveying a wide range of emotions, such as surprise, happiness, sadness, rage, and exhaustion. A vast variety of emotional signals, including AI-generated human facial expressions, are produced by subtle changes in facial muscles, such as the raising of eyebrows, wrinkling of the nose, or curving of the lips. These idioms are widely recognized and relevant because they are frequently innate and able to cross linguistic and cultural divides.
Understanding facial expressions can help one better understand emotional reactions, thought processes, and social interactions. Tools that can precisely analyze and interpret facial expressions have been developed as a result of technological breakthroughs, particularly in the field of computer vision. At the beginning of research in the field, the main focus of researchers was to develop a variety of methods for the identification and categorization of facial expressions using computer vision and machine learning techniques. Typically, these techniques depend on the extraction of face features, such as geometric features or facial landmarks, which are then used as the input layer to the neural network for identifying particular emotions [2]. In emotion detection systems based on facial expressions, extensive research has been conducted to evaluate a range of classifiers, including but not limited to Support Vector Machines (SVM), Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), and K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN). These studies using different classifiers have significantly helped in understanding emotions from facial expressions [9,10]. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) in particular have gained prominence in the deep learning field, mainly for image classification. Their adeptness in extracting and recognizing complex features has been well-documented [11]. These CNN architectures are powerful tools for image classification [12,13,14].
However, facial expression-based emotion recognition systems has its disadvantages like any other systems. These techniques depending on facial expressions might suffer from lighting conditions, head position, and head orientation, and they might also be affected by cultural contexts. Moreover, non-emotional factors like health conditions, fatigue, or unique personal characteristics may also affect facial expressions and, accordingly, the results from the designed classifier; this kind of noise may potentially reduce systems’ efficiency.
Notwithstanding these obstacles, advances in deep learning, multi-modal fusion, affective computing, and facial expression-based emotion recognition are promising avenues for future research toward even more precise and context-aware emotion recognition systems [15]. As technology develops, facial expression detection will be progressively integrated with other modalities and real-time applications to enhance emotional intelligence in artificial systems and human–computer interactions.
Multi-modal techniques, which combine facial expressions with additional indicators including verbal intonation, physiological signs, and contextual information, should be taken into consideration by researchers and developers. Emotion recognition systems can produce more reliable and accurate findings by combining different data sources that correspond better with the complexity and diversity of human emotions. Researchers have experimented with fusing different physiological signals or contextual information with facial expressions to improve the accuracy of emotion recognition [15,16,17].
1.2. Emotion Recognition through EEG Signals
EEG is important in emotion identification because it provides insight into the electrical activity of the brain linked with diverse emotional states. This non-invasive technique records the brain’s different activities when the human is exposed to different emotional stimuli in real time, revealing novel insights into the intricate dynamics of emotional processing. EEG data analysis allows researchers to discover precise patterns and variations in brain activity that correlate with various emotions such as happiness, sadness, anger, and fear. These patterns—which are distinguished by different frequency bands such as alpha, beta, and gamma, power spectral density, and event-related potentials—allow the creation of complex algorithms for reliably identifying emotions. Electrodes are applied to the scalp in the EEG technique to assess brain electrical activity. EEG signals are extremely tiny, usually measured in microvolts (). After being amplified and noise filtered, these signals are shown on a computer screen. The frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes are the four lobes that make up the brain. Different functions, including movement, attention, memory, and vision, are attributed to each lobe. Different cognitive states can be identified from the EEG signals collected from different brain lobes; emotions are generally captured in the frequency range of 0.5–100 Hz, as Table 1 illustrates.

Table 1.
EEG frequency bands and emotion recognition relevance.
Recent research has focused a lot of interest on EEG-based emotion detection because of its potential to shed light on the underlying brain mechanisms that underlie emotions. Electrodes are applied to the scalp to measure electrical brain activity, and thus makes EEG a non-invasive, easily accessible method for analyzing emotions.
Comparing EEG signals to various approaches for emotion identification reveals some important advantages. Because EEG-based emotion recognition algorithms have such a high temporal precision, scientists can record the quick changes in brain activity that coincide with transient feelings. EEG’s non-intrusiveness and safety make it a preferable choice for repeated brain assessments, posing no risk of side effects.
Presently, EEG is easy to use and that allows its usage in various applications in different fields, including medical and non-medical fields. One more advantage of using EEG signals over facial expressions for emotion recognition is its generality of use for different ages groups from infants to elderly.
EEG is useful for studying complicated emotional states and social interactions because it provides so much information about the human body. Its applications cover a wide range of real-world situations, highlighting its function in individualized emotion detection and treatment, from focused emotional therapies to emotion recognition in human–computer interactions. Overall, EEG offers significant insights into the neurological aspects of emotions, establishing it as a vital instrument in emotion recognition research.
The use of deep learning and machine learning techniques to identify emotional states from EEG data has been the focus of recent research [21,22]. These methods, like other machine learning methods, start by preprocessing the EEG data in order to remove noise. The next step for classification purposes is to identify important characteristics describing [23,24,25] event-related potentials (ERPs), power spectral density (PSD), and time–frequency representations, along with the most widely used characteristics, as described in [26]. Then, these EEG characteristics are used in machine learning algorithms such as SVM, Random Forest, KNN, and others though divide emotional states [27,28,29,30,31,32]. Additionally, deep learning models, including LSTM networks and RNNs, have proven effective in capturing the temporal dynamics within EEG data, enhancing the accuracy of emotion detection [33,34].
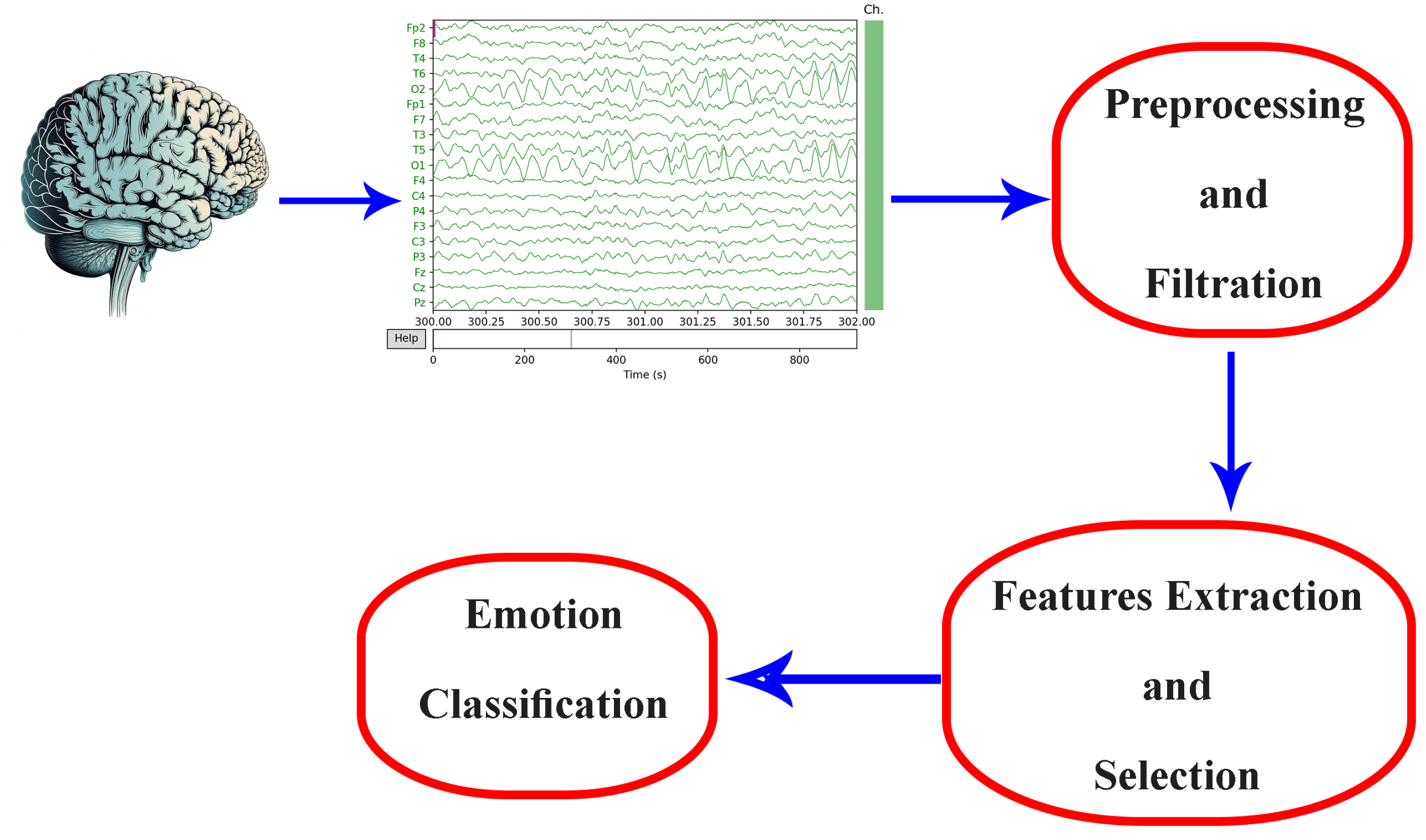
One of the key benefits of EEG-based emotion recognition is its ability to track emotional responses in real-time. This opens up potential applications in fields such as neuromarketing, human–machine interaction, and affective computing [17,21,35]. The process typically involves the preprocessing of raw data, extracting features, and classifying emotions, as illustrated in Figure 2.
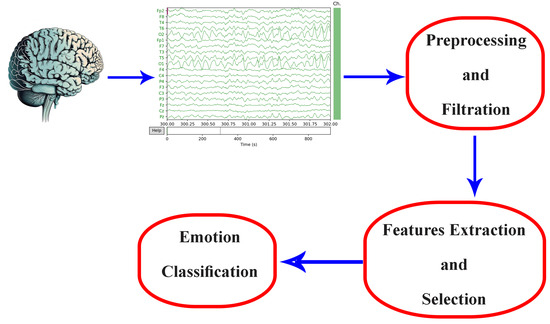
Figure 2.
EEG emotion recognition methodology.
EEG signals are increasingly utilized in neuro-feedback applications, enabling individuals to modulate their emotional states through real-time brain activity feedback. However, EEG-based emotion recognition encounters several challenges. The susceptibility of EEG signals to noise and artifacts, along with individual variations in brain structure and neural function, can affect recognition accuracy. Emotions, being complex and multi-dimensional, pose difficulties in precise classification based solely on EEG data. To address these issues and enhance recognition systems’ reliability, researchers are exploring the integration of EEG signals with other data sources, such as physiological signals or facial expressions [26,36]. However, only a few studies have used brain heat map topographies, which display relative gradient colors of brain activity across specific electrodes. The primary advantage of these topographies is their ability to show relative activity levels between different brain areas under varying conditions. Brain heat map representation is suitable for a wide range of subjects, including diverse racial and age groups [21,37,38,39,40,41].
1.3. Privacy and Ethical Considerations
The privacy and ethical concerns surrounding EEG and facial expression emotion recognition systems are paramount in today’s digital age. As these technologies delve deeper into understanding human emotions, they raise significant questions regarding data privacy and individual autonomy. EEG data, which directly reflect brain activity and facial expressions, intimate indicators of emotional states, contain sensitive information about an individual’s mental and emotional well-being. Consequently, there exists the risk of unauthorized access, misuse, or exploitation of this personal data, potentially leading to breaches of privacy and infringements on individual rights. Moreover, the development and deployment of these systems must adhere to ethical guidelines, ensuring transparent consent, data anonymization, and protection against discriminatory practices. As such, meticulous attention must be paid to establishing robust privacy protocols and ethical frameworks to safeguard the rights and dignity of individuals involved in EEG and facial expression emotion recognition research and applications [42].
2. Database and Data Collection
Efficient emotion recognition is important in different fields like psychology, medicine, and human–computer interaction. The regular way of emotion recognition mainly depends on external observations or self-reported emotions. On the other hand, EEG signals offers more dependable and impartial methods of emotions identification. EEG-based biometrics analysis of brainwave properties presents a novel method for objectively identifying emotions. EEG signals are useful for both long-term and real-time monitoring due to their high temporal resolution and non-invasive capacity to capture brain activity associated with emotions. Through the use of a database where participants report their feelings in real time while interacting with stimulus films, this study explores the application of EEG-based biometrics in emotion identification.
2.1. Headset Selection
Careful selection of the EEG data collection headset plays an important role in maintaining data integrity and accuracy during EEG analysis. The EMOTIV EPOC+ headset was selected for our data collection. The highlights of the Epoc+ headset selection for the process of data collection include its collection process method using 14 sensors, its user-friendly interfaces, its light weight, and its ease of use [43]. With a high sampling rate of 128 Hz, the EMOTIV EPOC+ is well suited to our study objectives as it captures a broad range of frequency bands that are essential for in-depth brainwave pattern analysis. With this configuration, precise tracking of brain activity is made possible by accurate EEG signal mapping to designated brain areas.
Another advantage of the EPOC+ is its strong software support, particularly the proprietary software from EMOTIV (version 3.8) and the accessible Python Software Development Kit (SDK), known as CORTEX V2. The SDK, along with the software suite, provides an easy-to-use interface for data collection and analysis, accommodating researchers with varying degrees of experience in EEG data processing. The software’s support for exporting raw data in standard formats (e.g., EDF, CSV) streamlines integration with diverse data analysis tools [21,43].
From an economic standpoint, the EMOTIV EPOC+ strikes a judicious balance between cost and performance. In comparison to other high-end, research-grade EEG systems, the EPOC+ delivers a similar functionality at a more budget-friendly price point, enhancing its appeal for large-scale database collection initiatives while acknowledging the EPOC+’s susceptibility to noise and artifacts. Our protocol systematically addresses these issues through meticulous electrode placement and sufficient saline use, ensuring a reported signal strength of 100% from all 14 electrodes to guarantee that the collected data have a high fidelity.
2.2. Consideration of Participant Situational Context
Each participant, and indeed every human being, encounters diverse situations throughout the day. These situational contexts invariably influence EEG signals. Participants are subject to a myriad of environmental, social, economic, psychological, and biological factors, all of which exert an impact on their brain activity. In this study, these factors were deliberately left unfiltered to optimize the generalizability of the emotion recognition system. Other than this, participants in this experiment were coming from different races. Subjects contributing to the database collection were instructed to abstain from snacks for a minimum of two hours prior to the session and abstain from main meals for at least four hours before recording commenced to ensure a more pronounced effect of the hunger stimulus videos [44].
2.3. Stimulus Videos
The experimental protocol involves presenting participants with four distinct groups of short clips, each comprising six clips. These clips exhibit durations ranging from 33 to 83 s, with an average duration of 53.46 s and a standard deviation of 9.62 s. This deliberate variation in clip duration accommodates the diversity in individual emotional processing times, intending to evoke a spectrum of emotional responses. Table 2 gives a detailed summary of the durations of all stimulus videos used in the study, serving as a reference for further analysis.

Table 2.
Experiment stimulus videos’ duration in seconds targeting different human emotions.
The study incorporates four video categories labeled as Happy, Angry, Sad, and Hungry, corresponding to the anticipated emotional reactions evoked by each video or group of videos. Importantly, these labels were not disclosed to participants during the experiment. This intentional withholding of information aims to prevent biasing participants’ responses, ensuring that their emotional reporting remains spontaneous and unguided. Participants are encouraged to report their emotions freely in response to the stimuli, devoid of any preconceived notions or expectations about the emotional content of the videos.
2.4. Experimental Setup
Creating an appropriate experimental setup is crucial for obtaining reliable EEG data. The setup should provide a controlled and comfortable environment for participants to experience and express different emotional states. Proper instructions and stimuli presentation protocols should be implemented to elicit genuine emotional responses.
The data acquisition methodology in this study centers on eliciting continuous emotional responses from participants, who are prompted to report and update their emotional states throughout the experiment [37]. Simultaneously, raw EEG signals are recorded using the EMOTIV EPOC+ headset, while facial expressions are captured via a webcam connected to the computer through a USB port. This multimodal approach aims to comprehensively capture emotional responses. Emotional elicitation is achieved through various stimuli, such as photographs, videos, short clips, or a combination of these mediums.
High-quality EEG data acquisition is essential for accurate emotion recognition. It involves the proper placement of electrodes on the participant’s scalp according to established standards (e.g., the 10–20 system [45]). Continuous monitoring of electrode signal quality is performed through the user interface which is reading the signal quality and battery level real-time values from the EMOTIV software. The objective here is to maintain the overall signal connectivity at 100 and the battery level above 70, as shown in the interface. Figure 3 shows the signal quality for all 14 electrodes on a scale of 1 to 4, where

Figure 3.
Signal Quality and Battery Level.
- 1 indicates no signal, suggesting that the electrode is most likely dead or disconnected;
- 2 indicates a very weak signal that is not usable;
- 3 indicates an acceptable signal reception;
- 4 indicates a good signal.
The commencement of the recording process ensues upon activation of the “Record” button, leading to the visual presentation of the video on the display. Moreover, participants are mandated to provide informed consent through the execution of an agreement elucidating the nature of the data collection and the underlying rationale for the utilization of emotionally evocative videos. To streamline the experimental protocol, participants are furnished with an EPOC+ headset, featuring meticulously calibrated sensors with a moistening solution to ensure optimal connectivity. Placement of the headset on the participant’s cranium is followed by the strategic positioning of a monitor at eye level, thereby enhancing attentiveness. A video camera is strategically positioned atop the display to capture the nuanced facial expressions of participants throughout the video sequences.
The experimental paradigm unfolds through several distinct stages. Commencing with a 60 s relaxation video devoid of recording, participants subsequently engage with a sequence of videos categorized into emotional states including Happiness, Anger, Sadness, Hunger, and Pain. Each video within this array spans a temporal range of 33 to 83 s, with an average duration of 53.42 s. As participants progress through the experiment, they are systematically prompted to articulate the emotions or affective states elicited during the video exposure. This is achieved through the manipulation of designated keys on the keyboard, as illustrated in Figure 4. The baseline emotional state at the initiation of each video recording is predefined as “Neutral”, affording participants the flexibility to modify their reported emotional state dynamically throughout the recording process.

Figure 4.
Keyboard with labeled keys for reporting different emotions.
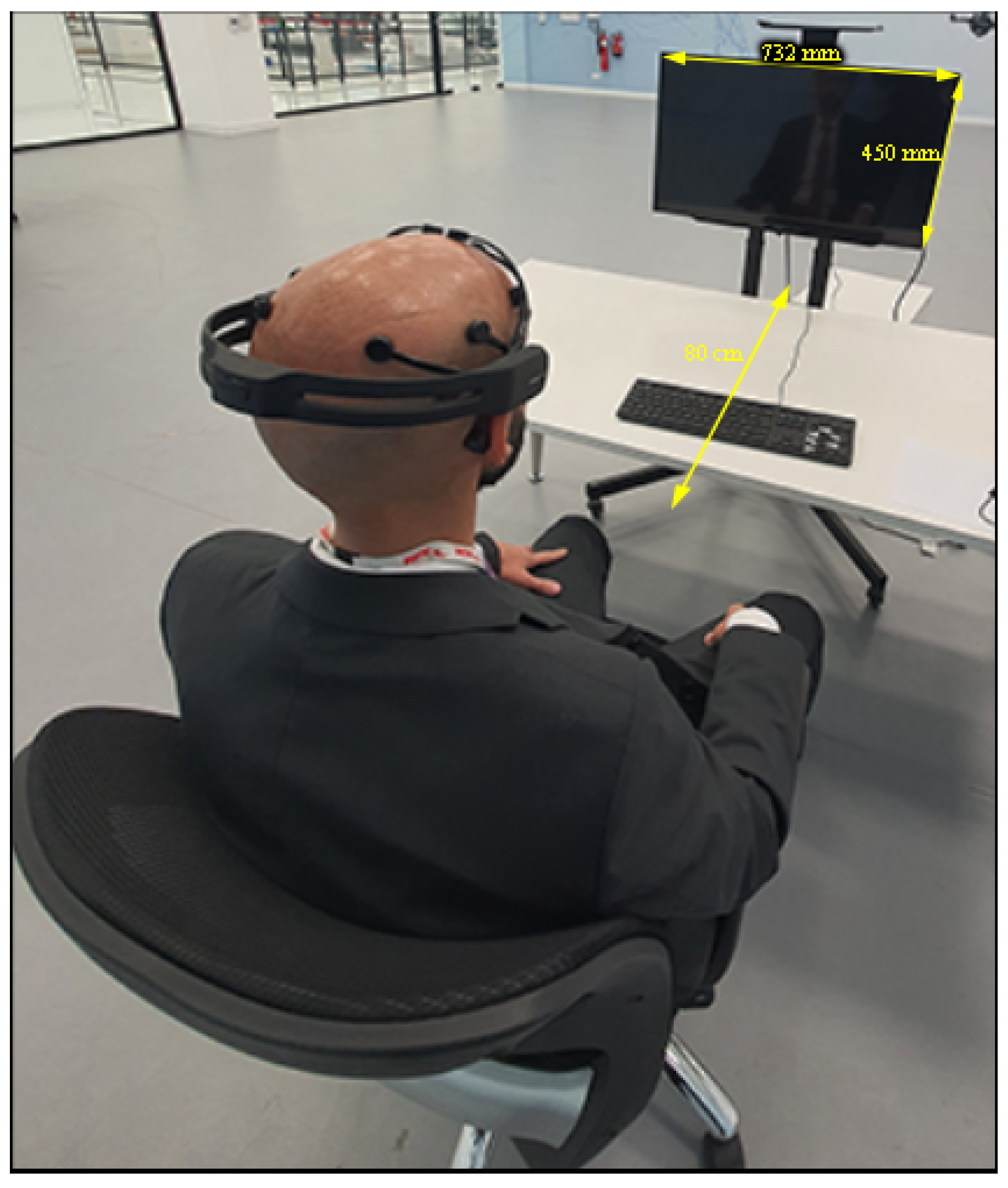
To ascertain the integrity of the collected data, a continuous monitoring mechanism is instituted to evaluate the connectivity of channels within the EPOC+ headset throughout the recording process. In the event of any channel exhibiting suboptimal connectivity, the ongoing recording is terminated to forestall potential inaccuracies in the data. Maintaining experimental rigor, participants are instructed to remain seated at a standardized distance of 80 cm from the display screen throughout the duration of the experiment. The utilized screen is an LED TV with a resolution of 1366 × 768, characterized by dimensions measuring 732 × 450 × 75 mm (width × height × depth), as depicted in Figure 5. Following the presentation of each video category, participants are afforded a 60 s interval for hydration without the removal of the EPOC+ headset, thereby minimizing disruptions to the established experimental conditions.
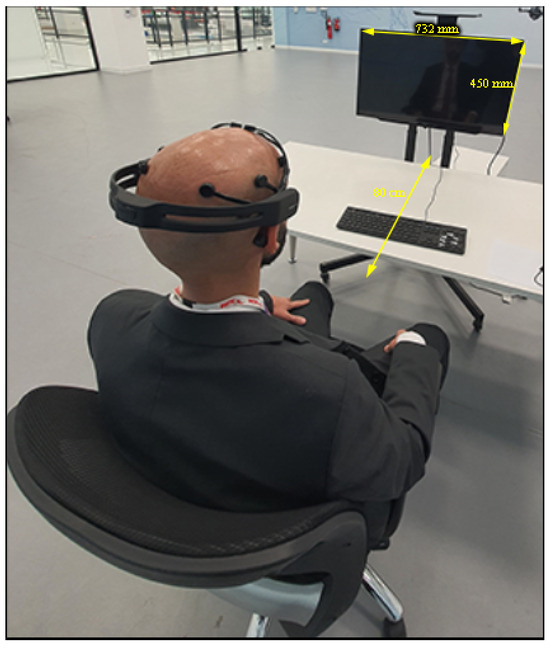

Figure 5.
Full experimental setup example showing the screen dimensions and the distance between the participant and the screen.
The constructed interface embodies a thoroughly developed graphical user interface, featuring an expansive presentation of personal information fields situated prominently on the right-hand side. The “Save Personal Data” command can be used to safely store the entered personal information. In addition, the interface includes battery level and signal strength indicators, which are carefully placed on the left side of the screen. A file explorer function is also smoothly integrated, enabling users to selectively mark videos for playback and EEG data for recording in addition to these functionalities. When “Record” is clicked after choosing a particular video file, the recording begins and the display of the selected visual stimuli is timed to coincide with the EEG data being captured.
The interface-managed data collecting procedure is carried out in a series of carefully thought-out procedures. First, participant data are input and stored with great care. Subsequently, a 60 s video featuring relaxing music is presented, exempt from the recording of EEG or facial expressions. Following this preliminary phase, videos are systematically chosen in a predetermined sequence for each categorical classification, and the recording process is initiated.
Throughout the video’s duration and extending an additional 10 s thereafter to ensure a comprehensive capture of emotional nuances, participants articulate their emotional experiences through the utilization of the designated keyboard. Concurrently, all 14 electrode signals, as well as facial expressions, are systematically recorded. Once this comprehensive recording cycle concludes, the subsequent video in the predetermined sequence is selected and presented, perpetuating the structured progression of the experiment.
3. Multi-Modal System EEG with Facial Expressions—Proposed Model
In the dynamic landscape of artificial intelligence and deep learning, the challenge of discerning and interpreting human emotions has captured considerable attention. The chapter at hand delves into the development of an emotion recognition system that harnesses the capabilities of CNNs within the framework of deep learning specialized in analyzing facial expressions and EEG topographies. This study not only reveals the intricacies of the system but also outlines the critical steps involved in the construction of a robust neural network system and the judicious division of data for training and validation [46]. Essentially, this work investigates the combination of two neural network outputs using a CNN-based methodology that could improve our system’s ability to recognize complex human emotions [47].
3.1. Facial Expression-Based Emotion Recognition
The accurate interpretation of facial expressions, which are key indicators of human emotions, is essential in developing a comprehensive emotion detection system. There are different studies and open-source systems using neural networks for facial expressions emotion recognition. The advanced DeepFace CNN a crucial neural network in facial expression analysis. DeepFace, a specialized and renowned CNN for face recognition and emotion detection, provides a reliable solution for this vital component of the emotion classification system. In the network structure of the DeepFace, a 48 × 48 grayscale image is considered to be the input. The neural network was designed using a 12-layered architecture between Conv, Maxpooling, and Average pooling layers [48]. Also, face recognition will facilitate the avoidance of wrong facial expressions being fed into the system. Noted for its accuracy, DeepFace is a powerful tool for identifying and categorizing facial expressions, including angry, fear, neutral, sad, disgust, happy, and surprise. DeepFace is a valuable tool in the design of emotion recognition systems [48]. Using the DeepFace neural network, we can take advantage of the extensive development and training that have went into DeepFace’s architecture as well as shorten the development time of our system by using the pre-trained CNN to extract and analyze facial features from images or video frames.
We will examine in this study how DeepFace is incorporated into our system, the preprocessing processes required for its optimal performance, and the techniques used to combine its output with EEG topographical data-based network output for improved emotion recognition in more detail. The addition of DeepFace to our framework is an example of how specialized CNNs and deep learning combine to enhance the ability of our framework to capture human emotions with enhanced improved accuracy. The emotion model was implemented using a 12-layered architecture because the FER-2013 database (48 × 48 × 1) was grayscale and had a lower resolution. The DeepFace CNN model is composed of twelve layers, including an output layer with seven nodes representing the following emotions: angry, disgust, fear, happy, sad, surprised, and neutral. There are also five convolution layers, three fully connected layers, two average pooling layers, and one max pooling layer. The input size for this model is 48 × 48 [48,49].
3.2. EEG Topographies and Brain Heat Maps
The characterization of EEG signal shape is dependent on demonstrating brain activity at the moment of capturing the waveform, which is dependent on the brain region that is active at that particular time. The human brain has three major lobes. The cerebrum, the largest in size and most vital human brain segment, is divided into two hemispheres, each housing four distinct lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital. The frontal lobe governs complex voluntary motions and influences judgment, personality, decision-making, and cognitive functions like abstract thought, language, and problem-solving. Processing somatosensory details, the parietal lobe handles touch sensation and movement coordination [50]. The temporal lobe manages auditory input, memory processing, and speech functions, while the smallest lobe, the occipital lobe, oversees vision, including color perception and spatial awareness. The brainstem controls vital life activities such as breathing, blood pressure regulation, and swallowing. Finally, the cerebellum is in charge of maintaining balance and precisely coordinating motions like walking and speech. EEG waves have diverse shapes that indicate different types of brain activity [51].
The EEG signal is usually shown and presented as a chronological sequence of voltage values, reflecting the electrical activity detected by electrodes and measured in microvolts (). This signal is regularly sampled at consistent intervals, typically falling within the range of 128 Hz to 1024 Hz. Standard EEG signals encompass a frequency spectrum of up to 45 Hz, but in unique situations, this range may extend beyond 200 Hz. Conventionally, theses are categorized into specific frequency bands: delta, theta, alpha, beta, and gamma waves. These EEG frequencies represent various electrical activities within the brain and offer insights into the functioning of different brain regions, as established by Ref. [52].
The utilization of EEG frequencies is widespread in the monitoring of brain activity during various activities such as relaxation, sleep, and meditation, as well as in the diagnosis and treatment of numerous neurological and psychiatric conditions [53]. For instance, deep sleep is characterized by higher signal power in the delta band, signifying specific brain activity during this sleep stage. Theta, alpha, and beta bands have empirically demonstrated interest in emotion identification, as documented in publications [33,54,55]. Unwanted frequency bands are filtered out using a second-order bandpass filter.
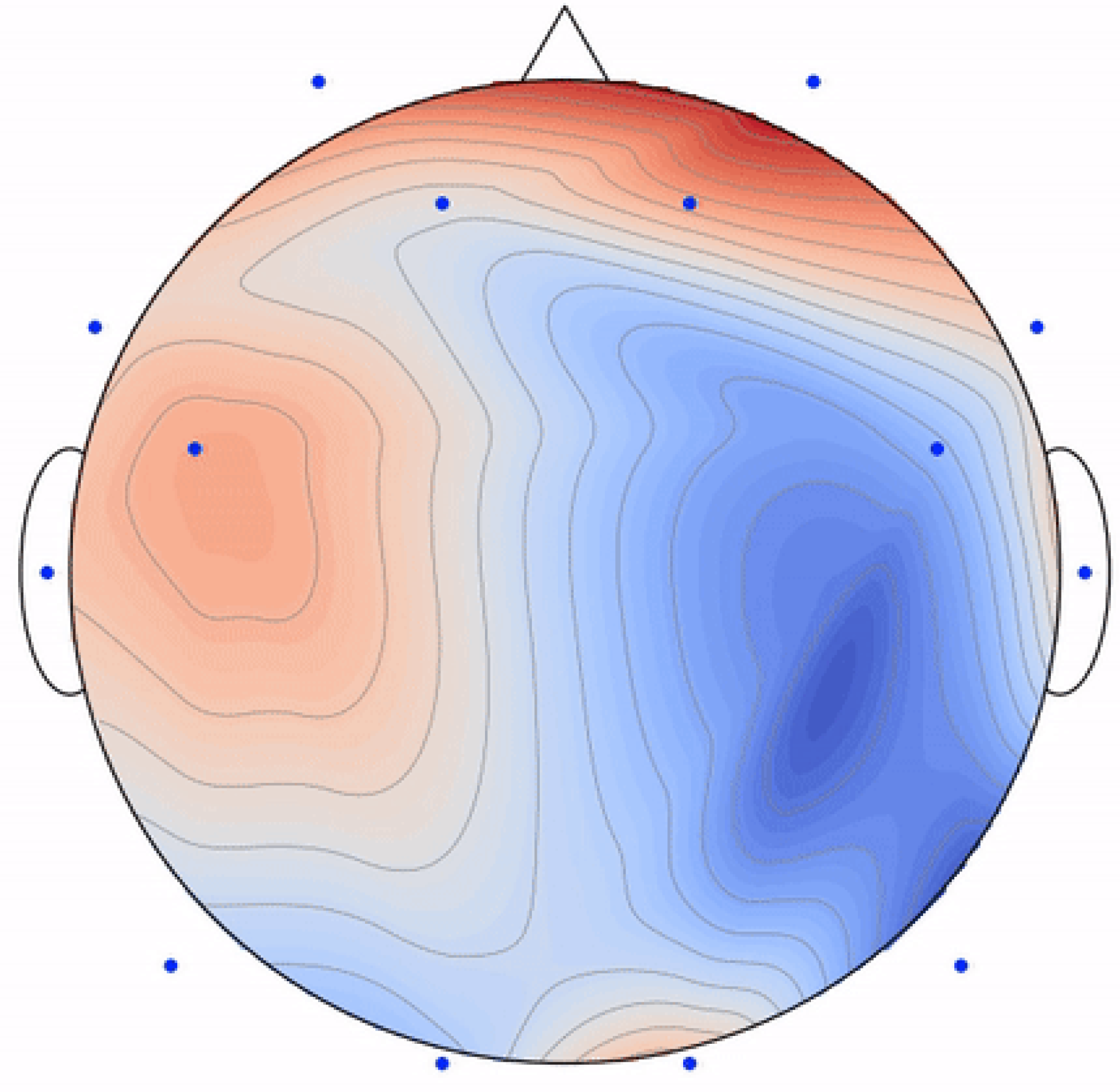
EEG topography stands as a non-invasive technique enabling researchers to create a real-time visual representation of the electrical activity within the brain. This method has found widespread application in neuroscience, facilitating the exploration of various facets of brain function, encompassing cognition, emotion, and perception. The EEG and brain heat map representation, called EEG topography, is shown in Figure 6. These topographies might look clearly different when there is a change in the set of electrodes, frequency ranges, or the window time frame used to build up the 2D map. In this study, each 1 s time frame is considered to be a single topography without overlap. Window size helps in reducing the noise to avoid problems that occur due to the continuous huge and fast changes in human brain signals. EEG signals are not stable since they are affected by every movement, thought, emotion, or feeling.
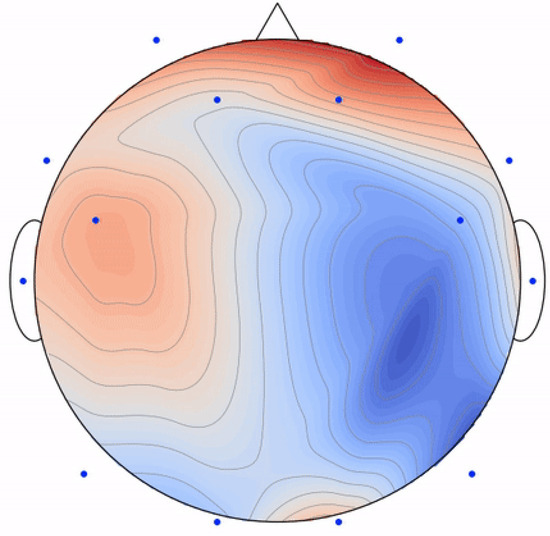
Figure 6.
An example of an EEG 2D topography.
The raw EEG data undergo analysis and processing to generate a brain activity heat map, showing the distribution of human brain signals as electrical activity all over the scalp using different electrodes placed in different locations. This technique has proven invaluable in unraveling the neural mechanisms that underlie behavior and cognition, establishing itself as an essential tool for researchers in neuroscience. The two-dimensional topography of EEG contains spatial information, making it particularly useful for optimizing electrode placement on the scalp. Consequently, these topographies serve as the input to an objective function aiming to maximize the discriminative ability between various emotional states.
3.3. EEG Electrode and Frequency Band Selection
The red, green, and blue layers are used to represent different colors on a digital display screen, and they are utilized to store the measured topographies that are gathered from the gathered database. In other words, each visible color is represented digitally by three values, and each one is between 0 and 255 per pixel. As a result, each topography can be thought of as a three-layered matrix, where R, G, and B are the colors that correspond to each layer. Each image in this study is considered to be a square of points with 64 × 64 points in each color layer, for a total of three squares. Each pixel in the image has three values or three points representing the amount of red, green, and blue colors intensities. According to Ref. [38], the objective function is selected to be the total of the three RGB layers of the absolute difference value between the averages of a set of EEG topographies collected for two distinct classes of emotions. For a given emotion axis (valence in this case) a total of N and M EEG topographic images are obtained for high and low valence, respectively, without sacrificing generality. The average of the pixel values computed independently for each layer or color C (R, G, B) determines the average EEG topographic heat map for each emotional level. The absolute difference between the high and low classes of each emotion’s average EEG topography is then computed [38]. The formula that is produced and maximized using simplicial homology global optimization (SHGO) [38] is
C represents one of the three colors (R, G, B), resulting in three absolute differences in the average topography. The overall sum of the matrix, composed of each , , , entails adding 64 by 64 by 3 for (R, G, and B), totaling 49,152 elements. These elements signify the variance in average pixel values between high and low categories on the valence or arousal scale. Three absolute variations in the average topography are produced in this case, where C represents one of the three (R, G, and B) colors and N and M are the numbers of high and low emotional axis topographies, respectively. The difference between the average value for each pixel between the high and low categories of the valence scale is represented by for (R, G, and B), or 49,152 elements or pixels, which make up the total sum of the matrix sum of each , , and .
As a result, SHGO approaches have shown encouraging results in terms of improving EEG emotion recognition channels. This method maximizes the difference between high and low levels of valence by optimizing the target frequency band of the measured signal, the number of EEG channels, and their placements. The objective function was maximized by using the SHGO optimization algorithm. The SHGO algorithm, like any optimization method, tests the consequences of changing each input parameter in order to investigate several alternatives. There are fifteen parameters to take into account in this scenario: the frequency range (0 = theta, 1 = alpha, 2 = beta, and 3 = gamma) and the fourteen EEG channels that can be active or deactivated (multiplied by 0 or 1). Thus, the total number of combinations is .
The power spectral density, which is derived from all 14 of the activated channels in one of the four frequency bands, is essentially what creates the topography heat map. In the topography, all inactive channels are represented by zero values (multiplied by zero). The resulting objective function to be maximized depends on maximizing the absolute difference between the two topographies representing the two opposite emotional axis levels pixel by pixel. Each average topography represents a level of the valence axis. The next step is to add up all of these absolute differences for each pixel among the 64 × 64 pixels to obtain a single number that expresses the difference between these two diametrically opposed feelings. Although optimization approaches normally yield just the ultimate optimal answer, this work documented and preserved all of the alternatives examined by the SHGO methodology for future examination. These different input possibilities tested during the optimization process helped in a way showing how we can choose different electrodes’ placements with frequency band to reach the optimum solution according to the criteria we have. For example, and as we are going to show in this study, we have reduced the number of sensors to increase the system’s simplicity while maintaining almost the same system efficiency.
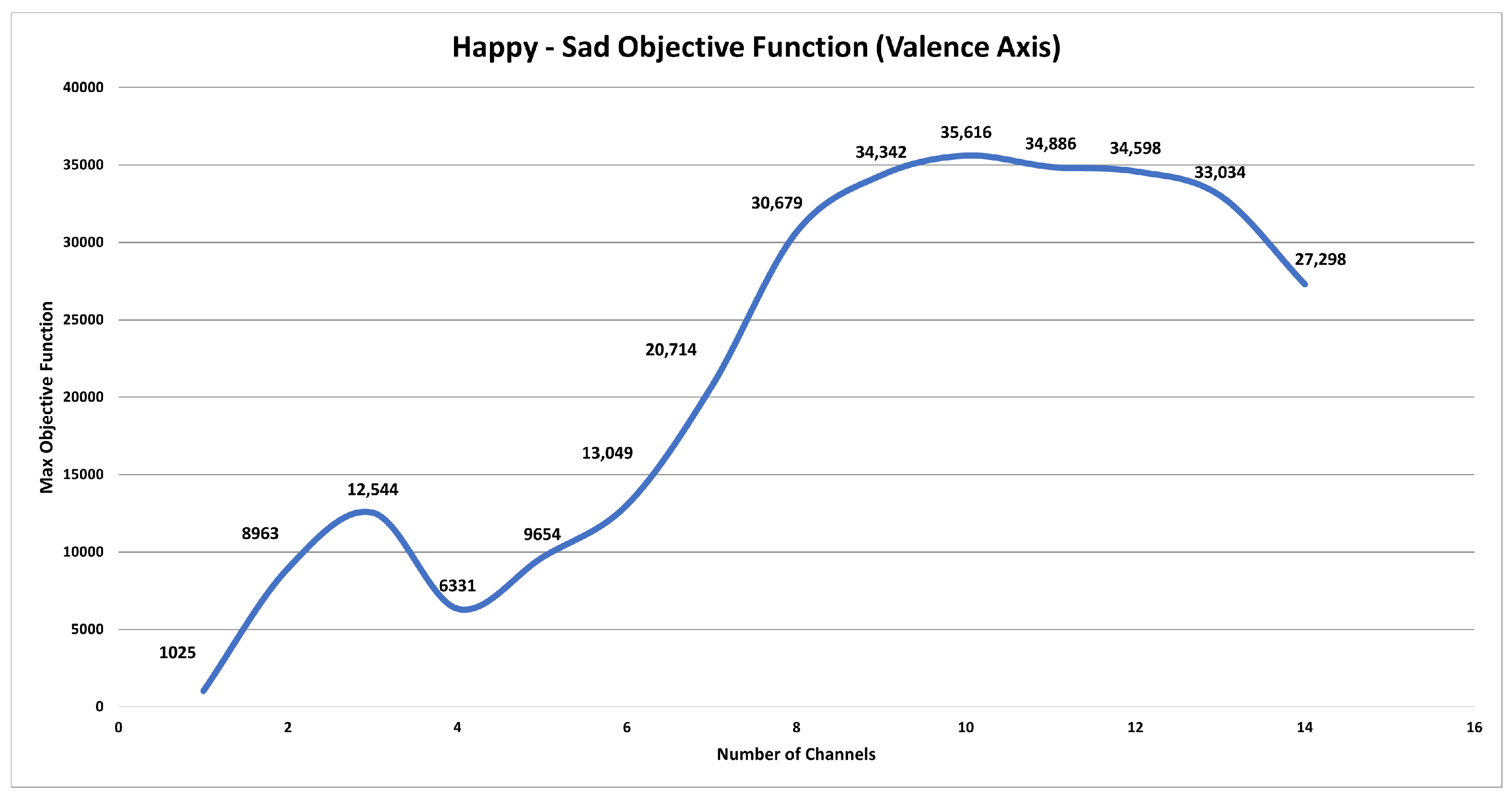
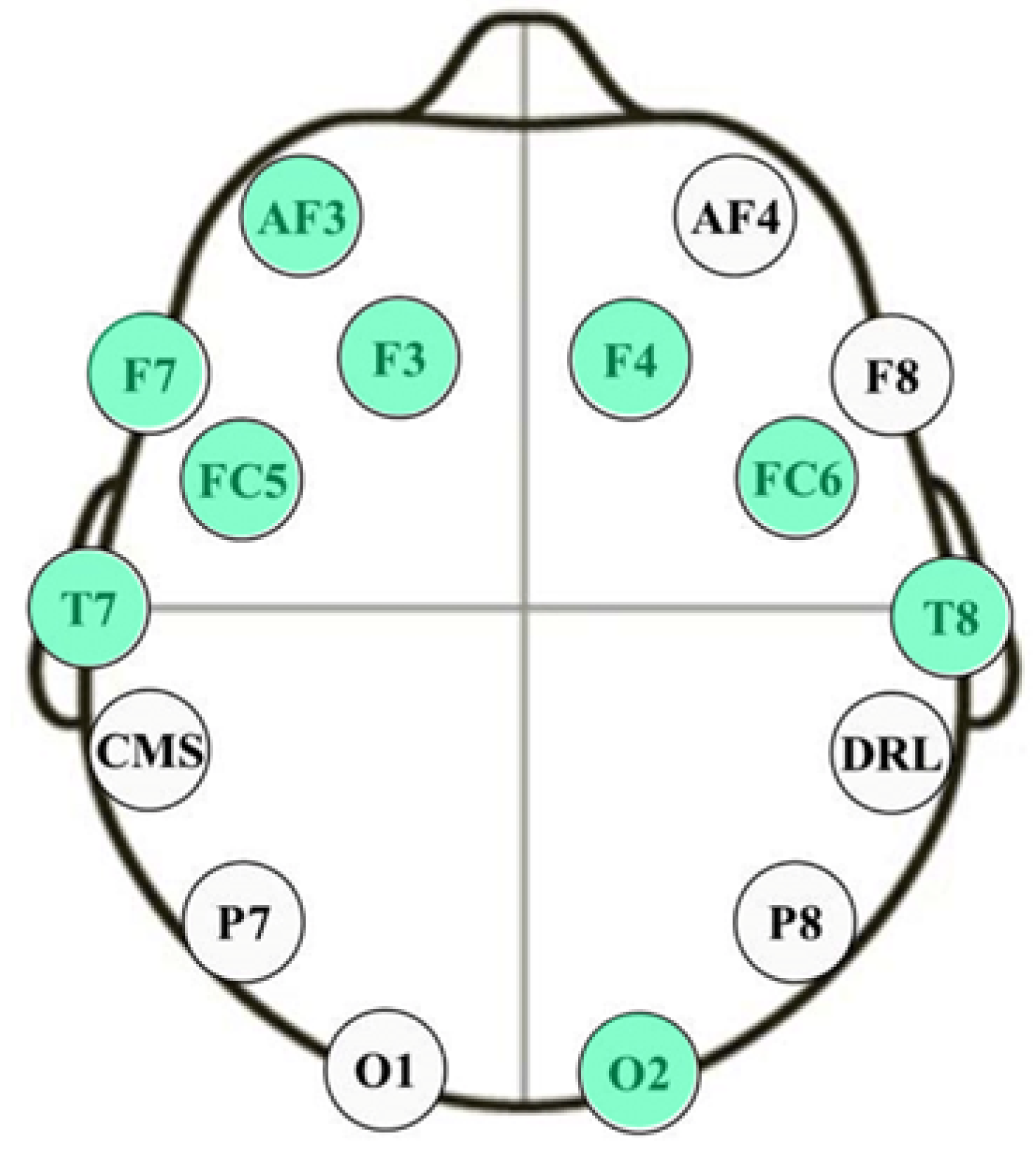
A chart showing the maximum objective function values for the valence emotional axis plotted against the number of channels is shown in Figure 7. The findings show that there is no big change in the valence emotional axis between using ten and nine sensors system. Nine channels, AF3, F7, F3, FC5, T7, O2, T8, FC6, and F4, are the best choice to have since more channels result in more noticeable differences between valence levels. Using four electrodes initially causes a reduction in the objective function value, but it subsequently increases again with five electrodes, although it remains lower than the value achieved with three electrodes. The objective function continues to rise until the use of ten electrodes, after which it gradually declines until reaching its lowest point when all 14 sensors are employed. Remarkably, this approach—and by choosing nine electrodes, which results in almost the same value of the objective function—yields a reduction in sensor complexity of over 35% compared to utilizing the full 14-sensor configuration, as illustrated in Figure 8.
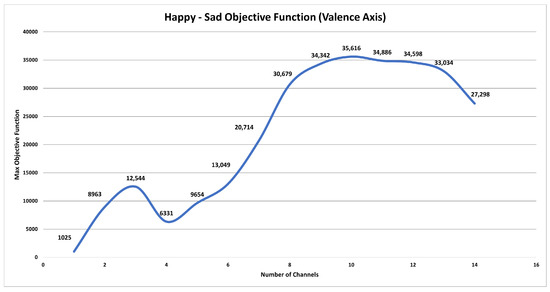
Figure 7.
Maximum objective function value against the number of channels—valence axis.
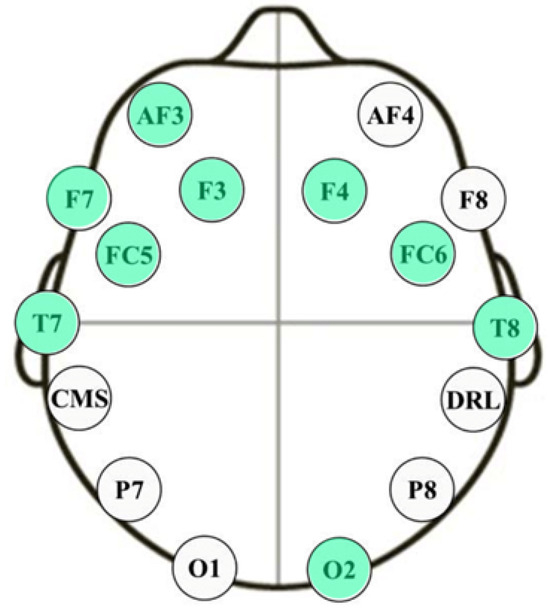
Figure 8.
The optimum nine channels selected for valence axis level classification.
3.4. EEG-Based Emotion Recognition
Emotion recognition from EEG signals has gained significant interest in recent years due to its potential applications in various domains, such as human–computer interaction, mental health monitoring, and emotion-driven personalized services. Deep learning, particularly CNNs, has shown promising results in extracting meaningful features from EEG data for emotion classification. EEG is a non-invasive technique that records electrical activity from the scalp, reflecting the underlying neural processes related to cognitive and emotional states. Emotions are believed to manifest distinct patterns in the brain’s electrical activity, making EEG an attractive modality for emotion recognition. Deep learning has revolutionized various domains, including computer vision and natural language processing. When applied to EEG emotion recognition, deep neural networks can automatically learn relevant features from raw EEG signals, mitigating the need for hand-engineering features [38]. CNNs are a particular kind of deep neural network and are used to handle data that resemble a grid, such as heat maps or topographies, or time series data like EEG or picture data. CNNs can detect local patterns and feature hierarchies, which are essential for determining spatial relationships in EEG signals, by employing convolutional layers. A heat map depiction of emotion topography depicts the spatial arrangement of brain activations linked to various emotions.
Another crucial step in simplifying the entire emotion identification system is determining the quantity of electrodes used to generate the heat maps and its placement locations on the human scalp. Studies frequently use the method of focusing on certain brain regions, such as the amygdala and prefrontal cortex, which are known to be involved in emotional processing [21,38,56]. Optimum channel selection can help the system identify emotions more accurately by cutting down on unwanted noise and irrelevant inputs. Furthermore, consistent EEG readings with fewer artifacts and interferences depend on accurate electrode placement. Following the universal 10–20 method for electrode placement guarantees consistent and standardized data gathering between participants, which enhances the performance and comparability of emotion recognition algorithms. The field of EEG-based emotion recognition can be greatly advanced, and the practical applicability of these systems in areas such as affective computing and mental health monitoring enhanced by fine-tuning the selection of channels and electrodes. This will yield more consistent and comprehensible results.
During the training process, the model fine-tunes its internal parameters, learning to minimize the classification error. This approach ensures that the model is thoroughly trained on a substantial portion of the available data, providing the model with a comprehensive understanding of the patterns associated with different emotional states as represented in the EEG signals. Evaluation of the model is performed on separate test databases (20%) to assess its generalization and performance on unseen data. These percentages for the data split are used for valence emotion axis level recognition. The EEG emotion recognition system based on CNNs using emotion topography heat map images has numerous potential applications. It can be integrated into real-time emotion-aware systems, affective computing, and mental health monitoring, enabling personalized services based on detected emotional states. Utilizing raw EEG signal recordings obtained via the headset, PSD values are computed at specific, optimized electrode locations, and subsequently employed to generate a cerebral heat map that visualizes patterns of brain activity.
The valence CNN architecture presented in Table 3 is designed for the analysis of EEG topographies. It specifically focuses on EEG data collected from the nine optimum electrodes, namely, AF3, F7, F3, FC5, T7, O2, T8, FC6, and F4, with a particular emphasis on the beta frequency range. The architecture begins with an input layer to receive EEG topography generated based on the data from these electrodes as a colored image represented digitally by the three color layers. It subsequently employs two convolutional layers, Conv1 and Conv2, to extract spatial features from the input data. Activation layers, Act1 and Act2, introduce non-linearity into the model. Max-pooling layers, MaxPool1 and MaxPool2, reduce the spatial dimensions of the feature maps. The Flatten layer prepares the data for fully connected layers, followed by Dense1 and Dense2, which process the flattened data for the final output. The table provides additional information, including the total number of parameters in the network (972), and distinguishes between trainable and non-trainable parameters. This architecture is tailored for EEG analysis, particularly in the context of beta frequency range topography. The designed network was trained and validated on a newly collected database with a total number of 16,764 topographies for high and low valence levels. To ensure robust evaluation, the database is divided into training and validation sets, accounting for 80% (13,411 topographies) and 20% (3353 topographies), respectively. This division facilitates both extensive model learning and independent validation, thereby enhancing generalization capabilities and fine-tuning. This comprehensive methodology manifests itself as an efficacious emotion recognition system rooted in topographic EEG data. Impressively, the system had an accuracy of 72.53% when using the full 14 electrodes while it attains 87.43% accuracy when using only 9 electrodes in distinguishing high and low valence levels.

Table 3.
Valence CNN layers structure.
3.5. Fusion of Networks’ Results
The difficult problem of emotion recognition is greatly improved by combining data from multiple modalities. It has recently been demonstrated that combining facial expression with EEG-based CNN outputs is a potential method for emotion identification. When facial expression-based CNNs like DeepFace are combined with the output of EEG-based networks that capture brain activity, a complete and powerful emotion identification system may be created. This section looks at the results of the fusion between the two neural networks outputs and its effect on the overall system efficiency. It also goes over potential tactics and guidelines for this integration.
The identification of emotional states, such as responses to certain stimuli or mental processes, may be preformed using EEG data. However, DeepFace CNN is made to use cameras to recognize facial expressions and provide accurate visual cues about emotional states that are observable from the outside. Enhancement of the efficiency and accuracy of the emotion identification system may be achieved via the merging of these two modalities. Data from EEG-based networks and DeepFace CNN output may be combined using a variety of fusion techniques [57,58,59]. Here are some possible methods for this fusion as examples:
- Feature-Level Fusion: Combines features extracted from both EEG and facial expression data before classification.
- Decision-Level Fusion: Independent decisions from each modality are combined to reach a final classification.
- Late Fusion: Integrating the models themselves, such as through ensemble methods or hybrid architectures.
- Early Fusion: Combining the input data from the DeepFace and EEG-based CNNs and sending them to a single CNN for collaborative feature learning.
In this study, we combine the outputs of DeepFace CNN with an EEG-based CNN, using a decision-level fusion technique to improve emotion recognition. By taking use of the unique advantages of each modality, this approach seeks to increase the accuracy and scope of emotion detection systems [60]. The main and key factor of this integration is the use of the neural networks’ confidence scores (CS) for each network’s output. The confidence score describes how confidently an input is classified by the model into a certain class or output. In the classification process, CNNs often give a CS, or the likelihood that the input belongs to a class. Typically, the class with the highest CS is selected for the final output. The softmax activation function is typically used to transform the output scores of the network into a probability distribution.
Using this method to combine the networks’ outputs is powerful for creating an emotion recognition system that is more accurate and reliable. Confidence scores play a critical role in determining if more validation or human intervention is necessary, particularly in critical applications like autonomous driving or medical diagnostics where the model’s decisions have far-reaching consequences. Moreover, CSs are essential to the decision-making process and overall performance evaluation since they help users evaluate and trust CNN’s outputs, as well as comprehend the behavior of the model. The CS score for the valence emotional axis, which summarizes the many combinations that may be made for emotion identification, is the basis for the system’s outcomes, as indicated in Table 4.

Table 4.
Valence emotion classifications possible combinations and reported emotional state.
4. Results and Discussion
The final step is the fusion between the two results from the two separate neural networks reporting human emotions using facial expressions and EEG heat maps. The fusion between networks’ outputs could be performed in different ways. In this study, a decision-level fusion technique was used based on the confidence score. As previously stated, and illustrated in Table 4, the confidence score threshold was established at 0.7. This number was derived by a through a statistical study designed to resolve instances of inaccurate categorization. The decision process involved manually adjusting the confidence score threshold. Subsequently, we computed the percentage of accurate results produced by the neural network when confidence scores exceeded the selected threshold, alongside the percentage of erroneous results when confidence scores fell below it. This assessment was conducted relative to the total number of attempts above and below the specified threshold, respectively. The study found that the vast majority of wrong classifications happened when the confidence score went below 0.7. In light of these findings, this threshold was carefully selected as the ideal spot for executing the fusion process. This approach guarantees a more dependable and accurate classification process by reducing the chance of mistakes associated with lower confidence levels, increasing the methodology’s overall efficiency by depending on facial expressions’ CNN results. The fusion technique depends on separately training EEG- and facial expression-based CNN models and combining their outputs using a weighted sum or majority voting to make the final emotion classification decision. The application of this mathematical expression involves considering the result from the EEG-based CNN when facial recognition by the camera yields negative results, when both CNNs have the same output, or when they have different emotion classes but the EEG-based CNN has a confidence score greater than 70%. The final situation is when each CNN reports a different emotional class and the EEG-based CNN has a confidence score less than or equal to 70%, in this case, the emotion reported with a higher confidence score will be considered. The subsequent amalgamation of outputs from the two aforementioned CNNs is manifested as an enhancement in the overall efficiency of emotional classification. The fusion system mainly depends on the EEG signals to avoid faking facial expressions or lighting and camera position misleading problems. As a result of applying the fusion equation to the results achieved by the two CNNs, the efficiency was improved from 87.43% to 91.21% by applying the algorithm on 3353 random images out of database samples previously labeled by the participants as happy or sad. Obviously, we can see that the multi-modal system depending on two different inputs enhances the overall system’s accuracy as well as generalizes the system’s usage.
The multimodal emotion recognition system finds applications in affective computing, where it can be used to create emotionally intelligent systems that respond to users’ emotional states. The system can enhance human–computer interaction by enabling devices and applications to adapt to users’ emotions, leading to more personalized and engaging experiences. In the context of mental health, our system can aid in monitoring and understanding emotional states, potentially assisting therapists and individuals in managing mental well-being. The high accuracy indicate the system’s robustness in accurately classifying human emotions using the combined information from EEG data and facial expressions. These metrics provide a quantitative measure of the system’s ability to correctly identify different emotional states.
5. Conclusions
This study investigates the fundamental components of database construction and information collection in order to develop an EEG-based emotion detection system and investigate using facial expressions to enhance recognition efficiency. EEG is the recommended method for emotion recognition analysis because of its superior temporal resolution, non-intrusiveness, and capacity to monitor brain activity linked to emotions. The EMOTIV EPOC+ headset was selected due to its wireless capability using Bluetooth, ease of use, and adaptability to many real-world scenarios. These properties also help in this study’s wide frequency band collection and cost criteria. In order to elicit a range of emotional reactions, participants are shown short video clips with different emotional content. During the experiment, facial expressions were recorded and monitored using webcam while an EEG EMOTIV EPOC+ headset was used to record EEG signals from 14 different electrode locations placed on different brain lobes.
Moreover, in this study, we have proposed the method of integrating the two outputs resulted from a facial expression-based CNN and an EEG signal-based CNN to enhance the overall emotion recognition system efficiency using decision-level fusion technique depending on confidence score values. This method has increased the recognition accuracy from 87.43% with only the EEG data represented as a brain activity map to 91.21% with the combined CNN output by including DeepFace CNN. Each CNN is designed and trained to recognize visual characteristics from pictures of facial expressions and EEG data presented as a topography in order to capture human emotional states and create a complete high-efficiency system that can recognize emotional states. Such an emotion recognition system is more efficient than most systems based on single data modalities in terms of accuracy and generalization capabilities. These advancements pave the way for future technology such as emotion-aware virtual assistants, immersive interactive entertainment, and attentive mental health monitoring, which will all be seamlessly integrated.
For future work, it is planned to delve deeper into the exploration of alternative fusion techniques. This includes conducting comparative studies between decision-level, feature-level, and hybrid fusion approaches to determine their respective advantages and limitations in the context of emotion recognition. Additionally, we aim to investigate novel fusion strategies that leverage advanced machine learning algorithms, such as deep learning architectures, to further improve the performance of our multimodal emotion recognition system. By systematically evaluating these fusion methods, we anticipate refinement of our system’s capabilities and contribution to the advancement of multimodal affective computing research. The extraction of different features from EEG signals for emotion recognition is also to be investigated in future work. In addition to this, there will be more analysis on other emotions included in the database, taking into consideration the ethical aspects and privacy concerns.
In conclusion, this research at the confluence of affective computing, machine learning, and computer vision is highly promising and spurs further exploratory studies. This merging of neural networks is set to enhance the development of human emotion recognition methods that are more intuitive, responsive, and emotionally intelligent. The system was trained on a self-collected database with instant emotion reporting. The data collected are meant to solve a very common problem, which is the reporting of one single emotion with one specific emotional degree per stimulus or session of the experiment. In the collected database, this problem is solved by asking the participant to report the emotions instantly, and whenever it changes, the participant is asked to update it. The potential for groundbreaking advancements in emotion recognition systems makes it imperative to continue pioneering research in this exciting area, promising revolutionary developments in emotion recognition.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.R., A.K., A.N.-a. and T.B.; methodology, A.R., A.K. and A.N.-a.; software, A.R.; validation, A.R. and S.A.K.; formal analysis, A.R. and A.N.-a.; investigation, A.R. and T.B.; resources, A.R. and T.B.; writing—original draft preparation, A.R. and A.K.; writing—review and editing, A.R., A.K. and S.A.K.; supervision T.B. and A.N.-a. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Almasoudi, A.; Baowidan, S.; Sarhan, S. Facial Expressions Decoded: A Survey of Facial Emotion Recognition. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2023, 185, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, S.C.; Tang, Y.M.; Lai, C.H.; Lee, C.K.M. Facial expression and body gesture emotion recognition: A systematic review on the use of visual data in affective computing. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2023, 48, 100545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancilin, J.; Milton, A. Improved speech emotion recognition with Mel frequency magnitude coefficient. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 179, 108046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Correa, J.A.; Abadi, M.K.; Sebe, N.; Patras, I. AMIGOS: A Dataset for Affect, Personality and Mood Research on Individuals and Groups. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2021, 12, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poria, S.; Cambria, E.; Bajpai, R.; Hussain, A. A review of affective computing: From unimodal analysis to multimodal fusion. Inf. Fusion 2017, 37, 98–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, W.B. The James-Lange theory of emotions: A critical examination and an alternative theory. Am. J. Psychol. 1927, 39, 106–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dror, O.E. The Cannon–Bard thalamic theory of emotions: A brief genealogy and reappraisal. Emot. Rev. 2014, 6, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Li, C. Review of Studies on Emotion Recognition and Judgment Based on Physiological Signals. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanth, P.C.; Nataraj, K.R. Facial Expression Recognition Using SVM Classifier. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Inform. IJEEI 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yl, M.; Kuilenburg, H. The FaceReader: Online Facial Expression Recognition. In Proceedings of the Measuring Behavior, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 30 August–2 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Yi, H. Facial Emotion Recognition Using a Novel Fusion of Convolutional Neural Network and Local Binary Pattern in Crime Investigation. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 2249417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Wu, S.; Gu, X. A facial expression recognition algorithm incorporating SVM and explainable residual neural network. Signal Image Video Process. 2023, 17, 4245–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donuk, K.; Ari, A.; Ozdemir, M.; Hanbay, D. Deep Feature Selection for Facial Emotion Recognition Based on BPSO and SVM. J. Polytech. 2021, 26, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Saurav, S.; Kumar, T.; Saini, R.; Vohra, A.; Singh, S. Facial expression recognition in videos using hybrid CNN & ConvLSTM. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2023, 15, 1819–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, G.; Long, S.; Yuan, H. Non-Contact Emotion Recognition Combining Heart Rate and Facial Expression for Interactive Gaming Environments. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 11896–11906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, T.; Bhattacharya, U.; Chandra, R.; Bera, A.; Manocha, D. M3er: Multiplicative multimodal emotion recognition using facial, textual, and speech cues. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 1359–1367. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Duan, F.; Solé-Casals, J.; Caiafa, C.F. A multimodal emotion recognition method based on facial expressions and electroencephalography. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 70, 103029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmony, T. The functional significance of delta oscillations in cognitive processing. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theódórsdóttir, D.; Höller, Y. EEG-correlates of emotional memory and seasonal symptoms. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miskovic, V.; Schmidt, L.A. Frontal brain electrical asymmetry and cardiac vagal tone predict biased attention to social threat. Biol. Psychol. 2010, 84, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshdy, A.; Al Kork, S.; Karar, A.; Al Sabi, A.; Al Barakeh, Z.; ElSayed, F.; Beyrouthy, T.; Nait-Ali, A. Machine Empathy: Digitizing Human Emotions. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Symposium on Electrical, Electronics and Information Engineering, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 19–21 February 2021; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piho, L.; Tjahjadi, T. A Mutual Information Based Adaptive Windowing of Informative EEG for Emotion Recognition. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2020, 11, 722–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zeng, W.; Shi, Y.; Deng, J.; Ma, Y. Intrinsic prior knowledge driven CICA fMRI data analysis for emotion recognition classification. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 59944–59950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Song, D.; Zhang, P.; Yu, G.; Hou, Y.; Hu, B. Emotion recognition from multi-channel EEG data through Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Shenzhen, China, 15–18 December 2016; pp. 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candra, H.; Yuwono, M.; Chai, R.; Handojoseno, A.; Elamvazuthi, I.; Nguyen, H.T.; Su, S. Investigation of window size in classification of EEG-emotion signal with wavelet entropy and support vector machine. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 7250–7253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudakov, E.; Laurent, L.; Cousin, V.; Roshdi, A.; Fournier, R.; Nait-ali, A.; Beyrouthy, T.; Kork, S.A. Multi-Task CNN model for emotion recognition from EEG Brain maps. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th International Conference on Bio-Engineering for Smart Technologies (BioSMART), Paris, France, 8–10 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayan, A.E.; Sen, D.; Sudheer, A. EEG-Based Emotion Recognition Using Statistical Measures and Auto-Regressive Modeling. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence & Communication Technology, Ghaziabad, India, 13–14 February 2015; pp. 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subasi, A.; Tuncer, T.; Dogan, S.; Tanko, D.; Sakoglu, U. EEG-based emotion recognition using tunable Q wavelet transform and rotation forest ensemble classifier. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 68, 102648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, H.T.T.; Dang, L.N.T.; Nguyen, V.T.N.; Huynh, V.T. A Survey of Machine Learning algorithms in EEG. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th NAFOSTED Conference on Information and Computer Science (NICS), Hanoi, Vietnam, 12–13 December 2019; pp. 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, A.; Baykara, M.; Alakus, T.B. A Novel Approach for Emotion Recognition Based on EEG Signal Using Deep Learning. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Chen, M.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Song, R.; Liu, A.; Chen, X. Emotion Recognition From Multi-Channel EEG via Deep Forest. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 25, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veeramallu, G.K.P.; Anupalli, Y.; Jilumudi, S.k.; Bhattacharyya, A. EEG based automatic emotion recognition using EMD and Random forest classifier. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kanpur, India, 6–8 July 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.L.; Zhu, J.Y.; Lu, B.L. Identifying Stable Patterns over Time for Emotion Recognition from EEG. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2019, 10, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zheng, X.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, X. EEG emotion recognition using fusion model of graph convolutional neural networks and LSTM. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 100, 106954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.J.; Boehm, S.G.; Healy, D.; Goebel, R.; Linden, D.E.J. Neurofeedback: A promising tool for the self-regulation of emotion networks. NeuroImage 2010, 49, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleymani, M.; Asghari-Esfeden, S.; Fu, Y.; Pantic, M. Analysis of EEG Signals and Facial Expressions for Continuous Emotion Detection. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2016, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topic, A.; Russo, M. Emotion recognition based on EEG feature maps through deep learning network. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2021, 24, 1442–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshdy, A.; Al Kork, S.; Beyrouthy, T.; Nait-ali, A. Simplicial Homology Global Optimization of EEG Signal Extraction for Emotion Recognition. Robotics 2023, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshdy, A.; Karar, A.S.; Al-Sabi, A.; Barakeh, Z.A.; El-Sayed, F.; alkork, S.; Beyrouthy, T.; Nait-ali, A. Towards Human Brain Image Mapping for Emotion Digitization in Robotics. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Bio-Engineering for Smart Technologies (BioSMART), Paris, France, 24–26 April 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayatdoost, S.; Rudrauf, D.; Soleymani, M. Expression-guided EEG representation learning for emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bashivan, P.; Rish, I.; Yeasin, M.; Codella, N. Learning representations from EEG with deep recurrent-convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.06448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, D. Ten challenges for EEG-based affective computing. Brain Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emotiv Systems Inc. Emotiv—Brain Computer Interface Technology; Emotiv Systems Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pehkonen, S.; Rauniomaa, M.; Siitonen, P. Participating researcher or researching participant? On possible positions of the researcher in the collection (and analysis) of mobile video data. Soc. Interact.-Video-Based Stud. Hum. Soc. 2021, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, R.W. The 10-20 electrode system and cerebral location. Am. J. EEG Technol. 1988, 28, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, M.; Poole, B.; Kleinberg, J.; Ganguli, S.; Sohl-Dickstein, J. On the expressive power of deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 2847–2854. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, Q.; Du, B.; Zhang, L. Weighted feature fusion of convolutional neural network and graph attention network for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 1559–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serengil, S.I.; Ozpinar, A. HyperExtended LightFace: A Facial Attribute Analysis Framework. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Engineering and Emerging Technologies (ICEET), Istanbul, Turkey, 27–28 October 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Yoo, J.H. CNN Learning Strategy for Recognizing Facial Expressions. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 70865–70872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rullmann, M.; Preusser, S.; Pleger, B. Prefrontal and posterior parietal contributions to the perceptual awareness of touch. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aileni, R.M.; Pasca, S.; Florescu, A. EEG-Brain Activity Monitoring and Predictive Analysis of Signals Using Artificial Neural Networks. Sensors 2020, 20, 3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingelkurts, A.A.; Fingelkurts, A.A. Morphology and dynamic repertoire of EEG short-term spectral patterns in rest: Explorative study. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 66, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Van Someren, E.J.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Gui, W.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lei, X. EEG spectral analysis in insomnia disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2021, 59, 101457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.L.; Lu, B.L. Investigating critical frequency bands and channels for EEG-based emotion recognition with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Auton. Ment. Dev. 2015, 7, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshdy, A.; Alkork, S.; Karar, A.S.; Mhalla, H.; Beyrouthy, T.; Al Barakeh, Z.; Nait-ali, A. Statistical Analysis of Multi-channel EEG Signals for Digitizing Human Emotions. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th International Conference on Bio-Engineering for Smart Technologies (BioSMART), Paris, France, 8–10 December 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apicella, A.; Arpaia, P.; Isgro, F.; Mastrati, G.; Moccaldi, N. A Survey on EEG-Based Solutions for Emotion Recognition with a Low Number of Channels. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 117411–117428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, J.; Peng, H. A medical image fusion method based on convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th International Conference on Information Fusion (Fusion 2017), Xi’an, China, 10–13 July 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, L.; Wang, T.; Zhao, M.; Wang, P. An adaptive multi-sensor data fusion method based on deep convolutional neural networks for fault diagnosis of planetary gearbox. Sensors 2017, 17, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.F.; Zhang, C.M.; Zhang, S. Two-stage structural damage detection using fuzzy neural networks and data fusion techniques. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Qi, P.; Chen, S.; Yang, X. Fusion Methods for CNN-Based Automatic Modulation Classification. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 66496–66504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).